excreted, in spite of its constant presence in the blood. Similarly, a salt-free diet will rapidly cause the practical disappearance of chlorides
|
|
|
- Maurice Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE REGULATION OF EXCRETION OF WATER BY THE KIDNEYS. I. By J. S. HALDANE, M.D., F.R.S. AND J. G. PRIESTLEY, B.M., Captain R.A.M.C., Beit Memorial Research Fellow. NUMEROUS observations tend to show that the excretory process by which the kidneys regulate the composition of the blood-plasma is most delicately regulated. It is known, for instance, that a very slight excess of urea, or sodium chloride, or water, or acid or alkali, introduced into the body will produce a compensatory excretion of these substances. A very slight increase in the percentage of sugar in the blood will cause an abundant excretion of sugar, although practically no sugar is normally excreted, in spite of its constant presence in the blood. Similarly, a salt-free diet will rapidly cause the practical disappearance of chlorides from the urine, in spite of their continued abundant presence in the blood. The stimulus to the excretion or retention of this or that substance by the kidneys is presumably a slight increase or diminution in its concentration in the blood-plasma; but quantitative data on this subject are as yet hardly existent. We therefore determined to set about the task of obtaining, as regards excretion by the kidneys, the same sort of information as we succeeded, some years ago, in obtaining with regard to the regulation of breathing by small changes in the CO2 content of the blood. The first question taken up has been the excretion of water. Our immediate object was to ascertain what dilution of the blood with water corresponds to a given rate of excretion of water by the kidneys. As a measure of dilution of the blood we at first took the haemoglobin percentage, since, if the blood is diluted with an excess of water during diuresis, there will presumably be a fall in the ha3moglobin percentage. For obvious reasons the experiments were made on man. As a means of increasing the excretion of water we adopted the method of simply drinking large quantities of water. To diminish the excretion we employed prolonged sweating in a respiration chamber kept at such a wet-bulb temperature as to produce a maximum amount of sweating without any considerable rise of body temperature.
2 WATER EXCRETION BY KIDNEYS. 297 For determining the effects of these procedures on the concentration of the blood the Gowers-Haldane hamoglobinometer was used, the samples of blood being taken from a finger in the usual way. By this method the haemoglobin can, with careful work, be determined to within 1 /0 of the normal concentration'. In some of the experiments we used the rather more delicate method of comparing the tints in two ordinary test-tubes, as described by Haldane and Lorrain Smith2. The results are given in terms of the Gowers-Haldane scale. The specific gravity of the urine was measured with an ordinary urinometer standardised by us beforehand, the observations being made at the temperature for which the instrument was standardised. The percentage of haemoglobin in the blood of any individual varies appreciably, within certain limits, and is affected by muscular exertion, as recently shown by Schneider and Havens3, and by Boothby and Berry4; but control experiments showed that if disturbing causes, such as meals, were avoided, it remained nearly steady during a stay in the laboratory of a few hours. In each of the first two experiments two litres of water were drunk in 15 minutes. The results were as follows: Urine urine last Hb 0/0 on passed in passed in c.c. Time scale Cc. per hour Sp. gr. Remarks F,xp a.m. - - Bladder emptied litres of water drunk p.m Exp. II. 2.0 p.m Bladder emptied * - 2 litres of water drunk This Journal, xxvr. p Ibid. xxv. p Amer. Journ. of Physiol. xxxvi. p Ibid. xxxvii. p ;5. PH. L. 20
3 298 J. S. HALDANE AND J. G. PRIESTLE Y. Of these experiments, the first gave a very slight and doubtful diminution of the haemoglobin during the height of the diuresis, while the second gave no diminution. A third experiment in which five litres of water were drunk gave the following results: Exp. III a.m p.m Urine Hb 0/0on pased in Time scale c.c urine last passed in c.c. per hour Sp. gr Remarks Bladder emptied 1 litre water drunk 4,,,. i,... i,,.. 4 litre water drunk i,... i,.,. 4,.., 2 cups of tea = 500 c.c. drunk Dinner In spite of the increased amount of water drunk in this experiment there was again no definite fall in the hwmoglobin percentage. During the diuresis, between a.m. and 7.0 p.m., 5460 c.c. of water had been excreted, while 5500 had been drunk. This volume of water (exceeding by about a third the volume of the blood) had been passed through the circulation without any appreciable dilution of the blood in the process, and possibly also without appreciable increase in the volume of the lymph and tissues. The maximum rate of excretion of urine was about 25 times an average normal rate, but was hardly greater in Exp. III than in Exp. I, in spite of the far greater amount of water drunk in Exp. III. There
4 WATER EXCRETION BY KIDNEYS. 299 were also indications that the maximum rate could not be kept up by the kidney, owing to fatigue. In order to test this point further, the following experiment was made, in which the water-drinking was spread out over a long period. The urine was also measured at short intervals. Hb /o on Time sale Exp. IV a.m p.m Urine passed in c.c *5 15* urine last passed in c.c. per hour Sp. gr. Remilrks Bladder emptied, 750 c.c. water drunk 750 c.c. water drunk Shivering. Nausea on drinking 750 c.c. water drunk 750 c.c. water drunk 20-2
5 300 J. S. HALDANE AND J. G. PRIESTLEY. Urine Hb 0/e on passed in Time scale c.c. Exp. IV (continued) p.m urine last passed in cc. per hour Sp. gr Shivering Remarks In this experiment the diuresis was pushed up gradually, and reached a maximum of only 888 c.c. per hour, after which there was a distinct decline, in spite of- the fact that three times as much water was being drunk, and that the excess of water within the body was rapidly accumulating. The kidneys appeared to be unable to keep up a water diuresis of more than about 750 c.c. per hour. Four hours after the last water had been drunk the diuresis was still unchecked, and only 4700 out of the 5500 c.c. of water drunk had been excreted. Exps. I to IV were all made on the same subject (J. G. P.). Another experiment was therefore made on a different subject (J. S. H.). It will be seen that the results confirm those previously obtained. Urine Hb 0/o on passed in Time scale c.c. Exp. V p.m urine last passed in c.c. per hour Sp. gr Remarks Bladder emptied 2 litres water drunk
6 WATER EXCRETION BY KIDNEYS. 301 In none of these experiments, nor in a further one which we need hardly quote, was there a diminution of the haemoglobin percentage parallel with the diuresis, and it seems clear that a diminished haemoglobin percentage, or increased volume of the blood, has nothing to do with the diuresis produced by drinking water. It was clearly necessary to seek elsewhere for the change in the blood which excites the excretion, so we decided to examine the conductivity of the serum. The results are given in* the succeeding paper. The fact that the haemoglobin percentage remains constant during even extreme water diuresis is nevertheless of great significance in enabling us to exclude certain mechanical factors to which the diuresis might be attributed. The urine secreted during water diuresis is of course no mere filtrate, and whatever changes in the composition of the blood lead to the enormous increase in the excretion of water, these changes are evidently very slight, and are comparable to the very minute changes in hydrogen ion concentration which cause enormous changes in the breathing. As no diminution in the hadmoglobin percentage was produced by drinking water, we' determined to try the effects of drinking dilute salt solution. In the first experiment 0-6 0/0 solution of NaCl was employed, and two litres were drunk in 15 minutes. Nausea was at once produced, and 800 c.c. were vomited, so the haemoglobin estimations were abandoned. Nevertheless a considerable diuresis followed, and the interesting observation was made, that the specific gravity of the urine fell rapidly to a value below that of the salt solution. At the height of the diuresis, with a rate of secretion of 604 c.c. per hour, the specific gravity of the urine was 1002, as compared with 1004 for the salt solution. In the succeeding paper further experiments with more palatable salt solutions.are recorded, and show that, apart from other blood changes, a marked fall in the haemoglobin percentage occurs. Owing to the war, we were only able to make very limited observations on the influence of sweating. As regards the influence of sweating on the heemoglobin percentage, several observations, made at the Oxford Physiological Laboratory, have already been recorded by E. H. Hunt in an interesting paper on "The Regulation of Body- Temperature in extremes of dry heat'." He found that in two subjects, each of whom had lost 2*3 kilos. during an exposure of 24 hours to dry heat in a Turkish bath, the haemoglobin percentage was the same before and after the exposure, although no liquid had -been drunk. He also found that, when collected with due precautions, the sweat 1 Journ. of Hygiene, xii. p
7 302 J. S. HALDANE AND J. G. PRIESTLEY. contained only about *210/0 of NaCl, even after prolonged sweating without liquid being drunk. Our first observation was a preliminary one, in which J. G. P. remained for 24 hours in a chamber with the wet-bulb at about 300. The loss of weight was only 870 grms., and the himoglobin was 109 before going in, and 111 half an hour after coming out. In a second experiment he stayed about 4w hours in the chamber, and lost 1*78 kilos. (of which only about *02 kilo. could be accounted for by respiratory exchange). The haemoglobin was before going in, 115 shortly after coming out, and 31 hours later, about 1600 c.c. of water having been drunk in the interval. There was thus a distinct fall in the hiemoglobin percentage after the sweating, though the fall would only account for about a sixth of the liquid lost. During the sweating, and including a period of 40 minutes before entering the chamber, 133 c.c. of urine had accumulated in the bladder, with a specific gravity of The mean rate of secretion during the sweating was thus a little under 30 c.c. per hour-a considerable diminution from the normal. Another experiment, made on J. S. H., gave the following results: Rate of secretion Mouth Temperature Urine since last tempera- in chamber passed passed Hb e/o on Time ture Wet bulb l)ry bulb in c.c. in c.c. Sp. gr. scale Remarks a.m. - - Bladder emptied p.m ' {Entered chamber Wt=76-48 kilos. after bladder emptied F C C B _ Left chamber. Wt=75-35 kilos In this experiment the gross loss of weight was 1*13 kilos. during the sweating. Of this loss, however, 05 was due to the urine passed,
8 WATER EXCRETION BY KIDNEYS. 303 and about *009 to respiratory exchange. The net loss, due to sweating and evaporation, was thus 1-07 kilos. The hemoglobin, as in Hunt's experiments, had not altered. After the first hour the rate of secretion of urine had fallen to about a third of the normal, but its specific gravity was only slightly increased. There was no sign of total stoppage of urine secretion. The rate of loss by sweating was somewhat disappointing. A greater rise of body-temperature seemed to be needed in order to produce the maximum of sweating. The last experiment shows clearly enough that, just as no fall in the haemoglobin percentage need accompany a great rise, due to ingestion of water, in excretion of water by the kidneys, so no rise in the haemoglobin need accoinpany a fall, due to withdrawal of water from the body, in the excretion of water. We must seek elsewhere than in mere alterations of the volume of the blood for the causes of increased or diminished excretion of water by the kidneys. CONCLUSIONS. The enormous diuresis caused by ingestion of water is not dependent on general dilution of the blood with liquid. The diminished excretion of urine following great sweating is not dependent on general concentration of the blood, although some general concentration may occur.
simultaneously excreted. They also brought forward some evidence to
 THE EXCRETION OF CHLORIDES AND BICARBON- ATES BY THE HUMAN KIDNEY. BY H. W. DAVIES, M.B., B.S., J. B. S. HALDANE, M.A. AND G. L. PESKETT, B.A. (From the Laboratory, Cherwell, Oxford.) AM BARD and PAPI
THE EXCRETION OF CHLORIDES AND BICARBON- ATES BY THE HUMAN KIDNEY. BY H. W. DAVIES, M.B., B.S., J. B. S. HALDANE, M.A. AND G. L. PESKETT, B.A. (From the Laboratory, Cherwell, Oxford.) AM BARD and PAPI
STUDIES IN BLOOD DIASTASE. FACTORS WHICH CAUSE. The effects of the following procedures on the blood diastase have
 STUDIES IN BLOOD DIASTASE. FACTORS WHICH CAUSE VARIATIONS IN THE AMOUNT OF DIASTASE IN THE BLOOD. By CHARLES REID and B. NARAYANA. From the Department of Physiology, Prince of Wales Medical College, Patna.
STUDIES IN BLOOD DIASTASE. FACTORS WHICH CAUSE VARIATIONS IN THE AMOUNT OF DIASTASE IN THE BLOOD. By CHARLES REID and B. NARAYANA. From the Department of Physiology, Prince of Wales Medical College, Patna.
College, London. NITROGEN IN THE URINE. BY OTTO VERAGUTH, steadily hour by hour to the fifth hour, when it reached its maximum
 THE EFFECT OF A MEAL ON THE EXCRETION OF NITROGEN IN THE URINE. BY OTTO VERAGUTH, M.D., Zurich. (Twelve Figures in Text.) From the Department of Pathological Chemistry, University College, London. DR TSCHLENOFF1
THE EFFECT OF A MEAL ON THE EXCRETION OF NITROGEN IN THE URINE. BY OTTO VERAGUTH, M.D., Zurich. (Twelve Figures in Text.) From the Department of Pathological Chemistry, University College, London. DR TSCHLENOFF1
GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which
 ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
for Medical Research. (Received May 10th, 1922.)
 XLV. NOTE ON URINARY TIDES AND EXCRETORY RHYTHM. BY JAMES ARGYLL CAMPBELL AND THOMAS ARTHUR WEBSTER. From the Department of Applied Physiology, National Institute for Medical Research. (Received May 10th,
XLV. NOTE ON URINARY TIDES AND EXCRETORY RHYTHM. BY JAMES ARGYLL CAMPBELL AND THOMAS ARTHUR WEBSTER. From the Department of Applied Physiology, National Institute for Medical Research. (Received May 10th,
(ethanol) suggests that it is similar to the diuresis following ingestion of water.
 435 J. Physiol. (I946) I04, 435-442 6I2.464.I THE EFFECT OF ETHYL ALCOHOL AND SOME OTHER DIURETICS ON CHLORIDE EXCRETION IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON AND ISABEL G. SMITH, From the Physiology Department,
435 J. Physiol. (I946) I04, 435-442 6I2.464.I THE EFFECT OF ETHYL ALCOHOL AND SOME OTHER DIURETICS ON CHLORIDE EXCRETION IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON AND ISABEL G. SMITH, From the Physiology Department,
(Received 27 September 1937)
 222 J. Physiol. (I937) 9I, 222-23I 6I2.46I:6I2.392.6 THE SECRETION OF URINE IN MAN DURING EXPERIMENTAL SALT DEFICIENCY BY R. A. McCANCE AND E. M. WIDDOWSON From the Biochemical Laboratory, King's College
222 J. Physiol. (I937) 9I, 222-23I 6I2.46I:6I2.392.6 THE SECRETION OF URINE IN MAN DURING EXPERIMENTAL SALT DEFICIENCY BY R. A. McCANCE AND E. M. WIDDOWSON From the Biochemical Laboratory, King's College
M6ller, McIntosh and Van Slyke (5) has been employed. The cases. changes in functional activity. Indications suggesting that such changes
 STUDIES OF UREA EXCRETION. VIII. THE EFFECTS ON THE UREA CLEARANCE OF CHANGES IN PROTEIN AND SALT CONTENTS OF THE DIET BY CUTHBERT L. COPE I (From the Hospital of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical
STUDIES OF UREA EXCRETION. VIII. THE EFFECTS ON THE UREA CLEARANCE OF CHANGES IN PROTEIN AND SALT CONTENTS OF THE DIET BY CUTHBERT L. COPE I (From the Hospital of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical
Disclaimer. Chapter 3 Disorder of Water, Electrolyte and Acid-base Professor A. S. Alhomida. Disorder of Water and Electrolyte
 Disclaimer King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry The texts, tables, figures and images contained in this course presentation (BCH 376) are not my own, they can be found on:
Disclaimer King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry The texts, tables, figures and images contained in this course presentation (BCH 376) are not my own, they can be found on:
changes in the blood comparable to the changes in hydrogen ion concentration estimations of the amount of haemoglobin in the blood before and during
 THE REGULATION OF THE EXCRETION OF WATER BY THE KIDNEYS. BY J. G. PRIESTLEY, Beit Memorial Research Fellow. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Oxford.) THE starting point of the present work was the well
THE REGULATION OF THE EXCRETION OF WATER BY THE KIDNEYS. BY J. G. PRIESTLEY, Beit Memorial Research Fellow. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Oxford.) THE starting point of the present work was the well
ansesthesia; an oncometer was used for measurement of the splenic Laboratory, Cambridge.)
 6I2.4I3:6I2.I43 CAUSE OF RHYTHMICAL. CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN. BY J. BARCROFT AN Y. NISIMARU' (Okayama). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) Roy [1881] was the first to discover the rhythmical
6I2.4I3:6I2.I43 CAUSE OF RHYTHMICAL. CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN. BY J. BARCROFT AN Y. NISIMARU' (Okayama). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) Roy [1881] was the first to discover the rhythmical
PHYSIOLOGICAL SOCIETY,
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE PHYSIOLOGICAL SOCIETY, March 16, 1929. A central chemical control of the heart rate. By R. J. S. MCDOWALL. (King's College, London.) Provided adequate measures are taken to avoid the
PROCEEDINGS OF THE PHYSIOLOGICAL SOCIETY, March 16, 1929. A central chemical control of the heart rate. By R. J. S. MCDOWALL. (King's College, London.) Provided adequate measures are taken to avoid the
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 3
 AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 3 340 minutes 340 marks Page 1 of 49 Q1. To stay healthy, the amount of sodium in your body must not change very much. On average, a girl takes in 10 grams of sodium a day in
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 3 340 minutes 340 marks Page 1 of 49 Q1. To stay healthy, the amount of sodium in your body must not change very much. On average, a girl takes in 10 grams of sodium a day in
disappeared, whereas if the carbohydrate were replaced by fat instead
 THE INFLUENCE OF CARBOHYDRATE AND FAT ON PROTEIN METABOLISM. IIL-THE EFFECT OF PHLORIDZIN GLYCOSURIA1. BY E. P. CATHCART AND M. ROSS TAYLOR. University of Glasgow. ONE of us (E. P. C.) has brought forward
THE INFLUENCE OF CARBOHYDRATE AND FAT ON PROTEIN METABOLISM. IIL-THE EFFECT OF PHLORIDZIN GLYCOSURIA1. BY E. P. CATHCART AND M. ROSS TAYLOR. University of Glasgow. ONE of us (E. P. C.) has brought forward
Visscher(6) that the oxygen consumption of the heart-lung preparation
 BY A. R. FEE1 AND A. HEMINGWAY. (From the Department of Physiology and Biochemistry, University College, London.) SEVERAL investigations of the metabolism of the kidney have been made to ascertain the
BY A. R. FEE1 AND A. HEMINGWAY. (From the Department of Physiology and Biochemistry, University College, London.) SEVERAL investigations of the metabolism of the kidney have been made to ascertain the
WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
fluid in the muscles of the rat and the frog following violent
 612.766.1: 612.014.461.3 THE CHANGES IN PLASMA AND TISSUE FLUID VOLUME FOLLOWING EXERCISE. By H. CULLUMBINE and A. C. E. KoCH. From the Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, University of Ceylon,
612.766.1: 612.014.461.3 THE CHANGES IN PLASMA AND TISSUE FLUID VOLUME FOLLOWING EXERCISE. By H. CULLUMBINE and A. C. E. KoCH. From the Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, University of Ceylon,
THE EFFECT OF SMOKING ON WATER DIURESIS IN MAN 1
 51 612.463.1:615.783.22 THE EFFECT OF SMOKING ON WATER DIURESIS IN MAN 1 By J. M. WALKER (From the Department of Pharmacology, Oxford) NICOTINE is the most widely used drug in this country and its effects
51 612.463.1:615.783.22 THE EFFECT OF SMOKING ON WATER DIURESIS IN MAN 1 By J. M. WALKER (From the Department of Pharmacology, Oxford) NICOTINE is the most widely used drug in this country and its effects
ANSWERS AND MARK SCHEMES. (a) excretion; 1. kidneys; 2. (c) (i) respiration; 1. (ii) lungs; 1. (iii) kidney; 1. kidney; lungs; 2
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 excretion; 1 skin; kidneys; 2 (i) respiration; 1 (ii) lungs; 1 (d) (iii) kidney; 1 2 of: skin; kidney; lungs; 2 QUESTIONSHEET 2 2500 cm 3 ; 1 1550 cm 3 ; 1 500 x 100; 1 2500 = 20%; 1 (d)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 excretion; 1 skin; kidneys; 2 (i) respiration; 1 (ii) lungs; 1 (d) (iii) kidney; 1 2 of: skin; kidney; lungs; 2 QUESTIONSHEET 2 2500 cm 3 ; 1 1550 cm 3 ; 1 500 x 100; 1 2500 = 20%; 1 (d)
A day at the sauna. Boardworks Ltd How does the body react to change?
 1 of 40 2 of 40 A day at the sauna 3 of 40 How does the body react to change? Saving energy? 4 of 40 Sayid has decided to save energy by staying in bed all day. How much of his energy do you think this
1 of 40 2 of 40 A day at the sauna 3 of 40 How does the body react to change? Saving energy? 4 of 40 Sayid has decided to save energy by staying in bed all day. How much of his energy do you think this
THE EXCRETION OF BORIC ACID FROM THE HUMAN BODY.
 THE EXCRETION OF BORIC ACID FROM THE HUMAN BODY. BY HARVEY W. WILEY, M.D. (From the Bureau of Chemistry, Washington, D. C.) (Received for publication, December 15, 1906.) In the studies which I have inaugurated
THE EXCRETION OF BORIC ACID FROM THE HUMAN BODY. BY HARVEY W. WILEY, M.D. (From the Bureau of Chemistry, Washington, D. C.) (Received for publication, December 15, 1906.) In the studies which I have inaugurated
Biology Notes. Homeostasis
 Biology Notes Homeostasis Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of constant internal conditions within organisms. The principle can be developed in a wide range of contexts, including the maintenance
Biology Notes Homeostasis Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of constant internal conditions within organisms. The principle can be developed in a wide range of contexts, including the maintenance
Conditions inside the body must be kept constant. Urea must be removed from the body. Name the organ which makes urea.
 Conditions inside the body must be kept constant. (a) Urea must be removed from the body. (i) Name the organ which makes urea. () Which organ removes urea from the body? () (iii) What is urea made from?
Conditions inside the body must be kept constant. (a) Urea must be removed from the body. (i) Name the organ which makes urea. () Which organ removes urea from the body? () (iii) What is urea made from?
3.4.6 The Excretory System in the Human
 3.4.6 The Excretory System in the Human Objectives What you will need to know from this section Explain the role of the excretory system in homeostasis -- the ability and necessity to maintain constancy
3.4.6 The Excretory System in the Human Objectives What you will need to know from this section Explain the role of the excretory system in homeostasis -- the ability and necessity to maintain constancy
:6I2.352.I2:6I observations of Ahlgren (3), who found that pituitary extract increases
 612.492.8:6I2.352.I2:6I6.37-089.87 THE ACTION OF EXTRACT OF PITUITARY ON THE BLOOD SUGAR AFTER PANCREATECTOMY. BY C. G. IMRIE. (Department of Physiology, The University, Sheffield.) THE experiments about
612.492.8:6I2.352.I2:6I6.37-089.87 THE ACTION OF EXTRACT OF PITUITARY ON THE BLOOD SUGAR AFTER PANCREATECTOMY. BY C. G. IMRIE. (Department of Physiology, The University, Sheffield.) THE experiments about
PHOSPHORUS CONTENT OF THE BLOOD IN DIABETES
 10 BLOOD PHOSPHORUS IN HEALTH AND DISEASE: IV-THE PHOSPHORUS CONTENT OF THE BLOOD IN DIABETES MELLITUS F B BYROM From the Dunn Laboratories, London Hospital Received for publication November 24th, 1928
10 BLOOD PHOSPHORUS IN HEALTH AND DISEASE: IV-THE PHOSPHORUS CONTENT OF THE BLOOD IN DIABETES MELLITUS F B BYROM From the Dunn Laboratories, London Hospital Received for publication November 24th, 1928
conductivity after its precipitation indicated that salts had been held freezing point or conductivity than the precipitation of the same
 THE EFFECT ON THE MOLECULAR CONCENTRATION AND ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY OF MUSCLE EXTRACTS OF REMOVAL OF THE PROTEIDS. BY G. N. STEWART, Western Reserve University, Cleveland, U.S.A. (Preliminary Note.)
THE EFFECT ON THE MOLECULAR CONCENTRATION AND ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY OF MUSCLE EXTRACTS OF REMOVAL OF THE PROTEIDS. BY G. N. STEWART, Western Reserve University, Cleveland, U.S.A. (Preliminary Note.)
Exercise increases water loss
 Exercise increases water loss During normal breathing, water is added to inspired air to protect delicate respiratory cells from drying out. Increased breathing during exercise increase this loss Heat
Exercise increases water loss During normal breathing, water is added to inspired air to protect delicate respiratory cells from drying out. Increased breathing during exercise increase this loss Heat
Since, for many months after section of the right vagus in the neck,
 THE INFLUENCE OF THE VAGUS ON THE ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Part II. The effect of cutting the vagus upon sugar tolerance. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Sheffield University.) IN Part
THE INFLUENCE OF THE VAGUS ON THE ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Part II. The effect of cutting the vagus upon sugar tolerance. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Sheffield University.) IN Part
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
blue, buffer excretion by titrating back to ph 3*7 with.1 N hydrochloric
 CALCIUM CHLORIDE ACIDOSIS. BY J. B. S. HALDANE, R. HILL, AND J. M. LUCK. (From the Biochemical Laboratory, Cambridge.) GYORGY(1) has shown that calcium chloride, when administered to babies, causes an
CALCIUM CHLORIDE ACIDOSIS. BY J. B. S. HALDANE, R. HILL, AND J. M. LUCK. (From the Biochemical Laboratory, Cambridge.) GYORGY(1) has shown that calcium chloride, when administered to babies, causes an
THE EFFECT OF DENATURATION ON THE VISCOSITY OF PROTEIN SYSTEMS BY M. L. ANSON A~D A. E. MIRSKY. (Accepted for publication, December 2, 1931)
 THE EFFECT OF DENATURATION ON THE VISCOSITY OF PROTEIN SYSTEMS BY M. L. ANSON A~D A. E. MIRSKY (From tke Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. Y., and the ttospital
THE EFFECT OF DENATURATION ON THE VISCOSITY OF PROTEIN SYSTEMS BY M. L. ANSON A~D A. E. MIRSKY (From tke Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. Y., and the ttospital
excreting chloride when the amount in the blood exceeds corresponding determinations of the rate of exeretion of chloride over I.
 612.46.6 ON THE RENAL THRESHOLD FOR CHLORDE N MAN. BY R. S. ATKEN. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Oxford, and the Medical Unit, the London Hospital.) NTRODUCTON. THE conception of a renal threshold
612.46.6 ON THE RENAL THRESHOLD FOR CHLORDE N MAN. BY R. S. ATKEN. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Oxford, and the Medical Unit, the London Hospital.) NTRODUCTON. THE conception of a renal threshold
The respiratory quotient is the relation by volume of the carbon dioxide DEXTROSE AND LE VULOSE IN HUMANS
 415 THE METABOLIC EFFECT OF ENEMA TA OF ALCOHOL, DEXTROSE AND LE VULOSE IN HUMANS By THORNZ, M. CARPZNTBR NUTRITION LABORATORY OF THU CARNEGIS INSTITUTION OF WASHINGTON, BOSTON, MASS. Communicated April
415 THE METABOLIC EFFECT OF ENEMA TA OF ALCOHOL, DEXTROSE AND LE VULOSE IN HUMANS By THORNZ, M. CARPZNTBR NUTRITION LABORATORY OF THU CARNEGIS INSTITUTION OF WASHINGTON, BOSTON, MASS. Communicated April
Lesson Overview. The Excretory System. Lesson Overview The Excretory System
 Lesson Overview 30.4 THINK ABOUT IT It s a hot day and you gulp down water. As you drink, you begin to wonder. Where s all that water going? Will it just dilute your blood, or is something in your body
Lesson Overview 30.4 THINK ABOUT IT It s a hot day and you gulp down water. As you drink, you begin to wonder. Where s all that water going? Will it just dilute your blood, or is something in your body
Westminster Hospital Medical School.) connection with the general problem of blood clotting, we have investigated. (Received June 18, 1935.
 173 6I2. II5.3 CHANGES IN THE COAGULABILITY OF THE BLOOD PRODUCED BY CITRIC ACID AND SOME OF ITS DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS. BY DAVID DE SOUZA AND F. D. M. HOCKING. (From the John Burford Carlill Laboratories,
173 6I2. II5.3 CHANGES IN THE COAGULABILITY OF THE BLOOD PRODUCED BY CITRIC ACID AND SOME OF ITS DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS. BY DAVID DE SOUZA AND F. D. M. HOCKING. (From the John Burford Carlill Laboratories,
necessity for an investigation into possible different types of urine acidity. In
 456 J. Physiol. (I947) io6, 456-465 6I2.46i SOME FACTORS AFFECTING THE ACIDITY OF URINE IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON From the Department of Physiology, University College, London (Received 22 February 1947)
456 J. Physiol. (I947) io6, 456-465 6I2.46i SOME FACTORS AFFECTING THE ACIDITY OF URINE IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON From the Department of Physiology, University College, London (Received 22 February 1947)
Hospital Medical School, London.)
 6i2.323. 3 THE MUCUS FACTOR IN THE AUTOMATIC REGULATION OF THE ACIDITY OF THE GASTRIC CONTENTS. By CHARLES BOLTON AND GORDON W. GOODHART. (From the Pathological Department of University College Hospital
6i2.323. 3 THE MUCUS FACTOR IN THE AUTOMATIC REGULATION OF THE ACIDITY OF THE GASTRIC CONTENTS. By CHARLES BOLTON AND GORDON W. GOODHART. (From the Pathological Department of University College Hospital
Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with
![Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with](/thumbs/91/106294335.jpg) 381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
Cushny(4) has shown, however, that the amount of urea in the kidney. by some vital process, retain those diflusible substances which are of
 THE FUNCTION OF THE TUBULES IN KIDNEY EXCRETION. BY E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) IT is becoming generally recognised that filtration through the glomeruli and some degree
THE FUNCTION OF THE TUBULES IN KIDNEY EXCRETION. BY E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) IT is becoming generally recognised that filtration through the glomeruli and some degree
Chapter 16. Urinary System and Thermoregulation THERMOREGULATION. Homeostasis
 Homeostasis Chapter 16 Urinary System and Thermoregulation! Homeostasis Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite fluctuations in the external environment! Examples of homeostasis Thermoregulation
Homeostasis Chapter 16 Urinary System and Thermoregulation! Homeostasis Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite fluctuations in the external environment! Examples of homeostasis Thermoregulation
Edinburgh.) IN a previous paper, I recorded observations on rabbits and dogs which
 THE EFFECT OF ADRENALIN ON SUGAR AND NITROGEN EXCRETION IN THE URINE OF BIRDS. BY D. NOEL PATON.. (From the Research Laboratory of the Royal College of Physicians, Edinburgh.) IN a previous paper, I recorded
THE EFFECT OF ADRENALIN ON SUGAR AND NITROGEN EXCRETION IN THE URINE OF BIRDS. BY D. NOEL PATON.. (From the Research Laboratory of the Royal College of Physicians, Edinburgh.) IN a previous paper, I recorded
points raised, and the following is an account of what I have done under touched, but my work has fallen under two main heads:
 NOTES ON CREATININE. BY P. C. COLLS, late Assistant Demonstrator in Physiology, King's College, London. (From the Physiological Laboratory, King's College, London.) ABOUT two years ago, a lengthy correspondence
NOTES ON CREATININE. BY P. C. COLLS, late Assistant Demonstrator in Physiology, King's College, London. (From the Physiological Laboratory, King's College, London.) ABOUT two years ago, a lengthy correspondence
J. Physiol. (I944) I02; :6I2.0I4.46I.2
 415 J. Physiol. (I944) I02; 45-428 612.463:6I2.0I4.46I.2 THE SECRETION OF URINE DURING DEHYDRATION AND REHYDRATION BY R. A. McCANCE AND W. F. YOUNG WITH THE ASSISTANCE OF D. A. K. BLACK From the Department
415 J. Physiol. (I944) I02; 45-428 612.463:6I2.0I4.46I.2 THE SECRETION OF URINE DURING DEHYDRATION AND REHYDRATION BY R. A. McCANCE AND W. F. YOUNG WITH THE ASSISTANCE OF D. A. K. BLACK From the Department
SOME OBSERVATIONS UPON SODIUM ALGINATE. By 0. M. SOLANDT. From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.
 582.6 SOME OBSERVATIONS UPON SODIUM ALGINATE. By 0. M. SOLANDT. From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge. (Received for publication 13th December 1940.) ALGINIC acid was discovered by Stanford in 1883
582.6 SOME OBSERVATIONS UPON SODIUM ALGINATE. By 0. M. SOLANDT. From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge. (Received for publication 13th December 1940.) ALGINIC acid was discovered by Stanford in 1883
THE RELATION OF HYPERGLYCEMIA TO THE RELATIVE BLOOD VOLUME, CHLORINE CONCENTRATION, AND CHLORINE DISTRIBUTION IN THE BLOOD OF DOGS.
 Published Online: 1 July, 1925 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.42.1.89 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 THE RELATION OF HYPERGLYCEMIA TO THE RELATIVE BLOOD VOLUME, CHLORINE CONCENTRATION,
Published Online: 1 July, 1925 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.42.1.89 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 THE RELATION OF HYPERGLYCEMIA TO THE RELATIVE BLOOD VOLUME, CHLORINE CONCENTRATION,
College of Medicine, Newcastle-upon-Tyne.)
 GLUCOSE ABSORPTION IN THE RENAL TUBULES OF THE FROG. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory of the University of Durham College of Medicine, Newcastle-upon-Tyne.) OPINION is divided on the
GLUCOSE ABSORPTION IN THE RENAL TUBULES OF THE FROG. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory of the University of Durham College of Medicine, Newcastle-upon-Tyne.) OPINION is divided on the
UNIT 3 Conditions supporting life
 Biology Form 4 Page 32 Ms. R. Buttigieg UNIT 3 Conditions supporting life In this unit we shall be seeing how an important condition that supports life is the ability of the organism to maintain a constant
Biology Form 4 Page 32 Ms. R. Buttigieg UNIT 3 Conditions supporting life In this unit we shall be seeing how an important condition that supports life is the ability of the organism to maintain a constant
increasing pressure registered in kilograms was applied until the subject began to feel a sensation of pain. With an intelligent person the responses
 VARIATIONS IN THE SENSIBILITY TO PRESSURE PAIN CAUSED BY NERVE STIMULATION IN MAN. BY R. C. SHAWE. (From the Royal Infirmary, Manchester.) IN a previous paper (Brit. Journ. Surgery, Jan. 1922) I have given
VARIATIONS IN THE SENSIBILITY TO PRESSURE PAIN CAUSED BY NERVE STIMULATION IN MAN. BY R. C. SHAWE. (From the Royal Infirmary, Manchester.) IN a previous paper (Brit. Journ. Surgery, Jan. 1922) I have given
Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4
 Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4 Mechanisms that control acid-base homeostasis Acids and bases continually enter and leave body Hydrogen ions also result from metabolic activity Acids Hydrogen ion donors
Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4 Mechanisms that control acid-base homeostasis Acids and bases continually enter and leave body Hydrogen ions also result from metabolic activity Acids Hydrogen ion donors
1. (U4C2L7:F1) True or False. If you have to be out in hot environments, you must take precautions to prevent heat emergencies.
 Lesson U4C2L7 FIT Questions 1. (U4C2L7:F1) True or False. If you have to be out in hot environments, you must take precautions to prevent heat emergencies. 2. (U4C2L7:F2) Why should you stay away from
Lesson U4C2L7 FIT Questions 1. (U4C2L7:F1) True or False. If you have to be out in hot environments, you must take precautions to prevent heat emergencies. 2. (U4C2L7:F2) Why should you stay away from
INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that adrenaline may
 REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
Glossary. Maintain keep up. Constant the same. Internal inside the body. Environment surroundings of the body.
 Homeostasis Glossary Maintain keep up. Constant the same. Internal inside the body. Environment surroundings of the body. What is Homeostasis? Body cells work best if they have the correct Temperature
Homeostasis Glossary Maintain keep up. Constant the same. Internal inside the body. Environment surroundings of the body. What is Homeostasis? Body cells work best if they have the correct Temperature
possibility of a secretion of adrenaline from the suprarenal glands resulting
 355 J Physiol. (I942) IOI, 355-36I 6i2.014.465:577 I74.5 THE EFFECT OF ANAESTHESIA ON THE ADRENALINE CONTENT OF THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS BY P. C. ELMES AND A. A. JEFFERSON From the Department of Pharmacology,
355 J Physiol. (I942) IOI, 355-36I 6i2.014.465:577 I74.5 THE EFFECT OF ANAESTHESIA ON THE ADRENALINE CONTENT OF THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS BY P. C. ELMES AND A. A. JEFFERSON From the Department of Pharmacology,
Overton,1 who has worked exhaustively at the subject, looked upon. considered by some to be due to the state of the fluid originally in the
 THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON THE OSMOTIC PROPER- TIES OF MUSCLE. By D. H. DE SOUZA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Sheffield.) (With six diagrams in the text.) (Received for publication
THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON THE OSMOTIC PROPER- TIES OF MUSCLE. By D. H. DE SOUZA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Sheffield.) (With six diagrams in the text.) (Received for publication
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q
 AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
during the 8 days prior to the first intraperitoneal
 EXPERIMENTAL HYPERTONICITY: ALTERATIONS IN THE DISTRIBUTION OF BODY WATER, AND THE CAUSE OF DEATH 1 By ALEXANDER W. WINKLER, J. RUSSELL ELKINTON,2 JAMES HOPPER, JR.,8 AND HEBBEL E. HOFF (From the Department
EXPERIMENTAL HYPERTONICITY: ALTERATIONS IN THE DISTRIBUTION OF BODY WATER, AND THE CAUSE OF DEATH 1 By ALEXANDER W. WINKLER, J. RUSSELL ELKINTON,2 JAMES HOPPER, JR.,8 AND HEBBEL E. HOFF (From the Department
Experimental. Schmidt, in his experiments, boiled his solutions
 PROTECTION OF TRYPSIN FROM DESTRUCTION BY HEAT. BY D. IL DE SOUZA. (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) E. W. SCHMIDT' has recently claimed: that trypsin in the presence of peptone,
PROTECTION OF TRYPSIN FROM DESTRUCTION BY HEAT. BY D. IL DE SOUZA. (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) E. W. SCHMIDT' has recently claimed: that trypsin in the presence of peptone,
The absorption of water from the whole stomach. or one of its parts has not been demonstrated. Many years ago Pavlov showed that water was a
 GASTRIC SECRETION. III. THE ABSORPTION OF HEAVY WATER FROM POUCHES OF THE BODY AND ANTRUM OF THE STOMACH OF THE DOG By OLIVER COPE, HESTER BLATT, AND MARGARET R. BALL (From the Surgical Research Laboratories
GASTRIC SECRETION. III. THE ABSORPTION OF HEAVY WATER FROM POUCHES OF THE BODY AND ANTRUM OF THE STOMACH OF THE DOG By OLIVER COPE, HESTER BLATT, AND MARGARET R. BALL (From the Surgical Research Laboratories
(Received 16 January 1946) Winternitz, 1920). Further experiments have been undertaken in an endeavour
 175 J. Physiol. (1946) 105, 175-I85 6I2.284:546.264. I3I -3I THE PRODUCTION AND[ REMOVAL OF OEDEMA FLUID IN THE LUNG AFTER EXPOSURE TO CARBONYL CHLORIDE (PHOSGENE) BY G. R. CAMERON AND F. C. COURTICE From
175 J. Physiol. (1946) 105, 175-I85 6I2.284:546.264. I3I -3I THE PRODUCTION AND[ REMOVAL OF OEDEMA FLUID IN THE LUNG AFTER EXPOSURE TO CARBONYL CHLORIDE (PHOSGENE) BY G. R. CAMERON AND F. C. COURTICE From
The table shows the concentrations of some substances in one person s blood plasma, kidney filtrate and urine. Water
 HOMEOSTASIS PART III Q1. The table shows the concentrations of some substances in one person s blood plasma, kidney filtrate and urine. Substance Concentration in grams per dm 3 Plasma Filtrate Urine Water
HOMEOSTASIS PART III Q1. The table shows the concentrations of some substances in one person s blood plasma, kidney filtrate and urine. Substance Concentration in grams per dm 3 Plasma Filtrate Urine Water
CASE 27. What is the response of the kidney to metabolic acidosis? What is the response of the kidney to a respiratory alkalosis?
 CASE 27 A 21-year-old man with insulin-dependent diabetes presents to the emergency center with mental status changes, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and rapid respirations. On examination, the patient
CASE 27 A 21-year-old man with insulin-dependent diabetes presents to the emergency center with mental status changes, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and rapid respirations. On examination, the patient
: : (From the Department of Physiology, University of Toronto.)
 94 612.352.2:547.435:612.34.089.87 CHOLINE AND LIVER FAT IN DIABETIC DOGS. BY C. H. BEST, G. C. FERGUSON AND J. M. HERSHEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Toronto.) IN the first completely
94 612.352.2:547.435:612.34.089.87 CHOLINE AND LIVER FAT IN DIABETIC DOGS. BY C. H. BEST, G. C. FERGUSON AND J. M. HERSHEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Toronto.) IN the first completely
Fluids and electrolytes
 Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
accompanying meals. In previous papers the variations in alveolar C02(1)
 VARIATIONS IN THE BLOOD CHLORIDES IN RELATION TO MEALS. Part I. BY E. 0. DODDS1 AND K. SHIRLEY SMITH. (From the Biochemical Department, Bland-Sutton Institute of Pathology, Middlesex Hospital.) THIS paper
VARIATIONS IN THE BLOOD CHLORIDES IN RELATION TO MEALS. Part I. BY E. 0. DODDS1 AND K. SHIRLEY SMITH. (From the Biochemical Department, Bland-Sutton Institute of Pathology, Middlesex Hospital.) THIS paper
Furthermore, added choline may exert relatively little effect when. naturally occurring lipotropic factors are present in appreciable amounts
 343 6I2.352.2:547.922 THE EFFECTS OF CHOLESTEROL AND CHOLINE ON LIVER FAT BY C. H. BEST AND JESSIE H. RIDOUT (From the School of Hygiene, University of Toronto) (Received January 27, 1936) THE results
343 6I2.352.2:547.922 THE EFFECTS OF CHOLESTEROL AND CHOLINE ON LIVER FAT BY C. H. BEST AND JESSIE H. RIDOUT (From the School of Hygiene, University of Toronto) (Received January 27, 1936) THE results
Making Connections Practice Mrs. Fornaro
 Making Connections Practice Mrs. Fornaro Name Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. Progressive Resistance Exercise Progressive resistance exercise
Making Connections Practice Mrs. Fornaro Name Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. Progressive Resistance Exercise Progressive resistance exercise
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 1
 AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 1 176 minutes 176 marks Page 1 of 48 ## (a) The table shows the compounds and ions dissolved in a student s urine. Compound or ion Percentage of total urea 60 negative ions 25
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 1 176 minutes 176 marks Page 1 of 48 ## (a) The table shows the compounds and ions dissolved in a student s urine. Compound or ion Percentage of total urea 60 negative ions 25
The Excretory System. Functions of the Excretory System. The Urinary System. Figure 9 The excretory system includes other body systems.
 The Excretory System Functions of the Excretory System It s your turn to take out the trash. You carry the bag outside and put it in the trash can. The next day, you bring out another bag of trash, but
The Excretory System Functions of the Excretory System It s your turn to take out the trash. You carry the bag outside and put it in the trash can. The next day, you bring out another bag of trash, but
2012 Heat Safety Kit
 2012 Heat Safety Kit PREVENTING HEAT-RELATED ILLNESSES HEAT ILLNESS AND EMERGENCIES Heat-related illnesses have many factors but can be caused when an individual is subjected to extreme temperatures and
2012 Heat Safety Kit PREVENTING HEAT-RELATED ILLNESSES HEAT ILLNESS AND EMERGENCIES Heat-related illnesses have many factors but can be caused when an individual is subjected to extreme temperatures and
Prevention of Heat Stress
 Prevention of Heat Stress Presentation Outline What is heat stress? Body s response to heat stress Why does heat stress occur? Heat stress predisposing factors Effects of heat Prevention Management Thermoregulation
Prevention of Heat Stress Presentation Outline What is heat stress? Body s response to heat stress Why does heat stress occur? Heat stress predisposing factors Effects of heat Prevention Management Thermoregulation
comparable with the normal resting condition of the organ in the unopened contraction, to determine the haomoglobin percentage of the blood, and
 ON THE OUTPUT OF HAEMOGLOBIN AND BLOOD BY THE SPLEEN. BY E. W. H. CRUICKSHANK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) BARCROFT'S(1) experiments on the protective effect of the spleen suggest that
ON THE OUTPUT OF HAEMOGLOBIN AND BLOOD BY THE SPLEEN. BY E. W. H. CRUICKSHANK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) BARCROFT'S(1) experiments on the protective effect of the spleen suggest that
induced by sham feeding is accompanied by an increased excretion of University College, London.)
 THE METABOLISM OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS. II. The blood sugar metabolism of the Submaxillary Gland. BY G. V. ANREP AND R. K. CANNAN (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (From the Institute of Physiology, University
THE METABOLISM OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS. II. The blood sugar metabolism of the Submaxillary Gland. BY G. V. ANREP AND R. K. CANNAN (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (From the Institute of Physiology, University
HUMAN SUBJECT 1. Syracuse, N. Y.) the urine of increasing quantities of these buffers, it has been found in man as in the dog that (1)
 THE RENAL REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE IN MAN. II. FACTORS AFFECTING THE EXCRETION OF TITRATABLE ACID BY THE NORMAL HUMAN SUBJECT 1 By W. A. SCHIESS, J. L. AYER, W. D. LOTSPEICH AND R. F. PITTS WITH
THE RENAL REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE IN MAN. II. FACTORS AFFECTING THE EXCRETION OF TITRATABLE ACID BY THE NORMAL HUMAN SUBJECT 1 By W. A. SCHIESS, J. L. AYER, W. D. LOTSPEICH AND R. F. PITTS WITH
JEROME, M.B. (Lond.), Lecturer in Medical Pharmacology and Materia Medica. (From the Pharmacological Department, Oxford.)
 THE RELATION OF THE DEGREE OF ACIDITY OF THE URINE AND THE PERCENTAGE OF URIC ACID THEREIN CONTAINED TO THE PRECIPI- TATION OF THE LATTER IN THE FORM OF URIC ACID GRAVEL. BY WILLIAM J. SMITH JEROME, M.B.
THE RELATION OF THE DEGREE OF ACIDITY OF THE URINE AND THE PERCENTAGE OF URIC ACID THEREIN CONTAINED TO THE PRECIPI- TATION OF THE LATTER IN THE FORM OF URIC ACID GRAVEL. BY WILLIAM J. SMITH JEROME, M.B.
The Kidneys. The kidneys are vital organs. Two bean-shaped organs, about the size of a fist
 Kidney Health Coach The Kidneys The kidneys are vital organs Two bean-shaped organs, about the size of a fist Each kidney connects to the bladder by a thin tube called a ureter What do the kidneys do?
Kidney Health Coach The Kidneys The kidneys are vital organs Two bean-shaped organs, about the size of a fist Each kidney connects to the bladder by a thin tube called a ureter What do the kidneys do?
Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + )
 Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration in body fluids Precise regulation of ph at
Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration in body fluids Precise regulation of ph at
THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM AND THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
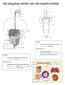 THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM AND THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Location: The location of the Excretory System Is the body. Major Function: Location: The Excretory System the toxic build up of wastes, such as ammonia or
THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM AND THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Location: The location of the Excretory System Is the body. Major Function: Location: The Excretory System the toxic build up of wastes, such as ammonia or
correlating the excretion of creatin in the urine with definite pathological
 THE EXCRETION OF CREATIN IN DIABETES. By R. A. KRAUSE, Crichton Research Scholar. (From the Chemical Laboratory of the Physiology Department, Edinburgh University.') (Received for publication 3rd August
THE EXCRETION OF CREATIN IN DIABETES. By R. A. KRAUSE, Crichton Research Scholar. (From the Chemical Laboratory of the Physiology Department, Edinburgh University.') (Received for publication 3rd August
Acid Base Balance. Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih. Clinical Chemistry Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih
 Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
A STUDY OF THE NITROGEN METABOLISM AND OF ACIDOSIS AFTER THE TRANSPLANTATION OF A URETER INTO THE DUODENUM IN DOGS.
 A STUDY OF THE NITROGEN METABOLISM AND OF ACIDOSIS AFTER THE TRANSPLANTATION OF A URETER INTO THE DUODENUM IN DOGS. BY KINGO GOTO, M.D. (From the Department of Surgical Research and the John Herr Musser
A STUDY OF THE NITROGEN METABOLISM AND OF ACIDOSIS AFTER THE TRANSPLANTATION OF A URETER INTO THE DUODENUM IN DOGS. BY KINGO GOTO, M.D. (From the Department of Surgical Research and the John Herr Musser
Temperature and Enzyme Activity.
 [ 723 ] Temperature and Enzyme Activity. By John R. Baker. (From the Department of Zoology and Oomparative Anatomy, Oxford.,. With 4 Figures in the Text. I HAVErecently carried out an experiment upon the
[ 723 ] Temperature and Enzyme Activity. By John R. Baker. (From the Department of Zoology and Oomparative Anatomy, Oxford.,. With 4 Figures in the Text. I HAVErecently carried out an experiment upon the
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion
 Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
skin in individuals whose activity was minimal Two normal adult male medical students were the and maintenance calories. The intake of tap water was
 MINIMAL SODIUM LOSSES THROUGH THE SKIN1 By KENNETH D. ARN AND ANN REIMER (From the Department of Internal Medicine, The Medical School, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Mich.) (Submitted for publication
MINIMAL SODIUM LOSSES THROUGH THE SKIN1 By KENNETH D. ARN AND ANN REIMER (From the Department of Internal Medicine, The Medical School, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Mich.) (Submitted for publication
Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration
Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration
II. THE EFFECT OF THE INGESTION OF GLYCINE ON THE EXCRETION OF ENDOGENOUS URIC ACID.
 PURINE METABOLISM. II. THE EFFECT OF THE INGESTION OF GLYCINE ON THE EXCRETION OF ENDOGENOUS URIC ACID. BY A. A. CHRISTMAN AND E. C. MOSIER. (From the Laboratory of Physiological Chemistry, Medical School,
PURINE METABOLISM. II. THE EFFECT OF THE INGESTION OF GLYCINE ON THE EXCRETION OF ENDOGENOUS URIC ACID. BY A. A. CHRISTMAN AND E. C. MOSIER. (From the Laboratory of Physiological Chemistry, Medical School,
Excretory System. Biology 2201
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System. Excretory System
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
The function of the kidney
 Homeostasis Carbon dioxide must be removed because when it dissolves it makes an acidic solution which can affect enzymes working Carbon dioxide is removed by diffusing into the blood stream and being
Homeostasis Carbon dioxide must be removed because when it dissolves it makes an acidic solution which can affect enzymes working Carbon dioxide is removed by diffusing into the blood stream and being
Structures of the Excretory System include: ü Skin ü Lung ü Liver ü Kidneys ü Ureter ü Urinary Bladder ü Urethra
 Excretory System Structures of the Excretory System include: ü Skin ü Lung ü Liver ü Kidneys ü Ureter ü Urinary Bladder ü Urethra Function of the Excretory System The function of the excretory system is
Excretory System Structures of the Excretory System include: ü Skin ü Lung ü Liver ü Kidneys ü Ureter ü Urinary Bladder ü Urethra Function of the Excretory System The function of the excretory system is
XXVI. STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION. OF AMINO-COMPOUNDS AND CARBOHYDRATES.
 XXVI. STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION. OF AMINO-COMPOUNDS AND CARBOHYDRATES. II. THE PREPARATION OF GLUCOSE UREIDE. BY ALEXANDER HYND. From the Department of Physiology, University of St Andrews. (Received
XXVI. STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION. OF AMINO-COMPOUNDS AND CARBOHYDRATES. II. THE PREPARATION OF GLUCOSE UREIDE. BY ALEXANDER HYND. From the Department of Physiology, University of St Andrews. (Received
Women are being encouraged to use longer-term methods of contraception to reduce their chances of having an unwanted pregnancy.
 HORMONAL COORDINATION IN HUMANS PART III Q1. A woman s fertility can be controlled by using hormones. Some contraceptive pills contain oestrogen. Name the gland which produces oestrogen. Women are being
HORMONAL COORDINATION IN HUMANS PART III Q1. A woman s fertility can be controlled by using hormones. Some contraceptive pills contain oestrogen. Name the gland which produces oestrogen. Women are being
The Urinary System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
Fal Fal P h y s i o l o g y 6 1 1, S a n F r a n c i s c o S t a t e U n i v e r s i t y
 Fall 12 OSMOTIC REGULATION OF THE RENAL SYSTEM: Effects of fasting and ingestion of water, coke, or Gatorade on urine flow rate and specific gravity Dorette Franks The purpose of the physiology experiment
Fall 12 OSMOTIC REGULATION OF THE RENAL SYSTEM: Effects of fasting and ingestion of water, coke, or Gatorade on urine flow rate and specific gravity Dorette Franks The purpose of the physiology experiment
Biology Slide 1 of 36
 Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
AGGLUTINATION PHENOMENA IN CANCER
 AGGLUTINATION PHENOMENA IN CANCER N. WATERMAN AND L. DB KROMME (Laboratory of the Antoni van Leeuwenhoekhuie, Amsterdam) In the course of our investigations into the cytolysis of cancer cells by different
AGGLUTINATION PHENOMENA IN CANCER N. WATERMAN AND L. DB KROMME (Laboratory of the Antoni van Leeuwenhoekhuie, Amsterdam) In the course of our investigations into the cytolysis of cancer cells by different
Note: During any ONE run the ph remains constant. It may be at any one of the above levels but it never change during a single run.
 1 BGYC34 (2007) PhysioEx Lab 10 AcidBase Balance Marking Scheme Part 1 Complete PhysioEx lab #10. Handin all of the pages associated with the lab. Note that there are 9 activities to be completed. You
1 BGYC34 (2007) PhysioEx Lab 10 AcidBase Balance Marking Scheme Part 1 Complete PhysioEx lab #10. Handin all of the pages associated with the lab. Note that there are 9 activities to be completed. You
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
