Anastasia Konstantinidou
|
|
|
- Kerry Potter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 XXXVIIth IPPA Advanced Course 2015 Fontainebleau, France CILIOPATHIES and SKELETAL DYSPLASIA Anastasia Konstantinidou National University of Athens, Greece Birmingham Women s Hospital, U.K.
2 Ciliary Skeletal Dysplasias The term ciliary skeletal dysplasias summarizes inherited conditions resulting from cilia malfunction affecting skeletal development in mammals. Cilia are hair-like organelles projecting from the surface of cells.
3 Cilia can be divided into two main subgroups: motile cilia - occuring in bundles of hundreds distinguished by their ability to beat rhythmically Restricted to: the respiratory tract, brain ventricles, reproductive tract, organizing fluid flow across the cell surface and mucociliary clearance, and the embryonic node in mammals, producing a leftward fluid flow so that the embryo knows Left from Right. non-motile (primary) cilia - single structures Primary cilia can be found on nearly every cell throughout the organism. They have chemosensory, osmosensory and phototransduction functions. Gene defects encoding for proteins of the ciliary motile apparatus lead to a cystic fibrosis-like disease named Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia (including Kartagener syndrome) presenting with bronchiectasis, infertility, and laterality defects, which are due to impaired motile ciliary function in the embryonic node. An expanding group of syndromic genetic conditions with a broad range of phenotypes are linked to malfunction of primary cilia: Bardet-Biedl syndrome Polycystic Kidney Disease, Nephronophthisis Joubert syndrome - Meckel syndrome. and the ciliary osteochondrodysplasias.
4 Primary cilia consist of nine pairs of microtubules (9+0). Motile cilia display an additional central pair (9+2). These motile cilia also contain other proteins necessary for the motile apparatus such as dynein arms and radial spokes, not observed in primary cilia. Ciliary ultrastructure The ciliary axoneme extends from the basal body which is formed from centrioles, complex microtubule-based structures, and directs the trafficking of vesicles and organelles. Transition zone fibers connect ciliary membrane with the cilium and are thought to form a barrier towards the cellular cytoplasm. The ciliary pocket has been identified as a hub for cell signaling pathways and it is thought that proteins produced within the cell body are transported to the ciliary pocket J Pediatr Genet 2014;3(2): 46 94
5 Ciliary proteins are thought to be transported to the cilium within vesicles that merge with the ciliary membrane in the ciliary pocket area. Delivery of ciliary cargo involves assembly of cilia from the ciliary base to the tip. Intraflagellar Transport (IFT) Anterograde intraflagellar transport (IFT) from the ciliary base to the tip is facilitated by IFT complex B, while retrograde transport back the base requires IFT complex A. Most genes found to be involved in ciliary chondrodysplasias encode for proteins of complex A and the associated motor complex, cytoplasmic dynein-2, which provides the power for ciliary assembly. However, EVC/EVC2, CSPP1 and NEK1 localize to the base of the cilium and TCTN3 is found at the ciliary transition zone. To date, no human mutations have been identified in the motor for complex B, kinesin-2. Hedgehog (Hh) signaling is essential to maintain a balance between cell proliferation and differentiation at the growth plates. In Hh signaling, activated GLI proteins (transcription factors) finally translocate to the nucleus where they influence gene expression. IFT mutant mice as well as mice lacking Evc function J Pediatr Genet 2014;3(2): 46 94
6 In the ciliary chondrodysplasias : Abnormal primary ciliary structure or function The causative gene product is localized to the ciliary apparatus or to associated complexes and pathways. Many of the disease-related proteins are not expressed in the cilium itself, but rather at its base, in the basal body (transition zone or centrosome). The ciliopathies form a class of genetic disease whose etiology purportedly lies not with dysfunction in a single-gene product but with dysfunction in an integrated aspect of cellular physiology. Baker K, Beales PL Making sense of cilia in disease: The human ciliopathies. Am J Med Genet Part C Semin Med Genet 151C:
7 Ciliary signaling in cartilage and bone cells Extensive signaling dialog between cilia and extracellular matrix The primary cilium protrudes like an antenna from the cell surface, sensing mechanical and chemical cues provided in the cellular environment. In the bone, ciliary protrusion into the extracellular matrix (ECM) allows response to compression forces. Articular chondrocytes sense mechanical forces including shear stress, rotation, pressure, and tension in part through interactions of the ECM with ciliary proteins (integrins and NG2 chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan). Hydrostatic loading of growth plate chondrocytes increases Indian hedgehog (IHH) signaling, governing chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation in the growth plate, dependent on intact cilia. Cilia are required for osteogenic and bone resorptive responses to fluid flow. Curr Opin Cell Biol October ; 24(5):
8 CILIARY CHONDRODYSPLASIAS (known to date) Short-Rib-Polydactyly (SRP) - SRP type 1/3 (Saldino-Noonan / Verma-Naumoff) - SRP type 2 (Majewski) - SRP type 4 (Beemer-Langer) - SRP type 5 WDR35 Asphyxiating Thoracic Dystrophies (ATD; Jeune) Chondroectodermal dysplasia (Ellis-van Creveld) Mainzer-Saldino syndrome (MZSD) 'conorenal syndrome Oral-facial-digital syndrome 4 (OFD4) Cranioectodermal dysplasia (CED; Sensenbrenner syndrome) Weyers Acrodental Dysostosis (WAD) A group of phenotypically and genetically related disorders, inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion. Short Rib Thoracic Dystrophies (SRTD 1-12) Autosomal Dominant does not affect the
9 CILIARY CHONDRODYSPLASIAS The skeletal phenotype is predominant. shortened limbs shortened ribs 'trident' acetabulae (horizontal acetabular roofs with spur-like projections at the lower margins of the sciatic notches) polydactyly - variably present (postaxial in SRP types 1, 2, 3, and EvC), preaxial or combined preaxial and postaxial in SRP type 2, rare in SRP type IV) (craniofacial malformations such as craniosynostosis) Extraskeletal involvement may be additionally present : cleft lip/palate kidneys, liver, brain, eye, heart, pancreas, intestines, genitalia laterality defects Within each organ, diseases can be developmental phenotypes presenting in utero, at birth or later in childhood. Often this may depend on the severity of the underlying mutation in addition to the number of defective proteins encoded where more than one mutation in a ciliary gene occurs. EVC and CED show ectodermal involvement (nails, hair, teeth, eccrine gland abnormalities). Phenotype severity varies significantly between the different conditions, but also between patients with the same condition.
10 Badano et al. in their review of ciliopathies [2006] had weighted 9 phenotypic features, according to their likely relevance to predict ciliary involvement : Phenotypic features likely to predict ciliary involvement (in descending order) 1. Dandy-Walker malformation 2. Agenesis of Corpus Callosum 3. Situs inversus 4. Posterior encephalocele 5. Multicystic renal disease 6. Post-axial polydactyly 7. Hepatic disease 8. Retinitis pigmentosa 9. Mental retardation Additional ciliopathy-related features 10. Cardiac defects 11. Skeletal dysplasia Badano JL, Mitsuma N, Beales PL, Katsanis N The ciliopathies: an emerging class of human genetic disorders. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 7:
11 D-W
12 CC agenesis
13 Renal dysplasia
14
15
16 Persisting Ductal CAM5.2
17 Ductal Plate Malformation
18 Abnormal genitalia
19 Pulmonary hypoplasia
20 CILIARY CHONDRODYSPLASIAS Prognosis The most severe thoracic constriction is usually seen in SRPs and Jeune-ATD. SRPs are always lethal, due to cardiorespiratory failure. ATD-Jeune shows 60% perinatal mortality. Ellis van Creveld may be compatible with life, but frequently shows severe heart defects. MZSDS and CED have a milder thoracic constriction but a higher rate of renal, retinal and liver disease that may lead to severe morbidity or mortality in childhood.
21 SHORT-RIB ± POLYDACTYLY SYNDROMES (SRP) SHORT-RIB THORACIC DYSTROPHIES (SRTD) SRP type 1/3 (Saldino-Noonan / Verma-Naumoff) SRP type 2 (Majewski) Gene locus DYNC2H1, IFT80, WDR34? NEK1, DYNC2H1 SRP type 4 (Beemer-Langer) -- SRP type 5 similar to type 3 with acromesomelic hypomineralization and camptomelia WDR35 The various phenotypic forms of SRTDs differ by visceral malformation and metaphyseal appearance. Overlapping phenotype between all types Cases that could not fit in one particular type characteristic of ciliary diseases Severe thoracic constriction Lethal in the early neonatal period
22 SRP-I Saldino-Noonan SRP 1 postaxial polydactyly hydropic appearance small thorax micromelia polycystic kidneys, liver DPM cardiac and gastrointestinal defects genital defects common flipper limb The typical hallmark of SRPS-I is extreme micromelia resulting in flipper-like
23 SRP-I Saldino-Noonan short horizontal ribs platyspondyly very short tubular bones with metaphyseal spurs ossification defects of hands and feet small ilia with flattened, trident acetabular roofs extremely short tubular bones
24 SRP-3 Verma-Naumoff SRP-3 with brachydactyly (STD8 cleft lip/palate urogenital defects less common than SRP-1 Skeletal Dysplasias. In: The Pediatric and Perinatal Autopsy Manual. MC Cohen, I Scheimberg, Eds. Cambridge University Press 2014 Micromelia is less severe than marked longitudinal metaphyseal spurs
25 SRP-2 Majewski overlapping with OFD-4 (Mohr-Majewski) in OFDs: bifid or lobulated tongue Cleft or pseudo-cleft lip/palate Pre- and postaxial poly(syn)dactyly Ambiguous genitalia common Kidney - Liver involvement Brain malformations Cardiac defects laryngeal malformation s bifid tongue or frenula
26 SRP-2 Majewski V-shaped metacarpals (osseous syndactyly) Smooth metaphyses The tibia is shorter than the fibula.
27 SRP-4 Beemer-Langer polydactyly often absent orofacial clefts kidney - liver involvement brain malformations cardiac defects X-ray Smooth metaphyses Bowed radius and ulna The tibia is not disproportionately short.
28 Ellis van Creveld Chondroectodermal Dysplasia The Pediatric and Perinatal Autopsy Manual. MC Cohen, I Scheimberg, Eds. Cambridge University Press 2014 Postaxial hexadactyly is constan Poor nail formation Cardiac defects are common. V-shaped metacarpals common in EvC and SRP-2
29 JEUNE ATD Genetically heterogeneous disorder. IFT80, IFT40, IFT172 DYNC2H1 WDR19, WDR60, WDR34 TTC21B CEP120 Compared to SRPs, the phenotype is less severe. Respiratory problems account for most of the mortality in JATD ranging from 20 60%, but patients seem to somewhat grow out of the respiratory phenotype. End-stage renal disease in childhood due to NPHP-like (and rarely cystic) kidney involvement affects less than 20% of all JATD. IFT140 and IFT172 mutations can predict this phenotype with nearly 100% probability. Patients with mutations in one of those two genes also develop retinal degeneration. Pancreatic lesions, elevated liver enzymes and brain malformations can also occur in JATD.
30 Note: the femurs are frequently angulated. JEUNE ATD Bell-shaped thorax Less severe restriction than SRPs Normal vertebrae Trident acetabulae Smooth metaphyses Polydactyly is infrequent.
31 JATD vs EvC In JATD cases with polydactyly, differentiation from Ellis-van Creveld syndrome may not be possible on radiologic grounds alone. Polydactyly is an inconstant feature of JATD and, when present, usually also affects the feet. In contrast, polydactyly of the hands is a constant feature in EVC, but the feet are uncommonly affected. The main visceral abnormality in JATD is renal, whereas it is cardiac in EVC. Ectodermal defects are common in EVC and not a feature of JATD.
32 Short Rib syndromes: Histology Variably: abnormal physeal border; retardation, disorganisation of the growth plate; disordered Jeun e
33 CRANIOECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA (CED) Sensenbrenner syndrome Patients with CED present characteristic craniofacial dysmorphic features and ectodermal defects including nail, hair and teeth abnormalities. Dolichocephalus and frontal bossing resulting from craniosynostosis of the sagittal suture, present at birth. The disease allows survival to childhood but is often complicated by early onset renal insufficiency due to a Nephronophthisis-like renal phenotype with the histological picture of tubulointerstitial nephritis and microscopic glomerular and tubular cysts. Heart defects and retinal dystrophy are less frequent.
34 CED: FAMILY CASE TOP of 2 female fetuses 23 wk and 19wk for U/S findings and family history USS findings: - Increased nuchal tranlslucency - Narrow thorax - Short long bones [< 5 th c] - Mesomelic [ < 3 rd c] - Posterior fossa cyst - Small kidneys with echogenic heterogeneity Family history: 1 affected 5 yr-old female child At birth: acromesomelic dysplasia with craniosynostosis severe renal insufficiency
35 Growth restricted Short limbs 3 yrs 46, XX Frontal bossing and protruding eyes (craniosynostosis) Retrognathia Brachydactyly 2-3 partial toe-syndactyly 9 yrs Fine sparse hair Hypodontia Reduced sweating Large cisterna magna on MRI Chronic renal failure on dialysis
36 CED TOP of two female fetuses at 23 and 19 weeks 19 weeks Micrognathia - Large lips Wide neck Large klitoris Narrow thorax Mesomelic shortening NO CRANIOSYNOSTOSIS
37 narrow thorax mesomelic shortening and benting 23w 19w
38 Extraskeletal findings Posterior fossa cyst Lung hypoplasia (lung : body weight ratio < 0.015) Atrial septal defect Renal microcysts (mostly tubular) Persisting ductal plate persisting ductal plate posterior fossa cyst
39 Renal tubular and glomerular microcysts Fetus 19 wk Fetus 23 wk
40 Fetus 23 wk Growth plate Femur x 100 Tibia x 100
41 Fetus 19 wk Fibula x 100 Ulna x 100 Tibia x 200
42 Cranioectodermal dysplasia Sensenbrenner syndrome Levin Syndrome I Autosomal Recessive no gene identified (2007) Poor prognosis (follow-up of 2 sibs) death before 6yrs (renal or cardiac failure) IPPA COURSE 2007 Constant findings Dolichocephaly (with sagittal craniosynostosis) Brachymelia Salzburg Reviewed by Tamai et al. (2002) 15 individuals reported (5 pairs of sibs + 5 individual cases) Variable findings Ectodermal dysplasia Short narrow thorax Cardiac defect Renal failure (tubulointerstitial nephropathy) Photoreceptor dystrophy
43 Badano et al. in their review of ciliopathies [2006] had weighted 9 phenotypic features, according to their likely relevance to predict ciliary involvement : Phenotypic features likely to predict ciliary involvement (in descending order) 1. Dandy-Walker malformation Posterior fossa cyst - Large cisterna magna 2. Agenesis of Corpus Callosum 3. Situs inversus 4. Posterior encephalocele 5. Multicystic renal disease Renal microcysts 6. Post-axial polydactyly 7. Hepatic disease Persisting ductal plate 8. Retinitis pigmentosa 9. Mental retardation Additional ciliopathy-related features 10. Cardiac defects ASD 11. Skeletal dysplasia + Badano JL, Mitsuma N, Beales PL, Katsanis N The ciliopathies: an emerging class of human genetic disorders. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 7:
44 Cranioectodermal Dysplasia: A Probable Ciliopathy AE Konstantinidou*, H Fryssira, et al. Am J Med Genet 2009;149A: Cranioectodermal dysplasia is a ciliopathy caused by mutations in the IFT122 gene. J Walczak-Sztulpa, J Eggenschwiler, et al. Am J Hum Genet 2010;86(6): Novel WDR35 mutations in patients with Cranioectodermal Dysplasia (Sensenbrenner syndrome) J Hoffer, AE Konstantinidou, et al. Clin Genet 2013 Jan;83(1):92-5. Epub 2012 Apr 9.
45 REFERENCES Miriam Schmidts. Clinical genetics and pathobiology of ciliary chondrodysplasias. J Pediatr Genet. 2014;3(2): Huber C, Cormier-Daire V. Ciliary disorder of the skeleton. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2012; 160C(3): Tamina Seeger-Nukpezah and Erica A. Golemis. The extracellular matrix and ciliary signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol October ; 24(5): Aoife M. Waters & Philip L. Beales. Ciliopathies: an expanding disease spectrum. Pediatr Nephrol (2011) 26: Baker K, Beales PL Making sense of cilia in disease: The human ciliopathies. Am J Med Genet Part C Semin Med Genet 151C: AE Konstantinidou, H Fryssira, et al. Cranioectodermal Dysplasia: A Probable Ciliopathy. Am J Med Genet 2009;149A: Badano JL, Mitsuma N, Beales PL, Katsanis N The ciliopathies: an emerging class of human genetic disorders. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 7:
46 END OF BONES. THANK YOU!
47 Rome Cimetière des Capucins
48 I wish to aknowledge: the patients demised before time and their parents for giving consent for teaching.
CilioPathy panel. 3-Jul-2018 (102 genen) Centrum voor Medische Genetica Gent. versie. OMIM gene ID
 versie 3-Jul-2018 (102 genen) CilioPathy panel Centrum voor Medische Genetica Gent Gene OMIM gene ID Associated phenotype, OMIM phenotype ID, phenotype mapping key and inheritance pattern AHI1 608894 Joubert
versie 3-Jul-2018 (102 genen) CilioPathy panel Centrum voor Medische Genetica Gent Gene OMIM gene ID Associated phenotype, OMIM phenotype ID, phenotype mapping key and inheritance pattern AHI1 608894 Joubert
Case A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI.
 Case 12659 A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 F. Vanhoenacker 1, 2 F. Malfait 3 D. Mortier 4 G.
Case 12659 A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 F. Vanhoenacker 1, 2 F. Malfait 3 D. Mortier 4 G.
Ultrasound Anomaly Details
 Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Utilization of the MiSeq in a clinical lab. Tony Krentz, PhD PreventionGenetics
 Utilization of the MiSeq in a clinical lab Tony Krentz, PhD PreventionGenetics PreventionGenetics Founded in 2004 in Marshfield, Wisconsin by James Weber ~90 employees Largest test menu in US Vision: Disease
Utilization of the MiSeq in a clinical lab Tony Krentz, PhD PreventionGenetics PreventionGenetics Founded in 2004 in Marshfield, Wisconsin by James Weber ~90 employees Largest test menu in US Vision: Disease
TERMINOLOGY. portion of a bone ossified from a primary center. portion of a bone ossified from a secondary center.
 Embryology APPENDICULAR SKELETON Consists of the pectoral and the pelvic girdles and the bones of the limbs. Beginning at the 4 th \ menstrual week primordial bone patterns evolve into cartilaginous bone
Embryology APPENDICULAR SKELETON Consists of the pectoral and the pelvic girdles and the bones of the limbs. Beginning at the 4 th \ menstrual week primordial bone patterns evolve into cartilaginous bone
Truncation and microdeletion of EVC accompanied by novel EFCAB7 missense mutation in Ellis-van Creveld syndrome with atypical congenital heart defect
 Truncation and microdeletion of EVC accompanied by novel EFCAB7 missense mutation in Ellis-van Creveld syndrome with atypical congenital heart defect NGUYEN Tran Quynh Nhu, MD. Department of Developmental
Truncation and microdeletion of EVC accompanied by novel EFCAB7 missense mutation in Ellis-van Creveld syndrome with atypical congenital heart defect NGUYEN Tran Quynh Nhu, MD. Department of Developmental
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review
 Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
Skeletal Dysplasias. Let me Count the Whys. Normal Skeletal Development. Fetal Musculoskeletal System & Skeletal Dysplasias 3/6/2017
 Fetal Musculoskeletal System & Skeletal Dysplasias Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager
Fetal Musculoskeletal System & Skeletal Dysplasias Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager
Renal Cystic Disease. Dr H Bierman
 Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease. Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology
 Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences. Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report
 International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE PATHOLOGY Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report Corresponding Author DR. N. HIMA BINDU Assistant Professor,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE PATHOLOGY Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report Corresponding Author DR. N. HIMA BINDU Assistant Professor,
CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View)
 Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Nicholas Katsanis, Ph.D.
 Ciliopathies and Oligogenic Phenomena Prof. Center for Human Disease Modeling Duke University 1 Some key questions in human genetics What variants cause disease? What variants are associated with disease
Ciliopathies and Oligogenic Phenomena Prof. Center for Human Disease Modeling Duke University 1 Some key questions in human genetics What variants cause disease? What variants are associated with disease
Prenatal Imaging of Skeletal Dysplasia. Dorothy Bulas MD Professor of Pediatrics and Radiology Children s National Medical Center
 Prenatal Imaging of Skeletal Dysplasia Dorothy Bulas MD Professor of Pediatrics and Radiology Children s National Medical Center OBJECTIVE Identify key features on prenatal imaging that aid in diagnosis
Prenatal Imaging of Skeletal Dysplasia Dorothy Bulas MD Professor of Pediatrics and Radiology Children s National Medical Center OBJECTIVE Identify key features on prenatal imaging that aid in diagnosis
Motile and non-motile cilia in human pathology: from function to phenotypes
 Motile and non-motile cilia in human pathology: from function to phenotypes Hannah M. Mitchison, 1* Enza Maria Valente 2,3* 1 Genetics and Genomic Medicine Programme, University College London, UCL Great
Motile and non-motile cilia in human pathology: from function to phenotypes Hannah M. Mitchison, 1* Enza Maria Valente 2,3* 1 Genetics and Genomic Medicine Programme, University College London, UCL Great
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Title. CitationPediatric Nephrology, 21(4): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type. File Information. Author(s) Michio; Sasaki, Satoshi
 Title Renal failure due to tubulointerstitial nephropathy Obikane, Katsuyuki; Nakashima, Taiji; Watarai, Yoshi Author(s) Michio; Sasaki, Satoshi CitationPediatric Nephrology, 21(4): 574-576 Issue Date
Title Renal failure due to tubulointerstitial nephropathy Obikane, Katsuyuki; Nakashima, Taiji; Watarai, Yoshi Author(s) Michio; Sasaki, Satoshi CitationPediatric Nephrology, 21(4): 574-576 Issue Date
Incidence of Skeletal Dysplasias in North Coastal Andhra Pradesh
 Incidence of Skeletal Dysplasias in North Coastal Andhra Pradesh *B Narasinga Rao, M Pramila Padmini Department of Anatomy, Maharajah s Institute of Medical Sciences, Nellimarla *Author for Correspondence:
Incidence of Skeletal Dysplasias in North Coastal Andhra Pradesh *B Narasinga Rao, M Pramila Padmini Department of Anatomy, Maharajah s Institute of Medical Sciences, Nellimarla *Author for Correspondence:
Centrosomes and Cilia
 Centrosomes and Cilia SMC6052/BIM6028/EXMD604 William Y. Tsang Research Unit Director, Cell Division and Centrosome Biology, IRCM Chercheur Adjoint, Faculté de medécine, Université de Montréal Adjunct
Centrosomes and Cilia SMC6052/BIM6028/EXMD604 William Y. Tsang Research Unit Director, Cell Division and Centrosome Biology, IRCM Chercheur Adjoint, Faculté de medécine, Université de Montréal Adjunct
28/04/2016. I have nothing to declare and no financial. interest or relationship to disclose
 I have nothing to declare and no financial interest or relationship to disclose Skeletal Anomalies are diverse range of complexities which is NOT Easy to diagnose. It is NOT Difficult to detect-just be
I have nothing to declare and no financial interest or relationship to disclose Skeletal Anomalies are diverse range of complexities which is NOT Easy to diagnose. It is NOT Difficult to detect-just be
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX
 DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
FETAL ICD-10 CODES QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE
 FETAL ICD-10 CODES QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Page CONTENTS 1 Cardiac Anomalies 3 Chromosome Abnormalities 4 Central Nervous System Anomalies 5 Extremity Anomalies 6 Face / Neck Anomalies 7 Gastrointestinal
FETAL ICD-10 CODES QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Page CONTENTS 1 Cardiac Anomalies 3 Chromosome Abnormalities 4 Central Nervous System Anomalies 5 Extremity Anomalies 6 Face / Neck Anomalies 7 Gastrointestinal
DIAGNOSIS OF PRIMARY CILIARY DYSKINESIA
 DIAGNOSIS OF PRIMARY CILIARY DYSKINESIA Kris De Boeck, MD PHD Pediatric Pulmonology, University of Leuven, Belgium Introduction Cause Congenital dysfunction of motile cilia Absence/dysfunction of one of
DIAGNOSIS OF PRIMARY CILIARY DYSKINESIA Kris De Boeck, MD PHD Pediatric Pulmonology, University of Leuven, Belgium Introduction Cause Congenital dysfunction of motile cilia Absence/dysfunction of one of
I have no disclosures
 I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
Next Generation Sequencing Panel for Joubert and Meckel Gruber Syndrome
 Next Generation Sequencing Panel for Joubert and Meckel Gruber Syndrome Joubert syndrome Joubert syndrome (JBTS) is characterized by hypotonia, oculomotor apraxia, nystagmus, and intellectual disability.
Next Generation Sequencing Panel for Joubert and Meckel Gruber Syndrome Joubert syndrome Joubert syndrome (JBTS) is characterized by hypotonia, oculomotor apraxia, nystagmus, and intellectual disability.
Otolaryngologic aspects of oral facial digital syndrome
 International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 53 (2000) 39 44 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijporl Case report Otolaryngologic aspects of oral facial digital syndrome Michael Matheny, Bryan Hall, Jose
International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 53 (2000) 39 44 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijporl Case report Otolaryngologic aspects of oral facial digital syndrome Michael Matheny, Bryan Hall, Jose
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
LU:research Institutional Repository of Lund University
 LU:research Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Acta Paediatrica. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher
LU:research Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Acta Paediatrica. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher
Genetics in Nephrology. Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory
 Genetics in Nephrology Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory Genetics in: A. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract B. Cystic Diseases of the Kidney C.
Genetics in Nephrology Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory Genetics in: A. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract B. Cystic Diseases of the Kidney C.
ANALYSIS OF THE CILIARY GENES GAS8 AND MKS6 REVEAL CONSERVED ROLES IN CILIA MOTILITY AND TRANSITION ZONE FUNCTION. by: WESLEY R.
 ANALYSIS OF THE CILIARY GENES GAS8 AND MKS6 REVEAL CONSERVED ROLES IN CILIA MOTILITY AND TRANSITION ZONE FUNCTION by: WESLEY R. LEWIS JAMES F. COLLAWN: COMMITTEE CHAIR BRADLEY K. YODER: MENTOR JOHN M.
ANALYSIS OF THE CILIARY GENES GAS8 AND MKS6 REVEAL CONSERVED ROLES IN CILIA MOTILITY AND TRANSITION ZONE FUNCTION by: WESLEY R. LEWIS JAMES F. COLLAWN: COMMITTEE CHAIR BRADLEY K. YODER: MENTOR JOHN M.
Expanding the genetic architecture and phenotypic spectrum in the skeletal ciliopathies
 Received: 3 July 2017 Revised: 12 October 2017 Accepted: 14 October 2017 DOI: 10.1002/humu.23362 RESEARCH ARTICLE Expanding the genetic architecture and phenotypic spectrum in the skeletal ciliopathies
Received: 3 July 2017 Revised: 12 October 2017 Accepted: 14 October 2017 DOI: 10.1002/humu.23362 RESEARCH ARTICLE Expanding the genetic architecture and phenotypic spectrum in the skeletal ciliopathies
High prevalence of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in a British Asian population
 High prevalence of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in a British Asian population Chris O Callaghan 1, Phil Chetcuti 2, Eduardo Moya 3 1. University of Leicester, Leicester, United Kingdom 2. Leeds General Infirmary,
High prevalence of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in a British Asian population Chris O Callaghan 1, Phil Chetcuti 2, Eduardo Moya 3 1. University of Leicester, Leicester, United Kingdom 2. Leeds General Infirmary,
Case Report Craniodentofacial Manifestations in a Rare Syndrome: Orofaciodigital Type IV (Mohr-Majewski Syndrome)
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 605892, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/605892 Case Report Craniodentofacial Manifestations in a Rare Syndrome: Orofaciodigital Type IV (Mohr-Majewski Syndrome)
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 605892, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/605892 Case Report Craniodentofacial Manifestations in a Rare Syndrome: Orofaciodigital Type IV (Mohr-Majewski Syndrome)
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Ellis van-creveld syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disorder
 Case Report May-August, 2016/Vol 36/Issue 2 Gauchan E 1, Sharma P 2 1 Dr. Eva Gauchan, MBBS, MD. Department of Paediatrics. 2 Dr. Prakash Sharma, MBBS, MD. Department of Radiology and Imaging. Both from
Case Report May-August, 2016/Vol 36/Issue 2 Gauchan E 1, Sharma P 2 1 Dr. Eva Gauchan, MBBS, MD. Department of Paediatrics. 2 Dr. Prakash Sharma, MBBS, MD. Department of Radiology and Imaging. Both from
MECKEL SYNDROME: GENETICS, PERINATAL FINDINGS, AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
 REVIEW ARTICLE MECKEL SYNDROME: GENETICS, PERINATAL FINDINGS, AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Chih-Ping Chen 1,2,3,4 * Departments of 1 Obstetrics and Gynecology, and 2 Medical Research, Mackay Memorial Hospital,
REVIEW ARTICLE MECKEL SYNDROME: GENETICS, PERINATAL FINDINGS, AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Chih-Ping Chen 1,2,3,4 * Departments of 1 Obstetrics and Gynecology, and 2 Medical Research, Mackay Memorial Hospital,
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases
 Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Elements of Dysmorphology I. Krzysztof Szczałuba
 Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics
 Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics Vitamin D physiology Introduction Etiology Clinical feature Radiology Diagnosis Lab Treatment Source: -Fish, liver and oil, - Human milk (30-40 IU/L) - Exposure to sun light
Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics Vitamin D physiology Introduction Etiology Clinical feature Radiology Diagnosis Lab Treatment Source: -Fish, liver and oil, - Human milk (30-40 IU/L) - Exposure to sun light
= Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue
 = Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue Common Orthopedic Problems Dwarfism Short Stature Pathologic Short Stature Normal Variant Short Stature Proportionate Short Stature Midget Endocrine/nutritional
= Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue Common Orthopedic Problems Dwarfism Short Stature Pathologic Short Stature Normal Variant Short Stature Proportionate Short Stature Midget Endocrine/nutritional
The Complexity of Simple Genetics
 The Complexity of Simple Genetics? The ciliopathies: a journey into variable penetrance and expressivity Bardet-Biedl Syndrome Allelism at a single locus is insufficient to explain phenotypic variability
The Complexity of Simple Genetics? The ciliopathies: a journey into variable penetrance and expressivity Bardet-Biedl Syndrome Allelism at a single locus is insufficient to explain phenotypic variability
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
Ciliopathies 00-Kenny-Prelims.indd i 22/07/13 11:15 AM
 Ciliopathies This page intentionally left blank Ciliopathies A reference for clinicians Edited by Thomas D. Kenny National Institute for Health Research Evaluations, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre,
Ciliopathies This page intentionally left blank Ciliopathies A reference for clinicians Edited by Thomas D. Kenny National Institute for Health Research Evaluations, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre,
Test Information Sheet
 Prenatal Joubert Syndrome and Related Disorders (JSRD) Panel Sequence Analysis and Exon-Level Deletion/Duplication Testing of 29 Genes Panel Gene List: AHI1, ARL13B, B9D1, B9D2, C5orf42, CC2D2A, CEP41,
Prenatal Joubert Syndrome and Related Disorders (JSRD) Panel Sequence Analysis and Exon-Level Deletion/Duplication Testing of 29 Genes Panel Gene List: AHI1, ARL13B, B9D1, B9D2, C5orf42, CC2D2A, CEP41,
Distinct Roles Of CCN1 And CCN2 In Limb Development
 Distinct Roles Of CCN1 And CCN2 In Limb Development Jie Jiang, PhD 1, Jessica Ong, BS 1, Faith Hall-Glenn, PhD 2, Teni Anbarchian, BS 1, Karen M. Lyons, PhD 1. 1 University of California, Los Angeles,
Distinct Roles Of CCN1 And CCN2 In Limb Development Jie Jiang, PhD 1, Jessica Ong, BS 1, Faith Hall-Glenn, PhD 2, Teni Anbarchian, BS 1, Karen M. Lyons, PhD 1. 1 University of California, Los Angeles,
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan
 ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
By Sally Pobojewski Photos by Scott Galvin. Secrets of the. Cilia. { long-overlooked organelles hold some hefty keys to human health }
 By Sally Pobojewski Photos by Scott Galvin Secrets of the Cilia { long-overlooked organelles hold some hefty keys to human health } Photo: Dr. G. Moscoso/Photo Researchers, Inc. 20 Fall 2007 Medicine at
By Sally Pobojewski Photos by Scott Galvin Secrets of the Cilia { long-overlooked organelles hold some hefty keys to human health } Photo: Dr. G. Moscoso/Photo Researchers, Inc. 20 Fall 2007 Medicine at
Stickler syndrome. Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium
 Stickler syndrome Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Third European Course in Clinical Dysmorphology Rome, November 20-21, 2009 Stickler syndrome
Stickler syndrome Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Third European Course in Clinical Dysmorphology Rome, November 20-21, 2009 Stickler syndrome
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nat Genet. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 November 08.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Genet. 2011 May 8; 43: 547 553. doi:10.1038/ng.832. Complex Interactions Between Genes Controlling Trafficking in Primary Cilia
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Genet. 2011 May 8; 43: 547 553. doi:10.1038/ng.832. Complex Interactions Between Genes Controlling Trafficking in Primary Cilia
Why did this happen? Genetic and teratologic considerations in CHD Jennifer Kussmann, MS,CGC. The Children's Mercy Hospital, 2014.
 Why did this happen? Genetic and teratologic considerations in CHD Jennifer Kussmann, MS,CGC The Children's Mercy Hospital, 2014. 03/14 Risk factors Family history Maternal medical condition/ illness Monochorionic
Why did this happen? Genetic and teratologic considerations in CHD Jennifer Kussmann, MS,CGC The Children's Mercy Hospital, 2014. 03/14 Risk factors Family history Maternal medical condition/ illness Monochorionic
Disclosures. Prenatal Diagnosis of Skeletal Dysplasias. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Skeletal Dysplasias. Lecture Outline
 Disclosures Prenatal Diagnosis of Skeletal Dysplasias Relevant Financial Relationships: Luis F., M.D Honoraria from Philips Health Care Philips Doppler course Luís F. Gonçalves, M.D. Division of Pediatric
Disclosures Prenatal Diagnosis of Skeletal Dysplasias Relevant Financial Relationships: Luis F., M.D Honoraria from Philips Health Care Philips Doppler course Luís F. Gonçalves, M.D. Division of Pediatric
Typical Cleft Hand. Windblown Hand. Congenital, Developmental Arrest. Congenital, Failure of Differentiation. Longitudinal (vs.
 Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Compound heterozygous mutations in the IFT140 gene cause Opitz trigonocephaly C syndrome in a patient with typical features of a ciliopathy
 Clin Genet 2017: 91: 640 646 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2016 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/cge.12924 Compound heterozygous
Clin Genet 2017: 91: 640 646 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2016 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/cge.12924 Compound heterozygous
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine
 The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
Central nervous system. Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile
 ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
The Indian Journal of Pediatrics
 13 The Indian Journal of Pediatrics November 2007; Volume 74 : Number 11 CONTENTS ORIGINAL ARTICLES Page Newly Developed WHO Growth Standards : Implications for Demographic Surveys and Child Health Programs
13 The Indian Journal of Pediatrics November 2007; Volume 74 : Number 11 CONTENTS ORIGINAL ARTICLES Page Newly Developed WHO Growth Standards : Implications for Demographic Surveys and Child Health Programs
Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XIX, nº 74, pág. 90-107, Abr.-Jun., 2007 Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood Ellen Chung Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Terminology Cyst Polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XIX, nº 74, pág. 90-107, Abr.-Jun., 2007 Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood Ellen Chung Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Terminology Cyst Polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
Central nervous system malformations in
 Case reports 659 Central nervous system malformations in Mohr's syndrome W REARDON*, M G HARBORDt, M A HALL-CRAGGSt, B KENDALLt, E M BRETTt, AND M BARAITSER *Mothercare Department of Paediatric Genetics,
Case reports 659 Central nervous system malformations in Mohr's syndrome W REARDON*, M G HARBORDt, M A HALL-CRAGGSt, B KENDALLt, E M BRETTt, AND M BARAITSER *Mothercare Department of Paediatric Genetics,
Craniomicromelic Syndrome: A Newly Recognized
 American Journal of Medical Genetics 58:348-352 (1995) Craniomicromelic Syndrome: A Newly Recognized Lethal Condition With Craniosynostosis, Distinct Facial Anomalies, Short Limbs, and Intrauterine Growth
American Journal of Medical Genetics 58:348-352 (1995) Craniomicromelic Syndrome: A Newly Recognized Lethal Condition With Craniosynostosis, Distinct Facial Anomalies, Short Limbs, and Intrauterine Growth
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Week 14. Development of the Musculoskeletal System
 Week 14 Development of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Derived from: paraxial mesoderm somites and somitomeres sclerotome sclerotome differentiation induced by SHH from notochord and floor plate
Week 14 Development of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Derived from: paraxial mesoderm somites and somitomeres sclerotome sclerotome differentiation induced by SHH from notochord and floor plate
Next Generation Sequencing Panel for Renal Cystic Disorders
 Next Generation Sequencing Panel for Renal Cystic Disorders Clinical Features: Renal cystic diseases are a genetically heterogeneous group of conditions characterized by isolated renal disease or renal
Next Generation Sequencing Panel for Renal Cystic Disorders Clinical Features: Renal cystic diseases are a genetically heterogeneous group of conditions characterized by isolated renal disease or renal
ISUOG Basic Training. Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon
 ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities
 ISUOG Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the planes required
ISUOG Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the planes required
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Kartagener s syndrome: Neonatal respiratory distress as initial symptom of primary ciliary dyskinesia
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Kartagener s syndrome: Neonatal respiratory distress as initial symptom of primary ciliary dyskinesia MAY 2005 2 Christen M, and Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Kartagener s syndrome: Neonatal respiratory distress as initial symptom of primary ciliary dyskinesia MAY 2005 2 Christen M, and Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive
Lecture 3: Skeletogenesis and diseases
 Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 3: Skeletogenesis and diseases Aug. 21, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Bone Development Mouse embryo, E14.5 Mouse embryo, E18.0
Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 3: Skeletogenesis and diseases Aug. 21, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Bone Development Mouse embryo, E14.5 Mouse embryo, E18.0
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Kidney Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 September 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Heterotaxie PCD (Primaire ciliaire dyskinesie) panel
 Heterotaxie PCD (Primaire ciliaire dyskinesie) panel versie V1 (92 genen) Centrum voor Medische Genetica Gent Gene OMIM gene ID Associated phenotype, OMIM phenotype ID, phenotype mapping key and inheritance
Heterotaxie PCD (Primaire ciliaire dyskinesie) panel versie V1 (92 genen) Centrum voor Medische Genetica Gent Gene OMIM gene ID Associated phenotype, OMIM phenotype ID, phenotype mapping key and inheritance
Congenital anomalies of upper extremity - What Radiologist should know
 Congenital anomalies of upper extremity - What Radiologist should know Poster No.: C-0955 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad; Hyderabad/IN Keywords: Congenital,
Congenital anomalies of upper extremity - What Radiologist should know Poster No.: C-0955 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad; Hyderabad/IN Keywords: Congenital,
Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis
 Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010
 Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Centrosomes and Cilia
 Centrosomes and Cilia SMC6052/BIM6027/516-604D William Y. Tsang Research Unit Director, Cell Division and Centrosome Biology, IRCM Chercheur Adjoint, Faculté de medécine, Université de Montréal Adjunct
Centrosomes and Cilia SMC6052/BIM6027/516-604D William Y. Tsang Research Unit Director, Cell Division and Centrosome Biology, IRCM Chercheur Adjoint, Faculté de medécine, Université de Montréal Adjunct
The Fetal Skeletal System
 The Fetal Skeletal System Ultrasound Assessment of Fetal Skeletal System Extremities Spine Calvarium Carol B. Benson, MD No Disclosures Extremities Assess To Exclude Size Skeletal dysplasia Presence Absent
The Fetal Skeletal System Ultrasound Assessment of Fetal Skeletal System Extremities Spine Calvarium Carol B. Benson, MD No Disclosures Extremities Assess To Exclude Size Skeletal dysplasia Presence Absent
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide Subject: Anatomy and Physiology
 RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
Skeletal System. Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section
 Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
A study of cilia density in sea urchin embryos during gastrulation
 A study of cilia density in sea urchin embryos during gastrulation Steve Das Independent Research Project Report Bio 254 Developmental Biology May 3, 2012 Introduction Embryo growth and development is
A study of cilia density in sea urchin embryos during gastrulation Steve Das Independent Research Project Report Bio 254 Developmental Biology May 3, 2012 Introduction Embryo growth and development is
The basic methods for studying human genetics are OBSERVATIONAL, not EXPERIMENTAL.
 Human Heredity Chapter 5 Human Genetics 5:1 Studying Human Genetics Humans are not good subjects for genetic research because: 1. Humans cannot ethically be crossed in desired combinations. 2. Time between
Human Heredity Chapter 5 Human Genetics 5:1 Studying Human Genetics Humans are not good subjects for genetic research because: 1. Humans cannot ethically be crossed in desired combinations. 2. Time between
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates December 2014 2 Abu Asbeh J, Bystricka A, Qadir M, Nikolay M, Khan J, Neonatal Intensive
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates December 2014 2 Abu Asbeh J, Bystricka A, Qadir M, Nikolay M, Khan J, Neonatal Intensive
Chromosome 13. Introduction
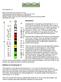 Chromosome 13 Chromosome Disorder Outreach Inc. (CDO) Technical genetic content provided by Dr. Iosif Lurie, M.D. Ph.D Medical Geneticist and CDO Medical Consultant/Advisor. Ideogram courtesy of the University
Chromosome 13 Chromosome Disorder Outreach Inc. (CDO) Technical genetic content provided by Dr. Iosif Lurie, M.D. Ph.D Medical Geneticist and CDO Medical Consultant/Advisor. Ideogram courtesy of the University
Case Report Joubert Syndrome Presenting with Motor Delay and Oculomotor Apraxia
 Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2011, Article ID 262641, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/262641 Case Report Joubert Syndrome Presenting with Motor Delay and Oculomotor Apraxia Harjinder Gill, 1 Brinda Muthusamy,
Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2011, Article ID 262641, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/262641 Case Report Joubert Syndrome Presenting with Motor Delay and Oculomotor Apraxia Harjinder Gill, 1 Brinda Muthusamy,
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
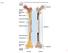 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Spondyloperipheral dysplasia
 JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
Interactions of the endocrine system, bone and oral health
 Interactions of the endocrine system, bone and oral health All bones are not equal! Dense high proportion of cortical bone High proportion of trabecular bone Mandible Functions: mastication, respiration,
Interactions of the endocrine system, bone and oral health All bones are not equal! Dense high proportion of cortical bone High proportion of trabecular bone Mandible Functions: mastication, respiration,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Dr. Najla a Aldaoud. Omar Ayman Khasawneh
 Pathology 1 Congenital & Cystic diseases of the kidney Dr. Najla a Aldaoud Omar Ayman Khasawneh 1 P a g e Slides are included بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Today is our first pathology lectures, Dr Najla' will
Pathology 1 Congenital & Cystic diseases of the kidney Dr. Najla a Aldaoud Omar Ayman Khasawneh 1 P a g e Slides are included بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Today is our first pathology lectures, Dr Najla' will
Ciliary Biology: Understanding the Cellular and Genetic Basis of Human Ciliopathies
 A R T I C L E American Journal of Medical Genetics Part C (Seminars in Medical Genetics) 151C:263 280 (2009) Ciliary Biology: Understanding the Cellular and Genetic Basis of Human Ciliopathies MAGDALENA
A R T I C L E American Journal of Medical Genetics Part C (Seminars in Medical Genetics) 151C:263 280 (2009) Ciliary Biology: Understanding the Cellular and Genetic Basis of Human Ciliopathies MAGDALENA
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93
 Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
a) They are the most common cause of pediatric kidney failure. b) They are always symptomatic. c) They can be asymmetric.
 Practice questions: 1. The paraxial mesoderm gives rise to somites. The structure of the somite a) is a loose mesenchymal sheet that will migrate toward the notochord. b) is an epithelial rosette with
Practice questions: 1. The paraxial mesoderm gives rise to somites. The structure of the somite a) is a loose mesenchymal sheet that will migrate toward the notochord. b) is an epithelial rosette with
CASE REPORT. 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Paediatrics, Vinayaka Missions Medical College, Karaikal
 A CASE OF KARTAGENER SYNDROME Pagadpally Srinivas 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Paediatrics, Vinayaka Missions Medical College, Karaikal CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Pagadpally Srinivas, 72, Vellai Pillaiyar
A CASE OF KARTAGENER SYNDROME Pagadpally Srinivas 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Paediatrics, Vinayaka Missions Medical College, Karaikal CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Pagadpally Srinivas, 72, Vellai Pillaiyar
Evaluation of Patients with Diffuse Bronchiectasis
 Evaluation of Patients with Diffuse Bronchiectasis Dr. Patricia Eshaghian, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Director, UCLA Adult Cystic Fibrosis Affiliate Program UCLA Division of Pulmonary
Evaluation of Patients with Diffuse Bronchiectasis Dr. Patricia Eshaghian, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Director, UCLA Adult Cystic Fibrosis Affiliate Program UCLA Division of Pulmonary
Dysmorphology. Sue White. Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase. Victorian Clinical Genetics Services
 Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
04/10/2013. Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT!
 04/10/2013 Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT! Did you know?? 1. The adult body is made up of: 100 trillion cells, 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. 2. Every square inch of
04/10/2013 Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT! Did you know?? 1. The adult body is made up of: 100 trillion cells, 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. 2. Every square inch of

