(From the Department of Public Health and Laboratory Diagnosis, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver)
|
|
|
- Myron Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Published Online: September, 944 Supp Info: Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November, 08 HEATOLOGICAL INDINGS IN THE GOLDEN HASTER (CRICETUS AURATUS) BY ABEL O, STEWART, LLOYD LORIO,.D., Am) EDWARD R. UGR~G]~,.D. (rom the Department of Public Health and Laboratory Diagnosis, University of Colorado School of edicine, Denver) (Received for publication, ay, 944) During the course of experimental work on the transmission of Colorado tick fever to the golden or Syrian hamster (Cricetus auratus), we found it neces- sary to know the normal blood picture of this animal. Since we could find no data in the literature concerning the blood elements of this rodent, we established the normal values with our own colony of hamsters. The colony, which was started from males and 3 females, x was kept in a separate animal room at an altitude of approximately 5,300 feet. The hamsters were freely given Purina rabbit chow, outside leaves of lettuce, and water, as well as whole corn kernels when available and a small number of Purina checkers. The hamsters were weaned when they were 4 weeks old and the separate sexes housed in wire cages in groups of to 0 animals. Separate cages were maintained for breeding purposes. One hundred and fourteen previously unused animals of both sexes and various ages were studied. The blood was obtained by cardiac puncture after several fruitless attempts to bleed other individuals by slitting the ear and clipping the small, blunt tail. The hamster was placed in a covered glass jar and enough ethyl chloride given to induce a light anesthesia. It was then immediately removed from the jar and anesthesia maintained with ether. A.0 cc. dry syringe with a short 3 G needle was used to obtain approximately 0.75 cc. of blood. The entire procedure from beginning of anesthesia to withdrawal of the blood never took more than minutes. Small shell vials were prepared containing a dried mixture of rag. of ammonium oxalate and 4 rag. of potassium oxalate. The blood from each animalwas immediately placed in one of these vials and mixed well. It was noted that coagulation began very quickly, and this large amount of anticoagulant was necessary to prevent clotting. All determinations were started within 30 minutes after obtaining the specimen. The bleeding was always done in the morning after the animals had settled down from the night% activities. ' Red and white blood cell dilutions were made in pipets which were known to be accurafe by check against Bureau of Standards pipets. Counts were done in duplicate allowing a discrepancy of not more than 00,000 cells for the red blood cell count and 500 cells per c. mm. for the white blood cell count, using a Bureau of Standards Neubauer counting chamber. The hemoglobin was determined in duplicate with a Klett modification of the Sahli instrument. This had been calibrated against the Van Slyke-Neill oxygen capacity method. Smith tubes were used for the determination of the volume of packed cells. The tubes were centrifugated for hour at 400 g.~.~r, before making the reading. Thin smears were made on slides and stained with Wright's stain by the usual technique. A hemogram of 300 cells was determined on each animal. The data are presented in Table I. There the animals are grouped by age and sex. The stock was obtained from r. Henry Bergman, Springfield, issouri. 89
2 90 I~ATOLOGICAL INDINGS IN TIlE GOLDEN HASTER Animal Sex Age No. TABLE I Hematological indings in 4 Normal Hamsters [.~. ~ P, '~., ~ ~ per per 00, enl " " ! " " " ( " C " " " " " 7.05' , ean ' tandarddeviation " ' " ' ".38~ ".9 7.3~ ~ " !48.0 5: " ' " !~ " " " i " Wean ! $tandarddeviation ! eanand 7.00!~ $tandarddeviation ~ ff " " " C " , " , " C 4, ,0.0 3 " , ".9 7, C " 7.0 8, "
3 . O. STEWART~ L. ]~LORIO~ AND. R. UGRAGE 9 TABLE I--C~inued Animal No ean. Standa
4 9 HEATOLOGICAL INDINGS IN THE GOLDEN HASTER TABLE I--Continued Animal No. ean. ean Standm ean ean. ean ]~ ean.
5 . O. STEWART, L. LORIO, AND E. R. 'UGRAGE 93 TABLE I--Convluded The standard error was determined for each sex within the age group, and wherever the difference between the means was less than 3 standard deviations, the data for the sexes were combined. The same technique was applied to the age groups. It will be seen from the table that the data on the sexes could be combined, while that on the different age groups could not be in all cases. Two types of polymorphonuclear neutrophils were seen, both appearing mature. The segmented form had or 3 divisions of the nucleus while the unsegmented form had a horse-shoe shaped or often a round doughnut-like nucleus. In each case the nucleus stained purple with a lilac-colored cytoplasm which was filled with small neutrophilic granules. Eosinophils had the same appearance except for the large, bright red granules. No basophils were seen. The lymphocytes were usually small with a dense, deep blue nucleus and a
6 ~.._ I mo$. - c~ c~ cc cc -4 I llg ~g ll lc ~g cc II II gl li ll 5-8 lc lc i and OVel c~ cc 4~ c~ TABLE II Size of Red Blood Cells in Hamsters Distribution of diameters icra 3.0 I II 3.. ~ ~ ] ~ s.3.0 " ] ] ] t ] ] 5 3 I 03] 58 ' 388] ] l ] ] ] ] ] ] i ] I i I ] 4 77, j t ] ! 9 95] Ii 5 ~ 4 3 7, 3 i I 4.8 I :
7 . O. STEWART, L. LORIO~ AND E. R. UGRAGE 95 very narrow band of light blue cytoplasm with a few cells containing fine azurophilic granules. The monocytes had a large, slightly indented nucleus with a stringy chromatin structure. The cytoplasm was a clear bright blue, with find red granules clumped in the indentation of the nucleus. In some cases there were large phagocytic cells. Their presence may depend on the heart chamber from which the blood was withdrawn (). They are included in the unclassified group of cells. The red blood cells are biconcave discs and take the acid stain. A few polychromatophilic cells were always present and occasionally a nucleated red blood cell was seen. ive hundred erythrocytes from different parts of a thin smear were measured on each of 4 animals using a euscope set-up as described by Andresen and ugrage (). These thin smears were the same ones used to determine the hemogram on the animals. The data are presented in Table II by age and sex. The slides on which these measurements were made were picked at random for each sex within each age group. The blood findings on each of these animals can be studied by referring to the corresponding numbers in Table I. A further experiment was carried out to determine the possible effect on the red blood cell size of the large amount of anticoagulant used. Six animals were bled from the heart in the usual way. Thin smears were made from small drops of blood directly from the needle without any anticoagulant. The remaining blood was immediately mixed with the dried oxalate from which smears were made within 30 minutes. The slides were subsequently stained and 500 cells on each smear with and without the anticoagulant were measured as described above. The results are shown in Table III. It will be seen that the average size of the cells in smears made directly from TABLE HI Comparison of Average Red Blood Cell Size with and "~tkout Anticoagulant Animal No. Without anticoagulant With anticoaguant Difference micra.8 micra micra Average... 0.
8 9 HEATOLOGICAL INDINGS IN THE GOLDEN HASTER the heart blood tended to be slightly larger than those collected in the oxalate mixture. The average shrinkage due to the anticoagulant is.5 per cent. This correction factor has not been applied to the cell volume as given in Table I nor to the red blood cell Size as~ given in Table II. SIY~ARY Values for hemoglobin, erythrocytes, volume of packed cells, leucocytes, and their distribution, and red blood cell diameter are presented as determined ona group of 4 hamsters of both sexes and of various ages. BIBLIOGRAPHY. Pattison, I. H., and ldiarmid, A., J. Path. and Bact., 943, lisp 7.., Andresen,. I., and ugrage, E. R., olia haematol., 938, ~ 0.
Blood DLC, Retic count, PCV, Hb and ESR. Dr. Tamara Alqudah
 Blood DLC, Retic count, PCV, Hb and ESR Dr. Tamara Alqudah Differential Leukocyte Count (DLC) There are 5 main types of WBCs: 1. Neutrophils: 40-80% 2. Eosinophils: 1-6 % 3. Basophils: < 1-2% 4. Lymphocytes:
Blood DLC, Retic count, PCV, Hb and ESR Dr. Tamara Alqudah Differential Leukocyte Count (DLC) There are 5 main types of WBCs: 1. Neutrophils: 40-80% 2. Eosinophils: 1-6 % 3. Basophils: < 1-2% 4. Lymphocytes:
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
1 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II PLATELETS. Mature Stage: No nucleus. Only 2-3 µm in diameter: significantly smaller than RBCs
 1 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II LAB BLOOD PLATES EOSINOPHIL Contains large red-staining granules Usually 2 lobes 12-17 µm: about the size of neutrophils (2X erythrocytes) regulation/reduction of Histamine.
1 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II LAB BLOOD PLATES EOSINOPHIL Contains large red-staining granules Usually 2 lobes 12-17 µm: about the size of neutrophils (2X erythrocytes) regulation/reduction of Histamine.
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
Blood: Functions. Liquid connective tissue 3 general functions 1. Transportation. 2. Regulation. 3. Protection
 Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Blood & Blood Formation
 Module IB Blood & Blood Formation Histology and Embryology Martin Špaček, MD (m.spacek@centrum.cz) http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/histologie Approximately 7% of a person's weight is blood (about 5 L) Blood consists
Module IB Blood & Blood Formation Histology and Embryology Martin Špaček, MD (m.spacek@centrum.cz) http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/histologie Approximately 7% of a person's weight is blood (about 5 L) Blood consists
LAB TIME/DATE. 1. most numerous leukocyte. 3. also called an erythrocyte; anucleate formed element. 6. ancestral cell of platelets
 ighapmlre29apg245_250 5/12/04 2:46 PM Page 245 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Blood LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise 29A Composition of Blood 1. What is the blood volume of an average-size
ighapmlre29apg245_250 5/12/04 2:46 PM Page 245 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Blood LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise 29A Composition of Blood 1. What is the blood volume of an average-size
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY
 BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs
 Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs Case History CMP-17 This urine sample is from a 48-year-old male with a 30-year history of diabetes mellitus and new onset renal failure. Laboratory data include:
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs Case History CMP-17 This urine sample is from a 48-year-old male with a 30-year history of diabetes mellitus and new onset renal failure. Laboratory data include:
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DIFFERENTIATING IMMATURE PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
temperature 38 o C (100.4 o F) The temperature of blood is slightly higher than the normal body temperature of 37 o C (98.6 o F).
 1 Chapter 1 Blood Definition -Blood is a type of connective tissue that consists of cells surrounded by a fluid extracellular matrix. -Blood, blood vessels, and the heart collectively form the cardiovascular
1 Chapter 1 Blood Definition -Blood is a type of connective tissue that consists of cells surrounded by a fluid extracellular matrix. -Blood, blood vessels, and the heart collectively form the cardiovascular
Chapter 14. Blood. Blood Volume. Blood Composition. Blood
 Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
Requirements: Glass slides Leishman stain Microscopes Disposable needles Vials containing anticoagulants Methylated-spirit Staining rack
 Aim: To make a blood smear and to count the different types of leucocytes present in a stained blood smear and express their relative counts in percentage Principle - The blood contains various types of
Aim: To make a blood smear and to count the different types of leucocytes present in a stained blood smear and express their relative counts in percentage Principle - The blood contains various types of
Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis
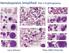 Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis Objectives are to: Identify the developmental cells of erythropoiesis
Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Hematopoiesis Simplified: Part 1 Erythropoiesis Objectives are to: Identify the developmental cells of erythropoiesis
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
Blood smear analysis in the emergency veterinary patient
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Blood smear analysis in the emergency veterinary patient Author : Ashley Wemple Categories : RVNs Date : April 1, 2010 Ashley
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Blood smear analysis in the emergency veterinary patient Author : Ashley Wemple Categories : RVNs Date : April 1, 2010 Ashley
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology
 Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Blood Cells. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Notes for the 2 nd histology lab
 Notes for the 2 nd histology lab Note : Please refer to the slides and see the morphological characteristics of each cell, as the practical exam will be in the form of figures. SLIDE #2 Erythropoiesis
Notes for the 2 nd histology lab Note : Please refer to the slides and see the morphological characteristics of each cell, as the practical exam will be in the form of figures. SLIDE #2 Erythropoiesis
Composition of Blood
 Blood is a connective tissue, specialized to transport the respiratory gasses as well as hormones, nutrients, and wastes, and the distribution of heat. The various cells of the blood perform specific functions.
Blood is a connective tissue, specialized to transport the respiratory gasses as well as hormones, nutrients, and wastes, and the distribution of heat. The various cells of the blood perform specific functions.
Continuous Cell Culture From a Patient With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. I. Propagation and Presence of Philadelphia Chromosome 1
 Continuous Cell Culture From a Patient With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. I. Propagation and Presence of Philadelphia Chromosome 1 LINDA S. LUCAS,2 JACQUELINE J. K..WHANG,3 J. H. TJIO,4 ROBERT A. MANAKER,2
Continuous Cell Culture From a Patient With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. I. Propagation and Presence of Philadelphia Chromosome 1 LINDA S. LUCAS,2 JACQUELINE J. K..WHANG,3 J. H. TJIO,4 ROBERT A. MANAKER,2
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Chapter 21 Outline. General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements
 Chapter 21 Outline General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements Introduction Blood serves many functions. Some examples
Chapter 21 Outline General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements Introduction Blood serves many functions. Some examples
The fluid medium (blood) is a highly specialized connective tissue that consists of various blood cells (formed elements) suspended in a fluid matrix
 Blood In Detail The fluid medium (blood) is a highly specialized connective tissue that consists of various blood cells (formed elements) suspended in a fluid matrix (blood plasma). The formed elements
Blood In Detail The fluid medium (blood) is a highly specialized connective tissue that consists of various blood cells (formed elements) suspended in a fluid matrix (blood plasma). The formed elements
Hemopoiesis and Blood
 Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
Hemopoiesis and Blood Blood Cells o o o Erythrocytes Leukocytes Thrombocytes Function o Transport nutrients and wastes throughout the bloodstream, fight foreign antigens and blood coagulation. Location
Practical Histology. Lab 3: Connective tissue
 Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
The % of blood consisting of packed RBCs is known as the hematocrit. Blood s color ranges from scarlet (oxygen-rich) to dark red (oxygen poor).
 Biology Blood Blood is a fluid connective tissue consisting of cells suspended in a liquid fibrous matrix. The cells are called formed elements and the liquid matrix is known as plasma. The formed elements
Biology Blood Blood is a fluid connective tissue consisting of cells suspended in a liquid fibrous matrix. The cells are called formed elements and the liquid matrix is known as plasma. The formed elements
Incorporating Differentials Into Every Complete Blood Count. Paige Flowers, LVT Dogwood Veterinary Internal Medicine
 Incorporating Differentials Into Every Complete Blood Count Paige Flowers, LVT Dogwood Veterinary Internal Medicine Complete Blood Count Diagnostic performed to evaluate the quantity and morphology of
Incorporating Differentials Into Every Complete Blood Count Paige Flowers, LVT Dogwood Veterinary Internal Medicine Complete Blood Count Diagnostic performed to evaluate the quantity and morphology of
Blood. Kris*ne Kra.s, M.D.
 Blood Kris*ne Kra.s, M.D. The most beau*ful thing we can experience is the mysterious. It is the source of all true art and science. - Albert Einstein Blood Lecture Objec*ves Be able to iden*fy and
Blood Kris*ne Kra.s, M.D. The most beau*ful thing we can experience is the mysterious. It is the source of all true art and science. - Albert Einstein Blood Lecture Objec*ves Be able to iden*fy and
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal 1 0.
 Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Blood and Haemopoiesis
 Blood and Haemopoiesis Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Connective Tissue Connective tissue proper Connective tissue with special properties Loose connective tissue Dense
Blood and Haemopoiesis Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Connective Tissue Connective tissue proper Connective tissue with special properties Loose connective tissue Dense
(From the Department of Public Health and Laboratory Diagnosis, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver)
 Published Online: September, Supp Info: http://doi.org/0.0/jem.0.. Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on September, 0 THE EXPERIMENTAL TRANSMISSION OF COLORADO TICK FEVER BY LLOYD FLORIO, M.D., MABEL O. STEWART,
Published Online: September, Supp Info: http://doi.org/0.0/jem.0.. Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on September, 0 THE EXPERIMENTAL TRANSMISSION OF COLORADO TICK FEVER BY LLOYD FLORIO, M.D., MABEL O. STEWART,
COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY
 CONTRIBUTOR NAME Daniel Heinrich, DVM CONTRIBUTOR EMAIL dheinric@umn.edu COAUTHORS Jed Overmann, DVM, DACVP; Davis Seelig DVM, PhD, DACVP & Matthew Sturos, DVM COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY University of Minnesota
CONTRIBUTOR NAME Daniel Heinrich, DVM CONTRIBUTOR EMAIL dheinric@umn.edu COAUTHORS Jed Overmann, DVM, DACVP; Davis Seelig DVM, PhD, DACVP & Matthew Sturos, DVM COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY University of Minnesota
PHLEBOTOMIST. person trained to draw blood from a patient for clinical or medical testing, transfusions, donations, or research.
 BLOOD PHLEBOTOMIST person trained to draw blood from a patient for clinical or medical testing, transfusions, donations, or research. Blood transports substances and maintains homeostasis in the body Hematophobia
BLOOD PHLEBOTOMIST person trained to draw blood from a patient for clinical or medical testing, transfusions, donations, or research. Blood transports substances and maintains homeostasis in the body Hematophobia
BLOOD. EEI n: t.ee# Required Name : Due : April 12,2018 COMPOSITION AND FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD. Beginningof Class
 t.ee# Required Name : Due : April 12,2018 Beginningof Class BLOOD Blood, the "life fluid" that courses through the body's blood vessels, provides the means by which the body's cells receive vital nutrients
t.ee# Required Name : Due : April 12,2018 Beginningof Class BLOOD Blood, the "life fluid" that courses through the body's blood vessels, provides the means by which the body's cells receive vital nutrients
BIOCHEMISTRY OF BLOOD
 BCH 471 BIOCHEMISTRY OF BLOOD Amal Alamri Experiment 1 Separation of Plasma and Serum from Whole Blood Whole Blood It is living tissue that circulates through the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries
BCH 471 BIOCHEMISTRY OF BLOOD Amal Alamri Experiment 1 Separation of Plasma and Serum from Whole Blood Whole Blood It is living tissue that circulates through the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries
Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz
 Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz Question Prompt: 1 Mononuclear white blood cells (agranulocyte) formed in lymph tissue, also a phagocyte and a precursor of macrophages are leukocytes. True False Question Prompt:
Blood Cells Med Terms Quiz Question Prompt: 1 Mononuclear white blood cells (agranulocyte) formed in lymph tissue, also a phagocyte and a precursor of macrophages are leukocytes. True False Question Prompt:
I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture.
 Name: Period: 10 Blood Study Guide I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture. 1. Composition and Function of Blood: 2. Hematopoiesis: 1 Miss School, Miss Out
Name: Period: 10 Blood Study Guide I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture. 1. Composition and Function of Blood: 2. Hematopoiesis: 1 Miss School, Miss Out
Agenda. Components of blood. Blood is Fluid Connective Tissue. Blood: General functions
 Agenda Chapter 19: Blood Major functions Major Components Structure of RBCs and WBCs ABO Blood Types, and Rh Factor Lab 34.1 and Blood Typing Blood: General functions Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients,
Agenda Chapter 19: Blood Major functions Major Components Structure of RBCs and WBCs ABO Blood Types, and Rh Factor Lab 34.1 and Blood Typing Blood: General functions Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients,
Blood ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
Blood ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
Formation of Blood Cells
 Hematopoiesis Lecture Objectives Name organs responsible for hematopoiesis in the fetus. List the developmental stages of hematopoiesis both prenatally and postnatally. Outline the major steps of post
Hematopoiesis Lecture Objectives Name organs responsible for hematopoiesis in the fetus. List the developmental stages of hematopoiesis both prenatally and postnatally. Outline the major steps of post
#2: BLOOD / HEMATOLOGY
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II. Lab #2: BLOOD / HEMATOLOGY For labs associated with Dr. Thompson s lectures References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II. Lab #2: BLOOD / HEMATOLOGY For labs associated with Dr. Thompson s lectures References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th
Blood ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
Hematopoie)c System. Kris)ne Kra2s, M.D.
 Hematopoie)c System Kris)ne Kra2s, M.D. Hematopoie)c System Lecture Objec)ves Describe the developmental stages of erythropoiesis. Describe the developmental stages of granulopoiesis. Describe the differences
Hematopoie)c System Kris)ne Kra2s, M.D. Hematopoie)c System Lecture Objec)ves Describe the developmental stages of erythropoiesis. Describe the developmental stages of granulopoiesis. Describe the differences
Blood. The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue. Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma
 Blood Blood The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma Blood Physical Characteristics of Blood Color range Oxygen-rich
Blood Blood The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma Blood Physical Characteristics of Blood Color range Oxygen-rich
MORPHOLOGY OF BONE MARROW ASPIRATES. Dr.Prasanna N Kumar Head Department of Pathology, Oman Medical College, Oman
 MORPHOLOGY OF BONE MARROW ASPIRATES Dr.Prasanna N Kumar Head Department of Pathology, Oman Medical College, Oman BONE MARROW ASPIRATION Sites Sternum Anterior or posterior iliac spines Aspiration from
MORPHOLOGY OF BONE MARROW ASPIRATES Dr.Prasanna N Kumar Head Department of Pathology, Oman Medical College, Oman BONE MARROW ASPIRATION Sites Sternum Anterior or posterior iliac spines Aspiration from
HEMOTOLOGY. B. Helps stabilize body temperature -heats up and cools down slowly which moderates body temp
 I. Body H 2 O = HEMOTOLOGY A. Variable quantities 1. sweating and urination ( ) decreases H 2 O 2. drinking H 2 O increases B. Water is found in two compartments 1. contains 2/3 of all water in your body
I. Body H 2 O = HEMOTOLOGY A. Variable quantities 1. sweating and urination ( ) decreases H 2 O 2. drinking H 2 O increases B. Water is found in two compartments 1. contains 2/3 of all water in your body
Blood Physiology. Rodolfo T. Rafael, M.D.,CFP
 Blood Physiology Rodolfo T. Rafael, M.D.,CFP http://clinical-updates.blogspot.com rtrafaelmd@gmail.com +639212147558 July 26, 2006 1 Blood Physiology General Consideration Plasma Cellular Elements of the
Blood Physiology Rodolfo T. Rafael, M.D.,CFP http://clinical-updates.blogspot.com rtrafaelmd@gmail.com +639212147558 July 26, 2006 1 Blood Physiology General Consideration Plasma Cellular Elements of the
G. Types of White Blood Cells
 1. White blood cells are also called leukocytes. G. Types of White Blood Cells 2. White blood cells function to protect against diseases. 3. Two hormones that stimulate white blood cell production are
1. White blood cells are also called leukocytes. G. Types of White Blood Cells 2. White blood cells function to protect against diseases. 3. Two hormones that stimulate white blood cell production are
COMPARISON OF THE HEMACYTOLOGICAI, CONSTITUTION OF MALE AND FEMALE RABBITS
 COMPARISON OF THE HEMACYTOLOGICAI, CONSTITUTION OF MALE AND FEMALE RABBITS BY PAUL D. ROSAHN, M.D., LOUISE PEARCE, M.D., AND CH'UAN-K'UEI HU, M.D. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for
COMPARISON OF THE HEMACYTOLOGICAI, CONSTITUTION OF MALE AND FEMALE RABBITS BY PAUL D. ROSAHN, M.D., LOUISE PEARCE, M.D., AND CH'UAN-K'UEI HU, M.D. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 2: Composition and Function of Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 2: Composition and Function of Lesson Objectives Upon completion
#2 - Hematology I Blood Typing
 #2 - Blood Typing Objectives: Learn the theory behind blood typing Be able to perform simulated blood typing and analysis Understand the theory behind blood transfusions (donors and recipients) Observe
#2 - Blood Typing Objectives: Learn the theory behind blood typing Be able to perform simulated blood typing and analysis Understand the theory behind blood transfusions (donors and recipients) Observe
Medical School Histology Basics. VIBS 289 lab. Blood
 Medical School Histology Basics VIBS 289 lab Blood Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Blood (definition and function) Blood - fluid tissue composed of erythrocytes (RBC), leukocytes (WBC), and platelets
Medical School Histology Basics VIBS 289 lab Blood Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Blood (definition and function) Blood - fluid tissue composed of erythrocytes (RBC), leukocytes (WBC), and platelets
Validation of the Efficacy of a Practical Method for Neutrophils Isolation from Peripheral Blood
 Validation of the Efficacy of a Practical Method for Neutrophils Isolation from Peripheral Blood JONATHAN DEGEL, MASIH SHOKRANI OBJECTIVE: The objectives of this study were to validate the Polymorphprep
Validation of the Efficacy of a Practical Method for Neutrophils Isolation from Peripheral Blood JONATHAN DEGEL, MASIH SHOKRANI OBJECTIVE: The objectives of this study were to validate the Polymorphprep
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood
 Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood vessels hematology = the
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood vessels hematology = the
five lineages of stem cells producing all of the various formed elements.
 Chapter 6 Blood Tissue 6.1. Basic Composition of Blood Blood is a connective tissue composed of free cells in a fluid matrix. Unlike other types of connective tissues, blood lacks fibers except during
Chapter 6 Blood Tissue 6.1. Basic Composition of Blood Blood is a connective tissue composed of free cells in a fluid matrix. Unlike other types of connective tissues, blood lacks fibers except during
The Anatomy and Physiology of the Circulatory System
 CHAPTER 5 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Circulatory System The Circulatory System Blood Heart Vascular System THE BLOOD Formed Elements of Blood Table 5-1 Cell Type Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells, RBCs)
CHAPTER 5 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Circulatory System The Circulatory System Blood Heart Vascular System THE BLOOD Formed Elements of Blood Table 5-1 Cell Type Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells, RBCs)
Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements
 Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements Plasma 55% of whole blood 90% water 8% proteins from liver 2% misc. Nutrients: AA, glucose, lipids vitamins, minerals Wastes: urea, uric acid, creatine, ammonium
Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements Plasma 55% of whole blood 90% water 8% proteins from liver 2% misc. Nutrients: AA, glucose, lipids vitamins, minerals Wastes: urea, uric acid, creatine, ammonium
Unit Seven Blood and Immunity
 Unit Seven Blood and Immunity I. Introduction A. Definition Blood is a sticky fluid that is heavier and thicker than water. Blood is a type of, whose cells and suspended in a liquid intercellular material.
Unit Seven Blood and Immunity I. Introduction A. Definition Blood is a sticky fluid that is heavier and thicker than water. Blood is a type of, whose cells and suspended in a liquid intercellular material.
Urine Sediment Photographs
 Urine Sediment Photographs Case History CMP-04 This urine sample is from a 35-year-old female as part of a routine exam. Laboratory data include: Specific Gravity = 1.015; ph = 7.0; ketones, glucose, protein,
Urine Sediment Photographs Case History CMP-04 This urine sample is from a 35-year-old female as part of a routine exam. Laboratory data include: Specific Gravity = 1.015; ph = 7.0; ketones, glucose, protein,
Capillary Action and Blood Components. Biology 20 Unit D: Body Systems Circulation
 Capillary Action and Blood Components Biology 20 Unit D: Body Systems Circulation 1 Remember. Capillaries are so small that blood cells can only pass through single file Important because they are the
Capillary Action and Blood Components Biology 20 Unit D: Body Systems Circulation 1 Remember. Capillaries are so small that blood cells can only pass through single file Important because they are the
CELL RESPIRATION STUDIES.
 Published Online: 1 July, 1927 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.46.1.53 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 7, 2018 CELL RESPIRATION STUDIES. II. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE OXYGEN CONSUMPTION
Published Online: 1 July, 1927 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.46.1.53 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 7, 2018 CELL RESPIRATION STUDIES. II. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE OXYGEN CONSUMPTION
Hematology Unit Lab 1 Review Material
 Hematology Unit Lab 1 Review Material - 2018 Objectives Laboratory instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Hematology Unit Lab 1 Review Material - 2018 Objectives Laboratory instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood
 Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System VS Cardiovascular System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood
Chapter 19(1) An Introduction to the Circulatory System and Blood Circulatory System VS Cardiovascular System circulatory system = heart, blood vessels and blood cardiovascular system = heart and blood
Normal Hematologic Values in the Cynomolgus Monkeys Aged from 1 to 18 Years
 Exp. Anim. 35(4) 443-447 1986 Normal Hematologic Values in the Cynomolgus Monkeys Aged from 1 to 18 Years Yasuko SUGIMOTO Kohji HANARI Hayato NARITA and Shigeo HONJO* The Corporation for Production and
Exp. Anim. 35(4) 443-447 1986 Normal Hematologic Values in the Cynomolgus Monkeys Aged from 1 to 18 Years Yasuko SUGIMOTO Kohji HANARI Hayato NARITA and Shigeo HONJO* The Corporation for Production and
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/
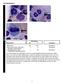 Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
Whole Blood. Lab 29A. Blood. Plasma. Whole Blood. Formed Elements. Plasma: Fluid component. Formed elements: Cells and fragments
 Whole Blood Lab 29A. Blood Plasma: Fluid component Water (90%) Dissolved plasma proteins Other solutes Formed elements: Cells and fragments RBCs (carry Oxygen) WBCs (immunity) Platelets (cell fragments
Whole Blood Lab 29A. Blood Plasma: Fluid component Water (90%) Dissolved plasma proteins Other solutes Formed elements: Cells and fragments RBCs (carry Oxygen) WBCs (immunity) Platelets (cell fragments
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted form Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System: Blood
 Adapted form Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System: Blood Introduction The cardiovascular system functions as a system to transport numerous substances throughout the body
Adapted form Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System: Blood Introduction The cardiovascular system functions as a system to transport numerous substances throughout the body
What is the composition of blood, including blood cells? What organs and structures control the flow of blood throughout the body?
 3 Chapter 10: Circulatory System and Lymphatic System In this chapter, you will learn about the structure and function of the circulatory system and lymphatic system. What is the composition of blood,
3 Chapter 10: Circulatory System and Lymphatic System In this chapter, you will learn about the structure and function of the circulatory system and lymphatic system. What is the composition of blood,
Activity Overview. P.L.E.P: Parts of Blood. Cast Your Net: Adventures With Blood. Activity 1A. Activity Objectives: Activity Description:
 P.L.E.P: Parts of Blood Activity 1A Activity Objectives: Students will be able to: Work in a collaborative group to complete a given task Examine the different parts of blood Identify the parts of blood
P.L.E.P: Parts of Blood Activity 1A Activity Objectives: Students will be able to: Work in a collaborative group to complete a given task Examine the different parts of blood Identify the parts of blood
Introduction to Haematology. Prof Roger Pool Department of Haematology University of Pretoria
 Introduction to Haematology Prof Roger Pool Department of Haematology University of Pretoria Suggested reading Haematology at a Glance Atul Mehta & Victor Hoffbrand Second Edition Published by Blackwell
Introduction to Haematology Prof Roger Pool Department of Haematology University of Pretoria Suggested reading Haematology at a Glance Atul Mehta & Victor Hoffbrand Second Edition Published by Blackwell
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 20-year-old female with sickle cell disease who presents with bilateral leg pain for 3 days. She is scheduled to have bilateral hip and leg
Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 20-year-old female with sickle cell disease who presents with bilateral leg pain for 3 days. She is scheduled to have bilateral hip and leg
Almost any suspected tumor can be aspirated easily and safely. Some masses are more risky to aspirate including:
 DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
Overview: Blood Composition and Function
 Chapter 17: Blood Overview: Blood Composition and Function Overview: Blood Composition and Function Formed elements 45% of whole blood Blood cells and cell fragments Erythrocytes Red blood cells (99.9%)
Chapter 17: Blood Overview: Blood Composition and Function Overview: Blood Composition and Function Formed elements 45% of whole blood Blood cells and cell fragments Erythrocytes Red blood cells (99.9%)
COMPOSITION OF BLOOD AND NORMAL ERYTHROPOIESIS
 Composition of Blood and Normal Erythropoiesis MODULE 1 COMPOSITION OF BLOOD AND NORMAL ERYTHROPOIESIS 1.1 INTRODUCTION Blood consists of a fluid component- plasma, and a cellular component comprising
Composition of Blood and Normal Erythropoiesis MODULE 1 COMPOSITION OF BLOOD AND NORMAL ERYTHROPOIESIS 1.1 INTRODUCTION Blood consists of a fluid component- plasma, and a cellular component comprising
Peripheral Blood Smear: Diagnostic Clues and Algorithms
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Blood. Water compartments
 Blood Water compartments 2/8 about 60% of our body is water (young-old, male-female) water is located in compartments, movement is regulated intracellular : extracellular 2:1, i.e. 40:20% interstitial
Blood Water compartments 2/8 about 60% of our body is water (young-old, male-female) water is located in compartments, movement is regulated intracellular : extracellular 2:1, i.e. 40:20% interstitial
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Unit 10 - Blood The only fluid tissue in the human body. c) Plasma rises to the top (55% of blood)
 Unit 10 - Blood 1 I. Unit 10: Blood A. Blood 1. The only fluid tissue in the human body 2. Classified as a connective tissue 3. Components of blood a) Living cells (1) Formed elements b) Non-living matrix
Unit 10 - Blood 1 I. Unit 10: Blood A. Blood 1. The only fluid tissue in the human body 2. Classified as a connective tissue 3. Components of blood a) Living cells (1) Formed elements b) Non-living matrix
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.1 Blood
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.1 Blood Blood Function Function Nutritive Respiratory Excretory Regulatory Protective Effects on Body Transporting nutrient molecules (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.1 Blood Blood Function Function Nutritive Respiratory Excretory Regulatory Protective Effects on Body Transporting nutrient molecules (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and
Lifeblood Lab Activity
 History of Blood: It is the universal symbol of horror, of death, yet it is the one thing that keeps you living. It is the blood that is coursing through your veins. But, what do you really know about
History of Blood: It is the universal symbol of horror, of death, yet it is the one thing that keeps you living. It is the blood that is coursing through your veins. But, what do you really know about
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE #403 GUIDELINES FOR BLOOD COLLECTION VOLUMES AND FREQUENCY
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE #403 GUIDELINES FOR BLOOD COLLECTION VOLUMES AND FREQUENCY 1. PURPOSE This Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) describes recommended volumes and frequency for blood collection
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE #403 GUIDELINES FOR BLOOD COLLECTION VOLUMES AND FREQUENCY 1. PURPOSE This Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) describes recommended volumes and frequency for blood collection
Blood. Plasma. The liquid part of blood is called plasma. 1. Pale yellow fluid; forms more than half the blood volume.
 11 Blood FOCUS: Blood consists of plasma and formed elements. The plasma is 91% water with dissolved or suspended molecules, including albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen. The formed elements include erythrocytes,
11 Blood FOCUS: Blood consists of plasma and formed elements. The plasma is 91% water with dissolved or suspended molecules, including albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen. The formed elements include erythrocytes,
Chapter 19. Openstax: Chapter 18. Blood
 Chapter 19 Blood Openstax: Chapter 18 Chapter 19 Learning Outcomes After completing Chapter 19, you will be able to: 1. Describe the components and major functions of blood and list the physical characteristics
Chapter 19 Blood Openstax: Chapter 18 Chapter 19 Learning Outcomes After completing Chapter 19, you will be able to: 1. Describe the components and major functions of blood and list the physical characteristics
FROM BLOOD AND PLASMA GRAVITIES
 1. din. Path. (1948), 1, 144. THE DETERMINATION OF PACKED CELL VOLUME FROM BLOOD AND PLASMA GRAVITIES IN INDIAN SOLDIERS BY H. LEHMANN From the General Headquarters (India) Medical Research Organization,
1. din. Path. (1948), 1, 144. THE DETERMINATION OF PACKED CELL VOLUME FROM BLOOD AND PLASMA GRAVITIES IN INDIAN SOLDIERS BY H. LEHMANN From the General Headquarters (India) Medical Research Organization,
THE KENYA POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY COLLEGE
 THE KENYA POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY COLLEGE SCHOOL OF HEALTH SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF BIOMEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DIPLOMA IN MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE END OF YEAR 1 EXAMINATION
THE KENYA POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY COLLEGE SCHOOL OF HEALTH SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF BIOMEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DIPLOMA IN MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCE END OF YEAR 1 EXAMINATION
THE MAINTENANCE OF A NORMAL PLASMA PROTEIN CONCENTRATION IN SPITE OF REPEATED PROTEIN LOSS BY BLEEDING
 Published Online: 1 May, 1932 Supp Info: http://doi.org/1.184/jem.55.5.683 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on September 3, 218 THE MAINTENANCE OF A NORMAL PLASMA PROTEIN CONCENTRATION IN SPITE OF REPEATED
Published Online: 1 May, 1932 Supp Info: http://doi.org/1.184/jem.55.5.683 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on September 3, 218 THE MAINTENANCE OF A NORMAL PLASMA PROTEIN CONCENTRATION IN SPITE OF REPEATED
PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY OF LEUCOCYTES IN D::FFERE T A MALS AND MA *
 PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY OF LEUCOCYTES IN D::FFERE T A MALS AND MA * P. c. GANGWAR"I AND G. G. UNTAWALA Department of Physiology, College of Veterinary Science and Animal Husbandry, 1. N. K. V. v., Jabalpur,
PEROXIDASE ACTIVITY OF LEUCOCYTES IN D::FFERE T A MALS AND MA * P. c. GANGWAR"I AND G. G. UNTAWALA Department of Physiology, College of Veterinary Science and Animal Husbandry, 1. N. K. V. v., Jabalpur,
ADVANCED HAEMATOLOGY BATTLE OF THE BANDS. Dennis B. DeNicola, DVM, PhD, DACVP IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. Westbrook, Maine, USA BACKGROUND
 ADVANCED HAEMATOLOGY BATTLE OF THE BANDS Dennis B. DeNicola, DVM, PhD, DACVP IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. Westbrook, Maine, USA BACKGROUND The identification of immature neutrophils (bands, metamyelocytes,
ADVANCED HAEMATOLOGY BATTLE OF THE BANDS Dennis B. DeNicola, DVM, PhD, DACVP IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. Westbrook, Maine, USA BACKGROUND The identification of immature neutrophils (bands, metamyelocytes,
A. Blood is considered connective tissue. RBC. A. Blood volume and composition 1. Volume varies - average adult has 5 liters
 A. Blood is considered connective tissue. RBC A. Blood volume and composition 1. Volume varies - average adult has 5 liters 2. 45% cells by volume called hematocrit (HCT) a. red blood cells (RBC) mostly
A. Blood is considered connective tissue. RBC A. Blood volume and composition 1. Volume varies - average adult has 5 liters 2. 45% cells by volume called hematocrit (HCT) a. red blood cells (RBC) mostly
CHAPTER 1. The Blood Film and Count
 CHAPTER 1 The Blood Film and Count Blood Blood is a life sustaining fluid that circulates through the heart and blood vessels. It carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and waste products to the lungs,
CHAPTER 1 The Blood Film and Count Blood Blood is a life sustaining fluid that circulates through the heart and blood vessels. It carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and waste products to the lungs,
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD. MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. BLOOD A connective tissue Average volume of 5 liters (70 kg male) 45% solid cells or formed elements (hematocrit [HCT] quantitation)
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. BLOOD A connective tissue Average volume of 5 liters (70 kg male) 45% solid cells or formed elements (hematocrit [HCT] quantitation)
Blood and Defense. Chapter 11
 Blood and Defense Chapter 11 Functions of Blood 1. Carry nutrients from the small intestine and oxygen from the lung to tissues in the body 2. Transport wastes from tissues to the kidneys and carbon dioxide
Blood and Defense Chapter 11 Functions of Blood 1. Carry nutrients from the small intestine and oxygen from the lung to tissues in the body 2. Transport wastes from tissues to the kidneys and carbon dioxide
