Trade off-based zooplankton feeding strategies in a global model
|
|
|
- Beatrix Bond
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Trade off-based zooplankton feeding strategies in a global model Fi Prowe 1,2 Ken Andersen 2 Andy Visser 2 Thomas Kiørboe 2 Bei Su 1 Markus Pahlow 1 Andreas Oschlies 1 1 GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel 2 Centre for Ocean Life, DTU Aqua, Denmark October 14, 2015 DynaTrait Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
2 Motivation Global zooplankton feeding strategies Low zooplankton diversity in models Ambush observations generic PFT model herbivore TL3 herbivore TL2 Z z p P Oithona sp.: obligate ambusher abundance fraction of total copepods (NMFS-COPEPOD database, Australian Antarctic Data Centre) Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
3 Motivation Global zooplankton feeding strategies Low zooplankton diversity in models Ambush observations generic PFT model herbivore TL3 herbivore TL2 carnivore Z z p 1 p 2 P 1 P 2 Oithona sp.: obligate ambusher abundance fraction of total copepods (NMFS-COPEPOD database, Australian Antarctic Data Centre) Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
4 Motivation Global zooplankton feeding strategies Low zooplankton diversity in models Ambush observations generic PFT model herbivore TL3 herbivore TL2 carnivore Z z Prowe p 1 p 2 P 1 P 2 Oithona sp.: obligate ambusher abundance fraction of total copepods (NMFS-COPEPOD database, Australian Antarctic Data Centre) Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
5 The model Trade-offs Feeding interactions are predator-prey-encounters predator trade-off traits & encounter size motility encounter rate = f (size selectivity, velocity, escape, threshold) prey trade-off nutrient uptake vs. edibility Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
6 The model Trade-offs Feeding interactions are predator-prey-encounters predator trade-off traits & encounter size motility encounter rate = f (size selectivity, velocity, escape, threshold) prey trade-off nutrient uptake vs. edibility Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
7 The model Trade-offs Feeding interactions are predator-prey-encounters predator trade-off mortality ambusher cruiser encounter rate (motility) traits & encounter size motility encounter rate = f (size selectivity, velocity, escape, threshold) prey trade-off nutrient uptake vs. edibility Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
8 The model Trade-offs Feeding interactions are predator-prey-encounters predator trade-off mortality ambusher cruiser encounter rate (motility) traits & encounter size motility encounter rate = f (size selectivity, velocity, escape, threshold) prey trade-off nutrient uptake vs. edibility Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
9 The model Trade-offs Feeding interactions are predator-prey-encounters predator trade-off mortality ambusher cruiser encounter rate (motility) traits & encounter size motility encounter rate = f (size selectivity, velocity, escape, threshold) prey trade-off encounter rate (predation) non motile nutrient uptake motile nutrient uptake vs. edibility Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
10 The model Structure & aim Encounter-based feeding interactions are diverse encounter model herbivore TL3 herbivore TL2 A carnivore C coupled to global MITgcm emergent community structure a c idealized e.g. basic nutrient dynamics 1 step more complex m n M N for testing hypotheses n small non-motile M large motile a small ambusher C large cruiser Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
11 Results 1. Ambusher fraction model predicts ambush biogeography Prowe Prowe Oithona sp.: proxy for A "best" estimate: highest values on top heterogeneous data (# taxa, months, total abundance) Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
12 Results 1. Ambusher fraction Ambusher fraction in detail model 2 main food chains: n, m c A N, (m) C C never dominates A biomass fraction Oithona abundance fraction m a and m,c A no feeding of C feeding threshold? find observations tune params, sensitivity tests Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
13 Results 1. Ambusher fraction Ambusher fraction in detail model 2 main food chains: n, m c A N, (m) C C never dominates m a and m,c A no feeding of C feeding threshold? find observations tune params, sensitivity tests Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
14 Results 1. Ambusher fraction Ambusher fraction in detail model 2 main food chains: n, m c A N, (m) C C never dominates m a and m,c A no feeding of C feeding threshold? find observations tune params, sensitivity tests Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
15 Results 2. Size structure Phyto size structure: trophic levels (TLs)? 3 TLs observations trophic links matter tuning issue? sensitivity tests challenges many parameters to tune (too) basic nutrient dynamics? rigid interactions? Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
16 Results 2. Size structure Phyto size structure: trophic levels (TLs)? 3 TLs 2 TLs observations trophic links matter tuning issue? sensitivity tests challenges many parameters to tune (too) basic nutrient dynamics? rigid interactions? Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
17 Results 2. Size structure Phyto size structure: trophic levels (TLs)? 3 TLs 2 TLs trophic links matter tuning issue? sensitivity tests Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) 2 TLs observations challenges many parameters to tune (too) basic nutrient dynamics? rigid interactions? Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
18 Outlook Flexible interactions Optimal foraging Bei Su, Dynatrait Non-motile Motile φ c I c φ a Respiration R Biomass I a E c E a Foraging Assimilation Excretion I ingestion φ prey capture coefficient E assimilation R respiration A 0 total activity A foraging activity c f foraging cost Pahlow & Prowe 2010 for multiple prey: non-motile prey high A: active (cruise) motile prey low A: ambush find A that maximizes growth = EI R strategy emerges from prey environment Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
19 Outlook Flexible interactions Optimal foraging Bei Su, Dynatrait Non-motile Motile φ c I c φ a A Respiration A 0 A c f R Biomass I a E c E a Foraging Assimilation Excretion I ingestion φ prey capture coefficient E assimilation R respiration A 0 total activity A foraging activity c f foraging cost Pahlow & Prowe 2010 for multiple prey: non-motile prey high A: active (cruise) motile prey low A: ambush find A that maximizes growth = EI R strategy emerges from prey environment Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
20 Outlook Flexible interactions model captures switching Bei Su, Dynatrait Ingestion (d 1 ) Clearance (m 3 gc 1 d 1 ) Diatom concentration (mg C m 3 ) B A copepod feeding on diatoms only diatoms and ciliates fits lab experiments with 2 prey types (Kiørboe et al. 1996) next steps adapt for several trophic levels fit to mesocosm data couple to global model Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
21 Summary predator-prey encounter model size, motility feeding strategy trade-off: feeding vs. predation risk PFT model, rigid interactions 1 step more complex observations & assessment Ambusher fraction phyto size structure tune model at 1D locations sensitivity studies robustness for testing hypotheses outlook optimal feeding strategy model fitted to lab experiments fit to mesocosm data implement in global model Fi (GEOMAR & DTU Aqua) Zooplankton feeding strategies October 14, / 10
Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling
 Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling Monika Winder Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences Stockholm University What does a more acidic
Ocean acidification effects on plankton communities, ecosystem structure and carbon cycling Monika Winder Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences Stockholm University What does a more acidic
Carbon & Energy Utilization OCN 621
 Carbon & Energy Utilization OCN 621 Lecture Outline 1) Materials Balance Approach defined 2) Sloppy Feeding 3) Egestion: as relates to Assimilation efficiency 4) Metabolism: Allometric Equation 1) Temperature
Carbon & Energy Utilization OCN 621 Lecture Outline 1) Materials Balance Approach defined 2) Sloppy Feeding 3) Egestion: as relates to Assimilation efficiency 4) Metabolism: Allometric Equation 1) Temperature
Respiration: Allometric Relationship
 Metabolism Defined as: all energy transformations, chemical reactions and pathways that make possible the properties of living organisms Measured as: the Respiration Rate, assumes all organism s energy
Metabolism Defined as: all energy transformations, chemical reactions and pathways that make possible the properties of living organisms Measured as: the Respiration Rate, assumes all organism s energy
Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean
 Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean Michael Landry Integrative Oceanography Division Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego SIBER Workshop
Zooplankton Grazing and Secondary Production in the Indian Ocean Michael Landry Integrative Oceanography Division Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego SIBER Workshop
EOSC Biology 3. Zooplankton Measurements
 EOSC 473-573 Biology 3 Zooplankton Measurements Zooplankton Biomass and Abundance Two Quantitative Procedures: Biomass Determination (mg C per m 3 or per m 2 ) Abundance (# individuals per m 3 or per m
EOSC 473-573 Biology 3 Zooplankton Measurements Zooplankton Biomass and Abundance Two Quantitative Procedures: Biomass Determination (mg C per m 3 or per m 2 ) Abundance (# individuals per m 3 or per m
Feeding Measurements
 Feeding Measurements Measures of Feeding Rates (or specific mortality rate) Clearance Rate Concept Clearance Rate (F) = Volume cleared of prey pred -1 time -1 predator prey A consumer may have different
Feeding Measurements Measures of Feeding Rates (or specific mortality rate) Clearance Rate Concept Clearance Rate (F) = Volume cleared of prey pred -1 time -1 predator prey A consumer may have different
Stoichiometry of mesopelagic zooplankton and carbon sequestration in the ocean
 Stoichiometry of mesopelagic zooplankton and carbon sequestration in the ocean Tom Anderson National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK Ocean Carbon & Biogeochemistry workshop, Woods Hole, 28 June 2017
Stoichiometry of mesopelagic zooplankton and carbon sequestration in the ocean Tom Anderson National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK Ocean Carbon & Biogeochemistry workshop, Woods Hole, 28 June 2017
IS THE CONDITION AND GROWTH OF EARLY LIFE STAGES OF NORTHERN ANCHOVY RELATED TO THE BIOCHEMICAL CLIMATOLOGY OF THE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA CURRENT?
 IS THE CONDITION AND GROWTH OF EARLY LIFE STAGES OF NORTHERN ANCHOVY RELATED TO THE BIOCHEMICAL CLIMATOLOGY OF THE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA CURRENT? Jessica A. Miller 1, William T. Peterson 2, Louise Copeman
IS THE CONDITION AND GROWTH OF EARLY LIFE STAGES OF NORTHERN ANCHOVY RELATED TO THE BIOCHEMICAL CLIMATOLOGY OF THE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA CURRENT? Jessica A. Miller 1, William T. Peterson 2, Louise Copeman
Zooplankton. Fall 2006
 Zooplankton Fall 2006 Plankton Classification Plankton Holoplankton Meroplankton Plankton Classification Picoplankton (0.2 2 µm) Plankton Nanoplankton (2-20 µm) Microplankton (20-200 µm) Mesoplankton (200-2000
Zooplankton Fall 2006 Plankton Classification Plankton Holoplankton Meroplankton Plankton Classification Picoplankton (0.2 2 µm) Plankton Nanoplankton (2-20 µm) Microplankton (20-200 µm) Mesoplankton (200-2000
Zooplankton Chapters 6-8 in Miller for more details. 1. Crustaceans- include shrimp, copepods, euphausiids ("krill")
 I. Major Groups Zooplankton Chapters 6-8 in Miller for more details Heterotrophs consume organic matter rather than manufacturing it, as do autotrophs. Zooplankton can be: herbivores carnivores (several
I. Major Groups Zooplankton Chapters 6-8 in Miller for more details Heterotrophs consume organic matter rather than manufacturing it, as do autotrophs. Zooplankton can be: herbivores carnivores (several
BIOS 35502: Practicum in Field Biology. Katherine Lumetta. Advisor: Patrick Kelly
 Feeding Rates of Chaoborus on Daphnia and Copepods and the Effect of Fish Presence BIOS 35502: Practicum in Field Biology Katherine Lumetta Advisor: Patrick Kelly 2014 Abstract Chaoborus can influence
Feeding Rates of Chaoborus on Daphnia and Copepods and the Effect of Fish Presence BIOS 35502: Practicum in Field Biology Katherine Lumetta Advisor: Patrick Kelly 2014 Abstract Chaoborus can influence
WHALE FOOD PYRAMID ACTIVITY
 WHALE FOOD PYRAMID ACTIVITY SEATTLE AQUARIUM GRADES: 9 12 DURATION: 30 60 minutes MATERIALS: - Student worksheet STANDARDS: WA state: - Systems: SYSB & SYSC - Life Sciences: LS1A Ocean Literacy Principles:
WHALE FOOD PYRAMID ACTIVITY SEATTLE AQUARIUM GRADES: 9 12 DURATION: 30 60 minutes MATERIALS: - Student worksheet STANDARDS: WA state: - Systems: SYSB & SYSC - Life Sciences: LS1A Ocean Literacy Principles:
Fig Draw a food chain for the organisms in the passages above. Table 6.1
 1 Moose, Alces americanus, shown in Fig. 6.1, are large herbivores that primarily live in northern parts of North America. They have a varied diet that includes young shoots of willow trees and aquatic
1 Moose, Alces americanus, shown in Fig. 6.1, are large herbivores that primarily live in northern parts of North America. They have a varied diet that includes young shoots of willow trees and aquatic
Predicting excretion rates of microzooplankton from carbon metabolism and elemental ratios
 468 Comment Limnol. Oceanogr., 38(2), 1993,468-472 0 1993, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Predicting excretion rates of microzooplankton from carbon metabolism and elemental
468 Comment Limnol. Oceanogr., 38(2), 1993,468-472 0 1993, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Predicting excretion rates of microzooplankton from carbon metabolism and elemental
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/03
 www.xtremepapers.com Centre Number Candidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/03 Paper 3 Extended Candidates
www.xtremepapers.com Centre Number Candidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/03 Paper 3 Extended Candidates
Rapid evolution of highly variable competitive abilities in a key phytoplankton species
 SUPPLEMENTARY Brief Communication INFORMATION https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-018-0474-x In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Rapid evolution of highly variable competitive abilities in a
SUPPLEMENTARY Brief Communication INFORMATION https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-018-0474-x In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Rapid evolution of highly variable competitive abilities in a
Estimating the Grazing Impact of Marine Micro-zooplankton *
 Marine Biology 67, 283-288 (1982) MARINE BIOLOGY 9 Springer-Verlag 1982 Estimating the Grazing Impact of Marine Micro-zooplankton * M. R. Landry and R. P. Hassett School of Oceanography, WB-10, University
Marine Biology 67, 283-288 (1982) MARINE BIOLOGY 9 Springer-Verlag 1982 Estimating the Grazing Impact of Marine Micro-zooplankton * M. R. Landry and R. P. Hassett School of Oceanography, WB-10, University
Food Chains & Food Webs. **Test on Tuesday, April 29, 2014**
 Name: Mrs. Merenda Date: Reading/Class & Homework Class work: Tuesday, April 22 Food Chains & Food Webs **Test on Tuesday, April 29, 2014** use your glossary to locate definitions #1-3 read booklet pp.
Name: Mrs. Merenda Date: Reading/Class & Homework Class work: Tuesday, April 22 Food Chains & Food Webs **Test on Tuesday, April 29, 2014** use your glossary to locate definitions #1-3 read booklet pp.
Plankton Lab 11/14 Integrated Science 1 Redwood High School Name: Period:
 Plankton Lab 11/14 Integrated Science 1 Redwood High School Period: Introduction Plankton (which comes from the Greek word for drifting) are often defined as organisms that float at or near the surface
Plankton Lab 11/14 Integrated Science 1 Redwood High School Period: Introduction Plankton (which comes from the Greek word for drifting) are often defined as organisms that float at or near the surface
Ingestion of microplastics by zooplankton in the western English Channel
 Ingestion of microplastics by zooplankton in the western English Channel Alice Wilson McNeal 1 ; Matthew Cole 2 ; James Clark 1 ; Pennie Lindeque 1 1. Plymouth Marine Laboratory. 2. University of Exeter.
Ingestion of microplastics by zooplankton in the western English Channel Alice Wilson McNeal 1 ; Matthew Cole 2 ; James Clark 1 ; Pennie Lindeque 1 1. Plymouth Marine Laboratory. 2. University of Exeter.
Chapter 4.3: Food Chains and Food Webs
 Chapter 4.3: Food Chains and Food Webs Food Chains All living things need food. It gives them energy as well as substances they need to build up their body. The sun is the starting point of every food
Chapter 4.3: Food Chains and Food Webs Food Chains All living things need food. It gives them energy as well as substances they need to build up their body. The sun is the starting point of every food
Plankton community properties determined by nutrients and size-selective feeding
 Vol. 413: 1 15, 1 doi: 1.3354/meps8716 FEATURE ARTICLE MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Mar Ecol Prog Ser Published August 6 OPEN ACCESS Plankton community properties determined by nutrients and size-selective
Vol. 413: 1 15, 1 doi: 1.3354/meps8716 FEATURE ARTICLE MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Mar Ecol Prog Ser Published August 6 OPEN ACCESS Plankton community properties determined by nutrients and size-selective
OFFCHANNEL MARSH HABITATS Base of aquatic food web Juvenile Chinook diet inferred from natural abundance stable isotopes
 OFFCHANNEL MARSH HABITATS Base of aquatic food web Juvenile Chinook diet inferred from natural abundance stable isotopes Tawnya D. Peterson (OHSU) & Estuary Partnership s EMP team http://www.flycraftangling.com
OFFCHANNEL MARSH HABITATS Base of aquatic food web Juvenile Chinook diet inferred from natural abundance stable isotopes Tawnya D. Peterson (OHSU) & Estuary Partnership s EMP team http://www.flycraftangling.com
Zooplankton community structure and size spectra linked to phytoplankton and hydrographic features on the Faroe Shelf in spring
 Zooplankton community structure and size spectra linked to phytoplankton and hydrographic features on the Faroe Shelf in spring Sólvá Jacobsen, Eilif Gaard, Karin M. H. Larsen, Sólvá K. Eliasen Faroe Islands
Zooplankton community structure and size spectra linked to phytoplankton and hydrographic features on the Faroe Shelf in spring Sólvá Jacobsen, Eilif Gaard, Karin M. H. Larsen, Sólvá K. Eliasen Faroe Islands
Microplastic ingestion: the role of taste
 Microplastic ingestion: the role of taste Renske Vroom 1,2, Claudia Halsband 1, Ellen Besseling 2, Bart Koelmans 2 1 Akvaplan-niva, Fram Centre, Tromsø, Norway 2 Wageningen University and Research Centre,
Microplastic ingestion: the role of taste Renske Vroom 1,2, Claudia Halsband 1, Ellen Besseling 2, Bart Koelmans 2 1 Akvaplan-niva, Fram Centre, Tromsø, Norway 2 Wageningen University and Research Centre,
Dispersants, oil, and time: The resulting toxicological and physiological effects on the Gulf Killifish
 Dispersants, oil, and time: The resulting toxicological and physiological effects on the Gulf Killifish Christopher C Green Aquaculture Research Station Louisiana State University AgCenter Response Time
Dispersants, oil, and time: The resulting toxicological and physiological effects on the Gulf Killifish Christopher C Green Aquaculture Research Station Louisiana State University AgCenter Response Time
Food Chains and Webs --- "What's for dinner?"
 Food Chains and Webs --- "What's for dinner?" Every organism needs to obtain energy in order to live. For example, plants get energy from the sun, some animals eat plants, and some animals eat other animals.
Food Chains and Webs --- "What's for dinner?" Every organism needs to obtain energy in order to live. For example, plants get energy from the sun, some animals eat plants, and some animals eat other animals.
Is sedimentation of copepod faecal pellets determined by cyclopoids? Evidence from enclosed ecosystems
 Is sedimentation of copepod faecal pellets determined by cyclopoids? Evidence from enclosed ecosystems CAMILLA SVENSEN* AND JENS C. NEJSTGAARD NORWEGIAN COLLEGE OF FISHERY SCIENCE, UNIVERSITY OF TROMSØ,
Is sedimentation of copepod faecal pellets determined by cyclopoids? Evidence from enclosed ecosystems CAMILLA SVENSEN* AND JENS C. NEJSTGAARD NORWEGIAN COLLEGE OF FISHERY SCIENCE, UNIVERSITY OF TROMSØ,
Competing for Food Food Chain; Plankton
 Competing for Food Food Chain; Plankton Adapted from: "Competing for food" in Living in Water. The National Aquarium in Baltimore. 1997. Grade Level: intermediate Duration: 1-2 class periods Setting: classroom
Competing for Food Food Chain; Plankton Adapted from: "Competing for food" in Living in Water. The National Aquarium in Baltimore. 1997. Grade Level: intermediate Duration: 1-2 class periods Setting: classroom
Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem
 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem Food Chains, Food Webs, Energy Pyramids 1 Ecosystems An ecosystem is all of the organisms living in an area together with their physical environment. Ex. An oak forest,
Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem Food Chains, Food Webs, Energy Pyramids 1 Ecosystems An ecosystem is all of the organisms living in an area together with their physical environment. Ex. An oak forest,
Patchiness of the Plankton
 Patchiness of the Plankton Within the geographical boundaries inhabited by any species, the individuals of that species are not distributed uniformly or randomly, but are usually aggregated into discrete
Patchiness of the Plankton Within the geographical boundaries inhabited by any species, the individuals of that species are not distributed uniformly or randomly, but are usually aggregated into discrete
Food Chains and Webs GLOSSARY. autotrophs: organisms, such as plants, that are capable of making their own food.
 Food Chains and Webs GLOSSARY autotrophs: organisms, such as plants, that are capable of making their own food. biological magnification: the process by which small amounts of a poisonous chemical become
Food Chains and Webs GLOSSARY autotrophs: organisms, such as plants, that are capable of making their own food. biological magnification: the process by which small amounts of a poisonous chemical become
Stoichiometrically Explicit Competition between Grazers: Species Replacement, Coexistence, and Priority Effects along Resource Supply Gradients
 vol. 164, no. 2 the american naturalist august 2004 Stoichiometrically Explicit Competition between Grazers: Species Replacement, Coexistence, and Priority Effects along Resource Supply Gradients Spencer
vol. 164, no. 2 the american naturalist august 2004 Stoichiometrically Explicit Competition between Grazers: Species Replacement, Coexistence, and Priority Effects along Resource Supply Gradients Spencer
Name: Period: Date: Day What happens to the temperature in a compost bin during decomposition? Interpret: Be able to interpret graphs.
 Review for 7 th Science 1 st Semester Exam 17-18 Answer the questions. Day 2 22. What happens to the temperature in a compost bin during decomposition? Increases Interpret: Be able to interpret graphs.
Review for 7 th Science 1 st Semester Exam 17-18 Answer the questions. Day 2 22. What happens to the temperature in a compost bin during decomposition? Increases Interpret: Be able to interpret graphs.
Food Chains and Webs --- "What's for dinner?"
 Food Chains and Webs --- "What's for dinner?" Every organism needs to obtain energy in order to live. For example, plants get energy from the sun, some animals eat plants, and some animals eat other animals.
Food Chains and Webs --- "What's for dinner?" Every organism needs to obtain energy in order to live. For example, plants get energy from the sun, some animals eat plants, and some animals eat other animals.
that it eats many organisms including mussels, abalone, chitons, barnacles and snails (Niesen
 Christopher Mertz Exploratory #2 Adaptations July 27,2008 Pisaster ochraceus Feeding Preference in Relation to the Optimal Foraging Theory Introduction Pisaster ochraceus is a voracious intertidal predator.
Christopher Mertz Exploratory #2 Adaptations July 27,2008 Pisaster ochraceus Feeding Preference in Relation to the Optimal Foraging Theory Introduction Pisaster ochraceus is a voracious intertidal predator.
In steady state, new production = carbon export
 In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
1st 9 Weeks Test Review Sheet
 1st 9 Weeks Test Review Sheet 1. Which two are reactants of photosynthesis? a. glucose and water b. carbon dioxide and water c. glucose and oxygen d. sunlight and ATP energy 2. Photosynthesis makes which
1st 9 Weeks Test Review Sheet 1. Which two are reactants of photosynthesis? a. glucose and water b. carbon dioxide and water c. glucose and oxygen d. sunlight and ATP energy 2. Photosynthesis makes which
Impact of zooplankton food selectivity on plankton dynamics and nutrient cycling
 Journal of Plankton Research plankt.oxfordjournals.org J. Plankton Res. (2015) 37(3): 519 529. First published online April 9, 2015 doi:10.1093/plankt/fbv020 Impact of zooplankton food selectivity on plankton
Journal of Plankton Research plankt.oxfordjournals.org J. Plankton Res. (2015) 37(3): 519 529. First published online April 9, 2015 doi:10.1093/plankt/fbv020 Impact of zooplankton food selectivity on plankton
modelling the role of Essential Fatty Acids in aquatic food webs
 modelling the role of Essential Fatty Acids in aquatic food webs Gurbir Perhar, George B. Arhonditsis University of Toronto Ecology & Evolutionary Biology g.perhar@utoronto.ca AGENDA: Introduction Objectives
modelling the role of Essential Fatty Acids in aquatic food webs Gurbir Perhar, George B. Arhonditsis University of Toronto Ecology & Evolutionary Biology g.perhar@utoronto.ca AGENDA: Introduction Objectives
Nutrient- vs. Energy-Limitation in the Sea:
 Nutrient- vs. Energy-Limitation in the Sea: The Red Sea and the Antarctic Ocean as Extreme Case Studies Max M. Tilzer University of Constance, Germany ISEEQS-Meeting, 29 May 1 June 2005 Katsushika Hokusai:
Nutrient- vs. Energy-Limitation in the Sea: The Red Sea and the Antarctic Ocean as Extreme Case Studies Max M. Tilzer University of Constance, Germany ISEEQS-Meeting, 29 May 1 June 2005 Katsushika Hokusai:
Global diversity patterns of marine phytoplankton and zooplankton
 AIV presentation 14/10/05 Claude Loverdo Sakina Ayata Global diversity patterns of marine phytoplankton and zooplankton X.Irigoien, J.Huisman and R.P.Harris Nature 429, 863-867 (2004) Presentation's overview
AIV presentation 14/10/05 Claude Loverdo Sakina Ayata Global diversity patterns of marine phytoplankton and zooplankton X.Irigoien, J.Huisman and R.P.Harris Nature 429, 863-867 (2004) Presentation's overview
Biology of fish larvae and fry gut and enzyme development
 Biology of fish larvae and fry gut and enzyme development Functions of the gut and intestine Digestion and absorption of nutrients Excretion of waste material-digesta, metabolites & toxins (entero-hepatic
Biology of fish larvae and fry gut and enzyme development Functions of the gut and intestine Digestion and absorption of nutrients Excretion of waste material-digesta, metabolites & toxins (entero-hepatic
Mesocosm Experiments Progress Report Ron Bassar, Andrés López-Sepulcre and David Reznick January 2011
 Mesocosm Experiments Progress Report Ron Bassar, Andrés López-Sepulcre and David Reznick January 2011 I. Summary of Mesocosm studies completed as of 12/10 1. Spring 2007. First trial to the Travis-Reznick
Mesocosm Experiments Progress Report Ron Bassar, Andrés López-Sepulcre and David Reznick January 2011 I. Summary of Mesocosm studies completed as of 12/10 1. Spring 2007. First trial to the Travis-Reznick
Unit 9: Food Chains and Food Webs
 Unit Focus Unit 9: Food Chains and Food Webs This unit reviews energy production in plants and animals, feeding relationships, and symbiosis in the ocean. Students will become familiar with the hierarchy
Unit Focus Unit 9: Food Chains and Food Webs This unit reviews energy production in plants and animals, feeding relationships, and symbiosis in the ocean. Students will become familiar with the hierarchy
Standard B-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the flow of energy within and between living systems.
 B-3.1 Summarize the overall process by which photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy and interpret the chemical equation for the process. Taxonomy Level: 2.4-B and 2.1-B Understand Conceptual
B-3.1 Summarize the overall process by which photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy and interpret the chemical equation for the process. Taxonomy Level: 2.4-B and 2.1-B Understand Conceptual
Lesson: Plankton. We will use each of these three categories in our investigations of plankton.
 Lesson: Plankton Plankton Most of the living organisms in the oceans we never see and rarely hear about. They are the plankton that float at or near the surface in ocean and freshwater environments. Plankton
Lesson: Plankton Plankton Most of the living organisms in the oceans we never see and rarely hear about. They are the plankton that float at or near the surface in ocean and freshwater environments. Plankton
Model building with craft materials Presented to grade 4; appropriate for grades K 12 with age appropriate modifications
 Unit: Lesson 1: Oceans of Energy Plankton Summary: In this lesson, students are introduced to phytoplankton and zooplankton as the oceans primary producers and consumers. Lesson includes two activities:
Unit: Lesson 1: Oceans of Energy Plankton Summary: In this lesson, students are introduced to phytoplankton and zooplankton as the oceans primary producers and consumers. Lesson includes two activities:
LAB-AIDS Correlations to New Mexico 9-12 Science Standards 1 HIGH SCHOOL BIOLOGY
 LAB-AIDS Correlations to New Mexico 9-12 Science Standards 1 HIGH SCHOOL BIOLOGY Science and Global Issues: Biology (SGI Biology) is written by the SEPUP group, at the Lawrence Hall of Science, University
LAB-AIDS Correlations to New Mexico 9-12 Science Standards 1 HIGH SCHOOL BIOLOGY Science and Global Issues: Biology (SGI Biology) is written by the SEPUP group, at the Lawrence Hall of Science, University
Danish Institute for Fisheries Research, Kavalergården 6, DK-2920 Charlottenlund, Denmark
 Seasonal changes in food quantity and quality for the development and egg production of the common North Sea copepods Temora longicornis and Pseudocalanus elongatus 1) Marja Koski, 1) Jörg Dutz and ) Wim
Seasonal changes in food quantity and quality for the development and egg production of the common North Sea copepods Temora longicornis and Pseudocalanus elongatus 1) Marja Koski, 1) Jörg Dutz and ) Wim
Light and nutrient supply mediate intraspecific variation in the nutrient stoichiometry of juvenile fish
 Light and nutrient supply mediate intraspecific variation in the nutrient stoichiometry of juvenile fish Kelsea N. Downs, 1 Nicole M. Hayes, 1,2,3 Amber M. Rock, 1,2 Michael J. Vanni, 1,2, and María J.
Light and nutrient supply mediate intraspecific variation in the nutrient stoichiometry of juvenile fish Kelsea N. Downs, 1 Nicole M. Hayes, 1,2,3 Amber M. Rock, 1,2 Michael J. Vanni, 1,2, and María J.
Zooplankton Migration Patterns at Scotton Landing: Behavioral Adaptations written by Lauren Zodl, University of Delaware
 Zooplankton Migration Patterns at Scotton Landing: Behavioral Adaptations written by Lauren Zodl, University of Delaware Summary: Zooplankton have evolved specific migration patterns that increase their
Zooplankton Migration Patterns at Scotton Landing: Behavioral Adaptations written by Lauren Zodl, University of Delaware Summary: Zooplankton have evolved specific migration patterns that increase their
A Study of the Predator-Prey Relationship
 Name: Block: v3/06 A Study of the Predator-Prey Relationship The predator-prey relationship is important to ecosystems. How can we measure that relationship? It would be difficult to follow a predator
Name: Block: v3/06 A Study of the Predator-Prey Relationship The predator-prey relationship is important to ecosystems. How can we measure that relationship? It would be difficult to follow a predator
Worksheet information for Ponds in Peril Classroom Experiment Note: For overall background information, refer to the Science Scope article
 Worksheet information for Ponds in Peril Classroom Experiment Note: For overall background information, refer to the Science Scope article Worksheet 1: Aquatic Nutrient Pollution - When to use: Beginning
Worksheet information for Ponds in Peril Classroom Experiment Note: For overall background information, refer to the Science Scope article Worksheet 1: Aquatic Nutrient Pollution - When to use: Beginning
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC.
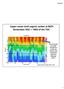 Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
FRCGC, JAMSTEC ECEM07,
 Comparing Optimal Uptake Kinetics and Michaelis-Menten by Assimilating Data from the SERIES Fe-Enrichment Experiment into a Marine Ecosystem Model S. Lan Smith, Naoki Yoshie 2 and Yasuhiro Yamanaka Ecosystem
Comparing Optimal Uptake Kinetics and Michaelis-Menten by Assimilating Data from the SERIES Fe-Enrichment Experiment into a Marine Ecosystem Model S. Lan Smith, Naoki Yoshie 2 and Yasuhiro Yamanaka Ecosystem
ORGANISMS IN ECOSYSTEMS. Dr. khalid M. Salih
 ORGANISMS IN ECOSYSTEMS Dr. khalid M. Salih Definition The study of cooperation and competition for biotic and abiotic parts of the environment needs to know three important things: Habitat which is the
ORGANISMS IN ECOSYSTEMS Dr. khalid M. Salih Definition The study of cooperation and competition for biotic and abiotic parts of the environment needs to know three important things: Habitat which is the
Lipids as trophic markers in Antarctic krill. II. Lipid composition of the body and digestive gland of Euphausia superba in controlled conditions
 MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 296: 65 79, 25 Published July 12 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Lipids as trophic markers in Antarctic krill. II. Lipid composition of the body and digestive gland of Euphausia superba
MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 296: 65 79, 25 Published July 12 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Lipids as trophic markers in Antarctic krill. II. Lipid composition of the body and digestive gland of Euphausia superba
3.3 Pyramid of Numbers and Pyramid Biomass
 3. Energy in Ecosystems 3.1 Energy Transfer and Loss 3.2 Pyramid of energy 3.3 Pyramid of Numbers and Pyramid Biomass Learning Intentions At the end of this section you should be able to: Explain how energy
3. Energy in Ecosystems 3.1 Energy Transfer and Loss 3.2 Pyramid of energy 3.3 Pyramid of Numbers and Pyramid Biomass Learning Intentions At the end of this section you should be able to: Explain how energy
Dietary shifts in the copepod Temora longicornis during spring: evidence from stable isotope signatures, fatty acid biomarkers and feeding experiments
 JOURNAL OF PLANKTON RESEARCH j VOLUME 31 j NUMBER 1 j PAGES 45 60 j 2009 Dietary shifts in the copepod Temora longicornis during spring: evidence from stable isotope signatures, fatty acid biomarkers and
JOURNAL OF PLANKTON RESEARCH j VOLUME 31 j NUMBER 1 j PAGES 45 60 j 2009 Dietary shifts in the copepod Temora longicornis during spring: evidence from stable isotope signatures, fatty acid biomarkers and
Level 1 Biology, 2014
 90929 909290 1SUPERVISOR S Level 1 Biology, 2014 90929 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) 2.00 pm Monday 17 November 2014 Credits: Three Achievement
90929 909290 1SUPERVISOR S Level 1 Biology, 2014 90929 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) 2.00 pm Monday 17 November 2014 Credits: Three Achievement
ABSTRACT THE EFFECTS OF LIGHT AND NUTRIENTS ON FOOD CHAIN EFFICIENCY IN THREE- LEVEL FOOD CHAINS WITH BLUEGILL. by Mia R. Hall
 ABSTRACT THE EFFECTS OF LIGHT AND NUTRIENTS ON FOOD CHAIN EFFICIENCY IN THREE- LEVEL FOOD CHAINS WITH BLUEGILL by Mia R. Hall Food chain efficiency in aquatic systems can be constrained by phytoplankton
ABSTRACT THE EFFECTS OF LIGHT AND NUTRIENTS ON FOOD CHAIN EFFICIENCY IN THREE- LEVEL FOOD CHAINS WITH BLUEGILL by Mia R. Hall Food chain efficiency in aquatic systems can be constrained by phytoplankton
The Food Chain. In order to understand the food chain, there are some vocabulary words you should learn. Look at the words and definitions below.
 Non-fiction: The Food Chain The Food Chain In order to understand the food chain, there are some vocabulary words you should learn. Look at the words and definitions below. Producers Organisms that make
Non-fiction: The Food Chain The Food Chain In order to understand the food chain, there are some vocabulary words you should learn. Look at the words and definitions below. Producers Organisms that make
Mangrove ecology: application of fatty acid biomarkers as trophic tracers in the ecosystem
 Kaiho Super Science High School Mangrove ecology: application of fatty acid biomarkers as trophic tracers in the ecosystem Prosper Mfilinge Advisor: Prof. Makoto Tsuchiya JSPS Self Introduction What are
Kaiho Super Science High School Mangrove ecology: application of fatty acid biomarkers as trophic tracers in the ecosystem Prosper Mfilinge Advisor: Prof. Makoto Tsuchiya JSPS Self Introduction What are
Determine the temporal and spatial distribution of all taxa. as individual counts and as biomass Assess as major taxonomic and functional groups.
 2013 TMDL Phytoplankton and Zooplankton monitoring Determine the temporal and spatial distribution of all taxa. as individual counts and as biomass Assess as major taxonomic and functional groups. 2013
2013 TMDL Phytoplankton and Zooplankton monitoring Determine the temporal and spatial distribution of all taxa. as individual counts and as biomass Assess as major taxonomic and functional groups. 2013
Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea
 Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea DOC distributions in the Atlantic Marine Microplankton Ecology OCN 626 Matthew Church Figures from Dennis Hansell DOC distributions in the Pacific Basin scale
Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea DOC distributions in the Atlantic Marine Microplankton Ecology OCN 626 Matthew Church Figures from Dennis Hansell DOC distributions in the Pacific Basin scale
Reality checks on microbial food web interactions in dilution experiments: responses to the comments of Dolan and McKeon
 Ocean Science, 1, 39 44, 2005 SRef-ID: 1812-0792/os/2005-1-39 European Geosciences Union Ocean Science Reality checks on microbial food web interactions in dilution experiments: responses to the comments
Ocean Science, 1, 39 44, 2005 SRef-ID: 1812-0792/os/2005-1-39 European Geosciences Union Ocean Science Reality checks on microbial food web interactions in dilution experiments: responses to the comments
Title. Author(s)KURASAWA, Hideo. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information
 Title The Phytoplankton Zooplankton Relationships in Two P Author(s)KURASAWA, Hideo 北海道大學理學部紀要 = JOURNAL OF THE FACULTY OF SCIENCE HOKKA CitationZOOLOGY, 13(1-4): 180-186 Issue Date 1957-08 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/27223
Title The Phytoplankton Zooplankton Relationships in Two P Author(s)KURASAWA, Hideo 北海道大學理學部紀要 = JOURNAL OF THE FACULTY OF SCIENCE HOKKA CitationZOOLOGY, 13(1-4): 180-186 Issue Date 1957-08 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/27223
Supplementary data. Dissolved extracellular polymeric substance (deps) dynamics and bacterial growth
 Polar Biology Supplementary data Dissolved extracellular polymeric substance (deps) dynamics and bacterial growth during sea ice formation in an ice tank study Shazia N Aslam 1*, Graham J.C. Underwood
Polar Biology Supplementary data Dissolved extracellular polymeric substance (deps) dynamics and bacterial growth during sea ice formation in an ice tank study Shazia N Aslam 1*, Graham J.C. Underwood
A probabilistic method for food web modeling
 A probabilistic method for food web modeling Bayesian Networks methodology, challenges, and possibilities Anna Åkesson, Linköping University, Sweden 2 nd international symposium on Ecological Networks,
A probabilistic method for food web modeling Bayesian Networks methodology, challenges, and possibilities Anna Åkesson, Linköping University, Sweden 2 nd international symposium on Ecological Networks,
Lecture 13, 09 Oct 2003 Chapter 10 Muscles. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.
 Lecture 13, 09 Oct 2003 Chapter 10 Muscles Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology 437 1. Muscles (Ch10) 2. Announcements
Lecture 13, 09 Oct 2003 Chapter 10 Muscles Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology 437 1. Muscles (Ch10) 2. Announcements
The role of zooplankton in cyanobacteria bloom development in Australian reservoirs
 The role of zooplankton in cyanobacteria bloom development in Australian reservoirs Ying Hong B.SC & M.SC (Ecolog y) Submitted in fu lfi lm en t of the req u irem en ts for the degr ee of Doct or of Philosop
The role of zooplankton in cyanobacteria bloom development in Australian reservoirs Ying Hong B.SC & M.SC (Ecolog y) Submitted in fu lfi lm en t of the req u irem en ts for the degr ee of Doct or of Philosop
Biology 1. Worksheet I
 Biology 1 Worksheet I Question #1 What does the first law of thermodynamics state? Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed No energy transformation is 100% efficient How is this law related
Biology 1 Worksheet I Question #1 What does the first law of thermodynamics state? Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed No energy transformation is 100% efficient How is this law related
1162 Notes. Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(5), 2000, , by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc.
 1162 Notes Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(5), 2000, 1162 1167 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Stoichiometric theory extended to micronutrients: Comparison of the roles of essential
1162 Notes Limnol. Oceanogr., 45(5), 2000, 1162 1167 2000, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Stoichiometric theory extended to micronutrients: Comparison of the roles of essential
Lake organisms. Those that go where the water takes them. Those that live on the lake bottom. BENTHOS = animals crustaceans, worms molluscs, insects
 Lake organisms Those that go where they choose Aquatic organisms may be classified as: Those that go where they choose ( ) Those that go where the water takes them ( ) Those that live on the lake bottom
Lake organisms Those that go where they choose Aquatic organisms may be classified as: Those that go where they choose ( ) Those that go where the water takes them ( ) Those that live on the lake bottom
Eutrophication and warming effects on long-term variation of zooplankton in Lake Biwa
 Biogeosciences, 8, 1383 1399, 2011 doi:10.5194/bg-8-1383-2011 Author(s) 2011. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Eutrophication and warming effects on long-term variation of zooplankton in Lake
Biogeosciences, 8, 1383 1399, 2011 doi:10.5194/bg-8-1383-2011 Author(s) 2011. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Eutrophication and warming effects on long-term variation of zooplankton in Lake
Accounting for grazing dynamics in nitrogen-phytoplankton-zooplankton models
 Limnol. Oceanogr., 52(2), 2007, 649 661 E 2007, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Accounting for grazing dynamics in nitrogen-phytoplankton-zooplankton models Aditee Mitra and
Limnol. Oceanogr., 52(2), 2007, 649 661 E 2007, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Accounting for grazing dynamics in nitrogen-phytoplankton-zooplankton models Aditee Mitra and
Carbon cycling and POC turnover in the mesopelagic zone of the ocean: Insights from a simple model
 1 Carbon cycling and POC turnover in the mesopelagic zone of the ocean: Insights from a simple model Thomas R. Anderson 1 and Kam W. Tang 2 1. National Oceanography Centre, Southampton SO14 3ZH, U.K. 2.
1 Carbon cycling and POC turnover in the mesopelagic zone of the ocean: Insights from a simple model Thomas R. Anderson 1 and Kam W. Tang 2 1. National Oceanography Centre, Southampton SO14 3ZH, U.K. 2.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2006 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer
UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2006 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer
GLOBEC CRUISE HX253 REPORT
 GLOBEC CRUISE HX253 REPORT 4 11 December 2001 Funding Source: Chief Scientist: NSF-NOAA (NA-67-RJ-0147) Thomas Weingartner* Institute of Marine Science University of Alaska Fairbanks, AK 99775-1080 Phone:
GLOBEC CRUISE HX253 REPORT 4 11 December 2001 Funding Source: Chief Scientist: NSF-NOAA (NA-67-RJ-0147) Thomas Weingartner* Institute of Marine Science University of Alaska Fairbanks, AK 99775-1080 Phone:
How to Escape a Predator Featured scientists: Amy Worthington and John Swallow from Washington State University and University of Colorado, Denver
 How to Escape a Predator Featured scientists: Amy Worthington and John Swallow from Washington State University and University of Colorado, Denver Research Background: Stalk-eyed flies are insects that
How to Escape a Predator Featured scientists: Amy Worthington and John Swallow from Washington State University and University of Colorado, Denver Research Background: Stalk-eyed flies are insects that
DOWNLOAD PDF WHAT SEA ANIMALS EAT (NATURES FOOD CHAINS)
 Chapter 1 : What Organisms Eat Seaweed? Sciencing The next level of the marine food chain is made up of animals that feast on the sea's abundant plant life. On the ocean's surface waters, microscopic animalsâ
Chapter 1 : What Organisms Eat Seaweed? Sciencing The next level of the marine food chain is made up of animals that feast on the sea's abundant plant life. On the ocean's surface waters, microscopic animalsâ
ABSTRACT LIGHT, NUTRIENT, AND PLANKTIVORY EFFECTS ON ZOOPLANKTON COMMUNITIES AND FOOD CHAIN EFFICIENCY. by Jennifer M. Bobson
 STRCT LIGHT, NUTRIENT, ND PLNKTIVORY EFFECTS ON ZOOPLNKTON COMMUNITIES ND FOOD CHIN EFFICIENCY by Jennifer M. obson The biomass, production, and community composition of zooplankton are affected by many
STRCT LIGHT, NUTRIENT, ND PLNKTIVORY EFFECTS ON ZOOPLNKTON COMMUNITIES ND FOOD CHIN EFFICIENCY by Jennifer M. obson The biomass, production, and community composition of zooplankton are affected by many
Effect of temperature on the growth rate of Tetrahymena thermophila. Rachael Callaghan, Petra Catsi, Pravnit Kooner and Nevrose Mangat
 Effect of temperature on the growth rate of Tetrahymena thermophila Rachael Callaghan, Petra Catsi, Pravnit Kooner and Nevrose Mangat Abstract In this experiment we studied the effect of temperature on
Effect of temperature on the growth rate of Tetrahymena thermophila Rachael Callaghan, Petra Catsi, Pravnit Kooner and Nevrose Mangat Abstract In this experiment we studied the effect of temperature on
Unit 4- Energy & Cell Processes
 Unit 4- Energy & Cell Processes Energy in the ecosystem ATP Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Fermentation By: Mrs. Stahl Biology Background knowledge Unit Layout Energy- where does it all come from?
Unit 4- Energy & Cell Processes Energy in the ecosystem ATP Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Fermentation By: Mrs. Stahl Biology Background knowledge Unit Layout Energy- where does it all come from?
The American Society of Naturalists
 The American Society of Naturalists Population Effects of Natural Selection Author(s): Robert H. MacArthur Source: The American Naturalist, Vol. 95, No. 882 (May - Jun., 1961), pp. 195-199 Published by:
The American Society of Naturalists Population Effects of Natural Selection Author(s): Robert H. MacArthur Source: The American Naturalist, Vol. 95, No. 882 (May - Jun., 1961), pp. 195-199 Published by:
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
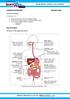 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
Three Attempts to Replicate the Behavioral Sunk-Cost Effect: A Note on Cunha and Caldieraro (2009)
 Cognitive Science 34 (2010) 1379 1383 Copyright Ó 2010 Cognitive Science Society, Inc. All rights reserved. ISSN: 0364-0213 print / 1551-6709 online DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-6709.2010.01136.x Three Attempts
Cognitive Science 34 (2010) 1379 1383 Copyright Ó 2010 Cognitive Science Society, Inc. All rights reserved. ISSN: 0364-0213 print / 1551-6709 online DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-6709.2010.01136.x Three Attempts
Studies on nutritional requirements and feed optimization for pikeperch larvae
 recent progress in pikeperch culture Faculty of Sciences and Technologies Nancy, France 27. Studies on nutritional requirements and feed optimization for pikeperch larvae Ivar Lund, DTU Aqua N. El Kertaoui;
recent progress in pikeperch culture Faculty of Sciences and Technologies Nancy, France 27. Studies on nutritional requirements and feed optimization for pikeperch larvae Ivar Lund, DTU Aqua N. El Kertaoui;
Chapter 12: Marine Mammals. By: Da Lynne Cousar, Megan Dudenbostel, Kyle Nemeth, Matt Boyle, and Steven Miller
 Chapter 12: Marine Mammals By: Da Lynne Cousar, Megan Dudenbostel, Kyle Nemeth, Matt Boyle, and Steven Miller Four different kinds of Marine Mammals Cetaceans- includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises
Chapter 12: Marine Mammals By: Da Lynne Cousar, Megan Dudenbostel, Kyle Nemeth, Matt Boyle, and Steven Miller Four different kinds of Marine Mammals Cetaceans- includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises
3 rd Form BIOLOGY YEARLY CURRICULUM. Text: Anne Tindale (2016) CSEC Biology Revision Credit Hours: 5 Teacher: Mr. Erick Santizo Contact No.
 3 rd Form BIOLOGY YEARLY CURRICULUM San Pedro High School San Pedro Town Belize District Telefax: 226-2045 Email Address: esantizo@sphs.edu.bz Text: Anne Tindale (2016) CSEC Biology Revision Credit Hours:
3 rd Form BIOLOGY YEARLY CURRICULUM San Pedro High School San Pedro Town Belize District Telefax: 226-2045 Email Address: esantizo@sphs.edu.bz Text: Anne Tindale (2016) CSEC Biology Revision Credit Hours:
Behavioral flexibility in prey selection by bacterivorous nanoflagellates
 NOTES Limnol. Oceanogr., 40(S), 1995, 1503-l 507 0 1995, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Behavioral flexibility in prey selection by bacterivorous nanoflagellates Abstract-We
NOTES Limnol. Oceanogr., 40(S), 1995, 1503-l 507 0 1995, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Behavioral flexibility in prey selection by bacterivorous nanoflagellates Abstract-We
Steller sea lion decline perspectives
 Steller sea lion decline perspectives Andrew W Trites North Pacific Universities Marine Mammal Research Consortium Alaska Aleutian Islands Fishing Predation 4, Abund dance 3, 2, 1, 196 198 2 Competitive
Steller sea lion decline perspectives Andrew W Trites North Pacific Universities Marine Mammal Research Consortium Alaska Aleutian Islands Fishing Predation 4, Abund dance 3, 2, 1, 196 198 2 Competitive
INTRODUCTION. common name: scientific name: Tursiops truncatus
 INTRODUCTION The animal I have chosen for this task is the bottlenose dolphin. First thing you would think is what a bottlenose dolphin looks like well it has two flippers on the underside toward the head
INTRODUCTION The animal I have chosen for this task is the bottlenose dolphin. First thing you would think is what a bottlenose dolphin looks like well it has two flippers on the underside toward the head
Supplemental Tables. Macroalgal. Porewater. Porewater. Water column. Water column. Water column chl a. Porewater.
 Supplemental Tables Supplemental Table 1. Test statistics for all response variables measured in clam and control mesocosms in 2009 and 2010. All results are from non-parametric Wilcoxon rank sum tests,
Supplemental Tables Supplemental Table 1. Test statistics for all response variables measured in clam and control mesocosms in 2009 and 2010. All results are from non-parametric Wilcoxon rank sum tests,
Phytoplankton Cell Size Reduction in Response to Warming Mediated by Nutrient Limitation
 Phytoplankton Cell Size Reduction in Response to Warming Mediated by Nutrient Limitation Kalista Higini Peter, Ulrich Sommer* GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, Kiel, Germany Abstract Shrinking
Phytoplankton Cell Size Reduction in Response to Warming Mediated by Nutrient Limitation Kalista Higini Peter, Ulrich Sommer* GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, Kiel, Germany Abstract Shrinking
Assembly of ribosomes begins here. Shapes, supports, and protects the cell
 Semester Review Identify the kingdoms that are able to perform cellular respiration. Assembly of ribosomes begins here Shapes, supports, and protects the cell 1 Contrast passive & active transport Describe
Semester Review Identify the kingdoms that are able to perform cellular respiration. Assembly of ribosomes begins here Shapes, supports, and protects the cell 1 Contrast passive & active transport Describe
THE ECOLOGY OF SCYPHOZOAN JELLYFISH IN LAKE ILLAWARRA
 THE ECOLOGY OF SCYPHOZOAN JELLYFISH IN LAKE ILLAWARRA Kylie A. Pitt 1, Klaus Koop 2, David Rissik 3 and M.J. Kingsford 4 1 Centre for Aquatic Processes and Pollution School of Environmental and Applied
THE ECOLOGY OF SCYPHOZOAN JELLYFISH IN LAKE ILLAWARRA Kylie A. Pitt 1, Klaus Koop 2, David Rissik 3 and M.J. Kingsford 4 1 Centre for Aquatic Processes and Pollution School of Environmental and Applied
MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. hog. Ser.
 Vol. 39: 49-68. 1987 l MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. hog. Ser. l Published July 27 Grazing control of phytoplankton stock in the open subarctic Pacific Ocean: a model assessing the role of
Vol. 39: 49-68. 1987 l MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Mar. Ecol. hog. Ser. l Published July 27 Grazing control of phytoplankton stock in the open subarctic Pacific Ocean: a model assessing the role of
