Inhibition of embryonic development by microcystin-lr in zebrafish, Danio Rerio
|
|
|
- Hugo Bridges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Toxicon 45 (2005) Inhibition of embryonic development by microcystin-lr in zebrafish, Danio Rerio Pei-Jen Wang a, Ming-Shan Chien b, Fong-June Wu a, Hong-Nong Chou a,c, Shyh-Jye Lee b,c, * a Institute of Fisheries Science, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, ROC b Institute of Zoology, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, ROC c Department of Life Sciences, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, ROC Received 7 September 2004; revised 22 October 2004; accepted 25 October 2004 Available online 10 December 2004 Abstract Microcystin-LR (MC-LR), a cyanobacterial toxin, is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) and protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). PP1 and PP2A are critical regulators in embryonic development. However, the effects of MC-LR in embryonic development have been controversial. MC-LR has been demonstrated to be highly toxic in medaka, but not in zebrafish or rabbit embryos. The causes of difference may be due to membrane impermeability that impaired the delivery of MC-LR into cytoplasm of zebrafish and rabbit embryos. Therefore, we microinjected MC-LR directly into developing zebrafish embryos and investigated the effects of MC-LR on embryonic development. We demonstrated that MC-LR induced the lethality of zebrafish embryos in a dose- and time-dependent manner. MC-LR also induced the loss of blastomere coherence via the interference of b-catenin and cadherins distributions. Furthermore, the MC-LR treated fry revealed various developmental defects. These results suggested that MC-LR might affect the phosphorylation equilibrium of signaling molecules, including b-catenin and cadherins, required early in zebrafish embryonic development. q 2004 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Keywords: Microcystin; PP1; PP2A; Zebrafish; Embryos; b-catenin and cadherin 1. Introduction The toxicity of MCs has been associated with fish killed worldwide (Watanabe et al., 1996). Among the fish species killed by MCs, cyprinids are most affected, and to a less extent to the others (Fischer and Dietrich, 2000). By analyzing the diets of affected species, it appears that the toxicity of MCs depends on the amount of toxin ingested. However, by gavaging a bolus dose of MC-LR containing * Corresponding author. Address: 1 Roosevelt Road, Section 4, Institute of Zoology, National Taiwan University, 209 Fisheries Science Building, Taipei, Taiwan 106, ROC. Tel.: C ; fax: C address: jefflee@ntu.edu.tw (S.-J. Lee). lyophilized cyanobacteria to carp or rainbow trout, it appears that carp is more susceptible to MC-LR compared to rainbow trout (Tencalla et al., 1994; Tencalla and Dietrich, 1997). Therefore, the MC-LR gavaging experiments appeared not to be consistent to serve as a bioassay system in fish. MC-LR is a potent inhibitor of serine/threonine protein phosphatase 1 and 2A (PP1 and PP2A) with an IC 50 of about nm (Honkanen et al., 1990). The inhibition of PP1 and PP2A results in hyperphosphorylation of proteins, which may be responsible for the toxicity of microcystins. During embryonic development, the equilibrium of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation status of signaling molecules is tightly regulated for the control of rapid cleavages and cellular differentiation. Dynamic changes in cytoskeleton play a major role in embryo /$ - see front matter q 2004 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi: /j.toxicon
2 304 P.-J. Wang et al. / Toxicon 45 (2005) reorganization. Microcystins have been demonstrated to impair cytosleleton by hyperphosphorylation of the major intermediate proteins keratin 8 and 18 in a dose- and timedependent manner (Ohta et al., 1992; Toivola et al., 1997). Microcystins have also been reported to perturb the functions of motor protein dynein (Runnegar et al., 1997) and tubulin (Ding et al., 2000). It is therefore reasonable to hypothesize that MC-LR should disrupt early embryonic development by interfering with the cytoskeletal dynamic within the embryo. A couple of attempts have been reported to evaluate the effects of MC-LR on early embryonic development, including rabbit (Frangez et al., 2003) and zebrafish (Oberemm et al., 1997, 1999) studies. However, both studies revealed no significant defects of early embryos treated with MC-LR. These results are clearly against our hypothesis and the well established PP1 and PP2A blocking ability by MC-LR. In both investigations, the membrane-intact embryos were used. It was very likely that the membrane barrier precluded MC- LR from entering cytoplasm. However, Wiegand et al. (1999), have shown that there was a detectable uptake of C-14 labeled MC-LR by early zebrafish embryos and the lack of toxicity may due to the activities of detoxication enzymes like glutathione S-transferase (GST). C-14 labeled MC-LR uptake reached 0.44 ng per egg, which seems to be high enough to exert MC-LR s functions. However, since the C-14 labeled MC-LR uptake was measured using the whole egg (the embryo itself, the chorion, and the perivitelline fluid), one could not exclude the possibility that MC-LR was trapped mainly in the chorion and perivitelline fluid. Therefore, instead of relying on cellular uptake of MC-LR, we took a more direct approach by microinjecting MC-LR into zebrafish embryos to bypass membrane barriers. We found that (1) MC-LR dose- and time-dependently induced embryonic malformation and death. (2) MC-LR caused the loss of blastomere coherence by disrupting the distributions of b-catenin and cadherin. 2. Materials and methods 2.1. Fish Husbandry and embryo collection Zebrafish, Danio rerio, were raised on a 14-h day/10-h night cycle at 26 8C. Eggs were collected at min intervals after spawning, washed and incubated in Ringer s solution (116 mm NaCl, 2.9 mm KCl, 1.8 mm CaCl 2 and 5 mm HEPES) at C until use. All chemicals were from Sigma (St Louis, MO) unless otherwise stated Purification of MC-LR MC-LR was extracted and purified from Microcystin aeruginosa as described in detail by Lee et al. (1998) Microinjection procedures Glass capillaries of 1.14 mm O.D. and 0.5 mm I.D. (World Precision Instrument Inc., Sarasota, FL) were pulled using a horizontal puller (P-97, Sutter Instrument, Navato, CA). Embryos at desired stages as judged according to Kimmel et al. (1995) were immobilized at an injection trough on a 100 mm 2% agar plate. MC-LR was dissolved in injection buffer (68.5 mm NaCl, 1.35 mm KCl, 5 mm Na 2 HPO 4 and 1 mm KH 2 PO 4 and 0.25% (w/v) phenol red) with different concentrations of MC-LR as indicated. An injection pipette was forced into the chorion and the yolk cell to reach the junction between yolk cell and blastodisc where 2.3 nl of solution was ejected by using a nanoliter injector (World Precision Instrument Inc., Sarasota, FL). After injection, embryos were recovered from injection troughs and cultured in Ringer s solution at C until examined Whole-mount immunocytochemistry and confocal microscopy Zebrafish embryos at designated stages were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS (137 mm NaCl, 2.7 mm KCl, 10 mm Na 2 HPO 4 and 2 mm KH 2 PO 4 ) overnight at 4 8C, washed in PBS and manually dechorionated. Twenty embryos were incubated with a polyclonal anti-b-catenin antibody (Sigma C2206, diluted at 1:400) or a polyclonal anti-pan cadherin antibody (Sigma C3678, diluted at 1:100) with continuous rotation at 4 8C overnight. After four washes in PBS containing 0.5% Triton X-100 (PBT), embryos were incubated in a 1:250 or 1:500 dilution of a FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibody (# , Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, West Grove, PA) for anti-b-catenin or anti-pan cadherin antibody-labeled embryos, respectively, at 4 8C overnight. Embryos were transferred to 30% glycerol first and then 50% glycerol for confocal microscopic observations at the Center of Two- Photon Laser Confocal Microscope, National Taiwan University. To reveal the nuclei, embryos were washed in PBT and then incubated in 10 mg/ml Hoechst dye for 30 mins at room temperature before examination. Unbound Hoechst dye was removed by washing in PBT and examined under an epifluorecent microscope Embryo observations and photography Observation of embryonic development was made at designated time under a Leica Mz75 stereomicroscope, a Leica DMIRB fluorescent microscope, or a Leica TCS SP2 confocal microscope equipped with an Ar Kr two photon laser system located. All photographs were taken by a Nikon digital camera and analyzed using Adobe Photoshop 7.0 except for the confocal images, which were photographed and edited utilizing the Leica Confocal Software.
3 P.-J. Wang et al. / Toxicon 45 (2005) Statistical analysis Experimental values are expressed as meansgstandard error of means and analyzed in Excel using Two-Factor ANOVA with Replication. 3. Results To study the toxicity of MC-LR in zebrafish, we microinjected MC-LR into 2 4 cell stage embryos. Within half an hour after injection of microcystin-lr (MC-LR), embryos showed signs of malformation. The most notable change in the MC-LR-injected embryos was the loss of coherence of blastomeres. A normal zebrafish embryo has a tightly adhered blastomeres arranged in tiers as shown in Fig. 1A. In contrast, MC-LR induced the deterioration of embryos by blocking the adherence of blastomeres (Fig. 1C). We were also interested to know if MC-LR affected nuclear division, since cell cycle progression is regulated by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. In the controlinjected embryo all nuclei were clearly visible by Hoechst dye staining except one nucleus was out of focus as shown in Fig. 1B. In contrast, we observed only two nuclei in an 8-cell stage embryo treated with 750 nm MC-LR in one focal plane Fig. 1. MC-LR causes the loss of adherence of blastomeres in zebrafish embryos. After the injection of 900 nm MC-LR, a zebrafish embryo could still divide, but the blastomeres lost compact adherence to each other (C) as compared to the controlinjected embryos (A). Blastomeres of the control-injected 8-cell embryos were nicely arranged into two tiers with nuclei clearly stained by Hoechst dye in each blastomere (B). One nucleus is out of focus in panel B. The nuclear cleavage appears not normal in MC-LR injected embryo at the first glance, since only 2 nuclei are visible on the focal plan shown in panel D. However, it was due to the irregular arrangement of blastomeres that we were able to locate all 8 nuclei in the 8-cell stage embryo by scanning through different focal planes. Fig. 2. MC-LR causes gradual death of zebrafish embryos in a dosedependent manner. An hour post injection with MC-LR at indicated amounts in nm gradual death occurred and the embryos survival rate continued to decrease until 24 h post injection. Fertilized eggs were injected at the 2 4 cell stage and cultured in Ringer s solution at C. Embryos were examined at the designated time and the white/opaque embryos were scored as dead. These results were cumulated data of five independent experiments. shown in Fig. 1D. However, by examining through different focal planes, we were able to find all 8 nuclei in the embryo treated with MC-LR (data not shown). Therefore, MC-LR appeared not interfering with the karyokinesis. Although, MC- LR-treated embryos could still develop, but they were gradually dying and embryos turned opaque and disintegrating. To analyze the dose-dependent lethality of MC-LR, we injected embryos with different amounts of MC-LR. Injecting embryos after the 1-cell stage allowed us to remove easily unfertilized eggs from our statistics. We then examined survival rates of embryos at designated time points (Fig. 2). As shown in Fig. 2, 93.2G4.8% (NZ5) of 311 control-injected embryos survived at 48 h post injection. As MC-LR was injected, the survival rates of embryos decreased with the increase in time of culture post fertilization and the elevation of intracellular MC-CR concentration from 300 to 900 nm. At the end of examination (48 h post fertilization), embryonic survival rate decreased significantly to 82.5G3.9% of 319 embryos, 51.5G12.1% of 353 embryos and 18.5G10.3% of 343 embryos injected with 300, 750 and 900 nm MC-LR, respectively, in 5 independent trials. Using the Two-Factor Analysis of Variance, the effects of intracellular MC-LR concentration and the time of culture post fertilization on embryonic survival were analyzed. Both factors and their interaction significantly (p%4.65e-23) affected the survival rate of MC-LR-injected embryos. Thus, MC-LR induced embryonic death in a dose- and time-dependent manner. For those MC-LR-treated fry survived at 48 h post injection, various defects were shown in Fig. 3. The most frequent observed defects appeared in tails. Tails were curving (Fig. 3A), bent or twisting (Fig. 3B). In some cases, cyclopia occurred while a residual eye was still visible (arrow) as shown in Fig. 3C. Fig. 3D shows a fry with edema in pericardial sac (PS) and hatching gland (HG). Some of those fry with edema could survive up to 6 7 days post fertilization, but the edema in
4 306 P.-J. Wang et al. / Toxicon 45 (2005) Fig. 3. MC-LR induces different developmental defects in zebrafish fry. MC-LR-treated embryos were cultured in Ringer s solution for 48 h and photographed except (E), which was taken at 6 days post fertilization. Various defects were detected in MC-LR-treated embryos, including trunk and tail curving (A), bent or twisting tails (B), cyclopia whose residual eye was indicated by an arrow (C), edema in pericardial sac (PS) and hatching gland (HG) (D), curving, rounding, deteriorated and eventually dying (F). Edema in pericardial sac and hatching gland could be worse where the curving of the trunk occurred if they survived in this case 6 days post fertilization (E). pericardial sac and hatching gland was worse that a curvature of trunk occurred (Fig. 3E). In some severe cases, the fry was curving, rounding, deteriorating and eventually dying (Fig. 3F). Due to the broad spectrum of defect patterns, we assume MC-LR perturbed the phosphorylation status of some key enzymes, which might interfere with downstream molecules required for proper embryonic development and subsequent organogenesis. Blocking of blastomeres coherence by MC-LR (Fig. 1) is an intriguing observation. Since E-cadherin has been shown to mediate the blastomere adherence via b-catenin (Gotz et al., 2000), we investigated whether MC-LR inhibits blastomeres coherence by disturbing b-catenin/cadherin signaling by examining the distributions of b-catenin and cadherins in embryos treated with or without MC-LR. In Fig. 4, weshow confocal photographs of a single section of 3 mm(fig. 4A, B, E, F) or 3D stacking graphs of 20 sections (Fig. 4C, D, G, H) for embryos treated in the presence (Fig. 4B, D, F, H) or absence (Fig. 4A, C, E, G) of 900 nm MC-LR. Both b-catenin (Fig. 4A, C) and cadherins (Fig. 4E, G) were clearly localized at the cleavage furrows between adjacent blastomeres in the absence of MC-LR. In contrast, b-catenin (Fig. 4B, D) and cadherins (Fig. 4F, H) were present only in the barely touched boundary between blastomeres. These results suggested that MC-LR perturbs the blastomere coherence by interfering with the localization of b-catenin and cadherin. 4. Discussion The sensitivity to MC-LR exposure is variable in developmental stages and among fish species. The main cause of variability is the MC-LR uptake that is presumably mediated by bile acid transporters (Eriksson et al., 1990; Runnegar et al., 1991, 1995). To assay the toxicity of MC-LR during early embryonic development in zebrafish, we microinjected MC-LR directly into embryos and we observed that (1) MC-LR dose- and time-dependently increased the lethality of embryos. (2) MC-LR caused various embryo abnormalities, which suggested that MC-LR affected the phosphorylation status of upstream factors mastering the embryonic development and subsequent organogenesis. (3) MC-LR induced the loss of blastomere coherence by interfering the distributions of b-catenin and cadherins. Zebrafish embryos and larvae were found to be insensitive to the toxicity of MC-LR or crude extracts of cyanobacteria. Although no acute effects were observed during embryonic development, a reduced survival rate and a retarded growth were reported in MC-LR and MC-RR preexposed larvae at 21 days of age (Oberemm et al., 1997, 1999). The lack of MC-LR toxicity in embryos is questionable, since the activities of MC-LR targets, PP1 and PP2A, have been shown to be critical for regulating cell cycle progression during embryonic development (Gotz et al., 2000). The most plausible explanation is the poor membrane permeability of microcystins in the absence of bile acid transporters. Jacquet et al. (2004) have nicely demonstrated the lethality of MC-LR on development of medaka fish embryos by microinjection. Using the similar approach and MC-LR dosages, we were able to demonstrate that MC-LR caused the death of embryos in a dose- and time-dependent manner (Fig. 2). We also observed a high rate in malformation in MC-LR-treated zebrafish embryos
5 P.-J. Wang et al. / Toxicon 45 (2005) Fig. 4. MC-LR disturbs the distributions of b-catenin and cadherin. The MC-LR treated embryos were cultured until 16-cell stage, then fixed and stained with antibodies against b-catenin (A D) or cadherin (E H) and anti-rabbit FITC conjugated antibodies. Photographs of a single section of 3 mm thick (A,B,E,F) and a 20-section stacking graph (C,D,G,H) are shown. Both b-catenin or cadherin were clearly located between blastomeres in the controlinjected embryos (A,C,E,G), but the presence of both proteins were severely aborted in the presence of MC-LR (B,D,F,H). The scale bar represents 200 mm. that is similar to reports in loach (Liu et al., 2002) and medaka (Jacquet et al., 2004). These results suggest that microinjection is a reliable bioassay system for embryonic toxicity of MC-LR. Furthermore, the effective MC-LR dosages ( nm intracellular concentration) are comparable to the effective dosages utilized in a MC-LR microinjection study in medaka (Jacquet et al., 2004), however those dosages are much higher than the reported IC 50 for PP1 and PP2A of about nm (Honkanen et al., 1990). The possible explanation is the neutralization by detoxication enzymes like GST in embryos (Wiegand et al., 1999; Pietsch et al., 2001). The interference of blastomeres coherence by MC-LR in early embryos is very interesting, since it implies the necessity of phosphorylation equilibrium for maintaining cell cell adhesion. In cell and cell adhesion, cadherins play a central role in the assembly of adherens junctions (Yap et al., 1997). Knocking down E-cadherin by morpholino results in irregular orientation of cleavage planes between blastomeres, unequal cell sizes, reduced adhesion between blastomeres, and less compact embryos (Babb and Marrs, 2004), which is very similar to the phenotypes of MC-LRinjected embryos (Fig. 1). These results suggest that MC-LR may inhibit the cadherin-dependent cellular adhesions. Disturbance of cadherins distribution in cleavage furrows by MC-LR (Fig. 4) further strengthens the involvement of cadherins in MC-LR-induced toxicity. The known targets of MC-LR are PP1 and PP2A. It would be interesting to know which phosphatase or both phosphatases is mediating the MC-LR-induced loss of blastomere adherence. The functions of classic cadherins are relying on its close association with catenins (Nagafuchi and Takeichi, 1988; Ozawa et al., 1989). Cadherin is also associated with b-catenin at the cleavage furrows in zebrafish embryos (Jesuthasan, 1998). Hyperphosphorylation of b-catenin on the serine-threonine residues induced by calyculin A and okadaic acid, known PP1 inhibitors, induced the loss of cell cell contacts in human epidermal cells (Serres et al., 1997). In this regards, MC-LR might inhibit PP1, which resulted in hyperphosphorylation of b-catenin, and the absence of both b-catenin and cadherin at the cleavage furrows (Fig. 4). Furthermore, PP2A has also been demonstrated to be critical in the regulation of b-catenin and E-cadherin via PP2A subunit Ca during embryonic development in mice (Gotz et al., 2000; Nunbhakdi-Craig et al., 2002). Therefore, both PP1 and PP2A may both involve in the MC-LR-mediated embryo malformation. Lastly, ezrin, a linker protein between the plasma membrane and the actin cytoskeleton, can regulate E-cadherin adherens junction assembly through rac1 activation (Pujuguet et al., 2003). More interestingly, phosphorylation of ezrin on threonine T567 was found to be critical for the compaction in early mouse embryos. It requires further investigation to see if the phosphorylation of zebrafish ezrin and subsequent activation of E-cadherin adherens junction assembly could be regulated by MC-LR mediated responses. In conclusion, we had demonstrated that MC-LR induced the malformation and lethality of zebrafish embryos and larvae by disrupting the blastomere coherence. The loss of blastomere coherence by MC-LR is mediated presumably via the interference of b-catenin and cadherin adherens junction assembly. Our results clarify the controversial effects of MC-LR in zebrafish development. More importantly, we demonstrate that toxicity responses of embryos could be a useful bioassay system for detecting MC-LR. Acknowledgements We thank Yih-Min Chen for help in preparation of MC-LR. Fong-June Wu was a recipient of Undergraduate
6 308 P.-J. Wang et al. / Toxicon 45 (2005) Research Grants (NSC C B) supported by National Science Council of Taiwan, R.O.C. References Babb, S.G., Marrs, J.A., E-cadherin regulates cell movements and tissue formation in early zebrafish embryos. Developmental Dynamics 230, Ding, W.X., Shen, H.M., Ong, C.N., Microcystic cyanobacteria extract induces cytoskeletal disruption and intracellular glutathione alteration in hepatocytes. Environmental Health Perspectives 108, Eriksson, J.E., Gronberg, L., Nygard, S., Slotte, J.P., Meriluoto, J.A., Hepatocellular uptake of 3H-dihydromicrocystin-LR, a cyclic peptide toxin. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta 1025, Fischer, W.J., Dietrich, D.R., Pathological and biochemical characterization of microcystin-induced hepatopancreas and kidney damage in carp (Cyprinus carpio). Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 164, Frangez, R., Zuzek, M.C., Mrkun, J., Suput, D., Sedmak, B., Kosec, M., Microcystin-LR affects cytoskeleton and morphology of rabbit primary whole embryo cultured cells in vitro. Toxicon 41, Gotz, J., Probst, A., Mistl, C., Nitsch, R.M., Ehler, E., Distinct role of protein phosphatase 2A subunit C alpha in the regulation of E-cadherin and beta-catenin during development. Mechanisms of Development 93, Honkanen, R.E., Zwiller, J., Moore, R.E., Daily, S.L., Khatra, B.S., Dukelow, M., Boynton, A.L., Characterization of Microcystin-Lr, A Potent Inhibitor of Type-1 and Type-2A Protein Phosphatases. Journal of Biological Chemistry 265, Jacquet, C., Thermes, V., de Luze, A., Puiseux-Dao, S., Bernard, C., Joly, J.S., Bourrat, F., Edery, M., Effects of microcystin- LR on development of medaka fish embryos (Oryzias latipes). Toxicon 43, Jesuthasan, S., Furrow-associated microtubule arrays are required for the cohesion of zebrafish blastomeres following cytokinesis. Journal of Cell Biology 111, Kimmel, C.B., Ballard, W.W., Kimmel, S.R., Ullmann, B., Schilling, T.F., Stages of embryonic-development of the zebrafish. Developmental Dynamics 203, Lee, T.H., Chen, Y.M., Chou, H.N., First report of microcystins in Taiwan. Toxicon 36, Liu, Y.D., Song, L.R., Li, X.Y., Liu, T.M., The toxic effects of microcystin-lr on embryo-larval and juvenile development of loach, Misguruns mizolepis Gunthe. Toxicon 40, Nagafuchi, A., Takeichi, M., Cell binding function of E- cadherin is regulated by the cytoplasmic domain. EMBO Journal 7, Nunbhakdi-Craig, V., Machleidt, T., Ogris, E., Bellotto, D., White, C.L., Sontag, E., Protein phosphatase 2A associates with and regulates atypical PKC and the epithelial tight junction complex. Journal of Cell Biology 158, Oberemm, A., Fastner, J., Steinberg, C.E.W., Effects of microcystin-lr and cyanobacterial crude extracts on embryolarval development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Water Research 31, Oberemm, A., Becker, J., Codd, G.A., Steinberg, C., Effects of cyanobacterial toxins and aqueous crude extracts of cyanobacteria on the development of fish and amphibians. Environmental Toxicology 14, Ohta, T., Nishiwaki, R., Komori, A., Suganuma, M., Fujiki, H., Hyperphosphorylation of Cytokeratins 8 and 18 by Microcystin-LR, a new liver-tumor promoter, in primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Carcinogenesis 13, Ozawa, M., Baribault, H., Kemler, R., The cytoplasmic domain of the cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin associates with three independent proteins structurally related in different species. EMBO Journal 8, Pietsch, C., Wiegand, C., Ame, M.V., Nicklisch, A., Wunderlin, D., Pflugmacher, S., The effects of a cyanobacterial crude extract on different aquatic organisms: evidence for cyanobacterial toxin modulating factors. Environmental Toxicology 16, Pujuguet, P., del Maestro, L., Gautreau, A., Louvard, D., Arpin, M., Ezrin regulates E-cadherin-dependent adherens junction assembly through Rac1 activation. Molecular Biology of the Cell 14, Runnegar, M.T., Gerdes, R.G., Falconer, I.R., The uptake of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin by isolated rat hepatocytes. Toxicon 29, Runnegar, M., Berndt, N., Kaplowitz, N., Microcystin uptake and inhibition of protein phosphatases: effects of chemoprotectants and self-inhibition in relation to known hepatic transporters. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 134, Runnegar, M., Wei, X., Zhang, L., HammAlvarez, S.F., Inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A leads to enhanced phosphorylation of kinesin and cytoplasmic dynein and their associated proteins and to decreased microtubule-based vesicle motility in intact hepatocytes. Hepatology 26, 537. Serres, M., Grangeasse, C., Haftek, M., Durocher, Y., Duclos, B., Schmitt, D., Hyperphosphorylation of beta-catenin on serine-threonine residues and loss of cell cell contacts induced by calyculin A and okadaic acid in human epidermal cells. Experimental Cell Research 231, Tencalla, F., Dietrich, D., Biochemical characterization of microcystin toxicity in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Toxicon 35, Tencalla, F.G., Dietrich, D.R., Schlatter, C., Toxicity of microcystis-aeruginosa peptide toxin to yearling rainbow-trout (Oncorhynchus-Mykiss). Aquatic Toxicology 30, Toivola, D.M., Goldman, R.D., Garrod, D.R., Eriksson, J.E., Protein phosphatases maintain the organization and structural interactions of hepatic keratin intermediate filaments. Journal of Cell Science 110, Watanabe, M.F., Harada, K.I., Carmicael, W.W., Fujiki, H., Toxic Microcystis. CRC press, Boca Raton, FL p Wiegand, C., Pflugmacher, S., Oberemm, A., Meems, N., Beattie, K.A., Steinberg, C.E.W., Codd, G.A., Uptake and effects of microcystin-lr on detoxication enzymes of early life stages of the zebra fish (Danio rerio). Environmental Toxicology 14, Yap, A.S., Brieher, W.M., Gumbiner, B.M., Molecular and functional analysis of cadherin-based adherens junctions. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology 13,
3. Studies of Cancer in Experimental Animals
 364 IARC MONOGRAPHS VOLUME 94 3. Studies of Cancer in Experimental Animals 3.1 Pure microcystin-lr (see Table 3.1) 3.1.1 Mouse A group of 13 male ICR mice, 5 weeks of age, received 100 intraperitoneal
364 IARC MONOGRAPHS VOLUME 94 3. Studies of Cancer in Experimental Animals 3.1 Pure microcystin-lr (see Table 3.1) 3.1.1 Mouse A group of 13 male ICR mice, 5 weeks of age, received 100 intraperitoneal
Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb. by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral
 Supplementary Information Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral obstruction Shao-Yu Yang 1,2, Shuei-Liong
Supplementary Information Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral obstruction Shao-Yu Yang 1,2, Shuei-Liong
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Edens and Levy, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201406004/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Nuclear shrinking does not depend on the cytoskeleton
Supplemental material Edens and Levy, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201406004/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Nuclear shrinking does not depend on the cytoskeleton
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit
 Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by
 The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Fluorescence Microscopy
 Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
Francesca G. Tencalla*, Daniel R. Dietrich, Christian Schlatter
 ELSEVIER Aquatic Toxicology 30 (1994) 215-224 AouAnc TIIXICBLOGY Toxicity of Microcystis aeruginosa peptide toxin to yearling rainbow trout ( Oncorhynchus mykiss) Francesca G. Tencalla*, Daniel R. Dietrich,
ELSEVIER Aquatic Toxicology 30 (1994) 215-224 AouAnc TIIXICBLOGY Toxicity of Microcystis aeruginosa peptide toxin to yearling rainbow trout ( Oncorhynchus mykiss) Francesca G. Tencalla*, Daniel R. Dietrich,
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set
 Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
cell movement and neuronal migration
 cell movement and neuronal migration Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 Cell migration Cell migration in 3 steps; protrusion,
cell movement and neuronal migration Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 Cell migration Cell migration in 3 steps; protrusion,
Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum...1. Trademarks: HiLyte Fluor (AnaSpec, Inc.)
 Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
Aquatic Toxicology 75 (2005)
 Aquatic Toxicology 75 (2005) 178 190 Uptake, tissue distribution and accumulation of microcystin-rr in Corydoras paleatus, Jenynsia multidentata and Odontesthes bonariensis A field and laboratory study
Aquatic Toxicology 75 (2005) 178 190 Uptake, tissue distribution and accumulation of microcystin-rr in Corydoras paleatus, Jenynsia multidentata and Odontesthes bonariensis A field and laboratory study
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (S-TSH) Thyroid Stimulating
 ab108659 Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (S-TSH) Human ELISA Kit Instructions for Use For the quantitative measurement of Human Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (S-TSH) concentrations in serum. This product is
ab108659 Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (S-TSH) Human ELISA Kit Instructions for Use For the quantitative measurement of Human Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (S-TSH) concentrations in serum. This product is
2-Deoxyglucose Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 2-Deoxyglucose Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA3753 100 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
2-Deoxyglucose Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA3753 100 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
The Increase in Embryonic Size of Zebrafish ( Danio rerio ) after Embryonic Vitamin D Exposure. Cindy Zheng
 The Increase in Embryonic Size of Zebrafish ( Danio rerio ) after Embryonic Vitamin D Exposure Cindy Zheng WInSTEP Research Paper 2018 AP Biology, Kohler High School, Kohler, Wisconsin [1] The Increase
The Increase in Embryonic Size of Zebrafish ( Danio rerio ) after Embryonic Vitamin D Exposure Cindy Zheng WInSTEP Research Paper 2018 AP Biology, Kohler High School, Kohler, Wisconsin [1] The Increase
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS
 Lesson 6: CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS Name: Group: MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS Permanent slide: onion rootlet stained with acetorcein The particular mitotic phases are visible in the onion rootlet cells. Chromosomes
Lesson 6: CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS Name: Group: MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS Permanent slide: onion rootlet stained with acetorcein The particular mitotic phases are visible in the onion rootlet cells. Chromosomes
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
See external label 2 C-8 C Σ=96 tests Cat # 3122Z MICROWELL ELISA THYROID STIMULATING HORMONE (TSH) ENZYME IMMUNOASSAY TEST KIT TSH.
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Imaging of Chromosomes at Nanometer-Scale Resolution, Using Soft X-Ray Microscope
 Imaging of Chromosomes at Nanometer-Scale Resolution, Using Soft X-Ray Microscope K. Takemoto, A. Yamamoto 1, I. Komura 2, K. Nakanishi 3, H. Namba 2 and H. Kihara Abstract In order to clarify the process
Imaging of Chromosomes at Nanometer-Scale Resolution, Using Soft X-Ray Microscope K. Takemoto, A. Yamamoto 1, I. Komura 2, K. Nakanishi 3, H. Namba 2 and H. Kihara Abstract In order to clarify the process
The Effects 1. The Effects of Nicotine and Ethanol on the Embryo Development of Zebrafish Maddy Brauer Brookfield Central High School Honors Biology
 The Effects 1 The Effects of Nicotine and Ethanol on the Embryo Development of Zebrafish Maddy Brauer Brookfield Central High School Honors Biology The Effects 2 Abstract The aim of this experiment was
The Effects 1 The Effects of Nicotine and Ethanol on the Embryo Development of Zebrafish Maddy Brauer Brookfield Central High School Honors Biology The Effects 2 Abstract The aim of this experiment was
Cytosolic Carboxypeptidase 5 and Cilia Development in Zebrafish
 Andrews University Digital Commons @ Andrews University Honors Theses Undergraduate Research 2014 Cytosolic Carboxypeptidase 5 and Cilia Development in Zebrafish Philip E. Giddings IV This research is
Andrews University Digital Commons @ Andrews University Honors Theses Undergraduate Research 2014 Cytosolic Carboxypeptidase 5 and Cilia Development in Zebrafish Philip E. Giddings IV This research is
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176
 human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
Roadmap Practical 1. Oocytes collection
 Roadmap Practical Oocytes collection Roadmap Practical Zebrafish (20 min) 2 groups of 4 trainees. Demonstration of sperm collection and then, retrieval of sperm by the trainees. 2. Demonstration of oocytes
Roadmap Practical Oocytes collection Roadmap Practical Zebrafish (20 min) 2 groups of 4 trainees. Demonstration of sperm collection and then, retrieval of sperm by the trainees. 2. Demonstration of oocytes
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Sperm Incorporation Independent of Fertilization Cone Formation in the Danio Egg
 Develop. Growth & Differ., 30 (6), 619-628 (1988) Sperm Incorporation Independent of Fertilization Cone Formation in the Danio Egg (Brachy danio / fertiliza tion / fertilizat ion cone / fish Ringer s solution)
Develop. Growth & Differ., 30 (6), 619-628 (1988) Sperm Incorporation Independent of Fertilization Cone Formation in the Danio Egg (Brachy danio / fertiliza tion / fertilizat ion cone / fish Ringer s solution)
klp-18 (RNAi) Control. supplementary information. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach
![klp-18 (RNAi) Control. supplementary information. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach klp-18 (RNAi) Control. supplementary information. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach](/thumbs/91/104639484.jpg) DOI: 10.1038/ncb1891 A. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach embryos let hatch overnight transfer to RNAi plates; incubate 5 days at 15 C RNAi food L1 worms adult worms
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1891 A. starting strain: AV335 [emb-27(g48); GFP::histone; GFP::tubulin] bleach embryos let hatch overnight transfer to RNAi plates; incubate 5 days at 15 C RNAi food L1 worms adult worms
Supporting Information For
 Supporting Information For MicroRNA-Catalyzed Cancer Therapeutics Based on DNA-Programmed Nanoparticle Complex Xucheng Luo, 1 Zhi Li, 1 Ganglin Wang, 1 Xuewen He, 2,3 Xiaoqin Shen, 1 Quanhong Sun, 1 Li
Supporting Information For MicroRNA-Catalyzed Cancer Therapeutics Based on DNA-Programmed Nanoparticle Complex Xucheng Luo, 1 Zhi Li, 1 Ganglin Wang, 1 Xuewen He, 2,3 Xiaoqin Shen, 1 Quanhong Sun, 1 Li
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
H5N1 ( Avian Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA Pair Set
 H5N1 ( Avian Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK002 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
H5N1 ( Avian Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK002 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Microinsemination (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) Microinsemination schedule. 1. Preparation of mediums
 Microinsemination (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) Masumi Hirabayashi Section of Mammalian Transgenesis, Center for Genetic Analysis of Behavior, National Institute for Physiological Sciences, National
Microinsemination (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) Masumi Hirabayashi Section of Mammalian Transgenesis, Center for Genetic Analysis of Behavior, National Institute for Physiological Sciences, National
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about cytoskeletal filaments is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cytoskeleton
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about cytoskeletal filaments is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cytoskeleton
-RR MC-LR MC-RR MC-YR, China Environmental Science , )
 27,27(3)382~386 China Environmental Science -RR 1,2, 1,2, 1, 1 (1., 3722., 19).1,1.,1.µg/mL-RR(MC-RR)BY-2,,(ACP).,2d,.MC-RR,2d5.57%;MC-RR.d,;7d.3,,7.98%76.7%8.%.3ACP. -RRBY-2 X53.23 A 16923(27)33825 Effect
27,27(3)382~386 China Environmental Science -RR 1,2, 1,2, 1, 1 (1., 3722., 19).1,1.,1.µg/mL-RR(MC-RR)BY-2,,(ACP).,2d,.MC-RR,2d5.57%;MC-RR.d,;7d.3,,7.98%76.7%8.%.3ACP. -RRBY-2 X53.23 A 16923(27)33825 Effect
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes. Reading Assignments. Selective and Semi-permeable Barriers
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Effects of weathered oil and dispersants on hatchling morphology, apical and molecular endpoints of Menidia beryllina embryo
 Effects of weathered oil and dispersants on hatchling morphology, apical and molecular endpoints of Menidia beryllina embryo Adeyemo, OK, Kroll, KJ, Garcia-Reyero, N, Denslow, ND OUTLINE Introduction Experimental
Effects of weathered oil and dispersants on hatchling morphology, apical and molecular endpoints of Menidia beryllina embryo Adeyemo, OK, Kroll, KJ, Garcia-Reyero, N, Denslow, ND OUTLINE Introduction Experimental
Plasma biochemical responses of the omnivorous crucian carp (Carassius auratus) to crude cyanobacterial extracts
 Fish Physiol Biochem (28 34:323 329 DOI 1.17/s1695-7-9191- Plasma biochemical responses of the omnivorous crucian carp (Carassius auratus to crude cyanobacterial extracts Xuezhen Zhang Æ Ping Xie Æ Weimin
Fish Physiol Biochem (28 34:323 329 DOI 1.17/s1695-7-9191- Plasma biochemical responses of the omnivorous crucian carp (Carassius auratus to crude cyanobacterial extracts Xuezhen Zhang Æ Ping Xie Æ Weimin
Supplementary Figures
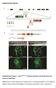 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Acid-Resistant Mesoporous Metal Organic Framework Toward Oral Insulin Delivery: Protein Encapsulation, Protection & Release Yijing Chen, Peng Li, Justin A. Modica, Riki J.
Supplementary Information for Acid-Resistant Mesoporous Metal Organic Framework Toward Oral Insulin Delivery: Protein Encapsulation, Protection & Release Yijing Chen, Peng Li, Justin A. Modica, Riki J.
VERGE 3 Lundeberg 1. Dependence of fertilization in sea urchins, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, on microfilament
 VERGE 3 Lundeberg 1 Dependence of fertilization in sea urchins, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, on microfilament formation and internal calcium concentration Megan Lundeberg Amy Ruggerio and Amy Isaacson
VERGE 3 Lundeberg 1 Dependence of fertilization in sea urchins, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, on microfilament formation and internal calcium concentration Megan Lundeberg Amy Ruggerio and Amy Isaacson
Furrow-associated microtubule arrays are required for the cohesion of zebrafish blastomeres following cytokinesis
 Journal of Cell Science 111, 3695-3703 (1998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1998 JCS3864 3695 Furrow-associated microtubule arrays are required for the cohesion of zebrafish
Journal of Cell Science 111, 3695-3703 (1998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1998 JCS3864 3695 Furrow-associated microtubule arrays are required for the cohesion of zebrafish
Mitosis vs. microtubule
 Mitosis vs. microtubule Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) Duplicated centrosomes align and begin separating in prophase Relation of centrosome duplication to the cell cycle. Parent centrioles
Mitosis vs. microtubule Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) Duplicated centrosomes align and begin separating in prophase Relation of centrosome duplication to the cell cycle. Parent centrioles
SUPPLEMENT. Materials and methods
 SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis: polar body and embryo biopsy
 Human Reproduction, Vol. 15, (Suppl. 4), pp. 69-75, 2000 Preimplantation genetic diagnosis: polar body and embryo biopsy Luca Gianaroli SISMER, Via Mazzini 12, 40138 Bologna, Italy Scientific Director
Human Reproduction, Vol. 15, (Suppl. 4), pp. 69-75, 2000 Preimplantation genetic diagnosis: polar body and embryo biopsy Luca Gianaroli SISMER, Via Mazzini 12, 40138 Bologna, Italy Scientific Director
High resolution structural evidence suggests the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum forms microdomains with Acidic Stores (lyososomes) in the heart.
 High resolution structural evidence suggests the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum forms microdomains with Acidic Stores (lyososomes) in the heart. Daniel Aston, Rebecca A. Capel, Kerrie L. Ford, Helen C. Christian,
High resolution structural evidence suggests the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum forms microdomains with Acidic Stores (lyososomes) in the heart. Daniel Aston, Rebecca A. Capel, Kerrie L. Ford, Helen C. Christian,
Pathological and Biochemical Characterization of Microcystin-Induced Hepatopancreas and Kidney Damage in Carp (Cyprinus carpio)
 Pathological and Biochemical Characterization of Microcystin-Induced Hepatopancreas and Kidney Damage in Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Pathological and Biochemical Characterization of Microcystin- Induced Hepatopancreas
Pathological and Biochemical Characterization of Microcystin-Induced Hepatopancreas and Kidney Damage in Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Pathological and Biochemical Characterization of Microcystin- Induced Hepatopancreas
PhosFree TM Phosphate Assay Biochem Kit
 PhosFree TM Phosphate Assay Biochem Kit (Cat. # BK050) ORDERING INFORMATION To order by phone: (303) - 322-2254 To order by Fax: (303) - 322-2257 To order by e-mail: cservice@cytoskeleton.com Technical
PhosFree TM Phosphate Assay Biochem Kit (Cat. # BK050) ORDERING INFORMATION To order by phone: (303) - 322-2254 To order by Fax: (303) - 322-2257 To order by e-mail: cservice@cytoskeleton.com Technical
A ph-dependent Charge Reversal Peptide for Cancer Targeting
 Supporting Information A ph-dependent Charge Reversal Peptide for Cancer Targeting Naoko Wakabayashi 1, Yoshiaki Yano 1, Kenichi Kawano 1, and Katsumi Matsuzaki 1 1 Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
Supporting Information A ph-dependent Charge Reversal Peptide for Cancer Targeting Naoko Wakabayashi 1, Yoshiaki Yano 1, Kenichi Kawano 1, and Katsumi Matsuzaki 1 1 Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
Supplementary materials
 Supplementary materials Chemical library from ChemBridge 50,240 structurally diverse small molecule compounds dissolved in DMSO Hits Controls: No virus added μ Primary screening at 20 g/ml of compounds
Supplementary materials Chemical library from ChemBridge 50,240 structurally diverse small molecule compounds dissolved in DMSO Hits Controls: No virus added μ Primary screening at 20 g/ml of compounds
Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE
 Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
8/7/18. UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function. I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory
 8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
TSH (Human) ELISA Kit
 TSH (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0197 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
TSH (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0197 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254)
 Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations Department: BIOLOGY. Title of Exam: Cell Biology
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Cell Biology Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total marks available
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Cell Biology Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total marks available
Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets. A.N.Balamurugan
 Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets A.N.Balamurugan Human Islets Functional Mass Preservation 18-25 min 10 min 8-12 min 10-15 min 45-60 min pancreas in chamber 37º Sub-Optimal
Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets A.N.Balamurugan Human Islets Functional Mass Preservation 18-25 min 10 min 8-12 min 10-15 min 45-60 min pancreas in chamber 37º Sub-Optimal
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules. LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07. Processes occurring during cell cycle
 Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide
 The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
Distributions of Mitochondria and the Cytoskeleton in Hamster Embryos Developed In Vivo and In Vitro
 J. Mamm. Ova Res. Vol. 23, 128 134, 2006 128 Original Distributions of Mitochondria and the Cytoskeleton in Hamster Embryos Developed In Vivo and In Vitro Hiroyuki Suzuki 1 *, Manabu Satoh 1 ** and Katsuya
J. Mamm. Ova Res. Vol. 23, 128 134, 2006 128 Original Distributions of Mitochondria and the Cytoskeleton in Hamster Embryos Developed In Vivo and In Vitro Hiroyuki Suzuki 1 *, Manabu Satoh 1 ** and Katsuya
2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit
 2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as
2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as
OxisResearch A Division of OXIS Health Products, Inc.
 OxisResearch A Division of OXIS Health Products, Inc. BIOXYTECH pl GPx Enzyme Immunoassay Assay for Human Plasma Glutathione Peroxidase For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog
OxisResearch A Division of OXIS Health Products, Inc. BIOXYTECH pl GPx Enzyme Immunoassay Assay for Human Plasma Glutathione Peroxidase For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog
MBios 401/501: Lecture 12.1 Signaling IV. Slide 1
 MBios 401/501: Lecture 12.1 Signaling IV Slide 1 Pathways that require regulated proteolysis 1. Notch and Delta 2. Wnt/ b-catenin 3. Hedgehog 4. NFk-B Our last topic on cell signaling are pathways that
MBios 401/501: Lecture 12.1 Signaling IV Slide 1 Pathways that require regulated proteolysis 1. Notch and Delta 2. Wnt/ b-catenin 3. Hedgehog 4. NFk-B Our last topic on cell signaling are pathways that
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle. 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Ananya Baksi CY11D042
 Insulin-Directed Synthesis of Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters: Preservation of Insulin Bioactivity and Versatility in Cell Imaging Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7056 7060 Chien-Liang Liu, Hung-Tsung Wu,
Insulin-Directed Synthesis of Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters: Preservation of Insulin Bioactivity and Versatility in Cell Imaging Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7056 7060 Chien-Liang Liu, Hung-Tsung Wu,
PK15 48 (1) :58 63, (intermediate filament, IF) D ( Traub et al., 1994) IF P K15 D. ( Fuchs et al., 1994), , ( Fuchs et al., 1992) (apoptosis)
 48 (1) :58 63, 2002 A cta Zoologica S inica 3 PK15 (, 100871) D P K15 ( Porcrne Kidney215) DNA, DNA ladder ;,,,, P K15 D (intermediate filament, IF) D ( Traub et al., 1994) IF P K15 ( Porcine Kidney215),,
48 (1) :58 63, 2002 A cta Zoologica S inica 3 PK15 (, 100871) D P K15 ( Porcrne Kidney215) DNA, DNA ladder ;,,,, P K15 D (intermediate filament, IF) D ( Traub et al., 1994) IF P K15 ( Porcine Kidney215),,
(Please activate your clickers)
 Organelles in prokaryotes and eukaryotes! Plasma membrane! Cell wall (in prokaryotes, plants, fungi, some protists)! Ribosomes! Nucleoid/nucleus! Mitochondria! Plastids (Please activate your clickers)
Organelles in prokaryotes and eukaryotes! Plasma membrane! Cell wall (in prokaryotes, plants, fungi, some protists)! Ribosomes! Nucleoid/nucleus! Mitochondria! Plastids (Please activate your clickers)
3.1 Activation of human peripheral blood T lymphocytes induces reversible association of cofilin with the actin cytoskeleton
 3. RESULTS 3.1 Activation of human peripheral blood T lymphocytes induces reversible association of cofilin with the actin cytoskeleton In unstimulated resting human peripheral blood T lymphocytes (PBTs)
3. RESULTS 3.1 Activation of human peripheral blood T lymphocytes induces reversible association of cofilin with the actin cytoskeleton In unstimulated resting human peripheral blood T lymphocytes (PBTs)
Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery. against melanoma
 Supplementary Information for Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery against melanoma Rie Wakabayashi,,a,b Masato Sakuragi,,a Shuto Kozaka, a Yoshiro Tahara, a Noriho
Supplementary Information for Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery against melanoma Rie Wakabayashi,,a,b Masato Sakuragi,,a Shuto Kozaka, a Yoshiro Tahara, a Noriho
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
Rabbit Polyclonal antibody to NFkB p65 (v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A (avian))
 Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
Supporting Information. Light-enhanced hypoxia-response of conjugated polymer nanocarrier. for successive synergistic photodynamic and chemo-therapy
 Supporting Information Light-enhanced hypoxia-response of conjugated polymer nanocarrier for successive synergistic photodynamic and chemo-therapy Xiaolong Zhang a,d, Ming Wu a,d, Jiong Li a,c,d, Shanyou
Supporting Information Light-enhanced hypoxia-response of conjugated polymer nanocarrier for successive synergistic photodynamic and chemo-therapy Xiaolong Zhang a,d, Ming Wu a,d, Jiong Li a,c,d, Shanyou
Supporting Information for:
 Supporting Information for: Tunable Heptamethine-Azo Dye Conjugate as an IR Fluorescent Probe for the Selective Detection of Mitochondrial Glutathione over Cysteine and Homocysteine Soo-Yeon Lim, 1 Keum-Hee
Supporting Information for: Tunable Heptamethine-Azo Dye Conjugate as an IR Fluorescent Probe for the Selective Detection of Mitochondrial Glutathione over Cysteine and Homocysteine Soo-Yeon Lim, 1 Keum-Hee
(FITC) or rhodamine blue isothiocyanate (RBITC) for use in mixed egg-transfer experiments. Both FITC and RBITC bind to the zona pellucida
 THE LABELLING OF LIVING RABBIT OVA WITH FLUORESCENT DYES J. W. OVERSTREET Department of Anatomy and International Institute for the Study of Human Reproduction, Columbia University, College of Physicians
THE LABELLING OF LIVING RABBIT OVA WITH FLUORESCENT DYES J. W. OVERSTREET Department of Anatomy and International Institute for the Study of Human Reproduction, Columbia University, College of Physicians
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
 The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 The Effects of Varying Amounts of Nicotine on the Development of Zebrafish Eggs Charlotte, Sydney Martins, Elyse Steingraeber Waukesha North High School ABSTRACT The purpose of the experiment was to see
The Effects of Varying Amounts of Nicotine on the Development of Zebrafish Eggs Charlotte, Sydney Martins, Elyse Steingraeber Waukesha North High School ABSTRACT The purpose of the experiment was to see
ab SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Embryo-Toxicity and Teratogenicity of Derris elliptica Leaf Extract on Zebra Fish (Danio rerio) Embryos
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Tolentino and Undan Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 4 (3): 16-20 (2016) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2293 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Tolentino and Undan Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 4 (3): 16-20 (2016) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2293 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Chapter 3. Expression of α5-megfp in Mouse Cortical Neurons. on the β subunit. Signal sequences in the M3-M4 loop of β nachrs bind protein factors to
 22 Chapter 3 Expression of α5-megfp in Mouse Cortical Neurons Subcellular localization of the neuronal nachr subtypes α4β2 and α4β4 depends on the β subunit. Signal sequences in the M3-M4 loop of β nachrs
22 Chapter 3 Expression of α5-megfp in Mouse Cortical Neurons Subcellular localization of the neuronal nachr subtypes α4β2 and α4β4 depends on the β subunit. Signal sequences in the M3-M4 loop of β nachrs
See external label 96 tests ULTRASENSITIVE THYROID STIMULATING HORMONE (u-tsh) TSH Ultra Sensitive
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
A Precise Bicoid Gradient is Nonessential During Cycles for Precise Patterning in the Drosophila Blastoderm
 Supporting Information for A Precise Bicoid Gradient is Nonessential During Cycles 11-13 for Precise Patterning in the Drosophila Blastoderm Elena M. Lucchetta, Meghan E. Vincent and Rustem F. Ismagilov*
Supporting Information for A Precise Bicoid Gradient is Nonessential During Cycles 11-13 for Precise Patterning in the Drosophila Blastoderm Elena M. Lucchetta, Meghan E. Vincent and Rustem F. Ismagilov*
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about mitosis is correct? Question #1 (A) Mitosis involves the dividing
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about mitosis is correct? Question #1 (A) Mitosis involves the dividing
p)robably reflects seasoinal variations in egg populations. No results were considered unless
 MITOTIC ABNORM1ALITIES IN SEA URCHIN EMBRYOS EXPOSED TO DACTINOMIYCIN* BY BARRY I. KIEFER, CHARLES F. ENTELIS, AND ANTHONY A. INFANTE DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY, WESLEYAN UNIVERSITY, MIDDLETOWN, CONNECTICUT
MITOTIC ABNORM1ALITIES IN SEA URCHIN EMBRYOS EXPOSED TO DACTINOMIYCIN* BY BARRY I. KIEFER, CHARLES F. ENTELIS, AND ANTHONY A. INFANTE DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY, WESLEYAN UNIVERSITY, MIDDLETOWN, CONNECTICUT
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. Phospho-Akt (pser 473 ) ELISA Kit for detection of human, mouse, or rat phospho-akt (pser 473 ) in cell and tissue lysates
 Phospho-Akt (pser 473 ) ELISA Kit for detection of human, mouse, or rat phospho-akt (pser 473 ) in cell and tissue lysates Catalog Number RAB0011 Storage Temperature 20 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description
Phospho-Akt (pser 473 ) ELISA Kit for detection of human, mouse, or rat phospho-akt (pser 473 ) in cell and tissue lysates Catalog Number RAB0011 Storage Temperature 20 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description
Epithelial cell death is an important contributor to oxidant-mediated acute lung injury SUPPORTING INFORMATION 60611, USA
 Epithelial cell death is an important contributor to oxidant-mediated acute lung injury SUPPORTING INFORMATION G.R. Scott Budinger 1,2 *, Gökhan M. Mutlu 1 *, Daniela Urich 2, Saul Soberanes 1, Leonard
Epithelial cell death is an important contributor to oxidant-mediated acute lung injury SUPPORTING INFORMATION G.R. Scott Budinger 1,2 *, Gökhan M. Mutlu 1 *, Daniela Urich 2, Saul Soberanes 1, Leonard
Definition of Fertilization
 Fertilization Definition of Fertilization is the fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism In animals, the process involves the fusion of an ovum with a sperm, which eventually
Fertilization Definition of Fertilization is the fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism In animals, the process involves the fusion of an ovum with a sperm, which eventually
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Cancer Cell Membrane-Biomimetic Nanoprobes with Two-Photon Excitation and Near-Infrared Emission for Intravital Tumor Fluorescence Imaging Yanlin Lv 1,2,, Ming Liu 3,4,, Yong Zhang
Supporting Information Cancer Cell Membrane-Biomimetic Nanoprobes with Two-Photon Excitation and Near-Infrared Emission for Intravital Tumor Fluorescence Imaging Yanlin Lv 1,2,, Ming Liu 3,4,, Yong Zhang
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
CD14 + S100A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
PREPARATION OF IF- ENRICHED CYTOSKELETAL PROTEINS
 TMM,5-2011 PREPARATION OF IF- ENRICHED CYTOSKELETAL PROTEINS Ice-cold means cooled in ice water. In order to prevent proteolysis, make sure to perform all steps on ice. Pre-cool glass homogenizers, buffers
TMM,5-2011 PREPARATION OF IF- ENRICHED CYTOSKELETAL PROTEINS Ice-cold means cooled in ice water. In order to prevent proteolysis, make sure to perform all steps on ice. Pre-cool glass homogenizers, buffers
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
