Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: Journal homepage:
|
|
|
- Ralf Taylor
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: Review Article A REVIEW ON FLOATING TABLET Chanchal *, Saurav Kumar, Satinder Kakar Department of Pharmacy, Himachal Institute of Pharmacy, Paonta Sahib (H.P), India ARTICLE INFO: Article history: Received: 15 November 2017 Received in revised form: 5 December 2017 Accepted: 10 December 2017 Available online: 30 March 2018 Keywords: Floating Tablet FDDS ABSTRACT Pharmaceutical industries have received much interest in pharmaceutical research in the area of oral drug delivery more over on Gastro retentive drug delivery system that is Floating Drug Delivery System (FDDS).The objective of this study to review on FDDS focusing on its current advancement and its future. Floating systems are low density systems that have sufficiently buoyancy to flow over the gastric contents and remain buoyant in the stomach without affecting the gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period of time. Floating dosage forms can be prepared as tablets, capsule by adding suitable ingredients with excipients like hydrocolloids, inert fatty materials and buoyancy increasing agents. Various categories of drugs like antacids, antidiabetic, antifungal and anticancer drugs are formulated into FDDS. FDDS have bulk density less than gastric fluids that have sufficient buoyancy to float over the gastric contents and remain in the stomach for longer duration of time. This review article is in pursuit of giving detailed information on the pharmaceutical basis of their design, classification, advantages and disadvantages, factors affecting gastric residence time of FDDS, applications, and formulation of floating tablet. Introduction Floating systems or dynamically controlled systems are low density systems that have sufficiently buoyancy to flow over the gastric contents and remain buoyant in the stomach without affecting the gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period of time. This result is an increased gastric retention time and a better control of the fluctuations in plasma drug concentration. Oral controlled release dosage forms have been developed over the past three decades due to their considerable therapeutic advantages such as: 1. Easily administrations. 2. Low cost of therapy. 3. Patient compliance and flexibility in formulation. The ultimate goal of any drug delivery is Effective disease / disorder management, minimum side effects and greater patient compliance in the cost effective manner. More than 50% of the drug delivery systems available in the market are oral drug delivery systems. Controlled release drug delivery systems (CRDDS) provide drug release at a predetermined, predictable, and controlled rate. Controlled release drug delivery system is capable of achieving the benefits like maintenance of optimum therapeutic drug concentration in blood with predictable and reproducible release rates for extended time period, enhancement of activity of duration for short half life drugs, elimination of side effects, reducing frequency of dosing and wastage of drugs, optimized therapy and better patient compliances. The controlled gastric retention of solid dosage forms may be achieved by mucoadhesive systems that causes bioadhesion to stomach mucosa, floating systems, swelling and expanding systems, modified-shape systems, high density systems and other delayed gastric emptying devices. Gastro retentive dosage form can remain in the gastric region for several hours and hence significantly prolong the gastric residence time of drugs. Prolonged gastric retention improves bioavailability, reduces drug waste, and improves solubility of drugs that are less soluble in a high ph environment. Gastro retention helps to provide better availability of new products with suitable therapeutic activity and substantial benefits for patients. The successful development of oral controlled drug delivery systems requires an understanding of the three aspects of the system, namely. Corresponding Author: Chanchal, Himachal Institute of Pharmacy, Paonta Sahib (H.P), India Satinder.kakkar5@gmail.com 22
2 1. The physiochemical characteristics of the drug. 2. Anatomy and physiology of GIT and Characteristics of Dosage forms[1]. Basic anatomy and physiology of stomach The main function of the stomach is to process and transport foo d. Substantial enzymatic digestion is initiated in stomach, particularly of proteins. Anatomically the stomach is divided into 3 regions: fundus, body, and antrum (pylorus). The proximal part made of fundus and body acts as a reservoir for undigested material, whereas the antrum is the main site for mixing motions and act as a pump for gastric emptying by propelling action. Gastric emptying occurs during fasting as well as fed states. The pattern of motility is however distinct in the 2 states. During the fasting state an inter digestive series of electrical events take place, which cycle both through stomach and intestine every 2 to 3 hours. This is called the interdigestive myloelectric cycle (IMC) or migrating myloelectric cycle (MMC), which is further divided into following 4 phases as described by Wilson and Washington.[2] 1. Phase I (basal phase) lasts from 40 to 60 minutes with rare contractions. 2. Phase II (pre-burst phase) lasts for 40 to 60 minutes with intermittent action potential and contractions. As the phase progresses the intensity and frequency also increases gradually. 3. Phase III (burst phase) lasts f or 4 to 6 minutes. It includes intense and regular contractions for short period. It is due to this wave that all the undigested material is swept out of the stomach down to the small intestine. It is also known as the housekeeper wave. 4. Phase IV lasts for 0 to 5 minutes and occurs between phases III and I of 2 consecutive cycles. Fig 1: Motility Pattern in GIT Advantages of Floating Drug Delivery System 1. The floating drug delivery systems are advantageous for drugs absorbed through the stomach or proximal part of the small intestine. E.g. Ferrous salts, furosemide. 2. The efficacy of the medicaments administered utilizing the sustained release principle of floating formulation has been found to be independent of the site of particular medicaments. 3. The floating drug delivery systems are advantageous for drugs meant for local action in the stomach. E.g. antacids 4. Acidic substances like aspirin cause irritation on the stomach wall when come in contact with it. Hence HBS formulation may be useful for the administration of aspirin and other similar drugs. 5. Complete absorption of the drug from the floating dosage form is expected even at the alkaline ph of the intestine. The dissolution of the drug in gastric fluid occurs and then the dissolved drug is available for absorption in the small intestine after emptying of the stomach contents. 6. Enhanced bioavailability. 7. Sustained drug delivery/reduced frequency of dosing. 8. Reduced counter-activity of the body. Disadvantages of Floating Drug Delivery System 1. Floating system is not feasible for those drugs that have solubility or stability problem in GI tract. Review Article 23
3 2. These systems require a high level of fluid in the stomach for drug delivery to float and work efficiently. 3. Drugs such as nifedipine, which under goes first pass metabolism may not be desirable for the preparation of these types of systems. 4. Drugs which are irritant to Gastric mucosa are also not desirable. 5. The drug substances that are unstable in the acidic environment of the stomach are not suitable candidates to be incorporated in the systems. Floating system Floating drug delivery systems (FDDS) have a bulk density less than gastric fluids and so remain buoyant in the stomach without affecting the gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period of time. While the system is floating on the gastric contents, the drug is released slowly at the desired rate from the system. After release of drug, the residual system is emptied from the stomach[3]. Classification of floating system Types of floating systems Non-effervescent system Effervescent system Raft Forming Systems Colloidal gel barrier system Bilayer floating tablets Volatile liquid containing system Gas generating system Micro porous compartment systems Alginate beads Hollow microsphers Fig 2: Classification of Floating System Non-effervescent system The non effervescent FDDS based on mechanism of swelling of polymer or bioadhesion to mucosal layer in GI tract. The most commonly used excipients in non effervescent FDDS are gel forming or highly swellable cellulose type hydrocolloids, polysaccharides and matrix forming material such as polycarbonate, polyacrylate, polymethacrylate, polystyrene as well as bio-adhesive polymer such as chitosan and carbopol. The various type of this systems are as follows: [4]. Colloidal Gel Barrier System Hydrodynamically balanced system first designed by Sheth and Tossounian. They remain buoyant in the stomach due to gelforming hydrocolloids and this enhances GRT and increases the amount of drug at the absorption site. Various gel forming agents used in this system are highly soluble cellulose type hydrocolloids which are hydroxyethyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, polysaccharides and matrix forming polymers such as polycarbophil, polystyrene[5]. Bilayer floating tablet A bilayer tablet contain two layer immediate release layer which release initial dose from system while the another sustained release layer absorbs gastric fluid, forming an impermeable colloidal gel barrier on its surface, and maintain a bulk density of less than unity and thereby it remains buoyant in the stomach[6]. Micro porous Compartment System In this inside the micro porous compartment which has pores in the top and bottom walls contains encapsulated drug reservoir. In drug reservoir peripheral walls are completely sealed due to this sealing direct contact of undissolved drug with gastric surface is prevented. Entrapped air in the floating chamber stimulates the system to float over gastric content. Through an aperture the gastric fluid enters which dissolves the drug for absorption across intestine [7]. Alginate beads Multi unit floating dosage forms are developed from freeze dried calcium alginate. Spherical beads of approximately 2.5 mm diameter can be prepared by dropping a sodium alginate solution into aqueous solution of calcium chloride, causing precipitation Review Article 24
4 of calcium alginate leading to formation of porous system, which can maintain a floating force for over 12 hours. When compared with solid beads, which gave a short residence, time of 1 hour, and these floating beads gave a prolonged residence time of more than 5.5 hours[1]. Hollow microspheres Hollow microspheres (microballons), loaded with drug in their outer polymer shells were prepared by a novel emulsion solvent diffusion method. The ethanol: dichloromethane solution of drug and enteric acrylic polymer was poured into an agitated aqueous solution of PVA that was thermally controlled at 400 C. The gas phase generated in dispersed polymer droplet by evaporation of dichloromethane formed an internal cavity in microsphere of polymer with drug. The microballons floated continuously over the surface of acidic dissolution media containing surfactant for more than 12 hours in vitro[8]. Effervescent system Effervescent systems include use of gas generating agents, carbonates (e.g. Sodium bicarbonate) and other organic acid (e.g. citric acid and tartaric acid) present in the formulation to produce carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) gas, thus reducing the density of system and making it float on the gastric fluid. An alternative is the incorporation of matrix containing portion of liquid, which produce gas that evaporate at body temperature[9]. These effervescent systems further classified into two types. Volatile liquid containing systems Inflatable chamber with a liquid can be incorporated which provide sustained gastric retention of drug delivery system. Liquids in this system include cyclopentane, ether that gasifies at body temperature which causes inflatation of the chamber in the stomach. They contain hollow deformable unit which are osmotically controlled floating systems. System is divided into two compartments first compartment contains drug and there is volatile liquid in the second compartment [10]. because of the buoyancy created by the formation of CO 2 and act as a barrier to prevent the reflux of gastric Contents like HCl and enzymes into the esophagus. Usually, the system contains a gel forming agent and alkaline bicarbonates or carbonates responsible for the formation of to make the system less dense and float on the gastric fluids [12]. Factors Affecting Gastric Residence Time of FDDS There are several factors that can affect gastric emptying of an oral dosage form which include density, size and shape of dosage form, feeding state, biological factors such as age, gender, posture, body mass index, disease state etc[13]. Effect of Dosage Form Size & Shape Small size tablets are emptied from the stomach during the digestive phase while large size units are expelled during the house keeping waves found that floating unit with a diameter equal or less than 7.5 mm had larger gastric residence time (GRT) compared to non-floating units but the GRT was similar for floating and non-floating units having a large diameter of 9.9 mm. They found that GRT of non-floating units were much more variable and highly dependent on their size which are in the order of small < medium < large units. Moreover, in supine subjects, size influences GRT of floating and non- floating form. Tetrahedron and ring shaped devices have a better GRT as compared with other shapes[14]. Gender Posture & Age Mean ambulatory GRT in males (3.4±0.6 hour) is less compared with their age and race-matched female counterparts (4.6±1.2 hour) regardless of their weight, height and body surface. Women emptied their stomach at a lower rate than men even when hormonal changes due to menstrual cycle were minimized. The mean GRT in the supine state (3.4±0.8 hour) was not stastically significant from that in the upright, ambulatory state (3.5±0.7 hour). In case of elderly, the GRT was prolonged especially in subject more than 70 years old (mean GRT 5.8 hour)[15]. Gas generating systems It basically contains polymers that gasify at body temperature effervescent compounds such as sodium bicarbonate, citric acid, tartaric acid, swellable polymers like methocel, and polysaccharides like chitosan. Resin beads loaded with bicarbonate and coated with ethylcellulose is the most common approach for preparation of these systems. The ethycellulose coating is insoluble but permeable to water which release carbon dioxide due to which it float[11]. Raft forming systems Raft forming systems have received much attention for the delivery of antacids and drug delivery for gastrointestinal infections and disorders. The basic mechanism involved in the raft formation includes the formation of viscous cohesive gel in contact with gastric fluids, wherein each portion of the liquid swells forming a continuous layer called a raft. The raft floats Effect of Food & Specific Gravity To float FDDS in the stomach, the density of dosage form should be less than gastric content i.e.1.0 g/cm 3. Since, the bulk density of a dosage form is not a sole measure to describe its buoyant capabilities because the magnitude of floating strength may vary as a function of time and gradually decrease after immersing dosage form into fluid as a result of development of its hydrodynamic equilibrium. Various studies have shown the intake of food as main determinant of gastric emptying rather than food. Presence of food is the most important factor effecting GRT than buoyancy. GRT is significantly increased under fed condition since onset of MMC is delayed. Studies show that GRT for both floating and non-floating single unit are shorter in fasted subjects (less than 2 hour), but significantly prolonged after a meal (around 4 hour)[16]. Review Article 25
5 Natural of Meal & Frequency of Food Feeding of indigestible polymers or fatty acid salts can change the motility pattern of the stomach to fed state, to increase gastric emptying rate and prolonging the drug release. Diet rich in protein and fat can increase GRT by 4-10 hours[17]. Application of floating drug delievery system Enhanced Bioavailability The bioavailability of riboflavin CR-GRDF is significantly enhanced in comparison to the administration of non-grdf CR polymeric formulations. There are several different processes, related to absorption and transit of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract, that act concomitantly to influence the magnitude of drug absorption[18]. Sustained Drug Delivery Oral CR formulations are encountered with problems such as gastric residence time in the GIT. These problems can be overcome with the HBS systems which can remain in the stomach for long periods and have a bulk density <1 as a result of which they can float on the gastric contents. These systems are relatively larger in size and passing from the pyloric opening is prohibited[19]. Site-Specific Drug Delivery These systems are particularly advantageous for drugs that are specifically absorbed from stomach or the proximal part of the small intestine, e.g., riboflavin and furosemide.e.g. Furosemide is primarily absorbed from the stomach followed by the duodenum. It has been reported that a monolithic floating dosage form with prolonged gastric residence time was developed and the bioavailability was increased. AUC obtained with the floating tablets was approximately 1.8 times those of conventional furosemide tablets[20]. Absorption or Bioavailability Enhancement Drugs that have poor Bioavailability because of site-specific absorption from the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract are potential candidates to be formulated as floating drug delivery systems, thereby maximizing their absorption. A significant increase in the Bioavailability of floating dosage forms (42.9%) could be achieved as compared with commercially available LASIX tablets (33.4%) and enteric-coated LASIX-long product (29.5%)[21]. Reduced fluctuations of drug concentration Continuous input of the drug following CRGRDF administration produces blood drug concentrations within a narrower range compared to the immediate release dosage forms. Thus, fluctuations in drug effects are minimized and concentration dependent adverse effects that are associated with peak concentrations can be prevented. This feature is of special importance for drugs with a narrow therapeutic index Formulation of floating tablets Polymers Sustained release polymer Effervescent generating system Hydrocolloids Inert fatty materials Release rate accelerants Release rate retardant Buoyancy increasing agents Low density material Miscellaneous 1. Polymers: The following polymers used in preparations of floating drugs - HPMC K4, HPMC K4 M, HPMC K15, Calcium alginate, Eudragit S100, Eudragit RL, Methocel K4M, Polyethylene oxide, a Cyclodextrin, HPMC 4000, HPMC 100, CMC, Polyethylene glycol, polycarbonate, PVA, Polycarbo-nate, Sodium alginate, HPC-L, CP 934P, HPC, Eudragit S, HPMC, Metolose S.M. 100, Propylene foam, Eudragit RS, ethyl cellulose, poly methyl methacrylate, PVP, HPC-H, HPC-M, Polyox, Acrylic polymer, E4 M and Carbopol. 2. Sustained release polymer: These are the polymers which are used for sustained release action. E.g. HPMC K100M, HPMC K15M, HPMC ELV, Polycarbonate, Polyethylene glycol, Sodium alginate, Carbopol, Eudragit 3. Effervescent generating system: E.g. Citric acid, Tartaric Acid, Sodium Bicarbonate, Citroglycine etc 4. Hydrocolloids: Suitable hydrocolloids are synthethics, anionic or non ionic like hydrophilic gumes, modified cellulose derivatives. E.g. Accasia, pectin, agar, alginates, gelatin, casein, bentonite, veegum, MC, HPC, HEC, and Na CMC can be used. The hydrocolloids must hydrate in acidic medium i.e. gastric fluid is having ph 1.2.Although the bulk density of the formulation may initially be more than one, but when gastric fluid is enter in the system, it should be hydrodynamically balanced to have a bulk density of less than one to assure buoyancy 5. Inert fatty materials: Edible, pharmaceutical inert fatty material, having a specific gravity less than one can be added to the formulation to decrease the hydrophilic property of formulation and hence increases the buoyancy. Example: Purified grades of beeswax, fatty acids, long chain alcohols, glycerides, and mineral oils can be used 6. Release rate accelerants: The release rate of the medicament from the formulation can be modified by including excipient like lactose and/or mannitol. These may be present from about 5-60% by weight Review Article 26
6 7. Release rate retardant: Insoluble substances such as dicalcium phosphate, talc, magnesium stearate decreased the solubility and hence retard the release of medicaments 8. Buoyancy increasing agents: Materials like ethyl cellulose, which has bulk density less than one, can be used for enhancing the buoyancy of the formulation. It may be adapted up to 80 % by weight Table 1: Polymers used in floating drug delivery 9. Low density material: Polypropylene foam powder 10. Miscellaneous: Pharmaceutically acceptable adjuvant like preservatives, stabilizers, and lubricants can be incorporates in the dosage forms as per the requirements. They do not adversely affect the hydrodynamic balance of the systems. Hydrochlorides HPMC 1000,HPMC 4000,, β Cyclodextrin, Sodium alginate, HPC-L, CP 934P, HPC, Eudragit S, HPMC, Metolose S.M. 100, PVP, HPC-H, HPC-M, HPMC K15, Polyox, HPMC K4, Acrylic polymer, E4 M and Carbopol. Inert fatty materials Beeswax, fatty acids, long chain fatty alcohols, Gelucires 39/01 and 43/01. Effervescent agents Sodium bicarbonate, citric acid, tartaric acid, Di-SGC (Di-Sodium Glycine Carbonate, CG (Citroglycine). Release rate accelerants(5%-60%) lactose, mannitol. Release rate retardants (5%-60%) Dicalcium phosphate, talc, magnesium stearate. Buoyancy increasing agents (upto80%) Ethyl cellulose. Methods of preparation 1. Methodology for single layer floating tablets: Basically single layer floating tablets are prepared by compression methods. For this normally three basic compression methods are used. They are as follows:- Direct compression, Dry granulation, Wet granulation. Direct compression method: Direct compression is the process of compressing tablets directly from powdered materials without modifying physical nature of materials into the tablets. This method is used for crystalline chemicals having good compressible characteristic and flow properties such as: Potassium salt (chloride, chlorate, bromide), Ammonium chloride, Sodium chloride, Methenamine etc. Compressed tablets are prepared by single compression using tablet machines. After a quantity of powdered or granulated tabletting material flow into a die, the upper and lower punches of the tablet machine compress the material under a high pressure (~tons/in 2 ). Dry granulation method: It is defined as the formation of granules by slugging, if the tablet ingredients are sensitive to moisture and/or unable to withstand elevated temperature during drying Wet granulation method: In wet granulation the active ingredient, diluents and disintegrants are mixed or blended well in a rapid mixer granulator (RMG). The RMG is a multi-purpose chopper which consists of an impeller and a chopper and is used for high speed dispersion of dry powders and aqueous or solvent granulations.moist materials from wet milling steps are placed on large trays and placed in drying chambers with a circulating air current and thermo stable heat controller. Commonly used dryers are tray dryer, fluidized bed dryer. After drying, the granules are reduced in particle size by passing through smaller mesh screen. After this, the lubricant or glidant is added as fine powder to promote flow of granules. These granules are then compressed to get a tablet. Dry granulation when compared with wet granulation has a shorter, more costeffective manufacturing process. Because it does not entail heat or moisture, dry granulation is especially suitable for active ingredients that are sensitive to solvents, or labile to moisture and elevated temperatures 2. Methodology for bilayer floating tablets a) Oros Push Pull Technology b) L-Oros Tm Technology c) DUROS Technology d) Elan Drug Technologies Dual Release Drug Delivery System e) EN SO TROL Technology f) Rotab Bilayer g) Geminex Technology Oros Push Pull Technology: It is two or three layer system, a drug layer and push layer. Drug layer contain drug with other agents and due to this drug is less soluble. Sometimes suspending agent and osmotic agent are also added. The tablet core is surrounded by semi permeable membrane L-Oros Tm Technology: Alza developed L-OROS system due to solubility problem. The system contain a drug in dissolved state in a lipid soft gel product which is produced first and then barrier membrane, after which osmotic membrane and semi permeable membrane coat is applied and is then drilled out through external orifice Review Article 27
7 DUROS Technology: This technology is also known as miniature drug dispensing system which works like a miniature syringe and release small quantity of drug consistently over a period of time.there is an outer cylindrical titanium alloy reservoir which has high impact strength due to which drug molecules inside it are protected from enzymes Elan Drug Technologies Dual Release Drug Delivery System: The DUREDASTM Technology provides combination release of drugs together and different release pattern of single drug i.e. it provides sustained release as well as immediate release. This technology provides various advantages i.e. two drug components provide tailored release and its another benefit is that it consist of bilayered tablet technology in which it contain modified as well as immediate release pattern in one tablet. In these different controlled release formulations are combined together. EN SO TROL Technology: An integrated approach is used by Shire laboratory for drug delivery system which focuses on identification and incorporation of enhancer which is identified to form optimized dosage form in controlled release system. By this enhancement in solubility is achieved RoTab Bilayer: RoTab bilayer when using is switched to production mode. Dose and compression force is automatically regulated by adjusting filling speed and die table. Hardness is also regulated when required Geminex Technology: In this drug delivery system at different times more than one drug can be delivered. This technology basically increases the therapeutic efficacy of the drug by decreasing its side effects. It is useful both to industry as well as patient as in single tablet it provides delivery of drug at different rates[21]. Conclusion Drug absorption in the gastrointestinal tract is a highly variable procedure and prolonging gastric retention of the dosage form extends the time for drug absorption. Gastroretentive floating drug delivery systems have emerged as an efficient means of enhancing the bioavailability and controlled delivery of many drugs. The increasing sophistication of delivery technology will ensure the development of increase number of gastroretentive drug delivery to optimize the delivery of molecules that exhibit absorption window, low bioavailability and extensive first pass metabolism. FDDS promises to be a potential approach for gastric retention. Although there are number of difficulties to be worked out to achieve prolonged gastric retention, a large number of companies are focusing toward commercializing this technique. References 1. Anupama Sarawade, M. P. Ratnaparkhi, Shilpa Chaudhari An Overview Floating Drug Delivery System, International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences,2014;3(5): C Narendra, M S Srinath, Ganesh Babu, Optimization of bilayer floating tablets containing metoprolol tartrate as a model drug for gastric retention. AAPS PharmSciTech; 2006;7(2): Dev A, Gopal NV, Shekar L, Ramarav B, Rao JV, Karunakar K, Surendra Y. A Review of Novel Approach in Bilayer Tablet Technology. International Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences.2012;1: D.Saritha, D. Sathish and Y. Madhusudan Rao Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Domperidone Maleate, Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science. 2012;02 (03): D M Patel, N M Patel, N M Pandya, P D Jogani, Formulation and optimization of carbamazepine floating tablets. Ind J Pharm Sci;2007;69(6): Garg S. and Sharma S. Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System, Business Briefing: Pharmatech.,2003;203; Kaushik Avinash, Dwivedi Abha, Kothari Praween, Govil Abhinav. Floating Drug Delivery System a Significant Tool for Stomach Specific Release of Cardiovascular Drugs Int. J. Drug Dev. & Res.,2012;4(4): Mayavanshi AV, Gajjar SS. Floating drug delivery systems to increase gastric retention of drugs: A Review. Research J. Pharm. and Tech.2008;1: Neha Narang, A Review On Floating Drug Delivery System, A International journal of applied pharmaceuticals,2011;(1): N. B Khavare et al. A Review on key parameters and components in Designing of Osmotic Controlled Oral Drug Delivery Systems; Indian Journal of Novel Drug delivery.2010; 2(4): Panchan HA, Tiwari AK. A Novel Approach of Bilayer Tablet Technology: A Review. International Research Journal of Pharmacy. 2012;3: Purnima Tripathi, U. Ubaidulla, Roop Kishan Khar, Vishwavibhuti, A Review On Floating Drug Delivery System, International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences, 2012;1(1): Shah SH, Patel JK, Patel NV. Stomach specific floating drug delivery system: A review. Int J Pharm Res 2009; 1(3): Satinder Kakar, Ramandeep singh, Shallu sandhan. Gastroretentive drug delivery system: A Review,AJPP;2012;5(3): Solakhia TM, Kosta AK, Agarwal S, Gupta D. Bi-Layer Tablets: An Emerging Trend. International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives. 2012;2; 3: Review Article 28
8 16. Sowmya C, Suryaprakash CR, Tabasum SG, Varma V. An Overview on Bi-Layer Tablets. International Journal of Pharmacy &Technology.2012; 4: Meenu Bhatt, Satinder Kakar, Ramandeep Singh. A Review On Floating Drug Delivery System. IJRAPR.2015;5(2): S Sharma, P Atmaram, Low-density multiparticulate system for pulsatile release of meloxicam. Int J Pharm; 2006; 313: Tripathi P, Ubaidulla U, Khar RK, Vishwavibhuti. Floating Drug Delivery System. International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences.;2012;1: Vishal Bhardwaj, Nirmala,S.L. Harikumar, A Review On Floating Drug Delivery System, Pharmacophore. International Research Journal.;2013;4(1): Satinder Kakar, Ramandeep Singh, Alok Semwal. Drug release characteristics of dosage forms: a review. Journal of Coastal Life Medicine;2014;2(4): Cite this article as: Chanchal, Saurav Kumar, Satinder Kakar, A review on floating tablet. Indian J. Pharm. Biol. Res.2018; 6 (1): All 2018 are reserved by Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research This Journal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial -Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. This article can be downloaded to ANDROID OS based mobile. Review Article 29
Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
Biswajit Biswal IRJP 2 (7)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
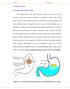 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Ph. D Synopsis. Mr. Mehul Pravinchandra Patel Page 1
 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin Bilayer Tablets
 CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
Easy, fast and reliable!
 Product Overview Easy, fast and reliable! Special easy-to-use preparations for film coating, sugar-coating, colouring and tabletting. s film coating products are one-step coating systems for pharmaceutical
Product Overview Easy, fast and reliable! Special easy-to-use preparations for film coating, sugar-coating, colouring and tabletting. s film coating products are one-step coating systems for pharmaceutical
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release. Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy
 Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Easy, fast and reliable!
 Product Overview Easy, fast and reliable! Special easy-to-use preparations for film coating, sugar-coating, colouring and tabletting. Tailormade formulated. s film coating products are one-step coating
Product Overview Easy, fast and reliable! Special easy-to-use preparations for film coating, sugar-coating, colouring and tabletting. Tailormade formulated. s film coating products are one-step coating
A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
Direct Compression. With the right ingredients it s a simple, cost-effective manufacturing process
 Direct With the right ingredients it s a simple, cost-effective manufacturing process TM Trademark of The Dow Chemical Company ( Dow ) or an affiliated company of Dow Speed and savings sounds good to us
Direct With the right ingredients it s a simple, cost-effective manufacturing process TM Trademark of The Dow Chemical Company ( Dow ) or an affiliated company of Dow Speed and savings sounds good to us
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review
 ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems
 Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
CONTENTS PAGE. Please note: Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications
 Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Pharma & Food Solutions. POLYOX TM Water Soluble Resins Combining Flexibility with Consistency
 Pharma & Food Solutions POLYOX TM Water Soluble Resins Combining Flexibility with Consistency POLYOX 9-13 POLYOX 9-13 POLYOX * are nonionic poly (ethylene oxide) polymers that meet all the specifications
Pharma & Food Solutions POLYOX TM Water Soluble Resins Combining Flexibility with Consistency POLYOX 9-13 POLYOX 9-13 POLYOX * are nonionic poly (ethylene oxide) polymers that meet all the specifications
Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Tablets Using Different Polymers: Guargum, Sodium Alginate, Hpmc100cps and Carbopol940
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use
 Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use 1. Solid Preparations (Tablet, Capsule, Pill) 2. Liquid Preparations (Aqua, Syrup, Elixir, Extract, Liquor, Emulsion, Mixture, Infusion, Decoction). 3. Powder
Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use 1. Solid Preparations (Tablet, Capsule, Pill) 2. Liquid Preparations (Aqua, Syrup, Elixir, Extract, Liquor, Emulsion, Mixture, Infusion, Decoction). 3. Powder
This PDF is available for free download
 Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation
 METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
PHARMACEUTICAL AID PREPARED BY B.KIRUTHIGA LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY
 PHARMACEUTICAL AID PREPARED BY B.KIRUTHIGA LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY Excipients are inactive ingredients used as carriers for the active ingredients in a pharmaceutical product. These may
PHARMACEUTICAL AID PREPARED BY B.KIRUTHIGA LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY Excipients are inactive ingredients used as carriers for the active ingredients in a pharmaceutical product. These may
Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery System
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept ISSN FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL
 Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS): A REVIEW
 25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
Suppository Chapter Content
 10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
Granulation Aggregation
 Granulation Aggregation Wet granulation Solvent granulation (crust granules) Binder granulation (sticked granules) Granulation liquid Water Water + alcohol mixture Macromolecular colloidal solution i.e.:
Granulation Aggregation Wet granulation Solvent granulation (crust granules) Binder granulation (sticked granules) Granulation liquid Water Water + alcohol mixture Macromolecular colloidal solution i.e.:
METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE
 METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface What is Metolose Substitution types Specifications 1) Available grades & viscosity 2) Nomenclature 3) Packaging Characteristics of Metolose Properties of Metolose 1) Powder
METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface What is Metolose Substitution types Specifications 1) Available grades & viscosity 2) Nomenclature 3) Packaging Characteristics of Metolose Properties of Metolose 1) Powder
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS. Tablets
 March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
Int J Pharm Bio Sci. Harshal P. Gahiwade *et al Available Online through IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH
 Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
Formulation and Evaluation
 Chapter-5 Formulation and Evaluation 5.1 OBJECTIVE After successful taste masking and solubility enhancement of drugs in preliminary studies, by using Mannitol Solid Dispersion, next step includes the
Chapter-5 Formulation and Evaluation 5.1 OBJECTIVE After successful taste masking and solubility enhancement of drugs in preliminary studies, by using Mannitol Solid Dispersion, next step includes the
FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels
 Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery Tablet
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY FLOATING APPROCHES
 Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
 Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF ETORICOXIB TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN- POLOXAMER PVPK30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES
 Volume: 2: Issue-4: Oct - Dec -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF ETORICOXIB TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN- POLOXAMER 407 - PVPK30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K.P.R. Chowdary*, K. Surya Prakasa
Volume: 2: Issue-4: Oct - Dec -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF ETORICOXIB TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN- POLOXAMER 407 - PVPK30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K.P.R. Chowdary*, K. Surya Prakasa
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet Formulation by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique
 Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Chapter 2 Rationale and Objective
 Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
LAB.2. Tablet Production Methods
 LAB.2 Tablet Production Methods Dry methods Direct compression Dry granulation Wet methods Wet granulation Regardless whether tablets are made by direct compression or granulation, the first step, milling
LAB.2 Tablet Production Methods Dry methods Direct compression Dry granulation Wet methods Wet granulation Regardless whether tablets are made by direct compression or granulation, the first step, milling
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage form of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride.
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets
 Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science
 Research article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of Metoprolol Tartrate Patel
Research article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of Metoprolol Tartrate Patel
Venkateswara Rao et.al Indian Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Biotechnology ISSN: (Print) ISSN: (Online)
 Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 1934-1942 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS K. VENUGOPAL * and K. P. R. CHOWDARY a Nirmala College
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 1934-1942 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS K. VENUGOPAL * and K. P. R. CHOWDARY a Nirmala College
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms. prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy
 Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation
 Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems
 29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
Dow Wolff Cellulosics. Using ingenuity and savvy. TM Trademark of The Dow Chemical Company ( Dow ) or an affiliated company of Dow
 Dow Wolff Cellulosics Pharmaceutical Excipients Using ingenuity and savvy to help design healthcare solutions TM Trademark of The Dow Chemical Company ( Dow ) or an affiliated company of Dow Enhancing
Dow Wolff Cellulosics Pharmaceutical Excipients Using ingenuity and savvy to help design healthcare solutions TM Trademark of The Dow Chemical Company ( Dow ) or an affiliated company of Dow Enhancing
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester
 University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
Non-Food Uses of Polysaccharides
 Non-Food Uses of Polysaccharides John Mitchell John.Mitchell@biopolymersolutions.co.uk Acknowledgements Fundamentals of Hydrocolloid Technology Course (2003-2009) Rob Winwood Colin Melia Steve Harding
Non-Food Uses of Polysaccharides John Mitchell John.Mitchell@biopolymersolutions.co.uk Acknowledgements Fundamentals of Hydrocolloid Technology Course (2003-2009) Rob Winwood Colin Melia Steve Harding
SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING
 SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING Dr. Dieter Lubda MilliporeSigma is a business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Agenda: Sustained release
SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING Dr. Dieter Lubda MilliporeSigma is a business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Agenda: Sustained release
Effect of Common Excipients on the Oral Drug Absorption of Biopharmaceutics Classification System Class 3 Drugs
 Effect of Common Excipients on the Oral Drug Absorption of Biopharmaceutics Classification System Class 3 Drugs James E. Polli jpolli@rx.umaryland.edu April 26, 2016 Topics BCS Class 3 excipient study
Effect of Common Excipients on the Oral Drug Absorption of Biopharmaceutics Classification System Class 3 Drugs James E. Polli jpolli@rx.umaryland.edu April 26, 2016 Topics BCS Class 3 excipient study
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE
 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE Mahajan Ashwini *, Dr. Sarode S. M., Prof. Sathe B.S., Dr. Vadnere G.P. Department Of Pharmaceutics. Smt. S.S.
FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE Mahajan Ashwini *, Dr. Sarode S. M., Prof. Sathe B.S., Dr. Vadnere G.P. Department Of Pharmaceutics. Smt. S.S.
1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al.6 (2007), Chaudhari et al.7 (2011), Sivabalan M et al.8 (2011), Punitha et al.9 (2010), Patel et al.
 1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al. 6 (2007), prepared floating tablets of famotidine by using Methocel K 15 M and Methocel K 100 M as gel forming agent and combination of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate
1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al. 6 (2007), prepared floating tablets of famotidine by using Methocel K 15 M and Methocel K 100 M as gel forming agent and combination of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate
Large scale production
 Large scale production Rotary capsule machine: This machine has two, side-by-side cylinders in each of which half-moulds are cut. These cylinders, like the rollers of a mangle, rotate in contrary direction
Large scale production Rotary capsule machine: This machine has two, side-by-side cylinders in each of which half-moulds are cut. These cylinders, like the rollers of a mangle, rotate in contrary direction
A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS
 Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS K. P. R. Chowdary *, Tanniru Adinarayana, T. Vijay, Mercy. R. Prabhakhar
Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS K. P. R. Chowdary *, Tanniru Adinarayana, T. Vijay, Mercy. R. Prabhakhar
Continuous Granulation Using a Twin-Screw Extruder. Lin Zhu, Ph.D. Manufacture Science and Technology AbbVie June, 2016
 Continuous Granulation Using a Twin-Screw Extruder Lin Zhu, Ph.D. Manufacture Science and Technology AbbVie June, 2016 What is a twin screw extruder and how to use it for continuous granulation? Dry feed:
Continuous Granulation Using a Twin-Screw Extruder Lin Zhu, Ph.D. Manufacture Science and Technology AbbVie June, 2016 What is a twin screw extruder and how to use it for continuous granulation? Dry feed:
STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(1), 2010, 405-414 STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS V. L. NARASAIAH, T. KARTHIK KUMAR, D. SRINIVAS, K. SOWMYA, P. L. PRAVALLIKA and Sk. Md. MOBEEN
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(1), 2010, 405-414 STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS V. L. NARASAIAH, T. KARTHIK KUMAR, D. SRINIVAS, K. SOWMYA, P. L. PRAVALLIKA and Sk. Md. MOBEEN
SENTRY TM POLYOX Water Soluble Resins
 SENTRY TM POLYOX Water Soluble Resins Technical Information on Stability Introduction Key Points Antioxidants SENTRY POLYOX WSR resins consist of a family of high molecular weight polyethers with nominal
SENTRY TM POLYOX Water Soluble Resins Technical Information on Stability Introduction Key Points Antioxidants SENTRY POLYOX WSR resins consist of a family of high molecular weight polyethers with nominal
TABLET DESIGN AND FORMULATION
 TABLET DESIGN AND FORMULATION PART 5 Industrial pharmacy 5th class 1st semester TABLET DESIGN AND FORMULATION Conventional oral tablets for ingestion usually contain the same classes of components in addition
TABLET DESIGN AND FORMULATION PART 5 Industrial pharmacy 5th class 1st semester TABLET DESIGN AND FORMULATION Conventional oral tablets for ingestion usually contain the same classes of components in addition
Tablet is a major category of solid dosage forms which are widely used worldwide. Extensive information is required to prepare tablets with good
 TABLET PRODUCTİON Tablet is a major category of solid dosage forms which are widely used worldwide. Extensive information is required to prepare tablets with good quality at high standards. Based on preformulation
TABLET PRODUCTİON Tablet is a major category of solid dosage forms which are widely used worldwide. Extensive information is required to prepare tablets with good quality at high standards. Based on preformulation
Scholars Research Library. Formulation Development of Pioglitazone Tablets Employing β Cyclodextrin- Poloxamer 407- PVP K30: A Factorial Study
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3 (6):24-30 (http:scholarsresearchlibrary.comarchive.html) ISSN 0974-248X USA CODEN: DPLEB4 Formulation
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3 (6):24-30 (http:scholarsresearchlibrary.comarchive.html) ISSN 0974-248X USA CODEN: DPLEB4 Formulation
Innovations in Design: NIA-West. Missy Lowery, MSc Head of Integrated Marketing Capsugel, now a Lonza company 11/13/2017
 Innovations in Design: NIA-West Missy Lowery, MSc Head of Integrated Marketing Capsugel, now a Lonza company 11/13/2017 1 Innovations in Design: How Do You Stand Out? If all other competitors are the same
Innovations in Design: NIA-West Missy Lowery, MSc Head of Integrated Marketing Capsugel, now a Lonza company 11/13/2017 1 Innovations in Design: How Do You Stand Out? If all other competitors are the same
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
