The rapid evolution of echocardiography during the past 25 years
|
|
|
- Corey Day
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evaluation of Myocardial Mechanics in the Fetus by Velocity Vector Imaging Adel K. Younoszai, MD, David E. Saudek, MD, Stephen P. Emery, MD, and James D. Thomas, MD, Denver, Colorado; Cleveland, Ohio; and Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania There are limited data on the properties of fetal myocardium with only a small number of Doppler tissue imaging based studies published. We evaluated the feasibility of using velocity vector imaging, a novel technique for analyzing 2-dimensional images offline, to study myocardial mechanics in the normal fetal heart at different of gestational ages. A single 2-dimensional 4-chamber image of the heart was interrogated offline using velocity vector imaging software. Longitudinal velocity, strain, and strain rate were measured in the right ventricular free wall, ventricular septum, and left ventricular free wall. Images from 24 of 27 (89%) were successfully analyzed. The systolic and diastolic longitudinal velocities increased with gestational age in all myocardial segments analyzed (r , P.05). Systolic strain and strain rate were not found to have significant correlation with gestational age in any of the wall segments. This implies that increasing velocities during normal gestation are the result of somatic growth rather than changes in myocardial contractility. The rapid evolution of echocardiography during the past 25 years hasledtoagreaterunderstandingoffetalcardiacphysiology.cardiac functionhastraditionallybeenmeasuredbysubjectiveassessmentof contractility and observation for hydrops fetalis. Newer indices such as the myocardial performance index, which measures the proportion of the time in isovolumic contraction and relaxation compared with ejection, are under evaluation as surrogate measures of global cardiac function; however, aprecise understanding of cardiac mechanics and function in the developing fetus is lacking. 1 The investigation of cardiac mechanics has become an area of increasing interest. Doppler tissue imaging (DTI) uses Doppler shifts ofthemyocardiumtoevaluatetissuedisplacementandvelocity.this techniquehasimprovedourunderstandingoftissuemotion,segmental deformation, and ventricular twisting. The use of longitudinal myocardial velocity profiles has significantly improved the ability to diagnose diastolic heart failure in the adult. It has also been used in combination with Doppler flow velocities across the mitral valve to predict left ventricular (LV) filling pressures. From displacement and velocity data, cardiac strain and strain rate can be calculated. Strain is definedasrelativedeformationofthemyocardiumandisthechange inlength(l)ofamyocardialsegmentreferencedtoitsoriginallength (L o ),asgivenbythefollowingequation:strain L L o /L o,whereas strain rate describes the rate of deformation, or how quickly atissue shortens or lengthens. Strain rate will be decreased when the tissue From Pediatric Cardiology, The University of Colorado (A.K.Y.), Denver, Colorado; Pediatric Cardiology (D.E.S.) and Cardiology (J.D.T.), The Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, Ohio; and Obstetrics and Gynecology, The University of Pittsburgh (S.P.E.), Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Disclosure: Siemens has provided funding for imaging research to the Cleveland Clinic, Department of Cardiology. Reprint requests: Adel K. Younoszai, MD, Cardiac Imaging, The Children s Hospital, 1056 E 19th Ave, Cardiology/B100, Denver, CO ( Younoszai.Adel@ tchden.org) /$34.00 Copyright 2008 by the American Society of Echocardiography. doi: /j.echo changes aspecific length more slowly or has adecreased change in length in the same time span. Cardiac strain is not affected by translational motion of the heart and is theoretically, therefore, more accurate than simple velocity measurement. The fetal myocardium has unique properties. It is made up of primarily noncontractile elements with fewer myocytes and is stiffer compared with the mature heart. 2 The presence of fluid-filled lungs that externally limit ventricular relaxation may also contribute to decreased compliance during fetal diastole. 3 Myocardial tissue motion and velocities have now been investigated in the fetal heart with the first published report indicating its feasibility appearing in 1999 by Harada et al. 4 Since that time a number of preliminary studies have been performed validating the techniqueandreportingnormallongitudinalvelocities. 4-8 Inarecent report, Di Salvo et al 9 demonstrated that evaluation of strain and strain rate can also be measured in the fetus with limited variability. These Doppler-based techniques are subject to some technical limitations and are dependent on obtaining an optimal angle of interrogation. Velocity vector imaging (VVI) is anew offline analysis software package that allows evaluation of myocardial tissue motion and velocitywithoutthelimitationsofdopplerechocardiography.ituses acombination of speckle tracking with complexgeometricanalysisto follow the myocardium through the cardiac cycle. It offers an intuitive analysisofmyocardialmechanics,however,ithasnotbeenwellstudied andtherearenoreportsofitsuseinthefetus.theaimofthisstudywas toevaluatethefeasibilityofperformingvviinthenormalfetalheartat avarietyofgestationalagesandevaluatethevariationinvelocity,strain, and strain rate with gestational development and heart rate. METHODS Image Acquisition Data were collected from normal obstetric ultrasounds performed on an ultrasound system (Sequoia, Siemens Medical Systems, Malvern, PA) in the department of perinatology. Cardiac imaging, including a4-chamber view, was obtained as part of the standard examination by an experienced perinatologist. Any fetus in which
2 Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography Younoszai et al 471 Volume 21 Number 5 Figure 1 Velocity vector profile. Example of processed velocity vector image. Pictures represent still frames of left ventricle (LV) with velocity vectors in diastole and systole. Length of each arrow represents magnitude of velocity in that direction of representative myocardium. LA, Left atrium; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle. Color figure online. Figure 2 Example of velocity, strain, and strain rate profiles of left ventricle superimposed on background M-mode. Green tracing represents sample at midseptal wall and red represents sample of mid-left ventricular free wall. Velocities are measured as moving toward (positive) or away (negative) from icon of transducer placed at apex of heart as point of reference (top left). Color figure online. there was a significant fetal anomaly, known chromosomal abnormality, abnormal cardiac rhythm, or inappropriate size for gestational age was excluded. All data were stored as standard Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine (DICOM) standard images with a frame rate of 30 Hz. Offline Analysis The images were interrogated offline using software (Axius VVI 2, Siemens Medical Solutions). The subendocardium of both ventricles was traced at end systole and a total of 2 to 3 cardiac cycles were averaged to obtain a velocity vector profile of myocardial motion (Figure 1). Longitudinal velocity measurements (peak systolic and peak diastolic) were performed at the right ventricular (RV) free wall, septum, and LV free wall at the level of the atrioventricular valves. A peak diastolic velocity was reported as the velocity profiles did not separate out early and late diastolic waveforms. Longitudinal strain and strain rate were measured in the midportion of the myocardium of the same 3 walls (Figure 2).
3 472 Younoszai et al Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography May 2008 Statistics Interobserver variation, defined as the difference of the values obtained between reviewers over the mean of those values, was calculated from a randomly chosen sample of 10 data sets. All variables of myocardial function were correlated with increasing gestational age and heart rate. RESULTS Feasibility Images from 27 fetal examinations were presented for offline analysis. Of these, 24 (89%) were successfully analyzed. The median gestational age was 25 and 3/7 weeks and ranged from 18 and 2/7 weeks to 39 weeks. The median fetal heart rate, calculated from reconstructed M-mode peak-to-peak cardiac intervals, was 146/min and ranged from 126 to 168/min. Interobserver Variability The interobserver variabilities for systolic velocity were 0.20,.018, and 0.22 in the RV free wall, septum, and LV free wall, respectively. Similar values for the diastolic velocity were 0.18, 0.24, and For strain they were 0.24, 0.17, and 0.15 and for strain rate they were 0.15, 0.30, and Changes with Gestational Age Systolic and Diastolic Annular Velocities The systolic and diastolic longitudinal velocities increased with gestational age in all myocardial segments measured (Figure 3). The strongest correlation was in the septum for both systolic and diastolic velocities (septal systolic r 0.78, P.0001, septal diastolic r 0.73, P.0001). The lowest correlation was in the RV free wall (RV systolic r 0.56, P.004, RV diastolic r 0.42, P.040) and the LV free wall was intermediate between the two (LV systolic r 0.65, P.0009, LV diastolic r 0.67, P.0006). Changes with Gestational Age Systolic Strain and Strain Rate Systolic strain and strain rate were not found to have significant correlation with gestational age in any of the wall segments (Figure 3). Changes with Heart Rate Systolic and diastolic velocities were not found to have a significant correlation with heart rate in any of the myocardial walls measured. Strain did not vary with heart rate either. Strain rate did appear to increase with an increase in heart rate in the RV free wall (r 0.55, P.01) and the septum (r 0.51, P.01). A similar trend was seen in the LV free wall (r P.12) (Figure 4). There was no significant change in heart rate with advancing gestational age. DISCUSSION VVI is a new technique for analyzing echocardiographic B-mode images offline that allows for assessment of myocardial mechanics. VVI uses complex mathematic modeling to track myocardial motion and then is able to calculate myocardial velocity, strain, and strain rate for these data. The software tracks echocardiographically generated speckles and factors annulus motion, periodicity, and border tracking to track the myocardium. Advantages of this technique include the ability to measure motion independent of the angle of image acquisition and the ability to measure motion in multiple directions (eg, longitudinal and radial motion) from a single image. These factors are Figure 3 Myocardial velocity, strain, and strain rate plotted versus gestational age. Plots of systolic and diastolic velocity, strain, and strain rate against advancing gestational age (weeks). Displayed range (y-axis) for systolic and diastolic velocity 0 to 5 cm/s, strain 0% to 40%, and strain rate 0 to 4/s. Note that there is statistically significant increase in velocity profiles with advancing gestational age (P.05). No significant variation in strain or strain rate is detected. LV, Left ventricle; RV, right ventricle. Color figure online. particularly important in fetal echocardiography when fetal positioning limits the angle of insonation. Feasibility Evaluation of myocardial dynamics in the fetus by VVI is feasible and was accomplished in the majority of fetal scans reviewed. The main reason for failing to obtain a reliable processed image for analysis was poor image quality. This is an ongoing challenge in imaging the fetus, especially in late gestation with increased shadowing from calcifying ribs and the spine. There was a learning curve to tracing the endocardium and it may be that future studies will yield a higher success rate. Interobserver variability was relatively high and likely also reflects a learning curve. As experience with this new technique increases, the reproducibility may improve as well. Changes with Gestational Age The systolic and diastolic velocities of all wall segments increased with gestational development; however, no significant change in strain or strain rate was observed. As the heart grows in fetal development, the distance that the myocardium travels in the longitudinal plane increases. Given that the time interval of the cardiac cycle remains constant, velocity increases proportionally. Strain is time independent and, therefore, a more reliable predictor of myocyte deformation. The fact that strain was not found to correlate with advancing gestational age and growth suggests that myocardial function is constant through mid and late gestation. This finding is supported by the variation of strain rate with heart rate. As the cardiac cycle length decreases the strain rate increases. This shows that within the normal
4 Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography Younoszai et al 473 Volume 21 Number 5 Figure 4 Strain rate versus heart rate. Strain rate (1/s) plotted against heart rate (beats/min). As heart rate increases, strain rate also increases in both right ventricular (RV) free wall and septum (P.05). There appears to be similar trend in left ventricular (LV) free wall (P.12). Color figure online. heart rate range of the developing fetus, myocardial strain appears to remain stable requiring the rate of deformation to compensate for the change in cycle length. If this finding is generalized to the entire myocardium, it would support a maintained stroke volume within the normal heart rate range, allowing an increase in heart rate to directly increase cardiac output. These data are consistent with the limited data available from chick embryos using microspheres to track strain. Taber et al 10 found that longitudinal and circumferential strain did not change during the early stages of ventricular looping. However, few other data are available. Data in adults (age years) using DTI have shown that strain does not change significantly with aging whereas myocardial velocities and strain rate decrease with advancing age. 11 Comparison with DTI Studies Several reports have used DTI to measure myocardial velocity, strain, and strain rate. Harada et al 4 published the first report using DTI to measure myocardial velocities. They found that RV and LV systolic velocities and early diastolic velocities at the RV, LV, and septum each correlated with gestational age. They did not show a correlation with systolic velocity at the septum or late diastolic velocity. Paladini et al 7 measured transverse myocardial velocities of the LV and RV at the subendocardium and subepicardium at various gestational ages. They found a significant correlation with gestational age at each point of measurement except late diastolic velocity of the subepicardium. More recently, Chan et al 5 looked at longitudinal myocardial velocities in 302 normal fetuses and found an increase in systolic and diastolic velocities in all segments. These previous reports measured peak myocardial velocities, whereas VVI measures mean modal velocity. Similar to findings in these studies that used DTI, we found an increase in longitudinal velocities through mid to late gestation. Little has been published regarding the evaluation of myocardial strain and strain rate in normal gestation. Using DTI, Di Salvo et al 9 found that strain and strain rate of the LV wall increased with gestational age. They did not report any data on changes in strain and strain rate for the RV free wall or septum. Therefore, it is unclear whether the correlation they found was consistent throughout all segments of the myocardium. In contrast, we found that strain and strain rate did not correlate with gestational age at any measured segment. Because VVI analysis is performed offline, measurements are made independent of imaging angle. This is particularly important in fetal echocardiography, where fetal positioning can limit the angle of insonation. Success in obtaining measurements using DTI ranged from 63% to 88% in studies requiring an angle of less than 30 degrees from the angle of measurement. 5,7,9 The 89% success rate using VVI in this study compares favorably with previous reports using DTI. Limitations This study had a limited number of patients. Further validation of this technique and its applicability in distinguishing normal from abnormal fetal cardiac function is warranted. Although VVI does not have the angle dependency of DTI, the ability to track the myocardium is reliant on adequate image quality and axial dropout should be minimized. Assessment of myocardial motion was further limited by the frame rate at which images were acquired. Although our imaging frame rates were higher (typically frames/s), the ultrasound system (Sequoia, Siemens Medical Systems) under standard settings saves DICOM images at a rate of 30 frames/s. Normal fetal heart rates vary from 120 to 160/min, meaning that a single cardiac cycle may have only 11 to 15 frames. Because temporal resolution was limited by the rate of image acquisition, the E wave and A wave in diastole were not distinct. As the frame rate of image acquisition is increased, VVI will be able to study myocardial mechanics with greater temporal resolution. Future Study The complexities of the mechanics of myocardial contraction are beginning to be understood in a more comprehensive way. The ventricles contract in the longitudinal, radial, and circumferential directions during systole. The heart also twists during systole, with clockwise rotation at the base and counterclockwise rotation at the apex in the healthy adult. Finally, the LV and RV normally contract in synchrony. Each of these components of ventricular contraction may be different during normal maturation or in pathologic states. New techniques, such as 2-dimensional image analysis through speckle tracking and related techniques and DTI, may allow for quantification of the different aspects of this complex motion. Previous work has shown that pressure overloading of embryonic chick hearts alters passive stress-strain relationships during development. 12 VVI may be a useful tool for quantification of changes in cardiac function in fetal distress and with developing congenital heart disease. Conclusions From mid to late gestation there is a progressive increase in myocardial longitudinal velocity in all measured cardiac segments with relatively stable myocardial deformation as measured by strain and
5 474 Younoszai et al Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography May 2008 strain rate. This suggests that the increase in velocity is the result of somatic growth of the heart rather than increasing contractility. This implies that the systolic contractile function of the myocyte is established as early as 18 weeks of gestation. Further investigation is required to optimize the temporal resolution; however, VVI holds significant promise for improved understanding of fetal myocardial function. REFERENCES 1. Falkensammer CB, Paul J, Huhta JC. Fetal congestive heart failure: correlation of Tei-index and Cardiovascular-score. J Perinat Med 2001; 29: Friedman WF. The intrinsic physiologic properties of the developing heart. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 1972;15: Grant DA. Ventricular constraint in the fetus and newborn. Can J Cardiol 1999;15: Harada K, Tsuda A, Orino T, Tanaka T, Takada G. Tissue Doppler imaging in the normal fetus. Int J Cardiol 1999;71: Chan LY, Fok WY, Wong JT, Yu CM, Leung TN, Lau TK. Reference charts of gestation-specific tissue Doppler imaging indices of systolic and diastolic functions in the normal fetal heart. Am Heart J 2005;150: Huhta JC, Kales E, Casbohm A. Fetal tissue Doppler a new technique for perinatal cardiology. Curr Opin Pediatr 2003;15: Paladini D, Lamberti A, Teodoro A, Arienzo M, Tartaglione A, Martinelli P. Tissue Doppler imaging of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16: Tutschek B, Zimmermann T, Buck T, Bender HG. Fetal tissue Doppler echocardiography: detection rates of cardiac structures and quantitative assessment of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;21: Di Salvo G, Russo MG, Paladini D, et al. Quantification of regional left and right ventricular longitudinal function in 75 normal fetuses using ultrasound-based strain rate and strain imaging. Ultrasound Med Biol 2005;31: Taber LA, Sun H, Clark EB, Keller BB. Epicardial strains in embryonic chick ventricle at stages 16 through 24. Circ Res 1994;75: Sun JP, Popovic ZB, Greenberg NL, et al. Noninvasive quantification of regional myocardial function using Doppler-derived velocity, displacement, strain rate, and strain in healthy volunteers: effects of aging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2004;17: Tobita K, Schroder EA, Tinney JP, Garrison JB, Keller BB. Regional passive ventricular stress-strain relations during development of altered loads in chick embryo. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2002; 282:H
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease
 Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Fetal cardiac function: what to use and does it make a difference?
 17 th International Conference on Prenatal Diagnosis and Therapy Lisbon, June 2013 Fetal cardiac function: what to use and does it make a difference? Fàtima Crispi Department of Maternal-Fetal Medicine,
17 th International Conference on Prenatal Diagnosis and Therapy Lisbon, June 2013 Fetal cardiac function: what to use and does it make a difference? Fàtima Crispi Department of Maternal-Fetal Medicine,
Velocity, strain and strain rate: Doppler and Non-Doppler methods. Thoraxcentre, Erasmus MC,Rotterdam
 Velocity, strain and strain rate: Doppler and Non-Doppler methods J Roelandt J. Roelandt Thoraxcentre, Erasmus MC,Rotterdam Basics of tissue Doppler imaging Instantaneous annular velocity profiles IVCT
Velocity, strain and strain rate: Doppler and Non-Doppler methods J Roelandt J. Roelandt Thoraxcentre, Erasmus MC,Rotterdam Basics of tissue Doppler imaging Instantaneous annular velocity profiles IVCT
DISCLOSURE. Myocardial Mechanics. Relevant Financial Relationship(s) Off Label Usage
 7th Annual Team Echocardiography: The Heart of Cardiovascular Medicine Tissue Doppler, Strain, Speckle: What? How? Christopher J Kramer RDCS Aurora Medical Group Advanced Cardiovascular Services, Aurora
7th Annual Team Echocardiography: The Heart of Cardiovascular Medicine Tissue Doppler, Strain, Speckle: What? How? Christopher J Kramer RDCS Aurora Medical Group Advanced Cardiovascular Services, Aurora
2/2/2011. Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? Movement vs Deformation. Doppler Myocardial Velocities. Movement. Deformation.
 Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease:
 Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease: Clinical Case Examples Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS Echocardiography Laboratory, University of Massachusetts
Advanced Multi-Layer Speckle Strain Permits Transmural Myocardial Function Analysis in Health and Disease: Clinical Case Examples Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS Echocardiography Laboratory, University of Massachusetts
Strain/Untwisting/Diastolic Suction
 What Is Diastole and How to Assess It? Strain/Untwisting/Diastolic Suction James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland,
What Is Diastole and How to Assess It? Strain/Untwisting/Diastolic Suction James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland,
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging. Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None a. Turn the wall filters on and turn down the receiver gain. b. Turn
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None a. Turn the wall filters on and turn down the receiver gain. b. Turn
Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function
 SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
Quantitative Assessment of Fetal Ventricular Function:
 Reprinted with permission from ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY, Volume 18, No. 1, January 2001 Copyright 2001 by Futura Publishing Company, Inc., Armonk, NY 1004-0418 Quantitative Assessment of Fetal Ventricular Function:
Reprinted with permission from ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY, Volume 18, No. 1, January 2001 Copyright 2001 by Futura Publishing Company, Inc., Armonk, NY 1004-0418 Quantitative Assessment of Fetal Ventricular Function:
Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When?
 Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
Strain and Strain Rate Imaging How, Why and When? João L. Cavalcante, MD Advanced Cardiac Imaging Fellow Cleveland Clinic Foundation Disclosures: No conflicts of interest Movement vs Deformation Movement
VECTORS OF CONTRACTION
 1/3/216 Strain, Strain Rate, and Torsion: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied VECTORS OF CONTRACTION John Gorcsan, MD University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA Shortening Thickening Twisting No
1/3/216 Strain, Strain Rate, and Torsion: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied VECTORS OF CONTRACTION John Gorcsan, MD University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA Shortening Thickening Twisting No
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
Diastology Disclosures: None. Dias2011:1
 Diastology 2011 James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio, USA Disclosures: None Dias2011:1 Is EVERYBODY a member!?!
Diastology 2011 James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio, USA Disclosures: None Dias2011:1 Is EVERYBODY a member!?!
Carlos Eduardo Suaide Silva, Luiz Darcy Cortez Ferreira, Luciana Braz Peixoto, Claudia Gianini Monaco, Manuel Adán Gil, Juarez Ortiz
 Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI -
 Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
How To Perform Strain Imaging; Step By Step Approach. Maryam Bo Khamseen Echotechnoligist II EACVI, ARDMS, RCS King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center- Riyadh
 How To Perform Strain Imaging; Step By Step Approach Maryam Bo Khamseen Echotechnoligist II EACVI, ARDMS, RCS King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center- Riyadh Outlines: Introduction Describe the basic of myocardium
How To Perform Strain Imaging; Step By Step Approach Maryam Bo Khamseen Echotechnoligist II EACVI, ARDMS, RCS King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center- Riyadh Outlines: Introduction Describe the basic of myocardium
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION
 LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 1 Objective way with which to quantify the minor amplitude and temporal
A modified myocardial performance (Tei) index based on the use of valve clicks improves reproducibility of fetal left cardiac function assessment
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 227 232 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1959 A modified myocardial performance (Tei) index based on the use of
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 227 232 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1959 A modified myocardial performance (Tei) index based on the use of
Effect of physiological heart rate changes on left ventricular dimensions and mitral blood flow velocities in the normal fetus
 ELSEVIER Early Human Development 40 (1995) 109-114 Effect of physiological heart rate changes on left ventricular dimensions and mitral blood flow velocities in the normal fetus P.B. Tsyvian a, K.V. Malkin
ELSEVIER Early Human Development 40 (1995) 109-114 Effect of physiological heart rate changes on left ventricular dimensions and mitral blood flow velocities in the normal fetus P.B. Tsyvian a, K.V. Malkin
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography
 Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman 1,
Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman 1,
Strain imaging in children: from Tissue Doppler to 3 D
 Strain imaging in children: from Tissue Doppler to 3 D Mark kk. Friedberg Fi Outline Deformation in the fetus and neonate Deformation in pediatric cardiomyopathy y (briefly!) Deformation in Congenital
Strain imaging in children: from Tissue Doppler to 3 D Mark kk. Friedberg Fi Outline Deformation in the fetus and neonate Deformation in pediatric cardiomyopathy y (briefly!) Deformation in Congenital
Fetal tissue Doppler echocardiography: detection rates of cardiac structures and quantitative assessment of the fetal heart
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 23; 21: 2 32 Published online 2 December 22 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI:.2/uog. Fetal tissue Doppler echocardiography: detection rates of cardiac structures
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 23; 21: 2 32 Published online 2 December 22 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI:.2/uog. Fetal tissue Doppler echocardiography: detection rates of cardiac structures
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice
 Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function
 Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function
 II Baltic Heart Failure Meeting and Congress of Latvian Society of Cardiology The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function Dr. Artem Kalinin Eastern Clinical University Hospital Riga 30.09.2010.
II Baltic Heart Failure Meeting and Congress of Latvian Society of Cardiology The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function Dr. Artem Kalinin Eastern Clinical University Hospital Riga 30.09.2010.
RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION
 RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION Edwin S. Tucay, MD, FPCC, FPCC, FPSE Philippine Society of Echocardiography Quezon City, Philippines Echo Mission, BRTTH, Legaspi City, July 1-2, 2016 NO DISCLOSURE
RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION Edwin S. Tucay, MD, FPCC, FPCC, FPSE Philippine Society of Echocardiography Quezon City, Philippines Echo Mission, BRTTH, Legaspi City, July 1-2, 2016 NO DISCLOSURE
New approaches in small animal echocardiography: imaging the sounds of silence
 New approaches in small animal echocardiography: imaging the sounds of silence Rashmi Ram, Deanne M. Mickelsen, Catherine Theodoropoulos and Burns C. Blaxall Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301:H1765-H1780,
New approaches in small animal echocardiography: imaging the sounds of silence Rashmi Ram, Deanne M. Mickelsen, Catherine Theodoropoulos and Burns C. Blaxall Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301:H1765-H1780,
Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography
 Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography Maryam Bokhamseen, RCS, RCDS, EACVI Echotechnologist ǁ, Non invasive Cardiac Laboratory King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center. Outline: Introduction. Background
Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography Maryam Bokhamseen, RCS, RCDS, EACVI Echotechnologist ǁ, Non invasive Cardiac Laboratory King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center. Outline: Introduction. Background
22 nd Annual Conference of the Saudi Heart Association Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
 22 nd Annual Conference of the Saudi Heart Association Riyadh, Saudi Arabia New Echocardiographic Modalities to Evaluate Ventricular Function in Congenital Heart Disease: Tissue Doppler & Strain Rate Imaging
22 nd Annual Conference of the Saudi Heart Association Riyadh, Saudi Arabia New Echocardiographic Modalities to Evaluate Ventricular Function in Congenital Heart Disease: Tissue Doppler & Strain Rate Imaging
Three-dimensional Wall Motion Tracking:
 Three-dimensional Wall Motion Tracking: A Novel Echocardiographic Method for the Assessment of Ventricular Volumes, Strain and Dyssynchrony Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS, FASE Jennifer L. Kane, RCS Gerard
Three-dimensional Wall Motion Tracking: A Novel Echocardiographic Method for the Assessment of Ventricular Volumes, Strain and Dyssynchrony Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS, FASE Jennifer L. Kane, RCS Gerard
좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function
 Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
Little is known about the degree and time course of
 Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi
 Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi Identify increased LV wall thickness (WT) Understand increased WT in athletes Understand hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Enhance understanding
Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi Identify increased LV wall thickness (WT) Understand increased WT in athletes Understand hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Enhance understanding
First Trimester Fetal Echocardiography: Insight Into the Fetal Circulation
 First Trimester Fetal Echocardiography: Insight Into the Fetal Circulation Lisa K. Hornberger, MD Fetal & Neonatal Cardiology Program Department of Pediatrics, Division of Cardiology Department of Obstetrics
First Trimester Fetal Echocardiography: Insight Into the Fetal Circulation Lisa K. Hornberger, MD Fetal & Neonatal Cardiology Program Department of Pediatrics, Division of Cardiology Department of Obstetrics
Normal pericardial fluid in the fetus: color and spectral Doppler analysis
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001; 18: 248 252 Normal pericardial fluid in the fetus: color and spectral Blackwell ORIGINAL Science, PAPERLtd Doppler analysis S.-J. YOO*, J.-Y. MIN and Y.-H. LEE *Department
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001; 18: 248 252 Normal pericardial fluid in the fetus: color and spectral Blackwell ORIGINAL Science, PAPERLtd Doppler analysis S.-J. YOO*, J.-Y. MIN and Y.-H. LEE *Department
Pathophysiology and Current Evidence for Detection of Dyssynchrony
 Editorial Cardiol Res. 2017;8(5):179-183 Pathophysiology and Current Evidence for Detection of Dyssynchrony Michael Spartalis a, d, Eleni Tzatzaki a, Eleftherios Spartalis b, Christos Damaskos b, Antonios
Editorial Cardiol Res. 2017;8(5):179-183 Pathophysiology and Current Evidence for Detection of Dyssynchrony Michael Spartalis a, d, Eleni Tzatzaki a, Eleftherios Spartalis b, Christos Damaskos b, Antonios
Research Article Changes in Mitral Annular Ascent with Worsening Echocardiographic Parameters of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function
 Scientifica Volume 216, Article ID 633815, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/633815 Research Article Changes in Mitral Annular Ascent with Worsening Echocardiographic Parameters of Left Ventricular
Scientifica Volume 216, Article ID 633815, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/633815 Research Article Changes in Mitral Annular Ascent with Worsening Echocardiographic Parameters of Left Ventricular
10/7/2013. Systolic Function How to Measure, How Accurate is Echo, Role of Contrast. Thanks to our Course Director: Neil J.
 Systolic Function How to Measure, How Accurate is Echo, Role of Contrast Neil J. Weissman, MD MedStar Health Research Institute & Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Washington, D.C. No Disclosures
Systolic Function How to Measure, How Accurate is Echo, Role of Contrast Neil J. Weissman, MD MedStar Health Research Institute & Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Washington, D.C. No Disclosures
Conflict of interest: none declared
 The value of left ventricular global longitudinal strain assessed by three-dimensional strain imaging in the early detection of anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity C. Mornoş, A. Ionac, D. Cozma, S. Pescariu,
The value of left ventricular global longitudinal strain assessed by three-dimensional strain imaging in the early detection of anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity C. Mornoş, A. Ionac, D. Cozma, S. Pescariu,
Alicia Armour, MA, BS, RDCS
 Alicia Armour, MA, BS, RDCS No disclosures Review 2D Speckle Strain (briefly) Discuss some various patient populations & disease pathways where Strain can be helpful Discuss how to acquire images for Strain
Alicia Armour, MA, BS, RDCS No disclosures Review 2D Speckle Strain (briefly) Discuss some various patient populations & disease pathways where Strain can be helpful Discuss how to acquire images for Strain
Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony in Patients Showing Diastolic Dysfunction without Overt Symptoms of Heart Failure
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2010.25.3.246 Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony in Patients Showing Diastolic Dysfunction without Overt Symptoms of Heart Failure Jae Hoon Kim, Hee Sang Jang, Byung Seok
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2010.25.3.246 Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony in Patients Showing Diastolic Dysfunction without Overt Symptoms of Heart Failure Jae Hoon Kim, Hee Sang Jang, Byung Seok
Assessment of cardiac function with 3D echocardiography. Đánh giá chức năng tim bằng siêu âm tim 3D
 Assessment of cardiac function with 3D echocardiography Đánh giá chức năng tim bằng siêu âm tim 3D TS. BS. Nguyễn Thị Thu Hoài Viện Tim Mạch Quốc Gia Việt Nam TỪ SIÊU ÂM M-mode ĐẾN SIÊU ÂM 3D TỪ SIÊU ÂM
Assessment of cardiac function with 3D echocardiography Đánh giá chức năng tim bằng siêu âm tim 3D TS. BS. Nguyễn Thị Thu Hoài Viện Tim Mạch Quốc Gia Việt Nam TỪ SIÊU ÂM M-mode ĐẾN SIÊU ÂM 3D TỪ SIÊU ÂM
Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function
 Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function J A F E R A L I, M D U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L S C A S E M E D I C A L C E N T E R S T A F F C A R D I O T
Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function J A F E R A L I, M D U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L S C A S E M E D I C A L C E N T E R S T A F F C A R D I O T
How does the heart pump? From sarcomere to ejection volume
 How does the heart pump? From sarcomere to ejection volume Piet Claus Cardiovascular Imaging and Dynamics Department of Cardiovascular Diseases University Leuven, Leuven, Belgium Course on deformation
How does the heart pump? From sarcomere to ejection volume Piet Claus Cardiovascular Imaging and Dynamics Department of Cardiovascular Diseases University Leuven, Leuven, Belgium Course on deformation
Myocardial Strain Imaging in Cardiac Diseases and Cardiomyopathies.
 Myocardial Strain Imaging in Cardiac Diseases and Cardiomyopathies. Session: Cardiomyopathy Tarun Pandey MD, FRCR. Associate Professor University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Disclosures No relevant
Myocardial Strain Imaging in Cardiac Diseases and Cardiomyopathies. Session: Cardiomyopathy Tarun Pandey MD, FRCR. Associate Professor University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Disclosures No relevant
Echo assessment of the failing heart
 Echo assessment of the failing heart Mark K. Friedberg, MD The Labatt Family Heart Center The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Ontario, Canada Cardiac function- definitions Cardiovascular function:
Echo assessment of the failing heart Mark K. Friedberg, MD The Labatt Family Heart Center The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Ontario, Canada Cardiac function- definitions Cardiovascular function:
Right Ventricular Strain in Normal Healthy Adult Filipinos: A Retrospective, Cross- Sectional Pilot Study
 Right Ventricular Strain in Normal Healthy Adult Filipinos: A Retrospective, Cross- Sectional Pilot Study By Julius Caesar D. de Vera, MD Jonnah Fatima B. Pelat, MD Introduction Right ventricle contributes
Right Ventricular Strain in Normal Healthy Adult Filipinos: A Retrospective, Cross- Sectional Pilot Study By Julius Caesar D. de Vera, MD Jonnah Fatima B. Pelat, MD Introduction Right ventricle contributes
Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula
 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2014; 2(2): 34-38 Published online April 10, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20140202.16 Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula
International Journal of Medical Imaging 2014; 2(2): 34-38 Published online April 10, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20140202.16 Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula
Myocardial performance index, Tissue Doppler echocardiography
 Value of Measuring Myocardial Performance Index by Tissue Doppler Echocardiography in Normal and Diseased Heart Tarkan TEKTEN, 1 MD, Alper O. ONBASILI, 1 MD, Ceyhun CEYHAN, 1 MD, Selim ÜNAL, 1 MD, and
Value of Measuring Myocardial Performance Index by Tissue Doppler Echocardiography in Normal and Diseased Heart Tarkan TEKTEN, 1 MD, Alper O. ONBASILI, 1 MD, Ceyhun CEYHAN, 1 MD, Selim ÜNAL, 1 MD, and
Diagnostic approach to heart disease
 Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Stephen G. Worthley. Cardiovascular Research Centre, Royal Adelaide Hospital and University of Adelaide, Adelaide, South Australia 5000, Australia
 RIGHT VENTRICULAR SPECKLE TRACKING STRAIN HAS A CLOSER CORRELATION WITH RIGHT VENTRICULAR EJECTION FRACTION THAN OTHER ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC INDICES OF RIGHT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION: A COMPARISON WITH CARDIAC
RIGHT VENTRICULAR SPECKLE TRACKING STRAIN HAS A CLOSER CORRELATION WITH RIGHT VENTRICULAR EJECTION FRACTION THAN OTHER ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC INDICES OF RIGHT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION: A COMPARISON WITH CARDIAC
MYOCARDIAL STRAIN MEASUREMENTS WITH MRI USING FEATURE TRACKING
 MYOCARDIAL STRAIN MEASUREMENTS WITH MRI USING FEATURE TRACKING Mercy Kataike Victoria MSc in Physics Submission date: May 2016 Supervisor: Pål Erik Goa, IFY Norwegian University of Science and Technology
MYOCARDIAL STRAIN MEASUREMENTS WITH MRI USING FEATURE TRACKING Mercy Kataike Victoria MSc in Physics Submission date: May 2016 Supervisor: Pål Erik Goa, IFY Norwegian University of Science and Technology
Novel echocardiographic modalities: 3D echo, speckle tracking and strain rate imaging. Potential roles in sports cardiology. Stefano Caselli, MD, PhD
 Novel echocardiographic modalities: 3D echo, speckle tracking and strain rate imaging. Potential roles in sports cardiology. Stefano Caselli, MD, PhD Ospedale San Pietro Fatebenefratelli Rome, Italy Differential
Novel echocardiographic modalities: 3D echo, speckle tracking and strain rate imaging. Potential roles in sports cardiology. Stefano Caselli, MD, PhD Ospedale San Pietro Fatebenefratelli Rome, Italy Differential
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
 ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
3D-stress echocardiography Bernard Cosyns, MD, PhD
 3D-stress echocardiography Bernard Cosyns, MD, PhD No Disclosure The Pro-Technology bias Sicari et al. Cardiovascular Ultrasound 2006, 4:11 Overview 2D stress echocardiography: main limitations 3D echocardiography:
3D-stress echocardiography Bernard Cosyns, MD, PhD No Disclosure The Pro-Technology bias Sicari et al. Cardiovascular Ultrasound 2006, 4:11 Overview 2D stress echocardiography: main limitations 3D echocardiography:
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False?
 Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Introduction. Cardiac Imaging Modalities MRI. Overview. MRI (Continued) MRI (Continued) Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03
 Introduction Cardiac Imaging Modalities Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03 Coronary heart disease: the vessels that supply oxygen-carrying blood to the heart, become narrowed and unable to carry a normal amount
Introduction Cardiac Imaging Modalities Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03 Coronary heart disease: the vessels that supply oxygen-carrying blood to the heart, become narrowed and unable to carry a normal amount
WHAT DO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGISTS WANT TO KNOW FROM ECHOCARDIOGRAPHERS BEFORE, DURING&AFTER CARDIAC RESYNCHRONIZATION THERAPY?
 WHAT DO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGISTS WANT TO KNOW FROM ECHOCARDIOGRAPHERS BEFORE, DURING&AFTER CARDIAC RESYNCHRONIZATION THERAPY? Mary Ong Go, MD, FPCP, FPCC, FACC OUTLINE What is CRT Who needs CRT What does the
WHAT DO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGISTS WANT TO KNOW FROM ECHOCARDIOGRAPHERS BEFORE, DURING&AFTER CARDIAC RESYNCHRONIZATION THERAPY? Mary Ong Go, MD, FPCP, FPCC, FACC OUTLINE What is CRT Who needs CRT What does the
Measuring cardiac tissue motion and strain
 Ultrasound Measuring cardiac tissue motion and strain Automated Cardiac Motion Quantification A.I. (acmq A.I. ) David Prater, MS, Clinical Scientist, Philips Jane Vogel, MD, Senior Product Manager, Philips
Ultrasound Measuring cardiac tissue motion and strain Automated Cardiac Motion Quantification A.I. (acmq A.I. ) David Prater, MS, Clinical Scientist, Philips Jane Vogel, MD, Senior Product Manager, Philips
Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index in Patients With Regional Wall Motion Abnormalities
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2010.40.3.114 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2010 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2010.40.3.114 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2010 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD
 COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors
 Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Outline. EuroScore II. Society of Thoracic Surgeons Score. EuroScore II
 SURGICAL RISK IN VALVULAR HEART DISEASE: WHAT 2D AND 3D ECHO CAN TELL YOU AND WHAT THEY CAN'T Ernesto E Salcedo, MD Professor of Medicine University of Colorado School of Medicine Director of Echocardiography
SURGICAL RISK IN VALVULAR HEART DISEASE: WHAT 2D AND 3D ECHO CAN TELL YOU AND WHAT THEY CAN'T Ernesto E Salcedo, MD Professor of Medicine University of Colorado School of Medicine Director of Echocardiography
Aortic valve Stenosis: Insights in the evaluation of LV function. Erwan DONAL Cardiologie CHU Rennes
 Aortic valve Stenosis: Insights in the evaluation of LV function Erwan DONAL Cardiologie CHU Rennes erwan.donal@chu-rennes.fr Preload Afterload Myocardial Fiber Shortening Circumferential Longitudinal
Aortic valve Stenosis: Insights in the evaluation of LV function Erwan DONAL Cardiologie CHU Rennes erwan.donal@chu-rennes.fr Preload Afterload Myocardial Fiber Shortening Circumferential Longitudinal
Early Diastolic Left Ventricular Relaxation in Normal Neonates is Influenced by Ventricular Stiffness and Longitudinal Systolic Function
 CLINICAL STUDY Early Diastolic Left Ventricular Relaxation in Normal Neonates is Influenced by Ventricular Stiffness and Longitudinal Systolic Function Yukako Homma, 1 MD, Yasunobu Hayabuchi, 2 MD, Tomomasa
CLINICAL STUDY Early Diastolic Left Ventricular Relaxation in Normal Neonates is Influenced by Ventricular Stiffness and Longitudinal Systolic Function Yukako Homma, 1 MD, Yasunobu Hayabuchi, 2 MD, Tomomasa
Echocardiographic assessment of the right ventricle in paediatric pulmonary hypertension.
 Echocardiographic assessment of the right ventricle in paediatric pulmonary hypertension. Mark K. Friedberg, MD No disclosures Outline RV response to increased afterload Echo assessment of RV function
Echocardiographic assessment of the right ventricle in paediatric pulmonary hypertension. Mark K. Friedberg, MD No disclosures Outline RV response to increased afterload Echo assessment of RV function
Review Article Transthoracic Echocardiography in Children and Young Adults with Congenital Heart Disease
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Pediatrics Volume 2012, Article ID 753481, 15 pages doi:10.5402/2012/753481 Review Article Transthoracic Echocardiography in Children and Young Adults with
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Pediatrics Volume 2012, Article ID 753481, 15 pages doi:10.5402/2012/753481 Review Article Transthoracic Echocardiography in Children and Young Adults with
The road to successful CRT implantation: The role of echo
 The road to successful CRT implantation: The role of echo Tae-Ho Park Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea Terminology Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) = Biventricular pacing (BiV) = Left ventricular
The road to successful CRT implantation: The role of echo Tae-Ho Park Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea Terminology Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) = Biventricular pacing (BiV) = Left ventricular
Objectives. Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. LV Diastolic Function: Introduction. LV Diastolic Function: Introduction
 Objectives Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Jacobo Kirsch, MD Cardiopulmonary Imaging, Section Head Division of Radiology Cleveland Clinic Florida Weston, FL To review the physiology and
Objectives Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Jacobo Kirsch, MD Cardiopulmonary Imaging, Section Head Division of Radiology Cleveland Clinic Florida Weston, FL To review the physiology and
B-Mode measurements protocols:
 Application Note How to Perform the Most Commonly Used Measurements from the Cardiac Measurements Package associated with Calculations of Cardiac Function using the Vevo Lab Objective The Vevo LAB offline
Application Note How to Perform the Most Commonly Used Measurements from the Cardiac Measurements Package associated with Calculations of Cardiac Function using the Vevo Lab Objective The Vevo LAB offline
Fetal cardiac muscle contractility decreases with gestational age: a color-coded tissue velocity imaging study
 Elmstedt et al. Cardiovascular Ultrasound 2012, 10:19 CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND RESEARCH Open Access Fetal cardiac muscle contractility decreases with gestational age: a color-coded tissue velocity imaging
Elmstedt et al. Cardiovascular Ultrasound 2012, 10:19 CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND RESEARCH Open Access Fetal cardiac muscle contractility decreases with gestational age: a color-coded tissue velocity imaging
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
Quantification of Cardiac Chamber Size
 2017 KSE 2017-11-25 Quantification of Cardiac Chamber Size Division of Cardiology Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center In-Cheol Kim M.D., Ph.D. LV size and function Internal linear dimensions PLX
2017 KSE 2017-11-25 Quantification of Cardiac Chamber Size Division of Cardiology Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center In-Cheol Kim M.D., Ph.D. LV size and function Internal linear dimensions PLX
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines - Update II
 Chamber Quantitation Guidelines - Update II Right Heart Measurements Steven A. Goldstein MD FACC FASE Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Medical Center MedStar Heart Institute Washington Hospital
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines - Update II Right Heart Measurements Steven A. Goldstein MD FACC FASE Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Medical Center MedStar Heart Institute Washington Hospital
Assessment of LV systolic function
 Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
HDlive Silhouette Mode With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation for Assessment of the Fetal Heart
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HDlive Silhouette Mode With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation for Assessment of the Fetal Heart Toshiyuki Hata, MD, PhD, Mohamed Ahmed Mostafa AboEllail, MD, Suraphan Sajapala, MD, Mari
ORIGINAL RESEARCH HDlive Silhouette Mode With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation for Assessment of the Fetal Heart Toshiyuki Hata, MD, PhD, Mohamed Ahmed Mostafa AboEllail, MD, Suraphan Sajapala, MD, Mari
Tissue Doppler Imaging
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Hesham Rashid* Tissue Doppler Imaging CARDIOLOGY Editorial Department of Cardiology, Benha University, Egypt *Corresponding Author: Hesham Rashid, Department of Cardiology, Benha University,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Hesham Rashid* Tissue Doppler Imaging CARDIOLOGY Editorial Department of Cardiology, Benha University, Egypt *Corresponding Author: Hesham Rashid, Department of Cardiology, Benha University,
Assessment of fetal heart function and rhythm
 Assessment of fetal heart function and rhythm The fetal myocardium Early Gestation Myofibrils 30% of myocytes Less sarcoplasmic reticula Late Gestation Myofibrils 60% of myocytes Increased force per unit
Assessment of fetal heart function and rhythm The fetal myocardium Early Gestation Myofibrils 30% of myocytes Less sarcoplasmic reticula Late Gestation Myofibrils 60% of myocytes Increased force per unit
First-Trimester Fetal Cardiac Function
 CME Article First-Trimester Fetal Cardiac Function Noirin E. Russell, MRCPI, Fionnuala M. McAuliffe, MD, FRCPI, MRCOG Objective. The purpose of this study was to establish normal values for fetal heart
CME Article First-Trimester Fetal Cardiac Function Noirin E. Russell, MRCPI, Fionnuala M. McAuliffe, MD, FRCPI, MRCOG Objective. The purpose of this study was to establish normal values for fetal heart
Altered left ventricular geometry and torsional mechanics in high altitude-induced pulmonary hypertension:
 Altered left ventricular geometry and torsional mechanics in high altitude-induced pulmonary hypertension: a 3-D echocardiographic study B.W. De Boeck,* S. Kiencke, C. Dehnert, K. Auinger, # M. Maggiorini,
Altered left ventricular geometry and torsional mechanics in high altitude-induced pulmonary hypertension: a 3-D echocardiographic study B.W. De Boeck,* S. Kiencke, C. Dehnert, K. Auinger, # M. Maggiorini,
HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain. V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen
 HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen Disclosure of interest: none Relative wall thickness (cm) M 0.22 0.42 0.43 0.47 0.48 0.52 0.53 F 0.24 0.42 0.43
HYPERTROPHY: Behind the curtain V. Yotova St. Radboud Medical University Center, Nijmegen Disclosure of interest: none Relative wall thickness (cm) M 0.22 0.42 0.43 0.47 0.48 0.52 0.53 F 0.24 0.42 0.43
Temporal and spatial performance of vector velocity imaging in the human fetal heart
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 37: 150 157 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.8815 Temporal and spatial performance of vector velocity imaging in the human
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2011; 37: 150 157 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.8815 Temporal and spatial performance of vector velocity imaging in the human
ISUOG Basic Training. Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA. Basic training. Editable text here
 ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
Distinguishing Right From Left: A Standardized Technique for Fetal Echocardiography
 Distinguishing Right From Left: A Standardized Technique for Fetal Echocardiography Timothy M. Cordes, MD, Patrick W. O'Leary, MD, James B. Seward, MD, and Donald J. Hagler, MD, Rochester, Minnesota Improved
Distinguishing Right From Left: A Standardized Technique for Fetal Echocardiography Timothy M. Cordes, MD, Patrick W. O'Leary, MD, James B. Seward, MD, and Donald J. Hagler, MD, Rochester, Minnesota Improved
Diastole is Not a Single Entity Four Components of Diastolic Dysfunction
 Physiology of Diastolic Function Made Easy James D. Thomas, MD, FACC, FASE Director, Center for Heart Valve Disease Bluhm Cardiovascular Institute Professor of Medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern
Physiology of Diastolic Function Made Easy James D. Thomas, MD, FACC, FASE Director, Center for Heart Valve Disease Bluhm Cardiovascular Institute Professor of Medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern
Assessment of foetal cardiac function by myocardial tissue doppler in foetal growth restriction
 International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Basu B et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Mar;6(3):1045-1051 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Basu B et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Mar;6(3):1045-1051 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
Global and Regional Myocardial Function Quantification by Two-Dimensional Strain Application in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 47, No. 6, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.10.061
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 47, No. 6, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.10.061
Assessment of right ventricular contraction by speckle tracking echocardiography in pulmonary hypertension patients.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (1): 173-177 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Assessment of right ventricular contraction by speckle tracking echocardiography in pulmonary hypertension patients. Yudong Peng,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (1): 173-177 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Assessment of right ventricular contraction by speckle tracking echocardiography in pulmonary hypertension patients. Yudong Peng,
L ecocardiografia nello Scompenso Cardiaco Acuto e cronico: vecchi dogmi e nuovi trends.
 V SESSIONE SCOMPENSO CARDIACO 2015 Genova, 13-14 Novembre 2015 L ecocardiografia nello Scompenso Cardiaco Acuto e cronico: vecchi dogmi e nuovi trends. Gian Paolo Bezante, MD, FACC UOC Clinica di Malattie
V SESSIONE SCOMPENSO CARDIACO 2015 Genova, 13-14 Novembre 2015 L ecocardiografia nello Scompenso Cardiaco Acuto e cronico: vecchi dogmi e nuovi trends. Gian Paolo Bezante, MD, FACC UOC Clinica di Malattie
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 LV MORPHOLOGY
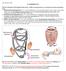 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 LV MORPHOLOGY The left ventricular wall comprises three layers- middle circumferential layer and superficial and deep longitudinal layers: 1. Subepicardial longitudinal layer (25%
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 LV MORPHOLOGY The left ventricular wall comprises three layers- middle circumferential layer and superficial and deep longitudinal layers: 1. Subepicardial longitudinal layer (25%
Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients
 Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
Feasibility and reproducibility of left ventricular rotation parameters measured by speckle tracking echocardiography
 European Journal of Echocardiography (2009) 10, 669 676 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jep036 Feasibility and reproducibility of left ventricular rotation parameters measured by speckle tracking echocardiography
European Journal of Echocardiography (2009) 10, 669 676 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jep036 Feasibility and reproducibility of left ventricular rotation parameters measured by speckle tracking echocardiography
Echocardiographic Assessment of the Left Ventricle
 Echocardiographic Assessment of the Left Ventricle Theodora Zaglavara, MD, PhD, BSCI/BSCCT Department of Cardiovascular Imaging INTERBALKAN EUROPEAN MEDICAL CENTER 2015 The quantification of cardiac chamber
Echocardiographic Assessment of the Left Ventricle Theodora Zaglavara, MD, PhD, BSCI/BSCCT Department of Cardiovascular Imaging INTERBALKAN EUROPEAN MEDICAL CENTER 2015 The quantification of cardiac chamber
Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied
 9/28/217 Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied John Gorcsan III, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Clinical Research Division of Cardiology VECTORS OF CONTRACTION Shortening Thickening
9/28/217 Strain Imaging: Myocardial Mechanics Simplified and Applied John Gorcsan III, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Clinical Research Division of Cardiology VECTORS OF CONTRACTION Shortening Thickening
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on)
 Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
