Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 15 No. 02 April 16
|
|
|
- Ezra Benson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
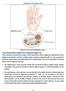
1 Case report Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 15 No. 02 April 16 Bilateral anatomical variations of the hand extensors Ferreira Arquez H Abstract: Background: The purpose of this paper is to describe an anatomical variation of the hand extensor on the little finger of the right hand which receives four tendons, condition unknown, as it is the first case reported so far in the literature. The human extensor tendons of hand often display an array of variations. Awareness of the anatomy and variations of the extensor tendons on the dorsum of the hand is necessary not only for the anatomist but also for surgeons when considering tendons for hand surgery, tendon rerouting or transplants. Materials and Methods: Bilateral anatomical variation in the upper limb was found during routine dissection in a 75-year-old male cadaver in the Morphology Laboratory at the University of Pamplona. The variations were recorded and photographed. Result: In the left hand the extensor digitorum there was a single tendon to the index, double tendon to the middle, triple tendon to the ring finger, a single tendon to the little finger or digiti minimi. The extensor digiti minimi has double tendon. In the right hand the extensor digitorum there was a single tendon to the index, triple tendon to the middle finger, triple tendons to the ring finger, a double tendon to the little finger. The extensor digiti minimi has double tendon. The little finger receives four tendons, 2 of extensor digitorum and 2 of extensor digiti minimi. The dorsum of the left hand and right showed juncturae tendinum type 2, between the extensors tendons in the 3rd intermetacarpal space; type 3, between the extensors tendons in the 4th inter metacarpal space. Conclusion: The presence of multiple tendons may alter the kinematics around the site of attachment to the phalanx. Knowledge of anatomical variations and normal anatomy of the extensor tendons, may be helpful while performing graft and tendon transfer operations. Keywords: anatomical variations; extensor digitorum muscle; extensor digiti minimi muscle; juncturae tendinum; extensor retinaculum; accessory tendons; dorsum; hand Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 15 No. 02 April 16. Page : Introduction The hand is one of the special organs of human body which is most frequently injured. The synergistic contraction of the extensor musculature along with the long flexors is mandatory for an efficient grip on different objects in daily life 1. A detailed knowledge of the extensor tendons anatomy is essential for under standing the consequences of tendon injury at various levels. This tendon injury may be either due to external trauma or spontaneous rupture as in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and distal radio ulnar joint osteoarthritis 2.Usually the dorsal surface of the hand is devoid of muscle bellies, it only contains the tendons of the extensor muscles of the hand. Between the dorsal carpal ligament and the carpal bones six compartments are formed for the passage of tendons. Found on the dorsum of the hand are the tendons of the extensor pollicis longus (EPL), extensor digitorum (ED), extensor indicis (EI), and the extensor digiti minimi (EDM). However, the existence of variant muscles on the dorsum of the hand has been documented in numerous publications 3.Finger extension involves simultaneous actions of both extrinsic and intrinsic extensor muscles. Extrinsic muscles originate in the elbow and forearm and include the following: extensor digitorum, extensor indicis, and extensor digiti minimi. The extensor digitorum muscle and ends in four tendons, one for each digit except for the thumb. The extensor digiti minimi muscle and ends in one tendon that inserts into the extensor expansion of the 5th finger. Corresponds to: Humberto Ferreira Arquez, University of Cartagena. University St. Thomas. Professor Human Morphology, Medicine Program, University of Pamplona. Morphology Laboratory Coordinator- University of Pamplona. humfear@unipamplona.edu.co 278
2 Bilateral anatomical variations of the hand extensors The primary function of these muscles is extension of the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and interphalangeal joints. The intrinsic muscles that originate and insert within the hand are the lumbrical and interosseous muscles. The function of these muscles is primarily to extend the interphalangeal joints and secondarily to contribute to flexion of the metacarpophalangeal joint. These groups of extrinsic and intrinsic muscles are coordinated by a series of stabilizing retinacular structures, which facilitate balanced transmission of muscular force. These structures are found in the dorsum of the carpum is extensor retinaculum, the hands is intertendinous connections, and the fingers are extensor hood, retinacular and triangular ligaments 4,5. Connexus intertendineus, juncturae tendinum (JT) or oblique tendinous connections between the extensor tendons of the fingers on the dorsum of the hand are commonlyobserved.three types of juncturae tendinum(jt) are identified between the tendons of extensor digitorum in the 2nd, 3rd and 4th intermetacarpal spaces (IMS) of hands.type 1 juncturae tendinum, made of thin filamentous intertendinous fascia; Type 2 juncturae tendinum, formed of dense thick well defined ligamentous bands; Type 3 juncturae tendinumwhich consisted of tendon slips, was the most frequently identified in all juncturae 6. Anatomical variation of the extrinsic extensor tendons are frequent and knowledge is important when assessing the traumatized or diseased hand and provide significant information to hand surgerons, when considering tendons for repair or transfer. Materials and methods The described human extensor tendons anatomic variations were found in the right and left side of a male cadaver of 75 years of age during routine upper limbs dissection in the Morphology Laboratory at the University of Pamplona developed by training medical students. The history of the individual and the cause of death are not known. The topographic details were examined by casual dissection and the variations were recorded and photographed. Results Left hand: In the left forearm the extensor digiti minimi (EDM) muscle originates to level lateral epicondyle of the humerus, passing inferiorly to the extensor retinaculum (ER) ends in double tendons that inserts into the extensor expansion of the 5th finger. The extensor digitorum(ed) muscle and continued downwards, passing inferiorly to the extensor retinaculum (ER) to split into individual tendons for each of the finger. There was a single tendon to the index, double tendon to the middle, triple tendon to the ring finger, a single tendon to the little finger. The dorsum of the hand showing juncturae tendineum type 2, between ED 3, ED 4 in the 3rd. intermetacarpal space of a left hand; juncturae tendineum type 3 between ED 6, ED 7 in the 4th intermetacarpal space of a left hand. The extensor digiti minimihas double tendon. The little finger receives three tendons. Figure 1. Left Hand: EI: Extensor indicis tendon; E.D: Extensor digitorum; ED 1: single tendon of extensor digitorum to the index finger; ED 2, ED 3: double tendon of extensor digitorum to the middle finger; ED 4, ED 5, ED 6 : triple tendons of extensor digitorum to the ring finger; ED 7: tendon of extensor digitorum to the little finger; EDM: Extensor digiti minimi; EDM 1, EDM 2: double tendon inserted into little finger. The dorsum of the hand showing juncturae tendinum type 2, between ED 3, ED 4 in the 3rd. intermetacarpal space of a left hand; and juncturae tendinum type 3, between ED 6, ED 7 in the 4th intermetacarpal space of a left hand. Right hand: In the right foream the extensor digiti minimi (EDM) muscle originates to level lateral epicondyle of the humerus, passing inferiorly to the extensor retinaculum (ER) ends in double tendons that inserts into the extensor expansion of the 5th finger. The extensor digitorum (ED) muscle continued downwards, passing inferiorly to the extensor retinaculum to split into individual tendons for each of the finger. There was a single tendon to the index, triple tendon to the middle finger, triple tendons to the ring finger, a double tendon to the little finger. The dorsum of the hand showing juncturae tendinum type 2, between ED 3, ED 4, ED 5 in the 3rd. intermetacarpal space of a right hand; juncturae tendinumtype 3, between ED 7, ED 8 in the 4th intermetacarpal space of a right hand. The extensor digiti minimihas double tendon. The little finger receives four (4) tendons 2 of extensor digiti minimi and 2 of extensor digitorum. Figure 2. Right hand. EI: Extensor indicis; ED: extensor digitorum; ED 1: single tendon to the index; ED 2,ED 3,ED 4: three tendons to the middle finger; ED 5, ED6, ED7: three tendons to the ring finger; ED 8, ED 9: double tendon inserted into little finger; EDM: extensor digiti minimi; EDM 1, EDM 2: double tendon inserted into little finger; The dorsum of the hand showing juncturae tendinum type 2, between ED 3, ED 4, 279
3 Ferreira Arquez H ED 5 in the 3rd. intermetacarpal space of a right hand; and juncturae tendinum type 3, between ED 7, ED 8 in the 4th intermetacarpal space of a right hand. The little finger receives four tendons, 2 of ED and 2 de EDM Discussions The tendon of the extensor digitorum may exhibit multiple variations in term of number. Even the standard textbooks of anatomy mention that the tendon ofextensor digitorum may be doubled or even tripled in any of the digits and such a variations has been reported to be more common in the index or the middle finger 7,8. Hence, even a double tendon to any of the digits may be taken as usual findings. There are even reports of double or triple tendons to the long fingers, single or double tendons to the little finger and occasionally double tendons to the little finger 9. Nayak et al. (2008) remarks, on this purpose, that the extensor compartment of the forearm is one of the regions of the human body with frequent variations of its content 10. Abdel-Hamid et al. (2013) report a single tendon of extensor indicis in all cases of the specimens studied 4. Dass et al. (2011) detected a single tendon ofextensor indicis in 98% of specimens 11. In the current case as well as previous studies 4,12,13, the extensor indicis tendon was always medial and deep to the tendon of extensor digitorum to the index finger. The extensor indicis permits independent extension of the index finger and is commonly used 280 Figure 1 Figure 2 for tendon transfer 14,15. The number of extensor digitorum tendons may vary from 3 to 7 proximal to the extensor retinaculum and from 4 to 8 distal to it. Although, the incidence of 4 tendons (32.6%) and 6 tendons (40%) were the commonest both proximal and distal to the extensor retinaculum 4. El-Badawi et al.(1995) reported 2 6 extensor digitorum tendons and 3 8 tendons proximal and distal to the ER respectively; 3 tendons (55.2%) and 4 tendons (60.77%) were the commonest 12. Hirai et al. (2001) declared the presence of single tendons of the extensor digitorum to the index finger in 92% of specimens studied 16 ; nevertheless, they were documented in all dissected specimens 11,12,13, Abdel-Hamid et al. (2013) report single tendons of extensor digitorum to the index finger in 96.8% of specimens and double tendons only in 3.2% of cases 4, in accordance to Von Schroeder et al. (1995) who detected them in 2% 9. Single tendons of extensor digitorum to the middle finger was reported by Abdel-Hamid et al. (2013) in (41,1%) 4. They were also recorded in 51 64% of specimens in previous studies 9, 12, 13, 16. Single tendons of extensor digitorum to the ring finger were found in (6.3%) 4. Also von Schroeder et al(1995) and Zilber et al. (2004) reported single tendons for extensor digitorum to the ring finger in 12% and 18% respectively 9,13. Contrary, much higher incidence of single tendon of extensor digitorum to the ring finger (62 96%)observed by others studies
4 Bilateral anatomical variations of the hand extensors 12, 17, 18.Double tendons of extensor digitorum to the middle finger and extensor digitorum to the ring finger were observed in 46.3% and 36.8%, respectively 4. However, a variable incidence was recorded for their duplication, as low as 4% and 2% for extensor digitorum to the middle finger and extensor digitorum to the ring finger, respectively 18 or as high as 39% for extensor digitorum to the middle finger 16 and 63% for extensor digitorum to the ring finger 9. Also, triple tendons of extensor digitorum to the middle finger (12.6%) and extensor digitorum to the ring finger (50.5%) was reported 4.Nevertheless, this incidence was variable in previous studies ranging between 2 and 19% 11, 12 forextensor digitorum to the middle finger and between 1 and 22% for extensor digitorum to the ring finger 12, 13. The percentage of quadruple tendons of extensor digitorum to the ring finger (6.3%) reported by Abdel-Hamid et al. (2013) was on average between that documented by Hirai et al. (2001)of 4% and by Zilber and Oberlin (2004) of 8%; though their existence could not be verified by some studies 11, 12, 18.The tendon of extensor digitorum to the little finger was reported absent 4. Yet, it was either replaced by a slip from the common bifurcating tendon to both ring and little fingers or by intertendinous connection with the ring finger. Similarly, the common bifurcating tendon and intertendinous connection were detected in 126/181 (69.61%) of studied specimens 12. Other researchers recorded different percentages of absent extensor digitorum to the little finger ranging between (2%) 18 and (66%) 11. In specimens studied by Abdel-Hamid et al. (2013) where extensor digitorum to the little finger was absent, extensor digiti minimi gave 2 to 3 tendons to the little finger to replace its absence. This was supported by Dass et al. (2011)who suggested that in case of absent extensor digitorum to the little finger or presence of a common tendon dividing for both ring and little fingers, the extensor digiti minimi compensated by giving 2 or 3 tendons to the little finger 11. A single tendon of extensor digiti minimi was found in all specimens proximal to the extensor retinaculum 4. In accordance, single tendonof extensor digiti minimi was previously documented proximal to the extensor retinaculum in (92 95%) 11, 12. Double tendons of extensor digiti minimi were detected in 75.8% and triple tendons in 15.8% distal to the extensor retinaculum (4). However, this duplication was recorded in (82 87%) 9,11,16 18 and triplication in (2 8%) 13,18. In the present case the little finger receives four tendons, 2 of extensor digiti minimi and 2 of extensor digitorum, this variations described is unique, has not been reported. Reports often refer the presence of tendinous, oblique tendinous or intertendinous connections (juncturae tendinum) slips between the extensor tendons on the dorsum of the hand. Von Schroeder et al. (1995) classify these Juncturae Tendinum(JT) of the extensor tendons into three types: Type I juncturae consist of filamentous regions within the intertendinous fascia; Type II consists of much thicker and well-defined connecting bands; and Type III consist of tendon slips from the extensor tendons and were subclassified into «y» or «r» subtypes, depending on shape 6. Hirai et al. (2001) in their series of 548 cadaveric hand dissections found that the most common pattern of intertendinous connections wereclassified into Type I in the second intermetacarpal space, into Type III-r in the third metacarpal space, and into type III-y in the fourth intermetacarpal space 16.The functional importance of these juncturaewould be to strengthen the frail tendons of the extensor mechanism of the fingers, at the cost of some loss of independence of the 4th finger 9, Accordance with Gövsa et al. (2011) who described the 4 th intermetacarpal spacesto contain the thickest type of Juncturae Tendinum (JT). This type can be used for repairing lacerated or torn tendons, this suggestion was supported by the histological similarity between type 3 Juncturae Tendinum and tendons 17. Injuries to the extensor tendons of the fingers are common because of their poorly protected anatomic location. Clinical reports emphasize the importance of initial treatment and postoperative rehabilitation in achieving a good outcome 24. Because the excursion of the extensor tendons over the fingers is less than that of the flexors, preservation of their length is far more critical to restoring the normal tendon balance 25. The relationship between the location of injury and the outcome is an important concept. The type of injury, deformity, and surgical outcome will be different according to the affected anatomic regions. As a result, the categorical classification of tendon injuries into anatomic zones is crucial to the diagnostic process. As already mentioned, Verdan s zone system is the most widely accepted 5,26. Conclusion Even though the extensor digitorum and extensor digiti minimi are asymptomatic in most cases, 281
5 Ferreira Arquez H authors feel it is still essential for surgeons to be aware of possible variations of the extensor tendons and to ensure these variations are not overlooked in the differential diagnosis. These variations may be asymptomatic but when requiring surgical interventions an extra care must be taken especially during routine hand surgeries. Presence of these types of variant tendons on the dorsum of the hand in persons who are involved in sports such as, golf, cricket, tennis, weight lifting were the excessive wrist movement is involved, may show some symptoms. The presence of such thin tendons may be vulnerable to rupture in diseases like rheumatoid arthritis. If there is detailed knowledge of the anatomy and prevalence of this variations, it can help to prevent diagnostic errors, influence surgical and interventional procedures and avoid surgical complications during hand surgery. Acknowledgements The author, on behalf of the University of Pamplona thanked to the Erasmo Meoz University Hospital for the donation of cadavers identified, unclaimed by any family, or persons responsible for their care, process subject to compliance with the legal regulations in force in the Republic of Colombia. Conflict of interest: None declared References 1. Sinnatamby CS (2006) Last s anatomy: regional and applied. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp Casal D, Pais D, Bilhim T, Ribeiro V, Cunha S, Damásio C,Fernandes R, Angélica-Almeida M, Goyri-O Neill J. A rare variation of the extensor indicis proprius tendon with important clinical implications. J Morphol Sci, 2011; 28: Singh K, Dennie D, Rao SR. Variant extensor muscles on the dorsum of the hand. Int J Anat Var (IJAV). 2009; 2: Abdel-Hamid GA, El-Beshbishy RA, Abdel Aal IH. Anatomical variations of the hand extensors. Folia Morphol (Warsz) Aug;72(3): Clavero JA, Golano P, Farinas O, Alomar X, Monill JM,Esplugas M Extensor mechanism of the fingers: MR imaging-anatomic correlation. Radiographics, 2003;23: Williams PL et al. Gray s Anatomy. The Anatomical Basis of Medicine and Surgery. 38 th Edition. Edinburgh, Churchill Livingstone 1997, p Sinnatamby CS. Last s Anatomy. Regional and Applied. 10 th Edition. Edinburgh, Churchill Livingstone, 2001, p Von Schroeder HP, Botte MJ. Anatomy of the Extensor Tendons of the Fingers: Variations and multiplicity. J Hand Surg Amer 1995; 20 (1): Nayak SR, Krishnamurthy A, Prabhu LV, Rai R, Ranade AV, Madhyastha S. Anatomical variation of radial wrist extensor muscles: a study in cadavers. Clinics. 2008;63: Dass P, Prabhu LV, Pai MM, Nayak V, Kumar G, Janardhanan JP. A comprehensive study of the extensor tendons to the medial four digits of the hand. Chang Gung Med J. 2011; 34: El-Badawi MG, Butt MM, Al-zuhair AGH, Fadel RA. Extensor tendons of the fingers; arrangement and variations: II. Clin Anat. 1995; 8: Zilber S, Oberlin C. Anatomical variations of the tendons to the fingers over the dorsum of the hand;a study of 50 hands and a review of the literature. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004; 113: Patel MR, Moradia VJ, Bassini L, Lei B. Extensor indicis proprius syndrome: a case report. J Hand Surg Am. 1996; 21: Reeder CA, Pandeya NK. Extensor indicis proprius syndrome secondary to an anomalous extensor indicis proprius muscle belly. J Am Osteopath Assoc.1991;91: Hirai Y, Yoshida K, Yamanaka K, Inoue A, Yamaki K, Yoshizuka M. An anatomic study of the extensor tendons of the human hand. J Hand Surg Am. 2001;26: Gövsa F, Pinar Y, Çelik S, Bilge O, Sezak M. Anatomical similarity between tendons and Type 3 intertendinous connections: suitability as local donor tissue. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2011; 45: Godwin Y, Ellis H. Distribution of the extensor tendons on the dorsum of the hand. Clin Anat. 1992; 5: Joshi SS, Joshi SD. Applied significance of variations of the first extensor compartment of wrist. J Anat Soc India. 2002; 51: Von Schroeder HP, Botte MJ. Functional anatomy of the extensor tendons of the digits. Hand Clin. 1997;13: Nimbarte AD, Kaz R, Li ZM. Finger joint motion generated by individual extrinsic muscles: a cadaveric study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2008;3: Klena JC, Riehlt JT, Beck JD. Anomalous extensor tendons to the long finger: a cadaveric study of incidence. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37: Pinar Y, Gövsa F, Bilge O, Celik S. Accessory tendon slip arising from the extensor carpi ulnaris and its importance for wrist pain. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2012;46: Blair WF, Steyers CM. Extensor tendon injuries. Orthop Clin North Am 1992; 23: Minamikawa Y, Peimer CA, Yamaguchi T, et al. Wrist position and extensor tendon amplitude following repair. J Hand Surg [Am] 1992; 17: Kleinert HE, Verdan C. Report of the Committee on Tendon Injuries. J Hand Surg [Am] 1983; 8:
Anatomical similarity between tendons and Type 3 intertendinous connections: suitability as local donor tissue
 ACTA ORTHOPAEDICA et TRAUMATOLOGICA TURCICA BASIC STUDY Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2011;45(5):370-375 doi:10.3944/aott.2011.2509 Anatomical similarity between tendons and Type 3 intertendinous connections:
ACTA ORTHOPAEDICA et TRAUMATOLOGICA TURCICA BASIC STUDY Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2011;45(5):370-375 doi:10.3944/aott.2011.2509 Anatomical similarity between tendons and Type 3 intertendinous connections:
Morphological Variations in Lumbricals of Hand A Cadaveric Study
 IBIMA Publishing Plastic Surgery: An International Journal http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/psij/psij.html Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 821692, 7 pages DOI: 10.5171/2013.821692 Morphological Variations
IBIMA Publishing Plastic Surgery: An International Journal http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/psij/psij.html Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 821692, 7 pages DOI: 10.5171/2013.821692 Morphological Variations
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Wrist and Hand Anatomy
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
1/13/2013. Anatomy Guy Dissection Sheet Extensor Forearm and Hand. Eastern Virginia Medical School
 Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment
 10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. In Slide #2 there was a mistake where the doctor mentioned lateral septum twice.
 We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
The Forearm 2. Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm
 The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles
 Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Anatomical Study on the Extensor Digitorum Profundus Muscle in the Japanese
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 66 (6): 339-354, March, 1990 Anatomical Study on the Extensor Digitorum Profundus Muscle in the Japanese By Yukio YOSHIDA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical University,
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 66 (6): 339-354, March, 1990 Anatomical Study on the Extensor Digitorum Profundus Muscle in the Japanese By Yukio YOSHIDA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical University,
10/10/2014. Structure and Function of the Hand. The Hand. Osteology of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Anatomy of the Hand and Nomenclature. R K Kankate Specialist Registrar St.George s Hospital
 Anatomy of the Hand and Nomenclature R K Kankate Specialist Registrar St.George s Hospital Bony skeleton muscles and ligaments nervous, arterial and venous system Ossification of bones: carpus Most carpal
Anatomy of the Hand and Nomenclature R K Kankate Specialist Registrar St.George s Hospital Bony skeleton muscles and ligaments nervous, arterial and venous system Ossification of bones: carpus Most carpal
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
divided by the bones ( redius and ulna ) and interosseous membrane into :
 fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries
 MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Hand and Wrist Editing file. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation
 Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper
 Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2
 Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
compartments of the forearm
 " forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
" forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
Variations of the abductor pollicis longus tendon: an anatomic study
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 72, No. 2, pp. 161 166 DOI: 10.5603/FM.2013.0027 Copyright 2013 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Variations of the abductor pollicis longus
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 72, No. 2, pp. 161 166 DOI: 10.5603/FM.2013.0027 Copyright 2013 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Variations of the abductor pollicis longus
forearm posterior compartment
 Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
Dorsal Digital Expansion Of Thumb
 Dorsal Digital Expansion Of Thumb Joshi, S.S., Joshi, S.D., Aavale S.A., Kishve, P. S. and Jadhav S.D. Rural Medical College,Pravara Institute of Medical Sciences, Loni Abstract: Human hands perform e
Dorsal Digital Expansion Of Thumb Joshi, S.S., Joshi, S.D., Aavale S.A., Kishve, P. S. and Jadhav S.D. Rural Medical College,Pravara Institute of Medical Sciences, Loni Abstract: Human hands perform e
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure
 Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Structure and Function of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand Some say it takes a village to raise a child, but it takes 19 bones and 19 joints in the hand for it to function smoothly. The Hand Dorsal aspect 2 3 4 The digits are
Structure and Function of the Hand Some say it takes a village to raise a child, but it takes 19 bones and 19 joints in the hand for it to function smoothly. The Hand Dorsal aspect 2 3 4 The digits are
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Small muscles of the hand
 By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7
 Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report
 Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
Anatomy - Hand. Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics. Osteology. Carpal Arch. Property of VOMPTI, LLC
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES
 LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
VARIANT ARTERIAL PATTERN IN THE FOREARM WITH ITS EMBRYOLOGICAL BASIS. Vaishnavi Joshi and Dr. Shaheen Sajid Rizvi
 Volume-8, Issue-3 July-Sept-2018 Coden:IJPAJX-CAS-USA, Copyrights@2018 ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 8 th June-2018 Revised: 15 th July-2018 Accepted: 16 th July-2018 DOI: 10.21276/Ijpaes http://dx.doi.org/10.21276/ijpaes
Volume-8, Issue-3 July-Sept-2018 Coden:IJPAJX-CAS-USA, Copyrights@2018 ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 8 th June-2018 Revised: 15 th July-2018 Accepted: 16 th July-2018 DOI: 10.21276/Ijpaes http://dx.doi.org/10.21276/ijpaes
Muscle and the Extensor Indicis Radialis Muscle in Japanese
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 71(6): 355-364, March, 1995 Anatomical Studies on the Extensor Pollicis et Indicis Accessorius Muscle and the Extensor Indicis Radialis Muscle in Japanese By Yukio YOSHIDA Department
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 71(6): 355-364, March, 1995 Anatomical Studies on the Extensor Pollicis et Indicis Accessorius Muscle and the Extensor Indicis Radialis Muscle in Japanese By Yukio YOSHIDA Department
SPECIAL ARTICLE. Missed tendon injuries INTRODUCTION
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 87-91 SPECIAL ARTICLE Missed tendon injuries H. R. GULY Consultant in A & E, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth INTRODUCTION The timing of the repair of divided tendons
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 87-91 SPECIAL ARTICLE Missed tendon injuries H. R. GULY Consultant in A & E, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth INTRODUCTION The timing of the repair of divided tendons
13 13/3/2012. Adel Muhanna
 13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
Musculoskeletal Imaging of the Digits. Arash David Tehranzadeh, MD UCSD MSK Radiology May 11 th, 2006
 Musculoskeletal Imaging of the Digits Arash David Tehranzadeh, MD UCSD MSK Radiology May 11 th, 2006 Musculoskeletal Imaging of the Digit Anatomy & Internal Derangement The Extensor System The Flexor System
Musculoskeletal Imaging of the Digits Arash David Tehranzadeh, MD UCSD MSK Radiology May 11 th, 2006 Musculoskeletal Imaging of the Digit Anatomy & Internal Derangement The Extensor System The Flexor System
Anatomy of the Forearm
 Anatomy of the Forearm Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 8 Editing file Objectives List the names of the Flexors Group of Forearm (superficial & deep muscles). Identify the common flexor origin of
Anatomy of the Forearm Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 8 Editing file Objectives List the names of the Flexors Group of Forearm (superficial & deep muscles). Identify the common flexor origin of
Anatomy of the Upper Limb
 Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
Muscle/Tendon Functions: Thumb. Extensor Tendon Healing. Digital Extension. Digital Extension. Supporting Ligaments: ORL. Supporting Ligaments
 Extensor Tendon Anatomy, Common Injury and Treatment Christina Schmidt, OTR/L, CHT University of California, Irvine Irvine, CA February 9-11, 2018 2 How Extensor Tendons Differ from Flexor Tendons Dorsum
Extensor Tendon Anatomy, Common Injury and Treatment Christina Schmidt, OTR/L, CHT University of California, Irvine Irvine, CA February 9-11, 2018 2 How Extensor Tendons Differ from Flexor Tendons Dorsum
Assessing hand ligaments and tendons lesions using MRI
 Assessing hand ligaments and tendons lesions using MRI Award: Certificate of Merit Poster No.: C-0691 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. M. Benitez Vazquez, M. I. Rossi Prieto, C.
Assessing hand ligaments and tendons lesions using MRI Award: Certificate of Merit Poster No.: C-0691 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. M. Benitez Vazquez, M. I. Rossi Prieto, C.
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
EFFECT OF WRIST POSTURE AND RATE OF FORCE DEVELOPMENT ON FINGER CONTROL AND INDEPENDENCE
 EFFECT OF WRIST POSTURE AND RATE OF FORCE DEVELOPMENT ON FINGER CONTROL AND INDEPENDENCE EFFECT OF WRIST POSTURE AND RATE OF FORCE DEVELOPMENT ON FINGER CONTROL AND INDEPENDENCE DURING ISOMETRIC CONTRACTION
EFFECT OF WRIST POSTURE AND RATE OF FORCE DEVELOPMENT ON FINGER CONTROL AND INDEPENDENCE EFFECT OF WRIST POSTURE AND RATE OF FORCE DEVELOPMENT ON FINGER CONTROL AND INDEPENDENCE DURING ISOMETRIC CONTRACTION
[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]
![[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]] [[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]](/thumbs/84/91174469.jpg) In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
Biceps Brachii. Muscles of the Arm and Hand 4/4/2017 MR. S. KELLY
 Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View
 Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction
 180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락
 Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
CADAVERIC STUDY OF VARIANT FLEXOR CARPI ULNARIS
 IJCRR Vol 04 issue 23 Section: Heathcare Category: Research Received on: 26/10/12 Revised on: 05/11/12 Accepted on:22/11/12 CADAVERIC STUDY OF VARIANT FLEXOR CARPI ULNARIS MUSCLE Sharadkumar Pralhad Sawant,
IJCRR Vol 04 issue 23 Section: Heathcare Category: Research Received on: 26/10/12 Revised on: 05/11/12 Accepted on:22/11/12 CADAVERIC STUDY OF VARIANT FLEXOR CARPI ULNARIS MUSCLE Sharadkumar Pralhad Sawant,
The hand. it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand**
 Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
10/15/2014. Wrist. Clarification of Terms. Clarification of Terms cont
 Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report
 SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments
 Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk
 Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
# Anatomy. Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla. Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil. Page 0 of 16
 #10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
#10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
Lab Activity 11: Group II
 Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful
 In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
Ulnar Neuropathy in the Distal Ulnar Tunnel
 Ulnar Neuropathy in the Distal Ulnar Tunnel DAVID W. SHUPE, PT, ATC' Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy A brief anatomical review of the ulnar nerve and areas of ulnar nerve entrapment is
Ulnar Neuropathy in the Distal Ulnar Tunnel DAVID W. SHUPE, PT, ATC' Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy A brief anatomical review of the ulnar nerve and areas of ulnar nerve entrapment is
The Foot. Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob:
 The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
The Elbow and the cubital fossa. Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
Tendon transfers for ulnar nerve palsy
 Tendon transfers for ulnar nerve palsy Caroline LECLERCQ, de la main Paris, France Gruppo MANUS Etiology - Distal palsy - Nerve laceration at forearm & wrist - Neuromuscular diseases CMT, leprosy - Lower
Tendon transfers for ulnar nerve palsy Caroline LECLERCQ, de la main Paris, France Gruppo MANUS Etiology - Distal palsy - Nerve laceration at forearm & wrist - Neuromuscular diseases CMT, leprosy - Lower
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON
 REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION
 CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION Management of the injured hand - Principles of assessment K. Karunadasa Plastic and Reconstructive Surgical Unit, North Colombo Teaching Hospital, Ragama, Sri Lanka Keywords:
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION Management of the injured hand - Principles of assessment K. Karunadasa Plastic and Reconstructive Surgical Unit, North Colombo Teaching Hospital, Ragama, Sri Lanka Keywords:
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Interesting Case Series. Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression
 Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation.
 Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
Myologia Part II Objective: Students will examine the muscles of a canine in order to identify the musculature of the body.
 Okay Anatomy Anatomy I: Lesson 11 Myologia Part II Objective: Students will examine the muscles of a canine in order to identify the musculature of the body. Practical Tasks: 6) carpal flexors, pronators
Okay Anatomy Anatomy I: Lesson 11 Myologia Part II Objective: Students will examine the muscles of a canine in order to identify the musculature of the body. Practical Tasks: 6) carpal flexors, pronators
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
8/25/2014. Radiocarpal Joint. Midcarpal Joint. Osteology of the Wrist
 Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
First & second layers of muscles of the sole
 The FOOT First & second layers of muscles of the sole introduction The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups; extrinsic and intrinsic muscles. The extrinsic muscles arise from
The FOOT First & second layers of muscles of the sole introduction The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups; extrinsic and intrinsic muscles. The extrinsic muscles arise from
Dynamic 22 Mhz ultrasound evaluation (HR-US) of the finger: a detailed didactic approach.
 Dynamic 22 Mhz ultrasound evaluation (HR-US) of the finger: a detailed didactic approach. Poster No.: C-2228 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Muda, D. Orlandi, V. Prono, S. Migone,
Dynamic 22 Mhz ultrasound evaluation (HR-US) of the finger: a detailed didactic approach. Poster No.: C-2228 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Muda, D. Orlandi, V. Prono, S. Migone,
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 67, No. 1, pp. 63 71 Copyright 2008 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The prevalence of accessory heads of the flexor pollicis longus and the
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 67, No. 1, pp. 63 71 Copyright 2008 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The prevalence of accessory heads of the flexor pollicis longus and the
Tendon Transfers. Variability muscle 2x stronger than another Greatest force at resting length. Drag:
 Tendon Transfers Joanne Mimm, MPT, CHT Restore balance Indications Nerve injury paralyzed muscle damaged tendon/muscle CNS lesion Consider action Functional gain Strength-ability to generate tension number
Tendon Transfers Joanne Mimm, MPT, CHT Restore balance Indications Nerve injury paralyzed muscle damaged tendon/muscle CNS lesion Consider action Functional gain Strength-ability to generate tension number
Ultrasonography of the wrist - a step-by-step approach to study protocols and normal findings
 Ultrasonography of the wrist - a step-by-step approach to study protocols and normal findings Poster No.: C-1779 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno, A. P. Pissarra,
Ultrasonography of the wrist - a step-by-step approach to study protocols and normal findings Poster No.: C-1779 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno, A. P. Pissarra,
Objectives. How your brain sees your hand. Surface anatomy Bones Joints Muscles Tendons Nerves Arteries
 Hand Therapy Review Course Washington University St. Louis, MO April 7 9, 2017 Over eighty percent of activities of daily living involve grasping or seizing objects with the hand. (Katz et al., 1970) Anatomy
Hand Therapy Review Course Washington University St. Louis, MO April 7 9, 2017 Over eighty percent of activities of daily living involve grasping or seizing objects with the hand. (Katz et al., 1970) Anatomy
BILATERAL MULTIPLE VARIATIONS IN THE UPPER EXTREMITY OF A HUMAN CADAVER: A CASE REPORT
 Case Report BILATERAL MULTIPLE VARIATIONS IN THE UPPER EXTREMITY OF A HUMAN CADAVER: A CASE REPORT Soniya A Gupta 1, Saiprasad P Bhavsar * 2, Medha V Ambiye 3, Seema N Khambatta 4. ABSTRACT International
Case Report BILATERAL MULTIPLE VARIATIONS IN THE UPPER EXTREMITY OF A HUMAN CADAVER: A CASE REPORT Soniya A Gupta 1, Saiprasad P Bhavsar * 2, Medha V Ambiye 3, Seema N Khambatta 4. ABSTRACT International
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside
 Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
Cubital fossa and forearm
 Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Extensor retinaculum avulsion anatomy ankle
 Мобильный портал WAP версия: wap.altmaster.ru Extensor retinaculum avulsion anatomy ankle Dec 26, 2017. The extensor retinaculum describes the set of. Interactive Anatomical Interface and also the extensor
Мобильный портал WAP версия: wap.altmaster.ru Extensor retinaculum avulsion anatomy ankle Dec 26, 2017. The extensor retinaculum describes the set of. Interactive Anatomical Interface and also the extensor
Swan-Neck Deformity. Introduction. Anatomy
 Swan-Neck Deformity Introduction Normal finger position and movement occur from the balanced actions of many important structures. Ligaments support the finger joints. Muscles hold and move the fingers.
Swan-Neck Deformity Introduction Normal finger position and movement occur from the balanced actions of many important structures. Ligaments support the finger joints. Muscles hold and move the fingers.
Practical 2 Worksheet
 Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
FINGER INJURIES. Chapter 24, pgs ,
 FINGER INJURIES Chapter 24, pgs 727 730, 741 743 1. Demonstrate mastery of anatomical references to the hand and fingers. 2. Compare and contrast Mallet Finger, Swan Neck Deformity and Boutonnière Deformity.
FINGER INJURIES Chapter 24, pgs 727 730, 741 743 1. Demonstrate mastery of anatomical references to the hand and fingers. 2. Compare and contrast Mallet Finger, Swan Neck Deformity and Boutonnière Deformity.
Upper Limb- Sports Medicine II
 Upper Limb- Sports Medicine II I. Palpation A. With patient sitting, supine, & prone, palpate for pain, specific tenderness, swelling, effusion, local hyperthermia B. Bony Palpation 1. Carpal Bones (8)
Upper Limb- Sports Medicine II I. Palpation A. With patient sitting, supine, & prone, palpate for pain, specific tenderness, swelling, effusion, local hyperthermia B. Bony Palpation 1. Carpal Bones (8)
Tendon and Neurovascular Bundle Displacement in the Palm With Hand Flexion and Extension: An MRI and Gross Anatomy Correlative Study
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 23:742 746 (2006) Clinical Note Tendon and Neurovascular Bundle Displacement in the Palm With Hand Flexion and Extension: An MRI and Gross Anatomy Correlative Study
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 23:742 746 (2006) Clinical Note Tendon and Neurovascular Bundle Displacement in the Palm With Hand Flexion and Extension: An MRI and Gross Anatomy Correlative Study
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Failed Extensor Indicis Proprius Tendon Transfer for Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon Rupture after Distal Radial Fracture
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):23-27. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.23 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Failed Extensor
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):23-27. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.23 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Failed Extensor
Viorel Nacu. The clinical anatomy of the Hand
 Viorel Nacu The clinical anatomy of the Hand The distal part of the upper limb is divided in to three regions: 1. The wrist (carpus) 2. The hand (metacarpus) 3. The digits (fingers) The landmarks of this
Viorel Nacu The clinical anatomy of the Hand The distal part of the upper limb is divided in to three regions: 1. The wrist (carpus) 2. The hand (metacarpus) 3. The digits (fingers) The landmarks of this
Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria
 TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
5/8/2017. Finger Injuries in Football. Tendon Injuries of the Hand and Wrist in Football Steve Kronlage, MD Andrews Institute Gulf Breeze, Florida
 Finger Injuries in Football Tendon Injuries of the Hand and Wrist in Football Steve Kronlage, MD Andrews Institute Gulf Breeze, Florida A jammed finger is an injury (at very least a torn ligament) A swollen
Finger Injuries in Football Tendon Injuries of the Hand and Wrist in Football Steve Kronlage, MD Andrews Institute Gulf Breeze, Florida A jammed finger is an injury (at very least a torn ligament) A swollen
