Conservative Interventions for the Hip Region
|
|
|
- Justina Jenkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anatomical Considerations Conservative Interventions for the Hip Region Shoulder vs. Hip RobRoy Martin, PhD PT Associate Professor Duquesne University Staff Physical Therapist UPMC/CRS Center for Sports Medicine 1 2 Evaluation Algorithms Purpose Efficient systematic collection of information Determine diagnosis and prognosis. Can work in concert with a classification-based treatment system. Classification-Based Treatment Purpose Define subgroups of patients who are likely to respond to a specific treatment approach Prioritize treatment plan 3 4 Classification System for Physical Therapists Lumbosacral Extra-articular Intra-articular Impingement Hypomobility Traumatic 5 Traumatic Hip vs Lumbosacral Spine Extra vs Intra-Articular ROM: Flexion-Internal Rotation Over Pressure Scours FABER History Altered WB Lumbar ROM Standing Flexion Long Sit Prone Knee Flexion Spring Test Eval and Treat Lumbosacral Pathology Eval and Treat Extra - Articular Pathology Palpation Flexibility tests Resisted tests Impingement Hypomobility Flex-Add-IR DIRI DERI Posterior Rim Distraction Beighton s Scale Log Roll Increased ROM Values- External Rotation Distraction Reduced ROM Flex and IR FABER 6 1
2 Lumbosacral Spine If tests are positive for a lumbosacral disorder, treatment may be directed toward this area. Re-evaluate response to treatment to see if hip symptoms resolve. Lumbosacral Spine Lumbosacral classification system Manipulation/mobilization (3/4 tests, hip >35IR) Stabilization (ASLR, prone instability test) Specific direction preference exercises (flexion, extension, or lateral shift) Traction Delitto A, Fritz JM, Cleland JA, Childs JD. Subgrouping patients with low back pain: evolution of a classification approach to physical therapy. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 37: , Manipulation/ Mobilization Manipulation/ Mobilization The technique involves positioning the patient, with respect to the lumbar spine, in side bending toward and rotation away from the painful side. A force directed anterior to posterior is applied to the ipsilateral anterior superior iliac spine in Grade 5 thrusting maneuver. It should be noted before this manipulation is applied contraindications for a thrust mobilization must be thoroughly cleared Manipulation/ Mobilization Childs et al. developed a clinical prediction rule for the mobilization category that involves the following 5 factors: duration of current symptoms being less that 16 days a score on the work subscale of the fear-avoidance belief questionnaire (FABQ) of less than 19 hypomobility of the lumbar spine (assessed with posterior to anterior pressure) internal rotation of 1 hip greater than 35 degrees symptoms not extending distal to the knee When 4 of these 5 factors were present the patient was very likely to improve with a mobilization treatment When 2 or fewer factors were present the mobilization treatment was almost always associated with failure. These findings are consistent with Brown et al. as it was found individuals with limited hip internal rotation were 3.63 times more likely to have a hip disorder than a spine disorder. Manipulation/ Mobilization Generally, patient s who fall into this category are also given: Lumbopelvic range of motion Stabilization exercises We find patients with hip pain commonly have signs and symptoms consistent with this category and often positively respond to some degree to this mobilization technique
3 Hip vs Lumbosacral Spine Extra vs Intra-Articular Eval and Treat Lumbosacral Pathology Eval and Treat Extra - Articular Pathology Traumatic Impingement Hypomobility 14 Common Extra-articular Pathologies Iliotibial Band/ trochanteric Bursitis Gluteal medius/ Minimus Tendinopathy Adductor Longus Tendinopathy Sports Hernia Deep Gluteal Nerve Syndrome Iliotibial Band Syndrome/ Trochanteric Bursitis The ITB is a wide, flat yet thick piece of connective tissue arising from: tensor fascia lata gluteus maximus muscles. The ITB runs over the Trochanteric bursa down the lateral aspect of the thigh Generally the symptoms are a result of the ITB/bursa rubbing on the greater trochanter. 16 Iliotibial Band Syndrome Iliotibial Band Syndrome Etiology usually an over-use problem The most common cause of ITB syndrome at the hip is a tight ITB. Can also be associated with excessive adduction( lateral lurch, pelvic drop) resulting from weak hip abductors. Training error Tight Adductors Weak Gluteus Medius Leg Length Discrepancy Increased pronation (internal rotation of lower extremity) Worn Shoes Direct trauma can cause trochanteric bursitis Symptoms Lateral hip pain Lateral snapping (Snapping Lateral Hip Syndrome) Epidemiology Incidence Unknown Age years of age Gender ITB Syndrome at the hip is more common in females than males
4 Iliotibial Band Syndrome Clinical exam findings- Reproduce Snapping!!! Flexibility Modified Thomas Obers MMT Gait Leg length Iliotibial Band Syndrome The standard progression of therapy (Decrease inflammation/improve ROM/increase strength and return to activity) is warranted. Proper ITB stretching (Hip extended/adducted/er with sidebending away) is important. It makes sense to incorporate components of hip flexion and extension into the abduction stretch. Increases in length of Tensor and Glut Max will gain additional length in the ITB. Manual stretching Soft Tissue Massage/ Mobilization Modalities may be indicated Treatment- 19 You cannot just treat the lateral hip pain and must correct any biomechanical abnormalities (including tightness and weakness) as well as educate in proper training techniques Foam Roller 24 4
5 25 26 Muscle Strain Common muscles that are involved include adductor longus (groin), gluteus medius, proximal hamstring, Hip flexor (psoas and rectus), and abdominal musculature (i.e. sports hernia). The increased injury risk is likely due to: Percentage of Type II muscle fibers Secondary to their multi-joint nature, the hip muscles are frequently in an elongated position while performing a deceleration (eccentric) task (increased length + eccentric contraction injury risk). The biceps femoris, which is frequently strained, serves as a good example. It is a 2-joint muscle, assists with decelerating the tibia during terminal swing and histologically is comprised predominantly of Type II muscle fibers Muscle Strain Muscle strain injuries range from minor to complete. A fourtier classification system has been proposed: Pain commonly located near the muscle tendon junction. Patients generally report an onset of acute pain during activity. Musculotendinous disorders including muscle strains and/or tendon disorders should be: painful with palpation Stretching resisted movements directed at the involved muscle and/or tendon. If the source of pain is solely from intraarticular origin, palpable pain is rarely present. Grade I Grade II Grade III Grade IV Few muscle fibers involved Moderate number of muscle fibers involved with fascia intact Many fibers involved with tearing of the fascia Complete Tear (rupture)
6 Treatment When treating soft tissues disorders around the hip an injury treatment program will depend on the phase of the injury that can be defined as either: Acute/ inflammatory Subacute Chronic/ remodeling. Acute Acute injuries are treated with: Modalities to promote healing, decrease pain and inflammation Massage Submaximal isometric exercises Passive range of motion Lumbopelvic stabilizing exercises. It is important to emphasize that all of these intervention techniques should be pain free Subacute Concentric movement through a full range of motion can be used as the criteria to progress to the subacute phase. Subacute injuries are treated with concentric exercises including functional closed chain/ weight bearing exercises. Progression includes the addition of lumbopelvic stabilization activities, general flexibility, and progressive balance/ stability exercises. Chronic/Remodeling Criteria to progress to chronic/ remodeling phase can include range of motion equal to uninvolved side and strength approximately 75% of uninvolved side. Pain with resisted testing should be minimal. The remodeling phase should emphasize eccentric exercises and sport specific training. Throughout this rehabilitation process, strengthening of the lumbopelvic stabilizing muscles should be encouraged. However, educating the patient to engage these muscles during sport specific activity we find to be critical Treatment Lower extremity biomechanics and muscle imbalances need to be carefully evaluated and corrected as appropriate. Our program often includes the use of foot orthotics or heel/shoe lift as well as educate in proper training techniques. Decrease Inflammation Restore ROM Improve Strength Return to Function. Education and injury prevention Proper warm-up Stretching strengthening Conditioning Training techniques Modalities
7 This generic program can be used to treat any musculotendon disorder, including those involving the gluteus medius, proximal hamstring, psoas, and abdominals. However, the adductor longus may be the most commonly treated musculo-tendon disorder. Holmich et al. found that compared to a passive physical therapy of massage, stretching, and modalities, an 8-12 week strengthening program produced better outcomes. Both strength and flexibility issues have been found to play a role in the onset of muscular-tendon injuries, however, Tyler et al. found strengthen deficits to play a larger role. 37 General Stretching Stretching Positions Psoas: Hip extension, slight abduction and internal rotation Iliotibial band: Hip adduction, slight extension, external rotation and side bend away Adductor longus: Hip abduction, slight extension and internal rotation Piriformis: External rotation with the hip near 90 degrees flexion General stretching to increase hip ROM can be done with basic physiological movements that are similar to goniometric positioning and movement
8 Deep ROTATOR Stretching in seated position, the patient crosses the leg that will be stretched with the foot positioned next to the knee. The patient pulls the knee towards the contralateral shoulder Prone Eccentrics/Contract Relax Offers new perspective on how to treat the deep rotators and associated neurovascular structures Sciatic Nerve Glides Stretching/manual therapy without causing impingement Further investigation is needed 45 With the patient in a siting position, the patient holds with both hands under the knee. (A) Cervical extension, knee flexion and dorsiflexion. (B) Cervical flexion, knee extension (under the limit for each phase), plantar flexion. The patient can apply lumbar flexion and extension during the exercise. 46 Sciatic Nerve Mobilizations Passive hip circumduction begin at 45 degrees of hip flexion Move to maximum external rotation Engaging the greater trochanter against the ischium to mobilize the sciatic nerve lateral. Traumatic Hip vs Lumbosacral Spine Extra vs Intra-Articular Impingement Eval and Treat Lumbosacral Pathology Eval and Treat Extra - Articular Pathology Hypomobility
9 Hip vs Lumbosacral Spine Extra vs Intra-Articular ROM: *Internal Rotation Over Pressure FADIR Scours FABER Lumbar ROM Standing Flexion Long Sit SI Compression SI Distraction Spring Test Eval and Treat Lumbosacral Pathology Eval and Treat Extra - Articular Pathology Palpation Flexibility tests Resisted tests Impingement: Location of Labral Tear DIRI DEXRI Posterior Rim Traumatic Hypomobility History Impingement Altered WB DIRI Distraction Reduced DEXRI ROM Flex and Posterior Rim IR FABER 49 Bony geometry Validity of Dynamic Impingement Testing for Determining the Location of Femoroacetabular Impingement: A Cadaveric Study Benjamin R Kivlan, et al, BAOJ Ortho : 1 1: 003 The DIRI and DEXRI tests may be used to discriminate the location of labral pathology from anteriorinferior (Zone 1) to posteriorinferior (Zone 5) positions. Femoral Anterversion/ Retroversion Gait Toeing in- Anteversion Toeing out- Retroversion Craig s test 15º Internal rotation normal > 15º Anteversion < 15º Retroversion ROM Increase internal rotation/ Decrease external rotation Anterversion Decrease internal rotation/ Increase external rotation Retroversion MR Arthrogram
10 Classification Based Treatment Impingement Joint Mobilization Work within the Pain-free limits Sagital Frontal Gluteus Medius Strengthening Trunk Stabilization Joint Mobilization Inferior Posterior Traumatic Hip vs Lumbosacral Spine Extra vs Intra-Articular Impingement Eval and Treat Lumbosacral Pathology Eval and Treat Extra - Articular Pathology Hypomobility Beighton Score Range of motion ER/IR Distinguish between femoral version and capsular laxity Distraction Anterior instability Log Roll Ligament Teres Test Squat test 57 Beighton Score Distraction 10
11 Anterior instability Log Roll/Bounce Back Ligamentum Teres LT can be defined as a rotational stabilizer in all hip positions but the primary rotational stabilizer in the upper range of flexion, greater than 90. The function of the LT may be described using a ball and string model where rotational movements of the femoral head that occur in the transverse and frontal planes cause LT to act as a sling as it wraps around the femoral head. LT tightens it pulls the femoral head into the actetabulum to increase stability as the hip is moved closer to end range. This stabilizing function becomes important when the capsular Ligaments are in a loose pack position of hip flexion, in those withosseous risk factors for instability, and may also be more important as the in those with capsular laxity. Martin RL, Martin HD. Function and Clinical Relevance of the Ligamentum Teres: A Current Concept Function and Clinical Relevance of the Ligamentum Teres: Current Orthopaedic Practice. 26: ; 2015 Martin HD, Hatem, MA, Kivlan BR, Martin RL. The function of the ligamentum teres in limiting hip rotation: A cadaveric study. Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery. 30: ; Martin RL, Kivlan BR, Clemente FR. A cadaveric model for ligamentum teres function: A pilot Study. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 21: ; This LT test was performed with the hip moved to 70 flexion and 30 short of full abduction. The hip was then internally and externally rotated through full range of motion assessing for reproduction of pain. Sensitivity and specificity values of.90 and.85, respectively. The authors concluded that partial LT tears could be identified by the LT test. It should be noted that the one subject is this study with a complete tear had a negative LT test. Because this test relies on the reproduction of pain it may not be useful for those with complete LT tears. Ligament Teres Test Kivlan BR, Clemente FR, Martin RL, Martin HD. Function of the ligamentum teres during multi-planar movement of the hip joint. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 21: ; Martin RL, Palmer I, Martin HD. Ligamentum teres: A functional description and potential clinical relevance. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 20: ; O Donnell J et al. The ligamentum teres test: A novel and effective test in diagnosing tears of the ligamentum teres. AM J Sports Med 2014 The LT was found to for a sling in flexion-abduction external rotation in a cadaver study Squat Test Classification Based Treatment Hip Stabilization Proprioception Gluteus Medius Strengthening Kivlan BR, Clemente FR, Martin RL, Martin HD. Function of the ligamentum teres during multi-planar movement of the hip joint. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 21: ; Trunk Stabilization 66 11
12
13 73 74 Eval and Treat Extra - Articular Pathology Pearls and Perils Myofascial pain Psoas Rectus femoris Gluteus Medius/Minimus Piriformis/Short Rotators Treatment Soft-tissue mob Stretching Strengthening Pearls and Perils Pearls and Perils tape 13
14 Pearls and Perils Hip vs Lumbosacral Spine Eval and Treat Lumbosacral Pathology Extra vs Intra-Articular Eval and Treat Extra - Articular Pathology Traumatic Impingement Hypomobility 80 Classification Based Treatment Hypomobility Joint mobilization Distraction Inferior Posterior Strengthening Pain free protected weight bearing ROM DEFICITS Joint Mobilization Long Axis Distraction Inferior Glide Posterior Glide Lateral Distraction Stretching Hand-Heel Rock Classification Based Treatment Hypomobility Joint mobilization Distraction Inferior Posterior DJD Treatment Education Assistive device Exercise Stretching/ joint mobilization Strengthening Pain free protected weight bearing
15 Aquatic Exercises DJD Education Patients should be counseled with respect to activities that negatively impact the disease process and alternative exercises suggested. Patients should be encouraged to move their hips frequently throughout the day to limit the stiffness and improve joint nutrition. Weight loss should also be discussed when indicated. It was found that for each pound of weight loss there is a 4-fold reduction in the load exerted per step at the knee during daily activities De-weighter DJD Assistive device Assistive device (i.e. cane) for use on the contra lateral (unaffected) side should be recommended if necessary to relieve pressure on the joint. The use of a cane for ambulation can be encouraged as 25% of the body weight can be offloaded from the lower extremity by using this device. Additionally, adaptive devices may be necessary to raise the height of chairs and commodes to make the process of sit stand transfers DJD Stretching and Joint Mobilization Increases in joint motion may be achieved by instituting a progressive series of joint mobilization techniques followed by stretching as tolerated. Given the capsular pattern of the hip, the posterior and inferior portions of the capsule should be addressed Improvements in motion should allow the patient a greater range in which to ambulate more normally and perform ADLs
16 Posterior Glide Joint Mobilization DJD Exercise Patients should be encouraged to participate in regular exercise that minimizes joint reaction forces. Specifically, aquatic exercise and cycling are excellent activities for the patient with hip OA. Strengthening All weak muscles should be addressed however the hip abductors are often characteristically weak. Sufficient weakness of the gluteus medius may cause the gait deviations. Strengthening of the gluteus medius in order to be effective must really be performed with the hip in extension avoiding external rotation. Increases in strength should assist with absorbing externally applied forces thereby lessening pressure at the joint. CLINICAL GUIDELINES MICHAEL T. CIBULKA, DPT DOUGLAS M. WHITE, DPT JUDITH WOEHRLE, PT, PHD MARCIE HARRIS-HAYES, DPT KEELAN ENSEKI, PT, MS TIMOTHY L. FAGERSON, DPT JAMES SLOVER, MD, MS JOSEPH J. GODGES, DPT Hip Pain and Mobility Deficits Hip Osteoarthritis: Clinical Practice Guidelines Linked to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health from the Orthopaedic Section of the American Physical Therapy Association
17 Recommendations* Pelvic and Trunk Stability Interventions Patient Education: Clinicians should consider the use of patient education to teach activity modification, exercise, weight reduction when overweight, and methods of unloading the arthritic joints. (Recommendation based on moderate evidence.) Functional, Gait, and Balance Training: Functional, gait, and balance training, including the use of assistive devices such as canes, crutches, and walkers, can be used in patients with hip osteoarthritis to improve function associated with weight bearing activities. (Recommendation based on weak evidence.) Manual Therapy: Clinicians should consider the use of manual therapy procedures to provide short-term pain relief and improve hip mobility and function in patients with mild hip osteoarthritis. (Recommendation based on moderate evidence.) Flexibility, Strengthening, and Endurance Exercises: Clinicians should consider the use of flexibility, strengthening, and endurance exercises in patients with hip osteoarthritis. (Recommendation based on moderate evidence.) Gluteus Medius Quadratus Lumborum Erector Spinae Abdominals i.e. Scapula stabilization Gluteus Medius Gluteus Medius Gluteus Medius Quadratus Lumborum Serratus and Lower Trap of the pelvis
18 Quadratus Lumborum Erector Spinae Erector Spinae Abdominals Athletic Pubalgia/ Sports Hernia PAIN PRESENTATION IN ATHLETIC PUBALGIA Term describing a spectrum of chronic pubic/inguinal pain A sports hernia, also known as athletic pubalgia, is a tear in the muscles of the lower abdomen
19 Treatment Muscle strain progression Will depend on the phase of the injury that can be defined as either: Acute/ inflammatory Subacute Chronic/ remodeling Conclusion We have integrated a general evaluation algorithm and classification based treatment that includes considerations for the: lumbosacral spine extraarticluar soft-tissue intraarticular structures Impingement hypomobility
20 Thank You
APPLICATION OF THE MOVEMENT SYSTEMS MODEL TO THE MANAGEMENT COMMON HIP PATHOLOGIES
 APPLICATION OF THE MOVEMENT SYSTEMS MODEL TO THE MANAGEMENT COMMON HIP PATHOLOGIES Tracy Porter, PT, DPT Des Moines University Department of Physical Therapy Objectives Review current literature related
APPLICATION OF THE MOVEMENT SYSTEMS MODEL TO THE MANAGEMENT COMMON HIP PATHOLOGIES Tracy Porter, PT, DPT Des Moines University Department of Physical Therapy Objectives Review current literature related
ARTHROSCOPIC GLUTEUS MEDIUS REPAIR PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL
 ARTHROSCOPIC GLUTEUS MEDIUS REPAIR PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL Jovan R. Laskovski, M.D. Hip Arthroscopy Sports Medicine & Orthopaedic Surgery Crystal Clinic Orthopaedic Center Please use appropriate clinical
ARTHROSCOPIC GLUTEUS MEDIUS REPAIR PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL Jovan R. Laskovski, M.D. Hip Arthroscopy Sports Medicine & Orthopaedic Surgery Crystal Clinic Orthopaedic Center Please use appropriate clinical
Hip pain: A comparison of Osteoarthritis and Femoroacetabular Impingement Kristine Flais, PT, DPT
 Hip pain: A comparison of Osteoarthritis and Femoroacetabular Impingement Kristine Flais, PT, DPT Most common cause of hip pain in older adults Prevalence of Hip OA Age Gender Race Developmental disorders
Hip pain: A comparison of Osteoarthritis and Femoroacetabular Impingement Kristine Flais, PT, DPT Most common cause of hip pain in older adults Prevalence of Hip OA Age Gender Race Developmental disorders
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT ***
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Hip pain in children may refer to the knee from Legg-Calve-Perthes
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Hip pain in children may refer to the knee from Legg-Calve-Perthes
Evaluation of the Hip
 Evaluation of the Hip Adam Lewno, DO PCSM Fellow, University of Michigan Primary Care Sports Update 2017 Disclosures Financial: None Images: I would like to acknowledge the work of the original owners
Evaluation of the Hip Adam Lewno, DO PCSM Fellow, University of Michigan Primary Care Sports Update 2017 Disclosures Financial: None Images: I would like to acknowledge the work of the original owners
Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Athletes
 Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Athletes John P Salvo, MD Sports Medicine Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA EATA Annual Meeting January, 2011 Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Anatomy History Physical Exam
Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Athletes John P Salvo, MD Sports Medicine Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA EATA Annual Meeting January, 2011 Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Anatomy History Physical Exam
Travis G. - 1 Maak, - MD Sports Medicine University of Utah Orthopaedics 590 Wakara Way Salt Lake City, UT Tel: Fax:
 Travis G. - 1 Maak, - MD Rehabilitation for Arthroscopic Osteochondroplasty with or without Labral Repair/Debridement General Guidelines: Normalize gait pattern with brace and crutches Continuous Passive
Travis G. - 1 Maak, - MD Rehabilitation for Arthroscopic Osteochondroplasty with or without Labral Repair/Debridement General Guidelines: Normalize gait pattern with brace and crutches Continuous Passive
Rehabilitation. Friday, October 14, :00 11:45am General Session Rehabilitation following FAI Surgery Mark Ryan, MS, ATC, CSCS USA
 Rehabilitation Friday, October 14, 2011 11:00 11:45am General Session Rehabilitation following FAI Surgery Mark Ryan, MS, ATC, CSCS USA Best Tip Srino Bharam, MD USA Best Tip Robroy Martin, PhD, PT USA
Rehabilitation Friday, October 14, 2011 11:00 11:45am General Session Rehabilitation following FAI Surgery Mark Ryan, MS, ATC, CSCS USA Best Tip Srino Bharam, MD USA Best Tip Robroy Martin, PhD, PT USA
Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Gluteus Medius Repair with or without Labral Debridement. Normalize gait pattern with brace (if indicated) and crutches
 General Guidelines: Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Gluteus Medius Repair with or without Labral Debridement Normalize gait pattern with brace (if indicated) and crutches Weight-bearing: 20 lbs foot flat
General Guidelines: Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Gluteus Medius Repair with or without Labral Debridement Normalize gait pattern with brace (if indicated) and crutches Weight-bearing: 20 lbs foot flat
ARTHROSCOPIC LABRAL REPAIR WITH CAPSULAR PLICATION PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL
 ARTHROSCOPIC LABRAL REPAIR WITH CAPSULAR PLICATION PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL Jovan R. Laskovski, M.D. Hip Arthroscopy Sports Medicine & Orthopaedic Surgery Crystal Clinic Orthopaedic Center Please use
ARTHROSCOPIC LABRAL REPAIR WITH CAPSULAR PLICATION PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL Jovan R. Laskovski, M.D. Hip Arthroscopy Sports Medicine & Orthopaedic Surgery Crystal Clinic Orthopaedic Center Please use
Evaluation of Posterior Hip Pain
 Evaluation of Posterior Hip Pain Anthony J. Ferretti, D.O., MHSA Hip Pain in the Adult Various etiologies: Traumatic Infectious Neurovascular Degenerative Congenital Pathologic 1 Hip Pain Complex interaction
Evaluation of Posterior Hip Pain Anthony J. Ferretti, D.O., MHSA Hip Pain in the Adult Various etiologies: Traumatic Infectious Neurovascular Degenerative Congenital Pathologic 1 Hip Pain Complex interaction
Hip Arthroscopy Protocol
 The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for progression of rehabilitation, it is not intended to serve as a substitute for clinical decision making. Progression through each phase of rehabilitation
The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for progression of rehabilitation, it is not intended to serve as a substitute for clinical decision making. Progression through each phase of rehabilitation
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
2. Iliotibial Band syndrome
 2. Iliotibial Band syndrome Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome (so called runners knee although often seen in other sports e.g. cyclists and hill walkers). It is usually an overuse injury with pain felt on
2. Iliotibial Band syndrome Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome (so called runners knee although often seen in other sports e.g. cyclists and hill walkers). It is usually an overuse injury with pain felt on
Travis G. - 1 Maak, - MD Sports Medicine University of Utah Orthopaedics 590 Wakara Way Salt Lake City, UT Tel: Fax:
 General Guidelines: Travis G. - 1 Maak, - MD Rehabilitation for Arthroscopic or Open Gluteus Medius Repair with or without Labral Debridement Normalize gait pattern with brace and crutches Weight-bearing:
General Guidelines: Travis G. - 1 Maak, - MD Rehabilitation for Arthroscopic or Open Gluteus Medius Repair with or without Labral Debridement Normalize gait pattern with brace and crutches Weight-bearing:
Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions
 Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions The success of total hip replacement (THR) is a result of predictable pain relief, improvements in quality of life, and restoration of
Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions The success of total hip replacement (THR) is a result of predictable pain relief, improvements in quality of life, and restoration of
Main Menu. Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
Knee Capsular Disorder. ICD-9-CM: Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified
 1 Knee Capsular Disorder "Knee Capsulitis" ICD-9-CM: 719.56 Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified Diagnostic Criteria History: Physical Exam: Stiffness Aching with prolonged weight
1 Knee Capsular Disorder "Knee Capsulitis" ICD-9-CM: 719.56 Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified Diagnostic Criteria History: Physical Exam: Stiffness Aching with prolonged weight
Diagnosis: Gluteus Medius Tear, Labral Tear, CAM / Pincer
 Physical Therapy Prescription: Hip Arthroscopy Diagnosis: Gluteus Medius Tear, Labral Tear, CAM / Pincer Procedure: Gluteus Medius Repair, CAM / Pincer Decompression, Labral refixation / Capsular Shift
Physical Therapy Prescription: Hip Arthroscopy Diagnosis: Gluteus Medius Tear, Labral Tear, CAM / Pincer Procedure: Gluteus Medius Repair, CAM / Pincer Decompression, Labral refixation / Capsular Shift
CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Rehabilitation Considerations Following Surgical Arthroscopy of the Hip. Joy Anderson PT, ATC, CSCS
 Rehabilitation Considerations Following Surgical Arthroscopy of the Hip Joy Anderson PT, ATC, CSCS 1 Best Rehab Program? Review of the Evidence paucity of evidence surrounding post-operative rehabilitation
Rehabilitation Considerations Following Surgical Arthroscopy of the Hip Joy Anderson PT, ATC, CSCS 1 Best Rehab Program? Review of the Evidence paucity of evidence surrounding post-operative rehabilitation
The Evaluation of Hip pain in the Athlete
 The Evaluation of Hip pain in the Athlete DREW ROGERS,MD The Evaluation of Hip pain in the Athlete Andrew Rogers, MD (Drew) Orthopedic Care Physician Network Chief of Orthopedics Morton Hospital Team Physician
The Evaluation of Hip pain in the Athlete DREW ROGERS,MD The Evaluation of Hip pain in the Athlete Andrew Rogers, MD (Drew) Orthopedic Care Physician Network Chief of Orthopedics Morton Hospital Team Physician
Active-Assisted Stretches
 1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
What This Is! What This Isn t! Insights Into Functional Training 5/27/15. #ideaworld. Chuck Wolf, MS, FAFS Thank you for coming!!!
 Insights Into Functional Training Insights Into Functional Training 2015 IDEA Health & Fitness Association. All Rights Reserved. www.ideafit.com/world P R E S E N T E D B Y Chuck Wolf, MS, FAFS Human Motion
Insights Into Functional Training Insights Into Functional Training 2015 IDEA Health & Fitness Association. All Rights Reserved. www.ideafit.com/world P R E S E N T E D B Y Chuck Wolf, MS, FAFS Human Motion
Overview. Overview. Introduction. Introduction Anatomy History Examination Common Disorders. Introduction Anatomy History Examination Common Disorders
 Common Hip Disorders in Figure Skaters 14 th Annual Meeting of Sports Medicine and Science in Figure Skating January 25, 2009 8:15-8:45am Robert J. Dimeff, MD Medical Director of Sports Medicine Overview
Common Hip Disorders in Figure Skaters 14 th Annual Meeting of Sports Medicine and Science in Figure Skating January 25, 2009 8:15-8:45am Robert J. Dimeff, MD Medical Director of Sports Medicine Overview
Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Procedure Form
 Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Procedure Form Femoracetabular Impingement (FAI) Femoral Osteochondroplasty Acetabular Rim Trimming Acetabular Labrum Repair Location: o clock to o clock Debridement Articular
Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Procedure Form Femoracetabular Impingement (FAI) Femoral Osteochondroplasty Acetabular Rim Trimming Acetabular Labrum Repair Location: o clock to o clock Debridement Articular
S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R
 S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R H I P A R T H R O S C O P Y W I T H L A B R A L R E P A I R P R O T O C O L This protocol provides appropriate guidelines
S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R H I P A R T H R O S C O P Y W I T H L A B R A L R E P A I R P R O T O C O L This protocol provides appropriate guidelines
Role Of The Fitness Professional. Causes of Fitness Related Injuries. The Assessments. Screening & Assessing: A Holistic Approach 2/9/2016
 Screening & Assessing: A Holistic Approach Role Of The Fitness Professional Fitness professionals must assess clientele, but need to understand the difference between medical diagnosis vs fitness limitations.
Screening & Assessing: A Holistic Approach Role Of The Fitness Professional Fitness professionals must assess clientele, but need to understand the difference between medical diagnosis vs fitness limitations.
Presentation Overview 8/8/12. Muscle Imbalances Revealed Assessment & Exercise for Personal Training
 Presentation Overview Common issues seen in many athletes from different sports Some important assessments that can be used for many varieties of athletes Exercise progressions that can fix imbalances
Presentation Overview Common issues seen in many athletes from different sports Some important assessments that can be used for many varieties of athletes Exercise progressions that can fix imbalances
CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT
 SPORTS REHABILITATION CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT A case study and rationale for treatment Written by Joanne Kemp and Kay Crossley, Australia BACKGROUND The hip joint and FAI
SPORTS REHABILITATION CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT A case study and rationale for treatment Written by Joanne Kemp and Kay Crossley, Australia BACKGROUND The hip joint and FAI
Algorithm #1 Lumbo-Pelvic Region Examination
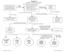 Red Screen for Potentially Serious Conditions (i.e., Red Flags) including Neurologic when indicated Positive Findings Algorithm #1 Lumbo-Pelvic Region Clinical Prediction Rule Screening: Duration of symptoms
Red Screen for Potentially Serious Conditions (i.e., Red Flags) including Neurologic when indicated Positive Findings Algorithm #1 Lumbo-Pelvic Region Clinical Prediction Rule Screening: Duration of symptoms
Routine Arthroscopic Procedure
 Katherine J. Coyner, MD UCONN Musculoskeletal Institute Medical Arts & Research Building 263 Farmington Ave. Farmington, CT 06030 Office: (860) 679-6600 Fax: (860) 679-6649 www.drcoyner.com Avon Office
Katherine J. Coyner, MD UCONN Musculoskeletal Institute Medical Arts & Research Building 263 Farmington Ave. Farmington, CT 06030 Office: (860) 679-6600 Fax: (860) 679-6649 www.drcoyner.com Avon Office
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS
 NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS The Pelvis The pelvis has 3 joints connecting it together 2 sacro-iliac joints at the back (posterior) and the pubic symphysis joint which is at the front (anterior). A
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS The Pelvis The pelvis has 3 joints connecting it together 2 sacro-iliac joints at the back (posterior) and the pubic symphysis joint which is at the front (anterior). A
BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD
 Physical Therapy Protocol Partial or full thickness gluteus medius repair with or without labral repair The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for your patient s therapy progression. It is
Physical Therapy Protocol Partial or full thickness gluteus medius repair with or without labral repair The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for your patient s therapy progression. It is
Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies
 Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies Melodie Kondratek, PT, DScPT, OMPT Bryan Kuhlman, PT, DPT, OMPT Oakland University Orthopedic Spine and Sports
Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies Melodie Kondratek, PT, DScPT, OMPT Bryan Kuhlman, PT, DPT, OMPT Oakland University Orthopedic Spine and Sports
How to GET RESULTS BETWEEN SESSIONS LumboPelvic Hip Complex HOMEWORK. LPHC Homework Presented by Dr. Bruce Costello
 How to GET RESULTS BETWEEN SESSIONS LumboPelvic Hip Complex HOMEWORK LPHC Homework Presented by Dr. Bruce Costello Spinal Mobilization Reaching for the Stars Side-Bend Modified Karate Punch Session Objectives
How to GET RESULTS BETWEEN SESSIONS LumboPelvic Hip Complex HOMEWORK LPHC Homework Presented by Dr. Bruce Costello Spinal Mobilization Reaching for the Stars Side-Bend Modified Karate Punch Session Objectives
WHEN THE HIP IS NOT THE HIP
 WHEN THE HIP IS NOT THE HIP M Cusí MBBS, FACSP, FFSEM (UK) Conditions that can be confused with hip pain 1. Referred pain lumbar spine Conditions that can be confused with hip pain 1. Referred pain lumbar
WHEN THE HIP IS NOT THE HIP M Cusí MBBS, FACSP, FFSEM (UK) Conditions that can be confused with hip pain 1. Referred pain lumbar spine Conditions that can be confused with hip pain 1. Referred pain lumbar
Labral Repair with a Microfracture
 Labral Repair with a Microfracture This protocol should be used as a guideline for progression and should be tailored to the needs of the individual patient. Strict protective weight bearing status for
Labral Repair with a Microfracture This protocol should be used as a guideline for progression and should be tailored to the needs of the individual patient. Strict protective weight bearing status for
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH Peter G Gerbino, MD, FACSM Orthopedic Surgeon Monterey Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Monterey, CA TPC, San Diego, 2017 The lecturer has no
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH Peter G Gerbino, MD, FACSM Orthopedic Surgeon Monterey Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Monterey, CA TPC, San Diego, 2017 The lecturer has no
Lesson 24. A & P Hip
 Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
Bryan T. Kelly, MD Center for Hip Pain and Preservation Hospital for Special Surgery
 Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Labral refixation with or without FAI Component General Guidelines: Limited external rotation to 20 degrees (2 weeks) No hyperextension (4 weeks) Normalize gait pattern with
Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Labral refixation with or without FAI Component General Guidelines: Limited external rotation to 20 degrees (2 weeks) No hyperextension (4 weeks) Normalize gait pattern with
Balanced Body Movement Principles
 Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER. Planes of Lumbar Pelvic Femoral (Back, Pelvic, Hip) Muscle Function
 BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
Prevention of common running injuries
 Prevention of common running injuries Lower limb and hip joint pain, along with soft tissue structures of the lower leg, can be extremely painful and frustrating injuries. Some of the most common running
Prevention of common running injuries Lower limb and hip joint pain, along with soft tissue structures of the lower leg, can be extremely painful and frustrating injuries. Some of the most common running
Young Adult Hip problems. Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth)
 Young Adult Hip problems Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) RNOH founded 1837 by William Little 14 year old presenting with limp Knee pain on and off 4 months Limps Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) The Royal
Young Adult Hip problems Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) RNOH founded 1837 by William Little 14 year old presenting with limp Knee pain on and off 4 months Limps Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) The Royal
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Open Hip Abductor (Gluteus Medius) Repair
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Open Hip Abductor (Gluteus Medius) Repair The hip joint is composed of the femur (the thigh bone) and the acetabulum (the socket which is from
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Open Hip Abductor (Gluteus Medius) Repair The hip joint is composed of the femur (the thigh bone) and the acetabulum (the socket which is from
Femoroacetabular Impingement in the Throwing Athlete. Michael Banffy, MD Sports Medicine, Hip Preservation Kerlan Jobe Institute
 Femoroacetabular Impingement in the Throwing Athlete Michael Banffy, MD Sports Medicine, Hip Preservation Kerlan Jobe Institute Disclosures None Baseball Hip Injuries - Background Abdominal/groin injuries
Femoroacetabular Impingement in the Throwing Athlete Michael Banffy, MD Sports Medicine, Hip Preservation Kerlan Jobe Institute Disclosures None Baseball Hip Injuries - Background Abdominal/groin injuries
Travis G. Maak, MD Sports Medicine University of Utah Orthopaedics 590 Wakara Way Salt Lake City, UT Tel: Fax:
 General Guidelines: Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Capsular Shift with or without FAI Labral Components No external rotation greater than 30 degrees for 4 weeks No hyperextension for 4 weeks Normalize
General Guidelines: Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Capsular Shift with or without FAI Labral Components No external rotation greater than 30 degrees for 4 weeks No hyperextension for 4 weeks Normalize
Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Protocol Dr. David Hergan Labral Repair with or without FAI Component
 Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Protocol Dr. David Hergan Labral Repair with or without FAI Component Initial Joint Protection Guidelines- (P.O. Day 1-4 wks): Joint Protection Patient education
Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Protocol Dr. David Hergan Labral Repair with or without FAI Component Initial Joint Protection Guidelines- (P.O. Day 1-4 wks): Joint Protection Patient education
Hip Arthroscopy Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) Ryan W. Hess, MD Tracey Pederson, PCC Office: (763) Fax: (763)
 Hip Arthroscopy Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) Ryan W. Hess, MD Tracey Pederson, PCC Office: (763) 302-2223 Fax: (763) 302-2401 GENERAL GUIDELINES: Despite the minimally invasive nature of hip arthroscopy,
Hip Arthroscopy Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) Ryan W. Hess, MD Tracey Pederson, PCC Office: (763) 302-2223 Fax: (763) 302-2401 GENERAL GUIDELINES: Despite the minimally invasive nature of hip arthroscopy,
Human anatomy reference:
 Human anatomy reference: Weak Glut Activation Weak gluteal activation comes from poor biomechanics, poor awareness when training or prolonged exposure in deactivated positions such as sitting. Weak Glut
Human anatomy reference: Weak Glut Activation Weak gluteal activation comes from poor biomechanics, poor awareness when training or prolonged exposure in deactivated positions such as sitting. Weak Glut
Hip Impingement and Arthritis: Preservation vs. Total Hip Arthroplasty. Faculty Disclosures. Objectives 11/17/2017
 Hip Impingement and Arthritis: Preservation vs. Total Hip Arthroplasty Jonathan R. Schiller, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedics Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Director, Adolescent
Hip Impingement and Arthritis: Preservation vs. Total Hip Arthroplasty Jonathan R. Schiller, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedics Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Director, Adolescent
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire
 Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
Hip Arthroscopy Labral Repair Protocol
 Hip Arthroscopy Labral Repair Protocol Applicability: Physician Practices Date Effective: 09/2013 Department: Rehabilitation Services Date Last Reviewed: 1/2018 Supersedes: n/a Administration Approval:
Hip Arthroscopy Labral Repair Protocol Applicability: Physician Practices Date Effective: 09/2013 Department: Rehabilitation Services Date Last Reviewed: 1/2018 Supersedes: n/a Administration Approval:
Protocol G Arthroscopic Surgery: Therapist Information
 Protocol G Arthroscopic Surgery: Therapist Information Please read entire protocol prior to initiating therapy Please do not hesitate to contact Dr. Wolff with questions or concerns. Rest is a vital component
Protocol G Arthroscopic Surgery: Therapist Information Please read entire protocol prior to initiating therapy Please do not hesitate to contact Dr. Wolff with questions or concerns. Rest is a vital component
Precautions following Hip Arthroscopy/FAI: (Refixation/Osteochondroplasty)
 Physical Therapy Prescription: Hip Arthroscopy Diagnosis: Labral Tear, CAM / Pincer Procedure: Labral Repair / Capsular Shift, CAM / Pincer Decompression RX: Evaluate / Treat, and follow attached protocol
Physical Therapy Prescription: Hip Arthroscopy Diagnosis: Labral Tear, CAM / Pincer Procedure: Labral Repair / Capsular Shift, CAM / Pincer Decompression RX: Evaluate / Treat, and follow attached protocol
The Hip Joint. Shenequia Howard David Rivera
 The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
Hip Pain in the Athlete: A Diagnostic Challenge
 : A Diagnostic Challenge Matthew Gimre MD Sports Medicine 11 th Annual Sports Medicine Conference Presented June 17, 2017 on: Month day, Year Presented to: Insert relevant presenter information Calibri
: A Diagnostic Challenge Matthew Gimre MD Sports Medicine 11 th Annual Sports Medicine Conference Presented June 17, 2017 on: Month day, Year Presented to: Insert relevant presenter information Calibri
5/14/2013. Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of Injury:
 Third Annual Young Athlete Conference: The Lower Extremity February 22, 2013 Audrey Lewis, DPT Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of Injury: I. Direct: blow to the patella II. Indirect: planted foot with a valgus
Third Annual Young Athlete Conference: The Lower Extremity February 22, 2013 Audrey Lewis, DPT Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of Injury: I. Direct: blow to the patella II. Indirect: planted foot with a valgus
Myoskeletal Alignment for Low Back, Hip, and Leg Pain DVDs
 Myoskeletal Alignment for Low Back, Hip, and Leg Pain DVDs Use these handy time markers to locate the specific treatment techniques on the Level 4 Dynamic Body 6 DVD set as demonstrated by Erik Dalton
Myoskeletal Alignment for Low Back, Hip, and Leg Pain DVDs Use these handy time markers to locate the specific treatment techniques on the Level 4 Dynamic Body 6 DVD set as demonstrated by Erik Dalton
HIP_CASE 2_OA. Hip Forces. Function of the Hip. Property of VOMPTI, LLC. For Use of Participants Only. No Use or Reproduction Without Consent 1
 HIP_CASE 2_OA Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Eric Magrum DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT 62 yo female AM stiffness Hip pain diffuse, variable ant>lateral>post Gradual onset Tennis
HIP_CASE 2_OA Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Eric Magrum DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT 62 yo female AM stiffness Hip pain diffuse, variable ant>lateral>post Gradual onset Tennis
IFAST Assessment. Name: Date: Sport: Review Health Risk Assessment on initial consult form. List Client Goals (what brings you here?
 IFAST Assessment Name: Date: Sport: Review Health Risk Assessment on initial consult form List Client Goals (what brings you here?) Cardiovascular Measurements Blood Pressure Resting Heart Rate Body Composition
IFAST Assessment Name: Date: Sport: Review Health Risk Assessment on initial consult form List Client Goals (what brings you here?) Cardiovascular Measurements Blood Pressure Resting Heart Rate Body Composition
Trigger Point Management
 Trigger Point Management What is a Trigger Point (TrP)? Ø A trigger point is a hyperirritable spot located in a taut band of skeletal muscle. They may form following a sudden trauma or may develop on a
Trigger Point Management What is a Trigger Point (TrP)? Ø A trigger point is a hyperirritable spot located in a taut band of skeletal muscle. They may form following a sudden trauma or may develop on a
JOHN M. REDMOND, M.D.
 Physical Therapy Protocol Gluteus Medius repair with or without labral repair The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for your patient s therapy progression. It is not intended to serve as
Physical Therapy Protocol Gluteus Medius repair with or without labral repair The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for your patient s therapy progression. It is not intended to serve as
The Young Adult Hip: FAI. Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California
 The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
Ilio-Tibial Band Syndrome
 Ilio-Tibial Band Syndrome Ilio-Tibial band syndrome (ITBS) is the most common cause of lateral knee pain in runners and cyclists. It is recognized by the sharp, burning pain that feels almost as if you
Ilio-Tibial Band Syndrome Ilio-Tibial band syndrome (ITBS) is the most common cause of lateral knee pain in runners and cyclists. It is recognized by the sharp, burning pain that feels almost as if you
Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Protocol
 Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Protocol 1. Concepts: a. Range of motion and weight bearing restrictions must be adhered to during the initial rehab process (4 total weeks of ROM and weight bearing restrictions)
Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Protocol 1. Concepts: a. Range of motion and weight bearing restrictions must be adhered to during the initial rehab process (4 total weeks of ROM and weight bearing restrictions)
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Initial Exercises (Weeks 1-3)
 Labral Repair This protocol should be used as a guideline for progression and should be tailored to the needs of the individual patient. Partial weight bearing (50%) (4 weeks). Encourage, but limit hip
Labral Repair This protocol should be used as a guideline for progression and should be tailored to the needs of the individual patient. Partial weight bearing (50%) (4 weeks). Encourage, but limit hip
Objectives. Objectives 9/26/2017. Evaluation and Rehab Management of the Patient with Hip Pain
 Evaluation and Rehab Management of the Patient with Hip Pain Joe Tupta, PT, OCS WPTA Fall Conference October 13 th, 2017 jtupta@uwhealth.org Objectives Screen the hip and adjacent regions for dysfunction
Evaluation and Rehab Management of the Patient with Hip Pain Joe Tupta, PT, OCS WPTA Fall Conference October 13 th, 2017 jtupta@uwhealth.org Objectives Screen the hip and adjacent regions for dysfunction
Diagnosis: Labral Tear, Internal Snapping Hip, CAM / Pincer. Procedure: Partial Psoas Release with CAM / Pincer Decompression and Labral Debridement
 Physical Therapy Prescription: Hip Arthroscopy Diagnosis: Labral Tear, Internal Snapping Hip, CAM / Pincer Procedure: Partial Psoas Release with CAM / Pincer Decompression and Labral Debridement RX: Evaluate
Physical Therapy Prescription: Hip Arthroscopy Diagnosis: Labral Tear, Internal Snapping Hip, CAM / Pincer Procedure: Partial Psoas Release with CAM / Pincer Decompression and Labral Debridement RX: Evaluate
Internal Rotation (turning toes/knee toward other leg) 30 degree limit. limit
 Hip Arthroscopy Patient Education Use of Brace and Crutches: - Wear the brace all times of weight bearing for the first 3 weeks after surgery. This is done to protect your hip and motion into hip extension
Hip Arthroscopy Patient Education Use of Brace and Crutches: - Wear the brace all times of weight bearing for the first 3 weeks after surgery. This is done to protect your hip and motion into hip extension
Compiled and Designed by: Sport Dimensions - 2 -
 SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation
 Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
Prater Chiropractic Wellness Center 903 W. South St. Kalamazoo, MI PH: (269)
 Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following a well-structured conditioning
Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following a well-structured conditioning
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
Human Anatomy Biology 255
 Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Hip Joint DX 612 Orthopedics and Neurology
 Hip Joint DX 612 Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Hip Anatomy Palpation Point tenderness Edema Symmetry Hip ROM Hip Contracture
Hip Joint DX 612 Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Hip Anatomy Palpation Point tenderness Edema Symmetry Hip ROM Hip Contracture
Hip Anatomy. Hip Joint DX 612 Orthopedics and Neurology. Hip ROM. Palpation
 Hip Joint DX 612 Orthopedics and Neurology Hip Anatomy James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Palpation Hip ROM Point tenderness Edema Symmetry Hip Contracture
Hip Joint DX 612 Orthopedics and Neurology Hip Anatomy James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Palpation Hip ROM Point tenderness Edema Symmetry Hip Contracture
Phase 1- Immediate Rehabilitation (1-3 weeks): Goals Precautions:
 Phase 1- Immediate Rehabilitation (1-3 weeks): Goals: Protection of the repaired tissue Prevent muscular inhibition and gait abnormalities Diminish pain and inflammation Precautions: 20 lb. flat-foot weight-bearing
Phase 1- Immediate Rehabilitation (1-3 weeks): Goals: Protection of the repaired tissue Prevent muscular inhibition and gait abnormalities Diminish pain and inflammation Precautions: 20 lb. flat-foot weight-bearing
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking
 1 p.177 2 3 The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking and running. The iliopsoas and adductor
1 p.177 2 3 The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking and running. The iliopsoas and adductor
Training Philosophy. There are numerous views on core conditioning.
 Abs Lab Presented by Helen Vanderburg BKin, ACE, CanFitPro, Yoga and Pilates 2005 IDEA Instructor of the Year 2006/ 1996 CanFitPro Presenter of the Year Nautilus and BOSU Fitness Education Team Introduction
Abs Lab Presented by Helen Vanderburg BKin, ACE, CanFitPro, Yoga and Pilates 2005 IDEA Instructor of the Year 2006/ 1996 CanFitPro Presenter of the Year Nautilus and BOSU Fitness Education Team Introduction
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Hip Pain in Adults: Evaluation 67th Annual McGill Refresher Course for Family Physicians Dec6/2016
 Hip Pain in Adults: Evaluation 67th Annual McGill Refresher Course for Family Physicians Dec6/2016 David J Zukor MD FRCSC Chief Department of Orthopedic Surgery SMBD-Jewish General Hospital Associate Professor
Hip Pain in Adults: Evaluation 67th Annual McGill Refresher Course for Family Physicians Dec6/2016 David J Zukor MD FRCSC Chief Department of Orthopedic Surgery SMBD-Jewish General Hospital Associate Professor
The Hip Joint: Myofascial and Joint Patterns
 The Hip Joint: Myofascial and Joint Patterns Marc Heller, DC, practices in Ashland, Ore. He can be contacted at mheller@marchellerdc.com or www.marchellerdc.com. For more information, including a brief
The Hip Joint: Myofascial and Joint Patterns Marc Heller, DC, practices in Ashland, Ore. He can be contacted at mheller@marchellerdc.com or www.marchellerdc.com. For more information, including a brief
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology POSTURE & GAIT ASSESSMENT
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology POSTURE & GAIT ASSESSMENT MSAK201-I Session 4 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of session 4, the student
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology POSTURE & GAIT ASSESSMENT MSAK201-I Session 4 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of session 4, the student
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics)
 Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
Spine Conditioning Program Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Muscles of the Gluteal Region
 Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Labral Refixation with or without FAI Component. Limited external rotation to 20 degrees (2 weeks)
 General Guidelines: 4140 Centennial Hills Boulevard Casper, WY 82609 (307) 265-7205 Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Labral Refixation with or without FAI Component Limited external rotation to 20 degrees
General Guidelines: 4140 Centennial Hills Boulevard Casper, WY 82609 (307) 265-7205 Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Labral Refixation with or without FAI Component Limited external rotation to 20 degrees
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Effective Treatments for Sciatica
 Effective Treatments for Sciatica Exact data on the incidence and prevalence of sciatica are lacking. In general an estimated 5%-10% of patients with low back pain have sciatica, whereas the reported lifetime
Effective Treatments for Sciatica Exact data on the incidence and prevalence of sciatica are lacking. In general an estimated 5%-10% of patients with low back pain have sciatica, whereas the reported lifetime
Alejandro Verdugo, M.D.
 Alejandro Verdugo, M.D. Physical Therapy Protocol Gluteus Medius repair with or without labral repair The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for your patient s therapy progression. It is
Alejandro Verdugo, M.D. Physical Therapy Protocol Gluteus Medius repair with or without labral repair The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for your patient s therapy progression. It is
PART ONE. Belly Dance Fitness Technique
 PART ONE Belly Dance Fitness Technique OVERVIEW Understanding belly dance movement The gentle, symmetrical, rhythmic undulations that we practice in Belly dance can help to revitalize almost every part
PART ONE Belly Dance Fitness Technique OVERVIEW Understanding belly dance movement The gentle, symmetrical, rhythmic undulations that we practice in Belly dance can help to revitalize almost every part
BENJAMIN G. DOMB, M.D.
 Arthroscopic Hip Surgery Physical Therapy Protocol The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for your patient s therapy progression. It is not intended to serve as a recipe for treatment. We
Arthroscopic Hip Surgery Physical Therapy Protocol The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for your patient s therapy progression. It is not intended to serve as a recipe for treatment. We
Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Procedure Form
 Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Procedure Form Femoracetabular Impingement (FAI) Femoral Osteochondroplasty Acetabular Rim Trimming Acetabular Labrum Repair Location: o clock to o clock Debridement Articular
Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Procedure Form Femoracetabular Impingement (FAI) Femoral Osteochondroplasty Acetabular Rim Trimming Acetabular Labrum Repair Location: o clock to o clock Debridement Articular
Knee Conditioning Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Michael McMurray PT, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville Patient Case
 SACROILIAC JOINT Michael McMurray PT, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Patient Case Reproduction Without Consent 1 Subjective Exam 26 yom fell playing
SACROILIAC JOINT Michael McMurray PT, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Patient Case Reproduction Without Consent 1 Subjective Exam 26 yom fell playing
