PK15 48 (1) :58 63, (intermediate filament, IF) D ( Traub et al., 1994) IF P K15 D. ( Fuchs et al., 1994), , ( Fuchs et al., 1992) (apoptosis)
|
|
|
- Jemima Sutton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 48 (1) :58 63, 2002 A cta Zoologica S inica 3 PK15 (, ) D P K15 ( Porcrne Kidney215) DNA, DNA ladder ;,,,, P K15 D (intermediate filament, IF) D ( Traub et al., 1994) IF P K15 ( Porcine Kidney215),, DAPI, ( ) ( DNA ) 20,,, ; ( Fuchs et al., 1994), ( ), ( Fuchs et al., 1992) (apoptosis),,,, ( Wyllie et 111 al., 1980), P K15,?, 10 % DMEM IF Rao (p H 712, Gibico ) 37, (1996) Takahashi (1996) Hank s, D (10 g/ (lamin) ml, promaga ) DMEM 37, Giese ( 1997) TPA DMEM 24 h Lecai DM IL MPC211 (vimentin) Liao (1997) 112 DAPI D NA HT29 42 P K15 D, 8 ; Caulin (1997) 18 (etoposide), 1 (10 g/ ml) 48 h, PBS 3, DAPI 5 min, PBS, Lecai , (No1G ),, 28,, : E2mail :
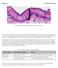
2 1 : P K15 59 DMRB 4 5 min, CSK 0125 % P K15 24 h - CSK 60 min, PBS 3, PBS 3 (10 1 % 2PBS 30 min, PBS 3 mmol/ L Tris, 10 mmol/ L NaCl, 1 mmol/ L ED TA, 100 mg/ L proteinase K, 10 g/ L SDS, p H 810), 37, r/ min 5 min 115,, 2 P K15 D (10-20, r/ min, DNA TE 118 % 1 SDS, SDS ( %, 15 %) P K15 D, 3 %BSA, (10 g/ ml) 48 h, PBS 3, AE1 AE3 (, AE1 5 min, PBS 011 % Triton X2100 PBS 3 min, C1562 ( Sigma ) 37 1 h, PBS, FITC 1 h, BCIP NB T min, PBS DAPI 5 min,, Lecai DMRB P K15 ( 1 : a) Zhai (1988), P K15 D (10 g/ ml) 24 h, Formar, PBS, 015 % Triton X2100 CSK ( 10 mmol/ L PIPES, 100 mmol/ L mmol/ L MgCl 2, 1 mmol/ L KCl, 300 mmol/ L, 3 EGTA, 112 mmol/ L PMSF, 1 % TritonX2100, p H 618) 5 min, RSB2Magik ( 4215 mmol/ L NaCl, 216 mmol/ L Tris, 815 mmol/ L MgCl 2 6H 2 O, 112 mmol/ L PMSF, 1 % Tween240, 015 %, p H 813),,, CO 2 g/ ml) 96 h,, PBS 3, AE3 ) 37 2 h, 37 2, 48 h 72 h, 96 h, ( 1 : b), ( 1 : c),,, ( 1 : a) ;,, 1 PK15 Fig11 The phase contrast micrograph of induced PK15 cells 100 a. (Normal cells before induction) b. 96 h (Cells induced for 96 h) c. (Control cells),, ; 96 h,, ;, ( Normal cells were extended and closed, the outlines of nucleus and nucleolus were clear ; most cells dropped from walls after induction for 96 h, cells contracted and condensed ; no obvious changes in control cells)
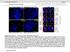
3 ( 1 : b) ; ( 2 : ( 1 : c) DAPI, ( 2 : c) ; : ( 2 : a) ; ( 2 : d) b) ;, 2 PK15 DAPI Fig12 Cells stained with DAPI after induction a. (Nucleus of normal cell) b. ( Chomatin condensation of induced cell) c. ( Apoptotic bodies in induced cell) d. ( ) [ One apoptotic body (array) was released from cell ] 3 DNA Fig13 The electrophesis pattern of isolated DNAs from induced cells M : DNA (Molecular size marker) 1 : DNA, (Control) 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 : 12, 24, 48, h DNA, DNA ladder ( Induction for 12, 24, 48, 72 and 96 h, DNAs were digested to fragments) 4 Fig14 Indirect immunofluorescence of keratin in apoptotic cells a. (Normal cells) b, c, d. (Apoptotic cells) a, b, c, d. a, b, c, d DAPI (DAPI staining of the same cells as in a, b, c and d) ;,,,, (b),, (c d) ( The spreading keratin filament network was welldistributed in normal cells. After induction the antigen of keratin still existed in apoptotic cells, but its distribution was not even, keratin fluorescence was condensed in some cells as in b, and distributed around chomatin as in c and d)
4 1 : P K Fig15 Whole mount micrograph of keratin network in apoptotic cells a., N, (Normal cell, showing spreading keratin network. N : nuclei) b., ch,, ( ) (Apoptotic cell, keratin network was intact in some area of the cell, but the filaments were shortened, and the filaments around chomatin were condensed) P K15 12 h 24 h 48 h 72 h 96 h DNA,, : DNA ladder (DNA AE3 43 ku ), DNA ( 29 ku ; 29 ku 3) D P K15, 212 P K15 c1562, DAPI, ( 4 : a, a ) ;,, ( 4 : b, b ),, DNA, DNA ( 4 : c, c, d, d ), P K15 6 Fig16 Western blot of keratin protein in apoptotic cells,, [ 5 : a ( N) ], b. AE1, 45 ku, ( 5 : a) ;, ( Western blot with AE1, showed type keratin of 45 ku [ 5 : b (ch) ],, M : (Standard protein marker) [ 5 : b ( ) ] 96 h P K15 a. AE3, 43 ku 29 ku ( Western blot with AE3, showed type keratin of 43 ku and it s degraded product of 29 ku) which did not degrade) 1 : 96 h ( Proteins of induced cells for 96 h) 2 : ( Proteins of control cells)
5 ( 6 : a) ; AE1 45 ku,,, ( 6 : b) 3,,,,? ( Fuchs et al., 1994),,,, ;?, :,,,, (Liao et al., 1997) : :,,,,?,,? ( Wyllie et al.,, 1980) ( References) Caulin, C., G. S. Salvesen and R. G. Oshima 1997 Caspase cleavage of keratin 18 and reorganization of intermediate filaments during epithelial cell apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 138 : Giese, G., J. Schmidt, M. Gilbert, R. Albrecht and P. Traub 1997 TPA induces apoptosis in MPC211 cells grown in serum free medium. Biol. Fuchs, E. and K. Fuchs, E. and P. Liao, J., N. O. Cell 89 : Weber 1994 Intermediate filament : structure, dynamics, function and disease. A nnu. Rev. Biochem. 63 : Coulombe 1992 Of mice and men : Genetics skin diseases of keratin. Cell 69 : Ku and M. B. Omary 1997 Stress, apoptosis, and mitosis induce phosphorylation of human karetin 8 at ser273 in tissues and cultures cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272 : Rao, L., D. Perez and E. White 1996 Lamin proteolysis facilitates nuclear events during apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 135 : Takahashi, A., E. S. Alnemri, Y. A. Lazebnik, T. F. Alnemri, G. Litwack and R. D. Moir 1996 Cleavage of lamin A by Mch2 but not cpp322 : multiple interleukin 1 2converting enzyme2related protease with distinct substrate recognition properties are active in apoptosis. N atl. Acad. Sci. USA 93 : Traub, P, R. and L. of Cytology 15 : Shoeman 1994 Intermediate filament proteins cytoskeletal elements with gene regulatory function? International Review Wyllie, A. H., J. F. R. Kerr and A. R. Currie 1980 Cell death : the significance of apoptosis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 68 : Zhai, Z. H., X. Wang and X. Y. Qian 1988 Alteration of intermediate filament2nuclear matrix system in Hela cells after adnovirus infection. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 12 : Proc.
6 1 : P K15 63 ( Abstract) CHANGES IN KERATIN D URING APOPTOSIS OF PK15 ( PORCINE KID NEY215) CELLS 3 CHEN Dan2Ying GAO Yun2Fei L I Li2Xia ZHAI Zhong2He ( L if e Science College, Peki ng U niversity, Beiji ng , Chi na) Intermediate filament ( IF) is a major component of cytoskeleton. Recent advances suggest t hat IFs not only play a cytoskeletal role in cooperation with microfilaments and microtubules, but are also involved in cell differentiation, signal t ransduction and gene expression. Apoptosis is a p hysiological form of cell deat h, it describes t he orchest rated collapse of a cell, staging membrane blebbing, cell shrinkage, protein f ragmentation, chromatin condensation and DNA degradation. How do IFs change in apoptotic process and what kind of role do they play? The answers to these questions would be of great importance to further study of their functions. Epit helial cell P K15 ( Porcine Kidney215) was induced to apoptosis by actinomycin D. The cell shapes changed from spreading to contracting and rounding during the induction process, and most of the cells dropped f rom t he wall after induction for 96 h. DAPI staining showed t he chromatin condensation and apoptotic bodies formation characterized by apoptosis in this process. At the same time DNA ladder was detected by elect rop horesis. Indirect immunofluorescence result s showed t hat t he fluorescence of keratin dist ributed unevenly in t he apoptotic cells, and in some cells t he keratin fluorescence cont racted around t he condensed chromatin. Using selective ext raction combined wit h whole mount elect ron microscopy, we detected t he intact keratin filament network in some area of apoptotic cells, and t he filament s were obviously shortened. In consistent wit h t he result of immunofluorescence, t he keratin filament s around chromatin were condensed in comparison with filaments in other areas. Western blot analysis further showed that part of type keratin protein degraded only partially during apoptosis, whereas type keratin protein molecules were intact. These results suggested that in apoptotic processing the structure changes of keratin network might lead to the changes of cell shape, and might participate t he formation of apoptotic bodies. Key words Pig, Porcine Kidney cell, P K15, Keratin, Intermediate filament, Actinomycin D, Apoptosis 3 This work was supported by the Special Funds for Major State Basic Research of China (No. G )
PREPARATION OF IF- ENRICHED CYTOSKELETAL PROTEINS
 TMM,5-2011 PREPARATION OF IF- ENRICHED CYTOSKELETAL PROTEINS Ice-cold means cooled in ice water. In order to prevent proteolysis, make sure to perform all steps on ice. Pre-cool glass homogenizers, buffers
TMM,5-2011 PREPARATION OF IF- ENRICHED CYTOSKELETAL PROTEINS Ice-cold means cooled in ice water. In order to prevent proteolysis, make sure to perform all steps on ice. Pre-cool glass homogenizers, buffers
Fig Intermediate Filaments
 Fig 16-20 Intermediate Filaments Overview: Intermediate filaments are easily bent and stretched but highly resistant to breaking. They provide mechanical strength to cells. Unlike actin filaments and microtubules,
Fig 16-20 Intermediate Filaments Overview: Intermediate filaments are easily bent and stretched but highly resistant to breaking. They provide mechanical strength to cells. Unlike actin filaments and microtubules,
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury
 Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D., Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Kenichiro Yahata, M.D.,
Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D., Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Kenichiro Yahata, M.D.,
Chapter 2 Cell. Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology
 Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Studying apoptosis in DT40 cells
 Studying apoptosis in DT40 cells Sandrine Ruchaud E12.5! Acridine Orange! Role of apoptosis in sculpting the mouse paw E13.5! E14.5! gift of William Wood & Paul Martin! University College, London! Normal
Studying apoptosis in DT40 cells Sandrine Ruchaud E12.5! Acridine Orange! Role of apoptosis in sculpting the mouse paw E13.5! E14.5! gift of William Wood & Paul Martin! University College, London! Normal
Cell cycle and apoptosis
 Cell cycle and apoptosis Cell cycle Definition Stages and steps Cell cycle Interphase (G1/G0, S, and G2) Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, karyokinesis, cytokinesis) Control checkpoints
Cell cycle and apoptosis Cell cycle Definition Stages and steps Cell cycle Interphase (G1/G0, S, and G2) Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, karyokinesis, cytokinesis) Control checkpoints
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell division
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Unicellular organisms
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
Structure and Function of Cells
 Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei Department of Histology & Embryology
 The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS SECOND EDITION URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The Key
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The Key
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage response at telomeres that determines cell survival Karolina O. Hain, Didier J. Colin, Shubhra Rastogi, Lindsey
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage response at telomeres that determines cell survival Karolina O. Hain, Didier J. Colin, Shubhra Rastogi, Lindsey
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments
 02.12.10 Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments Intermediate filaments Present in nearly all animals, but absent from plants and fungi Rope-like network of filaments in the cell Principle function is maintenance
02.12.10 Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments Intermediate filaments Present in nearly all animals, but absent from plants and fungi Rope-like network of filaments in the cell Principle function is maintenance
BIOH111. o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
(a) Reproduction. (b) Growth and development. (c) Tissue renewal
 100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about cytoskeletal filaments is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cytoskeleton
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about cytoskeletal filaments is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cytoskeleton
Supplementary Figure 1 P53 is degraded following Chlamydia infection independent of the cell lysis and protein sample preparation procedure applied.
 Supplementary Figure 1 P53 is degraded following Chlamydia infection independent of the cell lysis and protein sample preparation procedure applied. (a) Western blotting analysis showing degradation of
Supplementary Figure 1 P53 is degraded following Chlamydia infection independent of the cell lysis and protein sample preparation procedure applied. (a) Western blotting analysis showing degradation of
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview. Cellular Organization of the Genetic Material. Distribution of Chromosomes During Eukaryotic Cell Division
 CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living things from nonliving matter The continuity of life is based on the reproduction of cells,
CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living things from nonliving matter The continuity of life is based on the reproduction of cells,
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4. Outline. Early contributors to Understanding Cells. Cell Theory. Cell Size s Matt Schleiden & Ted Schann
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
Fig. 1. Simple columnar epithelial cells lining the small intestine.
 Mitosis Prelab Reading Fig. 1. Simple columnar epithelial cells lining the small intestine. The tall cells pictured in Fig. 1 form the lining of the small intestine in humans and other animals. These cells
Mitosis Prelab Reading Fig. 1. Simple columnar epithelial cells lining the small intestine. The tall cells pictured in Fig. 1 form the lining of the small intestine in humans and other animals. These cells
Introduction: 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt
 Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide
 The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
The role of keratin laments during nuclear envelope reassembly in Xenopus egg extracts
 FEBS Letters 428 (1998) 52^56 FEBS 20250 The role of keratin laments during nuclear envelope reassembly in Xenopus egg extracts Bo Zhang a, Ying Chen a, Zhiyang Han a, Hans Ris b, Zhonghe Zhai a; * a College
FEBS Letters 428 (1998) 52^56 FEBS 20250 The role of keratin laments during nuclear envelope reassembly in Xenopus egg extracts Bo Zhang a, Ying Chen a, Zhiyang Han a, Hans Ris b, Zhonghe Zhai a; * a College
THE CELL Cells: Part 1
 THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
47 (5) : , 2001
 47 (5) :535 541, 2001 A cta Zoologica S inica 3 33 (, 100875) (, 571158) ( L onchura st riata) ( robust nucleus of archistriatum, RA), (biotinylated dextran amine, BDA), (lateral nucleus magnocellularis
47 (5) :535 541, 2001 A cta Zoologica S inica 3 33 (, 100875) (, 571158) ( L onchura st riata) ( robust nucleus of archistriatum, RA), (biotinylated dextran amine, BDA), (lateral nucleus magnocellularis
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
Organelles in EUKARYOTIC CELLS. Pages 4 5: cell membrane, cytoplasm/cytosol, cytoskeleton, nucleus, chromatin/chromosomes, and centrioles
 Organelles in EUKARYOTIC CELLS Pages 4 5: cell membrane, cytoplasm/cytosol, cytoskeleton, nucleus, chromatin/chromosomes, and centrioles Use the info on the following slides to complete pages 4 5 in your
Organelles in EUKARYOTIC CELLS Pages 4 5: cell membrane, cytoplasm/cytosol, cytoskeleton, nucleus, chromatin/chromosomes, and centrioles Use the info on the following slides to complete pages 4 5 in your
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about mitosis is correct? Question #1 (A) Mitosis involves the dividing
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about mitosis is correct? Question #1 (A) Mitosis involves the dividing
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
BIOLOGY. The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
Mitosis vs. microtubule
 Mitosis vs. microtubule Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) Duplicated centrosomes align and begin separating in prophase Relation of centrosome duplication to the cell cycle. Parent centrioles
Mitosis vs. microtubule Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) Duplicated centrosomes align and begin separating in prophase Relation of centrosome duplication to the cell cycle. Parent centrioles
The Cell Cycle 4/10/12. Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Meiosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Mitosis & 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Mitosis Form of cell division that leads to identical daughter cells with the full complement of DNA Occurs in somatic cells Cells of body
Mitosis & 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Mitosis Form of cell division that leads to identical daughter cells with the full complement of DNA Occurs in somatic cells Cells of body
APOPTOSIS, NECROSIS AND CANCER. Dr. S. P. Pattanayak
 APOPTOSIS, NECROSIS AND CANCER Dr. S. P. Pattanayak LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Know the importance of cell death. Define various modes of cell death. Identify
APOPTOSIS, NECROSIS AND CANCER Dr. S. P. Pattanayak LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Know the importance of cell death. Define various modes of cell death. Identify
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Objectives. By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles
 Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle. Packet #9. Thursday, August 20, 2015
 1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection
 Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
The Cell. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE. In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for..
 Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5
 AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
Name: Per/row: Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology
 Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology Name: Per/row: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the box next to its description/function. Cell membrane Centrioles Chloroplast Chromatin
Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology Name: Per/row: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the box next to its description/function. Cell membrane Centrioles Chloroplast Chromatin
C-Phycocyanin (C-PC) is a n«sjfc&c- waefc-jduble phycobiliprotein. pigment isolated from Spirulina platensis. This water- soluble protein pigment is
 ' ^Summary C-Phycocyanin (C-PC) is a n«sjfc&c- waefc-jduble phycobiliprotein pigment isolated from Spirulina platensis. This water- soluble protein pigment is of greater importance because of its various
' ^Summary C-Phycocyanin (C-PC) is a n«sjfc&c- waefc-jduble phycobiliprotein pigment isolated from Spirulina platensis. This water- soluble protein pigment is of greater importance because of its various
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules. LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07. Processes occurring during cell cycle
 Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Chemical Modifications of GFAP in Alexander Disease
 Chemical Modifications of GFAP in Alexander Disease Natasha T. Snider Assistant Professor Department of Cell Biology and Physiology University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Alexander Disease Family
Chemical Modifications of GFAP in Alexander Disease Natasha T. Snider Assistant Professor Department of Cell Biology and Physiology University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Alexander Disease Family
SD-1 SD-1: Cathepsin B levels in TNF treated hch
 SD-1 SD-1: Cathepsin B levels in TNF treated hch. A. RNA and B. protein extracts from TNF treated and untreated human chondrocytes (hch) were analyzed via qpcr (left) and immunoblot analyses (right) for
SD-1 SD-1: Cathepsin B levels in TNF treated hch. A. RNA and B. protein extracts from TNF treated and untreated human chondrocytes (hch) were analyzed via qpcr (left) and immunoblot analyses (right) for
FAM83H and casein kinase I regulate the organization of. the keratin cytoskeleton and formation of desmosomes
 FAM83H and casein kinase I regulate the organization of the keratin cytoskeleton and formation of desmosomes Takahisa Kuga, Mitsuho Sasaki, Toshinari Mikami, Yasuo Miake, Jun Adachi, Maiko Shimizu, Youhei
FAM83H and casein kinase I regulate the organization of the keratin cytoskeleton and formation of desmosomes Takahisa Kuga, Mitsuho Sasaki, Toshinari Mikami, Yasuo Miake, Jun Adachi, Maiko Shimizu, Youhei
BIOLOGY. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS
 Lesson 6: CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS Name: Group: MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS Permanent slide: onion rootlet stained with acetorcein The particular mitotic phases are visible in the onion rootlet cells. Chromosomes
Lesson 6: CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS Name: Group: MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS Permanent slide: onion rootlet stained with acetorcein The particular mitotic phases are visible in the onion rootlet cells. Chromosomes
The Biochemistry of apoptosis
 The Biochemistry of apoptosis 1 1 The apoptosis is composed of multiple biochemical events 2 2 Biochemical, cellular, and molecular events in Apoptosis 1. Membrane blebbing; phosphatidyl serine exposure
The Biochemistry of apoptosis 1 1 The apoptosis is composed of multiple biochemical events 2 2 Biochemical, cellular, and molecular events in Apoptosis 1. Membrane blebbing; phosphatidyl serine exposure
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Effect of starvation-induced autophagy on cell cycle of tumor cells
 [Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:8, 102-108; August 2008]; 2008 Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center Basic Research Paper Effect of starvation-induced autophagy on cell cycle of tumor cells Jun-Na Ge, 1 Dan
[Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:8, 102-108; August 2008]; 2008 Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center Basic Research Paper Effect of starvation-induced autophagy on cell cycle of tumor cells Jun-Na Ge, 1 Dan
The Cell Cycle 4/10/12. Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division
 LECTURE PREENTATION For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, teven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Overview: The Key
LECTURE PREENTATION For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, teven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Overview: The Key
BIOLOGY 4/6/2015. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
Identification and characterization of genes responsive to apoptosis: Application of DNA chip technology and mrna differential display
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 1271-1 284 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and H istopat hology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Revie W Identification and characterization of genes
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 1271-1 284 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and H istopat hology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Revie W Identification and characterization of genes
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles Sexual reproduction mitosis
 meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Equine biological systems
 Equine biological systems Pack 9 How animal cells work Pack Code: EBS9 This pack you will help you to: Identify the main components of an animal cell Describe the functions of the main cell components
Equine biological systems Pack 9 How animal cells work Pack Code: EBS9 This pack you will help you to: Identify the main components of an animal cell Describe the functions of the main cell components
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1 Induction of non-apoptotic death of SV40-transformed and primary DKO MEFs, and DKO thymocytes. (A-F) STS-induced non-apoptotic death of DKO MEF. (A, B) Reduced viability of DKO MEFs after exposure
Figure S1 Induction of non-apoptotic death of SV40-transformed and primary DKO MEFs, and DKO thymocytes. (A-F) STS-induced non-apoptotic death of DKO MEF. (A, B) Reduced viability of DKO MEFs after exposure
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis. Dr H Awad 2017/18
 Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Key Concepts in Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Video: Sea Urchin Embryonic Development (time-lapse)
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Dr. Wendy era Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 12 1. Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells. 2. The mitotic phase alternates
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Dr. Wendy era Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 12 1. Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells. 2. The mitotic phase alternates
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05473 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1: Association of Runx2 with mitotic chromosomes Mitotic chromosome spreads were prepared for a. Human Saos-2
doi: 10.1038/nature05473 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1: Association of Runx2 with mitotic chromosomes Mitotic chromosome spreads were prepared for a. Human Saos-2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division. AP Biology
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle. 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
A Tour of the Cell. reference: Chapter 6. Reference: Chapter 2
 A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
Cellular compartments
 Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Supplementary figure legends
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Exposure of CRT occurs independently from the apoptosisassociated loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). (A) HeLa cells treated with MTX
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Exposure of CRT occurs independently from the apoptosisassociated loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). (A) HeLa cells treated with MTX
