Original Article J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr., 43, 69 74, September 2008
|
|
|
- Amice Stephany Harvey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr., 43, 69 74, September 2008 Effects JCBN Journal the Kyoto, jcbn /jcbn Original Society Japan of Article Clinical of for Free Astaxanthin Biochemistry Radical Research and Nutrition Japan on Human Blood Rheology Hiromi Miyawaki 1, Jiro Takahashi 2, *, Hiroki Tsukahara 2, and Isao Takehara 3 1 Miyawaki Orthopedic Clinic, Hokkaido , Japan 2 Life Science Division, Fuji Chemical Industry Co., Ltd, Toyama , Japan 3 Central Research Institute, New Drug Development Research Center, Inc., Hokkaido , Japan Received ; accepted Received 1 February, 2008; Accepted 19 February, 2008 Copyright Summary 2008 Effects JCBN of astaxanthin (AX) derived from H. pluvialis on human blood rheology were investigated in 20 adult men with a single-blind method. The experimental group was 57.5 ± 9.8 years of age and the placebo group was 50.8 ± 13.1 years of age. A blood rheology test that measures whole blood transit time was conducted using heparinized blood of the volunteers by a MC-FAN apparatus (microchannel array flow analyzer). After administration of AX 6 mg/day for 10 days, the values of the experimental group were decreased from 52.8 ± 4.9 s to 47.6 ± 4.2 s (p<0.01) and a comparison of the values between the experimental (47.6 ± 4.2 s) and the placebo (54.2 ± 6.7 s) groups showed a significant difference (p<0.05). There were no adverse effects resulting from the administration of AX 6 mg/day for 10 days. Informed consent was obtained from each subject. Key Words: astaxanthin, blood rheology, microchannel array flow analyzer, male volunteers, blood transit time Introduction Astaxanthin (AX), a form of carotenoid referred to as a xanthophyll, is a substance distributed widely in nature. Since being separated from lobster (Astacus gammaus L.) in 1938 by Kuhn, R. et al. [1], AX has been identified as the substance composing the red pigmentation in microorganisms [2, 3], fish [4], Crustacea [5] and other organisms. AX is the substance that gives salmon [6] and trout, two marine products enjoyed as favorite foods in Japan, their distinct color. Thus many people, especially northern peoples including Japanese who have long included seafood in their diets, have been ingesting AX for many years. While much research concerning the physiological action of AX has been reported, in research concerning the eyes, Grangaud, R, et al. [7] have reported on the effect found on *To whom correspondence should be addressed. Tel: Fax: takahashi@fujichemical.co.jp dry eye when AX was administered to rats. Tso, M.O.M., et al. [8] have reported AX was found to be effective for eye damage in rats, and that a recovery effect after application of optical stress to the eyes was found in a group administered AX when the thickness of the retina outer granular layer and rhodopsin decrease were measured and recovery from damage were compared. In addition, the xanthophyll group including AX has been reported to protect human eye lens epithelial cells from UVB-induced stress [9], and AX s protective action also has been found to be stronger than that of α-tocopherol. As effects of AX ingestion on the eyes, Sawaki et al. [10] reported improvement in visual acuity for depth and flicker fusion threshold, while Nagaki, Y. et al. [11] reported significant improvement in amplitude of accommodation before and after ingestion (no change in amplitude of accommodation in the control group) in a study employing VDT workers. Nakamura et al. [12] reported that as a result of administering 0 mg, 2 mg, 4 mg and 12 mg of AX to four groups, respectively, once per day for 28 days, there was improvement in far vision uncorrected visual acuity and 69
2 70 H. Miyawaki et al. shortened positive accommodation time for the 4 mg group and 12 mg group, respectively. In this paper, we report on a study of the effect of AX ingestion on human blood rheology as one clarification of the action mechanism for such effects. Materials and Methods Study materials and equipment Study food and placebo food. Study food capsules containing a preparation of AX 3 mg (as a free-form) derived from H. pluvialis from Fuji Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. (FHAX09) and placebo food capsules that did not contain AX (FHAX10) were used as a study food and placebo food. Study equipment. Vacuum blood collection tubes (Terumo) to which 0.25 ml of heparin liquid (Novo Heparin, 1000 units/ml Aventis Pharma Japan) had been added beforehand were used to collect 5 ml blood samples from subjects elbow veins, which were used as samples for the rheology evaluations. To perform the blood rheology evaluations, heparinized whole blood samples of approximately 200 μl were forced to flow through the microchannels of a Microchannel Array (Bloody 6-7; 8736 channels; width 7 μm, length 30 μm, depth 4.5 μm; Hitachi Haramachi Electronics Co., Ltd.) under a pressure difference of 20 cm H2O, and the transit time for 100 μl of blood was determined using a MC-FAN (Hitachi Haramachi Electronics Co., Ltd.), in accordance with the blood rheology procedure described in Kikuchi et al. [13]. The values obtained were shown by using the following equation to convert them into the values when the transit time for 100 μl isotonic saline solution is 12 s, based on the transit time for isotonic saline solution measured immediately before. Conversion equation: Converted value = Blood transit time 12 s. / Isotonic saline solution transit time Subjects The subjects were selected from individuals who had freely consented to participation in the study in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (individuals who had signed a consent form). Prior to undertaking the survey, the physicians in charge of the study handed the participants an explanation and consent form, and explained all necessary matters pertaining to the purpose, significance and method of the study, the anticipated results and risks, the fact the participant will not suffer any disadvantages if he/she does not consent to participation in the study, the fact the participant can withdraw at any time even after having consented to participation in the study, other related matters, and protection of the subject s human rights, and after having verified the participants had understood the details explained, obtained consent to voluntary participation in the study in writing from the participants. Examinations and measurements were performed at the first screening. From the subjects determined by the study physician to be suitable, 20 individuals who showed a stable blood transit time in a range of s/100 μl were selected at a second screening and made available for the study. Study method To create a balance between the two groups based on the blood transit times measured at the time of the screening examinations, ten individuals each were allocated to the study food ingestion group and the placebo food ingestion group. The subjects were asked to ingest two capsules of the study food or placebo (AX 6 mg/day or 0 mg/day) once each day after dinner, and were examined and their blood samples collected at the start before ingestion and after ten days. For the blood rheology values immediately prior to ingestion, the values at the time of the second screening were adopted. On the day before the day of each visit to the study hospital, subjects were required to finish dinner by 9:00 PM and consume no food or beverages (other than water); the subjects were examined the following morning in a fasting condition, and blood was collected from a vein in the elbow area. The daily ingestion amount of 6 mg and ingestion period of ten days were set based on the results of studies by Ohno et al. to set ingestion amount [14] and verify the results [15]. Evaluation procedure Mean value and standard deviation were determined for each evaluation item. The comparison before and after ingestion was performed by statistical analysis using a paired t test. In addition, the comparisons between the study food and placebo were verified for homoscedasticity using the F test. Student s t test was performed when the results were homoscedastic, and the Aspin-Welch t test was performed when the results were heteroscedastic. The significance levels were 5% for the F test and 5% and 1% for the t test. Results Preliminary study To establish the criteria for subject selection for the blood rheology study, a preliminary study was conducted. Seven adult males who had consented to participation of their own free will ingested two AX capsules identical to the study food once each day (AX 6 mg/day) after dinner for a ten-day period. Blood transit time measurement was performed by collecting blood samples, on the morning of the day ingestion began and on the morning of the day after the final ingestion day, and measuring transit times. The results are shown in Table 1. Because a tendency for the J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr.
3 Effects of Astaxanthin on Human Blood Rheology 71 Table 1. Subjects Preliminary study blood rheology Age Before ingestion After ingestion Difference Astaxanthin (AX) 6 mg/day; measured before and after ingestion for ten days Unit: Sec/100 μl Table 2. Subjects backgrounds Item Unit Placebo food Study food Number of subjects Persons Age Years 50.8 ± ± 9.8 Height Cm ± ± 3.8 Weight Kg ± ± 8.5 Body fat percentage % 22.5 ± ± 5.5 BMI 23.3 ± ± 2.6 Temperature C 36.1 ± ± 0.4 Mean value ± standard deviation value to decrease after ingestion was seen for cases in which the blood rheology values before ingestion were higher than 45 s/100 μl, we decided to select individuals who showed a value within the s/100 μl range for the human blood rheology measurement study as well. Human blood rheology measurement study Subjects backgrounds. The subjects physical examination backgrounds are shown in Table 2. At the start of ingestion, the subjects had a mean age of 57.5 ± 9.8 years in the study food ingestion group and 50.8 ± 13.1 years in the placebo food ingestion group. Body weight, body fat percentage, Body Mass Index (BMI), and other measures were all within normal ranges. As shown by the results, both the study food ingestion group and the placebo food ingestion group were structured to have nearly identical subject backgrounds. Adverse events and examination opinions. In the physician examinations implemented on the study food ingestion start day and after ingestion for ten days, no conditions corresponding to an adverse event were found. Furthermore, no anomalies of any kind were found in the subjective symptom opinions in the ingestion diaries in which the subjects themselves recorded information such as their study food ingestion circumstances or side effects for each day. Study food ingestion circumstances and meal questionnaire. The study food ingestion circumstances were 100% for all subjects. On the meal questionnaire completed on the screening day, there were no subjects with eating habits that deserved special mention. Blood rheology. A summary of the measurement results for each subjects blood transit time measurements is shown in Table 3 and Fig. 1. Compared with the values before ingestion, after ingestion for ten days, the blood transit times for the study food ingestion group were shortened significantly (52.8 ± 4.9 s 47.6 ± 4.2 s). In addition, after ingestion for ten days, compared with the placebo food ingestion group, the study food ingestion group showed significantly Table 3. Blood transit time (Unit: Sec/100 μl) Placebo food Study food Subject No. Ingestion Day 0 Ingestion Day 10 Subject No. Ingestion Day 0 Ingestion Day 10 A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B M ± SD 53.6 ± ± ± ± 4.2** # M ± SD: mean value ± standard deviation Vol. 43, No. 2, 2008
4 72 H. Miyawaki et al. Fig. 1. Summary of measurement results for each subject s blood transit time lower values for blood transit time (placebo food ingestion group: 54.2 ± 6.7 s; study food ingestion group: 47.6 ± 4.2 s). With ingestion of AX 6 mg/day for a ten-day period, the blood rheology of the study food ingestion group was improved significantly (p = 0.05) in both a comparison within the group (Day 0 and Day 10) and a comparison with the placebo food ingestion group. Discussion AX, a form of carotenoid referred to as a xanthophyll, possesses a chemical structure with the long chain conjugate double bond and β-ionone ring at both ends that has been replaced by a keto-group and hydroxyl-group. Since being separated as a natural pigment with a reddish orange color, much research has been conducted and its widespread presence as a pigment in marine products such as shrimp, crabs, salmon and salmon roe has been clarified. Such fish and crustaceans are consumed by humans for food, and considered historically AX is a substance the human race has ingested from centuries ago. Recently the strong antioxidant effect of AX has attracted attention, and AX is being tested actively in use as a health food supplement for maintaining human health. It is believed that microorganisms such as algae, yeasts and bacilli utilize AX s strong antioxidant effect to defend themselves from strong natural sunlight, and the fish and crustaceans that consume these microorganisms also use AX as a pigment because it is useful in protecting them from the ravages of light and stress. In addition, AX also is present abundantly in eggs spawned to produce the next generation, where it is thought to protect the eggs and be used for the protection and growth of young fish. While AX is assumed to be one of the substances with an antioxidant effect found in nature [16, 17] that shows the strongest antioxidant effect, at this point this is conjectured from its role in the world of living organisms. Research in recent years continues to clarify that AX shows not only an antioxidant effect but various other physiological actions. On the other hand, as societies evolve into societies in which people live longer, measures to prevent the lifestyle diseases that accompany longer lives also have grown in importance. Ingestion of AX and other antioxidant substances is likely to be considered as one such measure. AX demonstrates a variety of physiological actions and is considered suitable for this purpose. AX has attracted attention because its action is believed to work effectively against oxidation in lipid metabolism, given that AX is said to prevent overoxidation of lipids through its strong antioxidant effect and have action that controls oxidation of LDL [18], and also because it is widely distributed in the lipoprotein areas of the body [19, 20]. Such actions are though to work by preventing oxidation of biomembranes including cell membranes, and there is a possibility this will be linked to effects such as an arteriosclerosis prevention effect [21], an anti-inflammatory effect [22] and control of diabetes nephropathy (kidney disease) [23, 24]. Furthermore, AX has been reported to have an ocular accommodation improvement effect [10 15], and the dose setting study [14] and effect verification study [15] by Ohno et al. in particular provided results that strongly reconfirm the effect of AX on ocular accommodation. It is thought such promotion of recovery from asthenopia in this manner might contribute to the improvement of blood circulation in peripheral systems. Based on such conjecture, we performed a study of the effect of continuous ingestion of AX 6 mg/day for a ten-day period on blood rheology. In the study food ingestion group, compared with the values before ingestion a decrease in blood transit time was found in eight of ten individuals after ingestion for ten days, J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr.
5 Effects of Astaxanthin on Human Blood Rheology 73 and a significant shortening in time was shown for mean value as well. Moreover, after ingestion for ten days, blood transit time showed a significantly low value for the study food ingestion group compared with the placebo food ingestion group. A shortening of blood transit time, or in other words an improvement in blood rheology, was found from continuously ingesting AX 6 mg per day for ten days. In the survey of the subjects conducted at the same time, no abnormal findings or adverse events that appeared to result from ingestion of the study food were found in the subjective and objective findings. Other substances such as tocotrienol, an antioxidant derived from palm oil [25], and black vinegar [26] (which has shown antioxidant power) also have been reported as showing effects for improvement of blood rheology. Tocotrienol has been found to improve excessive sensitivity to cold (unpublished data) by improving precapillary circulation. Based on such reports, the possibility that improvement of blood rheology improves precapillary circulation is conjectured. The improvement in blood rheology from AX is conjectured to confer an antioxidant effect to the erythrocyte membrane or flexibility to the membrane, by means such as taking a position that enables it to traverse longitudinally the suitable membrane to demonstrate an antioxidant effect within and outside the lipid double membrane, in contrast to β-carotene, which is trapped in the lipid double membrane [27] or becomes difficult to convert into an excellent pro-oxidant for physical elimination of radicals [28]. Conclusion We found a shortening of blood transit time that is, an improvement of blood rheology when we studied healthy adult male volunteers with a blood transit time of s to evaluate the effect on blood rheology from continuous ingestion of AX 6 mg per day for a ten-day period. References [1] Kuhn, R. and Soerensen, N.A.: The coloring matters of the lobster (Astacus gammarus L.). Z. Angew. Chem., 51, , [2] Tischer, J.: Carotenoids of fresh-water algae V. The carotenoids of H. pluvialis. Z. Physiol. Chem., 252, , [3] Andrewes, A.G., Phaffia, H.J., and Starr, M.P.: Carotenids of Phaffa rhodozyma, a red pigmented fermenting yeast. Phyiochem., 15, , [4] Miki, W. and Fujita, T.: Fish and Carotenoid metabolization. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 23, , [5] De, Nicola. M.: Carotenoids of the carapace of the echinoderm. Ophidiaster Ophidianus. Biochem. J., 56, , [6] Khare, A., Moss, G.P., Weedon, B.C., and Matthews, A.D.: Identification of astaxanthin in Scottish salmon. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B, 45, , [7] Grangaud, R. and Massonet, R.: Anti-xerophthalmic activity of astaxanthin esters. C. R. Seances Soc. Biol. Fil., 148, , [8] Tso, M.O.M. and Lam, T.T.: Method of retarding and ameliorating central nervous system and eye damage. U.S. Patent, 5, , [9] Chitchumroonchokchai, C., Bomser, J.A., Glamm, J.E., and Failla, M.L.: Xanthophylls and alpha-tocopherol decrease UVB-induced lipid peroxidation and stress signaling in human lens epithelial cells. J. Nutr., 134, , [10] Sawaki, K., Yoshigi, H., Aoki, K., Koikawa, N., Azumane, A., Kaneko, K., and Yamaguchi, M.: Effect of astaxanthin on sports performance Effect on visual function and muscle fatigue recovery in athletes. J. Clin. Ther. and Med., 18, , [11] Nagaki, Y., Hayasaka, S., Yamada, T., Hayasaka, Y., Sanada, M., and Uonomi, T.: Effects of astaxanthin on accommodation, critical flicker fusion, and pattern visual evoked potential in visual display terminal workers. J. Trad. Med., 19, , [12] Nakamura, A., Isobe, A., Otaka, Y., Abematsu, Y., Nakata, D., Honma, Sakurai., Shimada, Y., and Horiguchi, M.: Change in visual function from astaxanthin. Jpn. J. Clin. Ophthalmol., 58, , [13] Kikuchi, Y., Sato, K., and Izuguchi, Y.: Modified cell-flow microchannels in a singlet-crystal silicon substrate and flow behavior of blood cells. Microvasc Res., 47, , [14] Nitta, T., Ohgami, K., Shiratori, K., Shinmei, Y., Chin, S., Yoshida, K., Tsukahara, H., and Ohno, S.: Effects of astaxanthin on accommodation and asthenopia dose finding study in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Ther. and Med., 21, , [15] Shiratori, K., Ohgami, K., Nitta, T., Shinmei, Y., Chin, S., Yoshida, K., Tsukahara, H., Takehara, I., and Ohno, S.: Effects of astaxanthin on accommodation and asthenopia efficacy identification study in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Ther. and Med., 21, , [16] Jorgensen, K. and Skibsted, L.H.: Carotenoid scavenging of radicals. Effect of carotenoid structure and oxygen partial pressure on antioxidative activity. Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch, 196, , [17] Shimizu, N., Goto, M., and Miki, W.: Carotenoids as singlet oxygen quenchers in marine organisms. Fisheries Science, 62, , [18] Iwamoto, T., Hosoda, K., Hirano, R., Kurata, H., Matsumoto, A., Miki, W., Kamiyama, M., Itakura, H., Yamamoto, S., and Kondo, K.: Inhibition of low-density lipoprotein oxidation by astaxanthin. J. Atheroscler. Theromb., 7, , [19] Osterlie, M., Bjerkeng, B., and Liaaen-Jensen, S.: Plasma appearance and distribution of astaxanthin E/'Z and R/S isomers in plasma lipoproteins of men after single dose administration of astaxanthin. J. Nutr. Biochem., 11, , Vol. 43, No. 2, 2008
6 74 H. Miyawaki et al. [20] Coral-Hinostroza, G.N., Ytrestoyl, T., Ruyter, B., and Bjerkeng, B.: Plasma appearance of unesterified astaxanthin geometrical E/Z and optical R/S isomers in men given single doses of a mixture of optical 3 and 3 R/S isomers of astaxanthin fatty acyl diesters. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol., 139, , [21] Li, W., Hellsten, A., Jacobsson, L.S., Blomqvist, H.M., Olsson, A.G., and Yuan, X.M.: Alpha-tocopherol and astaxanthin decrease macrophage infiltration, apoptosis and vulnerability in atheroma of hyperlipidaemic rabbits. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol., 37, , [22] Ohgami, K., Shiratori, K., Kotake, S., Nishida, T., Mizuki, N., Yazawa, K., and Ohno, S.: Effects of astaxanthin on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 44, , [23] Uchiyama, K., Naito, Y., Hasegawa, G., Nakamura, N., Takahashi, J., and Yoshikawa, T.: Astaxanthin protects betacells against glucose toxicity in diabetic db/db mice. Redox. Rep., 7, , [24] Naito, Y., Uchiyama, K., Aoi, W., Hasegawa, G., Nakamura, N., Yoshida, N., Maoka, T., Takahashi, J., and Yoshikawa, T.: Prevention of diabetic nephropathy by treatment with astaxanthin in diabetic db/db mice. Biofactors, 20, 49 59, [25] Takahashi, J., Uonomi, T., Ikushima, H., and Kikuchi, Y.: Effect of tocotrienol on blood rheology. Hemorheology and Related Research, 5, 31 34, [26] Saito, K. and Maruyama, I.: Effect of black vinegar on the blood rheology of male long distance athletes. Hemorheology and Related Research, 5, 31 34, [27] Goto, S., Kogure, K., Abe, K., Kimata, Y., Kitahama, K., Yamashita, E., and Terada, H.: Efficient radical trapping at the surface and inside the phospholipid membrane is responsible for highly potent antioxidative activity of the carotenoid astaxanthin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1512, , [28] Nielsen, B.R., Jorgensen, K., and Skibsted, L.H.: Triplettriplet extinction coefficients, rate constants of triplet decay and rate constants of anthraacene triplet sensitization by laser flash photolysis of astaxanthin, B-carotene, canthaxanthin and zeaxanthin in deaerated toluene at 298K. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A, 112, , J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr.
Astaxanthin as a Medical Food
 Functional Foods in Health and Disease 2013; 3(7):254-258 Page 254 of 258 Review Article Astaxanthin as a Medical Food Eiji Yamashita Open Access Department of Research & Development, Medical Nutrition
Functional Foods in Health and Disease 2013; 3(7):254-258 Page 254 of 258 Review Article Astaxanthin as a Medical Food Eiji Yamashita Open Access Department of Research & Development, Medical Nutrition
International Journal of Allied Medical Sciences and Clinical Research (IJAMSCR)
 International Journal of Allied Medical Sciences and Clinical Research (IJAMSCR) IJAMSCR Volume 4 Issue 3 July - Sep - 2016 www.ijamscr.com ISSN:2347-6567 Research article Medical research Astashine capsules:
International Journal of Allied Medical Sciences and Clinical Research (IJAMSCR) IJAMSCR Volume 4 Issue 3 July - Sep - 2016 www.ijamscr.com ISSN:2347-6567 Research article Medical research Astashine capsules:
AstaREAL, natural Astaxanthin Nature s way to fight the metabolic syndrome
 AstaREAL, natural Astaxanthin Nature s way to fight the metabolic syndrome by Petra Kindlund, BioReal AB Adiponectin Growing fat tissue Glucose ROS Inflammation NO NOx Hyperclycemia Hypertension Liver
AstaREAL, natural Astaxanthin Nature s way to fight the metabolic syndrome by Petra Kindlund, BioReal AB Adiponectin Growing fat tissue Glucose ROS Inflammation NO NOx Hyperclycemia Hypertension Liver
PURE ASTAXANTHIN. Characteristic. Origin. Concept. Function. Product
 ASTAXANTHIN 1 2 3 4 5 Characteristic Origin Concept Function Product Characteristic Astaxanthin is a carotenoid. It belongs to a larger class of phytochemicals known as terpenes, which are built from five
ASTAXANTHIN 1 2 3 4 5 Characteristic Origin Concept Function Product Characteristic Astaxanthin is a carotenoid. It belongs to a larger class of phytochemicals known as terpenes, which are built from five
Boost Your Endurance with FOR MUSCLE HEALTH. The most studied brand of Astaxanthin HOW TO INCREASE EFFICIENCY WHEN YOU EXERCISE
 Boost Your Endurance with ASTAREAL ASTAXANTHIN FOR MUSCLE HEALTH The most studied brand of Astaxanthin HOW TO INCREASE EFFICIENCY WHEN YOU EXERCISE IT ALL COMES DOWN TO HOW YOU RE POWERING YOUR BODY. Muscle
Boost Your Endurance with ASTAREAL ASTAXANTHIN FOR MUSCLE HEALTH The most studied brand of Astaxanthin HOW TO INCREASE EFFICIENCY WHEN YOU EXERCISE IT ALL COMES DOWN TO HOW YOU RE POWERING YOUR BODY. Muscle
1. Malmsten, C.L., "Dietaty supplement with astaxanthin - Rich algal meal improves muscle endurance - A double blind study on male students".
 BIOASTIN REFERENCES STRENGTH AND ENDURANCE 1. Malmsten, C.L., "Dietaty supplement with astaxanthin - Rich algal meal improves muscle endurance - A double blind study on male students". CANCER PREVENTION
BIOASTIN REFERENCES STRENGTH AND ENDURANCE 1. Malmsten, C.L., "Dietaty supplement with astaxanthin - Rich algal meal improves muscle endurance - A double blind study on male students". CANCER PREVENTION
Extraction of carotenoids from crustacean waste using organic solvents
 Extraction of carotenoids from crustacean waste using organic solvents Hanif Houshmand Kouchi 1, Marzieh Moosavi-Nasab 2, Bahareh Shabanpour 1 1 Department of Fishery, Gorgan University of Agricultural
Extraction of carotenoids from crustacean waste using organic solvents Hanif Houshmand Kouchi 1, Marzieh Moosavi-Nasab 2, Bahareh Shabanpour 1 1 Department of Fishery, Gorgan University of Agricultural
* Characterized by Visual Acuity and Muscular Fatigue. Improvement in Humans
 [6-1-l] Sports Performance Benefits from Taking Natural Astaxaxxthin * Characterized by Visual Acuity and Muscular Fatigue Improvement in Humans Keisuke Sawaki, Hiroshi Yoshigi, Kazubiro Aoki, Natsue Koikawa,
[6-1-l] Sports Performance Benefits from Taking Natural Astaxaxxthin * Characterized by Visual Acuity and Muscular Fatigue Improvement in Humans Keisuke Sawaki, Hiroshi Yoshigi, Kazubiro Aoki, Natsue Koikawa,
The Chemical Synthesis Route (Continued) FIGURE 2 SYNTHESIS OF CAROTENOIDS: FLOW CHART FOR PREPARATION OF BETA-IONONE FIGURE 3 SYNTHESIS
 CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCTION... 1 BACKGROUND... 1 REASONS FOR DOING THE STUDY... 2 INTENDED AUDIENCE... 2 SCOPE OF REPORT... 2 SCOPE OF REPORT (CONTINUED)... 3 METHODOLOGY AND INFORMATION SOURCES... 4 AUTHOR
CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCTION... 1 BACKGROUND... 1 REASONS FOR DOING THE STUDY... 2 INTENDED AUDIENCE... 2 SCOPE OF REPORT... 2 SCOPE OF REPORT (CONTINUED)... 3 METHODOLOGY AND INFORMATION SOURCES... 4 AUTHOR
Grafton New Zealand Ltd.
 Grafton New Zealand Ltd. Contact us webmaster@grafton-nz.com Grafton New Zealand Ltd. 1 What is Equixanthin TM? Equixanthin TM is produced by a natural (non-gmo) soil microbe using highly controlled cgmp
Grafton New Zealand Ltd. Contact us webmaster@grafton-nz.com Grafton New Zealand Ltd. 1 What is Equixanthin TM? Equixanthin TM is produced by a natural (non-gmo) soil microbe using highly controlled cgmp
Eliminate Virtually All Fish-Derived Toxins
 http://www.lifeextension.com Super Omega-3 Plus EPA/DHA with Sesame Lignans, Olive Extract, Krill & Astaxanthin 120 softgels, Item Catalog Number: 01988 The health benefits of eating cold-water fish are
http://www.lifeextension.com Super Omega-3 Plus EPA/DHA with Sesame Lignans, Olive Extract, Krill & Astaxanthin 120 softgels, Item Catalog Number: 01988 The health benefits of eating cold-water fish are
AstaREAL Astaxanthin THE 10 FACTORS Article Headline Atherosclerosis
 Issue 13 June 2010 Astaxanthin Targets the THE 10 FACTORS that Kills 1 Boomer Every 2 seconds AstaREAL Astaxanthin Reduced Incidences of Stroke up to 50%, Ruptured Plaques in the Arteries up to 49%, and
Issue 13 June 2010 Astaxanthin Targets the THE 10 FACTORS that Kills 1 Boomer Every 2 seconds AstaREAL Astaxanthin Reduced Incidences of Stroke up to 50%, Ruptured Plaques in the Arteries up to 49%, and
Protein ligand interaction analysis an insilico potential drug target identification in diabetes mellitus and nephropathy
 Journal of Bioinformatics and Sequence Analysis Vol. 2(5), pp. 95-99, June 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/jbsa ISSN 2141-2464 2011 Academic Journals Full length Research Paper
Journal of Bioinformatics and Sequence Analysis Vol. 2(5), pp. 95-99, June 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/jbsa ISSN 2141-2464 2011 Academic Journals Full length Research Paper
NM SACHINDRA JSPS Post-Doctoral Research Fellow. Prof. K MIYASHITA. Faculty of Fisheries Hokkaido University, Hakodate
 NM SACHINDRA JSPS Post-Doctoral Research Fellow Prof. K MIYASHITA Faculty of Fisheries Hokkaido University, Hakodate Mysore India Karnataka Working as: Scientist Central Food Technological Research Institute
NM SACHINDRA JSPS Post-Doctoral Research Fellow Prof. K MIYASHITA Faculty of Fisheries Hokkaido University, Hakodate Mysore India Karnataka Working as: Scientist Central Food Technological Research Institute
Color Your Customers Healthy With Carotenoids
 Color Your Customers Healthy With Carotenoids By Yousry Naguib, PhD Fruits and vegetables get their vibrant colors from carotenoids, a class of closely related chemicals. Approximately 600 carotenoids
Color Your Customers Healthy With Carotenoids By Yousry Naguib, PhD Fruits and vegetables get their vibrant colors from carotenoids, a class of closely related chemicals. Approximately 600 carotenoids
Microalgae Production and Their Use in Animal Feeds Cyanotech
 Microalgae Production and Their Use in Animal Feeds Cyanotech Gerald R. Cysewski, Ph.D. Chief Science Officer Cyanotech Corporation Cyanotech Specializing in Microalgae Technology Operating since 1984
Microalgae Production and Their Use in Animal Feeds Cyanotech Gerald R. Cysewski, Ph.D. Chief Science Officer Cyanotech Corporation Cyanotech Specializing in Microalgae Technology Operating since 1984
SCIENTIFIC OPINION. EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) 2. European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Parma, Italy
 SCIENTIFIC OPINION Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to astaxanthin and maintenance of joints, tendons, and connective tissue (ID 1918, 1978, 3142), protection of DNA, proteins
SCIENTIFIC OPINION Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to astaxanthin and maintenance of joints, tendons, and connective tissue (ID 1918, 1978, 3142), protection of DNA, proteins
EXPLORE CONSUMER PRODUCT OPPORTUNITIES WITH NATURAL ASTAXANTHIN
 EXPLORE CONSUMER PRODUCT OPPORTUNITIES WITH NATURAL ASTAXANTHIN An Introduction for Marketing and Supply Chain Teams PRESENTED BY SOLIX ALGREDIENTS, INC. OVERVIEW American consumers are taking a more proactive
EXPLORE CONSUMER PRODUCT OPPORTUNITIES WITH NATURAL ASTAXANTHIN An Introduction for Marketing and Supply Chain Teams PRESENTED BY SOLIX ALGREDIENTS, INC. OVERVIEW American consumers are taking a more proactive
ASTAXANTHIN - THE HEALTHY TEN
 ASTAXANTHIN - THE HEALTHY TEN THE HEALTHY TEN TEN CLINICALLY-VALIDATED BENEFITS OF NATURAL ASTAXANTHIN BRAIN HEALTH 4 Human Clinical Studies 50 Supporting Pre-Clinical Trials EYE HEALTH 14 Human Clinical
ASTAXANTHIN - THE HEALTHY TEN THE HEALTHY TEN TEN CLINICALLY-VALIDATED BENEFITS OF NATURAL ASTAXANTHIN BRAIN HEALTH 4 Human Clinical Studies 50 Supporting Pre-Clinical Trials EYE HEALTH 14 Human Clinical
International Journal of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences
 International Journal of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijcps Review Article Open Access Astashine Silver Capsules: An Excellent Choice as Anti-Diabetic
International Journal of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijcps Review Article Open Access Astashine Silver Capsules: An Excellent Choice as Anti-Diabetic
Ο ρόλος των τριγλυκεριδίων στην παθογένεια των μικροαγγειοπαθητικών επιπλοκών του σακχαρώδη διαβήτη
 Ο ρόλος των τριγλυκεριδίων στην παθογένεια των μικροαγγειοπαθητικών επιπλοκών του σακχαρώδη διαβήτη Κωνσταντίνος Τζιόμαλος Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Παθολογίας Α Προπαιδευτική Παθολογική Κλινική, Νοσοκομείο
Ο ρόλος των τριγλυκεριδίων στην παθογένεια των μικροαγγειοπαθητικών επιπλοκών του σακχαρώδη διαβήτη Κωνσταντίνος Τζιόμαλος Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Παθολογίας Α Προπαιδευτική Παθολογική Κλινική, Νοσοκομείο
Stability and changes in astaxanthin ester composition from Haematococcus pluvialis during storage*
 Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology Vol. No. 6, P. 8-89, 2 http://dx.doi.org/.7/s4--25- Stability and changes in astaxanthin ester composition from Haematococcus pluvialis during storage* MIAO
Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology Vol. No. 6, P. 8-89, 2 http://dx.doi.org/.7/s4--25- Stability and changes in astaxanthin ester composition from Haematococcus pluvialis during storage* MIAO
EXTRACTION OF ASTAXANTHIN FROM THE ENCYSTED CELLS OF HAEMATOCOCCUS PLUVIALIS WITH DIFFERENT SOLVENTS
 Original Research Article DOI - 10.26479/2018.0401.10 EXTRACTION OF ASTAXANTHIN FROM THE ENCYSTED CELLS OF HAEMATOCOCCUS PLUVIALIS WITH DIFFERENT SOLVENTS Surendra Singh, Ashaq Hussain Rather * Algal Biotechnology
Original Research Article DOI - 10.26479/2018.0401.10 EXTRACTION OF ASTAXANTHIN FROM THE ENCYSTED CELLS OF HAEMATOCOCCUS PLUVIALIS WITH DIFFERENT SOLVENTS Surendra Singh, Ashaq Hussain Rather * Algal Biotechnology
BIOASTIN Bioastin is product that contains 4 mg astaxantin and 50 i.e. vitamin E (α-tocopherol) per tabl.. Carotenoids are family of around 700 substa
 INTRODUCTION In 1956 Rebecca Gerchman and Daniel Gilbert detected toxic effect of superoxid on aerobs. Till today there are identificated many free radicals. Their toxic effect is registrated in more than
INTRODUCTION In 1956 Rebecca Gerchman and Daniel Gilbert detected toxic effect of superoxid on aerobs. Till today there are identificated many free radicals. Their toxic effect is registrated in more than
POTENTIAL USE OF MOUGEOTIA SP. ALGAE IN FOOD PRODUCTION, BASED ON ITS CAROTENOID CONTENT. Abstract
 E. Muntean, et all. Journal of Agroalimentary Processes and Technologies, Volume XIII, No.1 (2007), 143-148 Full Paper Natural Food Extract and Additives POTENTIAL USE OF MOUGEOTIA SP. ALGAE IN FOOD PRODUCTION,
E. Muntean, et all. Journal of Agroalimentary Processes and Technologies, Volume XIII, No.1 (2007), 143-148 Full Paper Natural Food Extract and Additives POTENTIAL USE OF MOUGEOTIA SP. ALGAE IN FOOD PRODUCTION,
Effects of Astaxanthin Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Fatigue in Mice
 2106 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 29(10) 2106 2110 (2006) Vol. 29, No. 10 Effects of Astaxanthin Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Fatigue in Mice Mayumi IKEUCHI, a Tomoyuki KOYAMA, a Jiro TAKAHASHI, b and Kazunaga
2106 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 29(10) 2106 2110 (2006) Vol. 29, No. 10 Effects of Astaxanthin Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Fatigue in Mice Mayumi IKEUCHI, a Tomoyuki KOYAMA, a Jiro TAKAHASHI, b and Kazunaga
Antihypertensive and Neuroprotective Effects of Astaxanthin in Experimental Animals
 January 2005 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28(1) 47 52 (2005) 47 Antihypertensive and Neuroprotective Effects of Astaxanthin in Experimental Animals Ghazi HUSSEIN,*,a,b Masami NAKAMURA, b Qi ZHAO, b Tomomi IGUCHI,
January 2005 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28(1) 47 52 (2005) 47 Antihypertensive and Neuroprotective Effects of Astaxanthin in Experimental Animals Ghazi HUSSEIN,*,a,b Masami NAKAMURA, b Qi ZHAO, b Tomomi IGUCHI,
Astaxanthin Provides Broad Spectrum Protection By Liam Hawkins
 Astaxanthin Provides Broad Spectrum Protection By Liam Hawkins Researchers in Japan have long looked to the sea for sources of new medications. A big focus has been on astaxanthin found in microalgae.1,2
Astaxanthin Provides Broad Spectrum Protection By Liam Hawkins Researchers in Japan have long looked to the sea for sources of new medications. A big focus has been on astaxanthin found in microalgae.1,2
Astaxanthin. Natural Astaxanthin: King of the Carotenoids. by Bob Capelli with Dr. Gerald Cysewski
 Astaxanthin Natural Astaxanthin: King of the Carotenoids by Bob Capelli with Dr. Gerald Cysewski Ironman triathlete, Max Burdick, competed for years, but was never able to finish a triathlon. Then he began
Astaxanthin Natural Astaxanthin: King of the Carotenoids by Bob Capelli with Dr. Gerald Cysewski Ironman triathlete, Max Burdick, competed for years, but was never able to finish a triathlon. Then he began
Cardiovascular impact of Sugar and Fat
 Professor Göran Petersson May 2011 Chemical and biological engineering Chalmers University of Technology Göteborg, Sweden Less sugar and soft drinks Less food with high GI Less omega-6 fatty acids More
Professor Göran Petersson May 2011 Chemical and biological engineering Chalmers University of Technology Göteborg, Sweden Less sugar and soft drinks Less food with high GI Less omega-6 fatty acids More
The World s Strongest & Highest Quality Natural Antioxidant
 Introduction Two young scientists working toward their doctorates in France way back in the 1940 s were really on to something. And they were clearly way ahead of their time. Before almost any scientist
Introduction Two young scientists working toward their doctorates in France way back in the 1940 s were really on to something. And they were clearly way ahead of their time. Before almost any scientist
Effects of astaxanthin on antioxidation in human aqueous humor
 Original Article JCBN Journal 0912-0009 1880-5086 the Kyoto, jcbn13-6 10.3164/jcbn.13-6 Original Society Japan of Article Clinical for Free Biochemistry Radical Research and Nutrition Japan Effects of
Original Article JCBN Journal 0912-0009 1880-5086 the Kyoto, jcbn13-6 10.3164/jcbn.13-6 Original Society Japan of Article Clinical for Free Biochemistry Radical Research and Nutrition Japan Effects of
Development of the Dietary Supplements, Astalift supplement and Astalift drink
 UDC 613.292+641.1 Development of the Dietary Supplements, Astalift supplement and Astalift drink Yasuyuki IZUMI*, Masao SATO*, Fumitaka UEDA*, Yukio SUDO*, Kumiko UJIIE**, Kouzou NAGATA*, Kenji IKEDA**,
UDC 613.292+641.1 Development of the Dietary Supplements, Astalift supplement and Astalift drink Yasuyuki IZUMI*, Masao SATO*, Fumitaka UEDA*, Yukio SUDO*, Kumiko UJIIE**, Kouzou NAGATA*, Kenji IKEDA**,
A(REDS) to Z(inc) Nutrition for eye health
 All eyes on the macula A(REDS) to Z(inc) Nutrition for eye health Professor Christine Purslow PhD, MCOptom, FBCLA, FIACLE Macula lutea = yellow spot Colour is determined by 3 carotenoids Lutein Zeaxanthin
All eyes on the macula A(REDS) to Z(inc) Nutrition for eye health Professor Christine Purslow PhD, MCOptom, FBCLA, FIACLE Macula lutea = yellow spot Colour is determined by 3 carotenoids Lutein Zeaxanthin
EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMER PROTECTION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMER PROTECTION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Directorate C - Scientific Opinions Unit C2 - Management of scientific committees; scientific co-operation and networks Update of the
EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMER PROTECTION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Directorate C - Scientific Opinions Unit C2 - Management of scientific committees; scientific co-operation and networks Update of the
Potent biological functions of palm fruit carotene against UV-induced skin lipid peroxidation and carcinogenesis
 Potent biological functions of palm fruit carotene against UV-induced skin lipid peroxidation and carcinogenesis Michiaki Murakoshi 1,2 and Hoyoku Nishino 2,3 1 Lion Corp., 2 Kyoto Pref. Univ. Med., 3
Potent biological functions of palm fruit carotene against UV-induced skin lipid peroxidation and carcinogenesis Michiaki Murakoshi 1,2 and Hoyoku Nishino 2,3 1 Lion Corp., 2 Kyoto Pref. Univ. Med., 3
A Comprehensive Review of Human Clinical Studies
 Natural Astaxanthin: A Comprehensive Review of Human Clinical Studies This document provides an overview of the current knowledge of the health benefits and mode of action of natural astaxanthin from Haematococcus
Natural Astaxanthin: A Comprehensive Review of Human Clinical Studies This document provides an overview of the current knowledge of the health benefits and mode of action of natural astaxanthin from Haematococcus
APPLICATION OF CAROTENOIDS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO MICROALGAE
 APPLICATION OF CAROTENOIDS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO MICROALGAE Dr. Ranga Rao Ambati Assistant Research Professor Department of Science and Technology Beijing Normal University-Hong Kong Baptist University
APPLICATION OF CAROTENOIDS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO MICROALGAE Dr. Ranga Rao Ambati Assistant Research Professor Department of Science and Technology Beijing Normal University-Hong Kong Baptist University
regulates the opening of blood vessels, important for unhindered blood flow.
 Vitamin E AT A GLANCE Introduction The term vitamin E describes a family of eight related, fat-soluble molecules. Among these, alphatocopherol has the highest biological activity and is the most abundant
Vitamin E AT A GLANCE Introduction The term vitamin E describes a family of eight related, fat-soluble molecules. Among these, alphatocopherol has the highest biological activity and is the most abundant
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
L 243/10 Official Journal of the European Union
 L 243/10 Official Journal of the European Union 15.7.2004 COMMISSION REGULATION (EC) No 1288/2004 of 14 July 2004 concerning the permanent authorisation of certain additives and the provisional authorisation
L 243/10 Official Journal of the European Union 15.7.2004 COMMISSION REGULATION (EC) No 1288/2004 of 14 July 2004 concerning the permanent authorisation of certain additives and the provisional authorisation
- Spontaneous hemorrhaging increase
 MEDCHEM 562-2014 Fat Soluble Vitamins Problem Set 1. Fill out the blanks in the table below. Vitamin Physiological Function Deficiency symptoms Toxicity A -Vision -Cell Differentiation -Inhibition of Cell
MEDCHEM 562-2014 Fat Soluble Vitamins Problem Set 1. Fill out the blanks in the table below. Vitamin Physiological Function Deficiency symptoms Toxicity A -Vision -Cell Differentiation -Inhibition of Cell
Commercial opportunities for carotenoid production by biotechnology
 Pure &App/. Chem., Vol. 69, No. 10, pp. 2169-2173,1997. Printed in Great Britain. Q 1997 IUPAC Commercial opportunities for carotenoid production by biotechnology Rodney L. Ausich Research and Development,
Pure &App/. Chem., Vol. 69, No. 10, pp. 2169-2173,1997. Printed in Great Britain. Q 1997 IUPAC Commercial opportunities for carotenoid production by biotechnology Rodney L. Ausich Research and Development,
New Developments in Health and Nutritional Function Promoted by Chicken Eggs
 65 Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi Vol. /2, No. 1, -.+ -./ (,*++) 341, New Developments in Health and Nutritional Function Promoted by Chicken Eggs Katsumi Imaizumi Trustee and Vice-President Kyushu
65 Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi Vol. /2, No. 1, -.+ -./ (,*++) 341, New Developments in Health and Nutritional Function Promoted by Chicken Eggs Katsumi Imaizumi Trustee and Vice-President Kyushu
Regulation of Enzyme Activity
 Regulation of Enzyme Activity Enzyme activity must be regulated so that the proper levels of products are produced at all times and places This control occurs in several ways: - biosynthesis at the genetic
Regulation of Enzyme Activity Enzyme activity must be regulated so that the proper levels of products are produced at all times and places This control occurs in several ways: - biosynthesis at the genetic
A farm that producing a consistent supply of pure Astaxanthin from Haematococcus Pluvialis microalgae. Astaxanthin. Microalga Technologies
 A farm that producing a consistent supply of pure Astaxanthin from Haematococcus Pluvialis microalgae. Astaxanthin Microalga Technologies Product description Astaxanthin - the substance is considered to
A farm that producing a consistent supply of pure Astaxanthin from Haematococcus Pluvialis microalgae. Astaxanthin Microalga Technologies Product description Astaxanthin - the substance is considered to
 Food, Supplements and Healthy Lifestyles in Slowing and Preventing Macular Degeneration Julie Mares, Professor For the Nutrition and Eye Health Research Team http://nutritionforeyes.ophth.wisc.edu Preserving
Food, Supplements and Healthy Lifestyles in Slowing and Preventing Macular Degeneration Julie Mares, Professor For the Nutrition and Eye Health Research Team http://nutritionforeyes.ophth.wisc.edu Preserving
ASTAXANTHOL - #1057. Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Aging Support for the Whole Body
 ASTAXANTHOL - #1057 Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Aging Support for the Whole Body Astaxanthol is a uniquely designed, nutraceutical formulation that is an extremely potent, highly bi-available, broad spectrum
ASTAXANTHOL - #1057 Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Aging Support for the Whole Body Astaxanthol is a uniquely designed, nutraceutical formulation that is an extremely potent, highly bi-available, broad spectrum
Food Science (#6201)
 AASD FAMILY AND CONSUMER EDUCATION CURRICULUM Food Science (#6201) Description The Food Science course gives students a hands-on, lab-based, experimental background in basic food science as it relates
AASD FAMILY AND CONSUMER EDUCATION CURRICULUM Food Science (#6201) Description The Food Science course gives students a hands-on, lab-based, experimental background in basic food science as it relates
Name Group Members. Table 1 Observation (include details of what you observe)
 Name Group Members Macromolecules, Part 1 - PROTEINS There are four classes of macromolecules that are important to the function of all living things. These include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and
Name Group Members Macromolecules, Part 1 - PROTEINS There are four classes of macromolecules that are important to the function of all living things. These include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and
AstaZine Natural Astaxanthin: The Supplement You Can Feel
 AstaZine Natural Astaxanthin: The Supplement You Can Feel Give your customers a supplement that they ll see and feel working in their bodies and that they ll tell their friends and family about! Natural
AstaZine Natural Astaxanthin: The Supplement You Can Feel Give your customers a supplement that they ll see and feel working in their bodies and that they ll tell their friends and family about! Natural
Nutritional Analysis of Wakame
 As a clinical term, medical obesity occurs when a person s Body Mass Index (BMI) exceeds a measurement of 30 or greater. http://www.nhlbisupport.com/bmi/ BMI is an internationally recognized measure of
As a clinical term, medical obesity occurs when a person s Body Mass Index (BMI) exceeds a measurement of 30 or greater. http://www.nhlbisupport.com/bmi/ BMI is an internationally recognized measure of
NanoVit oa Bioactive phyto-omegas 3, 6, 9 + 7
 NanoVit oa Bioactive phyto-omegas 3, 6, 9 + 7 NanoVit oa Bioactive phyto-omegas 3, 6, 9 + 7 Regeneration and Antioxidant Activity NanoVit oa is a nano-emulsion loaded with sea buckthorn pulp oil. Sea
NanoVit oa Bioactive phyto-omegas 3, 6, 9 + 7 NanoVit oa Bioactive phyto-omegas 3, 6, 9 + 7 Regeneration and Antioxidant Activity NanoVit oa is a nano-emulsion loaded with sea buckthorn pulp oil. Sea
PALM OLEIN BLENDING FOR TEMPERATE MARKET L/O/G/O
 PALM OLEIN BLENDING FOR TEMPERATE MARKET L/O/G/O Basic Facts on Oil Palm Originated from West Africa, palm oil is the rich source of edible oil and has become important resource of vegetable oil in the
PALM OLEIN BLENDING FOR TEMPERATE MARKET L/O/G/O Basic Facts on Oil Palm Originated from West Africa, palm oil is the rich source of edible oil and has become important resource of vegetable oil in the
β-carotene (trans or cis isomer)
 β-carotene (trans or cis isomer) Overview Natural beta-carotene contains a mixture of different isomers (cis and trans) of the betacarotene molecule. Synthetically produced beta-carotene is nature identical.
β-carotene (trans or cis isomer) Overview Natural beta-carotene contains a mixture of different isomers (cis and trans) of the betacarotene molecule. Synthetically produced beta-carotene is nature identical.
HEALTH BENEFITS OF TOCOTRIENOLS (SUPER VITAMIN E)
 HEALTH BENEFITS OF TOCOTRIENOLS (SUPER VITAMIN E) Western medicine is desperately searching for compounds that can help trigger the death signal in cancer cells, and the tocotrienol form of natural Vitamin
HEALTH BENEFITS OF TOCOTRIENOLS (SUPER VITAMIN E) Western medicine is desperately searching for compounds that can help trigger the death signal in cancer cells, and the tocotrienol form of natural Vitamin
FITEYE Tablets (Multivitamin + Minerals)
 Published on: 10 Jul 2014 FITEYE Tablets (Multivitamin + Minerals) Each Tablet Contains Vitamin C Vitamin E Vitamin A (as beta carotene) Vitamin B2 Lutein Zeaxanthin Zinc Copper Selenium L-Glutathione
Published on: 10 Jul 2014 FITEYE Tablets (Multivitamin + Minerals) Each Tablet Contains Vitamin C Vitamin E Vitamin A (as beta carotene) Vitamin B2 Lutein Zeaxanthin Zinc Copper Selenium L-Glutathione
Extraction and purification of carotenoids from vegetables
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(4):594-598 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Extraction and purification of carotenoids from
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(4):594-598 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Extraction and purification of carotenoids from
GSCI 2202 Food product and beverage for health
 GSCI 2202 Food product and beverage for health Functional food is any fresh or processed food claimed to have a health promoting or disease preventing property beyond the basic function of supplying
GSCI 2202 Food product and beverage for health Functional food is any fresh or processed food claimed to have a health promoting or disease preventing property beyond the basic function of supplying
Soluble Lutein (Lutemax2020 ) Prevents Retinal Damage in Streptozotocin (STZ)- induced Diabetic Rats
 Soluble Lutein (Lutemax2020 ) Prevents Retinal Damage in Streptozotocin (STZ)- induced Diabetic Rats Vijaya Juturu, Ph.D., F.A.C.N. OmniActive Health Technologies, Inc. Morristown, NJ Acknowledgements
Soluble Lutein (Lutemax2020 ) Prevents Retinal Damage in Streptozotocin (STZ)- induced Diabetic Rats Vijaya Juturu, Ph.D., F.A.C.N. OmniActive Health Technologies, Inc. Morristown, NJ Acknowledgements
VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri
![VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri](/thumbs/88/115610056.jpg) VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S 381-394] Deeba S. Jairajpuri VITAMIN A othe term retinoids includes both natural and synthetic forms of vitamin A essential for vision, reproduction, growth and maintenance
VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S 381-394] Deeba S. Jairajpuri VITAMIN A othe term retinoids includes both natural and synthetic forms of vitamin A essential for vision, reproduction, growth and maintenance
ect of Protamine from Chum Salmon Milt on Lipid Absorption in Humans
 360 Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi Vol. //, No. 2, -0* -00 (,**2) 6 * * The Suppressive E# ect of Protamine from Chum Salmon Milt on Lipid Absorption in Humans Yosuke Hoshino, Yoshinori Takahashi,
360 Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi Vol. //, No. 2, -0* -00 (,**2) 6 * * The Suppressive E# ect of Protamine from Chum Salmon Milt on Lipid Absorption in Humans Yosuke Hoshino, Yoshinori Takahashi,
THE WORLD CAROTENOIDS MARKET
 Science Market Regulation UBIC 2015 Marketing development Strategy consulting Partnership searches Information systems UBIC Technical & Competitive Scanning Regulations Manufacturers This comprehensive
Science Market Regulation UBIC 2015 Marketing development Strategy consulting Partnership searches Information systems UBIC Technical & Competitive Scanning Regulations Manufacturers This comprehensive
Targeted Health Regimen Every Targeted Health Regimen builds upon the Foundations of Optimal Health Regimen. Vision Health Regimen
 Targeted Health Regimen Every Targeted Health Regimen builds upon the Foundations of Optimal Health Regimen. Vision Health Regimen Declining vision is a result of the normal aging process. Why should we
Targeted Health Regimen Every Targeted Health Regimen builds upon the Foundations of Optimal Health Regimen. Vision Health Regimen Declining vision is a result of the normal aging process. Why should we
LYCOPENE FROM BLAKESLEA TRISPORA CHEMICAL AND TECHNICAL ASSESSMENT (CTA)
 1. Summary LYCOPENE FROM BLAKESLEA TRISPORA CHEMICAL AND TECHNICAL ASSESSMENT (CTA) Prepared by Zofia Olempska-Beer, Ph.D. Office of Food Additive Safety, Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition U.S.
1. Summary LYCOPENE FROM BLAKESLEA TRISPORA CHEMICAL AND TECHNICAL ASSESSMENT (CTA) Prepared by Zofia Olempska-Beer, Ph.D. Office of Food Additive Safety, Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition U.S.
Nutrition and the Eye
 Nutrition and the Eye A booklet provided to explain the importance of nutrition in ocular health Recent media and press coverage will have no doubt brought your attention to the new ideas involving nutrition
Nutrition and the Eye A booklet provided to explain the importance of nutrition in ocular health Recent media and press coverage will have no doubt brought your attention to the new ideas involving nutrition
Introduction to Lipid Chemistry
 Introduction to Lipid Chemistry Benjamin Schwartz Ontario SCC Education Day September 18, 2018 Lipid knowledge for the personal care industry What is a Lipid? Lipids are fatty acids and their derivatives,
Introduction to Lipid Chemistry Benjamin Schwartz Ontario SCC Education Day September 18, 2018 Lipid knowledge for the personal care industry What is a Lipid? Lipids are fatty acids and their derivatives,
Differences in skin carotenoid level with regard to subcutaneous adipose tissue thickness in patients with anorexia nervosa
 Differences in skin carotenoid level with regard to subcutaneous adipose tissue thickness in patients with anorexia nervosa Sonja Lackner, Sabrina Mörkl, Wolfram Müller, Maximilian Moser, Claudia Blesl,
Differences in skin carotenoid level with regard to subcutaneous adipose tissue thickness in patients with anorexia nervosa Sonja Lackner, Sabrina Mörkl, Wolfram Müller, Maximilian Moser, Claudia Blesl,
New Zealand Blackcurrant: A New Ergogenic Aid in Sport?
 New Zealand Blackcurrant: A New Ergogenic Aid in Sport? Mark Willems Professor in Exercise Physiology United Kingdom Blackcurrant The Stress Hero Sponsored by Vilnius - June 10-12, 2015 Take home prediction
New Zealand Blackcurrant: A New Ergogenic Aid in Sport? Mark Willems Professor in Exercise Physiology United Kingdom Blackcurrant The Stress Hero Sponsored by Vilnius - June 10-12, 2015 Take home prediction
FROM ABSTRACT Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) improve on a vegetarian diet or supplementation with fish oil.
 Anti-inflammatory effects of a low arachidonic acid diet and fish oil in patients with rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatol Int (2003) 23: 27 36 Olaf Adam, Corinna Beringer, Thomas Kless, Christa Lemmen, Alexander
Anti-inflammatory effects of a low arachidonic acid diet and fish oil in patients with rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatol Int (2003) 23: 27 36 Olaf Adam, Corinna Beringer, Thomas Kless, Christa Lemmen, Alexander
Astaxanthin and Human Health. Literature Survey
 Astaxanthin and Human Health Literature Survey June 2010 1 Table of content (I) Table of content 2 (1) Introduction 4 4 (1.1) The carotenoids 5 (2) Astaxanthin chemistry 7 (2.1) Astaxanthin chemical structure
Astaxanthin and Human Health Literature Survey June 2010 1 Table of content (I) Table of content 2 (1) Introduction 4 4 (1.1) The carotenoids 5 (2) Astaxanthin chemistry 7 (2.1) Astaxanthin chemical structure
Lipid & Fat: Overview
 Lipid & Fat: Overview What is a lipid? Triglycerides, Phospholipids and Sterols Triglycerides = Fat Saturated & unsaturated Essential fatty acids ü Omega 3 & Omega 6 Trans fat Why do you need fat? How
Lipid & Fat: Overview What is a lipid? Triglycerides, Phospholipids and Sterols Triglycerides = Fat Saturated & unsaturated Essential fatty acids ü Omega 3 & Omega 6 Trans fat Why do you need fat? How
4 Nutrient Intakes and Dietary Sources: Micronutrients
 Nutrient Intakes and Dietary Sources: Micronutrients New Zealanders obtain the energy and nutrients they require from a wide variety of foods and beverages, and in some cases from dietary supplements as
Nutrient Intakes and Dietary Sources: Micronutrients New Zealanders obtain the energy and nutrients they require from a wide variety of foods and beverages, and in some cases from dietary supplements as
Visit for Videos, Questions and Revision Notes. Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction
 Q1.(a) Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction. (b) In the Krebs cycle, acetylcoenzyme A combines with four-carbon oxaloacetate to form six-carbon citrate. This reaction is catalysed
Q1.(a) Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction. (b) In the Krebs cycle, acetylcoenzyme A combines with four-carbon oxaloacetate to form six-carbon citrate. This reaction is catalysed
Astaxanthin Production by Phaffia rhodozyma Fermentation of. Cassava Residues Substrate
 Astaxanthin Production by Phaffia rhodozyma Fermentation of Cassava Residues Substrate Jinsong Yang 1a, Haisheng Tan 1b, Rui Yang 1c, Xiaohuan Sun 1d,Hairui Zhai 1e, Kaimian Li f * Hainan University,Haikou,
Astaxanthin Production by Phaffia rhodozyma Fermentation of Cassava Residues Substrate Jinsong Yang 1a, Haisheng Tan 1b, Rui Yang 1c, Xiaohuan Sun 1d,Hairui Zhai 1e, Kaimian Li f * Hainan University,Haikou,
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Kinetics of Plasma- and Erythrocyte-Astaxanthin in Healthy Subjects Following a Single and Maintenance Oral Dose Ruiz Nunez, Begona; Schuitemaker, G. E.; Brouwer, Dineke; Muskiet,
University of Groningen Kinetics of Plasma- and Erythrocyte-Astaxanthin in Healthy Subjects Following a Single and Maintenance Oral Dose Ruiz Nunez, Begona; Schuitemaker, G. E.; Brouwer, Dineke; Muskiet,
A. There are about 100 elements; 25 of them are necessary for life. B. Carbon atoms can form long chains, leading to a huge number of possible
 Ch. 2 How Cells Function 2.1 Chemical reactions take place inside cells. 1. All cells are made of the same elements. A. There are about 100 elements; 25 of them are necessary for life. B. The smallest
Ch. 2 How Cells Function 2.1 Chemical reactions take place inside cells. 1. All cells are made of the same elements. A. There are about 100 elements; 25 of them are necessary for life. B. The smallest
Figure 2. Figure 1. Name: Bio AP Lab Organic Molecules
 Name: Bio AP Lab Organic Molecules BACKGROUND: A cell is a living chemistry laboratory in which most functions take the form of interactions between organic molecules. Most organic molecules found in living
Name: Bio AP Lab Organic Molecules BACKGROUND: A cell is a living chemistry laboratory in which most functions take the form of interactions between organic molecules. Most organic molecules found in living
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. 2. In plants, which characteristic or behavior is typically independent of the plant's environment?
 Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. AP Biology Living System and Free Energy Blizzard Bag 2014 2015 1. How is cellular respiration useful to the cell? A. producing ATP, which provides the nucleotides
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. AP Biology Living System and Free Energy Blizzard Bag 2014 2015 1. How is cellular respiration useful to the cell? A. producing ATP, which provides the nucleotides
Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: AP Biology
 Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: Lipids long term energy storage concentrated energy *9 Cal/gram Lipids: Triglycerides Lipids are composed of C, H, O u long hydrocarbon chains (H-C) Family groups u fats u phospholipids
Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: Lipids long term energy storage concentrated energy *9 Cal/gram Lipids: Triglycerides Lipids are composed of C, H, O u long hydrocarbon chains (H-C) Family groups u fats u phospholipids
Supplementary Figure 1. Funnel plots of meta-analytic residuals. Effect size (Zr) plotted against (a)
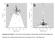 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Funnel plots of meta-analytic residuals. Effect size (Zr) plotted against (a) standard error and (b) precision (inverse of the standard error) n = 11 effect sizes. Screening
a b Supplementary Figure 1. Funnel plots of meta-analytic residuals. Effect size (Zr) plotted against (a) standard error and (b) precision (inverse of the standard error) n = 11 effect sizes. Screening
Membrane lipid peroxidation by ultrasound: Mechanism and implications
 J. Biosci., Vol. 15, Number 3, September 1990, pp. 211 215. Printed in India. Membrane lipid peroxidation by ultrasound: Mechanism and implications A. K. JANA, S. AGARWAL and S. N. CHATTERJEE* Biophysics
J. Biosci., Vol. 15, Number 3, September 1990, pp. 211 215. Printed in India. Membrane lipid peroxidation by ultrasound: Mechanism and implications A. K. JANA, S. AGARWAL and S. N. CHATTERJEE* Biophysics
Essential Biology 3.2 Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins. 1. Define organic molecule.
 1. Define organic molecule. An organic molecule is a molecule that contains carbon and is found in living things. There are many organic molecules in living things. The same (or very similar) molecules
1. Define organic molecule. An organic molecule is a molecule that contains carbon and is found in living things. There are many organic molecules in living things. The same (or very similar) molecules
Lipid & Fat: Overview
 Lipid & Fat: Overview What is a lipid? Triglycerides, Phospholipids and Sterols Triglycerides = Fat Saturated & unsaturated Essential fatty acids ü Omega 3 & Omega 6 Trans fat Why do you need fat? How
Lipid & Fat: Overview What is a lipid? Triglycerides, Phospholipids and Sterols Triglycerides = Fat Saturated & unsaturated Essential fatty acids ü Omega 3 & Omega 6 Trans fat Why do you need fat? How
Other Health Benefits of Flax
 Chapter 7 Other Health Benefits of Flax Previous chapters examined the benefits of flax and its key constituents the lignan secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG), dietary fibre and alpha-linolenic acid
Chapter 7 Other Health Benefits of Flax Previous chapters examined the benefits of flax and its key constituents the lignan secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG), dietary fibre and alpha-linolenic acid
Annette Sims, MD, Ophthalmologist next Tuesday! Hooray!!
 BI 358 Lecture 18 Annette Sims, MD, Ophthalmologist next Tuesday! Hooray!! I. Announcements Quiz 5 returned at end of lecture. Eye Dissection & Vision lab next Tuesday > Lecture by Dr. Sims! Final Quiz
BI 358 Lecture 18 Annette Sims, MD, Ophthalmologist next Tuesday! Hooray!! I. Announcements Quiz 5 returned at end of lecture. Eye Dissection & Vision lab next Tuesday > Lecture by Dr. Sims! Final Quiz
October 2016, Volume: 8, Issue: 10, Pages: , DOI:
 Electronic Physician (ISSN: 2008-5842) http://www.ephysician.ir October 2016, Volume: 8, Issue: 10, Pages: 3110-3115, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.19082/3110 Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity of R. Slooffiae,
Electronic Physician (ISSN: 2008-5842) http://www.ephysician.ir October 2016, Volume: 8, Issue: 10, Pages: 3110-3115, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.19082/3110 Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity of R. Slooffiae,
FATS & OILS GLOSSARY
 FATS & OILS GLOSSARY Antioxidant A substance that slows or interferes with the reaction of a fat or oil with oxygen. The addition of antioxidants to fats or foods containing them retard rancidity and increases
FATS & OILS GLOSSARY Antioxidant A substance that slows or interferes with the reaction of a fat or oil with oxygen. The addition of antioxidants to fats or foods containing them retard rancidity and increases
Hawaiian Spirulina Pacifica
 Hawaiian Spirulina Pacifica World s Healthiest Food More nutrition gram-per-gram than any other product in the world Spirulina Nutrient Comparison Spirulina has 300% more calcium than whole milk Good for
Hawaiian Spirulina Pacifica World s Healthiest Food More nutrition gram-per-gram than any other product in the world Spirulina Nutrient Comparison Spirulina has 300% more calcium than whole milk Good for
Annette Sims, MD, Ophthalmologist next Tuesday! Hooray!!
 BI 358 Lecture 18 Annette Sims, MD, Ophthalmologist next Tuesday! Hooray!! I. Announcements Quiz 5 returned at end of lecture. Eye Dissection & Vision lab next Tuesday > Lecture by Dr. Sims! Final Quiz
BI 358 Lecture 18 Annette Sims, MD, Ophthalmologist next Tuesday! Hooray!! I. Announcements Quiz 5 returned at end of lecture. Eye Dissection & Vision lab next Tuesday > Lecture by Dr. Sims! Final Quiz
Nutracode KrillCode A premium omega 3 solution.
 Nutracode KrillCode A premium omega 3 solution Krill Small Creature Big Advantage Antarctic Krill (Euphausia Superba) Antarctic Krill are swimming crustaceans that live in the Antarctic waters of the Southern
Nutracode KrillCode A premium omega 3 solution Krill Small Creature Big Advantage Antarctic Krill (Euphausia Superba) Antarctic Krill are swimming crustaceans that live in the Antarctic waters of the Southern
Association between Intake during Multiple Eating Occasions and Total Daily Intake among Japanese Young Women
 ARC Journal of Nutrition and Growth Volume 4, Issue 1, 2018, PP 4-9 ISSN No. (Online) 2455-2550 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2455-2550.0401002 www.arcjournals.org Association between Intake during Multiple
ARC Journal of Nutrition and Growth Volume 4, Issue 1, 2018, PP 4-9 ISSN No. (Online) 2455-2550 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2455-2550.0401002 www.arcjournals.org Association between Intake during Multiple
Arelative newcomer to the commercial
 The Biochemistry of Alternative Medicine The Potential of Astaxanthin A New Multipurpose, High-Power Antioxidant Joseph R. Cronin, Ph.D. Arelative newcomer to the commercial field of antioxidants is the
The Biochemistry of Alternative Medicine The Potential of Astaxanthin A New Multipurpose, High-Power Antioxidant Joseph R. Cronin, Ph.D. Arelative newcomer to the commercial field of antioxidants is the
Katra produces IPR protected Formulations and Bioactives from Natural Sources, backed by World Class Research and adheres to International Standards
 Lutein and Zeaxanthin, against MD: Science Brief Katra produces IPR protected Formulations and Bioactives from Natural Sources, backed by World Class Research and adheres to International Standards www.katraphyto.com
Lutein and Zeaxanthin, against MD: Science Brief Katra produces IPR protected Formulations and Bioactives from Natural Sources, backed by World Class Research and adheres to International Standards www.katraphyto.com
Free Fatty Acid Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 Product Manual Free Fatty Acid Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number STA-619 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Triglycerides (TAG) are a type of lipid
Product Manual Free Fatty Acid Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number STA-619 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Triglycerides (TAG) are a type of lipid
Physiological Indices of Visual Fatigue due to VDT Operation: Pupillary Reflexes and Accommodative Responses
 Industrial Health, 1994, 32, 57-66 57 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Physiological Indices of Visual Fatigue due to VDT Operation: Pupillary Reflexes and Accommodative Responses Susumu SAITOa)1, Midori SOTOYAMAa),
Industrial Health, 1994, 32, 57-66 57 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Physiological Indices of Visual Fatigue due to VDT Operation: Pupillary Reflexes and Accommodative Responses Susumu SAITOa)1, Midori SOTOYAMAa),
Kinetics of carotenoid concentration in human skin after topical and systemic administration of antioxidants
 Department of Dermatology and Allergology Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin Kinetics of carotenoid concentration in human skin after topical and systemic administration of antioxidants M. E. Darvin
Department of Dermatology and Allergology Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin Kinetics of carotenoid concentration in human skin after topical and systemic administration of antioxidants M. E. Darvin
1 The diagram represents two of the stages of aerobic respiration that take place in a mitochondrion.
 1 The diagram represents two of the stages of aerobic respiration that take place in a mitochondrion. a Name substance X. b Which stage of aerobic respiration takes place inside a mitochondrion and is
1 The diagram represents two of the stages of aerobic respiration that take place in a mitochondrion. a Name substance X. b Which stage of aerobic respiration takes place inside a mitochondrion and is
Essential Fatty Acids Essential for Good Health SIE
 Page 1 of 6 Essential Fatty Acids Essential for Good Health SIE By Yousry Naguib, PhD Essential fatty acids (EFAs) must be obtained through the diet and cannot be synthesized by the human body. EFAs are
Page 1 of 6 Essential Fatty Acids Essential for Good Health SIE By Yousry Naguib, PhD Essential fatty acids (EFAs) must be obtained through the diet and cannot be synthesized by the human body. EFAs are
Lipids are broadly classified in to simple, complex and derived, which are further subdivided into different groups.
 Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module -9: Classification of lipids Lipids are organic substances which are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are not polymers and exist
Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module -9: Classification of lipids Lipids are organic substances which are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are not polymers and exist
