Cytotoxic Effects of (5) Medicinal Plants on Mitosis in Allium cepa Root Tips
|
|
|
- Lindsay Marjorie Andrews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Current Research Journal of Biological Sciences 6(2): 71-75, 2014 ISSN: X, e-issn: Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2014 Submitted: September 04, 2013 Accepted: September 14, 2013 Published: March 20, 2014 Cytotoxic Effects of (5) Medicinal Plants on Mitosis in Allium cepa Root Tips 1 I.J. Udo, 1 G.A. Akpan and 2 I.K. Esenowo 1 Department of Botany and Ecological Studies, 2 Department of Zoology, University of Uyo, Uyo, Akwa-Ibom State, Nigeria Abstract: The study was conducted to investigate the effects that plant extracts from 5 medicinal plants may have on mitosis in Allium cepa. Root of A. cepa were immersed in alcoholic extracts at the concentrations of 0, 25, 50, 75 and 100 mg/ml, respectively for each of the following plants: Gnetum africanum Welw., Lasianther aafricana P. Beauv, Ocimum gratissimum Linn., Telfairia occidentalis Hook F. and Vernonia amygdalina Del. Leafy vegetable which are commonly used in herbal medicine. Results obtained show that the various concentrations of the extracts from test plants had toxic effects on the cells, which caused significant reduction (p<0.05) in the mitotic index when compared with the control. Other effects were prophase inhibition, the delay of mitosis and nuclear lesion. The cytotoxic effect makes a case for a precaution in the use of the leafy extracts in herbal medicine practice. Keywords: Alcohol, Allium cepa, cytotoxic effect, mitosis INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are a common, cheap and renewable source of pharmacological active substances and because of this it is extremely important that genotoxicity tests are applied to the active ingredients of these preparations in order to assess their mutagenic potential (Apostolides et al., 1996). The plants Lasianthera africana P. Beanv. (Icacinancea), Telfairia occidentalis Hook. F. (Cucurbitacea), Gnetum africanum Welw. (Gnetaceae). Vernonia amygdalina Del.; and Ocimum gratissimum Linn. Lasianthera africana are natives of the mostly tropical rain forest zone and are widely cultivated in home gardens and used as leafy vegetables (Dutta and Mukerji, 1952). The stem and leaves of Lasianthera africana have been reported to be rich in chemical compounds which prevents internal bleeding as well as provide other beneficial effects to the body (Ebana et al., 1996). The leaf extract of T. occidentis is drunk to treat anaemia (Etukudo, 2003). The leaves of Gnetum africanum are eaten raw by the Igbo s community as vegetable salad when sliced and mixed with palm oil and salt (Etukudo, 2003). The leaves of V. amgdalina are widely used for treating fevers as a quinine substitute. The leaves extract is also used for rheumatism. Ocimum gratissimum leaves extracts are used in the treatment of headache, diarrhea, worms and kidney function (Seung-Joo-Lee et al., 2004). This study seeks to throw some light on the possible cytotoxic effects of the alcoholic extracts of these vegetable and medicinal plants which are so commonly used in Nigeria communities. MATERIALS AND METHODS Collection of plant material: Lasianthera africana P. beavu., Telfairia occidentalis Hook F., Gnetum africanum Welw., Vernonia amygdalina Del. and Occimum gratissimum Linn were obtained from Botany Research Garden in University of Uyo. The plants were identified at the Herbarium unit of the Department of Botany and Ecological Studies, University of Uyo, where the voucher specimens have been deposited. The leaves were harvested and taken to the pharmacognosy Laboratory for the extraction. The leaves were air dried and pulverized using mortar and pistle in the laboratory as described by Mukhtar and Tukur (1999). Thereafter, alcoholic extracts of the plants were prepared using the method of Fatope et al. (1993). The extracts were serially diluted to the concentrations of 0, 25, 50 and 100 mg/ml, respectively. Treatment of onion root tips: Young sprouting roots at the base of the onion bulbs were immersed in the different concentrations of the plant extracts for 12 h. Thereafter, the onion bulbs were returned to distill water for 12 h to observed if there was recovery from any possible damage. The roots were fixed and stained using the aceto-orcein and mounted on slides. The slides were examined using high power objectives of the microscope (40x objectives). One hundred cells were examined on each slide and three slides were prepared for each concentration. Mitotic Index (M1) was recorded and cells with abnormalities were examined. The statistical evaluation was performed using one way analysis of variance and where this was significant, the Least Significant Difference (LSD) analyses was used to separate the means. Corresponding Author: I.K. Esenowo, Department of Zoology, University of Uyo, Uyo, Akwa-Ibom State, Nigeria 71
2 RESULTS Table 1 shows the mean mitotic indices of the control and the various alcoholic extract concentrations of the medicinal plants after 12 h treatments. Analyses of variance of the mitotic indices indicated significant differences between the various concentrations of the extracts in Gentum africanum, Lasianthera africanan, Ocimum gratissimum, Telfairia occidentalis and Vernonia amygdalina. Least Significant Difference (LSD) shows that mitotic index in root tips treated with the various concentrations of the alcoholic extracts of all the medicinal plants except V. amygdalina was significantly depressed (p<0.05) at all concentrations when compared with the control. However, there was no significant difference in the mitotic index at the concentrations of 75 and 100 mg/ml in the root tips treated with T. occidentalis extract. Table 2 shows the mean mitotic indices in the control and in the various concentrations of the alcoholic extracts of the medicinal plants after 12 h recovery in distilled water. The mean mitotic indices in the control and the various concentrations of the alcoholic extracts of the medicinal plants after 12 h recovery in distilled water are shown in Table 2. Analyses of variance of the mitotic indices indicated significant difference between the various extract concentrations. The analyses indicated that in G. africanum, L. africana and O. gratissimum the mitotic index was significantly reduced (p<0.05) at all concentrations when compared with the control. There was no apparent tend in the reduction of mitotic index but the data showed that this was most severe in the recovery treatment of 25 mg/ml G. africanum and 75 mg/ml L. africana. Figure 1A shows that the mean numbers of cells in prophase stage was more strongly reduced in Gnetum africanum, Lasianthera africana; and Ocimum gratissimum than in Telfaira occidentalis and Vernonia amygdalina at all the concentrations. There was also a noticeable increase in the mean number of prophase cells in Telfairia occidentalis as the concentration of the aqueous extract increased. From the graph in Fig. 1B it is evident that the mean number of cells in the metaphase stage was strongly increased in Telfairia occidentalis and Vernonia amygdalina above that of the control at 25 mg/ml concentration. This number dropped below that of the control at 50 mg/ml and increased when the roots were exposed to 75 mg/ml concentration of the aqueous extracts. However only the number of cells in T. occidentalis exceeded that of the control. At 100 mg/ml, the number of cells in the T. occidentalis treatment exceeded that of the control by 50% while that of Vernonia amygdalina dropped to about half of the control. Gnetum africanum, Lasianthera africana and Ocimum gratissimum showed reduction of the metaphase stage at all the concentrations. The graph in Fig. 2C shows that the mean number of cells in anaphase was reduced in Gnetum africanum, Ocimum gratissimum and Vernonia amygdalina with the increased in concentration of the aqueous solutions while in Telfairia occidentalis, there was a noticeable increased with increased in the concentrations when compared with the control. Lasianthera africana had the most severe depressive effect at 50 mg/ml treatment. The graph in Fig. 1A cells shows that the mean number of cells in prophase was more strongly reduced in Lasianthera africana and Ocimum gratissimum than in Gnetum africanum, Telfairia occidentalis and Vemonia amygdalina after 12 h recovery period. There was also a noticeable increase in the mean number of prophase cells in Vernonia amygdalina at 75 and 100 mg/ml concentrations. Table 1: Concentrations of alcoholic extract of the medicinal plants after 12 h treatment Mitotic index Concentration mg/ml G. africanum L. africana O. gratissimum T. occidentalis V. amygdalina * 10.51* 12.64* 13.71* * 10.59* 12.25* 12.54* * 11.64* 11.62* * 10.11* 11.19* LSD (p<0.05) *: Significantly different from the control (p<0.05) Table 2: Concentrations of the alcoholic extracts of the medicinal plants after 12 h recovery Mitotic index Concentration mg/ml G. africanum L. africana O. gratissimum T. occidentalis V. amygdalina * 10.98* 12.59* * * 11.56* 11.08* * 11.07* * 9.12* 12.04* * * 10.38* 11.30* * LSD (p<0.05) *: Significantly different from the control (p<0.05) 72
3 Fig. 1: Mean number of cells in telophase in the various concentrations after 12 h treatment and 12 h recovery in distilled water of A. cepa root tips, (A) prophase, (B) metaphase, (C) anaphase, (D) telophase Fig. 2: Mean number of cells in telophase in the various concentrations after 12 h treatment in distilled water of A. cepa root tips, (A) prophase, (B) metaphase, (C) anaphase, (D) telophase 73
4 Fig. 3: Nuclear lesions (arrowed) in onions interphase cells treated with concentrations of 50 mg/ml of extract of T. occidentalis after 12 h treatment The graph in Fig. 1B shows that mean number of cells in the metaphase stage was highly suppressed in Gnetum africanum, Lasianthera africana, Ocimum gratissimum, Telfairia occidentalis and V. amygdalina. Figure 1C shows that the mean number of cells in anaphase was strongly reduced in O. gratissimum at the 100 mg/ml treatment with 12 h recovery compared to control, V. amygdalina was less suppressed at 75 and 100 mg/ml than O. gratissimum, L. africana, G. africanum and T. occidentalis (Fig. 3). The graph in Fig. 1D shows that the mean number of cells in telophase was not so strongly reduced in V. amygdalina as in the other treatments at the 7 and the 100 mg/ml treatments with 12 h recovery. The abnormality that was observed in the root tips cells of Allium cepa at all the concentrations of the aqueous extracts was the appearance of nuclear lesions which is characterized by appearance of clear areas in the nucleus. Also, no chromosomal aberrations were observed using the test plant extracts at all stages of mitosis, though nuclear lesions were observed. The extracts from the various test plants had toxic effects on cell division as it caused a general reduction in mitotic index when compared with that of the control. DISCUSSION The reduced mitotic indices were due to delay in cell division imposed by the test plant extracts. A similar result was obtained by Burim et al. (1999) and Dias and Takahashi (1994) on Alphinia mutans extract in A. cepa root tip cells. It is likely that the extracts affected the protein components of the chromatin, leading to their dissolution, hence the lesions. The accumulation of prophase and telophase stages as observed in Fig. 1 and 2 may be due to lack of spindle fibres formation that would have introduced the cells to another stage, due to the interaction of the tested extracts. The results agree with the work of El- Ghamery et al. (2000) and Kumar and Rai (2007) on evaluation of cytological effects of Zn+ in relation of germination and root. The prophase stage was found to be higher in all treated plants when compared with the control. Prophase stage in both cases had highest mean number of cells. This is followed by the telophase, anaphase Curr. Res. J. Biol. Sci., 6(2): 71-75, and metaphase in that order. This differs from the findings of Moore (1976) where it was reported that herbicidal treatment of plants results to higher percentage in the order of prophase, telophase, metaphase and anaphase. Moore (1976) findings support preponderance of the prophase stage in the treated cells. Although cytotoxic effects was reversible with slight recovery in cell division after 12 h recovery in water. This agrees with the work of Itoyama et al. (1997) and Grisolia et al. (1995) which suggest that it is possible that a high concentration of any chemical will have an effect on the cell cycle; as has been shown for caffeine in Drosophila prosaltan and Progostemun heyneanes extracts in A. cepa root tip cells. The greater number of cells at the interphase stage in the treated root tips suggest that the effects of the extracts was also to delay the initiation of mitosis thus the extracts had an inhibitory effect on mitosis. Similar results were reported by Kabarity and Malallah (1980) and Formina et al. (1989) with the root tips of A. cepa. CONCLUSION The extract of these five traditional medicinal plants used in this study have been shown to have cytotoxic and possibly genotoxic effects on A. cepa root tips. They decreased the mitotic index at all concentration and also induced nuclear lesion. In view of the cytotoxic data gathered in this study the use of the plants for herbal medicinal purposed should be with caution. REFERENCES Apostolides, Z., D.A. Balentine, M.E. Harbowy and J.H. Weishburger, Inhibition of 2-amino-1- methyl-6-phenylimidazo (4,5-6) pyridine (Phip) Mutagenicity by black and green tea extracts and polyphenols. Mutat. Res., 359: Burim, R.V., R. Candle, J.L.S. Lopes and C.S. Takahashi, Genotoxic action of the sesquiterpene lactone glaucolide B on mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo. Genet. Mol. Biol., 22: Dias, F.L. and C.S. Takahashi, Cytogenetic evaluation of the effect of aqueous extracts of the medicinal plants Alpinia nutans Rosc (Zingiberaceae) and Pogostemun heyneanus Benth (Labiatae) on wistar rats and Allium cepa Linn. (Liliaceae) root tip cells. Rev. Brazil Genet., 17: Dutta, A.C. and B. Mukerji, Pharmacology of Indian leaf. Calcutta India. J. Pharmacol., 2: 96. Ebana, R.U., A.I. Essien and O.D. Ekpo, Potential medicinal values of leaves of L. African P. beauv. Glob. J. Pure Appl. Sci., 1: 2-7.
5 El-Ghamery, A.A., A.I. El-Nahas and M.M. Mansour, Effect of the herbicide goal oxyfluorfen on cell division and nucleic acids content in root tips of Allium cepa L. and Viciafaba L. Egypt J. Bot., 402: Etukudo, I., Ethnobotany: Conventional and Traditional Uses of Plants. 1st Edn., The Verdict Press, 20 Akpakpan Street, Uyo, Nigeria, pp: 24. Fatope, M.O. H. Ibrahim and Y. Takeda, Screening of higher plants reputed as pesticides using the brine shrimp lethality assay. Int. J. Pharmacogn., 31: Formina, Zh. N., N.V. Kolosentseva and L.A. Sen, Cytogenetic Consequences of radiation pollution of the environment in crop plant. Tezisy Dokdalo: Tom., 2: Grisolia, C.K., C.S. Takashashi and I. Ferrai, Invitro and in-vivo tests in humans confirm that the antimalarial drug mefloquine is not mutagenic. Braz. J. Genet., 18: Itoyama, M.M., H.E.M.C. Bicudo and J.A. Cordeiro, Effects of Caffeine on Mitotic index in Drosophila prosaltans (Diptera). Braz. J. Genet., 20: Kabarity, A. and G. Malallah, Mitodepressive effect of plant extract on the meristematic region of Allium cepa tips. Cytolgia, 45(4): Kumar, G. and P. Rai, Comparative genotoxic potential of mercury and cadmium in soybean. Turk. J. Biol., 31: Moore, D.M., Plant Cytogenetic. Chapman and Hall, London, pp: 529. Mukhtar, M.D. and A. Tukur, In-vitro screening for activity of Pistia stratiotes extracts. NISEB J., 1(1): Seung-Joo-Lee, K.U., S. Takayuki and L. Kwang- Guen, Identification of volatile components in Basil (Ocimum basilicum) and thyme leaves (Thymus vulgaris) and their antioxidant properties. Food Chem., 91:
Comparative effects of colchicine, 8-hydroxyquinoline and paradichlorobenzene on arm ratio of mitotic chromosomes of Allium cepa L.
 International Journal of Medicinal Plants and Alternative Medicine Vol. 2(2), pp. 021-026, August 2014 Available online at http://academeresearchjournals.org/journal/ijmpam ISSN 2327-560X 2013 Academe
International Journal of Medicinal Plants and Alternative Medicine Vol. 2(2), pp. 021-026, August 2014 Available online at http://academeresearchjournals.org/journal/ijmpam ISSN 2327-560X 2013 Academe
Cytological effects induced by Agil herbicide to onion
 Volume 16(1), 6-72, 212 JOURNAL of Horticulture, Forestry and Biotechnology www.journal-hfb.usab-tm.ro Cytological effects induced by Agil herbicide to onion Bonciu Elena 1* 1 University of Craiova, Faculty
Volume 16(1), 6-72, 212 JOURNAL of Horticulture, Forestry and Biotechnology www.journal-hfb.usab-tm.ro Cytological effects induced by Agil herbicide to onion Bonciu Elena 1* 1 University of Craiova, Faculty
Stages of Mitosis. Introduction
 Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test
 Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test 1. Purpose The Allium cepa assay is an efficient test for chemical screening and in situ monitoring for genotoxicity of environmental contaminants. The test has been
Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test 1. Purpose The Allium cepa assay is an efficient test for chemical screening and in situ monitoring for genotoxicity of environmental contaminants. The test has been
Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa
 Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa Maya George 1, Arya George 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Zoology, Alphonsa College Pala, Kottayam (Dist), Kerala,
Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa Maya George 1, Arya George 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Zoology, Alphonsa College Pala, Kottayam (Dist), Kerala,
Exercise 6. Procedure
 Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Science 10-Biology Activity 12 Experiment on Observing Cell Division
 Science 10-Biology Activity 12 Experiment on Observing Cell Division Name Due Date 10 Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Purpose: To observe and sketch plant cells and animal cells in various
Science 10-Biology Activity 12 Experiment on Observing Cell Division Name Due Date 10 Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Purpose: To observe and sketch plant cells and animal cells in various
MITOSIS INTRODUCTION. Cytokinesis. centromere. DNA Replication S-Phase. One Chromosome Two Chromatids. One Chromosome No Chromatids 10.
 MITOSIS INTRODUCTION Cell reproduction usually involves two processes: 1) mitosis is the orderly separation and division of chromosomes in the nucleus and 2) cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm.
MITOSIS INTRODUCTION Cell reproduction usually involves two processes: 1) mitosis is the orderly separation and division of chromosomes in the nucleus and 2) cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm.
Lab title: Cell Division author: Dr. Ruth Dahlquist-Willard (modified by D. Bell)
 Corresponding Readings: Lab title: Cell Division author: Dr. Ruth Dahlquist-Willard (modified by D. Bell) Campbell Ch. 8 BIOL-100L Safety Information: We will be using laboratory glassware such as microscope
Corresponding Readings: Lab title: Cell Division author: Dr. Ruth Dahlquist-Willard (modified by D. Bell) Campbell Ch. 8 BIOL-100L Safety Information: We will be using laboratory glassware such as microscope
STUDY OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY AND CHROMOSOMAL BEHAVIOUR IN ROOT MERISTEM OF Allium cepa L. TREATED WITH MAGNESIUM SULPHATE
 ECOPRINT 1: 3-, 200 ISSN 2- Ecological Society (ECOS), Nepal www.ecosnepal.com STUDY OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY AND CHROMOSOMAL BEHAVIOUR IN ROOT MERISTEM OF Allium cepa L. TREATED WITH MAGNESIUM SULPHATE Prabhakar
ECOPRINT 1: 3-, 200 ISSN 2- Ecological Society (ECOS), Nepal www.ecosnepal.com STUDY OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY AND CHROMOSOMAL BEHAVIOUR IN ROOT MERISTEM OF Allium cepa L. TREATED WITH MAGNESIUM SULPHATE Prabhakar
Toxicity and Genotoxicity of Pendimethalin in Maize and Onion
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 1010-1015 (2010) Toxicity and Genotoxicity of Pendimethalin in Maize and Onion Nuttapol Promkaew 1, Puangpaka Soontornchainaksaeng 1 *, Sansern Jampatong 2 and Piangchan Rojanavipart
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 1010-1015 (2010) Toxicity and Genotoxicity of Pendimethalin in Maize and Onion Nuttapol Promkaew 1, Puangpaka Soontornchainaksaeng 1 *, Sansern Jampatong 2 and Piangchan Rojanavipart
Mitotic index and Duration of the cell cycle
 Mitotic index and Duration of the cell cycle Objectives: Upon completion of this lab, the students should be able to: 1. Understand the meaning of mitotic index and duration of stages (phases) 2. Calculate
Mitotic index and Duration of the cell cycle Objectives: Upon completion of this lab, the students should be able to: 1. Understand the meaning of mitotic index and duration of stages (phases) 2. Calculate
You should wear eye protection throughout this practical.
 Practical 8 - Broad bean root tip squash This practical focuses on setting up and manipulating apparatus and making and recording observations. Further skills can be developed using additional information
Practical 8 - Broad bean root tip squash This practical focuses on setting up and manipulating apparatus and making and recording observations. Further skills can be developed using additional information
Effects of Some Growth Substances on Mitosis
 Cytologia 42: 323-329, 1977 Effects of Some Growth Substances on Mitosis Ganesh1 Prasad and K. Das2 Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi-221005, India Received
Cytologia 42: 323-329, 1977 Effects of Some Growth Substances on Mitosis Ganesh1 Prasad and K. Das2 Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi-221005, India Received
1.3.1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m43135 1 1.3.1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis * Daniel Williamson This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 The cell cycle and
OpenStax-CNX module: m43135 1 1.3.1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis * Daniel Williamson This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 The cell cycle and
Evaluation of cytotoxic effects of synthetic pesticide attack on root meristems of Allium cepa L.
 South Indian Journal Of Biological Sciences 2016; 2(1); 35 40 ONLINE ISSN: 2454 4787 Research Article Evaluation of cytotoxic effects of synthetic pesticide attack on root meristems of Allium cepa L. Soumya
South Indian Journal Of Biological Sciences 2016; 2(1); 35 40 ONLINE ISSN: 2454 4787 Research Article Evaluation of cytotoxic effects of synthetic pesticide attack on root meristems of Allium cepa L. Soumya
Cytological Studies on the Responses of Onion Root - Tip Cells to Water-Soluble Tobacco Smoke Extracts from Various Experimental Cigarettes1
 Cytologia 40: 383-388, 1975 Cytological Studies on the Responses of Onion Root - Tip Cells to Water-Soluble Tobacco Smoke Extracts from Various Experimental Cigarettes1 D. K. Gulati, P. S. Sabharwal and
Cytologia 40: 383-388, 1975 Cytological Studies on the Responses of Onion Root - Tip Cells to Water-Soluble Tobacco Smoke Extracts from Various Experimental Cigarettes1 D. K. Gulati, P. S. Sabharwal and
Mitosis in Plant Cells Lab
 Mitosis in Plant Cells Lab Names: Period # Reproduction of most cells in plants and animals uses the type of cell division called Mitosis. In this activity, you will study mitosis in plant cells by examining
Mitosis in Plant Cells Lab Names: Period # Reproduction of most cells in plants and animals uses the type of cell division called Mitosis. In this activity, you will study mitosis in plant cells by examining
BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS
 Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS
 The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
T R L J. Version 2, 2018 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. A B C D ... (1) ... (1)
 1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. X A B C D (a) Place stages A, B, C and D in the correct order.... (b) Name the structures labelled X.... Describe
1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. X A B C D (a) Place stages A, B, C and D in the correct order.... (b) Name the structures labelled X.... Describe
Cytological Effects of Paper Mills Effluents on Somatic Cells of Allium cepa
 Cytologia 44: 921-926, 1979 Cytological Effects of Paper Mills Effluents on Somatic Cells of Allium cepa K. B. Shanthamurthy and V. Rangaswamy Received April 6, 1978 Department of Post-Graduate Studies
Cytologia 44: 921-926, 1979 Cytological Effects of Paper Mills Effluents on Somatic Cells of Allium cepa K. B. Shanthamurthy and V. Rangaswamy Received April 6, 1978 Department of Post-Graduate Studies
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Cell Division. Learning Objectives: Introduction. Revised Fall 2018
 Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
Cell Cycle Phase. Interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ) Mitotic Phase (M phase) Prophase. Metaphase. Anaphase. Telophase
 Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE
 Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Cell Division Questions. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Cell Division Questions Mitosis and Meiosis 1 10 Do not write outside the box 5 Figure 3 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 3 E E e e F F f f 5 (a)
Cell Division Questions Mitosis and Meiosis 1 10 Do not write outside the box 5 Figure 3 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 3 E E e e F F f f 5 (a)
LAB. MITOSIS AND CANCER PART 1. NORMAL MITOSIS IN PLANTS FIGURE 1. DIAGRAMATIC GUIDE TO THE STAGES OF MITOSIS
 Period Date LAB. MITOSIS AND CANCER One of the basic tenets of biology is that all new cells come from living cells. New cells are formed by the process of cell division which includes both the division
Period Date LAB. MITOSIS AND CANCER One of the basic tenets of biology is that all new cells come from living cells. New cells are formed by the process of cell division which includes both the division
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Clastogenic effect of soft drink on root tip of Allium cepa
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 5 (2014) pp. 200-206 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Clastogenic effect of soft drink on root tip of Allium cepa Sandip Kumar Chandraker 1, Priyanka Singh
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 5 (2014) pp. 200-206 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Clastogenic effect of soft drink on root tip of Allium cepa Sandip Kumar Chandraker 1, Priyanka Singh
GENOTOXIC EFFECT OF FOUR MEDICINAL PLANT EXTRACTS ON PISUM SATIVUM CV. ARIKIL SAZADA SIDDIQUI*
 Bangladesh J. Bot. 43(1): 107-111, 2014 (June) - Short communication GENOTOXIC EFFECT OF FOUR MEDICINAL PLANT EXTRACTS ON PISUM SATIVUM CV. ARIKIL SAZADA SIDDIQUI* College of Science, Department of Biology,
Bangladesh J. Bot. 43(1): 107-111, 2014 (June) - Short communication GENOTOXIC EFFECT OF FOUR MEDICINAL PLANT EXTRACTS ON PISUM SATIVUM CV. ARIKIL SAZADA SIDDIQUI* College of Science, Department of Biology,
GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF OCIMUM BASILICUM L AND LEUCAS ZEYLANICA L IN ROOT TIP CELLS OF ALLIUM CEPA L
 J. Indian bot. Soc. ISSN - 0019-4468 Vol. 93 (1 & 2) 2014 : 135-139 GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF OCIMUM BASILICUM L AND LEUCAS ZEYLANICA L IN ROOT TIP CELLS OF ALLIUM CEPA L VISHNU SHANKAR SINHA AND NANDJEE KUMAR*
J. Indian bot. Soc. ISSN - 0019-4468 Vol. 93 (1 & 2) 2014 : 135-139 GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF OCIMUM BASILICUM L AND LEUCAS ZEYLANICA L IN ROOT TIP CELLS OF ALLIUM CEPA L VISHNU SHANKAR SINHA AND NANDJEE KUMAR*
Push down hard on the cover slip, but do not push the cover slip sideways
 Q1.A student investigated mitosis in the tissue from an onion root tip. (a) The student prepared a temporary mount of the onion tissue on a glass slide. She covered the tissue with a cover slip. She was
Q1.A student investigated mitosis in the tissue from an onion root tip. (a) The student prepared a temporary mount of the onion tissue on a glass slide. She covered the tissue with a cover slip. She was
EFFECTS OF DITHANE M-45 (A FUNGICIDE) ON ROOT MERISTEM OF VIGNA MUNGO (L.) HEPPER
 EFFECTS OF DITHANE M-45 (A FUNGICIDE) ON ROOT MERISTEM OF VIGNA Susanta Kumar Maity* MUNGO (L.) HEPPER Abstract: The cytotoxic effects of Dithane M-45, a fungicide were investigated in the mitotic cell
EFFECTS OF DITHANE M-45 (A FUNGICIDE) ON ROOT MERISTEM OF VIGNA Susanta Kumar Maity* MUNGO (L.) HEPPER Abstract: The cytotoxic effects of Dithane M-45, a fungicide were investigated in the mitotic cell
Unit 4: Reproduction. Traits. Heredity. Nucleus: The Control Center. DNA deoxyribonucleic acid 09/06/2016
 Unit 4: Reproduction Traits Traits: are physical features of an organism. They can vary in size or form from one individual to another. Examples include eye color, height and colour vision. Heredity Heredity:
Unit 4: Reproduction Traits Traits: are physical features of an organism. They can vary in size or form from one individual to another. Examples include eye color, height and colour vision. Heredity Heredity:
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Effects of radiofrequency radiation on root tip cells of Zea mays
 Roumanian Biotechnological Letters Vol. 14, No. 3, 2009, pp. 4365-4369 Copyright 2008 Bucharest University Printed in Romania. All rights reserved Roumanian Society of Biological Sciences ORIGINAL PAPER
Roumanian Biotechnological Letters Vol. 14, No. 3, 2009, pp. 4365-4369 Copyright 2008 Bucharest University Printed in Romania. All rights reserved Roumanian Society of Biological Sciences ORIGINAL PAPER
Genotoxicity of Euphorbia hirta: An Allium cepa Assay
 Molecules 2012, 17, 7782-7791; doi:10.3390/molecules17077782 Article OPEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules Genotoxicity of Euphorbia hirta: An Allium cepa Assay Kwan Yuet
Molecules 2012, 17, 7782-7791; doi:10.3390/molecules17077782 Article OPEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules Genotoxicity of Euphorbia hirta: An Allium cepa Assay Kwan Yuet
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Genotoxic evaluations of Allium cepa L. using different concentrations of synthesized butenolide
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 213, 3(4):8-12 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY Genotoxic evaluations of Allium cepa L. using different
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 213, 3(4):8-12 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY Genotoxic evaluations of Allium cepa L. using different
Cell plate Carcinogen Oncogenes. Haploid cell Diploid cell Chromosome. Telophase Keywords Mitosis
 Cell Division Cell plate Carcinogen Oncogenes Haploid cell Diploid cell Chromosome Gene Interphase Anaphase Metaphase Telophase Keywords Mitosis Meiosis Centromere Cleavage furrow Middle lamella What is
Cell Division Cell plate Carcinogen Oncogenes Haploid cell Diploid cell Chromosome Gene Interphase Anaphase Metaphase Telophase Keywords Mitosis Meiosis Centromere Cleavage furrow Middle lamella What is
Cell Division. Introduction. Chromatin, Chromosomes, and Chromatids, Oh My! The Cell Cycle
 Introduction Cell Division Just like a butterfly passes through different phases (such as caterpillar, chrysalis, and adult butterfly) there are a series of phases in a cell's life as it gets ready to
Introduction Cell Division Just like a butterfly passes through different phases (such as caterpillar, chrysalis, and adult butterfly) there are a series of phases in a cell's life as it gets ready to
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division. diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
 Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
10-2 Cell Division. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter Test A CHAPTER 9 Cellular Reproduction Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term or phrase that best answers each question. Part B: Matching 1. What can limit
Chapter Test A CHAPTER 9 Cellular Reproduction Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term or phrase that best answers each question. Part B: Matching 1. What can limit
Mitosis: Cell Division
 Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
Introduction: Alprazolam is a triazolobenzodiazepine used in panic disorders and other anxiety
 DOI: 10.5455/medarh.2013.67.388-392 Med Arh. 2013 Dec; 67(6): 388-392 Received: June 18th 2013 Accepted: October 15th 2013 Published online: 28/12/2013 Published print: 12/2013 ORIGINAL PAPER Chromosomal
DOI: 10.5455/medarh.2013.67.388-392 Med Arh. 2013 Dec; 67(6): 388-392 Received: June 18th 2013 Accepted: October 15th 2013 Published online: 28/12/2013 Published print: 12/2013 ORIGINAL PAPER Chromosomal
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division. AP Biology
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
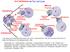 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall Cell Cycle Effects of Radiation
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
Onion Root Tip Lab Report
 Onion Root Tip Lab Report Hannah Scott Biology Ms. Carpenter February 25, 2013 Problem, Hypothesis and Prediction In this lab experiment, Hannah was to analyze an onion root tip under a microscope to observe
Onion Root Tip Lab Report Hannah Scott Biology Ms. Carpenter February 25, 2013 Problem, Hypothesis and Prediction In this lab experiment, Hannah was to analyze an onion root tip under a microscope to observe
EFFECTS OF CHRONIC GAMMA IRRADIATION ON SHALLOT CHROMOSOMES (Allium ascalonicum Linn)
 EFFECTS OF CHRONIC GAMMA IRRADIATION ON SHALLOT CHROMOSOMES (Allium ascalonicum Linn) Pechlada Rochanabanthit 1 and Peeranuch Jompuk 1, 2 1 Department of Applied Radiation and Isotopes, Faculty of Science,
EFFECTS OF CHRONIC GAMMA IRRADIATION ON SHALLOT CHROMOSOMES (Allium ascalonicum Linn) Pechlada Rochanabanthit 1 and Peeranuch Jompuk 1, 2 1 Department of Applied Radiation and Isotopes, Faculty of Science,
CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013
 CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at related terminology Discuss the cell cycle Look at the purpose of cell division Consider what is Mitosis Look at the
CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at related terminology Discuss the cell cycle Look at the purpose of cell division Consider what is Mitosis Look at the
Studies on Cellular Damage by Extracts of Betel Leaves Used for Chewing
 Cytologia 43: 203-208, 1978 Studies on Cellular Damage by Extracts of Betel Leaves Used for Chewing Received July 25, 1976 Susan Abraham and V. Dileep Cherian Department of Botany, University of Kerala,
Cytologia 43: 203-208, 1978 Studies on Cellular Damage by Extracts of Betel Leaves Used for Chewing Received July 25, 1976 Susan Abraham and V. Dileep Cherian Department of Botany, University of Kerala,
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer This Activity Packet belongs to:
 Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: At the end of the unit you will turn in this packet for a score. Record the completion due dates in the chart below.
Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: At the end of the unit you will turn in this packet for a score. Record the completion due dates in the chart below.
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
Available online:
 VOL.3 NO.2September 2014 - ISSN 2233 1859 Southeast Europe Journal of Soft Computing Available online: www.scjournal.com.ba GENOTOXICITY ANALYSIS OF FROMILID AND METHOTREXATE USING ALLIUM TEST Merisa Ćenanović
VOL.3 NO.2September 2014 - ISSN 2233 1859 Southeast Europe Journal of Soft Computing Available online: www.scjournal.com.ba GENOTOXICITY ANALYSIS OF FROMILID AND METHOTREXATE USING ALLIUM TEST Merisa Ćenanović
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF SODIUM NITRATE IN ONION ROOTS
 Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula Biologie Tom. XX, Issue 2, 13, pp. 71-79 GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF SODIUM NITRATE IN ONION ROOTS Maria-Mihaela ANTOFIE *, Elena DOROFTEI ** * Faculty of Agricultural
Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula Biologie Tom. XX, Issue 2, 13, pp. 71-79 GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF SODIUM NITRATE IN ONION ROOTS Maria-Mihaela ANTOFIE *, Elena DOROFTEI ** * Faculty of Agricultural
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Chromosome aberration and irregular cell cycle in Allium cepa root cells caused by different concentrations of Alprazolam
 407 Chromosome aberration and irregular cell cycle in Allium cepa root cells caused by different concentrations of Alprazolam Jasmin Musanovic 1*, Nerman Ramic 2, Hilada Nefić 3, Amela Dzubur 4 1 Department
407 Chromosome aberration and irregular cell cycle in Allium cepa root cells caused by different concentrations of Alprazolam Jasmin Musanovic 1*, Nerman Ramic 2, Hilada Nefić 3, Amela Dzubur 4 1 Department
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Lesson 1 Instructional Materials. What do you OBSERVE about this image? State what you SEE, not what you think.
 Lesson 1 Instructional Materials What do you OBSERVE about this image? State what you SEE, not what you think. Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials
Lesson 1 Instructional Materials What do you OBSERVE about this image? State what you SEE, not what you think. Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
6 REPLICATED CHROMOSOMES
 INTERPHASE 2 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL 6 REPLICATED CHROMOSOMES INTERPHASE 2 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL TWO CHROMATIDS INTERPHASE 6 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL DNA CONTENT DOUBLED INTERPHASE NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL
INTERPHASE 2 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL 6 REPLICATED CHROMOSOMES INTERPHASE 2 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL TWO CHROMATIDS INTERPHASE 6 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL DNA CONTENT DOUBLED INTERPHASE NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL
LABORATORY INQUIRY Part 2 Practicing Procedures and Developing Your Research Project
 LABORATORY INQUIRY Part 2 Practicing Procedures and Developing Your Research Project I. Researching Mitosis and Cellular Function For this research project, your team should choose some aspect of mitosis,
LABORATORY INQUIRY Part 2 Practicing Procedures and Developing Your Research Project I. Researching Mitosis and Cellular Function For this research project, your team should choose some aspect of mitosis,
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
(i) List these events in the correct order, starting with D.... (1)... (1)... (1)
 Q1. (a) Boxes A to E show some of the events of the cell cycle. A Chromatids seperate B Nuclear envelopes disappears C Cytoplasm divides D Chromosomes condense and become visible E Chromosomes on the equator
Q1. (a) Boxes A to E show some of the events of the cell cycle. A Chromatids seperate B Nuclear envelopes disappears C Cytoplasm divides D Chromosomes condense and become visible E Chromosomes on the equator
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 10
 The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
Exam 2 spring 2016 Page 1
 xam 2 spring 2016 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium
xam 2 spring 2016 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
Cellular Reproduction
 Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
_??_ 1987 by Cytologia, Tokyo C ytologia 52: , Meiotic Abnormalities Induced by Dye Industry Waste Water in Chlorophytum amaniense Engler
 _??_ 1987 by Cytologia, Tokyo C ytologia 52: 647-652, 1987 Meiotic Abnormalities Induced by Dye Industry Waste Water in Chlorophytum amaniense Engler Accepted July, 28, 1986 R. K. Somashekar Department
_??_ 1987 by Cytologia, Tokyo C ytologia 52: 647-652, 1987 Meiotic Abnormalities Induced by Dye Industry Waste Water in Chlorophytum amaniense Engler Accepted July, 28, 1986 R. K. Somashekar Department
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence And now look at you How did you get from there to
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence And now look at you How did you get from there to
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Cell Biology Lecturer: Assist. Prof. Dr. Altijana Hromić-Jahjefendić Assistant: Furkan Enes Oflaz LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells Objective After completing this exercise, you should
Cell Biology Lecturer: Assist. Prof. Dr. Altijana Hromić-Jahjefendić Assistant: Furkan Enes Oflaz LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells Objective After completing this exercise, you should
The Cell Cycle. Materials 2 pipe cleaners of one color and 2 of another color Drawing paper
 The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Student Exploration: Cell Division
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Division Vocabulary: cell division, centriole, centromere, chromatid, chromatin, chromosome, cytokinesis, DNA, interphase, mitosis Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Division Vocabulary: cell division, centriole, centromere, chromatid, chromatin, chromosome, cytokinesis, DNA, interphase, mitosis Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these
Cell Cycle. Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer
 Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Vocabulary: cell division, centriole, centromere, chromatid, chromatin, chromosome, cytokinesis, DNA, interphase, mitosis
 Cell Division Answer Key Vocabulary: cell division, centriole, centromere, chromatid, chromatin, chromosome, cytokinesis, DNA, interphase, mitosis Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
Cell Division Answer Key Vocabulary: cell division, centriole, centromere, chromatid, chromatin, chromosome, cytokinesis, DNA, interphase, mitosis Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
The Cell Cycle and Cell Division
 Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
 B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Mitosis: Cell Division
 Name Mitosis: Cell Division by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1.How do children grow? Do
Name Mitosis: Cell Division by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1.How do children grow? Do
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation
 B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
Unit 5: Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis & Drug Influence Influence on Nervous System
 Unit 5: Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis & Drug Influence Influence on Nervous System 1. Which of the following is NOT related to a cell s surface area to volume ratio? a. Cell size b. Number of nuclei c.
Unit 5: Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis & Drug Influence Influence on Nervous System 1. Which of the following is NOT related to a cell s surface area to volume ratio? a. Cell size b. Number of nuclei c.
Name Date Class. Interphase. (1) The. grows. DNA is duplicated.
 Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Chapter 6. Cell Reproduction
 Chapter 6 Cell Reproduction Chromosomes The growth and development of your body are controlled by instructions contained in your DNA DNA decides what you will be.. DNA & Chromosomes Very long molecules
Chapter 6 Cell Reproduction Chromosomes The growth and development of your body are controlled by instructions contained in your DNA DNA decides what you will be.. DNA & Chromosomes Very long molecules
LABORATORY INQUIRY Mechanisms of Mitosis
 LABORATORY INQUIRY Mechanisms of Mitosis The first person to ever observe and characterize cells was Robert Hooke in 1665, who observed the tiny holes that made up a slice of cork he was observing under
LABORATORY INQUIRY Mechanisms of Mitosis The first person to ever observe and characterize cells was Robert Hooke in 1665, who observed the tiny holes that made up a slice of cork he was observing under
Chapter 8: Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle
 Chapter 8: Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle 1. During metaphase, the chromosomes move to the equator of the spindle. Which of these illustrations shows metaphase? a. b. c. d. 2. Which one of these
Chapter 8: Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle 1. During metaphase, the chromosomes move to the equator of the spindle. Which of these illustrations shows metaphase? a. b. c. d. 2. Which one of these
2.1 The Importance of Cell Division
 2.1 The Importance of Cell Division Functions of cell division Growth Repair Reproduction Growth All organisms begin as a single cell. Cell divisions will increase as an organism s size increases. There
2.1 The Importance of Cell Division Functions of cell division Growth Repair Reproduction Growth All organisms begin as a single cell. Cell divisions will increase as an organism s size increases. There
Science 10-Biology Activity 11 Worksheet on Cell Reproduction
 Science 10-Biology Activity 11 Worksheet on Cell Reproduction Name Due Date 10 Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 356-362 in the Science Probe
Science 10-Biology Activity 11 Worksheet on Cell Reproduction Name Due Date 10 Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By NOTE: This worksheet is based on material from pages 356-362 in the Science Probe
Food Processing Studies
 Appendix 4a. Food Processing Studies Food technologies and market analyses develop post-harvest methods for processing and preservation of vegetables using technologies that can be readily adopted by local
Appendix 4a. Food Processing Studies Food technologies and market analyses develop post-harvest methods for processing and preservation of vegetables using technologies that can be readily adopted by local
