Doppler ultrasound measurements of renal functional reserve in healthy subjects.
|
|
|
- Arline Austin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original papers Med Ultrason 2015, Vol. 17, no. 4, DOI: Doppler ultrasound measurements of renal functional reserve in healthy subjects. Mehmet Zekai Pekkafalı, Kemal Kara Gulhane Military Medicine Academy, Haydarpasha Training Hospital, Department of Radiology, Istanbul, Turkey Abstract Aims: The aim of this study was to calculate the normal values of renal functional reserve in healthy individuals measuring the resistive index and pulsatility index using Doppler ultrasonography. Material and methods: Forty healthy volunteer adults were included in the study. Their basal resistive index and pulsatility index values were measured and after oral protein load at 30th, 75th and 120th minutes, resistive index and pulsatility index measurements were repeated. The maximum changes in resistive index and pulsatility index from baseline were calculated in each subject which represented the renal functional reserve. Results: The mean values of resistive index and pulsatility index decreased significantly starting with 30 minutes and consecutively at 75 and 120 minutes (for all p<0.05). The highest decrease compared to baseline values was recorded at 75 minutes and renal functional reserve values were calculated as 22.2% for resistive index and 25.4% for pulsatility index. Conclusion: Renal functional reserve can be calculated through Doppler resistive index and pulsatility index measures. We consider that it may be helpful to know normal values of renal functional reserve in healthy subjects. Keywords: protein intake, penal functional reserve, Doppler ultrasound, resistive index, pulsatility index Introduction Doppler investigations permit noninvasive monitoring of the perfusion of various organs. Recent developments have caused the widespread use of Doppler ultrasonography (US) in the assessment of various kidney diseases [1-3]. Doppler examination has been used in the diagnosis of renal artery stenosis, renal vein thrombosis, complications secondary to biopsy, assessment of renal inflammation, obstructive collecting system dilatation and in the evaluation of renal vascular resistance in various renal parenchymal diseases such as diabetic nephropathy, systemic lupus erythomatosus, autosomal-dominant Received Accepted Med Ultrason 2015, Vol. 17, No 4, Corresponding author: Mehmet Zekai Pekkafalı GATA Haydarpaşa Eğitim Hastanesi, Radyoloji Servisi Selimiye Mh. Tıbbiye Cd Üsküdar-Istanbul-Turkey Phone: / 4655 Fax: mzpekkafali@gata.edu.tr polycystic kidney disease, hepatorenal syndrome, hemolytic uremic syndrome, or interstitial nephritis [1,2,4-11]. The resistive index (RI) and pulsatility index (PI) measurements provide information about arterial impedance [1]. The RI value in the spectrum is the ratio of the difference between the peak systolic velocity (PSV) and the end diastolic velocity (EDV) divided by PSV value: RI= (PSV-EDV)/PSV. PI value is found by dividing the difference between peak systolic velocity (PSV) on Doppler spectrum and end diastolic velocity (EDV) with mean velocity (MV): PI=(PSV-EDV)/MV. The vessel diameters and the angle of the Doppler beam do not impact on both indices. In a healthy adult population, RI of 0.70 and PI of 1.20 are used as the threshold values for increased renal vascular resistance [1]. The RI and PI are indirect but sensitive indices of the degree of vasoconstriction. In addition, both indices are reflecting the resistance of the tissues against the blood flow in the vascular bed induced by changes such as cellular infiltration, interstitial edema, increased hydrostatic pressure and colloid osmotic pressure. The other factors that may influence RI and PI are the reduction of the vascular bed (such as glomerular capillary damage, destruction), the intrin-
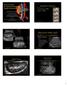
2 sic reduction of vascular diameter of causes different from vasospasm (such as stenosis, endothelial edema), and the venous outflow obstruction. For each index, the lower the value, the lower the resistance, thus, the flow increases. Several studies demonstrated that increased RI and PI can be found in various parenchymal kidney diseases such as hemolytic-uremic syndrome, interstitial nephritis, diabetic nephropathy, autosomal-dominant polycystic diseases [1,2,4,6,12]. On the other hand, new methods to reveal the impairment of the renal function in early stages are being investigated. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is usually accepted as the best overall index of kidney function in health and disease. Normal GFR varies according to age, sex, and body size. In young adults it is approximately ml/min/1.73 m 2 and declines with age. However, baseline GFR does not necessarily correspond to the extent of functioning renal mass. A test of stimulation to reach maximal GFR might be helpful to define the real situation of the subject in terms of renal function. It is known that the normal kidney has the ability to increase the GFR and renal blood flow in response to certain stimuli such as oral protein load, amino acid or dopamine infusion [13-15]. The concept of a baseline and maximal GFR in humans has been defined by the so called renal functional reserve (RFR). RFR is an index of the capability of the kidney to increase its function by vasodilatation of the arterioles and activate the dormant nephrons [13-15]. In 1984, Bosh et al [16] introduce this term, defining RFR as the capacity of a kidney to increase its GFR according to the incremental of metabolic demands or in response to an acute oral protein load. The reduction or the absence of RFR could imply that the residual nephrons are already in a state of permanent glomerular hyperfiltration. There is no constant value or nomogram for RFR but it has been shown to vary between 10% and 70% of the baseline GFR in healthy subjects [15,17]. Likewise, there is no constant relationship between the GFR and changes in RFR; the RFR may be decreased before any change occurs in the GFR [14,15]. As progressive renal impairment occurs, the RFR reaches zero value at some point of the decrease of the level of baseline GFR. The mechanisms of RFR that cause an increase in both GFR and renal blood flow following protein loading are not well known, but the hormones involved include glucagon, glomerulopressin, prostaglandins, and angiotensin-2 [13]. Changes in the tubular handling of sodium may also play a role. On the other hand, glomerular hyperfiltration occurring as a secondary effect of a high protein diet has been reported to accelerate the deterioration of renal functions [13,18]. Therefore, the decrease Med Ultrason 2015; 17(4): or absence of RFR may be an early indicator of impaired renal function. Pulsed Doppler US is a widely used technique which allows rapid, repeated, direct, noninvasive measurement of renal blood flow. Each recording takes only a few minutes after identification of the interlobar artery, and the results are instantly available. The RI and PI measurements can be used in the assessment of RFR [15,19]. The objective of this study was to determine normal RFR values, using the RI and PI measurements in healthy adults and to discuss what benefits this parameter may provide in clinical monitoring. Material and methods Forty healthy volunteer adults (21 male, 19 female, median age 41.5 years [range, 27-56], with no renal disease, diabetes, or hypertension) were recruited from subjects submitted for routine abdominal US between September 2014 and February All subjects signed an informed consent before inclusion and the study protocol was approved by the local Ethics Comittee. Routine biochemical and hemogram tests have been performed in every case before US examinations. Median body mass index (BMI) was calculated 23 kg/m 2 (range, 19-27). Obese patients whose US evaluation could not be performed optimally were excluded from the study. Renal function abnormalities (serum creatinine level >1.2 mg/ dl, creatinine clearance <90 ml/min, and proteinuria) and US renal abnormality (such as cysts, atrophy, nephrolithiasis) were also excluded. In order to minimize effects by personal factors, all measurements were made by a single radiologist experienced in Doppler US. Investigations were performed with a General Electric Logiq 9 machine using a 3.5 MHz convex probe, in the supine position via translomber approach applied to both kidneys. The flow spectra were obtained from the interlobar arteries in both kid- Fig 1. Renal PI and RI measurements obtained from the pulse Doppler flow spectra of the renal interlobar arteries.
3 466 Mehmet Zekai Pekkafalı et al Doppler ultrasound measurements of renal functional reserve in healthy subjects neys so that the highest Doppler frequency shift could be achieved. The software on the US computer memory was used to measure RI and PI values (fig 1). Renal RI and PI were measured from pulse Doppler waveforms obtained from interlobar arteries in three different regions from the upper, middle and lower third of the kidney. From each recording, the RI and PI were measured only when at least three consecutive Doppler waveforms with similar appearance were noted. The RI and PI for each kidney were calculated as an average of three RI and PI values. Also, a mean RI and PI were calculated by averaging mean RI and PI of the right and left kidney. No significant differences were found in the RI and PI between the right and left kidney for each subject. Doppler US examination was started at a.m., after fasting overnight. Fasting baseline RI and PI were measured. The volunteers then ate a 250g steak containing approximately 70g protein, without added salt, over a maximum of 30 minutes. They also drank 500 ml water. After oral protein loading, the RI and PI indices were measured again in the 30th, 75th and 120th minutes and the minimum RI and PI values obtained. The maximum changes in RI and PI from baseline were calculated in each subject representing the RFR (as a percentage change). The baseline RI and PI values of each subject before the steak meal worked as the control values. As the data were normally distributed, the student s t test for paired data was used to calculate the significance of differences between the baseline and minimum RI and PI. The results given as mean (standard deviation) and p<0.05 were considered significant. Fig 2. Baseline (fasting), after loading oral protein, 30th, 75th and 120th minutes mean RI and PI measurements. Table I. Normal kidneys baseline (fasting), after oral protein loading the 30th, 75th and 120th minutes RI and PI measurements (mean±sd) and RFR values. Study group (no=40) RI PI Baseline values 0.63 ± ± min 0.56 ± ± min 0.49 ± ± min 0.55 ± ± 0.08 RFR (%) 0.14 (22.2%) 0.28 (25.4%) RI: resistivity index, PI: pulsatility index, RFR: renal functional reserve Doppler US was successfully performed in all subjects enrolled. The RI and PI measurements and RFR calculations were recorded. The results on baseline (fasting), after loading oral protein, 30th, 75th and 120th minutes mean RI and PI measures and RFR values are in table I. As can be seen in the table, after the protein loading starting from the 30th minute, continuing with the 75th and 120th minutes, the RI and PI values were significantly decreased from the baselines values (for all p<0.05). The lowest values of both indices were obtained at the 75th minute. It was observed that the values from the 120th minute showed a tendency to return to baseline values (fig 2). For this reason, RFR values were calculated with baseline values compared with 75th minutes values and found as 22.2% for RI and 25.4% for PI. Age and sex did not affect RI and PI or RFR. There was no correlation between the BMIs and the values of RI, PI, and RFR. Likewise, no correlation was found between the serum creatinine levels and creatinine clearance and both indices and RFR values (for all p>0.05). Results Discussions Color duplex Doppler US enables visualization of blood flow in renal and intrarenal arteries and provides noninvasive evaluation of renal vascular resistance by measuring pulsatility and resistive indices. In addition, RI and PI could be useful predictors of renal function deterioration, and both indices were significantly correlated with organ damage including glomerular sclerosis, interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy, interstitial infiltration, and arteriolosclerosis [12,20,21]. However, there are only a few studies which have investigated RFR in patients with renal deterioration using Doppler US [15,19]. Until about the fourth decade, renal blood flow is maintained at approximately 600 ml/min. It then drops by approximately 10% every decade due to the activation of the sympathetic nervous system, the renin-angiotension-aldosterone system, and vasopressin secretion [22,23]. A series of studies have indicated that the aging kidney is characterized by a decline in renal function
4 and by a susceptibility to renal diseases and nephrotoxic injuries [22-24]. However, it is not clear whether the observed changes have hemodynamic, structural or both origins [24]. Esposito et al [24] divided healthy participants into young (age range years), middle-aged (44-74 years) and elderly (81-96 years) and concluded that renal function is preserved with aging in healthy subjects at the expense of a complete reduction of RFR. RFR may be wasted to compensate for the increased number of sclerotic glomeruli [24]. Kawai et al [12] investigated the correlation between RI and the influence of aging on renal hemodynamic status and they demonstrated that renal vascular resistance and intra-renal arteriosclerosis had a greater impact on renal function in older (age >75) than younger (age <75) subjects, reflecting the possible mechanisms of renal function reduction due to aging. In our study, we evaluated RFR using RI and PI in healthy adults (age range 27-56) and there was no significant correlation between Doppler indices and age, sex, BMI, serum creatinine, and creatinine clearance. Kalantarinia et al [25] utilized contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) to monitor the expected increase in renal blood flow following a high protein meal in healthy adults. CEUS is a suitable imaging technique for the assessment of renal blood flow, but the disadvantage of this technique is to inject intravenously ultrasound-contrast agents (gas-filled microbubbles) to enhance the ultrasound image. We utilized RI and PI measurements to calculate RFR. Renal Doppler US is a fast, noninvasive, and practical imaging technique. RI and PI measurements can be made on the same flow spectrum, and on the 75th minute after oral protein loading, RFR can easily be calculated using both indices. Sharkey et al had used only PI on the investigations of RFR in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) cases [15]. Chen et al [19] had used the RI before and after oral protein loading to determine the RFR in patient with COPD. We used RI and PI indices in combination to calculate RFR and aimed to use both indices as a confirmation of each other. The results are compatible with one another, and these two indices provide similar values to each other (22.2% for RI and 25.4% for PI). In this study, we demonstrated that RFR can be calculated by Doppler RI and PI measurements. Furthermore, for the first time the relationship between fasting and after protein meal was assessed using both indices in normal individuals. Our results show that intrarenal arterial resistance decreased with protein loading and the lowest values in both indices were obtained at the 75th minute after a protein meal in healthy subjects. This decreasing of RI and PI can be defined as Doppler RFR and its normal value should be approximately 20% or more in Med Ultrason 2015; 17(4): healthy subjects. Reduced or lost ratio refers to a pathological condition. This description in Doppler investigations could be useful in clinical practice for the determination of renal abnormalities. The limitation of this study is that normal Doppler RFR values are not calculated separated by age groups. In addition, more comprehensive Doppler US comparison studies are needed to assess the correlation between the creatinine clearance or GFR values and the Doppler RFR ratio. Furthermore, more studies with larger numbers of participants are required to confirm these findings, measuring hemodynamic indices. In conclusion, in the early diagnosis of renal functional impairment as a result of various diseases, RFR assessment can be performed by Doppler ultrasonography which is a noninvasive method. Doppler RFR values of normal individuals are considered useful to be known. References 1. Platt JF, Ellis JH, Rubin JM. Examination of native kidneys with duplex Doppler ultrasound. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 1991; 12: Patriquin HB, O Regan S, Robitaille P, Paltiel H. Hemolytic-uremic syndrome: intrarenal arterial Doppler patterns as a useful guide to therapy. Radiology 1989; 172: Mikkonen RH, Kreula JM, Virkkunen PJ. Reliability of Doppler ultrasound in follow-up studies. Acta Radiol 1998; 39: Gregorio F, Ambrosi F, Carle F, et al. Microalbuminuria, brain vasomotor reactivity, carotid and kidney arterial flow in Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Nutr Metab 2004; 17: Mostbeck GH, Kain R, Mallek R, et al. Duplex Doppler sonography in renal parenchymal disease. Histopathologic correlation. J Ultrasound Med 1991; 10: Erratum in: J Ultrasound Med 1991; 10: Brkljacic B, Sabljar-Matovinovic M, Putarek K, Soldo D, Morovic-Vergles J, Hauser M. Renal vascular resistance in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Evaluation with color Doppler ultrasound. Acta Radiol 1997; 38: Petersen LJ, Petersen JR, Talleruphuus U, Ladefoged SD, Mehlsen J, Jensen HA. The pulsatility index and the resistive index in renal arteries. Associations with long-term progression in chronic renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1997; 12: Malatino LS, Polizzi G, Garozzo M, et al. Diagnosis of renovascular disease by extra and intrarenal Doppler parameters. Angiology 1998; 49: Bude RO, Rubin JM. Detection of renal artery stenosis with Doppler sonography: it is more complicated than originally thought. Radiology 1995; 196: Viazzi F, Leoncini G, Derchi LE, Pontremoli R. Ultrasound Doppler renal resistive index: a useful tool for the manage- 467
5 468 Mehmet Zekai Pekkafalı et al Doppler ultrasound measurements of renal functional reserve in healthy subjects ment of the hypertensive patient. J Hypertens 2014; 32: Baumgartner I, Lerman LO. Renovascular hypertension: screening and modern management. Eur Heart J 2011; 32: Kawai T, Kamide K, Onishi M, et al. Relationship between renal hemodynamic status and aging in patients without diabetes evaluated by renal Doppler ultrasonography. Clin Exp Nephrol 2012; 16: Woods LL. Mechanisms of renal hemodynamic regulation in response to protein feeding. Kidney Int 1993; 44: Amiel C, Blanchet F, Freidlander G, Nitenberg A. Renal functional reserve. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1990; 5: Sharkey RA, Mulloy EMT, Kilgallen IA, O Neill SJ. Renal functional reserve in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 1997; 52: Bosch JP, Lauer A, Glabman S. Short-term protein loading in assesment of patients with renal disease. Am J Med 1984; 77: Ter Wee PM, Geerlings W, Rosman JB, Sluiter WJ, van der Geest S, Donker AJ. Testing renal reserve filtration capacity with an amino acid solution. Nephron 1985; 41: Martin WF, Armstrong LE, Rodriguez NR. Dietary protein intake and renal function. Nutr Metab 2005; 2: Chen CY, Hsu TW, Mao SJ, et al. Abnormal renal resistive index in patients with mild-to-moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD 2013; 10: Ikee R, Kobayashi S, Hemmi N, et al. Correlation between the resistive index by Doppler ultrasound and kidney function and histology. Am J Kidney Dis 2005; 46: Rosato E, Gigante A, Barbano B, et al. Intrarenal hemodynamic parameters correlate with glomerular filtration rate and digital microvascular damage in patients with systemic sclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2012; 41: Del Giudice A, Aucella F. Acute renal failure in the elderly: epidemiology and clinical features. J Nephrol 2012; 25 Suppl 19: S48-S Wang X, Bonventre JV, Parrish AR. The aging kidney: increased susceptibility to nephrotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci 2014; 15: Esposito C, Plati A, Mazzullo T, et al. Renal function and functional reserve in healthy elderly individuals. J Nephrol 2007; 20: Kalantarinia K, Belcik JT, Patrie JT, Wei K. Real-time measurement of renal blood flow in healthy subjects using contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2009; 297: F1129-F1134.
Prediction of Tubulo Interstitial Injuries by Doppler Ultrasound in Patients with Glomerular Disease: Value of Resistive Index and Atrophic Index
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 8, August 2015 1 Prediction of Tubulo Interstitial Injuries by Doppler Ultrasound in Patients with Glomerular Disease: Value
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 8, August 2015 1 Prediction of Tubulo Interstitial Injuries by Doppler Ultrasound in Patients with Glomerular Disease: Value
Duplex Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries. Duplex Ultrasound. In the Beginning
 Duplex Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries DIMENSIONS IN HEART AND VASCULAR CARE 2013 PENN STATE HEART AND VASCULAR INSTITUTE ROBERT G. ATNIP MD PROFESSOR OF SURGERY AND RADIOLOGY Duplex Ultrasound Developed
Duplex Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries DIMENSIONS IN HEART AND VASCULAR CARE 2013 PENN STATE HEART AND VASCULAR INSTITUTE ROBERT G. ATNIP MD PROFESSOR OF SURGERY AND RADIOLOGY Duplex Ultrasound Developed
Acute Protein Loading In The Assessment Of Renal Reserve
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Acute Protein Loading In The Assessment Of Renal Reserve C.S. Loo* M. Zaki* A.B. Sulaiman* A.B. Sukanya** Y.c. Voon** S.L. Kua*** * Institute of Urology and Nephrology, * * Department
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Acute Protein Loading In The Assessment Of Renal Reserve C.S. Loo* M. Zaki* A.B. Sulaiman* A.B. Sukanya** Y.c. Voon** S.L. Kua*** * Institute of Urology and Nephrology, * * Department
Renal artery stenosis
 Renal artery stenosis Dr. Alexander Woywodt Consultant Renal Physician, Royal Preston Hospital Preston, 31.10.2007 Menu anatomy of the renal arteries diseases of the large renal arteries atherosclerotic
Renal artery stenosis Dr. Alexander Woywodt Consultant Renal Physician, Royal Preston Hospital Preston, 31.10.2007 Menu anatomy of the renal arteries diseases of the large renal arteries atherosclerotic
The renal resistive index is a non-invasive indicator of hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhotics
 Journal of Advanced Clinical & Research Insights (2016), 3, 23 27 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The renal resistive index is a non-invasive indicator of hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhotics Mohsin Aslam, S. Ananth Ram,
Journal of Advanced Clinical & Research Insights (2016), 3, 23 27 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The renal resistive index is a non-invasive indicator of hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhotics Mohsin Aslam, S. Ananth Ram,
Title. CitationJournal of medical ultrasonics, 44(4): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type. File Information.
 Title Altered oscillation of Doppler-derived renal and ren patients Kudo, Yusuke; Mikami, Taisei; Nishida, Mutsumi; Okad Author(s) Satomi; Shibuya, Hitoshi; Kahata, Kaoru; Shimizu, Ch CitationJournal of
Title Altered oscillation of Doppler-derived renal and ren patients Kudo, Yusuke; Mikami, Taisei; Nishida, Mutsumi; Okad Author(s) Satomi; Shibuya, Hitoshi; Kahata, Kaoru; Shimizu, Ch CitationJournal of
AJNT. Original Article. Comparison between Doppler Ultrasound and Biopsy Findings in Patients with Suspected Kidney Transplant Rejection.
 . 2010 Jan;3(1):23-8 Original Article AJNT Comparison between Doppler Ultrasound and Biopsy Findings in Patients with Suspected Kidney Transplant Rejection Osama A Osman a*, Bernice Griffith b, Sally Classick
. 2010 Jan;3(1):23-8 Original Article AJNT Comparison between Doppler Ultrasound and Biopsy Findings in Patients with Suspected Kidney Transplant Rejection Osama A Osman a*, Bernice Griffith b, Sally Classick
1. Disorders of glomerular filtration
 RENAL DISEASES 1. Disorders of glomerular filtration 2. Nephrotic syndrome 3. Disorders of tubular transport 4. Oliguria and polyuria 5. Nephrolithiasis 6. Disturbances of renal blood flow 7. Acute renal
RENAL DISEASES 1. Disorders of glomerular filtration 2. Nephrotic syndrome 3. Disorders of tubular transport 4. Oliguria and polyuria 5. Nephrolithiasis 6. Disturbances of renal blood flow 7. Acute renal
HbA1c is an Independent Determinant of Renal Vascular Resistance Estimated by Doppler Sonography in Non-Diabetic Hypertensive Patients
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HbA1c is an Independent Determinant of Renal Vascular Resistance Estimated by Doppler Sonography in Non-Diabetic Hypertensive Patients Ken-ichi Miyoshi, Takafumi Okura, Tomoaki Nagao,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH HbA1c is an Independent Determinant of Renal Vascular Resistance Estimated by Doppler Sonography in Non-Diabetic Hypertensive Patients Ken-ichi Miyoshi, Takafumi Okura, Tomoaki Nagao,
Doppler Ultrasound of the Kidney
 Doppler Ultrasound of the Kidney Chang-Kyu Sung Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, SNU-SMG Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea Doppler ultrasound (US) is a very useful
Doppler Ultrasound of the Kidney Chang-Kyu Sung Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, SNU-SMG Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea Doppler ultrasound (US) is a very useful
Pediatric Imaging Original Research
 Interlobar Artery Parameters with Duplex Doppler Sonography Pediatric Imaging Original Research A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 186:828 832 0361 803X/06/1863 828 American Roentgen Ray
Interlobar Artery Parameters with Duplex Doppler Sonography Pediatric Imaging Original Research A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 186:828 832 0361 803X/06/1863 828 American Roentgen Ray
Evaluation of effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy on renal vasculature with Doppler ultrasonography
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 4, 273-277 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.154.sk2 Evaluation of effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy on renal vasculature with Doppler ultrasonography
Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 4, 273-277 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.154.sk2 Evaluation of effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy on renal vasculature with Doppler ultrasonography
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Physiology Lecture 2. What controls GFR?
 Physiology Lecture 2 Too much blood is received by the glomerular capillaries, this blood contains plasma, once this plasma enters the glomerular capillaries it will be filtered to bowman s space. The
Physiology Lecture 2 Too much blood is received by the glomerular capillaries, this blood contains plasma, once this plasma enters the glomerular capillaries it will be filtered to bowman s space. The
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Renal-Related Questions
 Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume. Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM
 Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Special Lecture 11/08/2013. Hypertension Dr. HN Mayrovitz
 Special Lecture 11/08/2013 Hypertension Dr. HN Mayrovitz Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) Major Factors Summarized Sympathetic Hormones Arteriole MAP ~ Q x TPR + f (V / C) SV x HR Renal SBP Hypertension =
Special Lecture 11/08/2013 Hypertension Dr. HN Mayrovitz Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) Major Factors Summarized Sympathetic Hormones Arteriole MAP ~ Q x TPR + f (V / C) SV x HR Renal SBP Hypertension =
Transducer Selection. Renal Artery Duplex Exam. Renal Scan. Renal Scan Echogenicity. How to Perform an Optimal Renal Artery Doppler Examination
 How to Perform an Optimal Renal Artery Doppler Examination Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging
How to Perform an Optimal Renal Artery Doppler Examination Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging
RADIOLOGY HEAD & NECK IMAGING. Iranian Journal of. Hadi Rokni Yazdi 1*, Safoura Faraji 2, Farokhlegha Ahmadi 3, Reza Shahmirzae 4
 HEAD & NECK IMAGING Iran J Radiol. 2012;9(1):12-16. DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.6730 Iranian Journal of RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGYwww.iranjradiol.com Color Doppler Indices of Orbital Arterial Flow in End-Stage Renal
HEAD & NECK IMAGING Iran J Radiol. 2012;9(1):12-16. DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.6730 Iranian Journal of RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGYwww.iranjradiol.com Color Doppler Indices of Orbital Arterial Flow in End-Stage Renal
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation
 Nephrol Dial Transplant ( 1997) 12: 1376 1380 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation The pulsatility index and the resistive index in renal arteries. Associations with long-term progression
Nephrol Dial Transplant ( 1997) 12: 1376 1380 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation The pulsatility index and the resistive index in renal arteries. Associations with long-term progression
Dr. Mehmet Kanbay Department of Medicine Division of Nephrology Istanbul Medeniyet University School of Medicine Istanbul, Turkey.
 The uric acid dilemma: causal risk factor for hypertension and CKD or mere bystander? Mehmet Kanbay, Istanbul, Turkey Chairs: Anton H. van den Meiracker, Rotterdam, The Netherlands Claudia R.C. Van Roeyen,
The uric acid dilemma: causal risk factor for hypertension and CKD or mere bystander? Mehmet Kanbay, Istanbul, Turkey Chairs: Anton H. van den Meiracker, Rotterdam, The Netherlands Claudia R.C. Van Roeyen,
Cardiovascular system
 Cardiovascular system L-4 Blood pressure & special circulation Dr Than Kyaw 27 February 2012 Blood Pressure (BP) Pressure generation and flow Blood is under pressure within its closed system. Pressure
Cardiovascular system L-4 Blood pressure & special circulation Dr Than Kyaw 27 February 2012 Blood Pressure (BP) Pressure generation and flow Blood is under pressure within its closed system. Pressure
Sympathetic Vasomotor Response Of The Radial Artery In Patients With End Stage Renal Disease
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nephrology Volume 2 Number 1 Sympathetic Vasomotor Response Of The Radial Artery In Patients With End Stage Renal Disease L Galea, M Schembri, M Debono Citation L Galea,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nephrology Volume 2 Number 1 Sympathetic Vasomotor Response Of The Radial Artery In Patients With End Stage Renal Disease L Galea, M Schembri, M Debono Citation L Galea,
Do ultrasound renal resistance indices reflect systemic rather than renal vascular damage in chronic kidney disease?
 NDT Advance Access published August 27, 2006 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2006) 1 of 8 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfl484 Original Article Do ultrasound renal resistance indices reflect systemic rather than renal vascular
NDT Advance Access published August 27, 2006 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2006) 1 of 8 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfl484 Original Article Do ultrasound renal resistance indices reflect systemic rather than renal vascular
COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB
 COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB CG Musso ¹, J Reynaldi¹, N Imperiali ¹, L Algranati ¹, DG Oreopoulos ² Nephrology Department Hospital Italiano
COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB CG Musso ¹, J Reynaldi¹, N Imperiali ¹, L Algranati ¹, DG Oreopoulos ² Nephrology Department Hospital Italiano
Goals. Access flow and renal artery stenosis evaluation by Doppler ultrasound. Reimbursement. WHY use of Doppler Ultrasound
 Access flow and renal artery stenosis evaluation by Doppler ultrasound Adina Voiculescu, MD Interventional Nephrology Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston Instructor at Harvard Medical School Understand
Access flow and renal artery stenosis evaluation by Doppler ultrasound Adina Voiculescu, MD Interventional Nephrology Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston Instructor at Harvard Medical School Understand
What effects will proximal or distal disease have on an waveform?
 Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director Director of of Ultrasound Ultrasound Education Education & & Quality Quality Assurance Assurance Baylor Baylor College College of of Medicine Medicine Division
Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director Director of of Ultrasound Ultrasound Education Education & & Quality Quality Assurance Assurance Baylor Baylor College College of of Medicine Medicine Division
What effects will proximal or distal disease have on a waveform?
 Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager Texas Children
Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager Texas Children
The Evaluation of Renal Hemodynamics with Doppler Ultrasonography
 The Evaluation of Renal Hemodynamics with Doppler Ultrasonography Mahir Kaya Department of Surgery, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Atatürk University, Erzurum Turkey 1 1. Introduction Gray-scale renal
The Evaluation of Renal Hemodynamics with Doppler Ultrasonography Mahir Kaya Department of Surgery, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Atatürk University, Erzurum Turkey 1 1. Introduction Gray-scale renal
Impact of Sickle Cell Disease in Renal Arteries Blood Flow Indices Using Ultrasonography
 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2017; 5(2): 9-13 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20170502.11 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN: 2330-832X (Online) Impact of Sickle
International Journal of Medical Imaging 2017; 5(2): 9-13 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20170502.11 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN: 2330-832X (Online) Impact of Sickle
US of Renovascular Hypertension. Jonathan R. Dillman, MD, MSc Associate Professor Director, Thoracoabdominal Imaging
 US of Renovascular Hypertension Jonathan R. Dillman, MD, MSc Associate Professor Director, Thoracoabdominal Imaging Disclosures Nothing Relevant Unrelated grant funding Siemens US Toshiba US Objectives
US of Renovascular Hypertension Jonathan R. Dillman, MD, MSc Associate Professor Director, Thoracoabdominal Imaging Disclosures Nothing Relevant Unrelated grant funding Siemens US Toshiba US Objectives
Pressure Diuresis 9 Sample Student Essays
 Pressure Diuresis 9 Sample Student Essays Below please find assembled consecutively in one document the brief analyses submitted by nine students in Mammalian Physiology 08 to the Teach Yourself Pressure
Pressure Diuresis 9 Sample Student Essays Below please find assembled consecutively in one document the brief analyses submitted by nine students in Mammalian Physiology 08 to the Teach Yourself Pressure
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal. Prof John Buscombe
 Renal Prof John Buscombe Renal nuclear Medicine Only consistent test of kidney func7on Many good tests for renal anatomy Ultrasound good looking at cysts and renal pelvis CT can look at perfusion, size
Renal Prof John Buscombe Renal nuclear Medicine Only consistent test of kidney func7on Many good tests for renal anatomy Ultrasound good looking at cysts and renal pelvis CT can look at perfusion, size
BIOL 2402 Renal Function
 BIOL 2402 Renal Function Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College 1 Renal Clearance and GFR Refers to the volume of blood plasma from which a component is completely removed in one minute by all
BIOL 2402 Renal Function Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College 1 Renal Clearance and GFR Refers to the volume of blood plasma from which a component is completely removed in one minute by all
Physiology of Circulation
 Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
Postnephrectomy Changes in Doppler Indexes of Remnant Kidney in Unrelated Kidney Donors
 Kidney Transplantation Postnephrectomy Changes in Doppler Indexes of Remnant Kidney in Unrelated Kidney Donors Abolfazl Bohlouli, 1 Mohammad Kazem Tarzamni, 2 Afshar Zomorrodi, 1 Sedigeh Abdollahifard,
Kidney Transplantation Postnephrectomy Changes in Doppler Indexes of Remnant Kidney in Unrelated Kidney Donors Abolfazl Bohlouli, 1 Mohammad Kazem Tarzamni, 2 Afshar Zomorrodi, 1 Sedigeh Abdollahifard,
What Do We Know? Disclosure Statement: 3/11/2015. Deep abdominal imaging
 Marsha M. Neumyer, BS, RVT, FSVU, FSDMS, FAIUM International Director Vascular Diagnostic Educational Services Vascular Resource Associates Harrisburg, PA Disclosure Statement: CME Calendar QR Code Marsha
Marsha M. Neumyer, BS, RVT, FSVU, FSDMS, FAIUM International Director Vascular Diagnostic Educational Services Vascular Resource Associates Harrisburg, PA Disclosure Statement: CME Calendar QR Code Marsha
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
The organs of the human body were created to perform ten functions among which is the function of the kidney to furnish the human being with thought.
 The organs of the human body were created to perform ten functions among which is the function of the kidney to furnish the human being with thought. Leviticus Rabba 3 Talmud Berochoth 6 1 b Outline &
The organs of the human body were created to perform ten functions among which is the function of the kidney to furnish the human being with thought. Leviticus Rabba 3 Talmud Berochoth 6 1 b Outline &
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to
 Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Renal Blood flow; Renal Clearance. Dr Sitelbanat
 Renal Blood flow; Renal Clearance Dr Sitelbanat Objectives At the end of this lecture student should be able to describe: Renal blood flow Autoregulation of GFR and RBF Regulation of GFR The Calcuation
Renal Blood flow; Renal Clearance Dr Sitelbanat Objectives At the end of this lecture student should be able to describe: Renal blood flow Autoregulation of GFR and RBF Regulation of GFR The Calcuation
The organs of the human body were created to perform ten functions among which is the function of the kidney to furnish the human being with thought.
 The organs of the human body were created to perform ten functions among which is the function of the kidney to furnish the human being with thought. Leviticus Rabba 3 Talmud Berochoth 6 1 b Nephrology
The organs of the human body were created to perform ten functions among which is the function of the kidney to furnish the human being with thought. Leviticus Rabba 3 Talmud Berochoth 6 1 b Nephrology
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Renal hemodynamics are affected by changes in
 The Acute Effects of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide on Renal Vascular Resistance in Patients With an Acute Exacerbation of COPD* Rose A. Sharkey, MRCPI; Eithne M.T. Mulloy, MRCPI; and Shane J. O Neill, FRCPI
The Acute Effects of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide on Renal Vascular Resistance in Patients With an Acute Exacerbation of COPD* Rose A. Sharkey, MRCPI; Eithne M.T. Mulloy, MRCPI; and Shane J. O Neill, FRCPI
Actualités néphrologiques Jean Hamburger 23 Avril Marie Courbebaisse, Service de Physiologie Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris
 Single nephron GFR Actualités néphrologiques Jean Hamburger 23 Avril 2018 Marie Courbebaisse, Service de Physiologie Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris Introdution Glomerular filtration and SNGFR
Single nephron GFR Actualités néphrologiques Jean Hamburger 23 Avril 2018 Marie Courbebaisse, Service de Physiologie Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris Introdution Glomerular filtration and SNGFR
Cardiac Pathophysiology
 Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries
 Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries Greg Curry Vascular Ultrasound Workshop Aug 2017 The Examination Technique Pathophysiology Role of US then and now Background Live Scanning Ultrasound Population: 20% Hypertensive
Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries Greg Curry Vascular Ultrasound Workshop Aug 2017 The Examination Technique Pathophysiology Role of US then and now Background Live Scanning Ultrasound Population: 20% Hypertensive
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Case 8038 Renal allograft complicated with renal artery stenosis
 Case 8038 Renal allograft complicated with renal artery stenosis Santiago I, Canelas A, Pinto AP Section: Cardiovascular Published: 2009, Nov. 30 Patient: 61 year(s), male Clinical History A 61-year-old
Case 8038 Renal allograft complicated with renal artery stenosis Santiago I, Canelas A, Pinto AP Section: Cardiovascular Published: 2009, Nov. 30 Patient: 61 year(s), male Clinical History A 61-year-old
Understanding the Doppler RI:
 Understanding the Doppler RI: Impact of Renal Arterial Distensibility on the RI in a Hydronephrotic Ex Vivo Rabbit Kidney Model Michael E. Murphy, PhD, Mitchell E. Tublin, MD The aim of this study was
Understanding the Doppler RI: Impact of Renal Arterial Distensibility on the RI in a Hydronephrotic Ex Vivo Rabbit Kidney Model Michael E. Murphy, PhD, Mitchell E. Tublin, MD The aim of this study was
Pathology of Hypertension
 2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
DOI: /jemds/2014/1968 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 STUDY OF RESISTIVE INDEX IN VARIOUS STAGES OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE IN CALCULATING THE RISK FOR HEPATORENAL SYNDROME J.S. Sikarwar 1, Shilpi Muchhoria 2, Rashmi Singh 3, Harish Bhujade 4,
STUDY OF RESISTIVE INDEX IN VARIOUS STAGES OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE IN CALCULATING THE RISK FOR HEPATORENAL SYNDROME J.S. Sikarwar 1, Shilpi Muchhoria 2, Rashmi Singh 3, Harish Bhujade 4,
Cardiovascular System. Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
Capillary vessel. A) permeability which can vary between tissues, within tissues at different times and along the capillary
 I. Capillary bed structure Single layer of endothelium supports diffusion MedSoc Teaching CRH Session 2 Capillary circualtion Chanel Tobinska Arteriole Capillary vessel Venules BLOOD Blood flow velocity
I. Capillary bed structure Single layer of endothelium supports diffusion MedSoc Teaching CRH Session 2 Capillary circualtion Chanel Tobinska Arteriole Capillary vessel Venules BLOOD Blood flow velocity
Blood Pressure. a change in any of these could cause a corresponding change in blood pressure
 Blood Pressure measured as mmhg Main factors affecting blood pressure: 1. cardiac output 2. peripheral resistance 3. blood volume a change in any of these could cause a corresponding change in blood pressure
Blood Pressure measured as mmhg Main factors affecting blood pressure: 1. cardiac output 2. peripheral resistance 3. blood volume a change in any of these could cause a corresponding change in blood pressure
A Closer Look: Renal Artery Stenosis. Renal artery stenosis (RAS) is defined as a TOPICS FROM CHEP. Shawn s stenosis
 TOPICS FROM CHEP A Closer Look: Renal Artery Stenosis On behalf of the Canadian Hypertension Education Program (CHEP), Dr. Tobe gives an overview of renal artery stenosis, including the prevalence, screening
TOPICS FROM CHEP A Closer Look: Renal Artery Stenosis On behalf of the Canadian Hypertension Education Program (CHEP), Dr. Tobe gives an overview of renal artery stenosis, including the prevalence, screening
Blood Pressure Regulation. Slides 9-12 Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = 1/3 systolic pressure + 2/3 diastolic pressure
 Sheet physiology(18) Sunday 24-November Blood Pressure Regulation Slides 9-12 Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = 1/3 systolic pressure + 2/3 diastolic pressure MAP= Diastolic Pressure+1/3 Pulse Pressure CO=MAP/TPR
Sheet physiology(18) Sunday 24-November Blood Pressure Regulation Slides 9-12 Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = 1/3 systolic pressure + 2/3 diastolic pressure MAP= Diastolic Pressure+1/3 Pulse Pressure CO=MAP/TPR
Cardiorenal Syndrome
 SOCIEDAD ARGENTINA DE CARDIOLOGIA Cardiorenal Syndrome Joint session ESC-SAC ESC Congress 2012, Munich César A. Belziti Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires I have no conflicts of interest to declare Cardiorenal
SOCIEDAD ARGENTINA DE CARDIOLOGIA Cardiorenal Syndrome Joint session ESC-SAC ESC Congress 2012, Munich César A. Belziti Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires I have no conflicts of interest to declare Cardiorenal
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE
 HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2
 Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2 Blood Pressure Main factors influencing blood pressure: Cardiac output (CO) Peripheral resistance (PR) Blood volume Peripheral resistance is a major factor
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2 Blood Pressure Main factors influencing blood pressure: Cardiac output (CO) Peripheral resistance (PR) Blood volume Peripheral resistance is a major factor
Colour Doppler sonography to screen for renal artery stenosistechnical
 2385 Colour Doppler sonography to screen for renal artery stenosistechnical points to consider B. Krumme and L. C. Rump University Hospital Freiburg, Department of Internal Medicine, Freiburg, Germany
2385 Colour Doppler sonography to screen for renal artery stenosistechnical points to consider B. Krumme and L. C. Rump University Hospital Freiburg, Department of Internal Medicine, Freiburg, Germany
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21)
 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow. Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD
 Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD Outline 1- Physical laws governing blood flow and blood pressure 2- Overview of vasculature 3- Arteries 4. Capillaries and venules
Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD Outline 1- Physical laws governing blood flow and blood pressure 2- Overview of vasculature 3- Arteries 4. Capillaries and venules
Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic
![Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic](/thumbs/90/103241154.jpg) Heart Failure Heart failure is the inability of the heart to deliver sufficient blood to the tissues to ensure adequate oxygen supply. Clinically it is characterized by signs of volume overload or symptoms
Heart Failure Heart failure is the inability of the heart to deliver sufficient blood to the tissues to ensure adequate oxygen supply. Clinically it is characterized by signs of volume overload or symptoms
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Physiology Unit 4
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
Atherosclerotic Renovascular Hypertension : Lessons from Recent Clinical Studies
 Review ISSN 1738-5997 (Print) ISSN 2092-9935 (Online) Electrolyte Blood Press 8:87-91, 2010 doi: 10.5049/EBP.2010.8.2.87 Atherosclerotic Renovascular Hypertension : Lessons from Recent Clinical Studies
Review ISSN 1738-5997 (Print) ISSN 2092-9935 (Online) Electrolyte Blood Press 8:87-91, 2010 doi: 10.5049/EBP.2010.8.2.87 Atherosclerotic Renovascular Hypertension : Lessons from Recent Clinical Studies
HD Scanning: Velocities and Volume Flow
 HD Scanning: Velocities and Volume Flow Non-Invasive Lab Symposium West Orange, NJ April 27, 2018 Volume Flow Cindy Sturt, MD, FACS, RVT 500,000 Americans on dialysis 20-25% annual mortality 65% 5 year
HD Scanning: Velocities and Volume Flow Non-Invasive Lab Symposium West Orange, NJ April 27, 2018 Volume Flow Cindy Sturt, MD, FACS, RVT 500,000 Americans on dialysis 20-25% annual mortality 65% 5 year
The Cardiorenal Syndrome in Heart Failure
 The Cardiorenal Syndrome in Heart Failure Van N Selby, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Advanced Heart Failure Program, UCSF October 9, 2015 Disclosures None 1 Cardiorenal Syndrome (CRS) A pathophysiologic
The Cardiorenal Syndrome in Heart Failure Van N Selby, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Advanced Heart Failure Program, UCSF October 9, 2015 Disclosures None 1 Cardiorenal Syndrome (CRS) A pathophysiologic
(Department of Radiology, Beylikdüzü State Hospital, İstanbul, Turkey) Corresponding Author: Dr. Mete Özdikici
 Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 5~ Issue 6 (2018) pp: 61-65 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Quantitative Measurements
Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 5~ Issue 6 (2018) pp: 61-65 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Quantitative Measurements
Heart. Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node. Lymphatic. system Arteriovenous anastomosis. (exchange vessels)
 Venous system Large veins (capacitance vessels) Small veins (capacitance vessels) Postcapillary venule Thoroughfare channel Heart Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node Lymphatic system Arteriovenous anastomosis
Venous system Large veins (capacitance vessels) Small veins (capacitance vessels) Postcapillary venule Thoroughfare channel Heart Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node Lymphatic system Arteriovenous anastomosis
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
Contrast Induced Nephropathy
 Contrast Induced Nephropathy O CIAKI refers to an abrupt deterioration in renal function associated with the administration of iodinated contrast media O CIAKI is characterized by an acute (within 48 hours)
Contrast Induced Nephropathy O CIAKI refers to an abrupt deterioration in renal function associated with the administration of iodinated contrast media O CIAKI is characterized by an acute (within 48 hours)
Hypovolemic Shock: Regulation of Blood Pressure
 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 81 Case 15 Hypovolemic Shock: Regulation of Blood Pressure Mavis Byrne is a 78-year-old widow who was brought to the emergency room one evening by her sister. Early in the day,
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 81 Case 15 Hypovolemic Shock: Regulation of Blood Pressure Mavis Byrne is a 78-year-old widow who was brought to the emergency room one evening by her sister. Early in the day,
Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions 14.1 Physical Law Governing Blood Flow and Blood Pressure 1. How do you calculate flow rate? 2. What is the driving force of blood
Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions 14.1 Physical Law Governing Blood Flow and Blood Pressure 1. How do you calculate flow rate? 2. What is the driving force of blood
Six main classes of blood vessels (on handout) Wall structure of arteries and veins (on handout) Comparison: Arteries vs. Veins (on handout)
 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with 64-MD-CT Angiography
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1. Resting membrane potential of the ventricular myocardium is: A. -55 to-65mv B. --65 to-75mv C. -75 to-85mv D. -85 to-95 mv E. -95 to-105mv 2. Regarding myocardial contraction:
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1. Resting membrane potential of the ventricular myocardium is: A. -55 to-65mv B. --65 to-75mv C. -75 to-85mv D. -85 to-95 mv E. -95 to-105mv 2. Regarding myocardial contraction:
Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output. Blood Vessels
 Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Made of smooth muscle, elastic and fibrous connective tissue Cells are not electrically coupled Blood Vessels Arteries arterioles
Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Made of smooth muscle, elastic and fibrous connective tissue Cells are not electrically coupled Blood Vessels Arteries arterioles
Collin County Community College RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Septic Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Rinaldo Bellomo Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Research Centre (ANZIC-RC) Melbourne Australia
 Septic Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Rinaldo Bellomo Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Research Centre (ANZIC-RC) Melbourne Australia Things we really, honestly know about septic AKI AKI is common
Septic Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Rinaldo Bellomo Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Research Centre (ANZIC-RC) Melbourne Australia Things we really, honestly know about septic AKI AKI is common
Blood Pressure Regulation. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
** Accordingly GFR can be estimated by using one urine sample and do creatinine testing.
 This sheet includes the lecture and last year s exam. When a patient goes to a clinic, we order 2 tests: 1) kidney function test: in which we measure UREA and CREATININE levels, and electrolytes (Na+,
This sheet includes the lecture and last year s exam. When a patient goes to a clinic, we order 2 tests: 1) kidney function test: in which we measure UREA and CREATININE levels, and electrolytes (Na+,
THE KIDNEY IN HYPOTENSIVE STATES. Benita S. Padilla, M.D.
 THE KIDNEY IN HYPOTENSIVE STATES Benita S. Padilla, M.D. Objectives To discuss what happens when the kidney encounters low perfusion To discuss new developments and clinical application points in two scenarios
THE KIDNEY IN HYPOTENSIVE STATES Benita S. Padilla, M.D. Objectives To discuss what happens when the kidney encounters low perfusion To discuss new developments and clinical application points in two scenarios
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
 LECTURE NO (2) Renal Physiology Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology The glomerulus Is a tuft of capillaries enclosed within a Bowman capsule. It is supplied by an afferent
LECTURE NO (2) Renal Physiology Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology The glomerulus Is a tuft of capillaries enclosed within a Bowman capsule. It is supplied by an afferent
Renal Doppler Diagnostics in Lead-, Nickel- and Manganese-Exposed Children
 666 Renal Doppler Diagnostics in Lead-, Nickel- and Manganese-Exposed Children Nina Zaitseva 1, Olga Ustinova 2, Olga Vozgoment 3, Alfiya Aminova 4 *, Alevtina Akatova 5, Yuliya Perlova 6, Irina Shtina
666 Renal Doppler Diagnostics in Lead-, Nickel- and Manganese-Exposed Children Nina Zaitseva 1, Olga Ustinova 2, Olga Vozgoment 3, Alfiya Aminova 4 *, Alevtina Akatova 5, Yuliya Perlova 6, Irina Shtina
Postoperative AV Fistula Evaluation. Postoperative examination protocol. Postoperative AVF Protocol. Hemodialysis Access Surveillance
 Hemodialysis Access Surveillance Postoperative AV Fistula Evaluation Failure of maturation Stenosis Perigraft mass/fluid collection Joseph L. Mills, Sr., M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular
Hemodialysis Access Surveillance Postoperative AV Fistula Evaluation Failure of maturation Stenosis Perigraft mass/fluid collection Joseph L. Mills, Sr., M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular
Chronic Kidney Disease. Dr Mohan B. Biyani A. Professor of Medicine University of Ottawa/Ottawa Hospital
 Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Mohan B. Biyani A. Professor of Medicine University of Ottawa/Ottawa Hospital Health Seminar Series Date 12 May 2013 Objectives Normal functioning of Kidneys. Risk factors to
Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Mohan B. Biyani A. Professor of Medicine University of Ottawa/Ottawa Hospital Health Seminar Series Date 12 May 2013 Objectives Normal functioning of Kidneys. Risk factors to
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY
 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
Cardiovascular System. Heart
 Cardiovascular System Heart Electrocardiogram A device that records the electrical activity of the heart. Measuring the relative electrical activity of one heart cycle. A complete contraction and relaxation.
Cardiovascular System Heart Electrocardiogram A device that records the electrical activity of the heart. Measuring the relative electrical activity of one heart cycle. A complete contraction and relaxation.
Significant Correlation between Brachial Pulse Pressure Index and Renal Resistive Index
 Mini Forum for Kidney and Heart Acta Cardiol Sin 2015;31:98 105 doi: 10.6515/ACS20140821D Significant Correlation between Brachial Pulse Pressure Index and Renal Resistive Index Meng-Kuang Lee, 1,2 Po-Chao
Mini Forum for Kidney and Heart Acta Cardiol Sin 2015;31:98 105 doi: 10.6515/ACS20140821D Significant Correlation between Brachial Pulse Pressure Index and Renal Resistive Index Meng-Kuang Lee, 1,2 Po-Chao
Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon
 Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Epidemiology & Definition Pathophysiology Clinical Studies Management Summary Hobart W. Harris,
Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Epidemiology & Definition Pathophysiology Clinical Studies Management Summary Hobart W. Harris,
The kidneys are excretory and regulatory organs. By
 exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
