A COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Logan Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ACPI Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 3(2), 2013, ISSN X A COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM MARINAGANTI RAJEEV KUMAR *, BONTHU SATYANARAYANA, NAGAKANYAKA DEVI PALADUGU, NEERUKONDAVAMSI, SHEIK MUDDASAR, SHAIK IRFAN PASHA, SPANDANA VEMIREDDY and DEEPTHI POLOJU Department of Pharmaceutics, MAX Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Velugumetla, Khammam Urban, KHAMMAM (A.P.) INDIA (Received : ; Revised : ; Accepted : ) ABSTRACT In recent years several advancements has been made in research and development of oral drug delivery system. Concept of novel drug delivery system arose to overcome certain aspect related to physicochemical properties of drug molecule and the related formulations. Purpose of this review is to compile the recent literature with special focus on various gastro retentive approaches that have recently become leading methodologies in the field of site-specific orally administered controlled release drug delivery. In order to understand various physiological difficulties to achieve gastric retention, we have summarized factors influencing gastric retention and also included various strategies for gastric retention. GRDDS has become leading methodology in site specific orally administered controlled release drug delivery system. Various drugs, which are unstable in alkaline ph, soluble in acidic ph, having narrow absorption window, site of action specific to stomach can be developed by using this technique. Key words: Gastro-retentive drug delivery system, Gastric resident time, Hydro dynamically balanced systems (HBS), Gastric retention time. INTRODUCTION Several approaches have been proposed to retain the dosage forms in the stomach. These methods include bioadhesive system, swelling system and expanding system and floating system. In fact the buoyant dosage unit enhances gastric residence time (GRT) without affecting the intrinsic rate of gastric emptying. 1 Unfortunately floating devices administered in a single unit form (Hydro dynamically balanced system) HBS are unreliable in prolonging the GRT owing to their all - or - nothing emptying process and, thus they may causes high variability in bioavailability and local irritation due to large amount of drug delivered at a particular site of the gastrointestinal tract. More often, drug absorption is unsatisfactory and highly variable among and between individuals, despite excellent in vitro release patterns. The reasons for this are essentially physiological and usually affected by the GI transit of the form, especially its gastric residence time (GRT), which appears to be one of the major causes of the overall transit time variability. Available online at * Author for correspondence; rajeev.maringanti@gmail.com; Mo.:
2 150 M. R. Kumar et al.: A Comprehensive Review on Gastro. Over the past three decades, the pursuit and exploration of devices designed to be retained in the upper part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract has advanced consistently in terms of technology and diversity, encompassing a variety of systems and devices such as floating systems, raft systems, expanding systems, swelling systems, bioadhesive systems and low-density systems. Gastric retention will provide advantages such as the delivery of drugs with narrow absorption windows in the small intestinal region. Also, longer residence time in the stomach could be advantageous for local action in the upper part of the small intestine, for example treatment of peptic ulcer disease. These drugs can be delivered ideally by slow release from the stomach. Many drugs categorised as once-a-day delivery have been demonstrated to have suboptimal absorption due to dependence on the transit time of the dosage form, making traditional extended release development challenging. Therefore, a system designed for longer gastric retention will extended release development challenging. Therefore, a system designed for longer gastric retention will extend the time within which drug absorption can occur in the small intestine. Scope 3 The development of oral controlled release systems has been a challenge to formulation scientists due to their inability to restrain and localise the system at targeted areas of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Controlled drug delivery systems aim to maintain plasma concentration of drugs within the therapeutic window for a longer period of time, thereby to ensure sustained therapeutic action and for that reason an increasing interest in their development exist. Moreover, many of new therapeutics under development are large molecules such as peptides, proteins, oligonucleotides, and vaccines. Need for GRDDS 2 Merits 4 Conventional oral delivery is widely used in pharmaceutical field to treat diseases. However, conventional delivery had many drawbacks and major draw-back is non-site specificity. Some drugs are absorbed at specific site only. They require release at specific site or a release such that maximum amount of drug reaches to the specific site. Pharmaceutical field is now focusing towards such drugs which require site specificity. Gastro-retentive delivery is one of the site specific delivery for the delivery of drugs either at stomach or at intestine. It is obtained by retaining dosage form into stomach and drug is being released at controlled manner to specific site either in stomach, duodenum and intestine. Delivery of drugs with narrow absorption window in the small intestine region. Longer residence time in the stomach could be advantageous for local action in the upper part of the small intestine, for example treatment of peptic ulcer disease. Improved bio-availability is expected for drugs that are absorbed readily upon release in the GI tract such as cyclosporine, ciprofloxacin, ranitidine, amoxycillin, captopril, etc. Patient compliance by making a once a day therapy. Improved therapeutic efficacy. Improved bioavailability due to reduced P-glycoprotein activity in the duodenum.
3 Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 3(2), Demerits 4 Reduces frequency of dosing. Targeted therapy for local ailments in the upper GI tract Floating systems has limitation, that they require high level of fluids in stomachfor floating and working efficiently. So more water intake is prescribed with such dosage form. In supine posture (like sleeping), floating dosage form may swept away (if not of larger size) by contractile waves. So patient should not take floating dosage form just before going to bed. Drugs having stability problem in high acidic environment, having very low solubility in acidic environment and drugs causing irritation to gastric mucosa cannot be incorporated into GRDDS. Bio/mucoadhesives systems have problem of high turnover rate of mucus layer, thick mucus layer & soluble mucus related limitations. Swellable dosage form must be capable to swell fast before its exit from stomach and achieve size larger than pylorus aperture. It must be capable to resist the housekeeper waves of Phase III of MMC. Physiology of the stomach 5 The Gatrointestinal tract is essentially a tube about nine metres long that runs through the middle of the body from the mouth to the anus and includes the throat (pharynx), oesophagus, stomach, small intestine (consisting of the duodenum, jejunum and ileum) and large intestine (consisting of the cecum, appendix, colon and rectum). The wall of the Gatrointestinal tract has the same general structure throughout most of its length from the oesophagus to the anus, with some local variations for each region. The stomach is an organ with a capacity for storage and mixing. The antrum region is responsible for the mixing and grinding of gastric contents. The interdigestive motility pattern is commonly called the migrating motor complex ( MMC ) and is organised in cycles of activity and quiescence. Each cycle lasts minutes and consists of four phases. The concentration of the hormone motilin in the blood controls the duration of the phases. In the interdigestive or fasted state, an MMC wave migrates from the stomach down the GI tract every minutes. A full cycle consists of four phases, beginning in the lower oesophageal sphincter/gastric pacemaker, propagating over the whole stomach, the duodenum and jejunum, and finishing at the ileum. Phase III is termed the housekeeper wave as the powerful contractions in this phase tend to empty the Stomach of its fasting contents and indigestible debris. The administration and subsequent ingestion of food rapidly interrupts the MMC cycle, and the digestive phase is allowed to take place. The upper part of the stomach stores the ingested food initially, where it is compressed gradually by the phasic contractions. The digestive or fed state is observed in response to meal ingestion. It resembles the fasting Phase II and is not cyclical, but continuous, provided that the food remains in the stomach. Large objects are retained by the stomach during the fed pattern but are allowed to pass during Phase III of the interdigestive MMC. It is thought that the sieving efficiency (i.e. the ability of the stomach to grind the food into smaller size) of the stomach is enhanced by the fed pattern or by the presence of food (Fig. 1 and 2).
4 152 M. R. Kumar et al.: A Comprehensive Review on Gastro. Fig. 1: Phases of gastric cycle Fig. 2: Physiology of stomach Different features of stomach Gastric ph: Fasted healthy subject 1.1 ± 0.15 Volume Fed healthy subject 3.6 ± 0.4 : Resting volume is about ml Gastric secretion: Acid, pepsin, gastrin, mucus and some enzymes about 60 ml with approximately 4 mmol of hydrogen ions per hour. Effect of food on Gastric secretion: About 3 liters of secretions are added to the food. Gastro intestinal transit time. Factors influencing gastric residence time 6 (i) (ii) Density of dosage form: Dosage forms having density lower than that of gastric fluids experience floating behaviour and greater gastric residence time. Size of dosage form: In most cases larger the size greater the gastric residence time because larger size will not allow dosage form to quickly pass through pyloric spincter to intestine. (iii) Food intake and nature of food: Usually presence of food in stomach increases the GRT of the dosage form and increases drug absorption by allowing it to stay at absorption site for longer time.
5 Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 3(2), (iv) (v) (vi) Affect of age, gender, posture and disease state: Elderly persons and females has slow gastric emptying rate. It was found that gastric emptying in women is slower than in men regardless of height, weight, body surface area. When individual rests on left side floating of dosage form will be towards pyloric antrum. If rests on right side it will be in opposite direction. Shape of dosage form: Tetrahedrons (each leg 2 cm long), rings (36 cm diameter) exhibited nearly 100% retention at 24 hrs where as on other hand cloverleaves ( cms) exhibit (40-67%) retention. Mechanistic approaches of gastric retentive drug delivery system 7 A number of systems have been used to increase the GRT of dosage forms by employing a variety of concepts. These systems have been classified according to the basic principles of gastric retention. Classification of gastro retentive drug delivery system shown in Fig. 3. Floating drug delivery system (FDDS) Fig. 3: Classification of gastroretentive drug delivery system Floating dosage form is also known as hydrodynamically balanced system (HBS). FDDS have a bulk density less than gastric fluids and so remain buoyant in the stomach without affecting the gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period of time while the system is floating on the gastric contents, the drug is released slowly at the desired rate. After release of drug, the residual system is emptied from the stomach. Classification of FDDS Based on the mechanism of buoyancy, floating systems can be classified into two distinct categories viz non-effervescent and effervescent systems. A. Non-Effervescent systems (i) Colloidal gel barrier systems: Hydrodynamically balanced system (HBS) of this type contains drug with gel forming or swellable cellulose type hydrocolloids, polysaccharides and matrix forming polymers. They help prolonging the GI residence time and maximize drug reaching its absorption site in the solution form ready for absorption. These systems incorporate high levels (20 to 75 % w/w) of one or more gel forming highly swellable cellulose type hydrocolloids e.g. hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC), hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC), sodium carboxy methyl cellulose (NaCMC) incorporated either in tablets or capsules (Fig. 4).
6 154 M. R. Kumar et al.: A Comprehensive Review on Gastro. Fig. 4: Hydrodynamically based system (HBS) (ii) Micro-porous compartment system: This technology is comprised of encapsulation of a drug reservoir inside a micro porous compartment with pores along its top and bottom surfaces. The peripheral walls of the drug reservoir compartment are completely sealed to prevent any direct contact of gastric mucosal surface with undissolved drug. In stomach, the floatation chamber containing entrapped air causes the delivery system to float over the gastric contents. Gastric fluid enters through the pores, dissolves the drug and carries the dissolved drug for continuous transport across the intestine for absorption (Fig. 5). Fig. 5: Floating drug delivery device with microporous membrane andfloatation chamber (iii) Alginate beads: Multiple unit floating dosage forms have been developed from freeze-dried calcium alginate. Spherical beads of approximately 2.5 mm in diameter were prepared by dropping a sodium alginate solution into aqueous solution of calcium chloride, causing a precipitation of calcium alginate. These beads were then separated; snap frozen in liquid nitrogen and freeze-dried at 40ºC for 24 hrs. leading to formation of porous system that maintained floating force for over 12 hrs. (iv) Hollow Microspheres: Hollow microspheres (microballoons), loaded with ibuprofen in their outer polymer shells were prepared by novel emulsion solvent diffusion method. The ethanol: dichloromethane solution of the drug and an enteric acrylic polymer were poured into an agitated aqueous solution of PVA that was thermally controlled at 400 C. The gas phase was generated in dispersed polymer droplet by evaporation of dichloromethane and formed an internal cavity in microsphere of polymer with drug. B. Effervescent systems A drug delivery system can be made to float in the stomach by incorporating a floating chamber, which may be filled with vacuum, air or inert gas. The gas in floating chamber can be introduced either by volatilization of an organic solvent or by effervescent reaction between organic acids and bicarbonate salts.
7 Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 3(2), Volatile liquid containing systems 8 These devices are osmotically controlled floating systems containing a hollow deformable unit that can be converted from a collapsed to an expanded position and returned to collapse position after an extended period. A deformable system consists of two chambers separated by an impermeable, pressure responsive, movable bladder. The first chamber contains the drug and the second chamber contains volatile liquid. The device inflates and the drug is continuously released from the reservoir into the gastric fluid. The device may also consist of bioerodible plug made up of PVA, polyethylene, etc. that gradually dissolves causing the inflatable chamber to release gas and collapse after a predetermined time to permit the spontaneous ejection of the inflatable system from the stomach (Fig. 6). Gas generating systems Fig. 6: Gastro inflatable drug delivery device These buoyant delivery systems utilize effervescent reaction between carbonate/bicarbonate salts and citric/tartaric acid to liberate CO 2 which gets entrapped in the jellified hydrochloride layer of the system, thus decreasing its specific gravity and making it float over chyme. These tablets may be either single layered wherein the CO 2 generating components are intimately mixed within the tablet matrix or they may be bilayer in which the gas generating components are compressed in one hydrocolloid containing layer, and the drug in outer layer for sustained release effect. Multiple unit type of floating pills that generates CO 2 have also been developed. These kinds of systems float completely within 10 minutes and remain floating over an extended period of 5-6 hrs. (Fig. 7). Fig. 7: The multiple units floating drug delivery system using gas generation technique
8 156 M. R. Kumar et al.: A Comprehensive Review on Gastro. Bioadhesive DDS Bioadhesive systems are those which bind to the gastric epithelial cell surface or mucin and serve as the potential means of extending the GRT of DDS in the stomach, by increasing the intimacy and duration of contact of drug with the biological membrane. The concept is based on self-protecting mechanism of GIT2. Mucus secreted continuously by the specialized goblet cells located throughout the GIT plays a cytoprotective role. Bioadhesion is an interfacial phenomenon in which two materials, at least one of which is biological, are held together by means of interfacial forces. The attachment could be between an artificial material andbiological substrate, such as adhesion between a polymer and a biological membrane. Swelling and expanding systems These are the dosage forms, which after swallowing, swell to an extent that prevent their exit from the pylorus. As a result, the dosage form is retained for a longer period of time. These systems may be named as plug type systems, since they exhibit the tendency to remain lodged at the pyloric sphincter. On coming in contact with gastric fluid, the polymer imbibes water and swells. The extensive swelling of these polymers is due to the presence of physical/chemical cross-links in the hydrophilic polymer network. These cross-links prevent the dissolution of the polymer and hence maintain the physical integrity of the dosage form. 9 High density systems These dosage forms have a density (3 g/ml) far exceeding that of normal stomach contents (1 g/ml) and thus retained in region of the stomach and are capable of withstanding its peristaltic movements. High density formulations include coated pellets that have density greater than that of stomach contents (1.004 g/cm 3 ). This is accomplished by coating the drug with heavy inert materials such as barium sulphate, zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, iron powder etc. The weighted pellet can then be covered with a diffusioncontrolling polymer membrane. Pharmacokinetic aspects Absorption window- that the drug is within the category of narrows absorption window agents In general, appropriate candidates for CR-GRDF are molecules that have poor colonic absorption but are characterized by better absorptionproperties at the upper parts of the GI tract. In the case of absorption by active transporters that are capacity limited, the efficacy of thetransport activity may increase following sustained presentation of the drug to the transporting enzymes in comparison to non CRmode of administration. Enhanced bioavailability Once it has been ascertained that the compound in question is defined as narrow absorption window, the possibility of improving bioavailability by continuous administration of the compound to the specific site should be tested. For example, certain bisphosphonates, including alendronate, are absorbed directly from the stomach. However, the magnitude of this pathway remains modest even in the case where the prolonged gastric retention of the bisphosphonate in rats is produced by experimental/surgicalmeans. Enhanced first pass biotransformation In a similar fashion to increased efficacy of active transporters exhibiting capacity limited activity, the pre-systemic metabolism of the tested compound may be considerably increased when the drug is
9 Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 3(2), presented to the metabolic enzymes (cytochrome P450, in particular CYP3A4) in a sustained manner, rather than by a bolus input. Table 1: Marketed products of GRDFs 10 S. No. Brand name Drug Company, Country Remarks 1 Madopar Levodopa (100 mg), Benserazide (25 mg) Roche products, USA 2 Valrelease Diazepam (15 mg) Hoffman-Laroche, USA 3 Liquid gaviscon Al. Hydroxide (95 mg), Mg. Carbonate (358 mg) Glaxo smith kline, India 4 Topalkan Al-Mg antacid Pierre fabre drug, France 5 Conviron Ferrous sulphate Ranbaxy, India 6 Cifran OD Ciprofloxacin (1 g) 7 Cytotec Misoprostol (100 mcg/200 mcg) 8 Oflin OD Ofloxacin (400 mg) Ranbaxy, India Pharmacia, USA Ranbaxy, India Floating CR capsule Floating capsule Effervescent floating liquid alginate preparation Floating liquid alginate preparation Colloidal gel forming FDDS Gas-generating floating tablet Bilayer floating capsule Gas generating floating tablet Improved bioavailability due to reduced P-glycoprotein (P-gp) activity in the duodenum In apparent contrast to the higher density of CYP3A4 at the upper part of the intestine, P-gpmRNA levels increase longitudinally along the intestine such that the highest levels are located in the colon. Therefore, for drugs that are P-gp substrate and do not undergo oxidative metabolism, such as digoxin, CR- GRDF may elevate absorption compared to the immediate and CR dosage forms. Reduced frequency of dosing For drugs with relatively short biological half-life, sustained and slow input from CR-GRDF may result in a flip-flop pharmacokinetics and enable reduced dosing frequency. This feature is associated with improved patient compliance, and thereby improves therapy. 11 Targeted therapy for local ailments in the upper GI tract The prolonged and sustained administration of the drug from the GRDF to the stomach may be advantageous for local therapy in the stomach and the small intestine. By this mode of administration, therapeutic drug concentrations may be attained locally while the systemic concentrations, following drug absorption and distribution, are minimal. Pharmacodynamics aspects 12 Reduced fluctuations of drug concentration Continuous input of the drug following CR-GRDF administration produces blood drug concentrations within a narrower range compared to the immediate release dosage forms. Thus, fluctuations
10 158 M. R. Kumar et al.: A Comprehensive Review on Gastro. in drug effects are minimized and concentration dependent adverse effects that are associated with peak concentrations can be prevented. This feature is of special importance for drugs with a narrow therapeutic index. Improved selectivity in receptor activation Minimization of fluctuations in drug concentration also makes it possible to obtain certain selectivity in the elicited pharmacological effect of drugs that activate different types of receptors at different concentrations. Reduced counter-activity of the body In many cases, the pharmacological response which intervenes with the natural physiologic processes provokes a rebound activity of the body that minimizes drug activity. Slow input of the drug into the body was shown to minimize the counter activity leading tohigher drug efficiency. Extended time over critical (effective) concentration For certain drugs that have non-concentration dependent pharmacodynamics, such as beta lactam antibiotics, the clinical response is not associated with peak concentration, but rather, with the duration of time over a critical therapeutic concentration. Minimized adverse activity at the colon Retention of the drug in the GRDF at the stomach minimizes the amount of drug that reaches the colon. Thus, undesirable activities of the drug in colon may be prevented. This pharmacodynamic aspect provides the rationale for GRDF formulation for beta-lactam antibiotics that are absorbed only from the small intestine, and whose presence in the colon leads to development of microorganism s resistance. Suitable drug candidates for gastro retention 13 In general, appropriate candidates for GRDDS are molecules that have poor colonic absorption but are characterized by better absorption properties at the upper parts of the GIT: (i) (ii) Narrow absorption window in GI tract, e.g., riboflavin and levodopa. Primarily absorbed from stomach and upper part of GItract, e.g., calcium supplements, chlordiazepoxide and cinnarazine (iii) Drugs that act locally in the stomach, e.g., antacids and misoprostol (iv) (v) Drugs that degrade in the colon, e.g., ranitidine HCl and metronidazole Drugs that disturb normal colonic bacteria, e.g., amoxicillin trihydrate. Drugs those are unsuitable for gastro retentive drug delivery systems 14 (i) (ii) Drugs that have very limited acid solubility e.g. phenytoin etc. Drugs that suffer instability in the gastric environment e.g. erythromycin etc. (iii) Drugs intended for selective release in the colon e.g. 5-amino salicylic acid and corticosteroids etc.
11 Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 3(2), Polymers and other ingredients used in the formulation of grdds 15 Category materials Polymers: HPMC K4 M, Calcium alginate, Eudragit S100 EudragitRL, Propylene foam, Eudragit RS, ethyl cellulose, poly methyl meth acrylate, Methocel K4M, Polyethylene oxide, β Cyclodextrin, HPMC 4000, HPMC 100, CMC, Polyethylene glycol, polycarbonate, PVA, Polycarbonate, Sodium alginate, HPC-L, CP 934P, HPC, Eudragit S, HPMC, Metolose S.M. 100, PVP, HPC-H, HPC-M, HPMC K15, Polyox, HPMC K4, Acrylic polymer, E4 M and Car-bopol Inert fatty materials (5%-75%) Edible, inert fatty materials having a specific gravity of less than one can be used to decrease the hydrophilic property of formu-lation and hence increase buoyancy. E.g. Beeswax, Fatty acids, long chain fatty alcohols, Gelucires 39/01 and 43/01. Other materials (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Evaluation 16 Effervescent agents:- Sodium bicarbonate, citric acid, tartaric acid, Di-SGC (Di- Sodium Glycine Carbo-nate, CG (Citroglycine) Release rate accelerants (5%-60%):- Lactose, mannitol Release rate retardants (5%-60%):- Dicalcium phosphate, talc, magnesium stearate Buoyancy increasing agents (upto80%):- Ethyl cellulose (v) Low density material:- Polypropylene foam powder (Accurel MP 1000 ) (A) in vitro evaluation (i) Floating systems (a) Buoyancy lag time: It is determined in order to assess the time takenby the dosage form to float on the top of the dissolution medium, after it is placed in the medium. These parameters can be measured as a part of the dissolution test. (b) Floating time: Test for buoyancy is usually performed in SGF-Simulated Gastric Fluid maintained at 370 C. The time for which the dosage form continuously floats on the dissolution media is termed as floating time. (c) Specific gravity/density: Density can be determined by the displacement method using Benzene as displacement medium. (d) Resultant weight: Now, we know that bulk density and floating time are the main parameters for describing buoyancy. But only single determination of density is not sufficient to describe the buoyancy because density changes with change in resultant weight as a function of time. For example a matrix tablet with bicarbonate and matrixing polymer floats initially by gas generation and entrapment but after some time, some drug is released and simultaneously some outer part of matrixing polymer may erode out leading to change in resultant weight of dosage form. The magnitude and direction of force/resultant weight (up or down) is corresponding to its buoyancy force (Fbuoy) and gravity force (Fgrav) acting on dosage form (Fig. 8).
12 160 M. R. Kumar et al.: A Comprehensive Review on Gastro. Fig. 8: Swelling systems-water uptake F = Fbuoy Fgrav, F = Df g V Ds g V, F = (Df Ds) g V, F = (Df M/V) g V Where, F = Resultant weight of object Df = Density of fluid Ds = Density of solid object g = Gravitational force M = Mass of dosage form V = Volume of dosage form So when Ds, density of dosage form is lower, F force is positive gives buoyancy and when it is Ds is higher, F will negative shows sinking. Plot of F vs. Time is drawn and floating time is time when F approaches to zero from positive values. (ii) Swelling systems (a) Swelling Index: After immersion of swelling dosage form into SGF at 37 0 C, dosage form is removed out at regular interval and dimensional changes are measured in terms of increase in tablet thickness/diameter with time. (b) Water Uptake 17 : It is an indirect measurement of swelling property of swellable matrix. Here dosage form is removed out at regular interval and weight changes are determined with respect to time. So it is also termed as Weight Gain. Where, Wt = Weight of dosage form at time t Wo = Initial weight of dosage form Water uptake = WU = (Wt Wo) * 100 / Wo In this assembly concentric circles with various diameters are drawn in computer and print out is laminated to make hydrophobic. This laminated piece is attached with some system which can facilitate up and down movement of assembly.
13 Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 3(2), This assembly is placed in beaker and tablet is placed exactly at center and then there is no disturbance given to tablet. Tablet is allowed to swell on laminated paper and diameter can be easily noted without removing out. To determine water uptake/weight gain, whole assembly can bring out. Weighing of assembly done after wiping off water droplets adhered at surface of assembly and then can be placed back as it is without touching to tablet. Rate of water penetration is also important parameter for swelling matrix, that how fast swelling occurs is determined by equation 18 : Water up take 2 x Area of tablet Penetration rate = x per unit time Water density (c) Continuous monitoring of water uptake 19 : Although previous method has advantage of un-disturbance of swollen tablet, but for measuring water uptake one has to remove whole assembly out of beaker, so process in not continuous. Continuous monitoring of water uptake is possible by following apparatus. In this apparatus, swelling tablet is placed on glass filter as support in one hallow cylinder with smooth surface inside, and one light weight punch is placed on it to prevent floating. This cylinder is placed pre-heated in dissolution medium. Another dissolution medium reservoir beaker is placed on digital balance and both are connected with media filled U tube as shown in figure and medium level is kept equal. As swelling of tablet started, it absorbs water and water level in outer part of cylinder is goes down. The decrease in water level is maintained by importing extra medium via U tube from reservoir beaker. As medium is transfer from reservoir, amount of water transfer can be determined by observing loss in weight by digital balance. B) in vitro dissolution tests 20 A. In vitro dissolution test is generally done by using USP apparatus with paddle and GRDDS is placed normally as for other conventional tablets. But sometimes as the vessel is large and paddles are at bottom, there is much lesser paddle force acts on floating dosage form which generally floats on surface. As floating dosage form not rotates may not give proper result and also not reproducible results. Similar problem occur with swellable dosage form, as they are hydrogel may stick to surface of vessel or paddle and gives irreproducible results. In order to prevent such problems, various types of modification in dissolution assembly made are as follows. B. To prevent sticking at vessel or paddle and to improve movement of dosage form, method suggested is to keep paddle at surface and not too deep inside dissolution medium. C. Floating unit can be made fully submerged, by attaching some small, loose, non-reacting material, such as few turns of wire helix, around dosage form. However this method can inhibit three dimensional swelling of some dosage form and also affects drug release.
14 162 M. R. Kumar et al.: A Comprehensive Review on Gastro. D. Other modification is to make floating unit fully submerged under ring or mesh assembly and paddle is just over ring that gives better force for movement of unit. E. Other method suggests placing dosage form between 2 ring/meshes. F. In previous methods unit have very small area, which can inhibit 3D swelling of swellable units, another method suggest the change in dissolution vessel that is indented at some above place from bottom and mesh is place on indented protrusions, this gives more area for dosage form. G. Inspite of the various modifications done to get the reproducible results, none of them showed corelation with the in vivo conditions. So a novel dissolution test apparatus with modification of Rossett-Rice test Apparatus was proposed. Rossett-Rice test is used for predicting in-vitro evaluation of directly acting antacid (action by chemical neutralization of acid), where HCl is added gradually to mimic the secretion rate of acid from the stomach. 22 In this modified apparatus as shown in figure, it has side arm from bottom of beaker such that it maintains volume of 70 ml in beaker and fresh SGF is added from burette at 2 ml/min rate. Thus sink condition is maintained. Stirring is done by magnetic stirrer at RPM (Fig. 9). (C) In vivo evaluation 21 Fig. 9: In vitro dissolution tests (a) Radiology: X-ray is widely used for examination of internal body systems. Barium Sulphate is widely used Radio Opaque Marker. So, BaSO 4 is incorporated inside dosage form and X-ray images are taken at various intervals to view GR. (b) -Scintigraphy: Similar to X-ray, -emitting materials are incorporated into dosage form and then images are taken by scintigraphy. Widely used -emitting material is 99Tc. (c) Gastroscopy: Gastroscopy is peroral endoscopy used with fiber optics or video systems. Gastroscopy is used to inspect visually the effect of prolongation in stomach. It can also give the detailed evaluation of GRDDS. (d) Magnetic marker monitoring: In this technique, dosage form is magnetically marked with incorporating iron powder inside, and images can be taken by very sensitive bio-magnetic measurement equipment. Advantage of this method is that it is radiation less and so not hazardous. (e) Ultrasonography: Used sometimes, not used generally because it is not traceable at intestine. (f) 13C Octanoic acid breath test: 13C Octanoic acid is incorporated into GRDDS. In stomach due to chemical reaction, octanoic acid liberates CO 2 gas which comes out in breath. The important Carbon atom which will come in CO 2 is replaced with 13C isotope. So time upto which 13CO 2 gas is observed in breath
15 Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 3(2), can be considered as gastric retention time of dosage form. As the dosage form moves to intestine, there is no reaction and no CO 2 release. So this method is cheaper than other. 23 Future potential 24 Offers advantages for drugs with poor bioavailability because their absorption is restricted to upper GI tract and they can be delivered efficiently their absorption and enhancing bioavailability. In some cases lower bioavailability of drugs could be balanced by clinical advantages of GRDDS. Example: In patients with advanced parkinson s disease, who experience fluctuations in symptoms while they take levodopa, a HBS dosage form offers better control of motor fluctuations. GRDDS offer beneficial strategy for treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers, also being exploited for development of several anti-reflux formulations. 25 Promising area of research regarding GRDDS is eradication of H. Pylori-causative of chronic gastritis and peptic ulcer. Its complete eradication requires high concentration of anti biotic. Sustained release of liquid preparation of ampicillin with using sodium alginate- that spreads and adheres to gastric mucosal surface where by drug is released continuously. CONCLUSION This study concludes that GRDDS is one of the efficient technique to maintain the sustained release of drug in gastric environment and there by increases its absorption and bioavailability. All these GRDDS are interesting and more feasible when compared to other drug delivery systems and have their own advantages and disadvantages. 26 Now a lot of research program is going on to develop new concepts regarding GRDDS for various drugs by which in the near future we can ultimately lead to improved efficiency of various types of pharmacotherapies. GRDDS is much safer dosage form and have systemic, localized actions as well GRDDS do help in the treatment of chronic diseases like ulcers and carcinoma of GIT, and also reduces dose frequency there by minimize contra indication, systemic toxicity, drug dependence. Ultimately GRDDS is an simple yet effective drug delivery system. 27 REFERENCES 1. G. S. Banker and N. R. Anderson, Tablets: The Theory and Practice of Industrial Pharmacy, 3 rd Edition, Varghese Pub. House, Bombay (2007). 2. W. ChienYie, Concepts and System Design for Rate Controlled Drug Delivery in Novel Drug Delivery System, 2 nd Edn., New york, Marcell Dekker Inc. (1992). 3. T. W. Lee and J. R. Robinson, Controlled Release Drug Delivery Systems In, Gennaro AR, 20 th Edition, Vol. I (2000). 4. Joseph R. Robinson and Vincent H. L. Lee, Controlled Drug Delivery, Fundamentals and Applications, 2 nd Edition, Revised and Expanded, Marcell. Dekker Inc., New York (2009). 5. Y. MadhusudanRao, A. V. Jithan, Advances in Drug Delivery, Vol. II, Pharma. Med. Press, Hyderabad (2011). 6. S. P. Vyas and Roop K. Khar, Controlled Drug Delivery, Concepts & Advances, Vallabh Prakashan, Delhi (2012).
16 164 M. R. Kumar et al.: A Comprehensive Review on Gastro. 7. Gilbert S. Banker and Christopher T. Rhodes, Modern Pharmaceutics, 4 th Edition, Revised and Expanded, Marcell Dekker Inc., New York (2007). 8. Donald L. Wise, Handbook of Pharmaceutical Controlled Release Technology, Marcell Dekker Inc., New York (2008). 9. S. P. Vyas and R. K. Khar, Targetted & Controlled Drug Delivery, Novel Carrier Systems, CBS Publications, Delhi (2012). 10. Aulton ME, Pharmaceutics: The Science of Dosage Form Design, International Student Edition, London, Churchill Livingstone (2002). 11. H. E. Junginger, Drug Targeting and Delivery Concepts in Dosage Form Design, Ellis Horwood, England (2010). 12. N. K. Jain, Controlled and Novel Drug Delivery, CBS Publications, Delhi (2008). 13. Milo Gibaldi Biopharmaceutics and Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 4th Edition, Pharma Book Syndicate, Hyderabad (2006). 14. K. C. Aterman, A Critical Review of Gastro Retentive Controlled Drug Delivery, Pharmaceutical Development and Technology, 12, 1-10 (2007). 15. P. G. Yale, S. Khan and V. F. Patel, Floating Drug Delivery Systems: Need and Development, Indian J. Pharamceut. Sci., 67, (2005). 16. S. Arora, J. Ali, A. Ahuja, R. K. Khar and S. Baboota, Floating Drug Delivery Systems: A Review, AAPS Pharma. Scitech., 6(3), E (2005). 17. G. M. Patel, H. R. Patel and M. Patel, Floating Drug Delivery System: An Innovative Approach to Prolong Gastric Retention. Pharmacoinfo.net (2007). 18. B. N. Singh and H. K. Kwon, Floating Drug Delivery Systems: An Approach to Oral Controlled Drug Delivery Via Gastric Retention, J. Controlled Release, 63(3), (2000). 19. E. A. Klausner, E. Lavy and M. Friedman, Hofmann, Expandable Gastro Retentive Dosage Forms, J. Controlled Release, 90(2), (2003). 20. B. Nath, L. K. Nath, B. Mazumdar, N. K. Sharma and M. K. Sarkar, Preparation and In Vitro Evaluation of Gastric Floating Microcapsules of Metformin HCl. Ind. J. Pharm. Educ. Res., 43(2), (2009). 21. G. S. Asane, Mucoadhesive Gastrointestinal Drug Delivery System: An Overview (2007) S. Baumgartner, K. Julijana, V. Franc, V. Polona and J. Bojon, Optimisation of Floating Matrixtablets and Evaluation of their Gastric Residencetime, Int J. Pharm., 239(12), (2000). 24. S. Garg and S. Sharma, Gastroretentive Drugdelivery Systems, Pharmatech., 3(1), (2003). 25. V. Iannucelli, G. Coppi, M. T. Bernabei and R. Camerorni, Air Compertment Multiple-Unitsystem for Prolonged Gastric Residence, Part-I. Formulation Study. Int J. Pharm., 174, (1998). 26. A. Hoffman, Pharmacodynamic Aspects of Sustained Release Preparation, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 33(3), (1998). 27. A. J. Moes, Gastroretentive Dosage Forms, Crit. Rev., Ther. Drug Carrier Syst., 10(2), (1993).
Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Biswajit Biswal IRJP 2 (7)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review
 ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems
 Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage form of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride.
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Tablets Using Different Polymers: Guargum, Sodium Alginate, Hpmc100cps and Carbopol940
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
2- Minimum toxic concentration (MTC): The drug concentration needed to just produce a toxic effect.
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
This PDF is available for free download
 Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Formulation and evaluation of immediate release salbutamol sulphate
 5 Formulation, optimization and evaluation of immediate release layer of salbutamol sulphate Salbutamol is moderately selective beta (2)-receptor agonist similar in structure to terbutaline and widely
5 Formulation, optimization and evaluation of immediate release layer of salbutamol sulphate Salbutamol is moderately selective beta (2)-receptor agonist similar in structure to terbutaline and widely
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
Int J Pharm Bio Sci. Harshal P. Gahiwade *et al Available Online through IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH
 Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride
 Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4
 CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(1), 2010, 405-414 STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS V. L. NARASAIAH, T. KARTHIK KUMAR, D. SRINIVAS, K. SOWMYA, P. L. PRAVALLIKA and Sk. Md. MOBEEN
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(1), 2010, 405-414 STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS V. L. NARASAIAH, T. KARTHIK KUMAR, D. SRINIVAS, K. SOWMYA, P. L. PRAVALLIKA and Sk. Md. MOBEEN
Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
Antacid therapy: Antacids side effects:
 Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
A. Incorrect! Histamine is a secretagogue for stomach acid, but this is not the only correct answer.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF FAMOTIDINE FLOATING TABLETS BY LIPID SOLID DISPERSION SPRAY DRYING TECHNIQUE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF FAMOTIDINE FLOATING TABLETS BY LIPID SOLID DISPERSION
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF FAMOTIDINE FLOATING TABLETS BY LIPID SOLID DISPERSION
A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
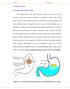 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H.
 Pharmaceutical Research Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H. pylori Infection Shikha Jain, Vikas Jain, S.C. Mahajan
Pharmaceutical Research Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H. pylori Infection Shikha Jain, Vikas Jain, S.C. Mahajan
STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 1934-1942 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS K. VENUGOPAL * and K. P. R. CHOWDARY a Nirmala College
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 1934-1942 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS K. VENUGOPAL * and K. P. R. CHOWDARY a Nirmala College
A STUDY ON SUITABILITY OF NIMESULIDE-BETACYCLODEXTRIN COMPLEX IN ORAL AND TOPICAL DOSAGE FORMS
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 1, Suppl 1, Nov.-Dec. 2009 Research Article A STUDY ON SUITABILITY OF NIMESULIDE-BETACYCLODEXTRIN COMPLEX IN ORAL AND TOPICAL DOSAGE
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 1, Suppl 1, Nov.-Dec. 2009 Research Article A STUDY ON SUITABILITY OF NIMESULIDE-BETACYCLODEXTRIN COMPLEX IN ORAL AND TOPICAL DOSAGE
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin Bilayer Tablets
 CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
Venkateswara Rao et.al Indian Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Biotechnology ISSN: (Print) ISSN: (Online)
 Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery Tablet
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: Journal homepage:
 Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability.
 Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Scholars Research Library. Formulation and evaluation of buccoadhesive tablet of Atenolol
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets of lisinopril
 Journal of GROVER Scientific & Industrial AGARWAL: Research FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUBLINGUAL TABLETS OF LISINOPRIL Vol. 71, June 2012, pp. 413-417 413 Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets
Journal of GROVER Scientific & Industrial AGARWAL: Research FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUBLINGUAL TABLETS OF LISINOPRIL Vol. 71, June 2012, pp. 413-417 413 Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
 Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Effect of Excipients on Dissolution: Case Studies with Bio-relevant/ Hydro-alcoholic Media
 Effect of Excipients on Dissolution: Case Studies with Bio-relevant/ Hydro-alcoholic Media Sandip B. Tiwari, Ph.D. Technical Director: South Asia Colorcon Asia Pvt. Ltd., Goa, India DISSO-INDIA 2013, May
Effect of Excipients on Dissolution: Case Studies with Bio-relevant/ Hydro-alcoholic Media Sandip B. Tiwari, Ph.D. Technical Director: South Asia Colorcon Asia Pvt. Ltd., Goa, India DISSO-INDIA 2013, May
ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF NIMESULIDE BY CYCLODEXTRINS, POLOXAMER AND PVP
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 9(2), 20, 637-646 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF NIMESULIDE BY CYCLODEXTRINS, POLOXAMER AND PVP K. P. R. CHOWDARY *, K.
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 9(2), 20, 637-646 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF NIMESULIDE BY CYCLODEXTRINS, POLOXAMER AND PVP K. P. R. CHOWDARY *, K.
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT "Carbellon" Tablets. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Active Constituents: Activated Charcoal Ph.Eur. Magnesium Hydroxide Ph.Eur.
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT "Carbellon" Tablets. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Active Constituents: Activated Charcoal Ph.Eur. Magnesium Hydroxide Ph.Eur.
International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science
 Research article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of Metoprolol Tartrate Patel
Research article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of Metoprolol Tartrate Patel
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p.
 Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin
 Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery System
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
FORMULATION AND EVALUATIONOF AMOXYCILLIN: THREE-LAYER GUAR GUM MATRIX TABLET
 Gupta and Singh, IJPSR, 2013; Vol. 4(7): 2683-2690. ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received on 05 March, 2013; received in revised form, 29 April, 2013; accepted, 29 June,
Gupta and Singh, IJPSR, 2013; Vol. 4(7): 2683-2690. ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received on 05 March, 2013; received in revised form, 29 April, 2013; accepted, 29 June,
EFFECT OF PVP ON CYCLODEXTRIN COMPLEXATION OF EFAVIRENZ FOR ENHANCING ITS SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article EFFECT OF PVP ON CYCLODEXTRIN COMPLEXATION OF EFAVIRENZ FOR ENHANCING ITS SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article EFFECT OF PVP ON CYCLODEXTRIN COMPLEXATION OF EFAVIRENZ FOR ENHANCING ITS SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION
Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets
 Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation
 METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Research Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF CLARITHROMYCIN ORAL DOSAGE FORM AGAINST HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF CLARITHROMYCIN ORAL DOSAGE FORM AGAINST HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION
Suppository Chapter Content
 10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
Ph. D Synopsis. Mr. Mehul Pravinchandra Patel Page 1
 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science ISSN Vol.4 (2), April-June, 2014 REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM PRAFULL GHORPADE* 1, SHRENIK KAMBLE 2 1 Marathwada Mitra Mandal s College of Pharmacy, Kalewadi (Thergaon), Pune, Maharashtra, India *Corresponding author
REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM PRAFULL GHORPADE* 1, SHRENIK KAMBLE 2 1 Marathwada Mitra Mandal s College of Pharmacy, Kalewadi (Thergaon), Pune, Maharashtra, India *Corresponding author
PREPARATION AND INVITRO EVALUATION OF RABEPRAZOLE SODIUM DELAYED RELEASE ENTERIC COATED TABLETS
 Page1000 Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2014 ISSN NO: 2231-6876 Journal home page: http:///index.php/en/ INDO AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH PREPARATION AND INVITRO EVALUATION
Page1000 Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2014 ISSN NO: 2231-6876 Journal home page: http:///index.php/en/ INDO AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH PREPARATION AND INVITRO EVALUATION
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):348-352 Formulation and in vitro evaluation of modified
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):348-352 Formulation and in vitro evaluation of modified
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 974-434 Vol.2, No.1, pp 341-347, Jan-Mar 1 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS Kothawade S. N. 1 *, Kadam
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 974-434 Vol.2, No.1, pp 341-347, Jan-Mar 1 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS Kothawade S. N. 1 *, Kadam
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Formulation and Evaluation
 Chapter-5 Formulation and Evaluation 5.1 OBJECTIVE After successful taste masking and solubility enhancement of drugs in preliminary studies, by using Mannitol Solid Dispersion, next step includes the
Chapter-5 Formulation and Evaluation 5.1 OBJECTIVE After successful taste masking and solubility enhancement of drugs in preliminary studies, by using Mannitol Solid Dispersion, next step includes the
Digestive System. - Food is ingested
 11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
Preparation and Evaluation of Ethyl Cellulose Coated Microcapsules of Carbamazepine for Controlled Release
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 20, No. 8 (2008), 5901-5907 Preparation and Evaluation of Ethyl Cellulose Coated Microcapsules of Carbamazepine for Controlled Release K.P.R. CHOWDARY* and MALLURU SUBBA
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 20, No. 8 (2008), 5901-5907 Preparation and Evaluation of Ethyl Cellulose Coated Microcapsules of Carbamazepine for Controlled Release K.P.R. CHOWDARY* and MALLURU SUBBA
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS): A REVIEW
 25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
Chapter 2 Rationale and Objective
 Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
