Dorsal Digital Expansion Of Thumb
|
|
|
- Leslie Dennis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
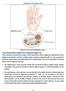
1 Dorsal Digital Expansion Of Thumb Joshi, S.S., Joshi, S.D., Aavale S.A., Kishve, P. S. and Jadhav S.D. Rural Medical College,Pravara Institute of Medical Sciences, Loni Abstract: Human hands perform e complicated functions of gripping, pinching, feeling and expressing. All ese activities depend on e coordinated actions of e umb and e fingers. The functional importance and e complexity of movements of umb are well reflected in an extensive representation of umb in e brain. The extensor apparatus of umb displays obvious structural variations in its proximo-distal expanse. There is no unanimity amongst various auors on e anatomy of dorsal digital expansion (DDE) of umb. Some (Schafer et al, 1923; Sinnatamby, 1999) are of e view at ere is no extensor expansion of e umb. Variations are described in e contributions made by various elements which go into e formation of DDE. We have undertaken a detailed study of formation and attachment of DDE of umb in 110 upper limbs (Rt- 55, Lt-55) available in e department. DDE of umb was present in all e limbs examined. It was triangular in shape. The anchoring fibers were well defined in e form of a hood over e dorsal surface of metacarpophalangeal (MP) joint. Medial margin of e expansion was well defined in all e cases; whereas, e lateral margin was variably developed. In 68% of umbs e lateral margin of DDE was contributed by abductor pollicis brevis (APB) out of ese in 60% is margin was well defined. In 98% cases e oblique head of adductor pollicis (AP) contributed fibres to medial margin of DDE. In 62.7% fibres of first palmar interosseous could also be traced to e medial margin. The mechanism of DDE permits for greater variations in extension of various joints of umb en would have been possible in its absence. Key words: Thumb, dorsal digital expansion, extensor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, adductor pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis Introduction: The dorsal apparatus of e umb is very similar to e arrangement of e fibres of dorsal digital expansion (DDE) of any oer fingers but shows obvious structural variations in its proximo-distal expanse. DDE forms a movable hood like structure over e dorsum of metacarpophalangeal (MP) joints of e fingers. The extensor hood moves distal to e MP joint during flexion and proximally when extended. This mechanism permits greater variation in extension an would be possible if a single extensor tendon was used for each joint. DDE allows for extension of e interphalangeal (IP) joints when MP joints are flexed by e flexors. Going rough e literature we find at ere is no unanimity amongst e various auors about e presence and formation of DDE of umb. Schafer et al (1923) stated at ere is no extensor expansion on e umb. Similar view was expressed by Sinnatamby (1999). The muscles of e umb can be compared to e stays attached to a mobile articulated mast. They are in a state of balance from which movements are carried out by contraction of some and relaxation of oers. This complexity of movements is well reflected in an extensive representation of umb in e brain (Lamb, Hooper and Kuczyski, 1989). The dorsal expansion occasionally adheres to e collateral ligaments and us an important anchorage unites e extensor apparatus to e immobile flexor tunnel. The construction of DDE permits independent extension of e distal phalanx Correspondence to :- Dr. Joshi S.S. Department of Anatomy, Rural Medical College, Pravara Institute of Medical Sciences, Loni Dist: Ahmednagar (Maharashtra). 135 (DP) by traction applied by e various constituents forming e expansion. Bade et al (1995) while describing e fibrous architecture of dorsal aponeurosis of umb have stated at dorsal connective tissue of umb forms different layers of collagen lamellae as a peritendinous system around e tendons of extensor pollicis longus (EPL) and extensor pollicis brevis (EPB). In eir opinion is is an expression of different topographical zones of stress along e lines of a balanced musculofibrous stabilization of e IP joint of umb. As ere is no unanimity about e presence, mode of formation and contribution of various muscle elements in e formation of DDE of umb, a detailed study was undertaken in 110 upper limbs (Right-55; Left-55) to study e formation and variations of DDE. Variations in e attachment of two long extensors of umb and e contribution made by various small muscles of umb in e formation of DDE were also studied. Material And Meods : For e present study 110 upper limbs (Rt- 55; Lt-55) were dissected over a period of 3 years. The region of dorsum of umb was dissected carefully. The tendons of EPL and EPB were exposed from e wrist up to eir insertion and variations in eir mode of insertion were noted. The dorsal digital expansion over e MP joint was exposed and its shape and anchoring fibers were noted. Medial and lateral margins of e expansion were cleaned and contributions from various short muscles of umb were carefully seen. Observations : DDE was found as a well defined entity, triangular in shape present on e dorsum of proximal phalanx of umb in all e limbs examined
2 Dorsal Digital Expansion Of Thumb...Joshi, S.S., Joshi, S.D., Aavale S.A., Kishve, P. S. and Jadhav S.D. (fig.1a,b). The base was directed proximally covering e dorsal aspect of MP joint as a hood. Medial margin of expansion was very prominent and well defined. Fig. 1a: Shows a well defined triangular expansion i.e. dorsal digital expansion (DDE) of umb, its base is joined by e tendons of EPB and EPL; at e angles of e base it is laterally joined by APB and medially by AP. Red arrows indicate e lateral and medial borders of DDE. The apex of DDE which is broad is getting attached to dorsal surface of terminal phalanx. Fig. 1b: Same as in 1a but here EPB tendon is very narrow. As seen in Table no. I: in 98 % cases oblique head of adductor pollicis contributed fibres to e medial margin of e expansion (fig.1a,b). Its transverse head also gave fibres to e medial margin of DDE in about 8 % specimens examined. In 62.7 % fibres of first palmar interosseous could also be traced to e medial margin of expansion (fig.2 b). Fig. 2a: The well defined triangular DDE has been pulled backwards. Passing rough e centre of it e tendon of EPL can be easily visualized. Margins of DDE are well defined. Tendon of EPB, which is placed deep to EPL and DDE, is getting inserted on e dorsum of base of PP. A superficial slip from EPB is seen joining e deep surface of DDE (red arrow). Fig. 2b: In is photograph e contribution of first palmar interosseous (FPI) to e medial margin of DDE is seen clearly. Table No. I Showing contribution from various muscles in e formation of DDE of umb (in percent): Muscle Right Left Average Abductor pollicis brevis Adductor Oblique head pollicis Transverse head First Palmar interosseous In about 60.8 % (Rt-58.1 %; Lt-63.6 %) e lateral margin of expansion was well defined. Even when it was not well defined, in 68.2 % cases fibres of APB could be traced to e lateral margin (fig.1a,b). In a very small percentage (3.6 %) fibres of FPB joined e lateral margin of expansion. Tendon of EPL could be traced to DP in 98.2 % umbs studied. In 1.8 % it was getting attached to bo proximal phalanx (PP) and DP. In e present series EPB was present in all e hands and in approximately 58 % it was getting attached to PP, whereas in % it extended upto DP. In 14.6 % e tendon of EPB was getting attached to bo PP and DP (fig.3) (Table no. II). Fig. 3: The components of DDE viewed from lateral aspect. EPB is seen joining bo e deep surface of DDE and inserting on dorsal surface of base of PP. Contribution from APB to e DDE and e formation of lateral margin is distinctly seen. The insertion of DDE to e terminal phalanx is very broad (white arrow). 136
3 Dorsal Digital Expansion Of Thumb...Joshi, S.S., Joshi, S.D., Aavale S.A., Kishve, P. S. and Jadhav S.D. Table No. II Showing insertions of extensor tendons of umb (in percent): EPL EPB Right Left Average DP PP DP + PP DP PP DP + PP Discussion : Human umb plays a crucial role in e functioning of e hand, and us it has a proportionately larger representation in e brain compared to oer fingers. Group of intrinsic and extrinsic muscles bring about e various movements of umb. Due to e presence of a dorsal digital expansion it enjoys greater variation in extension an would have been possible if a single extensor tendon was used. There is no unanimity amongst various workers about e presence of dorsal digital expansion of umb. Some (Schafer et al, 1923; Sinnatamby, 1999) believe at ere is no such entity; whereas, e vast majority have described a dorsal expansion of umb; alough e mode of formation and e contributions made by various muscles varies. The dorsal digital expansion of umb is mainly formed by tendons of EPL and EPB receiving an extension from adductor pollicis on e ulnar side and APB on e radial side. In approximately 98% e tendon of EPL could be traced upto e DP where its attachment was broad. On e left it gave an additional slip to e PP in 1.8% cases, whereas in 3.6% on e right it terminated on e PP. In such cases it was e EPB at reached e DP. Spinner (1984) has described at e tendon of EPL widens over e PP and is inserted over e dorsum of base of DP. Lamb et al (1989) have stated at e EPL extends all e joints of umb and rotates e first metacarpal laterally at e same time. Owing to its oblique course and side to side displacement of about 10mm it can also adduct e umb in e late stages of its action. EPL also assists in extension and abduction of e wrist and in supination. Sometimes e tendon of EPL may be double, and e division may progress proximally. Spinner (1984) while describing e variations of EPL has shown e presence of additional extensor (extensor accessorius); at supernumery extensor from extensor digitorum may reinforce EPL. In some cases a supernumery muscle may divide to join EPL and extensor indices. He furer states at EPL is e most mobile of e digital extensors. It has 50 mm longitudinal excursion and 13 mm mediolateral translation. EPL is usually wider an EPB; however, occasionally ey may be equal in wid or rarely EPB may be slightly wider. Romanes (1978) and Spinner (1984) have described at EPL tendon replaces e dorsal part of capsule of MP joint and forms a triangular expansion by being joined by APB on e lateral side and adductor pollicis on e medial side. The expansion may be joined by tendon of EPB. Schafer et al (1923) while describing e two extensors of umb have stated at e two tendons lie side by side and do not insert into e expansion and at on e sides ey are joined by in membranes connected wi slips from APB, first palmar interosseous and oblique head of adductor pollicis. In e present series in 6 cases (5.4%) e tendon of EPL splitted into ree and in 27 cases (24.5%) it divided into two tendons before inserting into DP. Lamb et al (1989) while discussing EPB have stated at as is tendon approaches e first metacarpal from e radial side, it can bring about abduction at CM joint of umb. It is inserted on e dorsal aspect of base of proximal phalanx and helps to replace e dorsal capsule of MP joint. Its superficial fibres continue distally along e lateral margin of EPL to reach e base of DP. It may be absent in 5% people or may have multiple tendons and at times it may be fused wi abductor pollicis longus (APL). According to Spinner (1984) EPB may not extend beyond e middle of metacarpal as is found in anropoid ape. It sends an expansion to e dorsal apparatus of umb. Hollinshead (1984) quoting Parson and Robinson (1982) states at EPB often shows doubling, eier at e wrist or on e dorsum of umb and in 72% EPB is inserted into PP, in 6.8% entirely on DP and in 21.2% it is inserted on bo e phalanges. In e present series EPB was present in all e cases studied and doubling was found in 17 cases (15.4%). It was found to be attached to e PP in 58.15%, to e DP in 27.5% and to e bo phalanges in 14.6%. Thus, ese findings are at variance from ose reported by above auor. In ose cases where EPB extends upto e DP it may act as extensor of DP when EPL is divided completely. Spinner (1984) has stated at over e dorsum of MP joint e two extensor tendons received e fibres of expansion of abductor and occasionally flexor pollicis brevis (FPB) on e radial side and adductor pollicis (AP) on e ulnar side. These fibres of expansion run directly across e extensors in e proximal part of dorsal apparatus and in a more oblique course towards distal part of umb. He states at some observers find no extension of abductor brevis into e DDE but in his own investigations he has constantly found is extension, and stimulation of 137
4 Dorsal Digital Expansion Of Thumb...Joshi, S.S., Joshi, S.D., Aavale S.A., Kishve, P. S. and Jadhav S.D. EPB produced abduction of umb combined wi extension of DP and a moderate flexion at MP joint. APB may be likened to e lumbrical muscle in oer digits. In e present series e contribution APB to DDE was seen in 68.21% umbs examined. Lamb et al (1989) have shown e extension of e first palmar interosseous muscle to e DDE of umb. Similarly Schafer et al (1923) had also described at e first palmar interosseous, as a in slip joins e extensor tendons of umb. In e present series in 62.7% cases we could observe a contribution from first palmar interosseous muscle to DDE of umb. Spinner (1987) and Lamb et al (1989) have described at e FPB like APB also joins extensor expansion of umb. In e present series we could observe contribution from FPB to e DDE of umb in 3.6% cases only. It is well documented at Adductor pollicis (AP) is inserted into e tubercle on ulnar side of base of PP, ulnar sesamoid of MP joint and into extensor expansion of umb. Schafer et al (1923) mention at e oblique part of is muscle is connected by membranous slips to extensors of umb. During evolution, e non opposable umb was converted into an opposable umb which was so very essential for power, prehensile and precision work. Alough it has been widely separated from medial four digits it can still be adducted primarily because of AP. It seems at e prominent medial margin of DDE of umb (in e DDE of oer digits e two margins are equal in size), where e fibres are derived from AP, is an expression of a dominant role of is muscle to keep e umb closer to oer digits during various movements of umb including extension. In contrast to e lateral margin e medial margin of DDE was prominent and well defined in all e cases examined and was mainly contributed by oblique head of adductor pollicis. Hunter et al (2002) have stated at e contribution of AP to DDE stabilizes e extensor tendons and transfers extensor forces to e IP joint. Spinner (1984) has shown at faradic stimulation of is muscle produces adduction wi simultaneous extension of e DP. We could not find any mention of separate contributions of e two heads of AP to e DDE as has been studied in present series (Table I). Unlike e division of DDE in oer digits, in e umb it does not divide into ree slips an intermediate and two collateral slips. Hollinshead (1982) has described at e EPL and EPB are more likely to be involved in tendovaginitis. The EPL is more commonly ruptured as a result of colles's fracture and in such cases e extensor indicis tendon can be used to replace is. Fasciotomy distal to e extensor retinaculum during surgery for dequervain's disease may alter e balance of forces of e umb. Rupture of EPB and dorsal fibres of extensor apparatus produce loss of MP joint extension and displacement of EPL may accentuate flexion of MP joint and contributes to hyperextension of e interphalangeal (IP) joint. 138 Rupture of EPL at e level of Lister's tubercle leads to loss of MP joint extension which is e most significant functional loss. Closed rupture of e EPL mimics e mallet tendon injury of e finger. Extension at e IP joint is by intrinsic muscles rough eir contribution to dorsal apparatus of umb. Thus, e construction of dorsal apparatus of umb permits extension of DP by traction applied separately by ree structures: e tendon of EPL; e tendon of EPB, when its insertion reaches e DP; and e enar muscles of umb - APB and AP, on e radial and ulnar side respectively. Conclusion : It's a well known fact e human umb plays an important role in prehension, opposition and in performance of intricate skilled and precision movements of hand. The functional importance and e complexity of movements of umb are well reflected in an extensive representation of umb in e brain (Lamb et al, 1989). Like in oer digits we have found a well defined dorsal digital expansion of umb in all e hands studied. It is triangular in outline wi base directed proximally. The medial margin, which is very well defined, receives e contribution mainly from e oblique head of adductor pollicis (%); alough in approximately 8% e transverse head of is muscle contributes fibres to is. Surprisingly in 62.7% hands ere is a contribution from e first palmar interosseous muscle also a fact not very well recognized by majority of e workers. APB in about 68% contributes fibres to e lateral margin of expansion (which is not as prominent as e medial). In 98% umbs EPL is inserted on e DP, in e remaining it was attached to bo e phalanges. In approximately 27% EPB reached e DP and in 14.6% it was attached to bo e phalanges. Thus, is complexity of muscular arrangements and e formation of DDE of umb can explain e varying ranges of movements at e various joints of umb and in contributing its major share in performance of composite movements of e hand. References : 1. Bade H, Krolak C, Koebke J; Fibrous architecture of dorsal aponeurosis of e umb. Anatomical Record 1995; 243 (4) Fahrer M. On e form and function of e abductor pollicis muscle. Aust N Z J surg Apr, 47(2) rd 3. Hollinshead WH; Anatomy for Surgeons.3 Edn; Vol III. Harper and Row Publishers. Philadelphia, 1982, pp Lamb DW,Hooper G and Kuczynski K, The practice of hand surgery In restoration of n d umb. 2 Edn. Blackwell scientific publications, 1989, pp Mackin EJ, Callahan AD, Skirven TM, Osterman AL in Hunter, Mackin, Callahan; Rehabilitation of e Hand and Upper Extremity. 5 Edn. Vol I. Mosby, St. Louis, London, Philadelphia 2002, pp
5 Dorsal Digital Expansion Of Thumb...Joshi, S.S., Joshi, S.D., Aavale S.A., Kishve, P. S. and Jadhav S.D. 6. Romanes G J; Cunningham's Textbook of anatomy. 11 Edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, New York, Tokyo, 1978, pp Schafer E S, Syrrington J, Bryce T H; Quain's Elements of Anatomy in Myology. 11 Edn; Longman's and Green and co. New York, Toronto, 1923, pp Spinner M. Kaplan's functional and surgical rd anatomy of hand in umb. 3 Edn. J.B. Lippincott Company, 1984, pp Synnatamby CS; In Last's Anatomy: Regional and Applied. 10 Edn. Churchill Livingstone,Edinburg, London, New York, 1999,pp
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
10/10/2014. Structure and Function of the Hand. The Hand. Osteology of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
Small muscles of the hand
 By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES
 LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. In Slide #2 there was a mistake where the doctor mentioned lateral septum twice.
 We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
Wrist and Hand Anatomy
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
Anatomy - Hand. Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics. Osteology. Carpal Arch. Property of VOMPTI, LLC
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Hand and Wrist Editing file. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation
 Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Biceps Brachii. Muscles of the Arm and Hand 4/4/2017 MR. S. KELLY
 Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
The Foot. Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob:
 The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
divided by the bones ( redius and ulna ) and interosseous membrane into :
 fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
First & second layers of muscles of the sole
 The FOOT First & second layers of muscles of the sole introduction The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups; extrinsic and intrinsic muscles. The extrinsic muscles arise from
The FOOT First & second layers of muscles of the sole introduction The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups; extrinsic and intrinsic muscles. The extrinsic muscles arise from
Morphological Variations in Lumbricals of Hand A Cadaveric Study
 IBIMA Publishing Plastic Surgery: An International Journal http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/psij/psij.html Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 821692, 7 pages DOI: 10.5171/2013.821692 Morphological Variations
IBIMA Publishing Plastic Surgery: An International Journal http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/psij/psij.html Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 821692, 7 pages DOI: 10.5171/2013.821692 Morphological Variations
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles
 Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure
 Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
The hand. it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand**
 Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
Lab Activity 11: Group II
 Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락
 Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries
 MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper
 Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
The Forearm 2. Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm
 The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
SPECIAL ARTICLE. Missed tendon injuries INTRODUCTION
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 87-91 SPECIAL ARTICLE Missed tendon injuries H. R. GULY Consultant in A & E, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth INTRODUCTION The timing of the repair of divided tendons
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 87-91 SPECIAL ARTICLE Missed tendon injuries H. R. GULY Consultant in A & E, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth INTRODUCTION The timing of the repair of divided tendons
Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria
 TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
Objectives. How your brain sees your hand. Surface anatomy Bones Joints Muscles Tendons Nerves Arteries
 Hand Therapy Review Course Washington University St. Louis, MO April 7 9, 2017 Over eighty percent of activities of daily living involve grasping or seizing objects with the hand. (Katz et al., 1970) Anatomy
Hand Therapy Review Course Washington University St. Louis, MO April 7 9, 2017 Over eighty percent of activities of daily living involve grasping or seizing objects with the hand. (Katz et al., 1970) Anatomy
Tendon transfers for ulnar nerve palsy
 Tendon transfers for ulnar nerve palsy Caroline LECLERCQ, de la main Paris, France Gruppo MANUS Etiology - Distal palsy - Nerve laceration at forearm & wrist - Neuromuscular diseases CMT, leprosy - Lower
Tendon transfers for ulnar nerve palsy Caroline LECLERCQ, de la main Paris, France Gruppo MANUS Etiology - Distal palsy - Nerve laceration at forearm & wrist - Neuromuscular diseases CMT, leprosy - Lower
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments
 Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful
 In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
1/13/2013. Anatomy Guy Dissection Sheet Extensor Forearm and Hand. Eastern Virginia Medical School
 Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
13 13/3/2012. Adel Muhanna
 13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
Structure and Function of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand Some say it takes a village to raise a child, but it takes 19 bones and 19 joints in the hand for it to function smoothly. The Hand Dorsal aspect 2 3 4 The digits are
Structure and Function of the Hand Some say it takes a village to raise a child, but it takes 19 bones and 19 joints in the hand for it to function smoothly. The Hand Dorsal aspect 2 3 4 The digits are
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
10/15/2014. Wrist. Clarification of Terms. Clarification of Terms cont
 Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
forearm posterior compartment
 Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
compartments of the forearm
 " forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
" forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside
 Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
The fibrous flexor sheaths of the fingers
 J. Anat. (1988), 156, pp. 185-196 185 With 9 figures Printed in Great Britain The fibrous flexor sheaths of the fingers MARILYN M. JONES AND A. A. AMIS* Division of Anatomy, United Medical and Dental Schools,
J. Anat. (1988), 156, pp. 185-196 185 With 9 figures Printed in Great Britain The fibrous flexor sheaths of the fingers MARILYN M. JONES AND A. A. AMIS* Division of Anatomy, United Medical and Dental Schools,
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7
 Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment
 10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction
 180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Anatomy of the Hand and Nomenclature. R K Kankate Specialist Registrar St.George s Hospital
 Anatomy of the Hand and Nomenclature R K Kankate Specialist Registrar St.George s Hospital Bony skeleton muscles and ligaments nervous, arterial and venous system Ossification of bones: carpus Most carpal
Anatomy of the Hand and Nomenclature R K Kankate Specialist Registrar St.George s Hospital Bony skeleton muscles and ligaments nervous, arterial and venous system Ossification of bones: carpus Most carpal
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 The Stiff Hand: Boutonniere & Sylvia Dávila, PT, CHT San Antonio, Texas Extensor Mechanism Central slip inserts into base of the middle phalanx Lateral bands lie dorsal to the PIP joint center of rotation
The Stiff Hand: Boutonniere & Sylvia Dávila, PT, CHT San Antonio, Texas Extensor Mechanism Central slip inserts into base of the middle phalanx Lateral bands lie dorsal to the PIP joint center of rotation
# Anatomy. Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla. Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil. Page 0 of 16
 #10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
#10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
Anatomy of the Upper Limb
 Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
Biomechanical Modelling and Animating Human Hand Movements
 Biomechanical Modelling and Animating Human Hand Movements O.A. Kuchar and J.N. Scrimger School of Computer Science, Technical University of Nova Scotia, Halifax, N.S., Canada, B3J 2X4 Abstract A different
Biomechanical Modelling and Animating Human Hand Movements O.A. Kuchar and J.N. Scrimger School of Computer Science, Technical University of Nova Scotia, Halifax, N.S., Canada, B3J 2X4 Abstract A different
medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages External surfaces of ribs 3-5
 MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]
![[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]] [[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]](/thumbs/84/91174469.jpg) In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation.
 Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
Metacarpophalangeal Joint Implant Arthroplasty REHABILITATION PROTOCOL
 Andrew McNamara, MD The Orthopaedic and Fracture Clinic 1431 Premier Drive Mankato, MN 56001 507-386-6600 Metacarpophalangeal Joint Implant Arthroplasty REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Patient Name: Date: Diagnosis:
Andrew McNamara, MD The Orthopaedic and Fracture Clinic 1431 Premier Drive Mankato, MN 56001 507-386-6600 Metacarpophalangeal Joint Implant Arthroplasty REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Patient Name: Date: Diagnosis:
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Anatomy of the Forearm
 Anatomy of the Forearm Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 8 Editing file Objectives List the names of the Flexors Group of Forearm (superficial & deep muscles). Identify the common flexor origin of
Anatomy of the Forearm Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 8 Editing file Objectives List the names of the Flexors Group of Forearm (superficial & deep muscles). Identify the common flexor origin of
Structure and function of the abductor pollicis longus muscle
 J. Anat. (1991), 174, pp. 221-227 221 With 5 figures Printed in Great Britain Structure and function of the abductor pollicis longus muscle ELVIRE VAN OUDENAARDE* University of Nijmegen, Department of
J. Anat. (1991), 174, pp. 221-227 221 With 5 figures Printed in Great Britain Structure and function of the abductor pollicis longus muscle ELVIRE VAN OUDENAARDE* University of Nijmegen, Department of
Assessing hand ligaments and tendons lesions using MRI
 Assessing hand ligaments and tendons lesions using MRI Award: Certificate of Merit Poster No.: C-0691 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. M. Benitez Vazquez, M. I. Rossi Prieto, C.
Assessing hand ligaments and tendons lesions using MRI Award: Certificate of Merit Poster No.: C-0691 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. M. Benitez Vazquez, M. I. Rossi Prieto, C.
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D
 Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View
 Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
The Elbow and the cubital fossa. Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
FINGER INJURIES. Chapter 24, pgs ,
 FINGER INJURIES Chapter 24, pgs 727 730, 741 743 1. Demonstrate mastery of anatomical references to the hand and fingers. 2. Compare and contrast Mallet Finger, Swan Neck Deformity and Boutonnière Deformity.
FINGER INJURIES Chapter 24, pgs 727 730, 741 743 1. Demonstrate mastery of anatomical references to the hand and fingers. 2. Compare and contrast Mallet Finger, Swan Neck Deformity and Boutonnière Deformity.
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON
 REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
eplasty: Vol. 8 Anatomic Landmarks for the First Dorsal Compartment
 eplasty: Vol. 8 Anatomic Landmarks for the First Dorsal Compartment Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Damon Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, University of Louisville School of Medicine,
eplasty: Vol. 8 Anatomic Landmarks for the First Dorsal Compartment Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Damon Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, University of Louisville School of Medicine,
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Supplied in part by the musculocutaneous nerve. Forms the axis of rotation in movements of pronation and supination
 Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
Poliomyelitis: Splints for the Upper Extremity
 Poliomyelitis: Splints for the Upper Extremity By C.E. IRWIN, M.D. Atlanta, Ga. The splints to be discussed in this presentation are designed and used for therapeutic reasons only. They are in no sense
Poliomyelitis: Splints for the Upper Extremity By C.E. IRWIN, M.D. Atlanta, Ga. The splints to be discussed in this presentation are designed and used for therapeutic reasons only. They are in no sense
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Tendon Transfers. Variability muscle 2x stronger than another Greatest force at resting length. Drag:
 Tendon Transfers Joanne Mimm, MPT, CHT Restore balance Indications Nerve injury paralyzed muscle damaged tendon/muscle CNS lesion Consider action Functional gain Strength-ability to generate tension number
Tendon Transfers Joanne Mimm, MPT, CHT Restore balance Indications Nerve injury paralyzed muscle damaged tendon/muscle CNS lesion Consider action Functional gain Strength-ability to generate tension number
ANATOMY. Su~,ect : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 1 3 Date :
 ANATOMY Su~,ect : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 1 3 Date : HAND Skin ~ Thick and shovv many flexure creases (folds). ~ Flexure creases are an important landmarks. 111 Proximal palmar crease.
ANATOMY Su~,ect : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 1 3 Date : HAND Skin ~ Thick and shovv many flexure creases (folds). ~ Flexure creases are an important landmarks. 111 Proximal palmar crease.
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures:
 Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
Practical 2 Worksheet
 Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Difference Between Angle You Can Bend Your Left Wrist Back vs Your Right Wrist Jenna Priest Science Department Altoona High School January 25, 2017
 Difference Between Angle You Can Bend Your Left Wrist Back vs Your Right Wrist Jenna Priest Science Department Altoona High School January 25, 2017 Background 1- The wrist joint (also known as the radiocarpal
Difference Between Angle You Can Bend Your Left Wrist Back vs Your Right Wrist Jenna Priest Science Department Altoona High School January 25, 2017 Background 1- The wrist joint (also known as the radiocarpal
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints. Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint
 Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow.
 MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
Dynamic 22 Mhz ultrasound evaluation (HR-US) of the finger: a detailed didactic approach.
 Dynamic 22 Mhz ultrasound evaluation (HR-US) of the finger: a detailed didactic approach. Poster No.: C-2228 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Muda, D. Orlandi, V. Prono, S. Migone,
Dynamic 22 Mhz ultrasound evaluation (HR-US) of the finger: a detailed didactic approach. Poster No.: C-2228 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Muda, D. Orlandi, V. Prono, S. Migone,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Extensor expansion of the rheumatoid hand
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31,112 Extensor expansion of the rheumatoid hand K. M. BACKHOUSE From the Royal College ofsurgeons ofengland, the Chielsea and Kensington Rheumatology Unit, and the Royal London
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31,112 Extensor expansion of the rheumatoid hand K. M. BACKHOUSE From the Royal College ofsurgeons ofengland, the Chielsea and Kensington Rheumatology Unit, and the Royal London
panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca)
 J. Anat. (1996) 189, pp. 587-592, with 12 figures Printed in Great Britain Functional anatomy of the radial sesamoid bone in the giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) 587 HIDEKI ENDO', NOBUO SASAKI2, DAISHIRO
J. Anat. (1996) 189, pp. 587-592, with 12 figures Printed in Great Britain Functional anatomy of the radial sesamoid bone in the giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) 587 HIDEKI ENDO', NOBUO SASAKI2, DAISHIRO
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
31yo M with chronic basilar thumb and wrist pain that started after cross-country bicycle ride 5 yrs ago.
 31yo M with chronic basilar thumb and wrist pain that started after cross-country bicycle ride 5 yrs ago. EPL EPB APL Full-thickness tear involving the dorsal deltoid ligament of the first carpometacarpal
31yo M with chronic basilar thumb and wrist pain that started after cross-country bicycle ride 5 yrs ago. EPL EPB APL Full-thickness tear involving the dorsal deltoid ligament of the first carpometacarpal
Muscles of the Upper Limb
 Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
8/25/2014. Radiocarpal Joint. Midcarpal Joint. Osteology of the Wrist
 Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Anatomy of the lower limb
 Anatomy of the lower limb Arches & sole of the foot Dr. Hayder ARCHES OF THE FOOT The foot as a mechanical unit performs two major functions: - It acts as a pliable platform to support the body weigh during
Anatomy of the lower limb Arches & sole of the foot Dr. Hayder ARCHES OF THE FOOT The foot as a mechanical unit performs two major functions: - It acts as a pliable platform to support the body weigh during
The plantar aponeurosis
 Anatomy of the foot The plantar aponeurosis Is a triangular thickening of the deep fascia Its apex is attached to the medial and lateral tubercles of the calcaneum. The base of the aponeurosis divides
Anatomy of the foot The plantar aponeurosis Is a triangular thickening of the deep fascia Its apex is attached to the medial and lateral tubercles of the calcaneum. The base of the aponeurosis divides
Cubital fossa and forearm
 Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Upper Limb- Sports Medicine II
 Upper Limb- Sports Medicine II I. Palpation A. With patient sitting, supine, & prone, palpate for pain, specific tenderness, swelling, effusion, local hyperthermia B. Bony Palpation 1. Carpal Bones (8)
Upper Limb- Sports Medicine II I. Palpation A. With patient sitting, supine, & prone, palpate for pain, specific tenderness, swelling, effusion, local hyperthermia B. Bony Palpation 1. Carpal Bones (8)
MORPHOFUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS OF THE FOREARM MUSCLE AT SHEEP AND DOG
 MORPHOFUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS OF THE FOREARM MUSCLE AT SHEEP AND DOG Ştefănescu, S., G. Predoi, C. Belu, B. Georgescu, I. Dumitrescu, Carmen Biţoiu, Anca Şeicaru Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Bucharest,
MORPHOFUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS OF THE FOREARM MUSCLE AT SHEEP AND DOG Ştefănescu, S., G. Predoi, C. Belu, B. Georgescu, I. Dumitrescu, Carmen Biţoiu, Anca Şeicaru Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Bucharest,
Learning Objectives. 07 Aug 12. Article E-1. At the end of this section the learner will be able to:
 Module 1: Comparative Functional Anatomy and Biomechanics Article E-1 Learning Objectives At the end of this section the learner will be able to: Describe the bones of the equine thoracic Describe the
Module 1: Comparative Functional Anatomy and Biomechanics Article E-1 Learning Objectives At the end of this section the learner will be able to: Describe the bones of the equine thoracic Describe the
CAUSES OF PROLAPSE AND COLLAPSE OF THE PROXIMAl" INTERPHALANGEAL JOINT J. C. VAN DER MEULEN. Rotterdam
 Causes of Prolapse and Collapse of the Proximal Interphalangeal Joint-f. C. Vander Meu{en CAUSES OF PROLAPSE AND COLLAPSE OF THE PROXIMAl" INTERPHALANGEAL JOINT J. C. VAN DER MEULEN. Rotterdam INTRODUCTION
Causes of Prolapse and Collapse of the Proximal Interphalangeal Joint-f. C. Vander Meu{en CAUSES OF PROLAPSE AND COLLAPSE OF THE PROXIMAl" INTERPHALANGEAL JOINT J. C. VAN DER MEULEN. Rotterdam INTRODUCTION
