VERILAST Technology. Published articles compendium. Technology Hips Polars Knees Cartilage
|
|
|
- Beatrix Johnson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VERILAST Technology Published articles compendium Technology Hips Polars Knees Cartilage
2 OXINIUM published articles compendium This compendium is designed to help Smith & Nephew sales representatives quickly and easily identify OXINIUM references in the medical literature. Our goal is to support your ongoing efforts to communicate the unique characteristics and value of OXINIUM products. Listed sources are conveniently divided by topic into five tabbed sections (Technology, Hips, Knees, Polars and Cartilage) and further defined according to the type of research (Clinical, Laboratory or Review). Within each of those sub-groups, papers are presented in reverse chronological order so that newer research appears first. Articles that include the title, author, reference, summary and positioning statement are grouped first, followed by articles with only a title, author and reference. Negative articles are shown in red for easy identification.
3 Table of Contents Frequently asked questions p. 1 Technology Laboratory p. 5 Review p. 12 Hips Clinical p. 25 Laboratory p. 30 Review p. 40 Polars Clinical p. 41 Laboratory p. 42 Review p. 43 Knees Clinical p. 45 Laboratory p. 47 Review p. 52 Cartilage Review p. 61
4
5 Surgeon question: What is an OXINIUM femoral head? Answer: OXINIUM is made from Zirconium with 2.5% Niobium metal alloy. Under special heating conditions it grabs oxygen from the environment. Oxygen mixes with Zirconium to form Zirconium Dioxide. Zirconium Dioxide is a true monoclinic (no phase change) ceramic. OXINIUM has a ceramic surface that is integral to the underlying metal. The ceramic is not a coating. It can bend and flex with the metal. OXINIUM is known as a functionally graded material meaning it starts as one material and under special conditions transforms to a different material. The ceramic surface is 5-7 microns thick with an underlying hard material known as the oxygen enriched zone. Below this is the Zirconium-Niobium alloy. OXINIUM implants provide: No risk of ceramic like chipping, squeaking or fracture. OXINIUM is a metal so it can not fracture like a ceramic. OXINIUM surface is a ceramic and is wettable like a ceramic meaning it is lubricious like a ceramic head. Since OXINIUM wears against XLPE it can not squeak like other hard-on-hard bearings. OXINIUM heads can deform but they can not fracture like a ceramic. OXINIUM heads are an unbreakable ceramic. A hypoallergenic solution for metal sensitive patients. OXINIUM heads contain no detectable Nickel, Cobalt, or Chromium which are the most allergen causing metal elements for humans. A reduced risk of osteolytic potential. Due to its lubricious nature, OXINIUM will wear like a ceramic head. OXINIUM on XLPE has been shown to produce fewer polyethylene particles than CoCr on XLPE even under active conditions. Less wear particles means less ostyletic potential. Supporting published literature in this compendium: 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15, 18, 53, 61, 64, 65, 70, 81 1
6 Surgeon question: Isn t OXINIUM a coating? Answer: The ceramic surface of OXINIUM is not a coating but is integral to the metal alloy. The ceramic surface can bend and move with the metal alloy. A coating would flake or crack when its substrate deforms. OXINIUM s ceramic surface does not flake or crack if the metal substrate deforms. It will move and deform with the metal substrate. Hence it is integral to the metal. Functionally graded materials like OXINIUM move or deform as a single entity because the differing materials through the thickness of the product was caused by molecular changes due to special conditions that functionally changed the phase of the material from one material to another. Demonstrate: Show the bent knee femoral or head and let the surgeon feel the smoothness of the ceramic surface to show no flaking or cracking. Show the cut femoral head to show it is metal at the core. Supporting published literature in this compendium: 8, 9, 13, 70, 81 Surgeon question: What are these scratches on OXINIUM heads I have read about? Answer: It is possible to scratch or gouge through the ceramic surface of OXINIUM heads. Typically this results from multiple dislocations or gouging the implant with a sharp instrument. Most of the scratching seen on pictures of the OXINIUM head is from metal transfer from the shell onto the femoral head. This is very noticeable due to the gray-on-black contrast. Yes these pictures look bad! Under a single dislocation event or from location of the head into the socket during implantation, the scratches are titanium transfer and is not a breach of the ceramic surface. 2
7 Under multiple dislocation events, it is possible to breach the ceramic surface of the OXINIUM head. The question to ask is: Is a multiple dislocator a fault of the bearing? The answer is No! Multiple dislocators are due to either malpositioned shell, soft tissue issue or patient noncompliance. In any case it requires surgical intervention. The fact remains that all multiple dislocators may damage the bearing surface. Ceramic heads can experience metal transfer, fracture or wear through the shell; CoCr heads also experience metal transfer, scratching, gouging or wear through the shell; OXINIUM heads experience metal transfer, scratching or wear through the shell. The scratching or metal transfer is just more noticeable on the black OXINIUM head than on the other head materials. What happens if the ceramic surface of OXINIUM heads is breached and it wears against the XLPE? Does it lead to runaway wear? The answer is that it does not lead to runaway wear. There has been a paper published that has taken scratched and damaged explanted OXINIUM heads from multiple dislocators and put them in a wear simulator. Results indicate that even in a damaged state, the damaged OXINIUM heads performed as well as pristine CoCr heads. Supporting published literature in this compendium: 2, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 18, 53, 61, 64, 70, 81 Surgeon question: Why should I use OXINIUM on XLPE? Answer: OXINIUM implants provide: No risk of ceramic like chipping, squeaking or fracture. OXINIUM is a metal so it can not fracture like a ceramic. OXINIUM surface is a ceramic and is wettable like a ceramic meaning it is lubricious like a ceramic head. Since OXINIUM wears against XLPE it can not squeak like other hard-on-hard bearings. OXINIUM heads can deform but they can not fracture like a ceramic. OXINIUM heads are an unbreakable ceramic. 3
8 A hypoallergenic solution for metal sensitive patients. OXINIUM heads contain no detectable Nickel, Cobalt or Chromium which are the most allergen causing metal elements for humans. A reduced risk of osteolytic potential. Due to its lubricious nature, OXINIUM will wear like a ceramic head. OXINIUM on XLPE has been shown to produce fewer polyethylene particles than CoCr on XLPE even under active conditions. Less wear particles means less ostyletic potential. 10 Mrad irradiated and remelted XLPE is recognized throughout the orthopaedic industry as providing the best wear reduction and producing the least amount of wear particles in every size range. Combine Smith & Nephew XLPE with the R3 acetabular shell designed specifically to protect for XLPE with: Flush seating liners to reduce impingement chances and increase ROM. Axial locking mechanism located lower in the shell where the poly is thicker and stresses can be distributed better. Ultracongruent shell to fully support the poly for better stress distribution. Large antirotation tabs for rotational stability. OXINIUM on XLPE provides ceramic performance by producing fewer wear particles with the intraoperative flexibility of different neck lengths. Supporting published literature in this compendium: 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15, 18, 53, 61, 64, 65, 70, 81 4
9 Technology OXINIUM published articles compendium
10
11 Technology Laboratory 1 Heat Generation and Dissipation Behavior of Various Orthopaedic Bearing Materials Tsai, S., Salehi, A., Aldinger, P., and Hunter, G. Bioceramics, Vol. 18, T. Nakamura, K. Yamashita, and M. Neo (eds.), Trans Tech Pub., Uetikon-Zuerich, Switz., 2006, pp This is a scientific article examining the temperatures at the articulating surface of various femoral head materials in a hip simulator. High interface temperatures have been theorized to cause high wear clinically, and can lead to errors in laboratory testing. The interfacial temperature of OXINIUM heads in the study was found to be similar to CoCr and alumina, whereas zirconia heads had a significantly higher temperature. This study was primarily designed to differentiate OXINIUM from zirconia, and show that it has a metallic substrate. Some surgeons believe the elevated interfacial temperature with zirconia heads may lead to tunneling wear. This article is a good reference to address these concerns. 2 Wettability Analysis of Orthopaedic Materials Using Optical Contact Angle Methods Salehi, A., Tsai, S., Pawar, V., Sprague, J., Hunter, G., Varma, S., and Namavar, F. Bioceramics, Vol. 18, T. Nakamura, K. Yamashita, and M. Neo (eds.), Trans Tech Pub., Uetikon-Zuerich, Switz., 2006, pp This article examines the ability of fluids to coat the surfaces of various orthopaedic bearing materials, thus reducing the wear. The study found that the wettability of OXINIUM was similar to other ceramics, and was superior to CoCr and a diamond-like carbon coating. 5
12 TechnologyLaboratory This is a basic science article that may be suitable for surgeons who have a specific question about the properties of OXINIUM. 3 Galvanic Corrosion Evaluation of Zr-2.5Nb Coupled with Orthopaedic Alloys Marek, M., Pawar, V., Tsai, S., Thomas, R., Sprague, J., Hunter, G., and Salehi, A. Medical Device Materials III, R. Venugopalan and M. Wu (eds.), ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2006, pp This is a scientific article that evaluates the galvanic corrosion potential for Zr-2.5Nb when in contact with other orthopaedic alloys, and concluded that the corrosion should be no different than current alloy couples. This article is extremely technical, and is suitable for any surgeon who requests in-depth analysis of the corrosion potential of the OXINIUM base alloy. 4 Acidic Fretting Tests of Oxidized Zr-2.5Nb, CoCr and SS Modular Heads Pawar, V., Jones, B., Sprague, J., Salehi, A., and Hunter, G. Medical Device Materials II, M. Helmus and D. Medlin (eds.), ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2005, pp Fretting corrosion testing of OXINIUM, CoCr, and SS femoral heads was performed under extreme test conditions of elevated temperature and acidic solution to demonstrate the resistance of OXINIUM to corrosion. The SS-SS combination was found to show the most damage, with the OXINIUM heads showing the least signs of fretting corrosion.
13 The test method in this study can be considered to be extreme and beyond the normal clinical situation. Even under these conditions, the OXINIUM heads showed minimal signs of corrosive attack. This paper can be used in conjunction with Tsai et al, SFB 2005 to address any concerns about the fretting corrosion of head tapers. 5 The Role of Joint Fluid in the Tribology of Total Joint Arthroplasty Mazzucco, D. and Spector, M. Clin. Orthop., 429, 2004, pp This study examined the friction between PE articulating against CoCr and OXINIUM under a variety of lubrication conditions. The study found that there was a significant reduction in the friction against OXINIUM compared to CoCr, and the reduction was more pronounced in lubrication situations that would likely result in higher wear for CoCr. This paper is good support for demonstrating one of the benefits of OXINIUM, lower friction. The lower friction and increased wettability of OXINIUM help to explain why OXINIUM exhibits better wear properties than CoCr in total joint arthroplasty. 6 Reduced Wear Using the Ceramic Surface on Oxidized Zirconium Heads Good, V., Widding, K., Heuer, D., and Hunter, G. Bioceramics in Joint Arthroplasty, J.Y Lazennec and M. Dietrich (eds.), Steinkopff Verlag, Darmstadt, Germany, 2004, pp
14 TechnologyLaboratory This lab study observed that against XLPE liners, poly wear produced by roughened OXINIUM heads was comparable to the wear produced by nonroughened CoCr heads. OXINIUM heads with XLPE liners were observed to reduce the poly wear by 98% compared to the standard CoCr/Conventional poly coupling. This wear reduction was observed to be comparable to the wear reduction obtained by other advanced bearings like Metal-on-Metal (97% wear reduction) and Ceramic-on-Ceramic (99% wear reduction). See Good et al, JBJS Polyethylene Wear Against Metal-Ceramic Composite Femoral Components Hermida, J.C., Patil, S., D'Lima, D.D., Colwell, Jr., C.W., and Ezzet, K.A. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 71st Ann. Mtg Proc., 5, 2004, p This is an independent study performed at Scripps Institute (San Diego, CA) comparing the wear rate of cobalt chrome and OXINIUM knees under normal and high demand activities (increased tibial rotation and varus moment). The study found a 44% wear reduction using OXINIUM knees under normal conditions, and a 40% wear reduction under high-demand conditions. Because this is an AAOS meeting abstract, there is only a short summary abstract with no in-depth handout. Similar data can be found in the Ezzet et al ORS abstract from
15 8 Friction of Oxidized Zirconium Versus Cobalt-Chromium Alloy Against Polyethylene Mazzucco, D., and Spector, M. Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc., 29, 2004, p This article is focused on determining factors that influence the friction between articulating joints, with one of the experiments examining the friction of CoCr and OXINIUM against UHMWPE. The study found a significant decrease in friction with OXINIUM compared to CoCr with bovine serum lubrication. This study can be used to address any questions regarding the friction of OXINIUM against UHMWPE. 9 Dynamic Contact Angle Measurements on Orthopaedic Ceramics and Metals Salehi, A., Aldinger, P., Sprague, J., Hunter, G., Bateni, A., Tavana, H., and Neumann, A.W. Medical Device Materials, S. Shrivatstava (ed.), ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2004, pp This article examines the ability of fluids to coat the surfaces of various orthopaedic bearing materials, thus reducing the wear. The study found that the wettability of OXINIUM was similar to other ceramics, and was superior to CoCr and a diamond-like carbon coating. This is a basic science article that may be suitable for surgeons who have a specific question about the properties of OXINIUM. 9
16 TechnologyLaboratory 10 Abrasive Wear of Oxidized Zr-2.5Nb, CoCrMo, and Ti-6Al-4V Against Bone Cement Hunter, G., and Long, M. 6th World Biomaterials Cong. Trans., Society For Biomaterials, Minneapolis, MN, 2000, p In this experiment, a bone cement pin with radiopacifying agent (hard ceramic particulate) was articulated against disks of CoCr and OXINIUM for 10 Mcycle. After testing, the OXINIUM disks showed 4,900 times less volumetric wear, 640 times less wear track depth, and 160 times lower post-test roughness than the CoCr samples. There was no visible wear track on the OXINIUM samples, while the CoCr samples showed an abraded region, and produced a cloudy solution. This article highlights the abrasion resistance of OXINIUM which is one of its key benefits. Retrieval studies have shown that CoCr articulating surfaces roughen with time in vivo, leading to higher wear. The abrasion resistance of OXINIUM helps to prevent scratching, which should result in lower wear. 11 Nano-hardness Measurements of Oxidized Zr-2.5Nb and Various Orthopaedic Materials Long, M., Riester, L., and Hunter, G. Trans. Soc. Biomaterials, 21, 1998, p Indentation testing performed on OXINIUM CoCr, zirconia, and Ti-6Al-4V found that the ceramic surface of OXINIUM material is over twice as hard as CoCr and Ti-6Al-4V, and is approximately 80% as hard as zirconia. Additionally, indentations made along increasing depth into the OXINIUM material show the presence of a transition region to the base alloy. The transition region is oxygen enriched, and helps explain the excellent adherence of the oxide to the base metal substrate. 10
17 The high hardness of the OXINIUM surface is one of the reasons behind the excellent abrasion resistance of the material, resulting in better wear performance of OXINIUM components compared to CoCr components. 12 The Influence of Scratches to Metallic Counterfaces on the Wear of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene Fisher, J., Firkins, P., Reeves, E.A., Hailey, J.L., and Issac, G.H. Proc Instn Mech Engrs, Vol. 209, This study examined the effect of scratches in CoCr on the wear of UHMWPE using a pin-on-disk simulator. Clinically, articulating surfaces can be scratched by bone particulate, bone cement debris, or metal/ha debris. In this study, a 2 micron deep scratch with a lip height of 1 micron resulted in a times increase in wear. Although OXINIUM is not mentioned in this article, it does show the real need for an abrasion resistant material to reduce the wear of the UHMWPE component over time. A single 2-micron deep scratch can result in a substantial increase in wear. Use this article with Hunter et al (WBC 2000) to highlight how OXINIUM's abrasion resistance will prevent scratches to the component over time, resulting in less wear. 11
18 13 Technology Review Creation of Oxidized Zirconium Orthopaedic Implants, Titanium, Niobium, Zirconium, and Tantalum for Medical and Surgical Applications Hunter, G., Dickinson, J., Herb, B., and Graham, R. ASTM STP 1471, L.D. Zardiackas, M.J. Kraay, and H.L. Freese (eds.), American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, PA, 2005, pp This study gives details about the history of oxidized zirconium in other industries and explains in detail the manufacturing process of OXINIUM material. The article also gives a high-level summary regarding the performance of OXINIUM in implants. This is a good background paper for any surgeons interested in the OXINIUM technology itself. 14 Biology of Foreign Bodies: Tolerance, Osteolysis, and Allergy Nasser, S. Total Knee Arthroplasty, J. Bellemans, M.D. Ries, and J. Victor (eds.), Springer Verlag, Heidelberg, Germany, 2005, pp This article is a summary of the biological responses that take place when foreign materials are introduced, differentiating between particle-induced osteolytic responses from immune hypersensitivity responses. The article describes these responses with reference to current orthopaedic materials. The article describes zirconium as a nearly inert material that has never been reported to induce immune reactions. This study also discusses the possible use of OXINIUM implants for patients that have some kind of metal sensitivity. 12
19 This is an excellent article for explaining the different types of tissue responses, and highlights the applicability of OXINIUM for metal-sensitive patients. As the topic of metal sensitivity in patients garners more attention, this article can be used to highlight a benefit of OXINIUM that no other major orthopaedic company can claim. 15 Metal Sensitivity in Patients with Orthopaedic Implants Hallab, N.J., Merritt, K., and Jacobs, J.J. J. Bone Joint Surg., 83-A, March, 2001, pp This is an excellent review article that discusses the different types of responses to implants and implant debris, and highlights the issue of metal sensitivity. The paper cites a number of clinical and case studies that describe metal hypersensitivity and discuss the incidence rate for these types of conditions. The area of metal sensitivity is gaining attention as a possible cause for implant failure. One of the key features of OXINIUM is that it contains no measurable amounts of Co, Cr, and Ni which are key sensitizers. Thus OXINIUM material can be an excellent option for metal sensitive patients. This paper highlights the possibility of metal hypersensitivity to CoCr alloys. 16 Initial Hemocompatibility Studies of Titanium and Zirconium Alloys: Prekallikrein Activation, Fibrinogen Adsorption, and Their Correlation with Surface Electrochemical Properties Yun,Y.H, Turitto, V.T., Daigle, K.P., Kovacs, P., Davidson, J.A., and Slack, S.M. 13
20 TechnologyReview J. Biomed Mater Res, 32(1):77-85, This is a highly technical article that looks at the acceptability of OXINIUM and the Zr-based alloy as a blood-contacting material. The study concludes that the materials are promising candidates for blood-contacting devices. This article is highly technical, and is likely not suitable for most surgeons. The article may be appropriate for research surgeons with a background in biochemistry. 17 Characteristics of Metal and Ceramic Total Hip Bearing Surfaces and Their Effect on Long-Term Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene Wear 18 Friction and Wear Characterization of UHMWPE in Reciprocating Sliding Contact with Co-Cr, Ti-6Al-4V and Zirconia Implant Bearing Surfaces Poggie, R.A., Wert, J.J., Mishra, A.K., and Davidson, J.A. 14
21 Wear and Friction of Elastomers, ASTM STP 1145, R. Denton and M.K. Keshavan (eds.), American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, 1992, pp When it articulates against polyethylene, the surface of oxidized zirconium has up to one half the coefficient of friction compared to cobalt chrome material. This greatly reduces adhesive wear, also known as stick and slide wear or wear due to friction. The main reason behind the low coefficient of friction of OXINIUM is its lubricious ceramic surface which is highly wettable and thus attracts fluids. The OXINIUM material also has a lower coefficient of friction against cartilage compared to cobalt chrome. This is important in unipolar hip replacement and in knee replacement in which the surgeon does not resurface the patella. 19 The Use of Functionally Gradient Materials in Medicine Narayan, R.J., Hobbs, L.W., Jin, C., and Rabiei, A. JOM, 58 (7), 2006, pp Creation of Oxidized Zirconium Orthopaedic Implants Hunter, G., Dickinson, J., Herb, B., and Graham, R. J. ASTM Intl., 2 (7),
22 TechnologyReview 21 Oxidation Microstructures and Interfaces in the Oxidized Zirconium Knee Hobbs, L.W., Rosen, V.B., Mangin, S.P., Treska, M., and Hunter, G. J. Appl. Ceram. Tech., 2 (3), 2005, pp Creation of Oxidized Zirconium Orthopaedic Implants Hunter, G., Dickinson, J., Herb, B., and Graham, R. J. ASTM Intl., 2 (7), Abrasive Wear of Modified CoCr and Ti-6Al-4V Surfaces Against Bone Cement Hunter, G., Pawar, V., Salehi, A., and Long, M. Medical Device Materials, S. Shrivatsava (ed.), ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2004, pp
23 24 Oxidized Zirconium - A Potentially Longer Lasting Hip Implant Good, V., Widding, K., Hunter, G., and Heuer, D. Tribology in Environmental Design 2003, M. Hadfield and Y. Wang (eds.), Professional Engineering Pub., Bury St. Edmunds, UK, 2003, pp Scratch Test Evaluations of CoCrMo, Ti-6Al-4V, and Zirconia Long, M., Hunter, G., and Blau, P.J. 6th World Biomaterials Cong. Trans., Society For Biomaterials, Minneapolis, MN, 2000, p Microstructural Investigation of the Oxide Scale on Zr-2.5Nb and its Interface With the Alloy Substrate Benezra, V., Mangin, S., Treska, M., Spector, M., Hunter, G., and Hobbs, L.W. Biomedical Materials, MRS Symp. Proc. 550, T. Neenan, M. Marcolongo, and R.F. Valentini (eds.), Materials Research Society, Warrendale, PA, 1999, pp
24 TechnologyReview 27 Ultrastructure and Adhesion of the Scale on Oxidized Zr-2.5Nb for Total Joint Arthroplasty Benezra, V., Mangin, S.P., Treska, M., Spector, M., and Hobbs, L.W. Trans. Soc. Biomaterials, 21, 1998, p Chemical and Electrochemical Aspects of the Biocompatibility of Titanium and its Alloys Kovacs, P., and Davidson, J.A. Medical Applications of Titanium and Its Alloys, ASTM STP 1272, S.A. Brown and J.E. Lemons (eds.), American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, PA, 1996, pp Effects of the Electrochemical Behavior of Implant Metals on Osteoblast and Oral Bacterial Adhesion Kovacs, P., and Davidson, J.A. Trans. 2nd Comb. Mtg. Orth. Res. Soc. USA, Japan, Can. and Eur., Orthopaedic Research Society, Palatine, IL, 1995, p
25 30 Initial Hemocompatibility Studies of ZrO2/Zr-2.5Nb Yun, Y.H., Turitto, V.T., Daigle, K.P., Kovacs, P., Davidson, J.A., and Slack, S.M. Trans. Soc. Biomaterials, 18, 1995, p Abrasive Wear of Ceramic, Metal, and UHMWPE Bearing Surfaces from Third-Body Bone, PMMA Bone Cement and Titanium Debris Davidson, J.A., Poggie, R.A. and Mishra, A. Biomed. Mater. Eng., 4 (3), 1994, pp Three-Body Abrasive Wear Behavior of Orthopaedic Implant Bearing Surfaces from Titanium Debris Poggie, R.A., Mishra, A.K., and Davidson, J.A. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med., 5 (6-7), 1993, pp
26 TechnologyReview 33 The Effect of Bone, Bone Cement, and Metal Debris on the Change in Roughness of Ceramic and Metal Orthopaedic Implant Bearing Surfaces 34 Zirconia/Zirconium: a New, Abrasion Resistant Material for Orthopaedic Applications 35 Histological Response to Cylinders of a Low Modulus Titanium Alloy (Ti-13Nb-13Zr) and a Wear Resistant Zirconium Alloy (Zr-2.5Nb) Implanted in the Rabbit Tibia 20
27 36 The Local and Systemic Response to Cylinders of a Low Modulus Titanium Alloy (Ti-13Nb-13Zr) and a Wear Resistant Zirconium Alloy (Zr-2.5Nb) Implanted in the Rabbit Tibia 37 The Local and Systemic Response to Cylinders of a Low Modulus Titanium Alloy (Ti-13Nb-13Zr) and a Wear Resistant Zirconium Alloy (Zr-2.5Nb) Implanted in the Rabbit Tibia 38 The Local and Systemic Response to Cylinders of a Low Modulus Titanium Alloy (Ti-13Nb-13Zr) and a Wear Resistant Zirconium Alloy (Zr-2.5Nb) Implanted in the Rabbit Tibia 21
28 TechnologyReview 39 Friction and UHMWPE Wear of Cobalt Alloy, Zirconia, Titanium Nitride, and Amorphous Diamond-Like Carbon Implant Bearing Surfaces 40 Sliding Friction and UHMWPE Wear Comparison Between Cobalt Alloy and Zirconia Surfaces 41 Abrasion Resistance of Candidate Coatings for Orthopaedic Articulating Surfaces 22
29
30 TechnologyReview Compendium_complete.indd :23
31 FAQs Technology Hips OXINIUM published articles compendium Hips Polars Knees Cartilage Compendium_complete.indd :23
32
33 Hips
34 HipsClinical Surface Damage in Retrieved OXINIUM Hip Replacements Wright, T., Danoff, J., Bostrom, M., and Pellicci, P. Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc., 33, 2008, p
35 In this study, eight retrieved OXINIUM heads (two for multiple dislocations) were examined for damage. The authors note finding scratches and gouges, in particular with the dislocated patients. They also damaged one head with a hammer and punch and noted cracking of the oxide around the crater. See SalesLife response from 3/3/08. The damage seen on the heads is similar to that created in other studies (Bragdon et al (ORS 2009) or Bourne et al (CORR 2005), which were found to not cause runaway wear. The six heads from the nondislocated patients don't show the same type of damage. The damage caused by the punch is an extreme situation, and not clinically relevant. Additionally, conversations with the author clinicians found that they still use OXINIUM heads despite their findings. 51 Surface Damage to an OXINIUM Femoral Head Prosthesis After Dislocation Evangelista, G.T., Fulkerson, E., Kummer, F., and Di Cesare, P.E. J. Bone Joint Surg., 89-B (4), 2007, pp The article is a case study of a patient that had a dislocation with an OXINIUM head. Examination of the head found damage that penetrated the oxide caused by articulation against the rim of the acetabular shell. The authors concluded that patients with OXINIUM heads that experience dislocation should be monitored. This article is part of a negative campaign by Stryker attacking the wear of OXINIUM femoral heads after macrodamage such as dislocation. Studies have shown that dislocation damage typically is located inferiorly on the head and is not in the location of peak load as it was in the author's wear study. Refer to the Bragdon et al study from ORS 2009 for a relevant wear test on clinically retrieved heads. 27
36 HipsClinical 52 Damage of OXINIUM Femoral Heads Subsequent to Hip Arthroplasty Dislocation Three Retrieval Case Studies Kop, A.M., Whitewood, C., and Johnston, D.J.L. J. Arthroplasty, 22 (5), 2007, pp This is a case study of three patients with OXINIUM femoral heads that were revised for multiple dislocations. In one case, the surgeon attempted closed reduction for 25 minutes. The article shows pictures of damaged OXINIUM heads, and recommends caution while performing closed reductions for patients with OXINIUM femoral heads. See SalesLife response from 8/22/07. In case 1, the dislocation damage is extreme as the surgeon attempted closed reduction of the head for 25 minutes. The author mentions that some of damage was in an area that may contact PE, but note that studies have shown that dislocation damage typically is located inferiorly on the head and is not in the location of peak load
37 This is a good clinical article to support the use of OXINIUM heads in combination with XLPE in the hip. The data is showing undetectable wear at one year for the OXINIUM on XLPE group. 54 Arthroplasty Options for the Young Patient. OXINIUM on Crosslinked Polyethylene Bourne, R.B., Barrack, R., Rorabeck, C.H., Salehi, A., and Good, V. Clin. Orthop., 441, 2005, pp This study highlights the abrasion resistance of OXINIUM femoral heads vs. CoCr femoral heads. The authors first present retrieval data showing that heads can scratch in vivo, and note that an abrasion resistant surface like OXINIUM should reduce scratching. A hip simulator test with dislocation-simulated damaged found equivalent wear rates for damaged OXINIUM heads and undamaged CoCr. Damaged CoCr heads had a significantly higher wear rate. This would be a good article to use to respond to any surgeons who question the benefit of OXINIUM heads. This may also counter any questions about Stryker's negative campaign where they show higher wear for dislocated heads. 29
38 Hips Laboratory 55 Scratch and Wear Performance of Prosthetic Femoral Head Components Against Crosslinked UHMWPE Sockets Lee, R., Essner, A., Wang, A., Jaffe, W.L. Wear, 267 (11), 2009, pp In this article, heads of various materials were damaged using a diamond indenter in a spiral pattern, and run in a wear simulator. The wear of OXINIUM was shown to be higher. This article is part of a negative campaign by Stryker attacking the wear of OXINIUM femoral heads after macrodamage such as dislocation. The damage imparted to the heads is not clinically relevant and is extreme. Additionally, studies have shown that dislocation damage typically is located inferiorly on the head and is not in the location of peak load as it was in the author's wear study. Refer to the Bragdon et al study from ORS 2009 for a more relevant wear test on clinically retrieved heads. 56 Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction: Effects on Polyethylene Wear Jaffe, W.L., Strauss, E.J., Cardinale, M., Herrera, L., and Kummer, F.J. J. Arthroplasty, 24 (6), 2009, pp Based on four retrieved heads, damage was created on new heads and run in a wear simulator. The wear of OXINIUM was shown to be higher than similarly damaged ceramic heads and related to the extent of damage to the head. 30
39 This article is part of a negative campaign by Stryker attacking the wear of OXINIUM femoral heads after macrodamage such as dislocation. The surgeon should note that the control comparison group was a ceramic head and not CoCr. The worst-case OXINIUM wear rate is actually similar to an undamaged CoCr against conventional PE. Additionally, studies have shown that dislocation damage typically is located inferiorly on the head and is not in the location of peak load as it was in the author's wear study. Refer to the Bragdon et al (ORS 2009) or Bourne et al (CORR 2005) for a more relevant wear test on clinically retrieved heads. 57 The Effect of In Vivo Damage of OXINIUM Femoral Heads on the Wear of Highly Crosslinked Polyethylene Bragdon, C., Wannomae, K., Lozynsky, A., Micheli, B., Malchau, H. Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc., 34, 2009, p This study ran six clinically retrieved damaged OXINIUM heads in a wear simulator. The damage was positioned in the highest load area, even though in vivo the damage is primary on the inferior portion of the head. The results indicated a measurable amount of wear for the damaged OXINIUM heads, but did not show runaway wear and was substantially lower than undamaged CoCr against conventional PE. 31
40 HipsLaboratory 58 Wear of Conventional and Highly Crosslinked Polyethylene Liners during Simulated Fast Walking/Jogging Parikh, A., Hill, P., Hines, G., Pawar, V. Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc., 34, 2009, p This is a wear simulator study of OXINIUM and CoCr femoral heads under more strenuous conditions (higher frequency and load). The results showed a statistically significant reduction in wear for the OXINIUM heads compared to the CoCr under conditions that simulated fast walking/jogging. This paper is another reference that shows a significant reduction in wear for OXINIUM heads. This paper can be used as further evidence of the benefits of OXINIUM heads in the younger, more active patients that want to perform more rigorous activities. 59 Wear Evaluation of the Effect of Head Damage due to Dislocation and Reduction Herrera, L., Cardinale, M., Essner, A., Racanelli, J., Jaffe, W., and Kummer, F. Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc., 33, 2008, p Based on four retrieved heads, damage was created on new heads and run in a wear simulator. The wear of OXINIUM was shown to be higher than similarly damaged ceramic heads and related to the extent of damage to the head. This article is part of a negative campaign by Stryker attacking the wear of OXINIUM femoral heads after macrodamage such as dislocation. The surgeon should note that 32
41 the control comparison group was a ceramic head and not CoCr. The worst-case OXINIUM wear rate is actually similar to an undamaged CoCr against conventional PE. Additionally, studies have shown that dislocation damage typically is located inferiorly on the head and is not in the location of peak load as it was in the author's wear study. Refer to the Bragdon et al (ORS 2009) or Bourne et al (CORR 2005) for a more relevant wear test on clinically retrieved heads. 60 Damage of OXINIUM Femoral Heads Subsequent to Hip Arthroplasty Dislocation Three Retrieval Case Studies Kop, A.M., Whitewood, C., and Johnston, D.J.L. J. Arthroplasty, 22 (5), 2007, pp This is an AAOS scientific exhibit that looked at the damage and subsequent hip simulator wear caused by dislocation to a number of different head and shell material combinations. The study found that dislocation damaged heads increased the PE wear rate regardless of material. OXINIUM was noted to be particularly susceptible to damage and significantly increased wear. This article is part of a negative campaign by Stryker attacking the wear of OXINIUM femoral heads after macrodamage such as dislocation. Studies have shown that dislocation damage typically is located inferiorly on the head and is not in the location of peak load as it was in the author's wear study. Refer to the Bragdon et al study from ORS 2009 for a more relevant wear test on clinically retrieved heads. 61 Comparison of Surface Characteristics and Prediction of Wear Properties Between Alumina and OXINIUM Femoral Heads Bal, B.S., Evans, R., Rahaman, M., Ellingsen, M.D., and Khanna, S.K. 33
42 HipsLaboratory Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc., 31, 2006, p This is an experimental study to compare the hardness, elastic modulus, scratch depth, and friction of alumina and OXINIUM material. The study found that alumina ceramic was harder, exhibited shallower scratches, and had a lower coefficient of friction compared to OXINIUM when tested with a diamond tip. The findings of this paper are consistent with the material properties of alumina and OXINIUM material. The paper outlines simple materials tests and doesn't make any extrapolations to in vivo performance. For surgeons, the clinical wear and abrasion resistance of alumina is not in question, rather the possibility of catastrophic fracture leading to complications with subsequent revisions. 62 Hip Simulator Wear-Aggravation of Crosslinked-PE Cups by Roughened CoCr and Zirconia Clarke, I.C., Robertson, B., Green, D.D., and Williams, P.A. Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc., 30, 2005, p In this simulator study, the wear of roughened and smooth 36 mm OXINIUM heads were compared to roughened and smooth 32 mm CoCr heads. The results indicated that the smooth 36 mm OXINIUM heads had no measurable wear, and roughened 36 mm OXINIUM had only slight wear. In contrast, the 32 mm CoCr heads had no measurable wear when smooth, but showed a large degree of wear when roughened. Although this study shows no measurable wear for OXINIUM heads, it would be recommended to use Good et al, JBJS 2003 for a more comprehensive applicable reference. 34
43 63 Arthroplasty Options for the Young Patient. OXINIUM on Crosslinked Polyethylene. Bourne, R.B., Barrack, R., Rorabeck, C.H., Salehi, A., and Good, V. Clin. Orthop., 441, 2005, pp This study highlights the abrasion resistance of OXINIUM femoral heads vs. CoCr femoral heads. The authors first present retrieval data showing that heads can scratch in vivo, and note that an abrasion resistant surface like OXINIUM should reduce scratching. A hip simulator test with dislocation-simulated damaged found equivalent wear rates for damaged OXINIUM heads and undamaged CoCr. Damaged CoCr heads had a significantly higher wear rate. This would be a good article to use to respond to any surgeons who question the benefit of OXINIUM heads. This may also counter any questions about Stryker's negative campaign where they show higher wear for dislocated heads. 64 Oxidized Zirconium - A Potentially Longer Lasting Hip Implant Good, V., Widding, K., Hunter, G., and Heuer, D. Mater. Design, 26 (7), 2005, pp This is a simulator study that was first presented at AAOS as a scientific exhibit. The study looked at hip simulator wear of OXINIUM and CoCr heads in both as-packaged and roughened conditions against both CPE and XLPE. The study showed a significant reduction in wear for OXINIUM for all test conditions. Under roughened conditions, the OXINIUM heads still had undetectable wear when articulated against XLPE. See Good et al, JBJS
44 HipsLaboratory 65 Fretting Corrosion Testing of Various Femoral Head/Taper Material Combinations Tsai, S., Heuer, D., Pawar, V., and Salehi, A. Trans. Soc. Biomaterials, 28, 2005, p. 85. This study examined the fretting corrosion between femoral heads coupled with hip stem tapers. The study found similar or lower metal ion release from OXINIUM heads compared to CoCr and SS heads. This study would be appropriate for any surgeons requesting more information about the Smith & Nephew taper design performance. The study shows that the use of OXINIUM femoral heads should produce fewer metal ions compared to CoCr heads. 66 Thermal Generation and Dissipation Behavior of Various Bearing Materials In a Hip Joint Simulator Tsai, S., Aldinger, P., Hunter, G., Thornberry, R.L., and Salehi, A. Trans. 7th World Biomaterials Cong., Australian Society for Biomaterials, Victoria, Austl., 2004, p This is a scientific article examining the temperatures at the articulating surface of various femoral head materials in a hip simulator. High interface temperatures have been theorized to cause high wear clinically, and can lead to errors in laboratory testing. The interfacial temperature of OXINIUM heads in the study was found to be similar to CoCr and alumina, whereas zirconia heads had a significantly higher temperature. 36
45 This study was primarily designed to differentiate OXINIUM from zirconia, and show that it has a metallic substrate. Some surgeons believe the elevated interfacial temperature with zirconia heads may lead to tunneling wear. This article is a good reference to address these concerns. 67 Simulator Comparison of XLPE Wear with 36mm CoCr and Oxidized Zirconium Balls In Smooth and Roughened Condition Clarke, I.C., Green, D.D., Williams, P.A., and Good, V. Trans. 7th World Biomaterials Cong., Australian Society for Biomaterials, Victoria, Austl., 2004, p This study compared the wear of CoCr and OXINIUM femoral heads under smooth and roughened conditions. The wear of the OXINIUM heads was found to be less than CoCr under both smooth and rough conditions. The abstract has multiple typos and the graphs are erroneously inverted. See Good et al, JBJS 2003 for a more applicable reference. 68 Mechanical Behavior of Zirconia, Alumina, and Oxidized Zirconium Modular Heads Sprague, J., Salehi, A., Tsai, S., Pawar, V., Thomas, R., and Hunter, G. ISTA 2003, Vol. 2, S. Brown, I.C. Clarke, and A. Gustafson (eds.), International Society for Technology in Arthroplasty, Birmingham, AL, 2004, pp
46 HipsLaboratory This test was conducted to compare the strength of OXINIUM and ceramic femoral heads. Femoral heads were loaded until fracture. OXINIUM femoral heads were observed to withstand a load of 20,000 pounds without fracturing, whereas alumina and zirconia femoral heads were observed to fail at loads of around 8,000 pounds and 14,500 pounds. The OXINIUM heads were also shown to be stable after autoclaving and didn't degrade like zirconia heads. This study was presented at ISTA and there is no easily obtainable reference from the conference. However, this information is contained in other marketing literature that can be used to show the advantages of OXINIUM over ceramic heads. The pieces of fractured ceramic heads can be very small, and are known to cause damage to subsequent bearings since the debris is difficult to fully remove. 69 Reduced Wear with Oxidized Zirconium Femoral Heads Good, V., Ries, M., Barrack, R.L., Widding, K., Hunter, G., and Heuer, D. J. Bone Joint Surg., 85-A (S4), 2003, pp This is a simulator study that was first presented at AAOS as a scientific exhibit. The study looked at hip simulator wear of OXINIUM and CoCr heads in both as-packaged and roughened conditions against both CPE and XLPE. The study showed a significant reduction in wear for OXINIUM for all test conditions. Under roughened conditions, the OXINIUM heads still had undetectable wear when articulated against XLPE. This should be the primary publication shown to surgeons to support the wear benefits of OXINIUM femoral heads. The study covers both CPE and XLPE and provides a direct comparison between OXINIUM and CoCr. Under all conditions, OXINIUM was shown to be superior to CoCr and led to significant reductions in wear. 38
47 70 Wear Performance of Damaged Oxidized Zr-2.5Nb Modular Femoral Heads Heuer, D., Good, V., and Widding, K. Trans. Soc. Biomaterials, 26, 2003, p This was a hip simulator study to examine the effect of macrodamage on the wear of OXINIUM femoral heads. The damage was created to simulate dislocation as well as articulation against porous coating beads. The study found that the damaged OXINIUM head had a similar wear rate to an undamaged CoCr femoral head against CPE. The wear of damaged OXINIUM on XLPE was significantly lower. 39
48 Hips Review 71 Low Wear with High-Cross Linked Polyethylene and In Combination with OXINIUM Heads: A RSA Evaluation Li, M.G., Zhou, Z.K., Rohrl, S., Wood, D.J., and Nivbrant, B. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. Ann. Mtg. Proc., 7, 2006, pp Surface Characteristics of Retrieved Cobalt-Chromium Femoral Heads With and Without Ion Implantation McGrory, B.J., Ruterbories, J., Pawar, V., Thomas, R., and Salehi, A. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. Proc., 6, 2005, p
49 Polars OXINIUM published articles compendium
50
51 Polars Clinical 73 Use of Oxidized Zirconium Hemiarthroplasty in Hip Fractures Sah, A.P., and Ready, J.E. J. Arthroplasty, 22 (8), 2007, pp This study is a clinical follow-up of 52 patients who received OXINIUM unipolar hemiarthroplasties between 1996 and Because the target patients for these types of implants have a known high mortality rate, the benefits of OXINIUM were not able to be proven. However, a retrieval analysis of one implant after eight years in vivo showed no signs of damage or wear, and the roughness was still within manufacturer's specification. This article would be a good reference for any surgeon looking to use OXINIUM unipolar heads articulating against native cartilage and has concerns about the damage to the articulating surface from the host bone and tissues. The article cites no measurable difference between the performance of CoCr and OXINIUM implants due to the high mortality rates of hemiarthroplasty patients, but shows a retrieved OXINIUM implant that demonstrates minimal damage after eight years in use. 41
52 Polars Laboratory 74 Tribological Evaluation of Oxidized Zirconium Using an Articular Cartilage Counterface: A Novel Material for Potential Use in Hemiarthroplasty Patel, A.M., and Spector, M. Biomaterials, 18 (5), 1997, pp This study examined the wear and friction between articular cartilage samples against CoCr and OXINIUM using pin-on-disk testing. The study found a significantly lower friction and a trend toward lower cartilage wear for OXINIUM compared to CoCr. This study may be relevant for surgeons asking about the use of OXINIUM for hemiarthroplasty. 42
53 Polars Review 75 Oxidized Zirconium for Hemiarthroplasty: An in Vitro Assessment Patel, A.M., and Spector, M. Bioceramics 8, J. Wilson, L.L. Hench, and D. Greenspan (eds.), Elsevier, Oxford, UK, 1995, pp
54
55 Knees OXINIUM published articles compendium
56
57 Knees Clinical 76 In Vivo Comparison of Wear Particles Between Oxidized Zirconium and Cobalt-Chrome Femoral Components in the Same Design of TKA Kim, Y.H., Kim, J.S., Huh, W.S., and Lee, K.H. The 22nd Annual Congress of the International Society for Technology in Arthroplasty, Big Island, Hawaii, A540, October 22-24, In this study, one surgeon implanted 100 patients with bilateral GENESIS II knee femorals where one was OXINIUM and the other was CoCr. Synovial fluid was drawn from the knees of 28 patients at one-two years postop and analyzed to look at the amount of PE in the synovial fluid sample, as well as the size and shape of the PE particles. The results indicate no difference in the performance of the knee implant materials, and no difference in the amount, size distribution, or shape of the PE wear debris. This study supports the use of OXINIUM as a safe and effective material for total knee arthroplasty. Both groups had excellent clinical and radiographic outcomes with no incidence of osteolysis. This represents a short-term implant duration. The benefit of OXINIUM's abrasion resistance prevents the types of scratches observed on clinical retrievals of CoCr which may show up in mid-term and long-term durations. 77 Lymphocyte Transformation Testing for Quantifying Metal-Implant-Related Hypersensitivity Responses Hallab, N.J. Dermatitis, 15 (2), 2004, pp
58 KneesClinical In this study, it was observed that up to 10% of the general population and 58% of revision patients have some kind of metal related allergies. Ni is the most common metal sensitizer in humans, followed by Co and Cr (CoCr alloy is made from cobalt and chromium, and it can have up to 0.5% Ni content). The area of metal sensitivity is gaining attention as a possible cause for implant failure. One of the key features of OXINIUM is that it contains no measurable amounts of Co, Cr, and Ni which are key sensitizers. Thus OXINIUM material can be an excellent option for metal sensitive patients. 78 An Oxidized Zr Ceramic Surfaced Femoral Component for Total Knee Arthroplasty Laskin, R.S. Clin. Orthop., 416, 2003, pp This clinical study was conducted by Dr. Richard Laskin at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, and contains the results at two years for patients receiving OXINIUM knee implants. In Dr. Laskin s study, 73 patients with OXINIUM knees showed excellent results at two years with no material related complications. In another randomized study, patients with OXINIUM femorals had comparable knee function scores to patients with cobalt chrome femorals at two years. This paper can be used as clinical evidence regarding the performance of OXINIUM implants. 46
59 Knees Laboratory 79 Wear of Polyethylene Against Metal-Ceramic Composite Femoral Component: Effect of Aggressive Kinematic Conditions Ezzet, K.A., Hermida, J.C., Patil, S., Steklov, N., Colwell Jr., C.W., and D'Lima, D.D. Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc., 30, 2005, p This is an independent study performed at Scripps Institute (San Diego, CA) comparing the wear of cobalt chrome and OXINIUM knees under different test conditions. The wear test was done under perfectly aligned conditions as well as with malalignment under either high rotation and in high varus. With the knee components properly aligned, the OXINIUM femorals reduced the wear rate of the polyethylene inserts by 42%. Under high rotation and in high varus conditions, the OXINIUM femoral reduced the wear rate by 40% to 60%. This study is similar to the Ezzet et al study from CORR (2004), and provides independent wear testing of OXINIUM for any surgeons that do not trust internal industry testing. 80 Oxidized Zirconium Femoral Components Reduce Polyethylene Wear In a Knee Wear Simulator Ezzet, K.A., Hermida, J.C., Colwell Jr., C.W., and D'Lima, D.D. Clin. Orthop., 428, 2004, pp
60 KneesLaboratory 81 UHMWPE in Vitro Wear Performance Under Roughened Oxidized Zirconium and CoCr Femoral Knee Components DesJardins, J.D. and LaBerge, M. Trans. Soc. Biomaterials, 26, 2003, p In this study performed at Clemson University, knee femoral components were tumbled in abrasive media to simulate clinical scratching of components, and then subjected to wear testing in a knee simulator. The OXINIUM knee femorals showed less increase in roughening upon tumbling than the CoCr, likely due to the improved abrasion resistance of the oxide. Knee simulator wear results indicated that OXINIUM femorals reduced the polyethylene wear rate by 82% compared to CoCr knee femorals. Clinical retrieval studies show that components do become scratched in vivo through contact with bone particles, bone cement particles, or other hard third-body debris. OXINIUM components are more resistant to abrasion, and will therefore maintain a lower wear rate than CoCr in the presence of these types of particles. 82 Polyethylene Wear Performance of Oxidized Zirconium and Cobalt-Chromium Knee Components Under Abrasive Conditions Ries, M.D., Salehi, A., Widding, K., and Hunter, G. J. Bone Joint Surg., 84-A (S2), 2002, pp In this study both the cobalt chrome and the OXINIUM femoral components were roughened, in other words, the components were abraded, or scratched. The femorals were roughened to the level that retrieved femorals were shown to roughen in-vivo. In other words, the femorals were roughened to simulate conditions more similar to those that exist in-vivo. 48
61 Results indicated that OXINIUM femorals reduced the polyethylene wear rate by 89% compared to cobalt chrome femorals. It was also observed that the roughened OXINIUM femorals produced virtually the same wear as brand new cobalt chrome femorals. This is a powerful statement to use when explaining the potential benefit of using OXINUM femorals. 83 Adhesion Testing of Oxidized Zirconium Hunter, G. Trans. Soc. Biomaterials, 24, 2001, p One of the misconceptions that some surgeons have about OXINIUM is that it's a coating, and may be susceptible to delamination. In this study, the oxide adherence was challenged by both an indentation punch test through the oxide, and a bone cement abrasion test across a milled groove through the oxide. In both cases, no delamination of the oxide was observed, demonstrating the integrity of the oxide bond. This article can be used to address any concerns a surgeon has about removal of the oxide layer. The oxide is created through a thermally driven transformation of the surface, and isn't a coating. Thus, it shows excellent adherence and will not come off of the component. 49
62 KneesLaboratory 84 Wear Performance of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene on Oxidized Zirconium Total Knee Femoral Components Spector, M., Ries, M.D., Bourne, R.B., Sauer, W.S., Long, M., and Hunter, G. J. Bone Joint Surg., 83-A (S2), 2001, pp This is a knee simulator study that compares the wear of OXINIUM and CoCr knee femoral components in the GENESIS II design. In this study, OXINIUM and CoCr knee femorals were tested against polyethylene inserts in a knee simulator for six million cycles. The OXINIUM femorals were observed to reduce the polyethylene wear rate by 85% compared to cobalt chrome femorals, and exhibited less scratching during testing. This is a good article to present to any surgeon wanting information about the wear of OXINIUM knee femorals, in particular for GENESIS II. There are other articles that cover wear results of roughened femorals and wear of other designs as well. 85 Mechanical Testing and Finite Element Analysis of Oxidized Zirconium Femoral Components Tsai, S., Sprague, J., Hunter, G., Thomas, R., and Salehi, A. Trans. Soc. Biomaterials, 24, 2001, p In order to demonstrate the strength of OXINIUM knee femoral components, the medial condyle of GENESIS II OXINIUM femoral components was repetitively loaded under 1,000 lbs. for 10 million cycles with no fractures. This corresponds to 13 times body weight, and is equivalent to the strength of the GENESIS II CoCr knee femoral component. At higher loads when fracture did occur, there was a clean break and no delamination of the oxide was observed. 50
63 This article can be given to surgeons that have questions regarding the strength of the OXINIUM material. Additionally, for any surgeons that believe that OXINIUM will fracture in a ceramic-like manner, this study demonstrates that fractures of OXINIUM components result in a metal-like fracture mechanism, with no debris generated. 86 Wear Testing of Materials and Surfaces for Total Knee Replacement Walker, P.S., Blunn, G.W., and Lilley, P.A. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 33 (3), 1996, pp This study used pin-on-disk testing to evaluate the effect of various parameters. The article mainly focuses on CoCr against PE, but did one comparison group against oxidized zirconium. The study found a significantly lower wear rate for the oxidized zirconium pin on PE disk. This is a basic tribology article, and is probably not useful for most surgeons since component-based wear test results are now available. 51
64 Knees Review 87 Ceramic Bearings in Total Knee Arthroplasty Bal, B.S., Garino, J., Ries, M., and Oonishi, H. J. Knee Surg., 20 (4), 2007, pp This is a review article that discusses the role of ceramics in knee arthroplasty, and some of the benefits such as lower wear and applicability for metal ion sensitive patients. OXINIUM is mentioned as one of the current ceramic knee options, as well as alumina and zirconia. The article mentions some of the benefits of the OXINIUM material and some of the preliminary clinical results. Overall, the article is complementary of the OXINIUM technology, but with only preliminary data it concludes that it may be too early to conclude any significant benefits. This article is a nice review of ceramics in knees, but since it doesn't have a strong conclusion in favor of OXINIUM, it may not help as support material. 88 Oxidized Zirconium Hunter, G., Jones, W.M., and Spector, M. Total Knee Arthroplasty, J. Bellemans, M.D. Ries, and J. Victor (eds.), Springer Verlag, Heidelberg, Germany, 2005, pp This paper first discusses the need for a damage-tolerant knee femoral component, and then discusses the development of OXINIUM. The paper discusses many of the OXINIUM materials testing performed to highlight the abrasion resistance, oxide adherence, biocompatability, and mechanical strength. 52
65 This paper is an excellent reference to demonstrate the need for an abrasion resistant, low wearing material for knee and hip articulation. The paper mostly focuses on the knee, but may be applicable to hips as well. The paper summarizes much of the material-level testing to demonstrate that OXINIUM meets many of the needs of articulating surfaces in joint arthroplasty. 89 Lymphocyte Transformation Testing for Quantifying Metal-Implant-Related Hypersensitivity Responses Hallab, N.J. Dermatitis, 15 (2), 2004, pp In this study, it was observed that up to 10% of the general population and 58% of revision patients have some kind of metal related allergies. Ni is the most common metal sensitizer in humans, followed by Co and Cr (CoCr alloy is made from cobalt and chromium, and it can have up to 0.5% Ni content). The area of metal sensitivity is gaining attention as a possible cause for implant failure. One of the key features of OXINIUM is that it contains no measurable amounts of Co, Cr, and Ni which are key sensitizers. Thus OXINIUM material can be an excellent option for metal sensitive patients. 53
66 KneesReview 90 Scratches on Condyles in Normal Functioning Total Knees Arthroplasty Levesque, M., Livington, B.J., Jones, W.M., and Spector, M. Orthopaedic Research Society, This retrieval study was performed by Myron Spector from MIT. After analyzing 13 consecutive retrievals, he concludes that femoral implants do roughen in vivo. When scratched, it s not really the scratch that counts - it s the peak next to the scratch that repeatedly gouges the poly over time and increases poly wear in the joint. Another significant contributing factor to poly wear is the orientation of the scratches - if it runs at an angle to articulation, it rubs across a larger area of the poly and will produce more wear than a scratch aligned with the A/P articulation. The retrieved components in this study were observed to have scratches in random directions. OXINIUM material with a harder ceramic surface is more abrasion resistant, thus reducing wear in the joints. 91 UHMWPE Wear Against Roughened Oxidized Zirconium and CoCr Femoral Knee Components During Force-Controlled Simulation DesJardins, J.D., Burnikel, B., and LaBerge. Wear, 264 (3-4), 2008, pp
67 92 Roughness of Retrieved CoCr vs. OxZr Femoral Knee Components Sebastian, Arun M.; Roy, Marcel E.; Whiteside, Leo A.; Azzam, Michael G. Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc., 33, 2008, p The Use of a Ceramic Surfaced Oxidized Zirconium Implant in Total Knee Replacement Laskin, R.S. Tech. Knee Surg., 6 (4), 2007, pp A Prospective Comparison of Ceramic and OXINIUM TKA Components in Metal Hypersensitivity Patients Nasser, S., Mott, M.P., and Wooley, P.H. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. Ann. Mtg. Proc., 8, 2007, pp
68 KneesReview 95 Wear Testing of Crosslinked and Conventional UHMWPE Against Smooth and Roughened Femoral Components Parikh, A., Morrison, M., and Jani, S. Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc., 32, 2007, p Wear of Polyethylene Against Metal-Ceramic Composite Femoral Component: Effect of Aggressive Kinematic Conditions Ezzet, K.A., Hermida, J.C., Steklov, N., Colwell Jr., C.W., and D Lima, D.D. Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc., 31, 2006, p Simulated Wear Test of Oxidized Zirconium Knee Implants Wardle, N.S., Lee, J.K.L., Haddad, F.S., and Blunn, G.W. J. Bone Joint Surg., 88-B (S2), 2006, p
69 98 Tribological Characteristics of a New High Flexion Guided Motion TKA Design Parikh, A., Good, V., and Ries, M. Trans. Soc. Biomaterials, 29, 2006, p Alternative Femoral Bearing Surface Options for Knee Replacement in Young Patients Hernigou, P., Nogier, A., Manicom, O., Poignard, A., De Abreu, L., and Filippini, P. The Knee, 11, 2004, pp Mechanical Testing of Macrotextured Oxidized Zirconium Femoral Components Aldinger, P., Salehi, A., and Tsai, S. Trans. Soc. Biomaterials, 26, 2003, p
70 KneesReview 101 Chemically Textured and Oxidized Zirconium Surfaces for Implant Fixation Heuer, D., Harrison, A., Gupta, H., and Hunter, G. Bioceramics 15, B. Ben-Nissan, D. Sher, and W. Walsh (eds.), Trans Tech Pub., Uetikon-Zuerich, Switz., 2003, pp Knee Simulator Protocol for Testing of Oxidized Zirconium and Cobalt Chrome Femoral Components Under Abrasive Conditions Widding, K., Hunter, G., Hines, G., and Salehi, A. Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc., 27, 2002, p Creating Abrasive Conditions in Knee Simulator Tests of Oxidized Zirconium and Cobalt-Chrome Femorals Salehi, A., Hunter, G., and Widding, K. Bioceramics 14, S. Brown, I. Clarke, and P. Williams (eds.), Trans Tech Pub., Uetikon-Zuerich, Switz., 2002, pp
71 104 Simulated Knee Wear with Cobalt Chromium and Oxidized Zirconium Knee Femoral Components White, S.E., Whiteside, L.A., McCarthy, D.S., Anthony, M., and Poggie, R.A. Clin. Orthop., 309, 1994, pp Simulated Knee Wear with CoCr and Zirconia (ZrO2)-coated Zirconium (Zr-2.5 Nb) Knee Femoral Components White, S.E., McCarthy, D.S., Daigle, K., Anthony, M., Poggie, R.A., and Whiteside, L.A. Orthop. Trans., 18 (4), 1994, p Zirconia (ZrO2)-coated Zirconium-2.5Nb Alloy for Prosthetic Knee Bearing Applications Davidson, J.A., Asgian, C.M., Mishra, A.K., and Kovacs, P. Bioceramics 5, T. Yamamuro, T. Kokubo, and T. Nakamura (eds.), Kobunshi Kankokai, Kyoto, Japan, 1992, pp
72
73 Cartilage OXINIUM published articles compendium
LEGION Total Knee System. Exceptional Durability
 LEGION Total Knee System Exceptional Durability How many knee systems have been lab-tested to 30 years of simulated wear? Just one: LEGION Primary Knee System with VERILAST Technology The LEGION Primary
LEGION Total Knee System Exceptional Durability How many knee systems have been lab-tested to 30 years of simulated wear? Just one: LEGION Primary Knee System with VERILAST Technology The LEGION Primary
Designed for life. Implant technology with unmatched wear performance
 Designed for life Implant technology with unmatched wear performance Designed for life Wear performance combined with a multitude of options so you can find the right combination to restore the joints
Designed for life Implant technology with unmatched wear performance Designed for life Wear performance combined with a multitude of options so you can find the right combination to restore the joints
OXINIUM Femoral Heads. *smith&nephew
 Femoral Heads *smith&nephew Less wear More options Without the risks Even the best cobalt chrome and ceramic femoral heads come with the risks of wear or breakage. But with femoral heads, those risks are
Femoral Heads *smith&nephew Less wear More options Without the risks Even the best cobalt chrome and ceramic femoral heads come with the risks of wear or breakage. But with femoral heads, those risks are
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction. Effects on Polyethylene Wear
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2008 Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction Effects on Polyethylene Wear William L. Jaffe, MD,* Eric J. Strauss,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2008 Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction Effects on Polyethylene Wear William L. Jaffe, MD,* Eric J. Strauss,
The power of simplicity
 The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
Surface Roughness of Femoral Head Prostheses After Dislocation
 An Original Study Surface Roughness of Femoral Head Prostheses After Dislocation Kenny T. Mai, MD, Christopher Verioti, DO, Darryl D Lima, MD, PhD, Clifford W. Colwell, Jr., MD, and Kace A. Ezzet, MD Abstract
An Original Study Surface Roughness of Femoral Head Prostheses After Dislocation Kenny T. Mai, MD, Christopher Verioti, DO, Darryl D Lima, MD, PhD, Clifford W. Colwell, Jr., MD, and Kace A. Ezzet, MD Abstract
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion. Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head
 Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
We would like to thank the following surgeons for their participation as part of the R3 Acetabular System design team:
 Design Rationale We would like to thank the following surgeons for their participation as part of the R3 Acetabular System design team: Robert Barrack, MD St. Louis, Missouri Robert Bourne, MD London Health
Design Rationale We would like to thank the following surgeons for their participation as part of the R3 Acetabular System design team: Robert Barrack, MD St. Louis, Missouri Robert Bourne, MD London Health
Why precision is powerful
 Why precision is powerful A new answer for isolated patellofemoral OA First generation PFJ implants had sharp, constraining trochlear grooves and were prone to complications such as maltracking and catching
Why precision is powerful A new answer for isolated patellofemoral OA First generation PFJ implants had sharp, constraining trochlear grooves and were prone to complications such as maltracking and catching
R3think your options. For US distribution only.
 R3think your options For US distribution only. R3think acetabular surgery It is widely accepted that total hip replacement surgery is one of the most successful procedures done today. Typically more thought
R3think your options For US distribution only. R3think acetabular surgery It is widely accepted that total hip replacement surgery is one of the most successful procedures done today. Typically more thought
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
Trusted technology. Trusted performance. Supporting healthcare professionals
 Trusted technology. Trusted performance. Supporting healthcare professionals Trusted technology. Trusted performance. The POLAR3 Total Hip Solution, powered by Smith & Nephew s proprietary VERILAST Technology,
Trusted technology. Trusted performance. Supporting healthcare professionals Trusted technology. Trusted performance. The POLAR3 Total Hip Solution, powered by Smith & Nephew s proprietary VERILAST Technology,
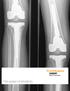
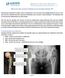
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?
![Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?](/thumbs/78/78456133.jpg) Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Damage of an Oxinium femoral head and polyethylene liner following routine total hip replacement
 CASE REPORT Damage of an Oxinium femoral head and polyethylene liner following routine total hip replacement R. W. McCalden, K. D. Charron, R. D. Davidson, M. G. Teeter, D. W. Holdsworth From London Health
CASE REPORT Damage of an Oxinium femoral head and polyethylene liner following routine total hip replacement R. W. McCalden, K. D. Charron, R. D. Davidson, M. G. Teeter, D. W. Holdsworth From London Health
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
PyroCarbon Implants Durability + Biocompatibility
 PyroCarbon Implants Durability + Biocompatibility What is PyroCarbon? PyroCarbon is a specific form of carbon that has been tailored for durability and biocompatibility. PyroCarbon exhibits favorable wear
PyroCarbon Implants Durability + Biocompatibility What is PyroCarbon? PyroCarbon is a specific form of carbon that has been tailored for durability and biocompatibility. PyroCarbon exhibits favorable wear
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Product Information. *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System
 APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST Technology for unmatched performance Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST
APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST Technology for unmatched performance Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System APPLYING SCIENCE TO MOBILITY Combined with VERILAST
Wear-Reduction Technology in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Our Innovation in Focus Steven Haas, MD, MPH 1, Ramprasad Papannagari, MS 2, Mark Morrison, PhD 2, Shilesh Jani, MS 2 1 Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, NY, USA 2 Smith & Nephew, Inc., Orthopaedics,
Our Innovation in Focus Steven Haas, MD, MPH 1, Ramprasad Papannagari, MS 2, Mark Morrison, PhD 2, Shilesh Jani, MS 2 1 Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, NY, USA 2 Smith & Nephew, Inc., Orthopaedics,
The challenge. Knee replacement patients report lower levels of satisfaction versus hip replacement patients. Return to sports activity post surgery
 The challenge Knee replacement patients report lower levels of satisfaction versus hip replacement patients. Return to sports activity post surgery THA 52% Post-op TKA 42% Preop 36% Preop 34% Post-op Total
The challenge Knee replacement patients report lower levels of satisfaction versus hip replacement patients. Return to sports activity post surgery THA 52% Post-op TKA 42% Preop 36% Preop 34% Post-op Total
Reaching new heights. Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple.
 Reaching new heights Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple. Various acetabular cup choices Compatible with the different head and liner options including VERILAST Technology Reach for proven OR efficient Instrumentation
Reaching new heights Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple. Various acetabular cup choices Compatible with the different head and liner options including VERILAST Technology Reach for proven OR efficient Instrumentation
Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
 Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
Zimmer TM. Continuum Acetabular System. Bringing together proven technologies.
 Zimmer TM Continuum Acetabular System Bringing together proven technologies. The power to meet individual patient needs. Zimmer Continuum Acetabular System provides highly flexible solutions for orthopaedic
Zimmer TM Continuum Acetabular System Bringing together proven technologies. The power to meet individual patient needs. Zimmer Continuum Acetabular System provides highly flexible solutions for orthopaedic
GENESIS II/ LEGION Total Knee System
 GENESIS II/ LEGION Total Knee System The GENESIS II/LEGION knee with the VERILAST technology The knee tested to simulate 30 years of wear performance DISCLAIMER: Always speak to your doctor about the options
GENESIS II/ LEGION Total Knee System The GENESIS II/LEGION knee with the VERILAST technology The knee tested to simulate 30 years of wear performance DISCLAIMER: Always speak to your doctor about the options
DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc. 700 Orthopaedic Drive Warsaw, IN USA Tel: +1 (800) Fax: +1 (574)
 References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
What Are Hip and Knee Replacement Implants Made Of?
 What Are Hip and Knee Replacement Implants Made Of? Hip and knee replacement surgery involve replacing the worn-out bone and cartilage lining your hip or knee joint with new implants that are composed
What Are Hip and Knee Replacement Implants Made Of? Hip and knee replacement surgery involve replacing the worn-out bone and cartilage lining your hip or knee joint with new implants that are composed
I want that next-generation knee
 I want that next-generation knee High flex Potentially longer-lasting More normal feeling Gender-optimized Less-invasive procedure Advanced design technology The last ten years have yielded an explosion
I want that next-generation knee High flex Potentially longer-lasting More normal feeling Gender-optimized Less-invasive procedure Advanced design technology The last ten years have yielded an explosion
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD
 UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
CERAMIC-ON-METAL. References: Cat No: version 2
 CERAMIC-ON-METAL References: 1. Beaule, P. E., et al. Jumbo femoral head for the treatment of recurrent dislocation following total hip replacement. J.Bone Joint Surg (2002). 84-A: 256-63. 2. Jolles, B.
CERAMIC-ON-METAL References: 1. Beaule, P. E., et al. Jumbo femoral head for the treatment of recurrent dislocation following total hip replacement. J.Bone Joint Surg (2002). 84-A: 256-63. 2. Jolles, B.
Cement Polished Tapered Stems of 12/14 Taper. 96 mm 98 mm 104 mm 110 mm 116 mm 122 mm 128 mm. Ceramic Femoral Head. Outer Diameter
 Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
Hip Resurfacing System
 Hip Resurfacing System The Arthrosurface HemiCAP Hip Hemiarthroplasty System restores the articular surface geometry of the femoral head and preserves functional structures using an innovative 3 dimensional
Hip Resurfacing System The Arthrosurface HemiCAP Hip Hemiarthroplasty System restores the articular surface geometry of the femoral head and preserves functional structures using an innovative 3 dimensional
Featuring. Technology. Product Rationale
 Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
ESC. Enhanced Stability Liners. Design Rationale & Surgical Technique
 ESC Enhanced Stability Liners Design Rationale & Surgical Technique Choice Without Compromise DePuy Synthes PINNACLE Hip Solutions are designed with a wide range of acetabular cup options, biological and
ESC Enhanced Stability Liners Design Rationale & Surgical Technique Choice Without Compromise DePuy Synthes PINNACLE Hip Solutions are designed with a wide range of acetabular cup options, biological and
Medical Products Division. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
Ceramic Femoral Heads and Acetabular Cup Liners
 Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution: Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution: Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation
 The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
Design Rationale and Surgical Technique. *smith&nephew TANDEM. Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System
 Design Rationale and Surgical Technique *smith&nephew TANDEM Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System Maximizing performance from every angle Saving time in the operating room is one of the most valuable solutions
Design Rationale and Surgical Technique *smith&nephew TANDEM Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System Maximizing performance from every angle Saving time in the operating room is one of the most valuable solutions
HOSPITAL "A" (2007) ORTHOPEDIC JOINT IMPLANT COMPONENT MATRIX
 HOSPITAL "A" (2007) ORTHOPEDIC JOINT IMPLANT COMPONENT MATRIX HIP IMPLANTS TOTAL HIPS Ultra High Demand (metal on metal) Femur, ingrowth Femoral head, metal Acetabular shell, ingrowth Acetabular liner,
HOSPITAL "A" (2007) ORTHOPEDIC JOINT IMPLANT COMPONENT MATRIX HIP IMPLANTS TOTAL HIPS Ultra High Demand (metal on metal) Femur, ingrowth Femoral head, metal Acetabular shell, ingrowth Acetabular liner,
BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code
 BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code Patrick Chaboche, MD patrick.chaboche@wanadoo.fr Former Head of Department of Orthopaedic Surgery. Centre
BIOTRIBOLOGICAL AND MECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTIY FAILURE: How to break the code Patrick Chaboche, MD patrick.chaboche@wanadoo.fr Former Head of Department of Orthopaedic Surgery. Centre
CeramTec Medical Products. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success. Zimmer Natural-Knee II System
 Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success Zimmer Natural-Knee II System CSTi Porous Coating Structurally similar to human bone CSTi porous coating combines the excellent biocompatibility of titanium with
Over 20 Years of Proven Clinical Success Zimmer Natural-Knee II System CSTi Porous Coating Structurally similar to human bone CSTi porous coating combines the excellent biocompatibility of titanium with
Zimmer Segmental System
 Zimmer Segmental System Simple solutions for solving complex salvage cases A Step Forward The Zimmer Segmental System is designed to address patients with severe bone loss associated with disease, trauma
Zimmer Segmental System Simple solutions for solving complex salvage cases A Step Forward The Zimmer Segmental System is designed to address patients with severe bone loss associated with disease, trauma
Revision of a tibial baseplate using a customized oxinium component in a case of suspected metal allergy A case report
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 691-695 CASE REPORT Revision of a tibial baseplate using a customized oxinium component in a case of suspected metal allergy A case report Nick VAN OPStAl, Frank VERhEyDEN
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 691-695 CASE REPORT Revision of a tibial baseplate using a customized oxinium component in a case of suspected metal allergy A case report Nick VAN OPStAl, Frank VERhEyDEN
Active Articulation E1
 Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Design Rationale Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Dual Mobility: Not a
Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Design Rationale Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Dual Mobility: Not a
1Acetabular Reaming. 2Shell Sizing and Positioning. Trial Range of Motion. Trabecular Metal Natural Cup System
 Trabecular Metal Natural Cup System 1Acetabular Reaming Use progressively larger reamers to prepare the acetabulum. Hold the reamer steady in the same position in which the cup will be implanted (approximately
Trabecular Metal Natural Cup System 1Acetabular Reaming Use progressively larger reamers to prepare the acetabulum. Hold the reamer steady in the same position in which the cup will be implanted (approximately
RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence.
 RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence Design 1973 RM Classic Cup First uncoated RM Classic Cup out of Polyacetal was inserted by E. Morscher
RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence Design 1973 RM Classic Cup First uncoated RM Classic Cup out of Polyacetal was inserted by E. Morscher
The power of robotics in your skilled hands. Supporting healthcare professionals. Supporting healthcare professionals
 The power of robotics in your skilled hands The NAVIO Surgical System provides accuracy, flexibility and confidence utilizing real-time imaging (without the need for preoperative CT), handheld robotics,
The power of robotics in your skilled hands The NAVIO Surgical System provides accuracy, flexibility and confidence utilizing real-time imaging (without the need for preoperative CT), handheld robotics,
Gold standard of a TKA. Conflicting goals? POLYETHYLENE WEAR THE SOLUTION: MOBILE BEARING KNEES. MOBILE BEARING A totally new approach (1977)
 Changing designs : the case against mobile bearing? Gold standard of a TKA Goal of a TKA: 1. Pain 2. Motion 3. Longevity Stress Guy BELLIER M.D. PARIS France Conformity = Durability w/o constraints = non
Changing designs : the case against mobile bearing? Gold standard of a TKA Goal of a TKA: 1. Pain 2. Motion 3. Longevity Stress Guy BELLIER M.D. PARIS France Conformity = Durability w/o constraints = non
MicroSeal Total Hip Acetabular System. Like Nothing Else
 MicroSeal Total Hip Acetabular System Like Nothing Else Like Nothing Else Unique Patented Sealing and Locking Design The MicroSeal design features: Locking/Sealing mechanisms work together to minimize
MicroSeal Total Hip Acetabular System Like Nothing Else Like Nothing Else Unique Patented Sealing and Locking Design The MicroSeal design features: Locking/Sealing mechanisms work together to minimize
Technique Guide Hip Resurfacing System
 Technique Guide Hip Resurfacing System Approximately 5%-18% of all hip arthroplasties are completed on patients with a primary diagnosis of osteonecrosis. Patients are generally younger adults age 35 years
Technique Guide Hip Resurfacing System Approximately 5%-18% of all hip arthroplasties are completed on patients with a primary diagnosis of osteonecrosis. Patients are generally younger adults age 35 years
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System. Product Features and Instructions for Use
 BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed of 75% aluminum oxide and approximately 25% zirconia.
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed of 75% aluminum oxide and approximately 25% zirconia.
Design Rationale. ECHELON Primary Hip System
 Design Rationale ECHELON Primary Hip System ECHELON Primary Total Hip System Addressing clinical issues of cementless hip arthroplasty Cementless total hip arthroplasty has provided a proven method of
Design Rationale ECHELON Primary Hip System ECHELON Primary Total Hip System Addressing clinical issues of cementless hip arthroplasty Cementless total hip arthroplasty has provided a proven method of
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System
 BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Technology Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Technology Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed
Talar Dome System Surgical Technique
 Talar Dome System Surgical Technique CAP TALAR DOME RESURFACING HEMIARTHROPLASTY IMPLANT Surgical Technique Guide Description The HemiCAP Contoured Articular Prosthetic incorporates an articular resurfacing
Talar Dome System Surgical Technique CAP TALAR DOME RESURFACING HEMIARTHROPLASTY IMPLANT Surgical Technique Guide Description The HemiCAP Contoured Articular Prosthetic incorporates an articular resurfacing
Painful Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 21 No. 2 2006 Painful Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty Cambize Shahrdar, MD,* Pat Campbell, PhD,y Joseph Mirra, MD,y and Lawrence D. Dorr, MD* Abstract: Two patients
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 21 No. 2 2006 Painful Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty Cambize Shahrdar, MD,* Pat Campbell, PhD,y Joseph Mirra, MD,y and Lawrence D. Dorr, MD* Abstract: Two patients
Newer designs in Knee replacement The good,bad & ugly! Dr VAIBHAV BAGARIA
 Newer designs in Knee replacement The good,bad & ugly! Dr VAIBHAV BAGARIA MBBS, MS, FCPS, DIP SICOT. Arthroplasty fellow- USA, Germany, Aus Joint replacement surgeon COLUMBIA ASIA HOSPITAL, GZB. Fresh
Newer designs in Knee replacement The good,bad & ugly! Dr VAIBHAV BAGARIA MBBS, MS, FCPS, DIP SICOT. Arthroplasty fellow- USA, Germany, Aus Joint replacement surgeon COLUMBIA ASIA HOSPITAL, GZB. Fresh
[ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor
![[ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor [ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor](/thumbs/88/117546298.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES MODELING AND FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF KNEE JOINT PROSTHESIS U.D.S.Prathap varma *1,S.Rajesh 2, B.Suresh Kumar 3 & P.Rama Murthy Raju 4 *1 M.TechScholar,
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES MODELING AND FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF KNEE JOINT PROSTHESIS U.D.S.Prathap varma *1,S.Rajesh 2, B.Suresh Kumar 3 & P.Rama Murthy Raju 4 *1 M.TechScholar,
Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners. Design Rationale Surgical Technique
 Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners Design Rationale Surgical Technique The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System was designed to maximize the number of options available to the surgeon, and provide those options
Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners Design Rationale Surgical Technique The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System was designed to maximize the number of options available to the surgeon, and provide those options
Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces
 Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces Timothy L. Tan, BS 1, Brenna C. Moeljadi, BS 2, Edward Ebramzadeh, PhD 3, Patricia Campbell, PhD 3, Sophia Nicole
Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces Timothy L. Tan, BS 1, Brenna C. Moeljadi, BS 2, Edward Ebramzadeh, PhD 3, Patricia Campbell, PhD 3, Sophia Nicole
Stability without compromise. Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert
 Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
The Challenge of Durability in Hip Replacement
 The Challenge of Durability in Hip Replacement Gregory A. Tocks, D.O. Orthopedic Associates of Lancaster Ltd. INTRODUCTION Hip replacement is a very common operation, and the number of long-term postoperative
The Challenge of Durability in Hip Replacement Gregory A. Tocks, D.O. Orthopedic Associates of Lancaster Ltd. INTRODUCTION Hip replacement is a very common operation, and the number of long-term postoperative
Identify the role of the skeletal system particularly in relation to maintaining an upright stance and protecting vital organs.
 9.3.3 The wide range of movements, continual absorption of shocks and diseases make the skeletal system vulnerable to damage but new technologies are allowing the replacement of some damaged structures.
9.3.3 The wide range of movements, continual absorption of shocks and diseases make the skeletal system vulnerable to damage but new technologies are allowing the replacement of some damaged structures.
*smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System. Product Information
 Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System Dual Mobility 30 Years of Clinical Experience Concept combining an extended ROM, a low rate of dislocation and unexpectedly limited wear.
Product Information *smith&nephew POLARCUP Dual Mobility System Dual Mobility 30 Years of Clinical Experience Concept combining an extended ROM, a low rate of dislocation and unexpectedly limited wear.
One system for all revision types
 Design Rationale 1 Introduction Revisions today are anything but routine. As more patients have their first total hip at a younger age, it s becoming common for many to have multiple revision surgeries
Design Rationale 1 Introduction Revisions today are anything but routine. As more patients have their first total hip at a younger age, it s becoming common for many to have multiple revision surgeries
A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY by Timothy McTighe, Exec. Dir., JISRF, Chagrin Falls, Ohio Ying Ko, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio Russell B. Bennett, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio James
A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY by Timothy McTighe, Exec. Dir., JISRF, Chagrin Falls, Ohio Ying Ko, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio Russell B. Bennett, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio James
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. UNISYN HIP SYSTEM
 CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. UNISYN HIP SYSTEM Instructions for Use (IFU) IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. UNISYN HIP SYSTEM Instructions for Use (IFU) IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR
National Joint Replacement Registry. Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement
 National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
Instrumentation Options
 Instrumentation Options With the introduction of Microplasty and Premier Instrumentation platforms and advancements such as our patented Slidex Technology, the Vanguard Complete Knee System is the surgeon
Instrumentation Options With the introduction of Microplasty and Premier Instrumentation platforms and advancements such as our patented Slidex Technology, the Vanguard Complete Knee System is the surgeon
What is the Best Bearing Type? 1/11/2011
 What is the Best Bearing Type? 1/11/2011 A comparison of modern bearing types. Thomas P. Gross, M.D. As a patient there are four reasons you should consider a metal-on-metal bearing total hip replacement
What is the Best Bearing Type? 1/11/2011 A comparison of modern bearing types. Thomas P. Gross, M.D. As a patient there are four reasons you should consider a metal-on-metal bearing total hip replacement
Exeter. Designed for Anatomic Restoration. Clinical Evidence Education
 Exeter Designed for Anatomic Restoration Clinical Evidence Education Anatomic Restoration Exeter re-creating biomechanics In hip replacement, the smallest adjustment can make a big difference. Stryker
Exeter Designed for Anatomic Restoration Clinical Evidence Education Anatomic Restoration Exeter re-creating biomechanics In hip replacement, the smallest adjustment can make a big difference. Stryker
Description Materials Indications Patient selection factors to be considered include: Contraindications Absolute contraindications include:
 Description The Patello-Femoral Wave Arthroplasty Systems incorporate a distal femoral trochlear surface articular component that mates to a taper post via a taper interlock, and an all-polyethylene patella
Description The Patello-Femoral Wave Arthroplasty Systems incorporate a distal femoral trochlear surface articular component that mates to a taper post via a taper interlock, and an all-polyethylene patella
2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J BIOMATERIALS FOR JOINT REPLACEMENT
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s/massachusetts General Hosp. VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J BIOMATERIALS FOR JOINT REPLACEMENT M.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s/massachusetts General Hosp. VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J BIOMATERIALS FOR JOINT REPLACEMENT M.
Ceramic Bearings Should Be Routinely Used in THA. Disclosures 5/4/2015
 5/4/2015 Ceramic Bearings Should Be Routinely Used in THA Gwo-Chin Lee, MD Assistant Professor University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA USA University of Pennsylvania Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
5/4/2015 Ceramic Bearings Should Be Routinely Used in THA Gwo-Chin Lee, MD Assistant Professor University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA USA University of Pennsylvania Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC.
 CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS HIP SYSTEMS Instructions for Use (IFU) IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS HIP SYSTEMS Instructions for Use (IFU) IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR
39 year old, 260 lb. park ranger. TKA in situ: 4 Years. First reported Metal-backed, non-modular PCA knee. 16% incidence. Modular metalbacked
 Designer (Royalty income) - DePuy A Johnson & Johnson Company Consultant on Knee Products for Smith & Nephew Orthopaedics General Research Funding Inova Health System and the U.S. Army Medical Research
Designer (Royalty income) - DePuy A Johnson & Johnson Company Consultant on Knee Products for Smith & Nephew Orthopaedics General Research Funding Inova Health System and the U.S. Army Medical Research
Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report
 Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants, 18(1): 69 74 (2008) Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report W. Siebert, 1 S. Mai, 1 & S. Kurtz 2 1 Orthopädische Klinik
Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants, 18(1): 69 74 (2008) Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report W. Siebert, 1 S. Mai, 1 & S. Kurtz 2 1 Orthopädische Klinik
6.1 Primary Total Knee Replacement with a Zirconia
 New Applications for Ceramics 183 6.1 Primary Total Knee Replacement with a Zirconia Ceramic Femoral Component B. S. Bal, D. D. Greenberg and T. J. Aleto Abstract This report presents the minimum two-year
New Applications for Ceramics 183 6.1 Primary Total Knee Replacement with a Zirconia Ceramic Femoral Component B. S. Bal, D. D. Greenberg and T. J. Aleto Abstract This report presents the minimum two-year
Trabecular Metal Primary Hip Prosthesis
 Trabecular Metal Primary Hip Prosthesis Quick-Reference Guide The Best Thing Next to Bone Trabecular Metal Primary Hip Prosthesis Quick-Reference Guide Key Features & Benefits Proximal Trabecular Metal
Trabecular Metal Primary Hip Prosthesis Quick-Reference Guide The Best Thing Next to Bone Trabecular Metal Primary Hip Prosthesis Quick-Reference Guide Key Features & Benefits Proximal Trabecular Metal
Dr. John Masonis Charlotte, NC OrthoCarolina. Dr. James Waddell Toronto, Ontario University of Toronto, St. Michael s Hospital
 Design Rationale Design surgeon list Smith & Nephew thanks the following surgeons for their participation as part of the REDAPT Revision Acetabular System design team: Dr. Robert Bourne London, Ontario
Design Rationale Design surgeon list Smith & Nephew thanks the following surgeons for their participation as part of the REDAPT Revision Acetabular System design team: Dr. Robert Bourne London, Ontario
Developing techniques for the dimensional assessment of true clinical wear in retrieved total joint replacements.
 Developing techniques for the dimensional assessment of true clinical wear in retrieved total joint replacements. P. Bills*, L. Blunt*, G. Chakrabarty** *University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield, UK **West
Developing techniques for the dimensional assessment of true clinical wear in retrieved total joint replacements. P. Bills*, L. Blunt*, G. Chakrabarty** *University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield, UK **West
MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene
 MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene Fixation First... 1 Wear Reduction... 2 Oxidative Stability... 3 Mechanical Integrity... 4 Proven Technology...5-6 References... 7 Fixation First FIXATION FIRST Prodigy
MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene Fixation First... 1 Wear Reduction... 2 Oxidative Stability... 3 Mechanical Integrity... 4 Proven Technology...5-6 References... 7 Fixation First FIXATION FIRST Prodigy
Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER A COMPREHENSIVE ACETABULAR REVISION SYSTEM DURALOC CONSTRAINED LINER Introduction Dislocation is the most common postoperative complication in total hip reconstruction.
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER A COMPREHENSIVE ACETABULAR REVISION SYSTEM DURALOC CONSTRAINED LINER Introduction Dislocation is the most common postoperative complication in total hip reconstruction.
Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene. Clinical Value Dossier - APAC
 Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Clinical Value Dossier - APAC Table of Contents 1 Executive Summary...................................................... 1 2 Burden of Illness........................................................
Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Clinical Value Dossier - APAC Table of Contents 1 Executive Summary...................................................... 1 2 Burden of Illness........................................................
POLARCUP Dual Mobility System. General Safety Instructions. Instructions for Use. Duty to inform the patient. Implant passport
 Important Notice to Users in the United States: This package insert is for product distributed in US only. U.S. Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. General Safety
Important Notice to Users in the United States: This package insert is for product distributed in US only. U.S. Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. General Safety
1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe
 1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe Abstract Introduction: Osteolysis generated by wear debris remains a problem
1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe Abstract Introduction: Osteolysis generated by wear debris remains a problem
Trident Ceramic Acetabular System Technical Monograph
 Trident Ceramic Acetabular System Technical Monograph Introduction Clinical research and laboratory testing have demonstrated the benefits of ceramic-on-ceramic bearings in THA. Among these benefits are
Trident Ceramic Acetabular System Technical Monograph Introduction Clinical research and laboratory testing have demonstrated the benefits of ceramic-on-ceramic bearings in THA. Among these benefits are
The latest and greatest in Orthopedics!
 The latest and greatest in Orthopedics! Disclosures: None Objectives: "The most important changes in contemporary orthopedics" Locking plates for fractures Advanced bearing surfaces for hip and knee replacements
The latest and greatest in Orthopedics! Disclosures: None Objectives: "The most important changes in contemporary orthopedics" Locking plates for fractures Advanced bearing surfaces for hip and knee replacements
Exeter. Technical Guide
 Exeter Technical Guide Exeter Hip System Anatomic Restoration The Exeter hip system allows interoperative changes in offset, leg length and version, all independent of one another. This flexibility facilitates
Exeter Technical Guide Exeter Hip System Anatomic Restoration The Exeter hip system allows interoperative changes in offset, leg length and version, all independent of one another. This flexibility facilitates
D E S I G N R A T I O N A L E
 D E S I G N R A T I O N A L E FREEDOM TO CHOOSE 1 PROVEN MODULAR SOLUTIONS The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System is uniquely designed with a range of acetabular cup options, biological and mechanical fixation
D E S I G N R A T I O N A L E FREEDOM TO CHOOSE 1 PROVEN MODULAR SOLUTIONS The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System is uniquely designed with a range of acetabular cup options, biological and mechanical fixation
REFLECTION Constrained Liner Introduction
 Surgical Technique REFLECTION Constrained Liner Introduction Surgical treatment of recurrent dislocation should be directed toward correction of any mechanical abnormalities. If dislocation is caused
Surgical Technique REFLECTION Constrained Liner Introduction Surgical treatment of recurrent dislocation should be directed toward correction of any mechanical abnormalities. If dislocation is caused
Orthopaedics Business. Dave Illingworth, President February
 Orthopaedics Business Dave Illingworth, President February 23 2005 1 Smith & Nephew Orthopaedics Attractive market Strong performance Momentum 2 Attractive market Demographics - 2x Growth by 2020 Active
Orthopaedics Business Dave Illingworth, President February 23 2005 1 Smith & Nephew Orthopaedics Attractive market Strong performance Momentum 2 Attractive market Demographics - 2x Growth by 2020 Active
Understanding Hip Implant Options
 Understanding Hip Implant Options Cup (Socket) Bearing (Liner) Head Stem (Femur) Modern Hip Implants (Ball) Metal Femoral Head on Marathon Cross-linked Polyethylene Liner Proven materials Polyethylene
Understanding Hip Implant Options Cup (Socket) Bearing (Liner) Head Stem (Femur) Modern Hip Implants (Ball) Metal Femoral Head on Marathon Cross-linked Polyethylene Liner Proven materials Polyethylene
Sulzer Orthopedics Joint & Fracture Care
 Sulzer Orthopedics Joint & Fracture Care Natural-Knee Family Anatomic design for superior clinical results. Natural-Knee Natural-Knee Family: A solution for every knee. Asymmetric design increases coverage
Sulzer Orthopedics Joint & Fracture Care Natural-Knee Family Anatomic design for superior clinical results. Natural-Knee Natural-Knee Family: A solution for every knee. Asymmetric design increases coverage
Pseudo tumor a cystic or solid mass (MRI or ultrasound) 1% of MOM pts develop pseudo tumors by 5 years 17 pts, all female, Pandit et al (JBJS, 2008)
 Pseudo tumor a cystic or solid mass (MRI or ultrasound) 1% of MOM pts develop pseudo tumors by 5 years 17 pts, all female, Pandit et al (JBJS, 2008) 8% at 5yrs FU indicated by preliminary study from same
Pseudo tumor a cystic or solid mass (MRI or ultrasound) 1% of MOM pts develop pseudo tumors by 5 years 17 pts, all female, Pandit et al (JBJS, 2008) 8% at 5yrs FU indicated by preliminary study from same
ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ACETABULAR CUP DEVICE INDICATIONS FOR USE The ICONACY I-Hip total hip replacement is indicated for the following conditions: 1. A severely painful and/or disabled hip
ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ACETABULAR CUP DEVICE INDICATIONS FOR USE The ICONACY I-Hip total hip replacement is indicated for the following conditions: 1. A severely painful and/or disabled hip
Regenerex Porous Titanium Construct. Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology
 Regenerex Porous Titanium Construct Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1 million times per year, Biomet helps one surgeon provide personalized
Regenerex Porous Titanium Construct Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1 million times per year, Biomet helps one surgeon provide personalized
