SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION
|
|
|
- Marion Reed
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Model Answer SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may vary but the examiner may try to assess the understanding level of the candidate. 3) The language errors such as grammatical, spelling errors should not be given more Importance (Not applicable for subject English and Communication Skills.) 4) While assessing figures, examiner may give credit for principal components indicated in the figure. The figures drawn by candidate and model answer may vary. The examiner may give credit for any equivalent figure drawn. 5) Credits may be given step wise for numerical problems. In some cases, the assumed constant values may vary and there may be some difference in the candidate s answers and model answer. 6) In case of some questions credit may be given by judgement on part of examiner of relevant answer based on candidate s understanding. 7) For programming language papers, credit may be given to any other program based on equivalent concept. Page no : 1/14
2 Model Answer Q. No. Sub Q.N SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Answer Subject Code: Marking Scheme Q.1 A) Attempt any THREE: 12 a) Define pacemaker. Write down need of pacemaker. Ans : Pacemaker : SA node is a natural pacemaker which generates the pulses for the working of the heart. Whenever SA node fails to generate the pulse or if the pulse generated is not proper in that case we use instrument is known as pacemaker. Need: When the heart's natural pacemaker is defective, the heartbeat may be too fast, too slow or irregular. Rhythm problems also can occur because of a blockage of heart s electrical pathways. The pacemaker's pulse generator sends electrical impulses to the heart to help it pump properly. b) Differentiate between A.C & D.C defibrillator.(any 4 points) A.C defibrillator D.C defibrillator 1. It is not commonly used. 1. It is commonly used. 2. It produce undesirable side effect. 2. It does not produce undesirable side effect Capacitor is not used. 4. Capacitor is used. 5. At transformer secondary side diode is 5. At transformer secondary side diode is not used. used. c) Write down the application of suction apparatus. Ans : (any four) 1. Suction may be used to clear the airway of blood, saliva, vomit, or other secretions so that a patient may breathe. 2. Suctioning can prevent pulmonary aspiration, which can lead to lung infections. 3. In pulmonary hygiene, suction is used to remove fluids from the airways, to facilitate breathing and prevent growth of microorganisms. 4. In surgery suction can be used to remove blood from the area being operated on to allow surgeons to view and work on the area. 5. Suction may also be used to remove blood that has built up within the skull after an intracranial hemorrhage. Page no : 2/14
3 d) Draw a neat labelled block diagram of bedside monitor. (B) a) Attempt any ONE: Draw the circuit diagram of D.C Defibrillator. State the function of each block Ans: CHARGING CIRCUIT: A variable auto transformer T1 forms the primary of a high voltage transformer T2. The output voltage of the transformer is rectified by a diode rectifier and is connected to a vacuum type high voltage change over switch. In position A, the switch is connected to one end of an oil filled 16 micro fared capacitor. in this position the capacitor charges to voltage set by positioning of the auto transformer DISCHARGING CIRCUIT : When the shock is to be delivered to the patient, a foot switch or a push button mounted on a handle of the electrode is operated The high voltage switch changes over to position B and the capacitor is discharged across the heart through the electrodes. In a defibrillator.an enormous voltage approximately 4000v is initially applied to the patient. 03 Page no : 3/14
4 b) Draw the schematic diagram of Heart lung bypass machine and explain in detail. (any relevant diagram should be consider) 03 During open heart surgery for installation of a valve prosthesis or correction of a congenital mal formation the heart cannot maintain the circulation. It is then necessary to provide extra- corporeal circulation with a special machine called heart lunge machine.usually two cannulas are inserted in to the right side of the heart to collect the returning venous blood as shown in fig. Using heart lung machine extracorporeal circulation can be possible and in which the lungs and heart are replaced by the OXIGENERATOR and BLOOD PUMP respectively. The collected venous blood is directed in to a receiving reservoir of heart lung machine by gravity drainage. The accumulated blood in the operating field is also collected and passed in to the receiving reservoir by suction devices. From here the blood is passed in to the setting reservoir or dabbling chamber and then it is passed in to oxygenator. In the oxygenator the blood is exposed to an atmosphere rich in oxygen. From oxygenator a pump raises the pressure of the blood to the mean arterial pressure from which it flows in to an arterial heat exchanger. Arterial heat exchanger is necessary during hypothermic or low temperature operation which is followed for two reasons the first is to reduce body metabolism and therefore to reduce oxygen consumption during the operation. And secondly the brai n damage due to oxygen starvation is reduced. In the heat exchanger the blood is maintained at the human body temperature. From the heat exchanger the blood passes through a filter to prevent the possibility of partials or bubbles returning to the body. Systematic circulation is maintained by returning the arterial oxygenated blood to a major artery. Q2 Attempt any Four of the following 16 a) State different types of pacemaker. Draw block diagram of any one. Ans There are following types of pacemaker:(any 2 types should be considered) 1) External pacemaker 2) Internal pacemaker 3) Asynchronous pacemaker 4) Synchronous pacemaker 03 Page no : 4/14
5 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION b) Block diagram of Internal pacemaker ( any relevant diagram of any one type should be considered) Draw the block diagram of baby incubator. Ans.:4 c) d) List any four technical specifications of suction apparatus. 1. Power Supply-230V 50Hz. 2. Rating of Motor- continuous 3. Suction Bottle Capacity- 2 x 2000 ml minimum (with safety valve) 4. Gauge- 0 to760 mm Hg 5. Pump- Oil lubricates rotary pump 6. Suction Tubing- ID 7 mm, 5m long and non-collapsible. 7. Vacuum capacity: 18 litres/mim 8. Maximum depression: -75kPa (-563mmHg) 9. Working temperature range: +5 to +40 C. 4 Explain the need of central monitor. Ans.:Need of Central monitor: Central monitoring is the process of acquiring & recording the physiological parameter of different patients simultaneously on a single monitor at central station. In ICU the no. of critical patient is always high monitoring the physiological parameter for each patient is done by using bedside monitor but in some cases to reduce the manpower require delivering care. 4 Page no : 5/14
6 e) Describe the need of baby incubator. Need: 1. To provide controlled environment for new born or premature babies, who needs special care. 2. To monitor different aspects of children s environment in order to create ideal conditions for survival. 3. To regulate oxygen temperature and humidity level to protect infant from pollutants and infections. f) Differentiate between internal and external pacemaker. (any two point) 4 Internal pacemaker 1. Internal pacemakers are used in longterm pacing cases. 2. These types of pacemakers are used when there is permanent damage to the heart. 3. Internal pacemakers are implanted beneath the skin along with its electros. External pacemaker 1. External pacemakers used in short time pacing cases. 2. These types of pacemakers are used when the heart block presents as an emergency. 3. External pacemaker is applied externally on the surface of body by using metal electrodes. 4. Internal pacemakers are small in size. 4. External pacemakers are large in size. Q3 Attempt any Four 16 a) Differentiate between endocardial & myocardial leads. ( any two points) Endocardial pacemaker leads Myocardial pacemaker leads. 1. This is connected to inner side of heart chamber. 1. This is connected to outer wall of heart muscle. 2. This is used in external pacemaker. 2. This is used in internal pacemaker. 3. The endocardial lead is inserted into the inside of the heart via a vein, usually in the chest area. 4.Example : Porous tip electrode 3. This type of lead is most often used when other cardiac surgery is being performed and there is already access to the heart. 4. Example: Steroid eluting electrode. Page no : 6/14
7 b) Write down steps for trouble shooting of defibrillator. (any two steps should be consider) Fault Cause Action Unit is not getting switched on. No supply Check and provide proper Fuse blown supply Capacitor is not discharging. Keys are not functioning. LCD contrast is not varying. ECG trace not available. ECG printout is too dark. Improper electrode placement Discharge button may be faulty Keys may be broken or faulty Connection cable may be faulty Check the contrast varying knob Display may be faulty ECG cable may not be attached or loosely attached Synchronous mode may not be active Incorrect settings Faulty printing assembly Replace fuse Connect electrode properly Check for discharge buttons on electrode, replace if necessary Replace the keys Check and replace the connection cable Replace if faulty Change the display Connect ECG cable properly, replace if necessary Check the settings. Select synchronous mode Check the settings and select proper contrast and brightness. Check and replace if necessary. c) Draw block diagram of nebulizer and explain its working. R.F.Current Ultrasonic Energy To patient Generator Ultrasonic Transducer Chamber Medicine (any relevant diagram should be considered) Nebulizer is an instrument which is used in drug delivery. When therapy requires that water or some types of medications be suspended in the air as an aerosol, a device called nebulizer is used. In this device water or medication is picked up by a high velocity jet of oxygen or some other gas and thrown against one or more baffles or other surface. To brake the substance into controllable sized droplates or particles which are then applied to the patients via respirator. Page no : 7/14
8 d) Draw block diagram of programmable microprocessor based infusion pump. e) List the technical specification of Heart-lung machine. (Any ) ( other relevant technical specification should be consider) 1. Console supply voltage: 230V 50 Hz. 2. Main fuses: 6A 3. Roller pump module: i) Master speed, forward and reverse: RPM ii) supply voltage: 24 V DC 4. Temperature measurement range: 0 C to + 50 C 5. Pressure measurement range: 200 mmhg to +800 mmhg or 26.7 kpa to kpa Q4. A) Attempt any THREE: 12 a) Differentiate between synchronous and asynchronous pacemaker. Ans (any points should be considered) Synchronous pacemaker Asynchronous pacemaker 1.Synchronous pacemaker delivers a 1.Asynchronous pacemaker delivers stim pacing stimulus only when the heart's intrinsic pacemaker fails to function at a uli at a fixed rate,independent of any atril or ventricular activity predetermined rate. 2. This type is commonly used. 2. This type is now rarely used. 3.Synchronous pacemaker detect spontaneous ventricular activity and the output of the pacemaker is either suppressed or discharged in order to make the impulse fall within the safe period of the QRS complex. 3. In asynchronous pacemaker, there is a small risk of producing dangerous dysrhythmias if the impulse coincides with the vulnerable period of the T wave. Page no : 8/14
9 b ) List technical specification of ventilator. Ans :(any four) Power Source: - 220/230 V Ac 50 Hz supply. Ventilation parameters: - 1. Tidal volume ML (Adult patient). 50 to 300 ML (Paediatric PC mode). 2. Respiratory rate BPH. 3. Pressure cm H2O. 4. Inspiratory Peak Flow /min. 5. Minute volume /min. 6. Oxygen Concentration % 7. Inspiratory pause sec. 8. PEEP/CPAP - 30 cm H2O. Ventilation modes : 1. Pediatric mode. 2. Controlled mode. 3. Asst. Controlled mode. 4. Pressure Controlled Ventilation. 5. SIMV/V and SIMV/P. 6. Bipressure Ventilation. 7. CPAP and PEEP. 8. Facility for Non-Invasive ventilation c) Write down need of central monitor. Ans: Need of Central monitor: Central monitoring is the process of acquiring & recording the physiological parameter of different patients simultaneously on a single monitor at central station. In ICU the no. of critical patient is always high monitoring the physiological parameter for each patient is done by using bedside monitor but in some cases to reduce the manpower require delivering care d ) Draw a labelled block diagram of suction apparatus. Ans: (any relevant diagram should be considered) Page no : 9/14
10 Q.4 B) Attempt any ONE : 06 a ) Give steps for maintenance of Defibrillator Ans: 1. To get good defibrillation paddles should be clean. So that if it is dirty cleans them with sprit. 2. Check the insulation of coil chord, mains cable. 3. Check the battery. 4. Check the fuses and consumable. 5. Check the switches such as joules, charge, discharge, synchonisation 06 b) Draw the neat block diagram of Hemodialysis machine. List technical specification of it. Ans: 03 Technical specification: ( Any 3 relevant technical specification should be consider) 1. Power input to be VAC, 50Hz. 2. Dialysate temperatures selectable between 35 degrees C to 39 deg.c. 3. Variable conductivity setting between 12 to Dialysate flow ml/mt. 5. Heparin pump with syringe sizes 20 to 30 ml with pump flow rate from 1-10 ml/hr. 6. Ultra filtration 0.1 to 2.5 liters/hr. 7. Blood pump rate from ml/min. 03 Page no : 10/14
11 Q.5 Attempt any FOUR: 16 a ) Draw the block diagram of atrial synchronous pacemaker. Ans : OR b) Explain the following modes of ventilator: (i) Assist (ii) Assist/Control Ans: i) Assist: A ventilator which augments the inspiration of the patient s inspiratory effort. A pressure sensor detects the slight negative pressure that occurs each time the patient attempts to inhale and triggers the process of inflating the lungs. Thus the ventilator helps the patient to inspire when needed. A sensitivity adjustment provided on the equipment helps to select the amount of effort required on the patient s part to trigger the inspiration process. The assist mode is required for those patients who are able to breathe but is unable to inhale a sufficient amount of air or for whom breathing requires a great deal of effort. ii) Assist/Control: A ventilator which combines both the controller and assistor functions. In these devices, if the patient fails to breathe within a pre-determined time, a timer automatically triggers inspiration process to inflate the lungs. Therefore, the breathing is controlled by the patient as long as it is possible, but in case the patient should fail to do so, the machine is able to take over the function. Such devices are most frequently used in critical care units. Page no : 11/14
12 c) State the troubleshooting steps carried out for bedside monitor. Ans: Following any two steps should be consider Problem Cause Action Nothing is displayed Mains not available. Fuse blown. Mains switch gets ON. Replace the fuse. Parameters are absent Faulty modules. Check and replace the faulty modules. Cannot store data in memory Improper connection between memory and processor. Correct the connection between memory and processor. Alarm dose not ring Improper alarm setting. Replace the SpO 2 module. Replace the sensor. d) Describe the concept of AED. Ans : An important development in the field of defibrillator has been the development and successful use of smart automatic or advisory external defibrillator (AED) which are capable of accurately analyzing the ECG and of making reliable shock decision. They are designed to detect ventricular fibrillation with sensitivity and specificity comparable to that of well trained paramedics then deliver or recommended (advisory) an appropriate high energy defibrillating shock.aed require self adhesive electrode instead of hand held paddles for two reasons. Firstly, the ECG signal acquired from self adhesive electrodes usually contains less noise and has higher quality. Hence, it allows a faster and more accurate analysis of ECG and therefore facilitates better shock decision. Secondly, Hand-off: defibrillation is safe procedure for the operator.especially if the operator has little or no training. An automatic external defibrillator is the ability of the device to accurately assess the patient s heart and appropriate therapy decision. It is small, light and virtually maintenance free. While it is on standby mode for long periods, the device automatically self tests its electronic circuitry every day and periodically performs an internal discharge and recalibration. The device is powered by long life disposable lithium battery with enough capacity for 75 discharges and one year of self test. It uses a low energy biphasic waveform. e) List different types of oxygenators and give its impotance. Ans : There are two types of oxygenators which are used in heart-lung machine: 1. Bubble oxygenators 2. Membrane oxygenators Importance : Oxygenator is a device that is capable of exchange in oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood of human body during surgical procedure. The oxygenators repeatedly draw of the blood from the veins, reoxygenates and pumps it into the arterial system. The oxygenator serves as the lung during the open heart surgery as the lung. Page no : 12/14
13 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION f) Q6) a) 4 marks State the need of : (i) Anesthesia machine (ii) Suction apparatus Ans: i) Anesthesia machine: A surgical method of treatment consists mainly of operations which are normally carried out under some form of anesthesia. So anesthesia ensures that the patient does not feel pain and minimizes patient discomfort. It provides the surgeon with favorable conditions for the work. ii) Suction apparatus: The main function of this device to remove liquids and gases (such as vomiting, saliva) from mouth and respiratory tract, and also during surgeries to remove fluid from operated area. 16 Attempt any FOUR: Draw neat diagram of Anesthesia machine. Ans : b) Write down need of Pacemaker leads. State different leads used for pacemaker. Ans: Need: Leads are thin, soft, insulated wires about the size of spaghetti noodles. The leads carry the electrical impulse from the pacemaker to your heart and relay information about the heart s natural activity back to your pacemaker. Pacemaker lead: 1. Unipolar: In uniplar system one electrode in inside or on the heart & is the stimulating electrode, & the second electrode is usually a large metal plate attached to the pulse generator. The current in this case flows between the pacing electrode in the heart & the indifferent electrode via the body tissue. 2. Bipolar leads: Bipolar leads which have two electrodes positioned in the heart are designed with a coaxial connector requiring only a single receptacle resulting in improvement in the size of bipolar pacemaker connector. In the bipolar electrode system both electrodes are approximately of the same size and both are placed inside or on the heart so that current flows between the two electrodes. 3. Myocardial leads: This is connected to outer wall of heart muscle. 4. Endocardial leads: This is connected to inner side of heart chamber. Page no : 13/14
14 c) Draw the block diagram of conventional method and closed loop control drug delivery system. Ans : Fig a. Conventional method drug delivery system Fig b. Closed loop control drug delivery system d) Write technical specification of baby incubator. Ans: (any ) 1) Air temperature control range: 25 C -38 C (>37 C temperature setting.) 2) Skin temperature control range:35 C - 37 C 3) Power supply: 230v AC 50 Hz. 4) Humidity control range:40-95%rh 5) Water tank capacity: ml 6) Weight 89 kgs Approx e) Describe concept of heart block. Ans : Heart block occurs whenever the conduction system fails to transmit the pacing impulses from the atria to the ventricles properly. In first degree block an excessive impulse delay at AV junction occurs that causes the P- R interval to exceed 0.2 second for normal adults. Second degrees block result in the complete but intermittent inhibition of pacing impulse, which may also occur at the AV node. A total and continuous impulse blockage is called third degree block. It may occur at the AV node or elsewhere in the conduction system. In this case, the ventricles usually continue to contract but a sharply reduced rate (40BPM) because of impulses that only periodically originate from the atria. Page no : 14/14
Biomedical Instrumentation
 Biomedical Instrumentation Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr naydin@ieee.org http://www.yildiz.edu.tr/~naydin Therapeutic and Prosthetic Devices 1 Figure 13.1 Block diagram of an asynchronous
Biomedical Instrumentation Prof. Dr. Nizamettin AYDIN naydin@yildiz.edu.tr naydin@ieee.org http://www.yildiz.edu.tr/~naydin Therapeutic and Prosthetic Devices 1 Figure 13.1 Block diagram of an asynchronous
DEFIBRILLATORS ATRIAL AND VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION
 1 DEFIBRILLATORS The two atria contract together and pump blood through the valves into the two ventricles, when the action potentials spread rapidly across the atria surface. After a critical time delay,
1 DEFIBRILLATORS The two atria contract together and pump blood through the valves into the two ventricles, when the action potentials spread rapidly across the atria surface. After a critical time delay,
OBJECTIVE. 1. Define defibrillation. 2. Describe Need and history of defibrillation. 3. Describe the principle and mechanism of defibrillation.
 Defibrillators OBJECTIVE 1. Define defibrillation. 2. Describe Need and history of defibrillation. 3. Describe the principle and mechanism of defibrillation. 4. Types and classes of defibrillator 5. Describe
Defibrillators OBJECTIVE 1. Define defibrillation. 2. Describe Need and history of defibrillation. 3. Describe the principle and mechanism of defibrillation. 4. Types and classes of defibrillator 5. Describe
The heart's "natural" pacemaker is called the sinoatrial (SA) node or sinus node.
 PACEMAKER Natural pacemaker: The heart's "natural" pacemaker is called the sinoatrial (SA) node or sinus node. Artificial pacemaker: It is a small, battery-operated device that helps the heart beat in
PACEMAKER Natural pacemaker: The heart's "natural" pacemaker is called the sinoatrial (SA) node or sinus node. Artificial pacemaker: It is a small, battery-operated device that helps the heart beat in
DEFIBRILLATORS. Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah
 DEFIBRILLATORS Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Basics Defibrillation is definitive treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias such as ventricular fibrillation Defibrillation consists of delivering therapeutic
DEFIBRILLATORS Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah Basics Defibrillation is definitive treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias such as ventricular fibrillation Defibrillation consists of delivering therapeutic
Manual Defibrillators, Automatic External Defibrillators, Cardioversion, and External Pacing. D. J. McMahon cewood rev
 Manual Defibrillators, Automatic External Defibrillators, Cardioversion, and External Pacing D. J. McMahon 141001 cewood rev 2017-10-04 Key Points Defibrillators: - know the definition & electrical value
Manual Defibrillators, Automatic External Defibrillators, Cardioversion, and External Pacing D. J. McMahon 141001 cewood rev 2017-10-04 Key Points Defibrillators: - know the definition & electrical value
Newer pacemakers also can monitor your blood temperature, breathing, and other factors and adjust your heart rate to changes in your activity.
 Pacemakers & Defibrillators A pacemaker system consists of a battery, a computerized generator and wires with sensors called electrodes on one end. The battery powers the generator, and both are surrounded
Pacemakers & Defibrillators A pacemaker system consists of a battery, a computerized generator and wires with sensors called electrodes on one end. The battery powers the generator, and both are surrounded
The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012
 The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 What does the heart do? 3 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The heart is a muscular organ located in the thorax. It pumps blood continuously around
The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 What does the heart do? 3 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The heart is a muscular organ located in the thorax. It pumps blood continuously around
Defibrillator. BiomedGuy
 Defibrillator BiomedGuy Medtronic Physiocontrol LifePak 10 Introduction This life-support system is used by paramedic, hospital staff, and other trained authorized healthcare providers. Provides, ECG,
Defibrillator BiomedGuy Medtronic Physiocontrol LifePak 10 Introduction This life-support system is used by paramedic, hospital staff, and other trained authorized healthcare providers. Provides, ECG,
Manual Defibrillators, Automatic External Defibrillators, Cardioversion, and External Pacing
 Manual Defibrillators, Automatic External Defibrillators, Cardioversion, and External Pacing Key Points Defibrillators: - know the definition & electrical value of a joule - monophasic vs biphasic types:
Manual Defibrillators, Automatic External Defibrillators, Cardioversion, and External Pacing Key Points Defibrillators: - know the definition & electrical value of a joule - monophasic vs biphasic types:
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Cardiac Cycle. Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time.
 The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
Arrhythmias. Pulmonary Artery
 Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Introduction to Lesson 2 - Heartbeat
 Introduction to Lesson 2 - Heartbeat Activity: Locate your pulse at rest. Count how many times it beats in 15 seconds (look at a clock), then multiply this number by 4. This is your pulse rate Approximately
Introduction to Lesson 2 - Heartbeat Activity: Locate your pulse at rest. Count how many times it beats in 15 seconds (look at a clock), then multiply this number by 4. This is your pulse rate Approximately
The Automated Defibrillator: A Biomedical Engineering Success Story. Dr. James A. Smith
 The Automated Defibrillator: A Biomedical Engineering Success Story Dr. James A. Smith A Aorta VCS Superior Vena Cava RA Right Atrium RV Right Ventricle LV Left Ventricle The Heart Beating Heart: Video
The Automated Defibrillator: A Biomedical Engineering Success Story Dr. James A. Smith A Aorta VCS Superior Vena Cava RA Right Atrium RV Right Ventricle LV Left Ventricle The Heart Beating Heart: Video
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 10: Pacemaker Rhythms and Bundle Branch Block Learning Outcomes 10.1 Describe the various pacemaker rhythms. 10.2
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 10: Pacemaker Rhythms and Bundle Branch Block Learning Outcomes 10.1 Describe the various pacemaker rhythms. 10.2
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
EKG Sensor Product Number: ENEKG189
 imagine explore learn EKG Sensor Product Number: ENEKG189 Overview An electrocardiogram abbreviated as EKG or ECG is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical
imagine explore learn EKG Sensor Product Number: ENEKG189 Overview An electrocardiogram abbreviated as EKG or ECG is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical
MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa
 MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa INTENSIVE CARE POLICY & PROCEDURES Policy Number: R-25 Subject: Policy: Purpose: Cardioversion - Synchronized An RN may perform a synchronized
MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa INTENSIVE CARE POLICY & PROCEDURES Policy Number: R-25 Subject: Policy: Purpose: Cardioversion - Synchronized An RN may perform a synchronized
Outline. Electrical Activity of the Human Heart. What is the Heart? The Heart as a Pump. Anatomy of the Heart. The Hard Work
 Electrical Activity of the Human Heart Oguz Poroy, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Biomedical Engineering The University of Iowa Outline Basic Facts about the Heart Heart Chambers and Heart s The
Electrical Activity of the Human Heart Oguz Poroy, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Biomedical Engineering The University of Iowa Outline Basic Facts about the Heart Heart Chambers and Heart s The
Puzzling Pacemakers Cheryl Herrmann, APN, CCRN, CCNS-CSC-CMC
 Puzzling Pacemakers Cheryl Herrmann, APN, CCRN, CCNS-CSC-CMC Pacemaker: An electric device implanted in the body to regulate the heart beat. Delivers electrical stimuli over leads with electrodes in contact
Puzzling Pacemakers Cheryl Herrmann, APN, CCRN, CCNS-CSC-CMC Pacemaker: An electric device implanted in the body to regulate the heart beat. Delivers electrical stimuli over leads with electrodes in contact
ICD Implantation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm ICD Implantation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers (the right atrium
Melbourne Heart Rhythm ICD Implantation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers (the right atrium
EC6001 MEDICAL ELECTRONICS
 EC6001 MEDICAL ELECTRONICS UNIT I ELECTRO-PHYSIOLOGY AND BIO-POTENTIAL RECORDING The origin of Bio-potentials; bio-potential electrodes, biological amplifiers, ECG, EEG, EMG, PCG, lead systems and recording
EC6001 MEDICAL ELECTRONICS UNIT I ELECTRO-PHYSIOLOGY AND BIO-POTENTIAL RECORDING The origin of Bio-potentials; bio-potential electrodes, biological amplifiers, ECG, EEG, EMG, PCG, lead systems and recording
Figure 2. Normal ECG tracing. Table 1.
 Figure 2. Normal ECG tracing that navigates through the left ventricle. Following these bundle branches the impulse finally passes to the terminal points called Purkinje fibers. These Purkinje fibers are
Figure 2. Normal ECG tracing that navigates through the left ventricle. Following these bundle branches the impulse finally passes to the terminal points called Purkinje fibers. These Purkinje fibers are
QUICK SETUP GUIDE SECULIFE DFBASE
 QUICK SETUP GUIDE SECULIFE DFBASE SECULIFE DFBASE is a microprocessor-based instrument that is used in the testing of defibrillators. It measures the energy output and provides information about the defibrillator
QUICK SETUP GUIDE SECULIFE DFBASE SECULIFE DFBASE is a microprocessor-based instrument that is used in the testing of defibrillators. It measures the energy output and provides information about the defibrillator
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular
 Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
CORONARY ARTERIES HEART
 CARDIAC/ECG MODULE THE HEART CORONARY ARTERIES FIBRILLATING HEART CORONARY ARTERIES HEART PRACTICE RHYTHMS PRACTICE RHYTHMS ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION SA Node (60 100) Primary pacemaker AV Node (40 60) ***Creates
CARDIAC/ECG MODULE THE HEART CORONARY ARTERIES FIBRILLATING HEART CORONARY ARTERIES HEART PRACTICE RHYTHMS PRACTICE RHYTHMS ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION SA Node (60 100) Primary pacemaker AV Node (40 60) ***Creates
ΤΟ ΗΚΓ ΣΤΟΝ ΒΗΜΑΤΟΔΟΤΟΥΜΕΝΟ ΑΣΘΕΝΗ
 ΤΟ ΗΚΓ ΣΤΟΝ ΒΗΜΑΤΟΔΟΤΟΥΜΕΝΟ ΑΣΘΕΝΗ ΤΖΩΡΤΖ ΔΑΔΟΥΣ ΕΠΙΚΟΥΡΟΣ ΚΑΘΗΓΗΤΗΣ Α.Π.Θ. ΜΑΡΙΑ ΚΑΡΑΛΙΟΛΙΟΥ ΕΙΔΙΚΕΥΟΜΕΝΗ ΙΑΤΡΟΣ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ Β ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ Α.Π.Θ. ΙΠΠΟΚΡΑΤΕΙΟ Γ.Ν.Θ. 5 Why a Pacemaker is Implanted
ΤΟ ΗΚΓ ΣΤΟΝ ΒΗΜΑΤΟΔΟΤΟΥΜΕΝΟ ΑΣΘΕΝΗ ΤΖΩΡΤΖ ΔΑΔΟΥΣ ΕΠΙΚΟΥΡΟΣ ΚΑΘΗΓΗΤΗΣ Α.Π.Θ. ΜΑΡΙΑ ΚΑΡΑΛΙΟΛΙΟΥ ΕΙΔΙΚΕΥΟΜΕΝΗ ΙΑΤΡΟΣ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ Β ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ Α.Π.Θ. ΙΠΠΟΚΡΑΤΕΙΟ Γ.Ν.Θ. 5 Why a Pacemaker is Implanted
Sinus rhythm with premature atrial beats 2 and 6 (see Lead II).
 Cardiac Pacemaker Premature Beats When one of ectopic foci becomes irritable, it may spontaneously fire, leading to one or more premature beats. Atrial and junctional foci may become irritable from excess
Cardiac Pacemaker Premature Beats When one of ectopic foci becomes irritable, it may spontaneously fire, leading to one or more premature beats. Atrial and junctional foci may become irritable from excess
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information Normal Heart Function The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information Normal Heart Function The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two
About atrial fibrillation (AFib) Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) What is AFib? What s the danger? Who gets AFib?
 Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
TO THE OPERATOR AND PERSON IN CHARGE OF MAINTENANCE AND CARE OF THE UNIT:
 fabian HFO Quick guide TO THE OPERATOR AND PERSON IN CHARGE OF MAINTENANCE AND CARE OF THE UNIT: This Quick Guide is not a substitute for the Operation Manual. Read the Operation Manual carefully before
fabian HFO Quick guide TO THE OPERATOR AND PERSON IN CHARGE OF MAINTENANCE AND CARE OF THE UNIT: This Quick Guide is not a substitute for the Operation Manual. Read the Operation Manual carefully before
Atrial Fibrillation. Damage to your heart caused by a heart attack or rheumatic heart disease
 Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease
 Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
2
 1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
Adult Intubation Skill Sheet
 Adult Intubation 2. Opens the airway manually and inserts an oral airway *** 3. Ventilates the patient with BVM attached to oxygen at 15 lpm *** 4. Directs assistant to oxygenate the patient 5. Selects
Adult Intubation 2. Opens the airway manually and inserts an oral airway *** 3. Ventilates the patient with BVM attached to oxygen at 15 lpm *** 4. Directs assistant to oxygenate the patient 5. Selects
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
Essentials of Pacemakers and ICD s. Rajesh Banker, MD, MPH
 Essentials of Pacemakers and ICD s Rajesh Banker, MD, MPH Pacemakers have 4 basic functions: Stimulate cardiac depolarization Sense intrinsic cardiac function Respond to increased metabolic demand by providing
Essentials of Pacemakers and ICD s Rajesh Banker, MD, MPH Pacemakers have 4 basic functions: Stimulate cardiac depolarization Sense intrinsic cardiac function Respond to increased metabolic demand by providing
M Series with Rectilinear Biphasic Waveform Defibrillator Option Indications for Use
 DEFIBRILLATOR OPTION General Information Introduction M Series products are available with an advanced electrical design that provides a unique rectilinear biphasic waveform for defibrillation and cardioversion.
DEFIBRILLATOR OPTION General Information Introduction M Series products are available with an advanced electrical design that provides a unique rectilinear biphasic waveform for defibrillation and cardioversion.
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER EC6001 MEDICAL ELECTRONICS Regulation 2013 Academic Year
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER EC6001 MEDICAL ELECTRONICS Regulation 2013 Academic Year
Pediatric pacemakers & ICDs:
 Pediatric pacemakers & ICDs: perioperative management Manchula Navaratnam Clinical Assistant Professor LPCH, Stanford SPA 2016 Conflict of interest: none Objectives Indications in pediatrics Components
Pediatric pacemakers & ICDs: perioperative management Manchula Navaratnam Clinical Assistant Professor LPCH, Stanford SPA 2016 Conflict of interest: none Objectives Indications in pediatrics Components
PERIOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT: CARDIAC PACEMAKERS AND DEFIBRILLATORS
 PERIOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT: CARDIAC PACEMAKERS AND DEFIBRILLATORS DR SUSAN CORCORAN CARDIOLOGIST ONCE UPON A TIME.. Single chamber pacemakers Programmed at 70/min VVI 70 UNIPOLAR SYSTEMS A Unipolar Pacing
PERIOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT: CARDIAC PACEMAKERS AND DEFIBRILLATORS DR SUSAN CORCORAN CARDIOLOGIST ONCE UPON A TIME.. Single chamber pacemakers Programmed at 70/min VVI 70 UNIPOLAR SYSTEMS A Unipolar Pacing
X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary Introduction A pacemaker is a device that regulates the heart beat. More than half a million Americans use a pacemaker. If your doctor recommends that you have a pacemaker,
X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary Introduction A pacemaker is a device that regulates the heart beat. More than half a million Americans use a pacemaker. If your doctor recommends that you have a pacemaker,
Reviewed Date: Supersedes (Policy #/description & date): Prepared by: Jacque Callis, RN Approved by: D.R. Johnson, MD
 External Pacemaker Set-up and Revised Date: 11/13/2014 Page 1 of 5 POLICY: The transcutaneous external pacemaker will be used as a noninvasive method of delivering electrical stimuli to the myocardium
External Pacemaker Set-up and Revised Date: 11/13/2014 Page 1 of 5 POLICY: The transcutaneous external pacemaker will be used as a noninvasive method of delivering electrical stimuli to the myocardium
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibril. Defibrillators. Ratko Magjarević
 Implantable Cardioverter-Defibril Defibrillators Ratko Magjarević University of Zagreb Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Croatia ratko.magjarevic@fer.hr Ventricular Fibrillation Ventricular
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibril Defibrillators Ratko Magjarević University of Zagreb Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Croatia ratko.magjarevic@fer.hr Ventricular Fibrillation Ventricular
ICD: Basics, Programming and Trouble-shooting
 ICD: Basics, Programming and Trouble-shooting Amir AbdelWahab, MD Electrophysiology and Pacing Service Cardiology Department Cairo University Feb 2013 Evolution of ICD Technology ICD Evolution Indications
ICD: Basics, Programming and Trouble-shooting Amir AbdelWahab, MD Electrophysiology and Pacing Service Cardiology Department Cairo University Feb 2013 Evolution of ICD Technology ICD Evolution Indications
The Normal Electrocardiogram
 C H A P T E R 1 1 The Normal Electrocardiogram When the cardiac impulse passes through the heart, electrical current also spreads from the heart into the adjacent tissues surrounding the heart. A small
C H A P T E R 1 1 The Normal Electrocardiogram When the cardiac impulse passes through the heart, electrical current also spreads from the heart into the adjacent tissues surrounding the heart. A small
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
Sample. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
This leaflet is intended for patients with permanent pacemakers and their parents.
 Permanent PACEMAKER This leaflet is intended for patients with permanent pacemakers and their parents. It serves as an information tool and a guide that offers some advice in order to live safely. General
Permanent PACEMAKER This leaflet is intended for patients with permanent pacemakers and their parents. It serves as an information tool and a guide that offers some advice in order to live safely. General
STATE OF OKLAHOMA 2014 EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES PROTOCOLS
 3K NON-INVASIVE POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION (NIPPV) ADULT EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC Indications: 1. Dyspnea Uncertain Etiology Adult. 2. Dyspnea Asthma Adult. 3. Dyspnea Chronic
3K NON-INVASIVE POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION (NIPPV) ADULT EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC Indications: 1. Dyspnea Uncertain Etiology Adult. 2. Dyspnea Asthma Adult. 3. Dyspnea Chronic
Mini Pulse Electronic Stimulator
 Mini Pulse Electronic Stimulator Model: PM-180 Operating Manual IMPORTANT: Please read all instructions before using this product. Retain this manual for future reference. www.santamedical.com IMPORTANT
Mini Pulse Electronic Stimulator Model: PM-180 Operating Manual IMPORTANT: Please read all instructions before using this product. Retain this manual for future reference. www.santamedical.com IMPORTANT
Life saver 9. Life saver 9. Life saver 9. Life saver 8. Mobility of device 3. Mobility of device 1. PET scan. Ultra Violet Lamp. MRI scanner.
 Ultra Violet Lamp MRI scanner Used to stop jaundice in babies helping the tiny liver clean the blood. Also used to treat people with TB, Lupus or even treat acne. Mobility of device 3 Uses magnets to change
Ultra Violet Lamp MRI scanner Used to stop jaundice in babies helping the tiny liver clean the blood. Also used to treat people with TB, Lupus or even treat acne. Mobility of device 3 Uses magnets to change
DEFIB «U S E-HEART. CardioStart MEDICAL MEDIO TECHNOLOGIES BIPHASIC DEFIBRILLATORS К-ИЕЛКГ. Wmwie
 «U S DEFIB Т^П MEDICAL MEDIO TECHNOLOGIES BIPHASIC DEFIBRILLATORS i E-HEART CardioStart К-ИЕЛКГ Wmwie E-HEART CardioStart The lightest! ONLY 8,82 lbs 4Kg With the innovative flip down display. Multiple
«U S DEFIB Т^П MEDICAL MEDIO TECHNOLOGIES BIPHASIC DEFIBRILLATORS i E-HEART CardioStart К-ИЕЛКГ Wmwie E-HEART CardioStart The lightest! ONLY 8,82 lbs 4Kg With the innovative flip down display. Multiple
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
OG TAL ODUCT CA PR e e HEALTH
 PRODUCT CATALOG e e HEALTH MODEL: OC 5 HEALTH OXYGEN CONCENTRATOR ACCESSORIES FILTER AIR FILTER NASAL CANNULA BUBBLE HUMIDIFIER Oxygen concentrator is a device that generates oxygen with a purity of %90-92
PRODUCT CATALOG e e HEALTH MODEL: OC 5 HEALTH OXYGEN CONCENTRATOR ACCESSORIES FILTER AIR FILTER NASAL CANNULA BUBBLE HUMIDIFIER Oxygen concentrator is a device that generates oxygen with a purity of %90-92
Airway Clearance Devices
 Print Page 1 of 11 Wisconsin.gov home state agencies subject directory department of health services Search Welcome» August 2, 2018 5:18 PM Program Name: BadgerCare Plus and Medicaid Handbook Area: Durable
Print Page 1 of 11 Wisconsin.gov home state agencies subject directory department of health services Search Welcome» August 2, 2018 5:18 PM Program Name: BadgerCare Plus and Medicaid Handbook Area: Durable
Model 5392 EPG Temporary Pacer
 Model 5392 EPG Temporary Pacer Compatible Components Reference Card 5392 Surgical Cables 5487 Disposable, short 5487L Disposable, long 5832S Reusable, small clip 5833S 5833SL Disposable, small clip, short
Model 5392 EPG Temporary Pacer Compatible Components Reference Card 5392 Surgical Cables 5487 Disposable, short 5487L Disposable, long 5832S Reusable, small clip 5833S 5833SL Disposable, small clip, short
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
 Pacemaker Simulator ST2361 Learning Material Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Save paper, save trees, save earth Dear User, We request you to use the Learning material in the CD form provided with this
Pacemaker Simulator ST2361 Learning Material Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Save paper, save trees, save earth Dear User, We request you to use the Learning material in the CD form provided with this
Chapter 3 Biological measurement 3.1 Nerve conduction
 Chapter 3 Biological measurement 3.1 Nerve conduction Learning objectives: What is in a nerve fibre? How does a nerve fibre transmit an electrical impulse? What do we mean by action potential? Nerve cells
Chapter 3 Biological measurement 3.1 Nerve conduction Learning objectives: What is in a nerve fibre? How does a nerve fibre transmit an electrical impulse? What do we mean by action potential? Nerve cells
Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System
 Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System 2018 ALCTE Summer Conference EKG Basics Brian Gober, MAT, ATC, NRP, CSCS Education Services Manager ECC Training Center Coordinator Birmingham Regional
Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System 2018 ALCTE Summer Conference EKG Basics Brian Gober, MAT, ATC, NRP, CSCS Education Services Manager ECC Training Center Coordinator Birmingham Regional
Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias)
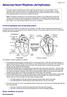 Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias) Page 1 of 5 The heart needs a small electrical current to pass through the heart in a very set pattern. This is called the heart's conduction system. This leaflet explains
Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias) Page 1 of 5 The heart needs a small electrical current to pass through the heart in a very set pattern. This is called the heart's conduction system. This leaflet explains
Biomedical Instrumentation
 University of Zagreb Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Biomedical Instrumentation Safety of electrical medical devices prof.dr.sc. Ratko Magjarević Medical technology Achievements Significant
University of Zagreb Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Biomedical Instrumentation Safety of electrical medical devices prof.dr.sc. Ratko Magjarević Medical technology Achievements Significant
SLEEP IMPROVING WRISTBAND. Item No Owner s Guide
 SLEEP IMPROVING WRISTBAND Item No. 205350 Owner s Guide Thank you for purchasing the Sharper Image Sleep Improving Wristband. Based on ancient Chinese acupuncture principles, this biofeedback device uses
SLEEP IMPROVING WRISTBAND Item No. 205350 Owner s Guide Thank you for purchasing the Sharper Image Sleep Improving Wristband. Based on ancient Chinese acupuncture principles, this biofeedback device uses
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG)
 PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG) The technique of listening to sounds produced by the organs and vessels of the body is called auscultation. The areas at which the heart sounds are heard better are called auscultation
PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG) The technique of listening to sounds produced by the organs and vessels of the body is called auscultation. The areas at which the heart sounds are heard better are called auscultation
WELCOME. Welcome to the Children s Hospital PICU (Pediatric Intensive Care Unit). We consider it a privilege to care for your child and your family.
 ECMO FAMILY GUIDE WELCOME Welcome to the Children s Hospital PICU (Pediatric Intensive Care Unit). We consider it a privilege to care for your child and your family. This book was created to give you the
ECMO FAMILY GUIDE WELCOME Welcome to the Children s Hospital PICU (Pediatric Intensive Care Unit). We consider it a privilege to care for your child and your family. This book was created to give you the
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System
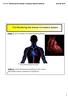 12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview
 Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview Components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Vascular system Blood Figure 12-1 Plasma includes water, ions, proteins, nutrients, hormones, wastes,
Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview Components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Vascular system Blood Figure 12-1 Plasma includes water, ions, proteins, nutrients, hormones, wastes,
Defibrillators TEC-8300K series. It s all seamless
 Defibrillators TEC-8300K series It s all seamless The one you need in an emergency ECG, SpO 2, NIBP, MULTI connectors, Pacing* * Pacing available with TEC-8332K/8352K Pre-hospital Out-of-hospital 12-lead
Defibrillators TEC-8300K series It s all seamless The one you need in an emergency ECG, SpO 2, NIBP, MULTI connectors, Pacing* * Pacing available with TEC-8332K/8352K Pre-hospital Out-of-hospital 12-lead
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES
 UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
8/13/11. RSPT 1410 Humidity & Aerosol Therapy Part 3. Humidification Equipment. Aerosol Therapy
 1 RSPT 1410 Humidity & Aerosol Therapy Part 3 Wilkins: Chapter 35, p. 775-799 Cairo: Chapter 4, p. 88-143 2 Humidification Equipment A humidifier is a device that adds molecular liquid (e.g. water vapor)
1 RSPT 1410 Humidity & Aerosol Therapy Part 3 Wilkins: Chapter 35, p. 775-799 Cairo: Chapter 4, p. 88-143 2 Humidification Equipment A humidifier is a device that adds molecular liquid (e.g. water vapor)
EI2311 BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION
 66 EI2311 BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION 1. What is meant by cell? UNIT I PHYSIOLOGY AND TRANSDUCERS The basic living unit of the body is cell. The function of organs and other structure of the body is understood
66 EI2311 BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION 1. What is meant by cell? UNIT I PHYSIOLOGY AND TRANSDUCERS The basic living unit of the body is cell. The function of organs and other structure of the body is understood
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.2 Heart
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Pacing Lead Implant Testing. Document Identifier
 Pacing Lead Implant Testing 1 Objectives Upon completion of this presentation, the participant should be able to: Name the two primary surgical options for implanting pacing leads Describe three significant
Pacing Lead Implant Testing 1 Objectives Upon completion of this presentation, the participant should be able to: Name the two primary surgical options for implanting pacing leads Describe three significant
11/18/13 ECG SIGNAL ACQUISITION HARDWARE DESIGN. Origin of Bioelectric Signals
 ECG SIGNAL ACQUISITION HARDWARE DESIGN Origin of Bioelectric Signals 1 Cell membrane, channel proteins Electrical and chemical gradients at the semi-permeable cell membrane As a result, we get a membrane
ECG SIGNAL ACQUISITION HARDWARE DESIGN Origin of Bioelectric Signals 1 Cell membrane, channel proteins Electrical and chemical gradients at the semi-permeable cell membrane As a result, we get a membrane
Carina. The compact wonder. Emergency Care Perioperative Care Critical Care Perinatal Care Home Care
 Carina The compact wonder Emergency Care Perioperative Care Critical Care Perinatal Care Home Care The new sub-acute ventilator Carina Sub-acute care is a rapidly growing medical care service for patients
Carina The compact wonder Emergency Care Perioperative Care Critical Care Perinatal Care Home Care The new sub-acute ventilator Carina Sub-acute care is a rapidly growing medical care service for patients
Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc.
 Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc. The Miracle of Living February 21, 2018 Matthew Ostrom MD,FACC,FHRS Division of
Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc. The Miracle of Living February 21, 2018 Matthew Ostrom MD,FACC,FHRS Division of
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
CORONARY ARTERIES. LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral wall of left vent Anterior 2/3 of interventricluar septum R & L bundle branches
 CORONARY ARTERIES RCA Right atrium Right ventricle SA node 55% AV node 90% Posterior wall of left ventricle in 90% Posterior third of interventricular septum 90% LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral
CORONARY ARTERIES RCA Right atrium Right ventricle SA node 55% AV node 90% Posterior wall of left ventricle in 90% Posterior third of interventricular septum 90% LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral
Relax and Learn At the Farm 2012
 Relax and Learn At the Farm Session 9: Invasive Hemodynamic Assessment and What to Do with the Data Carol Jacobson RN, MN Cardiovascular Nursing Education Associates Function of CV system is to deliver
Relax and Learn At the Farm Session 9: Invasive Hemodynamic Assessment and What to Do with the Data Carol Jacobson RN, MN Cardiovascular Nursing Education Associates Function of CV system is to deliver
PACEMAKER INTERPRETATION AND DEVICE MANAGEMENT PART I
 1 PACEMAKER INTERPRETATION AND DEVICE MANAGEMENT PART I Cynthia Webner DNP, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC Karen Marzlin DNP, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC 2 PROFESSIONAL NURSING PRACTICE CAN ONLY ADVANCE AS MUCH AS INDIVIDUAL
1 PACEMAKER INTERPRETATION AND DEVICE MANAGEMENT PART I Cynthia Webner DNP, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC Karen Marzlin DNP, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC 2 PROFESSIONAL NURSING PRACTICE CAN ONLY ADVANCE AS MUCH AS INDIVIDUAL
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG)
 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) The heart is a muscular organ, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, as well as assists in
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) The heart is a muscular organ, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, as well as assists in
Circulatory System Notes
 Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Defibrillators TEC-8300K series. Improving quality of resuscitation
 Defibrillators TEC-8300K series Improving quality of resuscitation Transitioning back to life For intensive treatment and advanced life support Pre-hospital Out-of-hospital 12-lead ECG acquisition and
Defibrillators TEC-8300K series Improving quality of resuscitation Transitioning back to life For intensive treatment and advanced life support Pre-hospital Out-of-hospital 12-lead ECG acquisition and
Analyzing the Heart with EKG
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG LabQuest An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG LabQuest An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION
 CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
TECHNOCARE MEDISYSTEMS
 TECHNOCARE MEDISYSTEMS TM 109 Patient Monitor Essential Monitoring Special Care Just what you ordered. A monitoring solution to support any care decision. For any care environment, National Medical delivers
TECHNOCARE MEDISYSTEMS TM 109 Patient Monitor Essential Monitoring Special Care Just what you ordered. A monitoring solution to support any care decision. For any care environment, National Medical delivers
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Circulatory System. Functions and Components of the Circulatory System. Chapter 13 Outline. Chapter 13
 Circulatory System Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Outline Functions and Components of the Circulatory System Composition of Blood Structure of the Heart Cardiac Cycle and Heart Sounds Electrical Activity of the
Circulatory System Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Outline Functions and Components of the Circulatory System Composition of Blood Structure of the Heart Cardiac Cycle and Heart Sounds Electrical Activity of the
EKG Competency for Agency
 EKG Competency for Agency Name: Date: Agency: 1. The upper chambers of the heart are known as the: a. Atria b. Ventricles c. Mitral Valve d. Aortic Valve 2. The lower chambers of the heart are known as
EKG Competency for Agency Name: Date: Agency: 1. The upper chambers of the heart are known as the: a. Atria b. Ventricles c. Mitral Valve d. Aortic Valve 2. The lower chambers of the heart are known as
NEIL CISPER TECHNICAL FIELD ENGINEER ICD/CRTD BASICS
 NEIL CISPER TECHNICAL FIELD ENGINEER ICD/CRTD BASICS OBJECTIVES Discuss history of ICDs Review the indications for ICD and CRT therapy Describe basic lead and device technology Discuss different therapies
NEIL CISPER TECHNICAL FIELD ENGINEER ICD/CRTD BASICS OBJECTIVES Discuss history of ICDs Review the indications for ICD and CRT therapy Describe basic lead and device technology Discuss different therapies
Project Title Temporary Pacemaker Training Simulator
 Project Title Temporary Pacemaker Training Simulator Project Description Problem: There is no available training device for temporary pacemakers (pacemakers). A training device will have to essentially
Project Title Temporary Pacemaker Training Simulator Project Description Problem: There is no available training device for temporary pacemakers (pacemakers). A training device will have to essentially
