Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Fall Meeting September 2015 Intraoperative Consultation in Gynecological Pathology: The Adnexal Mass
|
|
|
- Regina Young
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Fall Meeting September 2015 Intraoperative Consultation in Gynecological Pathology: The Adnexal Mass Julie Irving, MD Department of Pathology, University of British Columbia and the Royal Jubilee Hospital, Victoria, Canada
2 Or, How to render a foolproof diagnosis on 1 mediocre frozen section of a 32 cm complex adnexal mass in 6 minutes or less
3 OVARIAN MASS NYD Non-neoplastic Neoplastic Primary Metastatic Epithelial -Stromal Germ Cell Sex cord- Stromal Other Benign Borderline Malignant } Subtype
4 Informal survey What is your level of confidence in IOC dx of an adnexal mass? (Scale 1-10) What areas do you find the most (a) Challenging? (b)straightforward? What factors would improve your ability to render an accurate IOC dx? 9-10 for benign & straightforward cases 6-7 or less for difficult cases Primary vs Metastatic Florid borderline vs carcinoma Subtype classification in carcinoma Rare tumors & anything in young women Benign tumors, dermoid cysts Clinical information Gyne path feedback on final pathology Technologist assistance
5 Intraoperative Consultation of an Adnexal Mass Fine tune the approach to IOC Pitfalls and limitations in frozen section Emphasis on ovarian tumors prone to discrepant final diagnosis Understand the clinical consequences of IOC diagnosis
6 Victoria General Hospital (frozen section coverage - not so subspecialty AP) Royal Jubilee Hospital (Subspecialty AP)
7 IOC in Gyne Pathology 10% of IOC overall 50-75% adnexal mass Our center >90% (Others = Uterus, vulvovaginal, lymph nodes) IOC expectations have evolved with improved understanding and histotyping of ovarian carcinomas
8 IOC of the adnexal mass: Surgeon s perspective Needs a tissue diagnosis Impact on surgical staging Preservation of ovarian tissue Fertility Hormonal benefits to age 65
9 The surgeon s perspective 1. Known diagnosis of high grade serous ca Interval debulking after 3-4 cycles chemotherapy Tumor banking Generally little or no role for frozen section 2. Adnexal mass NYD Usually no prior tissue diagnosis Often sent for frozen section
10 Intraoperative Diagnosis Young Surgery Old(er) Benign Cystectomy SO TAH-BSO Borderline SO +/- staging* TAH-BSO + staging* Malignant: Primary surface-epithelial Malignant: Sex cord stromal, germ cell Metastatic SO + staging* SO +/- staging TAH-BSO, debulking, staging* TAH-BSO, staging Often conservative surgery Exploration of peritoneum and viscera Appendectomy if mucinous*
11 IOC dx of primary ovarian malignancy: Potential Consequences Patient has the necessary and appropriate surgery Especially for clinically stage I tumors (extra-ovarian spread subclinical in 25%) Conversion to laparotomy, longer OR time, higher postoperative morbidity HGSC +/- Intraperitoneal catheter
12 IOC dx of primary ovarian malignancy: Potential Consequences if final pathology = Metastatic Unnecessary radical surgery Surgeon may have performed more extensive exploration for primary, or called in general surgeon to assist
13 IOC dx of malignant ovarian tumors Realistic comments General gynecologists unlikely to perform full staging surgery In young patients, conservative is the rule and can await final pathology (can do second surgery, but cannot put parts back)
14 IOC dx of malignant ovarian tumors Realistic comments Maintain open dialogue with surgical colleagues Adnexal mass sent for IOC may not yield the whole story unless you ask specific questions Presume that IOC is of value (to the surgeon and in best interest of the patient)
15 The pathologist s perspective Huge range of ovarian tumor types Diversity within tumor categories Benign, borderline, or malignant? Experience with rarer germ cell and sex cord stromal tumors may be limited Primary or metastatic? Not every adnexal mass is a tumor Non-neoplastic lesions can mimic clinically advanced malignancy
16 The pathologist s perspective Clinical information often lacking Concern about immediate surgical consequences Professional and practical desire to make the right diagnosis
17 Frozen section diagnosis of ovarian tumors Diagnostic accuracy 59-96% What are the most problematic tumors? Can accuracy be improved?
18 Intraoperative assessment of ovarian tumors Stewart CJR et al, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2006;25: Retrospective 5-year review of 914 consecutive ovarian tumor frozen sections 60% benign, 10% borderline, 30% malignant Overall accuracy = 95.3% Borderline tumors: Serous - 90%; mucinous - 65% Malignant: Primary - 86%; metastatic - 59%
19 Intraoperative assessment of ovarian tumors Stewart CJR et al, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2006;25: cases (4.7%) significant diagnostic discrepancy Pathologist misinterpretation (53%), sampling error (40%), poor quality slides (20%) Under-diagnosis in 32 cases (75%), usually mucinous Over-diagnosis in 11 cases (25%), usually serous
20 Song T, et al. Accuracy of frozen section diagnosis of borderline ovarian tumors. Gynecol Oncol 2011;122: FS diagnosis in 1104 borderline tumors (data pooled from 7 studies) Overall accuracy 67.1% (741/1104) Under-diagnosis in 20% (mucinous histology as a significant predictor) Cautious surgical decision-making for BTs based on FS dx, especially in mucinous tumors
21 What s the problem? Under-diagnosis Large tumors, mucinous tumors (sampling) Unilateral tumors, tumor confined to ovary (clinical bias) Over-diagnosis Serous neoplasms (interpretation) Extra-ovarian spread (clinical bias) Metastatic tumors Morphologic overlap with primary tumors Houck et al Obstet Gynecol 2000;95:839-43
22 An Approach to the Intraoperative Diagnosis of an Adnexal Mass Pre-IOC IOC Post-IOC
23 Pre-IOC homework
24 Pre-IOC homework: Clinical synopsis Presentation, signs and symptoms Any unusual flags eg. hirsutism Previous gyne history/surgery Previous history malignancy Physical examination findings Clinical impression and plan
25 Pre-IOC homework: Imaging Cystic, solid, solid-cystic Complex ovarian mass 25% malignant Benign 30% malignant Unilateral or bilateral Any extra-ovarian spread (omentum), ascites Status of uterus, and of abdominal organs
26 Bilaterality of stage I* ovarian tumors Serous Borderline 25-40% Carcinoma 15%* Mucinous Borderline -Intestinal 5-10% -Endocervical type 40% Carcinomas 5-10% Endometrioid Benign/borderline Rare Carcinomas 15% Clear cell Carcinomas 2% Clement & Young 2008
27 Germ cell tumors Sex cordstromal tumors Mature cystic teratoma 15% Dysgerminoma 20% YST Rare Immature teratoma Rare AGCT <5% JGCT 2% Fibroma 8% Thecoma 3% SLCT Rare Metastatic tumors 70%
28 Pre-IOC homework: Tumor markers CA 125 High levels (>500) often present in advanced stage HGSC Normal in 25% of stage I ovarian ca Can be in non-neoplastic lesions (eg. endometriosis) Can be colorectal ca, mesothelioma, also breast, lung, pancreas, bladder
29 Pre-IOC homework: Tumor markers CA 19-9 (GI, 1 ovarian mucinous tumors) CA 15-3 (Breast, 1 ovarian serous tumors) CEA (GI, lung, breast, sometimes ovary) Others AFP, LDH, hcg (germ cell panel) Androgens Serum calcium (hypercalcemic small cell ca)
30 Ovarian Carcinoma Subtypes Are Different Diseases: Implications for Biomarker Studies M. Köbel, S.E. Kalloger, N. Boyd, S. McKinney, E. Mehl, C. Palmer, S. Leung, N.J. Bowen, D.N. Ionescu, A. Rajput, L.M. Prentice, D. Miller, J. Santos, K. Swenerton, C.B. Gilks, D. Huntsman PLoS Med 2008;5(12): e232 doi: /journal.pmed
31 Histotype Surface-epithelial ovarian carcinoma: 5 major histologic subtypes Proportion of cases Proportion of early stage ca (I-II) Proportion of advanced stage ca (III-IV) Advanced stage at dx (by subtype) High grade serous 68-71% 36% 88% >90% Clear cell 12-13% 27% 5% Often stage I Endometrioid 9-11% 26% 3% Often stage I Mucinous 3% 8% 1% <3% Low grade serous 2.4% - - >90% Seidman JD, et al 2004; Kobel et al, 2010; Conkin & Gilks 2013
32 The postmenopausal patient Abdominal discomfort/distension, urinary frequency, change in bowel habit, early satiety, +/- PMB High levels Ca-125 Adnexal mass (bilateral or large irregular pelvic mass), omental cake, ascites High grade serous carcinoma
33 The pre- to peri-menopausal patient Irregular periods, pelvic pain History of endometriosis Mild to moderate elevation CA 125 Unilateral solid-cystic adnexal mass on pelvic U/S No evidence of extra-ovarian disease Broad ddx but be alert to endometrioid or clear cell ca
34 The adult young patient (18-30) Benign: Mature cystic teratoma! Epithelial tumors less common (often mucinous) Malignant rule: Germ cell (dysgerminoma) - sex cord-stromal (JGCT, SLCT) Surface-epithelial (mucinous BT) Other eg. hypercalcemic small cell ca Mets are very uncommon but do occur Crum PC et al, Intraoperative evaluation of ovarian tumors 2006;
35 The IOC: Gross evaluation of the ovarian tumor NYD Dimensions x 3 (and weight) Orient what tissue is actually received? Cystectomy, SO, TAH-BSO, wedge biopsy Fallopian tube Ovarian surface Intact? Excrescences, nodules, adhesions?
36 Tumor sampling: Go for the money Sample the area that looks most worrisome If heterogeneous, try to include adjacent different areas Attempt to open most cyst locules Consider more than one section (mucinous) +/- Smears
37
38 Case 1 61year-old woman Booked for TAH-BSO, omentectomy No clinical notes available Ca 125 = 886 Imaging adnexal mass, omental cake, ascites IOC - 10 cm solid-cystic adnexal mass
39
40 FS Dx:
41 Case 1 - Surgical outcome Completion of TAH-BSO, omentectomy as booked Debulked to minimal residual disease Residual small (<1 cm) sub-diaphragmatic tumor plaque not resected Final pathology = HGSC, pt3c
42 Case 2 60 year-old woman TAH-BSO +/- omentectomy Breast cancer 6 years ago, remote hysterectomy Normal tumor markers Imaging 15 cm solid-cystic right ovarian mass Nil else
43
44 Frozen section
45 FS Dx:
46 Final Dx:
47 DDx of HGSC on frozen section Other primary high grade ca Clear cell carcinoma Endometrioid carcinoma Metastasis breast Poorly differentiated ductal check pre-ioc and OR findings; may have to defer (Lobular Krukenberg)
48 Case 3 51 year-old, fullness Booked for TAH-BSO, omentectomy 10 cm solid-cystic adnexal mass No ascites CA-125 = 297, CEA normal IOC 10 cm solid-cystic ovarian mass, normal tube. FSx1 and smears
49
50
51 FS Dx:
52 Permanent sections
53 Final Dx:
54 Dysgerminoma Yolk sac tumor
55 Case 4 58 year-old, lower abd pain, heaviness x 2 months TAH-BSO, omentectomy Imaging cm solid-cystic adnexal mass, no ascites CA-125 = 111; normal CEA, 15-3, 19-9 IOC 14 cm solid-cystic tubo-ovarian mass
56
57 FS Dx:
58 Permanent sections
59 Final Dx:
60 Case 4 - Surgical outcome Completion of TAH-BSO, omentectomy as booked Final pathology = HGSC, pt3c Operative report Large pelvic mass, nodularity in cul-de-sac 100 ml ascites Plaque of tumor rectosigmoid colon, omental nodules 2-3 cm
61 FS looks primary epithelial ca, but? subtype.. Ask about the operative findings (other ovary/tube, omentum, ascites) Is the quality of FS acceptable? Use of smears depends on comfort level with cytology Gross fimbrial tumor?
62
63 HGSC vs CCC - clues Feature HGSC CCC Stage Advanced Confined to ovary Gross Architecture Fimbrial/tubo-ovarian mass Solid-cystic, papillary Lush papillae with tufting, slit-like spaces, solid TCClike, glandular Normal tube Solid area or nodules within unilocular cyst Rounded papillae with cores and minimal stratification; tubulocystic, solid, hyaline Nuclei Pleomorphic, grade 3 Grade 3 but scattered Mitoses High Low
64 Case 5 56 year-old woman, pelvic discomfort Booked for USO, possible TAH-BSO IOC: 15 cm left ovarian cystic mass, normal tube Unilocular cyst with turbid brown fluid Smooth internal lining with foci of brown granularity and a 2.0 cm nodule with calcification
65 Intraoperative diagnosis: Grossly benign and intact (probable mature cystic teratoma)
66 The surgeon said Tumor markers normal No ascites Uterus normal, atrophic right ovary and tube No other visible disease in pelvis or abdomen Closed after USO
67 Permanent sections
68 Permanent sections Clear cell carcinoma arising in endometriotic cyst
69 Unilocular AGCT Cystic struma ovarii
70 Case 6 32 year-old woman 10 cm complex ovarian mass Booked for cystectomy, possible SO Normal tumor markers No ascites
71 FS Dx =
72 Case 6 - Surgical outcome SO, peritoneal washings No evidence of extra-ovarian disease; omental biopsy and peritoneal biopsies Final pathology = SBT, stage pt1a
73
74 Serous borderline tumor in pregnancy lush papillae
75
76 Dx = Micropapillary serous borderline tumor
77 Dx = HGSC
78 Dx = LGSC
79 Benign vs SBT Serous tumors: IOC targets Firm, bulbous papillae, vs velvety soft excrescences Simple papillae with bland nuclei, vs hierarchical branching, tufting, exfoliation, with mild-moderate nuclear atypia SBT vs HGSC Exuberant papillae can lead to misinterpretation of SBT as serous ca nuclei are key (and mitoses)
80 HGSC vs.. Serous tumors: IOC targets CCC: architectural patterns, endometriosis, low stage EC: squamous diff, endometriosis, low stage CCC/EC may be cystic with multiple small nodules High grade ovarian carcinoma, (favor.) (LGSC: Nuclei, mitoses) (Metastasis - breast)
81 Case 7 48 year-old woman Abnormal uterine bleeding Imaging: 9 cm solid-cystic ovarian mass
82
83
84 FS Dx:
85 Final Dx:
86
87 53 year old with 8 cm solid ovarian mass AGCT
88 Case 8 87 year-old woman Not on regular OR slate Pelvic mass submitted for FS 19 cm right ovarian mass, solid-cystic tumor with surface involvement; attached normal tube
89
90 FS Dx:
91 Case 8: Surgical outcome Pathologist: Any history of colon cancer? Surgeon: Yes, we re doing the resection right now
92 Ovarian endometrioid carcinoma: IOC targets Glandular architecture, low grade nuclei, squamous differentiation High grade EC are difficult Endometriosis 15-20% have endometrioid ca of endometrium Be wary of: Many histological variants of EC Mimics eg. sex cord stromal (AGCT, SLCT) Metastasis, especially colorectal ca
93 Mucinous tumors
94 Primary ovarian mucinous tumors Benign Borderline Intestinal type Endocervical-like type (seromucinous) Malignant Expansile invasion Infitrative invasion
95 IMBT Mucinous ca, expansile
96 Mucinous neoplasms: Primary vs Metastatic Simple algorithm: Unilateral and 13 cm = Primary All others (bilateral* or < 13 cm) = Metastatic *5-10% of primary IMBT and mucinous ca are bilateral! Seidman et al. Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27: Yemelyanova et al. Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:128-38
97 68 year old with 28 cm unilateral left ovarian mass
98 FS Dx = Final Dx:
99
100 58 year old with 20 cm unilateral right ovarian mass
101 FS Dx =
102 Case 9 28 year old woman, G0P0 12 cm complex right ovarian cyst Right ovarian cystectomy Incised to drain cyst fluid, and removed in 3 fragments No frozen section
103 IMBT
104 6 mths later, follow-up U/S: 10 cm right ovarian cyst Laparotomy #2: RSO, appendectomy, omental bx Recurrent IMBT Irving and Clement, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2014
105 Median age 36 yrs 95/97 Stage I Recurrence rate 13.4% (48 months F/U) 7 borderline, 7 invasive carcinoma Single prognostic indicator for recurrence = CYSTECTOMY
106 Mucinous tumors: IOC targets Primary - Benign vs borderline vs carcinoma Tendency to undercall Take more than 1 section Mental check re: possibility of metastasis Experience with typical appearance of primary mucinous neoplasia helps (follow-up with final path) At least borderline is entirely acceptable
107 Mucinous neoplasms: Metastatic Colorectal* Appendix Stomach**, small bowel Pancreas**, gall bladder Endocervical* Lung, breast *Most likely to violate the algorithm; **May be occult
108 Primary vs metastatic mucinous neoplasms Unilateral Smooth external surface Expansile invasion Complex papillary pattern Benign & borderline areas (or teratoma, Brenner) Bilateral Surface involvement Hilar involvement Multinodular Infiltrative invasion with preservation Single cells or signetring cells LVI Lee and Young Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:281-92
109 Krukenberg tumor
110 Metastatic adenoca (colorectal primary) Metastatic adenoca (endocervical primary)
111 Case year-old Pelvic mass on clinical examination CA 125 = 346, CA 19-9 = 638 IOC - 19 cm ovarian mass, intact, smooth surface; normal tube Solid-cystic with copious mucin, necrosis
112
113
114 FS Dx =
115 Permanent sections
116 Final Dx =
117 76 year-old woman Case 11 3-mth hx increasing girth TAH 30 years prior CA 125 = 120, Ca 19-9 = 126; CEA 5.3, normal CA 15-3 Imaging = 25 cm cystic ovarian mass, no solid components IOC = 25 cm cystic mass, smooth surface
118
119 FS Dx =
120 Permanent sections
121 Permanent sections
122 + CK7, CK20, CDX2; focal weak PAX8; - ER, TTF-1, GATA-3 Final Dx =
123 Case 11: Follow-up Remains asymptomatic CA 19-9 stable elevation Post-op CT 2 months later heterogeneous mass body/tail of pancreas 19 x 13 mm, communicates with pancreatic duct
124 Case year-old woman Left ovarian mass, NYD Operative findings inspissated jelly-like fluid IOC 18 cm multiloculated cystic ovarian mass
125
126
127
128 FS Dx: Well differentiated mucinous neoplasm,? borderline mucinous tumor Recommend appendectomy
129 Permanent sections CK-20 and CDX-2 positive CK-7 negative
130 Final Diagnosis: Low grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm metastatic to ovary
131 Mucinous tumors: IOC targets Algorithm one tool only, use with caution Primary IMBT and mucinous ca can be bilateral Mets can be large and unilateral Mets can exhibit maturation Appendectomy? Low grade mucinous neoplasm, cannot exclude metastasis OR if appendix is abnormal
132 Mucinous tumors: IOC targets Surface involvement and histology discordant with primary mucinous neoplasia ( odd-looking ) can speak volumes Deceptively bland glands and cysts of bizarre shape & sizes, small gland pattern, ++ signet rings think metastasis
133 1. Pre-IOC 2. IOC 3. Post-IOC: Follow-up with final pathology Patient outcome Formally track FS-Final correlation
134
135 Summary viewpoints Improved accuracy in subtyping of ovarian carcinoma can extend to FS With careful, considered approach, and awareness of pitfalls, improved accuracy is obtainable in IOC dx in mucinous, borderline, and metastatic tumors
MPH Quiz. 1. How many primaries are present based on this pathology report? 2. What rule is this based on?
 MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma
 Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine 50 year old woman with chief complaint of shortness of breath
Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine 50 year old woman with chief complaint of shortness of breath
3 cell types in the normal ovary
 Ovarian tumors 3 cell types in the normal ovary Surface (coelomic epithelium) the origin of the great majority of ovarian tumors (neoplasms) 90% of malignant ovarian tumors Totipotent germ cells Sex cord-stromal
Ovarian tumors 3 cell types in the normal ovary Surface (coelomic epithelium) the origin of the great majority of ovarian tumors (neoplasms) 90% of malignant ovarian tumors Totipotent germ cells Sex cord-stromal
Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Beirut, Lebanon. Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology
 Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Beirut, Lebanon Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology Primary Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Cystadenoma Borderline (Tumor of Low Malignant Potential/Atypical
Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Beirut, Lebanon Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology Primary Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Cystadenoma Borderline (Tumor of Low Malignant Potential/Atypical
How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens
 How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens Wenxin Zheng, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Gynecology University of Arizona zhengw@email.arizona.edu http://www.zheng.gynpath.medicine.arizona.edu/index.html
How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens Wenxin Zheng, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Gynecology University of Arizona zhengw@email.arizona.edu http://www.zheng.gynpath.medicine.arizona.edu/index.html
of 20 to 80 and subsequently declines [2].
![of 20 to 80 and subsequently declines [2]. of 20 to 80 and subsequently declines [2].](/thumbs/80/81450506.jpg) - - According to the 2014 World Health Organization (WHO) classification and tumor morphology, primary ovarian tumors are subdivided into three categories: epithelial (60%), germ cell (30%), and sex-cord
- - According to the 2014 World Health Organization (WHO) classification and tumor morphology, primary ovarian tumors are subdivided into three categories: epithelial (60%), germ cell (30%), and sex-cord
General history. Basic Data : Age :62y/o Date of admitted: Married status : Married
 General history Basic Data : Age :62y/o Date of admitted:940510 Married status : Married General history Chief Complain : bilateral ovarian cyst incidentally being found out during pap smear. Present Illness
General history Basic Data : Age :62y/o Date of admitted:940510 Married status : Married General history Chief Complain : bilateral ovarian cyst incidentally being found out during pap smear. Present Illness
Gynecologic Oncologist. Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Hormonal Therapy Immunotherapy. Cervical cancer
 Gynecologic Oncology Pre invasive vulvar, vaginal, & cervical disease Vulvar Cervical Endometrial Uterine Sarcoma Fallopian Tube Ovarian GTD Gynecologic Oncologist Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy
Gynecologic Oncology Pre invasive vulvar, vaginal, & cervical disease Vulvar Cervical Endometrial Uterine Sarcoma Fallopian Tube Ovarian GTD Gynecologic Oncologist Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy
Female Genital Tract Lab. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan
 Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
Pathology of Ovarian Tumours. Dr. Jyothi Ranganathan MD ( Path) AFMC Pune PDCC (Cytopathology) PGI Chandigarh
 Pathology of Ovarian Tumours Dr. Jyothi Ranganathan MD ( Path) AFMC Pune PDCC (Cytopathology) PGI Chandigarh Outline Incidence Risk factors Classification Pathology of tumours Tumour markers Prevention
Pathology of Ovarian Tumours Dr. Jyothi Ranganathan MD ( Path) AFMC Pune PDCC (Cytopathology) PGI Chandigarh Outline Incidence Risk factors Classification Pathology of tumours Tumour markers Prevention
Ovarian carcinoma classification. Robert A. Soslow, MD
 Ovarian carcinoma classification Robert A. Soslow, MD soslowr@mskcc.org WHO classification Serous Mucinous Endometrioid Clear cell Transitional Squamous Mixed epithelial Undifferentiated Introduction Rationale
Ovarian carcinoma classification Robert A. Soslow, MD soslowr@mskcc.org WHO classification Serous Mucinous Endometrioid Clear cell Transitional Squamous Mixed epithelial Undifferentiated Introduction Rationale
3 cell types in the normal ovary
 Ovarian tumors 3 cell types in the normal ovary Surface (coelomic epithelium) the origin of the great majority of ovarian tumors 90% of malignant ovarian tumors Totipotent germ cells Sex cord-stromal cells
Ovarian tumors 3 cell types in the normal ovary Surface (coelomic epithelium) the origin of the great majority of ovarian tumors 90% of malignant ovarian tumors Totipotent germ cells Sex cord-stromal cells
ACCME/Disclosures. Risk of Gyne Ca in HBOC. Molecular basis of HBOC. Hereditary Ovarian and Breast Cancer Syndrome
 Hereditary Ovarian and Breast Cancer Syndrome C. Blake Gilks, MD Dept of Pathology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia Blake.gilks@vch.ca The USCAP requires that anyone in a position
Hereditary Ovarian and Breast Cancer Syndrome C. Blake Gilks, MD Dept of Pathology Vancouver General Hospital University of British Columbia Blake.gilks@vch.ca The USCAP requires that anyone in a position
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017
 Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Mousa. Najat kayed &Renad Al-Awamleh. Nizar Alkhlaifat
 6 Mousa Najat kayed &Renad Al-Awamleh Nizar Alkhlaifat P a g e 1 This sheet written based on record 13 on website Cover slide( 95-117 ) No need to go back to slide FALLOPIAN TUBE PATHOLOGY In general fallopian
6 Mousa Najat kayed &Renad Al-Awamleh Nizar Alkhlaifat P a g e 1 This sheet written based on record 13 on website Cover slide( 95-117 ) No need to go back to slide FALLOPIAN TUBE PATHOLOGY In general fallopian
Mody. AIS vs. Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES: Ovarian Cancer
 GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES: Ovarian Cancer KRISTEN STARBUCK, MD ROSWELL PARK CANCER INSTITUTE DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY DIVISION OF GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY APRIL 19 TH, 2018 Objectives Basic Cancer Statistics Discuss
GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES: Ovarian Cancer KRISTEN STARBUCK, MD ROSWELL PARK CANCER INSTITUTE DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY DIVISION OF GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY APRIL 19 TH, 2018 Objectives Basic Cancer Statistics Discuss
Unexpected Gynecologic Findings at Laparotomy. Susan A. Davidson, MD University of Colorado, Denver School of Medicine
 Unexpected Gynecologic Findings at Laparotomy Susan A. Davidson, MD University of Colorado, Denver School of Medicine Adnexal Mass: Gyn Etiologies Uterine Leiomyomas Pregnancy Malignancy Tubal Pregnancy
Unexpected Gynecologic Findings at Laparotomy Susan A. Davidson, MD University of Colorado, Denver School of Medicine Adnexal Mass: Gyn Etiologies Uterine Leiomyomas Pregnancy Malignancy Tubal Pregnancy
Joseph Misdraji, M.D. GI pathology Unit Massachusetts General Hospital
 Joseph Misdraji, M.D. GI pathology Unit Massachusetts General Hospital jmisdraji@partners.org Low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm (LAMN) High-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm (HAMN) Adenocarcinoma
Joseph Misdraji, M.D. GI pathology Unit Massachusetts General Hospital jmisdraji@partners.org Low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm (LAMN) High-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm (HAMN) Adenocarcinoma
Case Scenario 1. Pathology report Specimen from mediastinoscopy Final Diagnosis : Metastatic small cell carcinoma with residual lymphatic tissue
 Case Scenario 1 Oncology Consult: Patient is a 51-year-old male with history of T4N3 squamous cell carcinoma of tonsil status post concurrent chemoradiation finished in October two years ago. He was hospitalized
Case Scenario 1 Oncology Consult: Patient is a 51-year-old male with history of T4N3 squamous cell carcinoma of tonsil status post concurrent chemoradiation finished in October two years ago. He was hospitalized
The Adnexal Mass. Handout NCUS 3/18/2017 Suzanne Dixon, MD
 The Adnexal Mass Handout NCUS 3/18/2017 Suzanne Dixon, MD Objectives: Pelvic mass differential Characteristics of the normal ovary Standard terminology for ovarian masses Benign vs. malignant features
The Adnexal Mass Handout NCUS 3/18/2017 Suzanne Dixon, MD Objectives: Pelvic mass differential Characteristics of the normal ovary Standard terminology for ovarian masses Benign vs. malignant features
Characterizing Adnexal Masses: Pearls and Pitfalls 20 th Annual Summer Practicum SCBT-MR Jackson Hole August 11, 2010
 Characterizing Adnexal Masses: Pearls and Pitfalls 20 th Annual Summer Practicum SCBT-MR Jackson Hole August 11, 2010 Evan S. Siegelman MD University of Pennsylvania Medical Center Adnexal Masses: Pearls
Characterizing Adnexal Masses: Pearls and Pitfalls 20 th Annual Summer Practicum SCBT-MR Jackson Hole August 11, 2010 Evan S. Siegelman MD University of Pennsylvania Medical Center Adnexal Masses: Pearls
Work up of a Pelvic Mass
 Work up of a Pelvic Mass Considerations from the north where primary care and CON clinic / GPO work interface Dr. Shannon Douglas, GPO Vanderhoof with support by Dr Margaret Smith and Dr. Ursula Lee Nov
Work up of a Pelvic Mass Considerations from the north where primary care and CON clinic / GPO work interface Dr. Shannon Douglas, GPO Vanderhoof with support by Dr Margaret Smith and Dr. Ursula Lee Nov
The Diagnostic Challenges of Low Grade and High Grade Tubo-Ovarian Serous Carcinomas. W Glenn McCluggage Belfast, Northern Ireland
 The Diagnostic Challenges of Low Grade and High Grade Tubo-Ovarian Serous Carcinomas W Glenn McCluggage Belfast, Northern Ireland Enterprise Interest None OVARIAN SEROUS CARCINOMA (OSC) RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
The Diagnostic Challenges of Low Grade and High Grade Tubo-Ovarian Serous Carcinomas W Glenn McCluggage Belfast, Northern Ireland Enterprise Interest None OVARIAN SEROUS CARCINOMA (OSC) RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
Low-grade serous neoplasia. Robert A. Soslow, MD
 Low-grade serous neoplasia Robert A. Soslow, MD soslowr@mskcc.org Outline Orientation Ovarian tumor overview Non serous borderline tumors Serous borderline tumors Clinical summary Morphologic description
Low-grade serous neoplasia Robert A. Soslow, MD soslowr@mskcc.org Outline Orientation Ovarian tumor overview Non serous borderline tumors Serous borderline tumors Clinical summary Morphologic description
Pathology of the female genital tract
 Pathology of the female genital tract Common illnesses of the female genital tract Before menarche Developmental anomalies Tumors (ovarial teratoma) Amenorrhea Fertile years PCOS, ovarian cysts Endometriosis
Pathology of the female genital tract Common illnesses of the female genital tract Before menarche Developmental anomalies Tumors (ovarial teratoma) Amenorrhea Fertile years PCOS, ovarian cysts Endometriosis
Section 1. Biology of gynaecological cancers: our current understanding
 Section 1 Biology of gynaecological cancers: our current understanding Chapter 1 Morphological sub-types of ovarian carcinoma: new developments and pathogenesis W Glenn McCluggage 1 Introduction In most
Section 1 Biology of gynaecological cancers: our current understanding Chapter 1 Morphological sub-types of ovarian carcinoma: new developments and pathogenesis W Glenn McCluggage 1 Introduction In most
Triage of Ovarian Masses. Andreas Obermair Brisbane
 Triage of Ovarian Masses Andreas Obermair Brisbane Why Triage? In ovarian cancer, best outcomes for patients can be achieved when patients are treated in tertiary centres by a multidisciplinary team led
Triage of Ovarian Masses Andreas Obermair Brisbane Why Triage? In ovarian cancer, best outcomes for patients can be achieved when patients are treated in tertiary centres by a multidisciplinary team led
Ovarian Tumors. Andrea Hayes-Jordan MD FACS, FAAP Section Chief, Pediatric Surgery/Surgical Onc. UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 Ovarian Tumors Andrea Hayes-Jordan MD FACS, FAAP Section Chief, Pediatric Surgery/Surgical Onc. UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Case 13yo female with abdominal pain Ultrasound shows huge ovarian mass Surgeon
Ovarian Tumors Andrea Hayes-Jordan MD FACS, FAAP Section Chief, Pediatric Surgery/Surgical Onc. UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Case 13yo female with abdominal pain Ultrasound shows huge ovarian mass Surgeon
NAACCR Webinar Series 1 Q&A. Fabulous Prizes. Collecting Cancer Data: Ovary 11/3/2011. Collecting Cancer Data: Ovary
 NAACCR 2011 2012 Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data: Ovary Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
NAACCR 2011 2012 Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data: Ovary Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
6/5/2010. Outline of Talk. Endometrial Alterations That Mimic Cancer & Vice Versa: Metaplastic / reactive changes. Problems in Biopsies/Curettages
 Outline of Talk Endometrial Alterations That Mimic Cancer & Vice Versa: Problems in Biopsies/Curettages Metaplastic / reactive changes Mucinous change Microglandular hyperplasia-like change Squamous metaplasia
Outline of Talk Endometrial Alterations That Mimic Cancer & Vice Versa: Problems in Biopsies/Curettages Metaplastic / reactive changes Mucinous change Microglandular hyperplasia-like change Squamous metaplasia
UTERINE SARCOMA EXAMPLE OF A UTERINE SARCOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE
 UTERINE SARCOMA EXAMPLE OF A UTERINE SARCOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Adenosarcoma with heterologous elements and stromal overgrowth o TAH, BSO, omentectomy, staging biopsies of cul-de-sac, bladder
UTERINE SARCOMA EXAMPLE OF A UTERINE SARCOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Adenosarcoma with heterologous elements and stromal overgrowth o TAH, BSO, omentectomy, staging biopsies of cul-de-sac, bladder
OVARIES. MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L13 Dr: Ali Eltayb.
 OVARIES MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L13 Dr: Ali Eltayb. OBJECTIVES Recognize different disease of ovaries Classify ovarian cyst Describe the pathogenesis, morphology
OVARIES MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L13 Dr: Ali Eltayb. OBJECTIVES Recognize different disease of ovaries Classify ovarian cyst Describe the pathogenesis, morphology
Case Scenario 1. 1/2/13 History: 64-year-old white female presented with right leg swelling and redness, abdominal pain.
 Case Scenario 1 1/2/13 History: 64-year-old white female presented with right leg swelling and redness, abdominal pain. 1/02/13 CT Abdomen/Pelvis: Abnormal area of nodular mesenteric and left anterior
Case Scenario 1 1/2/13 History: 64-year-old white female presented with right leg swelling and redness, abdominal pain. 1/02/13 CT Abdomen/Pelvis: Abnormal area of nodular mesenteric and left anterior
Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust Ovarian Endometrial Vulvo-vaginal Cervical Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford
Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust Ovarian Endometrial Vulvo-vaginal Cervical Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم. Prof soha Talaat
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CA 125. Learning Outcomes
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CA 125 Learning Outcomes Upon completion of this exercise, participants will be able to: discuss the use of CA 125 levels in monitoring patients undergoing treatment for ovarian
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CA 125 Learning Outcomes Upon completion of this exercise, participants will be able to: discuss the use of CA 125 levels in monitoring patients undergoing treatment for ovarian
Survival Analysis and Prognosis for Patients with Serous and Mucinous Borderline Ovarian Tumors: 14-Year Experience from a Tertiary Center in Iran
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Survival Analysis and Prognosis for Patients with Serous and Mucinous Borderline Ovarian Tumors: 14-Year Experience from a Tertiary Center in Iran Katayoun Ziari, Ebrahim Soleymani, and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Survival Analysis and Prognosis for Patients with Serous and Mucinous Borderline Ovarian Tumors: 14-Year Experience from a Tertiary Center in Iran Katayoun Ziari, Ebrahim Soleymani, and
 DIAGNOSIS A. RIGHT OVARY: Krukenberg tumor (20 cm in maximum dimension, see comment). B. LEFT OVARY: Krukenberg tumor (8.5 cm in maximum dimension, see comment). C. UTERUS (130 Grams): Cervix: Metastatic
DIAGNOSIS A. RIGHT OVARY: Krukenberg tumor (20 cm in maximum dimension, see comment). B. LEFT OVARY: Krukenberg tumor (8.5 cm in maximum dimension, see comment). C. UTERUS (130 Grams): Cervix: Metastatic
Current Concept in Ovarian Carcinoma: Pathology Perspectives
 Current Concept in Ovarian Carcinoma: Pathology Perspectives Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine Current Concept in Ovarian
Current Concept in Ovarian Carcinoma: Pathology Perspectives Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine Current Concept in Ovarian
Wendy L Frankel. Chair and Distinguished Professor
 1 Wendy L Frankel Chair and Distinguished Professor Case 1 59 y/o woman Abdominal pain No personal or family history of cancer History of colon polyps Colonoscopy Polypoid rectosigmoid mass Biopsy 3 4
1 Wendy L Frankel Chair and Distinguished Professor Case 1 59 y/o woman Abdominal pain No personal or family history of cancer History of colon polyps Colonoscopy Polypoid rectosigmoid mass Biopsy 3 4
Institute of Pathology First Faculty of Medicine Charles University. Ovary
 Ovary Barrett esophagus ph in vagina between 3.8 and 4.5 ph of stomach varies from 1-2 (hydrochloric acid) up to 4-5 BE probably results from upward migration of columnar cells from gastroesophageal junction
Ovary Barrett esophagus ph in vagina between 3.8 and 4.5 ph of stomach varies from 1-2 (hydrochloric acid) up to 4-5 BE probably results from upward migration of columnar cells from gastroesophageal junction
Epithelial Ovarian Cancer 8/2/2013. Tu-be or Not Tu-be: Is the Fallopian Tube the Source of Ovarian Cancer?
 Tu-be or Not Tu-be: Is the Fallopian Tube the Source of Ovarian Cancer? Ann E. Smith Sehdev, MD Director, Center for Gynecologic Pathology Cascade Pathology, Portland, Oregon Ann E. Smith Sehdev has no
Tu-be or Not Tu-be: Is the Fallopian Tube the Source of Ovarian Cancer? Ann E. Smith Sehdev, MD Director, Center for Gynecologic Pathology Cascade Pathology, Portland, Oregon Ann E. Smith Sehdev has no
The relative frequency and histopathological patterns of ovarian lesions: study of 116 cases
 Original article: The relative frequency and histopathological patterns of ovarian lesions: study of 116 cases Dr Dimple Mehta*,Dr Alpesh Chavda**, Dr Hetal Patel*** *Assistant Professor, **Tutor, ***3
Original article: The relative frequency and histopathological patterns of ovarian lesions: study of 116 cases Dr Dimple Mehta*,Dr Alpesh Chavda**, Dr Hetal Patel*** *Assistant Professor, **Tutor, ***3
CA125 in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer: the art in medicine
 CA125 in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer: the art in medicine Dr Marcia Hall Consultant Medical Oncology Mount Vernon Cancer Centre Hillingdon Hospital Wexham Park Hospital Epidemiology Ovarian cancer
CA125 in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer: the art in medicine Dr Marcia Hall Consultant Medical Oncology Mount Vernon Cancer Centre Hillingdon Hospital Wexham Park Hospital Epidemiology Ovarian cancer
Article begins on next page
 Pseudopapillary Granulosa Cell Tumor: A Case of This Rare Subtype Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/50622/story/]
Pseudopapillary Granulosa Cell Tumor: A Case of This Rare Subtype Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/50622/story/]
Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Question 1. Each of the following statements about cervical adenocarcinoma is true except: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix SAMS a) A majority of women with cervical adenocarcinoma have stage I tumors at diagnosis.
Question 1. Each of the following statements about cervical adenocarcinoma is true except: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix SAMS a) A majority of women with cervical adenocarcinoma have stage I tumors at diagnosis.
GENERAL DATA. Sex : female Age : 40 years old Marriage status : married
 GENERAL DATA Sex : female Age : 40 years old Marriage status : married CHIEF COMPLAINT Bilateral ovarian tumors discovered by sonography accidentally PRESENT ILLNESS 2003-06-26 :bilateral ovarian tumors
GENERAL DATA Sex : female Age : 40 years old Marriage status : married CHIEF COMPLAINT Bilateral ovarian tumors discovered by sonography accidentally PRESENT ILLNESS 2003-06-26 :bilateral ovarian tumors
L/O/G/O. Ovarian Tumor. Xiaoyu Niu Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Sichuan University West China Second Hospital
 L/O/G/O Ovarian Tumor Xiaoyu Niu Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Sichuan University West China Second Hospital Essentials classification of ovarian tumor clinical manifestation of ovarian tumor metastatic
L/O/G/O Ovarian Tumor Xiaoyu Niu Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Sichuan University West China Second Hospital Essentials classification of ovarian tumor clinical manifestation of ovarian tumor metastatic
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
Case Scenario 1. 1/2/13 History: 64-year-old white female presented with right leg swelling and redness, abdominal pain.
 Case Scenario 1 1/2/13 History: 64-year-old white female presented with right leg swelling and redness, abdominal pain. 1/02/13 CT Abdomen/Pelvis: Abnormal area of nodular mesenteric and left anterior
Case Scenario 1 1/2/13 History: 64-year-old white female presented with right leg swelling and redness, abdominal pain. 1/02/13 CT Abdomen/Pelvis: Abnormal area of nodular mesenteric and left anterior
Q: In order to use the code 8461/3 (serous surface papillary) for ovary, does it have to say the term "surface" on the path report?
 Q&A Session for Collecting Cancer Data: Ovary Q: In order to use the code 8461/3 (serous surface papillary) for ovary, does it have to say the term "surface" on the path report? A: We reviewed both the
Q&A Session for Collecting Cancer Data: Ovary Q: In order to use the code 8461/3 (serous surface papillary) for ovary, does it have to say the term "surface" on the path report? A: We reviewed both the
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007
 International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
IMMATURE TERATOMA: SURGICAL TREATMENT
 CARAVAGGIO 10-12 MAGGIO 2010 IMMATURE TERATOMA: SURGICAL TREATMENT G. Mangili, E. Garavaglia, C. Sigismondi R VIGANO Dipartimento Materno Infantile, UF Ginecologia Oncologica IRCCS San Raffaele Milano
CARAVAGGIO 10-12 MAGGIO 2010 IMMATURE TERATOMA: SURGICAL TREATMENT G. Mangili, E. Garavaglia, C. Sigismondi R VIGANO Dipartimento Materno Infantile, UF Ginecologia Oncologica IRCCS San Raffaele Milano
Bibliography. Serous Tumors of the Ovary. Nomenclature
 Bibliography Serous Tumors of the Ovary Nomenclature 1. Allison KH, Swisher EM, Kerkering KM, et al. Defining an appropriate threshold for the diagnosis of serous borderline tumor of the ovary: when is
Bibliography Serous Tumors of the Ovary Nomenclature 1. Allison KH, Swisher EM, Kerkering KM, et al. Defining an appropriate threshold for the diagnosis of serous borderline tumor of the ovary: when is
Bladder Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT. Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT)
 Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
4/12/2018. MUSC Pathology Symposium Kiawah Island April 18, Jesse K. McKenney, MD
 MUSC Pathology Symposium Kiawah Island April 18, 2018 Jesse K. McKenney, MD 1 Urothelial Carcinoma with Alternative Differentiation 2 Urothelial Carcinoma with Alternative Differentiation Recognition as
MUSC Pathology Symposium Kiawah Island April 18, 2018 Jesse K. McKenney, MD 1 Urothelial Carcinoma with Alternative Differentiation 2 Urothelial Carcinoma with Alternative Differentiation Recognition as
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE
 Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
Pre-operative assessment of patients for cytoreduction and HIPEC
 Pre-operative assessment of patients for cytoreduction and HIPEC Washington Hospital Center Washington, DC, USA Ovarian Cancer Surgery New Strategies Bergamo, Italy May 5, 2011 Background Cytoreductive
Pre-operative assessment of patients for cytoreduction and HIPEC Washington Hospital Center Washington, DC, USA Ovarian Cancer Surgery New Strategies Bergamo, Italy May 5, 2011 Background Cytoreductive
OVARIAN CARCINOMA Immune Therapy. Antibodies to CA-125 (Ovarex) Vaccine therapy
 OVARIAN CARCINOMA Immune Therapy Antibodies to CA-125 (Ovarex) Vaccine therapy OVARIAN CARCINOMA Targeted Therapy Bevacizumab (Avastin): GOG- 218 Anti-VEGF, angiogenesis inhibitor TLK 286 (Telcyta): Glutathione
OVARIAN CARCINOMA Immune Therapy Antibodies to CA-125 (Ovarex) Vaccine therapy OVARIAN CARCINOMA Targeted Therapy Bevacizumab (Avastin): GOG- 218 Anti-VEGF, angiogenesis inhibitor TLK 286 (Telcyta): Glutathione
David Nunns on behalf of the Gynae Guidelines Group Date:
 Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Borderline tumours of the ovary management and follow-up Author: Contact Name and Job Title Directorate & Speciality
Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Borderline tumours of the ovary management and follow-up Author: Contact Name and Job Title Directorate & Speciality
Gynaecological Malignancies
 Gynaecological Malignancies Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Overview Genital tract tumors
Gynaecological Malignancies Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Overview Genital tract tumors
Clinical History USCAP Specialty Conference. Gynecologic Pathology Case 3
 2010 USCA Specialty Conference Gynecologic athology Case Kathleen R. Cho, M.D. Department of athology Clinical History 46 yo woman presented with bilateral ovarian masses and elevated CA-125 TAH/BSO, pelvic
2010 USCA Specialty Conference Gynecologic athology Case Kathleen R. Cho, M.D. Department of athology Clinical History 46 yo woman presented with bilateral ovarian masses and elevated CA-125 TAH/BSO, pelvic
See the latest estimates for new cases of ovarian cancer and deaths in the US and what research is currently being done.
 About Ovarian Cancer Overview and Types If you have been diagnosed with ovarian cancer or are worried about it, you likely have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to start. What Is
About Ovarian Cancer Overview and Types If you have been diagnosed with ovarian cancer or are worried about it, you likely have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to start. What Is
Patient Presentation. 32 y.o. female complains of lower abdominal mass CEA = 433, CA125 = 201
 Patient Presentation 32 y.o. female complains of lower abdominal mass CEA = 433, CA125 = 201 CT shows: Thickening of the right hemidiaphragm CT shows: Fluid in the right paracolic sulcus CT shows: Large
Patient Presentation 32 y.o. female complains of lower abdominal mass CEA = 433, CA125 = 201 CT shows: Thickening of the right hemidiaphragm CT shows: Fluid in the right paracolic sulcus CT shows: Large
Borderline Ovarian Tumours. Andreas Obermair Brisbane
 Borderline Ovarian Tumours Andreas Obermair Brisbane Definition First described in 1929 Cellular features of malignancy Cellular atypia Mitotic activity No stromal invasion An entity per se??? (or precursor
Borderline Ovarian Tumours Andreas Obermair Brisbane Definition First described in 1929 Cellular features of malignancy Cellular atypia Mitotic activity No stromal invasion An entity per se??? (or precursor
Endosalpingiosis. Case report
 Case report Endosalpingiosis Michael D. Holmes, M.D. Howard S. Levin M.D. Department of Pathology Lester A. Ballard, Jr., M.D. Department of Gynecology Endosalpingiosis, a term referring to tuballike epithelium
Case report Endosalpingiosis Michael D. Holmes, M.D. Howard S. Levin M.D. Department of Pathology Lester A. Ballard, Jr., M.D. Department of Gynecology Endosalpingiosis, a term referring to tuballike epithelium
Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory.
 Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory. Nội mạc tử cung Nội mạc tử cung Cyclic changes in endometrium.. Approximate relationship of useful microscopic changes. Arias-Stella reaction in endometrial
Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory. Nội mạc tử cung Nội mạc tử cung Cyclic changes in endometrium.. Approximate relationship of useful microscopic changes. Arias-Stella reaction in endometrial
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Case # 4 Low-Grade Serous Carcinoma (Macropapillary) of the Ovary Arising in an Atypical Proliferative Serous Tumor
 Case # 4 Low-Grade Serous Carcinoma (Macropapillary) of the Ovary Arising in an Atypical Proliferative Serous Tumor Robert J Kurman, M.D. Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Case History A 53 year
Case # 4 Low-Grade Serous Carcinoma (Macropapillary) of the Ovary Arising in an Atypical Proliferative Serous Tumor Robert J Kurman, M.D. Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Case History A 53 year
Gestione dei tumori borderline iniziali e avanzati nelle donne in età fertile
 Gestione dei tumori borderline iniziali e avanzati nelle donne in età fertile Pierandrea De Iaco pierandrea.deiaco@aosp.bo.it SSD ONCOLOGIA GINECOLOGICA AOU SANT ORSOLA-MALPIGHI BOLOGNA Borderline ovarian
Gestione dei tumori borderline iniziali e avanzati nelle donne in età fertile Pierandrea De Iaco pierandrea.deiaco@aosp.bo.it SSD ONCOLOGIA GINECOLOGICA AOU SANT ORSOLA-MALPIGHI BOLOGNA Borderline ovarian
Proliferative Breast Disease: implications of core biopsy diagnosis. Proliferative Breast Disease
 Proliferative Breast Disease: implications of core biopsy diagnosis Jean F. Simpson, M.D. Breast Pathology Consultants, Inc. Nashville, TN Proliferative Breast Disease Must be interpreted in clinical and
Proliferative Breast Disease: implications of core biopsy diagnosis Jean F. Simpson, M.D. Breast Pathology Consultants, Inc. Nashville, TN Proliferative Breast Disease Must be interpreted in clinical and
05/07/2018. Types of challenges. Challenging cases in uterine pathology. Case 1 ` 65 year old female Post menopausal bleeding Uterine Polyp
 Types of challenges Challenging cases in uterine pathology Nafisa Wilkinson Gynaecological Pathologist UCLH London Lack of complete history often, NO clinical history at all! Cases from other centres often
Types of challenges Challenging cases in uterine pathology Nafisa Wilkinson Gynaecological Pathologist UCLH London Lack of complete history often, NO clinical history at all! Cases from other centres often
Case 3 - GYN. History: 66 year old, routine Pap test. Dr. Stelow
 Case 3 - GYN History: 66 year old, routine Pap test Dr. Stelow Case 3 66 year year old woman Routine Pap Test Cytologic Features 3 dimensional clusters of cells with small to moderate amount of
Case 3 - GYN History: 66 year old, routine Pap test Dr. Stelow Case 3 66 year year old woman Routine Pap Test Cytologic Features 3 dimensional clusters of cells with small to moderate amount of
A Serous Borderline Tumor of the Fallopian Tube Detected Incidentally
 A Serous Borderline Tumor of the Fallopian Tube Detected Incidentally Imrana Tanvir, Ghania Ali, Haseeb Ahmed Khan and Ahmed Nasir Hanifi* Dept. of Histopathology, FMH College of Medicine & Dentistry,
A Serous Borderline Tumor of the Fallopian Tube Detected Incidentally Imrana Tanvir, Ghania Ali, Haseeb Ahmed Khan and Ahmed Nasir Hanifi* Dept. of Histopathology, FMH College of Medicine & Dentistry,
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX Site Group: Gynecology Cervix Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING AND
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX Site Group: Gynecology Cervix Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING AND
Immunohistochemistry on Fluid Specimens: Technical Considerations
 Immunohistochemistry on Fluid Specimens: Technical Considerations Blake Gilks Dept of Pathology University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada Disclosures None Learning Objectives At the end of
Immunohistochemistry on Fluid Specimens: Technical Considerations Blake Gilks Dept of Pathology University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada Disclosures None Learning Objectives At the end of
2/24/19. Ovarian pathology: IOTA ADNEXAL MASSES. Content. IOTA terms for description of an adnexal mass. IOTA terms for description of an adnexal mass
 Content Ovarian pathology: IOTA ADNEXAL MASSES X SIMPLE COMPLEX Dr DESCRIBE WHAT YOU SEE FRANZCOG, MPH, DDU, COGU Sonologist Clinically useful Benign Malignant Communication between clinicians/research
Content Ovarian pathology: IOTA ADNEXAL MASSES X SIMPLE COMPLEX Dr DESCRIBE WHAT YOU SEE FRANZCOG, MPH, DDU, COGU Sonologist Clinically useful Benign Malignant Communication between clinicians/research
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University
 objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
TUMOR AND TUMOR-LIKE CONDITIONS OF THE PERITONEUM AND OMENTUM/MESENTERY 40 th. Annual Meeting SCBTMR September 9-13, 2017, Nashville, Tennessee
 TUMOR AND TUMOR-LIKE CONDITIONS OF THE PERITONEUM AND OMENTUM/MESENTERY 40 th. Annual Meeting SCBTMR September 9-13, 2017, Nashville, Tennessee Isaac R Francis University of Michigan Department of Radiology
TUMOR AND TUMOR-LIKE CONDITIONS OF THE PERITONEUM AND OMENTUM/MESENTERY 40 th. Annual Meeting SCBTMR September 9-13, 2017, Nashville, Tennessee Isaac R Francis University of Michigan Department of Radiology
Icd 10 ovarian stroma
 Icd 10 ovarian stroma Struma ovarii; Micrograph of a struma ovarii. Characteristic thyroid follicles are seen on the right, and ovarian stroma on the left. H&E stain. Classification and. Free, official
Icd 10 ovarian stroma Struma ovarii; Micrograph of a struma ovarii. Characteristic thyroid follicles are seen on the right, and ovarian stroma on the left. H&E stain. Classification and. Free, official
A Practical Approach to Adnexal Masses
 A Practical Approach to Adnexal Masses Darcy J. Wolfman, MD Section Chief of Genitourinary Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Clinical Associate Johns Hopkins Community Radiology Division
A Practical Approach to Adnexal Masses Darcy J. Wolfman, MD Section Chief of Genitourinary Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Clinical Associate Johns Hopkins Community Radiology Division
Gynecologic Cancer Surveillance and Survivorship: Informing Practice and Policy
 Gynecologic Cancer Surveillance and Survivorship: Informing Practice and Policy Stephanie Yap, M.D. University Gynecologic Oncology Northside Cancer Institute Our Learning Objectives Review survival rates,
Gynecologic Cancer Surveillance and Survivorship: Informing Practice and Policy Stephanie Yap, M.D. University Gynecologic Oncology Northside Cancer Institute Our Learning Objectives Review survival rates,
Ovarian Lesion Benign vs Malignant?
 Ovarian Lesion Benign vs Malignant? Michele Keenan 1,2 Bernice Dunne 2 Mary Moran 1 Therese Herlihy 1 1. Radiography and Diagnostic Imaging, School of Medicine, University College Dublin, Ireland 2. Midland
Ovarian Lesion Benign vs Malignant? Michele Keenan 1,2 Bernice Dunne 2 Mary Moran 1 Therese Herlihy 1 1. Radiography and Diagnostic Imaging, School of Medicine, University College Dublin, Ireland 2. Midland
Ovarian Cancer What you need to know
 Ovarian Cancer What you need to know www.ovarian.org.uk Contents Your body and your ovaries What is ovarian cancer? Your body and your ovaries 3 What is ovarian cancer? 3 Not one disease, but many 4 The
Ovarian Cancer What you need to know www.ovarian.org.uk Contents Your body and your ovaries What is ovarian cancer? Your body and your ovaries 3 What is ovarian cancer? 3 Not one disease, but many 4 The
PRIMARY ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE FALLOPIAN TUBE - A CASE REPORT
 PRIMARY ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE FALLOPIAN TUBE - A CASE REPORT MANDAKINI BT, HAKEEM A, RAJASHREE P, SHAGUFTA R, PATTANKAR VL DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY & OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY KHAJA BANDANAWAZ INSTITUTE
PRIMARY ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE FALLOPIAN TUBE - A CASE REPORT MANDAKINI BT, HAKEEM A, RAJASHREE P, SHAGUFTA R, PATTANKAR VL DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY & OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY KHAJA BANDANAWAZ INSTITUTE
Hitting the High Points Gynecologic Oncology Review
 Hitting the High Points is designed to cover exam-based material, from preinvasive neoplasms of the female genital tract to the presentation, diagnosis and treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and
Hitting the High Points is designed to cover exam-based material, from preinvasive neoplasms of the female genital tract to the presentation, diagnosis and treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and
H&E, IHC anti- Cytokeratin
 Cat No: OVC2281 - Ovary cancer tissue array Lot# Cores Size Cut Format QA/QC OVC228101 228 1.1mm 4um 12X19 H&E, IHC anti- Cytokeratin Recommended applications: For Research use only. RNA or protein ovary
Cat No: OVC2281 - Ovary cancer tissue array Lot# Cores Size Cut Format QA/QC OVC228101 228 1.1mm 4um 12X19 H&E, IHC anti- Cytokeratin Recommended applications: For Research use only. RNA or protein ovary
Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography with color doppler imaging techniques in adnexal masses and correlation with histopathological analysis
 Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography with color doppler imaging techniques in adnexal masses and correlation with histopathological analysis Neha Gupta 1*, Poonam Gupta 2, Omvati Gupta
Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography with color doppler imaging techniques in adnexal masses and correlation with histopathological analysis Neha Gupta 1*, Poonam Gupta 2, Omvati Gupta
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Page # 1. Endometrium. Cellular Components. Anatomical Regions. Management of SIL Thomas C. Wright, Jr. Most common diseases:
 Endometrium Pathology of the Endometrium Thomas C. Wright Columbia University, New York, NY Most common diseases: Abnormal uterine bleeding Inflammatory conditions Benign neoplasms Endometrial cancer Anatomical
Endometrium Pathology of the Endometrium Thomas C. Wright Columbia University, New York, NY Most common diseases: Abnormal uterine bleeding Inflammatory conditions Benign neoplasms Endometrial cancer Anatomical
Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions
 Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies
 Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
CPC 4 Breast Cancer. Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast.
 CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES
 DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON Case 1 43 year-old female,
DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON Case 1 43 year-old female,
Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma
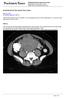 May 26, 2011 By Sushila Ladumor, MD [1] Endometrial stromal sarcoma (ESS) is a rare malignant tumor of the endometrium, occurring in the age group of 40-50 years. History The 50-year-old, female patient
May 26, 2011 By Sushila Ladumor, MD [1] Endometrial stromal sarcoma (ESS) is a rare malignant tumor of the endometrium, occurring in the age group of 40-50 years. History The 50-year-old, female patient
04/10/2018. Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast INTRADUCTAL PAPILLOMA
 Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
New Developments in Immunohistochemistry for Gynecologic Pathology
 New Developments in Immunohistochemistry for Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Gynecologic Oncology Immunohistochemistry in Gynecologic Pathology Majority
New Developments in Immunohistochemistry for Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Gynecologic Oncology Immunohistochemistry in Gynecologic Pathology Majority
Gynaecological Oncology Cases
 Gynaecological Oncology Cases 1. Tamoxifen and the endometrium 2. Cancer and the older woman Dr Julie M Lamont Consultant Gynaecological Oncologist Epworth Freemasons Hospital 21 st April 2015 Mrs FS 66
Gynaecological Oncology Cases 1. Tamoxifen and the endometrium 2. Cancer and the older woman Dr Julie M Lamont Consultant Gynaecological Oncologist Epworth Freemasons Hospital 21 st April 2015 Mrs FS 66
