Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science ISSN Vol.4 (2), April-June, 2014 REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Kristian Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM PRAFULL GHORPADE* 1, SHRENIK KAMBLE 2 1 Marathwada Mitra Mandal s College of Pharmacy, Kalewadi (Thergaon), Pune, Maharashtra, India *Corresponding author praful.ghorpade@yahoo.in Telephone Abstract: It is a new drug delivery system to maximize effectiveness and compliance. The advantage of floating drug delivery system is, to prolongs the release of the drug, increases gastric residency time, and enhances bioavailability by superior technology of floatation to achieve gastric retention technological attempts have been made in the research and development of rate-controlled oral drug delivery systems to overcome physiological adversities, It including floating drug delivery systems (FDDS), swelling and expanding systems, polymeric bioadhesive systems, high-density systems, modified-shape systems and other delayed gastric emptying devices. Gastric emptying is a complex process and makes in vivo performance of the drug delivery systems uncertain. The floating drug delivery systems are useful approach to avoid this variability with increase the retention time of the drug-delivery systems for more than 12 hours. Effervescent and non-effervescent are two class of floating drug delivery system and can formulate either in single unit dosage form or in multiple unit dosage form, and their classification and formulation aspects are covered in detail. Although tremendous advances have been seen in oral controlled drug delivery system in the last two decades, this system has been of limited success in the case of drugs with a poor absorption window throughout the GIT (Gastro Intestinal Tract). Key words: Floating drug delivery system, Gastrointestinal tract, Gastric-retention Introduction: The oral route is considered as the most promising route of drug delivery. Conventional drug delivery system achieves as well as maintains the drug concentration within the therapeutically effective range needed for treatment, only when taken several times a day. The idea of gastric retention comes from the need to localize drugs at a specific region of gastrointestinal tract (GIT) such as stomach in the body. Many drugs get absorbed only in the upper intestinal tract, designing such molecules as once-daily formulations are exclusive for these molecules. Often, the extent of drug absorption is limited by the gastric residence time (GRT) of the drug at the absorption site. If the drugs are poorly soluble in intestine due to alkaline ph, gastric retention may increase solubility before they are emptied, resulting in improved gastrointestinal absorption of drugs with narrow absorption window as well as for controlling release of drugs having sitespecific absorption limitation 1. Gastroretention would also facilitate local drug delivery to the stomach and proximal small intestine. Thus, gastroretention could help to provide greater availability of new products and consequently improved therapeutic activity and substantial benefits to patients. Gastro-retentive drug delivery system belongs to oral controlled drug delivery system group that are capable to retain in the stomach by passing the gastric transit. These dosage forms are also defined as floating drug delivery system, which can float in the contents of the stomach and release the drug in a controlled manner for prolonged 1 P a g e Available online on Review Article
2 periods of time 2. The release rate will be controlled depending upon the type and concentration of the polymer that swells, leads to diffusion and erosion of the drug 3. The real challenge in the development of a gastro-retentive drug delivery system is not just sustain the drug release but also to prolong the presence of the dosage form in the stomach or the upper part of the GIT until all the drug is completely released. This can be accomplished by floating drug delivery system which helps to retain dosage form in the stomach and releases the drug in controlled manner for longer period of time. GRDDS is retained for longer periods of time in the stomach e.g. Hydrophilic matrix tablets, floating capsules and bioadhesive tablet. Thus the longer period of gastric-retention as compared to other oral controlled drug delivery system can be attributed. The floating results in release of the drug in to the stomach and the small intestine rather than into the large intestine where drug absorption is poor or erratic. This is achieved by adjusting the time period of release for the drugs by changing the concentrations of polymers 4. Basic gastrointestinal tract physiology The stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal. The main function of the stomach is to store food temporarily, grind it, and then release it slowly in to the duodenum. The stomach is a site of enzyme production. Due to its small surface, The excellent concept of floating system suffers from a disadvantage that it is effective only when the fluid level in the stomach is sufficiently high 5. However, as the stomach empties and the tablet is at the pylorus, the buoyancy of the dosage form may be impeded. Area very little absorption takes place from the stomach. It provides a barrier to the delivery of drugs to the small intestine. The stomach is located below the diaphragm. Various factors such as volume ingested, posture and skeletal build affect the exact position of the stomach. Figure 1: Anatomy of the gastrointestinal tract Anatomically the stomach is divided into 3 regions: fundus, body, and antrum (pylorus). The proximal part made of fundus and body acts as a reservoir for undigested material, whereas the antrum is the main site for mixing motions and act as a pump for gastric emptying by propelling actions. Gastric emptying occurs during fasting as well as fed states. The pattern of motility is however distinct in the 2 states. During the fasting state an interdigestive series of electrical events take place, which cycle both through stomach and intestine every 2 to 3 hours. This is called the interdigestive myloelectric cycle or migrating myloelectric cycle (MMC), which is further divided into 4 phases (5-7). 2 P a g e Available online on Review Article
3 Phase I (basal phase) lasts from 40 to 60 minutes with rare contractions. Phase II (preburst phase) lasts for 40 to 60 minutes with intermittent action potential and contractions. As the phase progresses the intensity and frequency also increases gradually. Phase III (burst phase) lasts for 4 to 6 minutes. It includes intense and regular contractions for short period. It is due to this wave that all the undigested material is swept out of the stomach down to the small intestine. It is also known as the HOUSEKEEPER WAVE. Phase IV lasts for 0 to 5 minutes and occur between phases III and 1 of 2 consecutive cycles. After the ingestion of a mixed meal, the pattern of contractions changes from fasted to that of fed state. This is also known as digestive motility pattern and comprises continuous contractions as in phase II of fasted state. These contractions result in reducing the size of food particles (to less than 1 mm), which are propelled toward the pylorus in a suspension form. During the fed state onset of MMC is delayed resulting in slowdown of gastric emptying rate. Scintigraphic studies determining gastric emptying rates revealed that orally administered controlled release dosage forms are subjected to basically 2 complications, that of short gastric residence time and unpredictable gastric emptying rate. FACTORS AFFECTING GASTRIC RETENTION Various attempts have been made to retain the dosage form in the stomach as a way of increasing the retention time. Most of these approaches are influenced by a number of factors that affect their bioavailability and efficacy of the gastro retentive system (8-11). i. Density: Density of the dosage form should be less than the gastric contents (1.004gm/ml). ii. Size: dosage forms with the diameter more than 7.5 mm are reported to have greater gastric retention time (GRT). iii. Fed or Unfed State: Under fasting conditions, the GI motility is characterized by periods of strong motor activity or the migrating myloelectric complexes (MMC) that occurs every 1.5 to 2 hours. The MMC sweeps undigested material from the stomach and if the timing of administration of the formulation coincides with that of the MMC, the GRT of the unit can be expected to be very short. However, in the fed state, MMC is delayed and GRT is considerably longer. iv. Nature of the meal: Feeding of indigestible polymers of fatty acid salts can change the motility pattern of the stomach to a fed state, thus decreasing the gastric emptying rate and prolonging the drug release. v. Caloric Content: GRT can be increased between 4 to 10 hours with a meal that is high in proteins and fats. vi. Frequency of feed: The GRT can increase by over 400 minutes when successive meals are given compared with a single meal due to the low frequency of MMC. 3 P a g e Available online on Review Article
4 vii. Gender: Gastric residence time in males (3.4±0.4 hours) is less as compare to female (4.6±1.2 hours), regardless of the weight, height and body surface. So dosage form does not retain in male for longer duration of time in stomach as compared to female. viii. Age: Elderly people, especially those over 70 years have a significantly longer GRT. ix. Posture: GRT can vary between supine and upright ambulatory states of the patients. x. Concomitant drug administration: Anticholinergic like atropine and propantheline opiates like codeine and prokinetic agents like metoclopramide and cisapride decrease gastric motility and increase gastric residence time if dosage forms. Advantages of gastroretentive drug delivery systems FDDS is highly advantageous in the treatment of the disorders related to the stomach. As the prime objective of such systems is to produce a gastro-retentive product or a product which has an enhanced retention time in the stomach (12) i. Enhanced bioavailability: The bioavailability of riboflavin CR-GRDF is significantly enhanced in comparison to the administration of non-grdf CR polymeric formulations. There are several different processes, related to absorption and transit of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract, that act concomitantly to influence the magnitude of drug absorption. ii. Enhanced first-pass biotransformation: In a similar fashion to the increased efficacy of active transporters exhibiting capacity limited activity, the pre-systemic metabolism of the tested compound may be considerably increased when the drug is presented to the metabolic enzymes (cytochrome P450, in particular CYP3A4) in a sustained manner, rather than by a bolus input. iii. Sustained drug delivery: Reduced frequency of dosing for drugs with relatively short biological half-life, sustained and slow input from CR-GRDF may result in a flip-flop pharmacokinetics and enable reduced dosing frequency. This feature is associated with improved patient compliance, and thereby improves therapy. iv. Targeted therapy for local ailments in the upper GIT: The prolonged and sustained administration of the drug from GRDF to the stomach may be advantageous for local therapy in the stomach and small intestine. By this mode of administration, therapeutic drug concentrations may be attained locally while systemic concentrations, following drug absorption and distribution, are minimal. v. Reduced fluctuations of drug concentration: Continuous input of the drug following CRGRDF administration produces blood drug concentrations within a narrower range compared to the immediate release dosage forms. Thus, fluctuations in drug effects are minimized and concentration dependent adverse effects that are associated with peak concentrations can be prevented. vi. Improved selectivity in receptor activation: Minimization of fluctuations in drug concentration also makes it possible to obtain certain selectivity in the elicited pharmacological effect of drugs that activate different types of receptors at different concentrations. vii. Reduced counter-activity of the body: In many cases, the pharmacological response which intervenes with the natural physiologic processes provokes a rebound activity of the body that minimizes drug activity. Slow input of the drug into the body was shown to minimize the counter activity leading to higher drug efficiency. viii. Extended time over critical (effective) concentration: For certain drugs that have non-concentration dependent pharmacodynamics, such as beta-lactum antibiotics, the clinical response is not associated with peak 4 P a g e Available online on Review Article
5 concentration, but rather with the duration of time over a critical therapeutic concentration. The sustained mode of administration enables extension of the time over a critical concentration and thus enhances the pharmacological effects and improves the clinical outcomes. ix. Minimized adverse activity at the colon: Retention of the drug in the GRDF at the stomach minimizes the amount of drug that reaches the colon. Thus, undesirable activities of the drug in colon may be prevented. This pharmacodynamics aspect provides the rationale for GRDF formulation for beta-lactum antibiotics that are absorbed only from the small intestine, and whose presence in the colon leads to the development of microorganism s resistance. x. Site specific drug delivery: A floating dosage form is a feasible approach especially for drugs which have limited absorption sites in upper small intestine. The controlled, slow delivery of drug to the stomach provides sufficient local therapeutic levels and limits the systemic exposure to the drug. This reduce s side effects that are caused by the drug in the blood circulation. In addition, the prolonged gastric availability from a site directed delivery system may also reduce the dosing frequency. Disadvantages of GRDDS: The major disadvantage of floating system is requirement of a sufficient high level of fluids in the stomach for the drug delivery to float. However this limitation can be overcome by coating the dosage form with the help of bioadhesive polymers that easily adhere to the mucosal lining of the stomach (13). Gastric- retention is influenced by many factors such as gastric motility, ph and presence of food. These factors are never constant and hence the buoyancy cannot be predicted. Drugs that cause irritation and lesion to gastric mucosa are not suitable to be formulated as floating drug delivery systems. High variability in gastric emptying time due to its all (or) non-emptying process. Patients should not be dosed with floating forms just before going to bed. Floating system is not feasible for those drugs that have solubility (or) stability problem in gastric fluids. The dosage form should be administered with a minimum of glass full of water ( ml). The drugs, which are absorbed throughout GIT, which under go first-pass Propranolol etc), are not desirable candidate. metabolism (Nifedipine, Suitable drug candidates for FDDS Various drugs have their greatest therapeutic effect when released in the stomach, particularly when the release is prolonged in a continuous, controlled manner. In general, appropriate candidates for FDDS are molecules that have poor colonic absorption but are characterized by better absorption properties at the upper parts of the GIT (14-18). Drugs with narrow absorption window in GIT, e.g., Riboflavin and Levodopa Drugs that primarily absorbed from stomach and upper part of GIT, e.g., Calcium supplements, chlordiazepoxide and cinnarazine. 5 P a g e Available online on Review Article
6 Drugs that act locally in the stomach, e.g., Antacids and Misoprostol. Drugs that degrade in the colon, e.g., Ranitidine HCl and Metronidazole. Drugs that disturb normal colonic bacteria, e.g., Amoxicillin Trihydrate Approaches to gastric retention A number of approaches have been used to increase gastric-retention time (GRT) of a Dosage form in stomach by employing a variety of concepts (19) 1 Floating systems 2 High-density systems 3 Swellable and Expandable systems 4 Mucoadhesive or bio- adhesive systems 5 Super porous Hydro- gel 6 Magnetic systems. Figure 2: Approaches to gastro retentive drug delivery system Different types of FDDS Based on the mechanism of buoyancy, floating systems can be classified into two distinct categories viz. Non-effervescent and effervescent systems 1. Non-Effervescent systems: A. Colloidal gel barrier systems: Hydro-dynamically balanced system (HBS) of this type contains drug with gel forming or swellable cellulose type hydrocolloids, polysaccharides and matrix forming polymers. They help prolonging the GI residence time and maximize drug reaching its absorption site in the solution form ready for absorption. These systems incorporate high levels (20 to 75 % w/w) of one or more gel forming highly swellable cellulose type hydrocolloids e.g. hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) Hydroxy-propyl cellulose (HPC) hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC), sodium carboxy methyl cellulose (NaCMC) incorporated either in tablets or capsules. When such a system comes in contact with the gastric fluid, the hydrochloride in the system hydrates and forms a colloidal gel barrier around its surface. This gel barrier controls the rate of the fluid penetration into the device and consequent release of drug from it. As the exterior surface of the dosage form goes in to the solution, the adjacent hydrochloride layer becomes hydrated and thus maintains the gel layer. The air trapped inside the swollen polymer maintains the density less than unity and confers buoyancy to these dosage forms. The Hydrodynamically balanced system (HBS) must comply with following three major criteria: 1. It must have sufficient structure to form cohesive gel barrier. 6 P a g e Available online on Review Article
7 2. It must maintain an overall specific density lower than that of gastric contents. 3. It should dissolve slowly enough to serve as reservoir for the delivery system (20). A Bilayer tablet can also be prepared to contain one immediate release and other sustained release layer. Immediate release layer delivers the initial dose whereas sustained release layer absorbs gastric fluid and forms a colloidal gel barrier on its surface. This results in system with bulk density lesser than that of gastric fluid and allows it to remain buoyant in the stomach for an extended period of time. A multi-layer, flexible, sheathlike device buoyant in gastric juice showing sustained release characteristics have also been developed. The device consists of at least one dry self-supporting carrier film made up of water insoluble polymer matrix having a drug dispersed/dissolved therein, and a barrier film overlaying the carrier film. Both carrier and barrier films are sealed together along their periphery and in such a way as to entrap a plurality of small air pockets, which bring about the buoyancy to the laminated films (21). B. Micro-porous compartment system: This technology is based on the encapsulation of drug reservoir inside a Micro porous compartment with aperture along its top and bottom wall. The peripheral walls of the drug reservoir compartment are completely sealed into prevent any direct contact of the gastric mucosal surface with the undissolved drug. In stomach the floatation chamber containing entrapped air causes the delivery system to float over the gastric contents. Gastric fluid enters through the apertures, dissolves the drug, and carries the dissolve drug for continuous transport across the intestine for absorption (22). C. Alginate beads: Multiple unit floating dosage forms have been developed from freeze-dried calcium alginate. Spherical beads of approximately 2.5 mm in diameter were prepared by dropping a sodium alginate solution into aqueous solution of calcium chloride, causing a precipitation of calcium alginate. These beads were then separated; snap frozen in liquid nitrogen and freeze-dried at 40ºC for 24 hrs, leading to formation of porous system that maintained floating force for over 12 hrs. They were compared with non-floating solid beads of same material. The latter gave a short residence time of 1 hr, while floating beads gave a prolonged residence time of more than 5.5 hrs10. Floating systems comprising of calcium alginate core separated by an air compartment from a membrane of calcium alginate or a calcium alginate/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) have also been developed (23). The porous structure generated by leaching of PVA (water soluble additive in coating composition) was found to increase membrane permeability and thus preventing the collapse of air compartment D. Hollow Microspheres: Microspheres (micro balloons), loaded with drug in their outer polymer shells are prepared by a novel emulsion-solvent diffusion method. The ethanol: dichloromethane solution of the drug and an enteric acrylic polymer is poured into an agitated aqueous solution of PVA that is thermally controlled at 40 C. The gas phase generated in dispersed polymer droplet by evaporation of dichloromethane forms an internal cavity in microsphere of polymer with drug. The micro -balloons float continuously over the surface of acidic dissolution media containing surfactant for more than 12 hours (24). 7 P a g e Available online on Review Article
8 B. Effervescent systems: A drug delivery system can be made to float in the stomach by incorporating a floating chamber, which may be filled with vacuum, air or inert gas. The gas in floating chamber can be introduced either by volatilization of an organic solvent or by effervescent reaction between organic acids and bicarbonate salts (25). 1. Volatile liquid containing systems: These devices are osmotically controlled floating systems containing a hollow deformable unit that can be converted from a collapsed to an expanded position and returned to collapse position after an extended period. A deformable system consists of two chambers separated by an impermeable, pressure responsive, movable bladder. The first chamber contains the drug and the second chamber contains volatile liquid. The device inflates and the drug is continuously released from the reservoir into the gastric fluid. The device may also consist of bioerodible plug made up of PVA, polyethylene, etc. that gradually dissolves causing the inflatable chamber to release gas and collapse after a predetermined time to permit the spontaneous ejection of the inflatable system from the stomach (26). 2. Gas generating systems: These buoyant delivery systems utilize effervescent reaction between carbonate/ bicarbonate salts and citric/tartaric acid to liberate CO2 which gets entrapped in the jellified hydrochloride layer of the system, thus decreasing its specific gravity less than 1 and making it to float. These tablets may be either single layered wherein the CO2 generating components are intimately mixed within the tablet matrix or they may be Bilayer in which the gas generating components are compressed in one hydrocolloid containing layer, and the drug in outer layer for sustained release effect. Figure 3: Gas-generating systems, Schematic monolayer drug delivery system (a) Bilayer gas-generating systems, with (c) or without (b) semi permeable membrane: Figure 4: Schematic representation of floating pill proposed by Ichikawa (a). The penetration of water into effervescent layer leads to a CO2 generation and makes the system float (b). 8 P a g e Available online on Review Article
9 3. Matrix Tablets: Single layer matrix tablet is prepared by incorporating bicarbonates in matrix forming hydrocolloid gelling agent like HPMC, chitosan, alginate or other polymers and drug. Bilayer tablet can also be prepared by gas generating matrix in one layer and second layer with drug for its sustain release effect. Floating capsules also prepared by incorporating such mixtures. Triple layer tablet also prepared having first swellable floating layer, second sustained release layer of 2 drugs (Metronidazole and Tetracycline) and third rapid dissolving layer of bismuth salt. This tablet is prepared as single dosage form for Triple Therapy of H.Pylori (27). Figure 5: Schematic presentation of the structure of the floating matrix tablets C. Bioadhesive drug delivery system Bioadhesive systems are those which bind to the gastric epithelial cell surface or mucin and serve as the potential means of extending the GRT of DDS in the stomach, by increasing the intimacy and duration of contact of drug with the biological membrane. The concept is based on self-protecting mechanism of GIT. Mucus secreted continuously by the specialized goblet cells located throughout the GIT plays a cytoprotective role. Bioadhesion is an interfacial phenomenon in which two materials, at least one of which is biological, are held together by means of interfacial forces. The attachment could be between an artificial material and biological substrate, such as adhesion between a polymer and a biological membrane. In the case of polymer attached to the mucin layer of a mucosal tissue, the term Muco-adhesion is used. The mucosal layer is presenting indifferent of regions of the body including the gastro-intest inal tract, the urogential tract, the airways, the ear, nose and eye. These represent potential sites for attachment of bioadhesive system and hence, the Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems could be designed for buccal, oral, vaginal, rectal, nasal and ocular routes of administration (28). Examples of Materials commonly used for Bioadhesion are poly (acrylic acid) (Carbopol, polycarbophil), chitosan, Cholestyramine, tragacanth, sodium alginate. D. Swelling and expanding systems These are the dosage forms, which after swallowing, swell to an extent that prevent their exit from the pylorus. As a result, the dosage form is retained for a longer period of time. These systems may be named as plug type systems, since they exhibit the tendency to remain lodged at the pyloric sphincter. On coming in contact with gastric fluid, the polymer imbibes water and swells. The extensive swelling of these polymers is due to the presence of physical/chemical cross-links in the hydrophilic polymer network. These cross-links prevent the dissolution of the polymer and hence maintain the physical integrity of the dosage form. A balance between the extent and duration of swelling is maintained by the degree of crosslinking between the polymeric chains. A high degree of cross-linking retards the swelling ability of the 9 P a g e Available online on Review Article
10 system maintaining its physical integrity for prolonged period. On the other hand, a low degree of crosslinking results in the extensive swelling of the system, succeeded by the rapid dissolution of the polymer (29) Figure 6: Swelling and expanding system E. High density systems These dosage forms have a density (3 g/ml) far exceeding that of normal stomach contents (1 g/ml) and thus retained in rugae of the stomach and are capable of withstanding its peristaltic movements (30). The density of these systems should at least be g/ml. This is accomplished by coating the drug with heavy inert materials such as barium sulphate, zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, iron powder etc. Figure 7: High density system F. Modified shape systems These are non-disintegrating geometric shapes molded from silastic elastomer or extruded from polyethylene blends which extend the GRT depending on size, shape and flexural modulus of the drug delivery system. G. Combination of floating, mucoadhesion and swellable systems These systems combine floating, mucoadhesion and swelling mechanism for gastric retention of dosage forms. A preferred formulation comprises a mixture of a high or medium viscosity (HPMC) and a high or medium viscosity (HEC). The formulations optionally may comprise a low viscosity HPMC. It also includes a salt being capable of releasing gaseous carbon dioxide alkaline metal carbonates can be used, an acid may be added, such as citric acid and maleic acid. These systems mainly act by three different mechanisms such as swelling, floating due to gas and mucoadhesion (31). H. Magnetic systems This system is based on a simple idea that the dosage form contains a small internal magnet and a magnet placed on the abdomen over the position of the stomach. Used this technique in rabbits with bioadhesive granules containing ultrafine ferrite (g-fe2o3). They guided them to the esophagus with an external magnet (1700 G) for the initial 2 min and almost all the granules were retained in the region after 2 h. although these systems seem to work, the external magnet must be positioned with a degree of precision that might compromise patient compliance. 10 P a g e Available online on Review Article
11 I. Raft-forming systems This system is used for delivery of antacids and drug delivery for treatment of gastrointestinal infections and disorders. The mechanism involved in this system includes the formation of a viscous cohesive gel in contact with gastric fluids, wherein each portion of the liquid swells, forming a continuous Figure 8: Barrier formed by Raft forming system Table 1: Drug used in the gastro-retentive formulation (32-33) Type Floating microspheres Example Aspirin, Griseofulvin, ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, P-nitro aniline, Indomethasone, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Piroxicam, Verapamil, orlistat, Cholestyramine, Theophylline, Nifedipine, Nicardipine, captorlil, cimetidine, Dipyridamol, Tranilast and Terfinadine Floating Diclofenac sodium, Indomethacin and Prednisolone, Ranitidine Hydrochloride-Gelucire. granules Films Cinnarizine, Albendazole Floating tablets and Acetaminophen, Acetylsalicylic acid, Ampicillin, Amoxicillin trihydrate, Atenolol, Cephalexin, Cefuroxime, Fluorouracil, Isosorbide mononitrate, Isoniazide, Para-amino pills benzoic acid, Piretanide, Theophylline, Verapamil hydrochloride, Chlorpheniramine maleate, Aspirin, Calcium Carbonate, Fluorouracil, Prednisolone, Sotalol, Pentoxyfilline and DiltiazemHCl Table 2: Other Excipients (Excipients used in (GRDDS) (34) Type Example Polymers hydroc Acacia, Pectin, Chitosan, Agar, Casein, Bentonite, Veegum, Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC) (K4M, K100M and K15M), Gellan gum(gelrite ), Sodium Carboxy Methyl Cellulose (CMC), Methyl Cellulose (MC), Hydroxy Propyl Cellulose (HPC). Inert fatty material Effervescent agents Release rate accelerators Increasing agents- Low density material Bees wax, Fatty acids, Long chain fatty alcohols, Gelucires 39/01 and 43/01. Sodium bicarbonate, Citric acid, Tartaric acid, Di-SGC (Di-Sodium Glycine Carbonate), CG (Citroglycine). Lactose, Mannitol Ethyl cellulose. Polypropylene foam powder (Accurel MP 1000 ). 11 P a g e Available online on Review Article
12 Evaluation of floating drug delivery system 1) Evaluation of powder blend fora) Angle of Repose b) Bulk Density c) Percentage porosity 2) Evaluation of tablets fora) Buoyancy capabilities b) In vitro floating and dissolution behavior c) Weight variation d) Hardness & friability e) Particle size analysis, surface characterization (for floating microspheres and beads) f) X Ray/Gamma Scintigraphy Evaluation of powder blend (35) a) Angle of repose Angle of repose is defined as the maximum angle possible between the surface of the pile of powder and the horizontal plane. Lower the angle of repose, better the flow properties. The angle of repose may be calculated by measuring the height (h) of the pile and the radius of the base(r) with ruler. Tan θ = h/r b) Bulk density Bulk density denotes the total density of the material. It includes the true volume of interparticle spaces and intraparticle pores. The packing of particles is mainly responsible for bulk. Bulk density is defined as: When particles are packed, it is possible that a large amount of gaps may be present between the particles. Therefore, trapping of powder allows the particles to shift and remove the voids to minimum volume. The volume occupied by the powder in this condition represents the bulk volume. Substituting this volume for a given weight of powder in below equation gives the bulk density. Bulk density = weight of the powder Bulk volume of powder c) Percentage porosity Whether the powder is porous or nonporous, the total porosity expression for the calculation remains the same. Porosity provides information about hardness, disintegration, total porosity etc. % porosity, = void volume 100 Bulk volume % porosity, = (bulk volume true volume) 100 True density Evaluation of floating tablets (36) a) Measurement of buoyancy capabilities of the FDSS The floating behavior is evaluated with resultant weight measurements. The experiment is carried out in two different media, deionised water and simulated meal. The results showed that higher molecular weight polymers wit slower rate of hydration had enhanced floating behaviour and it was observed more in simulated meal medium compared to deionised water. b) In Vitro floating and dissolution behaviour: The dissolution tests are generally performed on various drugs using USP dissolution apparatus. USP 28 states the dosage unit is allowed to sink to the bottom of the vessel before rotation of the blade is started. A small, loose piece of nonreactive material with not more than a few turns of a wire helix may be attached to the dosage units that would otherwise float. However, standard USP 12 P a g e Available online on Review Article
13 or BP methods have not been shown to be reliable predictors of in vitro performance of floating dosage forms. c) Weight variation: In practice, composite samples of tablets (usually 10) are taken and weighed throughout the compression process. The composite weight divided by 10, however provides an average weight but contains a problem of averaged value. To help alleviate this problem, the United States pharmacopeia (USP) provides limits for the permissible variations in the weights of individual tablets expressed as a percentage of the average weight of the sample. The USP provides the weight variation test by weighing 20 tablets individually, calculating the average weight, and comparing the individual tablet weights to the average. The tablets meet the USP test if no more than 2 tablets are outside the percentage limit, and if no tablet differs by more than 2 times the percentage limit. d) Hardness & friability Hardness is defined as the force required to break a tablet in diametric compression test. Hardness is hence, also termed as the tablet crushing strength. Some devices which are used to test hardness are Monsanto tester, strong Cobb tester, Pfizer tester, etc. The laboratory friability tester is known as the Roche Friabilator. This consists of a device which subjects a number of tablets to the chamber that revolves at 25 rpm & drops the tablet to a distance of six inches with each revolution. Normally, a pre weighed tablet sample is place in the friabilator which is then operated for 1oo revolution Conventional compressed tablets that lose less than 0.5 to 1.0 % of their weights are generally considered acceptable. Most of the effervescent tablet undergoes high friability losses, which accounts for the special stack packaging that may be required for this type of tablet. e) Particle size analysis, surface characterization (for floating microspheres and beads) the particle size and the size distribution of beads or microspheres are determined in the dry state using the optical microscopy method. The external and cross sectional morphology (surface characterization) is done by scanning electron microscope (SEM). f) X-ray /gamma Scintigraphy X Ray/Gamma Scintigraphy is a very popular evaluation parameter for floating dosage form nowadays. It helps to locate dosage form in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), by which one can predict and correlate the gastric emptying time and the passage of dosage form in the GIT. Here the inclusion of a radio opaque material into a solid dosage form enables it to be visualized by X rays. Similarly, the inclusion of a γ emitting radionuclide in a formulation allows indirect external observation using a γ camera or scintiscanner. In case of γ Scintigraphy, the γ rays emitted by the radionuclide are focused on a camera, which helps to monitor the location of the dosage form in the GIT. Application of floating drug delivery systems Floating drug delivery offers several applications for drugs having poor bioavailability because of the narrow absorption window in the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract. It retains the dosage form at the site of absorption and thus enhances the bioavailability. These are summarized as follows (36) 1. Sustained drug delivery: FDDS can remain in the stomach for long periods and hence can release the drug over a prolonged period of time. The problem of short gastric residence time encountered with an oral controlled release formulation hence can be overcome with these systems. These systems have a bulk density of <1 as a result of which they can float on the gastric contents. These systems are relatively large in size and 13 P a g e Available online on Review Article
14 passing from the pyloric opening is prohibited. E.g. Sustained release floating capsules of Nicardipine Hydrochloride 2. Site-specific drug delivery: These systems are particularly advantageous for drugs that are specifically absorbed from stomach or the proximal part of the small intestine. E.g. Riboflavin and Furosemide 3. Absorption enhancement: Drugs that have poor bioavailability because of site specific absorption from the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract are potential candidates to be formulated as floating drug delivery systems, thereby maximizing their absorption. E.g. A significantly increase in the bioavailability of floating dosage forms (42.9%) could be achieved as compared with commercially available LASIX tablets (33.4%) and enteric coated LASIX-long product (29.5%) Table 1: Marketed products of FDDS (37-38) Sr no Product Active ingredients 1 Madopar Levodopa and Benserazide 2 Valrelease Diazepam 3 Topalkan Aluminum magnesium antacid 4 Almagate Flat coat Antacid 5 Liquid gavi-son Alginic acid and sodium bicarbonate Refernces 1. Modi SA. Sustained release drug delivery system: A review. Int. J.Pharma Res Develp. 2011; 2: Chien Y, Novel drug delivery systems. 2 nd edition, Marcel Dekker, New York.(1992) 3. Bansal A, Chawla G, Gupta P & Koradia V, Gastroretention a means to address regional variability in intestinal drug absorption, Pharmaceutical technology, 2003, Talukder R & Fassihi R,,Introduction to controlled release and oral controlled drug delivery systems. The Eastern Pharmacist 1991; 45: vol. 30, Vishal Cristan. A review on Gastro-retentive delivery systems: A mini review, Drug delivery of indian pharmaceutics, Int. J. Pharma. Res Develp, 2011; Vol 3(6), N. K. Jain; Controlled & novel drug delivery system ; Pharmaceutical product development; C. Deepa latha, G. Nagaveni. G. Vijaya lakshmi. A review on Floating Drug Delivery System., Int. J. Current Pharma Res, Vol 3 (4), (2011) 8. Rocca D. J.G, Omidian H, Shah K. Progresses in gastroretentive drug delivery systems, Business Briefing. Pharmatech, 2003; AJ. Gastric-retention systems for oral drug delivery. Business Briefing. Pharmatech 2003; AJ. Gastro-retentive dosage forms, Crit Rev Their Drug Carrier System 1993; 10(2), Roop K. Khar, Controlled Drug Delivery, Gastro-retentive system, 4 th edition, Deshpande A.A, Shah N.H, Rhodes C.T, Malick W. Pharma Res. 1997, 14: Davis S.S, Stockwell A.F, Taylor M.J. Pharm Res 1986, 3: Lehr CM. Crit Rev Their drug carrier system 1994; 11: Groning R, Heun G. Drug Delivery Indian Pharmaceutics 1984, 10: Klausner EA, Lavy E, Friedman M, Hoffman A. J. Cont Release, 2003, 90: P a g e Available online on Review Article
15 17. The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: A history Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, Volume 37( 2), 1991, S1-S Shiv Shankar Hardenia et al. Asian J. Pharm Life Sci, Vol. 1 (3), 2011: Grabowski SR. Principles of anatomy and physiology. 10 th edition. New York: John Willey and Sons; KRW, Waugh A. Anatomy and physiology in health and illness. 9 th edition, London: Churchill Livingstone, Arora S, Ali J, Ahuja A, Khar K R, Baboota S., Floating Drug Delivery Systems: A review. Asian J. Pharma. Sci.Tech. 2005; 6(3), Rajnikanth P, Mishra B., Floating in situ gelling system for stomach site specific delivery of clarithromycin to eradicate H.pylori. J. of Controlled Release.2008; 25: P.L. Bardonnet, V. Faivre, W.J. Pugh, J.C. Piffaretti, F. Falson., Gastroretentive dosage forms: Overview and special case of Helicobacter pylori., J. of Controlled Rel 111 (2006) S. Garg, S. Sharma, Gastroretentive drug delivery systems, Business Briefing: Pharma Tech, 2003, B.N. Singh, K.H. Kim, Floating drug delivery systems: an approach to oral controlled drug delivery via gastric- retention, J. Controlled Rel. 2000, 63(3), L.H. Reddy, R.S. Murthy, Floating dosage systems in drug delivery, Crit Rev. Their drug carrier system. 2002, 19 (6), S. Kockisch, G.D. Rees, S.A. Young, J. Tsibouklis, J.D. Smart, Polymeric microspheres for drug delivery to the oral cavity: An in vitro evaluation of Mucoadhesive potential, J. Pharma Sci.2003, 92 (8), Kavitha K, Sudhir K Yadav, Tamizh Mani T. The need of floating drug delivery system: A review. RJPBCS [ISSN: ] 2010; 1(2), Garg R, Gupta GD. Progress in controlled gastroretentive delivery systems. Trop J. Pharma Res, 2008; 7(3), V.H.K. Li, J.R. Robinson, V.H.L. Lee. Influence of drug properties and routes of drug administration of the design of sustained and controlled release systems. Controlled drug delivery 1987, 29(2), Bhise S.D, NH Aloorkar, Formulation and invitro evaluation of floating capsules of Theophylline, Ind J. Pharma Sci, 2008; 70(2), Nayak K Amit, Maji Ruma, Das Biswarup. Gastroretentive drug delivery systems: A review. Asian J. Pharma Clinical Research [ISSN ]. 2010; 3(1), Mayavanshi AV, Gajjar SS. Floating drug delivery systems to increase gastric retention of drugs: A Review. Res J. Pharma. Tech [ISSN ]. 2008; 1(4), Arora S, Ali J, Khar RK, Baboota S. Floating drug delivery systems: A review. AAPS Pharm Science Technology 2005; 6(3), Soppimath KS, Kulkarni AR, Rudzinski W E, Aminabhavi TM. Microspheres as floating drug delivery system to increase the gastric residence of drugs. Drug metabolism Review. 2001; 33, Moursy NM, Afifi NH, Ghorab DM, El-Saharty Y. Pharmazie 2003; 58, Faraz Jamil1, Review on Stomach specific drug delivery systems, Development and Evaluation, 2011, 2 (4): Klausner EA, Lavy E, Friedman M,Hoffman A. Expandable gastroretentive dosage form. J. Cont. Rel. 2003, 90: P a g e Available online on Review Article
Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
Biswajit Biswal IRJP 2 (7)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
This PDF is available for free download
 Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS): A REVIEW
 25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems
 29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation Review Article
 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Review Article FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A NOVEL APPROACH Mahale G. S.* and Derle Nikita D. Department of Pharmaceutics, M.V.P.s
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Review Article FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A NOVEL APPROACH Mahale G. S.* and Derle Nikita D. Department of Pharmaceutics, M.V.P.s
Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Tablets Using Different Polymers: Guargum, Sodium Alginate, Hpmc100cps and Carbopol940
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol
 Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems
 Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Review Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review
 ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
Int J Pharm Bio Sci. Harshal P. Gahiwade *et al Available Online through IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH
 Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4
 CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
2- Minimum toxic concentration (MTC): The drug concentration needed to just produce a toxic effect.
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage form of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride.
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p.
 Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
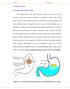 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate
 Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate Lokesh Kumar*, Virendra Singh, Rakesh Kumar Meel Department of Pharmaceutics, Goenka College of Pharmacy, NH-11,
Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate Lokesh Kumar*, Virendra Singh, Rakesh Kumar Meel Department of Pharmaceutics, Goenka College of Pharmacy, NH-11,
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: Journal homepage:
 Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science
 Research article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of Metoprolol Tartrate Patel
Research article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of Metoprolol Tartrate Patel
Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin Bilayer Tablets
 CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets
 Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY FLOATING APPROCHES
 Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
CONTENTS PAGE. Please note: Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications
 Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Venkateswara Rao et.al Indian Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Biotechnology ISSN: (Print) ISSN: (Online)
 Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual,
 Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual, buccal, GI, and rectal absorption. For most drugs,
Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual, buccal, GI, and rectal absorption. For most drugs,
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin
 Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet Formulation by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique
 Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation
 METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs
 Mansoura University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs Thesis presented by Ali Saeed
Mansoura University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs Thesis presented by Ali Saeed
Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery System
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation
 Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 1934-1942 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS K. VENUGOPAL * and K. P. R. CHOWDARY a Nirmala College
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 1934-1942 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS K. VENUGOPAL * and K. P. R. CHOWDARY a Nirmala College
ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE
 PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
A COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ACPI Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 3(2), 2013, 149-164 ISSN 2277-288X A COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM MARINAGANTI RAJEEV KUMAR *, BONTHU SATYANARAYANA, NAGAKANYAKA DEVI PALADUGU,
ACPI Acta Chim. Pharm. Indica: 3(2), 2013, 149-164 ISSN 2277-288X A COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM MARINAGANTI RAJEEV KUMAR *, BONTHU SATYANARAYANA, NAGAKANYAKA DEVI PALADUGU,
FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels
 Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Chapter 2 Rationale and Objective
 Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery Tablet
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
Ph. D Synopsis. Mr. Mehul Pravinchandra Patel Page 1
 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS: OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE
 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS: OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE S. PRATHYUSHA 1, Y. MOHAN KUMAR 2, D. LAVANYA 3, M. KIRAN KUMAR 4 1 M.pharm, Department of pharmacognosy, Tirupathi,
PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRO RETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS: OF QUETIAPINE FUMARATE S. PRATHYUSHA 1, Y. MOHAN KUMAR 2, D. LAVANYA 3, M. KIRAN KUMAR 4 1 M.pharm, Department of pharmacognosy, Tirupathi,
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release. Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy
 Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING
 SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING Dr. Dieter Lubda MilliporeSigma is a business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Agenda: Sustained release
SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING Dr. Dieter Lubda MilliporeSigma is a business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Agenda: Sustained release
FORMULATION AND EVALUATIONOF AMOXYCILLIN: THREE-LAYER GUAR GUM MATRIX TABLET
 Gupta and Singh, IJPSR, 2013; Vol. 4(7): 2683-2690. ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received on 05 March, 2013; received in revised form, 29 April, 2013; accepted, 29 June,
Gupta and Singh, IJPSR, 2013; Vol. 4(7): 2683-2690. ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received on 05 March, 2013; received in revised form, 29 April, 2013; accepted, 29 June,
Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H.
 Pharmaceutical Research Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H. pylori Infection Shikha Jain, Vikas Jain, S.C. Mahajan
Pharmaceutical Research Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H. pylori Infection Shikha Jain, Vikas Jain, S.C. Mahajan
FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF FAMOTIDINE FLOATING TABLETS BY LIPID SOLID DISPERSION SPRAY DRYING TECHNIQUE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF FAMOTIDINE FLOATING TABLETS BY LIPID SOLID DISPERSION
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article FORMULATION AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF FAMOTIDINE FLOATING TABLETS BY LIPID SOLID DISPERSION
Factors responsible for the impaired bioavailability and instability rifampicin FDC
 Table of contents 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Oral multiparticulate drug delivery system...2 1.2 Methods of preparing pellets...3 1.3 Extrusion-spheronization...3 1.4 Theory of pellet formation and growth...4
Table of contents 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Oral multiparticulate drug delivery system...2 1.2 Methods of preparing pellets...3 1.3 Extrusion-spheronization...3 1.4 Theory of pellet formation and growth...4
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept ISSN FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL
 Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Gastro retentive Drug Delivery System: A Review
 Volume 1, issue1 (2011), 01-13 Review Article International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences Gastro retentive Drug Delivery System: A Review Shivram Shinde*, Imran Tadwee, Sadhana Shahi
Volume 1, issue1 (2011), 01-13 Review Article International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences Gastro retentive Drug Delivery System: A Review Shivram Shinde*, Imran Tadwee, Sadhana Shahi
Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets of lisinopril
 Journal of GROVER Scientific & Industrial AGARWAL: Research FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUBLINGUAL TABLETS OF LISINOPRIL Vol. 71, June 2012, pp. 413-417 413 Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets
Journal of GROVER Scientific & Industrial AGARWAL: Research FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUBLINGUAL TABLETS OF LISINOPRIL Vol. 71, June 2012, pp. 413-417 413 Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets
EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH
 ejpmr, 2015,2(4), 185-203 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.ejpmr.com Vishvesh et al. SJIF Impact Factor 2.026 Review Article ISSN 3294-3211 EJPMR RAFT FORMING TABLETS: A NOVEL
ejpmr, 2015,2(4), 185-203 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.ejpmr.com Vishvesh et al. SJIF Impact Factor 2.026 Review Article ISSN 3294-3211 EJPMR RAFT FORMING TABLETS: A NOVEL
Formulation And Evaluation Of Flurbiprofen Matrix Tablets For Colon Targeting
 Formulation And Evaluation Of Flurbiprofen Matrix Tablets For Colon Targeting Biresh Kumar Sarkar* 1, Devananda Jain 1, Mamta Parwal 2 1. Bhagwant University, Dept.of Pharmaceutical Tech and Sciences,
Formulation And Evaluation Of Flurbiprofen Matrix Tablets For Colon Targeting Biresh Kumar Sarkar* 1, Devananda Jain 1, Mamta Parwal 2 1. Bhagwant University, Dept.of Pharmaceutical Tech and Sciences,
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al.6 (2007), Chaudhari et al.7 (2011), Sivabalan M et al.8 (2011), Punitha et al.9 (2010), Patel et al.
 1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al. 6 (2007), prepared floating tablets of famotidine by using Methocel K 15 M and Methocel K 100 M as gel forming agent and combination of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate
1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al. 6 (2007), prepared floating tablets of famotidine by using Methocel K 15 M and Methocel K 100 M as gel forming agent and combination of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate
Formulation and evaluation of immediate release salbutamol sulphate
 5 Formulation, optimization and evaluation of immediate release layer of salbutamol sulphate Salbutamol is moderately selective beta (2)-receptor agonist similar in structure to terbutaline and widely
5 Formulation, optimization and evaluation of immediate release layer of salbutamol sulphate Salbutamol is moderately selective beta (2)-receptor agonist similar in structure to terbutaline and widely
A STUDY ON SUITABILITY OF NIMESULIDE-BETACYCLODEXTRIN COMPLEX IN ORAL AND TOPICAL DOSAGE FORMS
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 1, Suppl 1, Nov.-Dec. 2009 Research Article A STUDY ON SUITABILITY OF NIMESULIDE-BETACYCLODEXTRIN COMPLEX IN ORAL AND TOPICAL DOSAGE
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 1, Suppl 1, Nov.-Dec. 2009 Research Article A STUDY ON SUITABILITY OF NIMESULIDE-BETACYCLODEXTRIN COMPLEX IN ORAL AND TOPICAL DOSAGE
Scholars Research Library. Formulation and evaluation of buccoadhesive tablet of Atenolol
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS. Tablets
 March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester
 University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
Formulation and Evaluation
 Chapter-5 Formulation and Evaluation 5.1 OBJECTIVE After successful taste masking and solubility enhancement of drugs in preliminary studies, by using Mannitol Solid Dispersion, next step includes the
Chapter-5 Formulation and Evaluation 5.1 OBJECTIVE After successful taste masking and solubility enhancement of drugs in preliminary studies, by using Mannitol Solid Dispersion, next step includes the
D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper
 D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper Introduction This background paper is intended to provide a basic rationale for initial formulation efforts, and define some of the terminology
D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper Introduction This background paper is intended to provide a basic rationale for initial formulation efforts, and define some of the terminology
Is the science that study relation of physicochemical properties of drug, dosage form, & route of administration on rate and extent of drug
 Chapter 5 Is the science that study relation of physicochemical properties of drug, dosage form, & route of administration on rate and extent of drug absorption. It is the study of the kinetics of absorption,
Chapter 5 Is the science that study relation of physicochemical properties of drug, dosage form, & route of administration on rate and extent of drug absorption. It is the study of the kinetics of absorption,
