Iron deposits in the knee joints of a thalassemic patient
|
|
|
- Berenice Henderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Iron deposits in the knee joints of a thalassemic patient The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Economides, Charalambos P, Elpidoforos S Soteriades, Michalis Hadjigavriel, Ioannis Seimenis, and Apostolos Karantanas Iron deposits in the knee joints of a thalassemic patient. Acta Radiologica Short Reports 2 (1): doi: / dx.doi.org/ / Published Version doi: / Citable link Terms of Use This article was downloaded from Harvard University s DASH repository, and is made available under the terms and conditions applicable to Other Posted Material, as set forth at nrs.harvard.edu/urn-3:hul.instrepos:dash.current.terms-ofuse#laa
2 Case report Iron deposits in the knee joints of a thalassemic patient Charalambos P Economides 1,2, Elpidoforos S Soteriades 1,3, Michalis Hadjigavriel 4, Ioannis Seimenis 5 and Apostolos Karantanas 6 1 Cyprus Institute of Biomedical Sciences (CIBS), Nicosia, Cyprus; 2 Agios Therissos MRI Diagnostic Center, Department of MRI, Nicosia, Cyprus; 3 Harvard School of Public Health, Department of Environmental Health, Environmental and Occupational Medicine and Epidemiology (EOME), Boston, MA, USA; 4 Limassol General Hospital, Department of Internal Medicine, Limassol, Cyprus; 5 Democritus University of Thrace, Medical School, Laboratory of Medical Physics, Alexandroupoli, Greece; 6 University of Crete, Department of Medical Imaging, Heraklion-Crete, Crete Correspondence to: Charalambos P Economides. ceconomides@cibs.org.cy Abstract The overall prognosis for patients with b-thalassemia has improved considerably during the past decades mainly due to regular blood transfusions, improvements in chelation therapy, and enhanced surveillance with imaging studies examining iron overload and other clinical complications. However, the prolonged survival of these patients leads to the development of other health problems including degenerative diseases such as arthropathies, which require further attention since they have a significant impact on the quality of life. In the current case report, we present a 45-year-old white man with b-thalassemia complaining of non-traumatic pain and restriction in the range of motion of both knees. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a tear in the medial meniscus of the left knee as well as iron deposits in both knees. Histological findings confirmed the presence of hemosiderin in both joints. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of macroscopically documented iron deposits in the knee joints of a patient with b-thalassemia using MRI. Keywords: MR imaging, knee, arthritides, hematologic diseases Submitted October 7, 2012; accepted for publication January 15, 2013 Patients with thalassemia constitute a significant public health problem. Providing comprehensive care to such patients has been viewed by many as a sensitive indicator of the level and quality of healthcare services in each country. Blood transfusions and iron overload of liver, spleen, and heart and their associated complications have received considerable attention by clinicians and researchers alike due to their significant impact on morbidity and mortality of these patients (1, 2). However, as the above problems have gradually been studied and appropriate therapies have been introduced in a relatively successful fashion, contributing to a dramatic increase of patients overall survival, other health problems affecting quality of life eventually may require further attention. Such problems may be associated with aging and/or degenerative processes, which appear to have an accelerated pace in patients with b-thalassemia or may also be related to iron deposits in other organs including pancreas, pituitary gland, and joints (3, 4). Arthropathy is one of the emerging chronic health problems affecting a significant number of patients with b-thalassemia, which, so far, has received limited attention by the scientific, clinical, and public health community (2, 5 7). Although magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been regularly utilized in assessing iron deposits in liver, spleen, and heart and to a lesser extent in pancreas and pituitary gland, no studies have, to date, been published on the assessment of possible iron deposits in joints of patients with b-thalassemia (1, 3, 4, 8). Case report A 45-year-old white man with b-thalassemia major was referred for MRI of the left knee due to prominent nontraumatic chronic medial and lateral pain ( past 1 2 years), as well as partial locking and restriction in the range of motion. Neither previous nor recent traumatic knee injury nor other suspicious events were reported. The patient had been undergoing regular blood transfusions twice a month maintaining a hemoglobin level of about 9.5 mg/dl and a ferritin level of 3000 ng/ml. The patient reported receiving chelation therapy with only oral deferiprone for Acta Radiologica Short Reports 2013:1. DOI: /
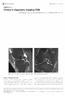
3 2 CP Economides et al. Table 1 Time trends of T2 measurements of liver and heart Mean T2 (ms) Organ Liver Heart Iron deposits assessed by T2 liver measurements range from mild to moderate severity. Liver measurements were obtained from a region of interest prescribed in the segment V/VIII of the right liver lobe Iron deposits assessed by T2 heart measurements range from normal to moderate severity. Heart measurements were obtained from a region of interest prescribed in the intraventricular region Fig. 1 A fat-suppressed, PD-w image in the coronal plane of the left knee shows a longitudinal tear in the body of medial meniscus (long arrow) and the displaced meniscal fragment within the intercondylar notch (short arrow). In addition, osteoarthritic changes with minimal subcortical cyst formations and reactive bone marrow edema are noted in the medial tibial plateau (open arrow) the past 13 years at a dose of 75 mg/kg/day. Occasional chelation with desferioxamine was also used during the same time period. T2 measurements from previous MRI examinations on heart and liver are presented in Table 1. It was evident from the decreasing T2 measurements of heart and liver, that there was progressive increase in the degree of iron deposits in the above two organs in parallel with clinical observations of poor adherence to chelation therapy compatible with high levels of plasma ferritin. Following regular assessment, the patient underwent MRI of the left knee. Subsequent MR scanning of the right knee was also performed for comparison purposes. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this manuscript and accompanying images. MRI technique MRI was performed with a 3.0 Tesla scanner (Achieva, Philips Medical Systems, Best, The Netherlands) to assess Fig. 2 (a) A T2 -w sagittal image in the left knee represents foci of iron deposits within the supra patellae pouch right above the superior pole of the patellae (short arrow) and also in contact with the patellae cartilage at the upper pole (long arrow), as well as within the Hoffa s fat pad in contact with the patellae cartilage in its inferior pole (open arrow) and in the cartilage surface over the trochlea (doted arrow). (b) A fat-suppressed PD-w image in the sagittal plane in the left knee shows foci of iron deposition along the surface of the cartilage over the lateral trochlea (short arrow). We note the drop of signal in the area of iron deposits, which is less prominent in comparison with the corresponding T2 -w image arthropathy including potential iron deposits in the knee joints. We used the built-in quadrature radiofrequency (RF) body coil and a phased array 8-channel knee coil for proton excitation and signal detection, respectively. MRI scanning protocol included several multislice pulse sequences routinely performed for morphological imaging
4 Iron deposits in the knee joints of a thalassemic patient 3 Fig. 3 This image represents four corresponding axial images from different pulse sequences of the left knee. (a) is a T2 -w image, (b) is an ultra short time echo (UTE) image, (c) was obtained with susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI), and (d) represents PD-w imaging with a turbo spin echo sequence. In (a), we note a large area of iron deposit in contact with the patellae and trochlea groove cartilage presented as a low signal intensity focus (arrow). In (b) and (c) we highlight a further exaggeration of the signal loss in the area of iron deposits on the UTE and SWI sequences, respectively (arrows). In (d) we note less conspicuous signal loss of the iron deposit area in the PD-w sequence (arrow) (in each case, 28 slices were acquired with a field-of-view of 170 mm, a section thickness of 2.8 mm, and a pixel size of mm); T1-weighted (T1-w) (repetition time [TR], 674 ms; echo time [TE], 18 ms; total scan time [ST], 2.5 min) turbo spin echo (TSE) in the sagittal plane; T2 -weighted (T2 -w) (TR, 575 ms; TE, 12 ms; ST, 2.4 min) gradient recalled echo (GRE) in the axial plane; proton density-weighted (PD-w) (TR, 2342 ms; TE, 35 ms; ST, 2.9 min) TSE with spectral fat suppression in the coronal and axial planes. Three-dimensional (3D) susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) and ultra short echo time (UTE) GRE pulse sequences were also prescribed in the axial plane. The former utilizes an echo-shifting technique that allows the employment of relatively long echo times (TE, 21 ms) in a time-efficient way (TR, 15 ms; ST, 1.5 min for 100 slices with an acquisition resolution of mm). The latter uses a radial data sampling technique achieving an ultra short TE of 14 ms (TR, 7.5 ms; ST, 9.8 min; 144 slices; 1 mm 3 acquisition voxel size). The sequence used for quantitative T2 measurements was also prescribed in the sagittal plane. A single-slice (acquisition voxel size of mm) Carr Purcel Meibomm Gill (CPMG) spin echo sequence employing 16 equidistant echoes, a short echo spacing of 6 ms and a TR of 2s was used (ST, 5.7 min). MRI findings in the left knee Left knee MR images revealed several pathological findings compatible with the prominent clinical symptomatology. The imaging findings included a flap tear of the medial meniscus with a displaced meniscal fragment in the medial intercondylar notch (Fig. 1). In addition, osteoarthritis was noted in the medial joint compartment with marked attenuation of the articular cartilage, reactive subcortical bone marrow edema in the medial tibial plateau, and minimal subcortical cystic changes (Fig. 1). Furthermore, there was mild attenuation of the patellar cartilage indicating chondromalacia patellae grade II. Foci of iron deposits were identified macroscopically within the supra-patellar pouch right above the superior pole of the patellae and also in contact with the patellae cartilage at the upper pole, as well as within the Hoffa s fat pad in contact with the patellae cartilage in its inferior pole and in the cartilage surface over the trochlea (Fig. 2a). Finally, iron deposits were also noted along the surface of the medial plica in the supra-patellar pouch. The iron deposits were detected as low signals intensity foci in all MRI sequences used. However, iron deposits were less conspicuous on the T1-w and PD-w sequences, with particular signal loss on gradient echo (Fig. 2B). During the above study we
5 4 CP Economides et al. Table 2 Measurements of T2 in different areas of the cartilage of the left knee Mean T2 (SD) (ms) Articular surface (lateral femoral condyle) Articular surface (lateral tibial plateau) Lateral Patella trochlea Time (ms) 60 (11.5) 79 (8.8) 63 (18.6) 40 (8.9) also noticed further exaggeration of the signal loss on the SWI and UTE sequences (Fig. 3). In Table 2 we present mean T2 measurements for regions of interest prescribed in different areas of the cartilage in the left knee. The T2 measurement of normal Hoffa s fat pad was 215 ms (18.8 SD), while in Hoffas fat pad with iron deposits T2 measurement was 54.8 ms (11 SD) and in the supra-patellar pouch with iron deposits T2 was 51.1 ms (4.4 SD), respectively. Such findings indicate iron deposits in the above regions with decreased T2 measurements. MRI of the right knee was also performed mainly for comparison purposes. Iron deposits were also noted in the right knee (Fig. 4). Iron deposits were noted in contact with the inferior pole of the patellar cartilage, as well as in contact with the anterior articular surface of the lateral femoral condyle. Histology results Following MRI studies, the patient underwent an arthroscopy of the left knee in order to explore the pathological imaging findings and repair the meniscal tear. Biopsy of the synovium showed edema of the basal membrane with papillary morphology and hemosiderin deposits. Histiocytes with hemosiderin moieties were also noted along with hyperplastic serous cells. Discussion To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of iron deposits in the knee joint of a patient with b-thalassemia major potentially associated with clinical symptoms. Our case report poses an important question regarding the prevalence of iron deposits in knee and other major joints of patients with b-thalassemia major, especially those of the lower extremities. In addition, this particular case raises further clinical concerns as to whether iron deposits in joints may be associated with clinical arthropathy in such patients. Furthermore, we pose a scientific question on the potential association of iron deposits in joints leading to the development of synovitis and/or cartilage damage (2, 5 7). Finally, our findings lead to significant clinical questions with respect to the effectiveness of the traditional chelation therapy to remove iron deposits from the joints of patients with b-thalassemia. The examination of our case was facilitated by MRI techniques based on the GRE method that allow the visualization of small foci of iron deposits. Such techniques include Fig. 4 AT2 -w sagittal image of the right knee obtained with a gradient recalled echo (GRE) pulse sequence. Iron deposits are noted in contact with the inferior pole of the patellae cartilage (short arrow), as well as in contact with the anterior cartilage surface of the lateral femoral condyle (long arrow) the traditional T2 -w as well as the novel UTE and SWI methods (9). The high sensitivity of the UTE pulse sequence to iron is due to the ultra short echo time that employs, which allows visualization of short T2 species. SWI is also a relatively new MRI sequence, which evaluates and exploits the magnetic properties of tissues. Paramagnetic substances like deoxyhemoglobin, a product of blood degradation, and ferritin, a non-heme iron, are known sources of magnetic susceptibility in the tissues and they appear as hypointense foci. Albeit the high sensitivity of UTE and SWI sequences in the detection of iron deposits, CPMG and GRE sequences are more suited for quantitative imaging in tissues, since the presence of paramagnetic species reduce regional transverse relaxation times. Therefore, T2 and T2 measurements are widely used for liver and heart iron load evaluation. As UTE and SWI are much more sensitive at lower concentrations of iron, they can be used to detect small foci of iron deposits that conventional spin echo and GRE pulse sequences fail to depict. In addition, because of their 3D nature, UTE and SWI offer the possibility of rigorous and thorough inspection of the joint for iron. Thus, they can effectively guide the correct prescription of the single-slice sequences used for quantitative transverse relaxation time measurements. Due to the negative contrast effect of iron foci, a major challenge is to distinguish regions of signal void due to iron from those due to low signal tissues or susceptibility artifacts. Therefore, T2 measurements were only performed at regions which appeared hypointense in both UTE and SWI images. MRI and the documented pathological picture of the left knee, excluding the meniscal flap tear, showed advanced
6 Iron deposits in the knee joints of a thalassemic patient 5 degenerative changes, which are thought to be noncompatible with the patient s age and clinical history. This is an interesting finding in view of the macroscopically noted iron deposits and the poor adherence to chelation therapy. Further studies are warranted in order to examine the prevalence of iron deposits in the joints of patients with b-thalassemia and their potential association with accelerated degenerative changes especially in the lower extremities. In addition, there should be enhanced clinical interest on the evaluation of the effectiveness of chelation therapy for removing iron deposits from joints in a similar fashion with other organs such as liver and heart. Our case report, although raising important epidemiological and clinical questions, may not be representative of the majority of patients with b-thalassemia in the developed countries, where patients may adhere to chelation therapy, since the particular patient had a poor adherence to chelation treatment. An additional limitation of our case may be associated with our inability to dissociate the documented clinical pathology in the knee joint with the degenerative changes and allocate potential partial etiology to iron deposits. Although the case is an interesting example of iron deposits in knee joints, the causal relationship with arthropathy/meniscal rupture documented with MRI and arthroscopy is purely speculative. Further epidemiological studies with case series, case-control, and cohort studies are warranted to explore the above scientific questions. In conclusion, our case report highlights a new and emerging chronic problem of patients with b-thalassemia; namely arthropathy, which may be potentially related to accelerated degenerative changes in the joints of the above patients in association with iron deposits. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors thank Philips Medical Systems Inc., Best, The Netherlands for their kind provision of the ultra short TE pulse sequence. REFERENCES 1 Anderson LJ, Westwood MA, Prescott E, et al. Development of thalassaemic iron overload cardiomyopathy despite low liver iron levels and meticulous compliance to desferrioxamine. Acta Haematol 2006;115: Chan Y, Li C, Chu WC, et al. Deferoxamine induced bone dysplasia in the distal femur and patella of pediatric patients and young adults: MR Imaging Appearance. Am J Roentgenol 2000;175: Anderson LJ, Westwood MA, Holden S, et al. Myocardial iron clearance during reversal of siderotic cardiomyopathy with intravenous desferrioxamine: a prospective study using T2 cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Br J Haematol 2004;127: de Assis RA, Ribeiro AA, Kay FU, et al. Pancreatic iron stores assessed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in beta thalassemic patients. Eur J Radiol 2012;81: Chand G, Chowdhury V, Manchanda A, et al. Deferiprone-induced arthropathy in thalassemia: MRI findings in a case. Indian J Radiol Imaging 2009;19: Berkovitch M, Laxer RM, Inman R, et al. Arthropathy in thalassemia patients receiving deferiprone. Lancet 1994;343: Kellenberger JC, Schmugge M, Saurenmann T. Radiographic and MRI features of deferiprone related arthtropathy of the knees in patients with b- thalassaemia. Am J Roentgenol 2004;182: Noetzli LJ, Panigrahy A, Mittelman SD, et al. Pituitary iron and volume predict hypogonadism in tranfusional iron overload. Am J Hematol 2011 Nov 4 [Epub ahead of print] 9 Hall-Craggs MA, Porter J, Gatehouse PD, et al. Ultrashort echo time (UTE) MRI of the spine in thalassaemia. Br J Radiol 2004;77: # 2013 The Foundation Acta Radiologica This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( org/licenses/by-nc/2.0/), which permits non-commercial use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies
 Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Part II: MRI v. Metal
 Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know.
 Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A
 Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Personalized Solutions. MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides
 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides 2 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides Purpose and Summary This protocol is applicable for the Zimmer Biomet
Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides 2 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides Purpose and Summary This protocol is applicable for the Zimmer Biomet
MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after competition
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Clinical Applications
 C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System
 MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
Imaging of Articular Cartilage
 Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
Functional Orthopedic Imaging Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion. Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy.
 Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion dynamic volume CT Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2013. All rights reserved.
Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion dynamic volume CT Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2013. All rights reserved.
Available online at
 Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma
 Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Case study #11 Rt. knee
 The patient is a 55 year old female who presents with bilateral knee pain. Patient is a collegiate softball coach and has a very active lifestyle and career that is hampered by her chronic knee pain. She
The patient is a 55 year old female who presents with bilateral knee pain. Patient is a collegiate softball coach and has a very active lifestyle and career that is hampered by her chronic knee pain. She
Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR Imaging
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA
 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
Oak foundation for donating the 3T Siemens Verio scanner. Board of directors BBH and Frh Hospitals for supporting the
 Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel
 ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA
 Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA Meniscal Tears -linear increased signal extending to an articular surface is the hallmark
Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA Meniscal Tears -linear increased signal extending to an articular surface is the hallmark
KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol
 KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol Sample referral sticker Referral Sticker Insert here Corin 17 Bridge Street Pymble NSW Australia 2073 P: +61 (0)2 9497 7400 F: +61 (0)2 9497 7498 E: KAS.customerservice@coringroup.com
KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol Sample referral sticker Referral Sticker Insert here Corin 17 Bridge Street Pymble NSW Australia 2073 P: +61 (0)2 9497 7400 F: +61 (0)2 9497 7498 E: KAS.customerservice@coringroup.com
醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 肌肉骨骼磁振造影. 本週課程內容 General Technical Considerations 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系
 本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI of the musculoskeletal system (5th/6th edition) Editor: Thomas H. Berquist MD 2 General
本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI of the musculoskeletal system (5th/6th edition) Editor: Thomas H. Berquist MD 2 General
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis
 In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
MR Advance Techniques. Cardiac Imaging. Class III
 MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class III Black Blood Imaging & IR Blue= O2 poor blood Red=O2 rich blood Inversion pulses can produce black blood imaging in GRE pulse sequences. Specially on the
MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class III Black Blood Imaging & IR Blue= O2 poor blood Red=O2 rich blood Inversion pulses can produce black blood imaging in GRE pulse sequences. Specially on the
Unlocking the locked Knee
 Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2023/14
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2023/14 BEFORE: A. T. Patterson: Vice-Chair HEARING: November 3, 2014 at Toronto Oral DATE OF DECISION: April 17, 2015 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2015
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2023/14 BEFORE: A. T. Patterson: Vice-Chair HEARING: November 3, 2014 at Toronto Oral DATE OF DECISION: April 17, 2015 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2015
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls
 Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
MRI of Cartilage. D. BENDAHAN (PhD)
 MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
MENISCAL INJURY. Meniscus. Anterior Roots. Medial Meniscus. Lateral Meniscus. Posterior Roots. MRI and Arthroscopic Findings
 Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Disclosures. Background. Background
 Kinematic and Quantitative MR Imaging Evaluation of ACL Reconstructions Using the Mini-Two Incision Method Compared to the Anteromedial Portal Technique Drew A. Lansdown, MD Christina Allen, MD Samuel
Kinematic and Quantitative MR Imaging Evaluation of ACL Reconstructions Using the Mini-Two Incision Method Compared to the Anteromedial Portal Technique Drew A. Lansdown, MD Christina Allen, MD Samuel
Why measure heart iron?
 Why measure heart iron? It predicts impending cardiac dysfunction. It predicts noncardiac complications It cannot be inferred by measurements of liver iron Heart iron loading occurs occultly in patients
Why measure heart iron? It predicts impending cardiac dysfunction. It predicts noncardiac complications It cannot be inferred by measurements of liver iron Heart iron loading occurs occultly in patients
Original Research JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22: (2005)
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
Meniscal Tears: Role of Axial MRI Alone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes
 Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Original Research JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 29: (2009)
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 29:853 859 (2009) Original Research Assessment of Iron Distribution Between Liver, Spleen, Pancreas, Bone Marrow, and Myocardium by Means of R2 Relaxometry With MRI
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 29:853 859 (2009) Original Research Assessment of Iron Distribution Between Liver, Spleen, Pancreas, Bone Marrow, and Myocardium by Means of R2 Relaxometry With MRI
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries
 Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils
 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils Elena Ferrer 1 ; Rafael Coronado Santos 2 1 Radiology Department, Clínica Creu Blanca, Barcelona,
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils Elena Ferrer 1 ; Rafael Coronado Santos 2 1 Radiology Department, Clínica Creu Blanca, Barcelona,
Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee
 Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia
 MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
MRI of the Knee: Part 4 - normal variants that may simulate disease Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia discuss the most common normal variants in the pediatric knee that may simulate pathology
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
How Much Tesla Is Too Much?
 How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
Knee: Cruciate Ligaments
 72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN. David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging
 MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
Are radiographs needed when MR imaging is performed for non-acute knee symptoms in patients younger than 45 years of age?
 Skeletal Radiol (2007) 36:1129 1139 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0384-5 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Are radiographs needed when MR imaging is performed for non-acute knee symptoms in patients younger than 45 years of
Skeletal Radiol (2007) 36:1129 1139 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0384-5 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Are radiographs needed when MR imaging is performed for non-acute knee symptoms in patients younger than 45 years of
Benjamin E. Plotkin, M.D., Vishal K. Agarwal, M.D., and Rajeev Varma, M.D.
 Stump Entrapment of the Torn Anterior Cruciate Ligament Benjamin E. Plotkin, M.D., Vishal K. Agarwal, M.D., and Rajeev Varma, M.D. Citation: Plotkin BE, Agarwal VK, Varma R. Stump Entrapment of the Torn
Stump Entrapment of the Torn Anterior Cruciate Ligament Benjamin E. Plotkin, M.D., Vishal K. Agarwal, M.D., and Rajeev Varma, M.D. Citation: Plotkin BE, Agarwal VK, Varma R. Stump Entrapment of the Torn
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
Traumatic Patellar Dislocation and Cartilage Injury A Follow- Up Study of Long-Term Cartilage Deterioration
 Traumatic Patellar Dislocation and Cartilage Injury A Follow- Up Study of Long-Term Cartilage Deterioration Salonen EE 1 M.D., Magga T 2 M.D., Sillanpää PJ 3 M.D. Ph.D., Kiekara T 2 M.D., Ph.D., Mäenpää
Traumatic Patellar Dislocation and Cartilage Injury A Follow- Up Study of Long-Term Cartilage Deterioration Salonen EE 1 M.D., Magga T 2 M.D., Sillanpää PJ 3 M.D. Ph.D., Kiekara T 2 M.D., Ph.D., Mäenpää
Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears
 Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are difficult to diagnose and treat (DeFranco). The preoperative
Comparative study of sensitivity and specificity of MRI versus GNRB to detect ACL complete and partial tears Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are difficult to diagnose and treat (DeFranco). The preoperative
Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study
 Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study Ashraf Elmansori, Timothy Lording, Raphaël Dumas, Khalifa Elmajri, Philippe Neyret, Sebastien
Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study Ashraf Elmansori, Timothy Lording, Raphaël Dumas, Khalifa Elmajri, Philippe Neyret, Sebastien
Medial tibial condyle friction syndrome: MRI study of a new entity
 Medial tibial condyle friction syndrome: MRI study of a new entity Poster No.: C-0420 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Klontzas, I. Akoumianakis, I. Vagios, A. H.
Medial tibial condyle friction syndrome: MRI study of a new entity Poster No.: C-0420 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Klontzas, I. Akoumianakis, I. Vagios, A. H.
Imaging the Athlete s Knee. Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado
 Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process
 ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
BASELINE QUESTIONNAIRE (SURGEON)
 SECTION A: STUDY INFORMATION Subject ID: - - Study Visit: Baseline Site Number: Date: / / Surgeon ID: SECTION B: INITIAL SURGEON HISTORY B1. Previous Knee Surgery: Yes No Not recorded B2. Number of Previous
SECTION A: STUDY INFORMATION Subject ID: - - Study Visit: Baseline Site Number: Date: / / Surgeon ID: SECTION B: INITIAL SURGEON HISTORY B1. Previous Knee Surgery: Yes No Not recorded B2. Number of Previous
Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients
 Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study
 Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration
 Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Comparison between different software programs and techniques for liver iron concentration assessment with MRI in thalassemic patients
 Comparison between different software programs and techniques for liver iron concentration assessment with MRI in thalassemic patients Poster No.: C-1580 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Comparison between different software programs and techniques for liver iron concentration assessment with MRI in thalassemic patients Poster No.: C-1580 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
The mandibular condyle fracture is a common mandibular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
Publication for the Philips MRI Community
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 Pediatric MSK imaging benefits from tailored scan protocols Vanderbilt University Children s Hospital builds dedicated scans
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 Pediatric MSK imaging benefits from tailored scan protocols Vanderbilt University Children s Hospital builds dedicated scans
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries. Laura W. Bancroft, M.D.
 Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference. Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16
 Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee. M Lucas Murnaghan MD, MEd, FRCSC
 Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee M Lucas Murnaghan MD, MEd, FRCSC Outline 1. Clinical Presentation 2. Investigations 3. Classification 4. Non-operative Treatment 5. Operative Treatment 6. Treatment
Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee M Lucas Murnaghan MD, MEd, FRCSC Outline 1. Clinical Presentation 2. Investigations 3. Classification 4. Non-operative Treatment 5. Operative Treatment 6. Treatment
Case 27 Clinical Presentation
 53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor
 MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
a - CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) !Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) CASE PRESENTATION
 !Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 283 CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) Wei Yang Liml, MBBS, FRCR, Nor Azam Mahmud2, MD, MMed, Wilfred CG Peh3, FRCP, FRCR a - - - Fig. 1 Sagittal
!Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 283 CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) Wei Yang Liml, MBBS, FRCR, Nor Azam Mahmud2, MD, MMed, Wilfred CG Peh3, FRCP, FRCR a - - - Fig. 1 Sagittal
High Field MR of the Spine
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
ACR MRI Accreditation Program. ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update. Educational Objectives. ACR accreditation. History. New Modular Program
 ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives Present requirements of the new
ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives Present requirements of the new
MRI of LEFT KNEE. There is a fluid collection seen anterior to and inferior to the superiorly displaced patella.
 MRI of LEFT KNEE Protocol: Multiplanar MRI of the left knee joint performed in the sagittal, coronal and transverse planes using T1 weighted spin echo, T2 and proton-density weighted fast spin echo, fatsaturated
MRI of LEFT KNEE Protocol: Multiplanar MRI of the left knee joint performed in the sagittal, coronal and transverse planes using T1 weighted spin echo, T2 and proton-density weighted fast spin echo, fatsaturated
Dimensions of the intercondylar notch and the distal femur throughout life
 Dimensions of the intercondylar notch and the distal femur throughout life Poster No.: P-0089 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Hirtler, S. Röhrich, F. Kainberger; Vienna/AT Keywords:
Dimensions of the intercondylar notch and the distal femur throughout life Poster No.: P-0089 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Hirtler, S. Röhrich, F. Kainberger; Vienna/AT Keywords:
Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 357463, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/357463 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation Aki Fukuda,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 357463, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/357463 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation Aki Fukuda,
Localized anterior arthrofibrosis (Cyclops lesion) with no history of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: MRI findings.
 Localized anterior arthrofibrosis (Cyclops lesion) with no history of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: MRI findings. Poster No.: P-0145 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L.
Localized anterior arthrofibrosis (Cyclops lesion) with no history of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: MRI findings. Poster No.: P-0145 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L.
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 1081e1085 ª 2006 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.05.011 MRI of bone marrow
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 1081e1085 ª 2006 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.05.011 MRI of bone marrow
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These bones are supported by a large
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These bones are supported by a large
D. Doré 1, C. Ding 1,2, J.P. Pelletier 3, J. Martel-Pelletier 3, F. Cicuttini 2, G. Jones 1.
 Responsiveness of qualitative and quantitative MRI measures over 2.7 years D. Doré 1, C. Ding 1,2, J.P. Pelletier 3, J. Martel-Pelletier 3, F. Cicuttini 2, G. Jones 1. 1 Menzies Research Institute Tasmania,
Responsiveness of qualitative and quantitative MRI measures over 2.7 years D. Doré 1, C. Ding 1,2, J.P. Pelletier 3, J. Martel-Pelletier 3, F. Cicuttini 2, G. Jones 1. 1 Menzies Research Institute Tasmania,
Where to Draw the Line:
 Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans
 Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans Ting Song 1, Jing An 2, Qun Chen 2, Vivian Lee 2, Andrew Laine 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans Ting Song 1, Jing An 2, Qun Chen 2, Vivian Lee 2, Andrew Laine 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
Sport Specific MRI. The symptoms of the majority, if not all sports injuries are experienced when upright, and weight-bearing
 Sport Specific MRI The symptoms of the majority, if not all sports injuries are experienced when upright, and weight-bearing A complete, accurate MRI assessment can only be made when in the position of
Sport Specific MRI The symptoms of the majority, if not all sports injuries are experienced when upright, and weight-bearing A complete, accurate MRI assessment can only be made when in the position of
LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION
 LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION R. ŚMIGIELSKI, B. DOMINIK, U, ZDANOWICZ, Z. GAJEWSKI, K. SKIERBISZEWSKA, K. SIEWRUK,
LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION R. ŚMIGIELSKI, B. DOMINIK, U, ZDANOWICZ, Z. GAJEWSKI, K. SKIERBISZEWSKA, K. SIEWRUK,
Bilateral Simultaneous Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury: A Case Report and National Survey of Orthopedic Surgeon Management Preference
 Bilateral Simultaneous Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury: A Case Report and National Survey of Orthopedic Surgeon Management Preference The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Bilateral Simultaneous Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury: A Case Report and National Survey of Orthopedic Surgeon Management Preference The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
