The Microscopic Structure of the Kidney
|
|
|
- Patience Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Microscopic Structure of the Kidney Dr. Mahmud Abuauba MBChB, DCH, MD, PhD Consultant Pediatrician & pediatric Nephrologist Assistant Professor of Pediatrician Zawia Kidney Center 5 th May 2018
2 برعاية مركز عالج أمراض الكلى-الزاوية
3 THE URINARY SYSTEM SIX ORGANS Paired kidneys (2) Paired ureters (2) Unpaired urinary bladder (1) Unpaired urethra (1)
4 THE URINARY SYSTEM
5 THE KIDNEYS
6 CORTEX & MEDULLA Coronal or long. section: two regions: Outer, darker, granular region Renal cortex Cortical labyrinth Cortical Medullary rays arch Inner lighter, striated region Renal medulla ~10-18 medullary pyramids
7
8
9
10
11
12 RENAL CORTEX Renal lobule= medullary ray + neighbuoring cortical labyrinth, with medullary ray in the center of lobule bounded by interlobular As Renal lobe= renal pyramid + renal column + cortical arch Renal lobe is a segment drains through the renal papilla
13
14 RENAL MEDULLA Composed of conical-shaped medullary tissue; renal or medullary pyramids Base toward the CM border Apex points toward the hilum, renal papillae, project into minor calyx Renal papillae perforated by opening of ducts of Bellini forming area cribosa Renal pyramids separated by corticallike tissue (renal column of Bertin)
15
16 RENAL MEDULLA Contains Straight portion of PT & DT Henle s loop, ALH & DLH Vasa recta MCT Papillary or ducts of Bellini
17
18 RENAL CORTEX Cortical arch is portion of cortex overlying renal pyramid Formed of cortical labyrinth & medullary rays Cortical labyrinth consists of renal corpuscle & convoluted tubules Medullary ray, straight tubules of several nephrons with single or more collecting tubules
19
20 RENAL CORTEX Contains Glomeruli PCT, DCT Connecting tubules CCT
21 URINIFEROUS TUBULE Uriniferous tubule is the basic functional unit of the kidney Uriniferous tubule formed of nephron & collecting tubule UT entirely is epithelial in nature UT are densely packed so the CT of kidney (stroma) is scant
22 Uriniferous tubule
23 NEPHRON I Nephron = renal corpuscle + renal tubules Each kidney has approx. a million ( million) nephrons
24
25 NEPHRON II Several nephrons (10) are drained by a single CCT Several CCT join to form larger tubule, MCT Several MCT join to form ducts of Bellini, perforate & open at papilla There are 250 collecting ducts Each collects urine from nephrons
26 NEPHRON III Cclassifications All nephrons are in the cortex Cortical nephrons (85%); have short Henle s loop, to outer medulla with short thin des HL & no thin Asc HL Superficial nephrons Mid-cortical nephrons
27 NEPHRON III Juxtamedullary nephrons (15%=1/7); have very long Henle s loop, sometimes descend to the tip of papilla Have short thick des HL, long thin Dec HL & thin Asc HL & thick Asc HL To establish medullary hypertonicity for concentrating urine
28
29 S1 Cortical nephron JM nephron S2 S3
30
31 NEPHRON IV Each nephron consists of: Renal corpuscle Renal tubule
32 RENAL CORPUSCLE Each renal corpuscle cconsists of: Glomerulus, a tuft of capillaries Bowman s capsule, a doublewalled epithelial capsule Has two poles: vascular & urinary pole
33 Renal Corpusle
34
35
36
37 GLOMERULUS I About m A tuft of capillaries Invaginated into Bowman s capsule Formed from AGA AGAs are short, stright, enter renal corpuscle at vascular pole Filtrating surface area is 0.8 m2
38
39
40 GLOMERULUS II Each AGA divides into 3-5 branches; into a tuft of capillaries (20-40 loops) glomerulus Fenestrated endothelial cells (70-90 nm); no diaphragm, act as a physical barrier Capillaries coalesce again to form efferent glomerular arteriole EGA is longer & narrower
41 Neck of the PT at urinary pole Bowman s capsule Consists of two layers: Visceral layer; internal; modified epithelial cells called podocytes Parietal layer; external, single layer of squamous epith supported by basal lamina & reticular fibers In between, Bowman s or urinary space, receives ultrafiltrate
42 PODOCYTES Modified epithelial cells of visceral layer Have cell body & primary processes (arise from body) both not in contact with the capillary Secondary processes or pedicels arise from the primary processes Pedicels in intimate contact with LRE
43
44
45
46
47 FILTRATION SLIT Pedicels interdigitate forming filtration slit 25 nm (20-40) & covered by slit diaphragm 6 nm thick SD has circular pores of 3-5 nm Acts as a physical barrier Pedicels covered by glycocalyx Glycocalyx contains sialoprotein (podocalyxin)
48
49
50 Filtration Slit
51 Proteinuria
52 GLOMERULAR BASEMENT MEMBRANE Is produced by fusion of basal lamina of endothelial cells & podocytes As a physical & charge barrier Consists of three layers: Lamina rara interna Lamina densa; collagen IV Lamina rara externa Laminin, fibrenectin, heparan sulphate
53 FILTRATION BARRIER Is a barrier between blood in capillaries & Bowman s space Consists of three layers: Fenestrated endothelial cells GBM Filtration slits of podocytes Glycocalyx
54 FILTRATION BARRIER Lamina densa is a meshwork of type IV collagen & laminin in a matrix containing vely charged proteoglycan (heparan sulfate) acts as a charge & physical barriers Laminae rarae contain fibronectin that binds them to cells
55 FILTRATION BARRIER Particles >10 nm in diameter don t cross GBM While vely charged proteins with MWt > 69 kda pass sparingly The largest protein succeeded to cross GBM has MWt 70kDa, therefore small amounts of albumin appear in urine
56 MESANGIUM Located between glomerular capillaries & consists of: Mesangial matrix & mesangial cells Mesangial cells: Intraglomerular mesangial cells Extraglomerular mesangial cells Supporting, phagocytosis, contraction, resorption
57
58
59 Mesangial cells They are contractile & have Ang II receptors that when activated the glomerular blood flow is reduced Also contain ANF receptors that relax mesangial cells & RBF Therefore, they regulate the RBF & glomerular filtration
60 RENAL TUBULE The second part of the nephron
61
62 RENAL TUBULE Is the part of uriniferous tubule orginates at the urinary pole of the renal corpuscle Divided into 12 segments
63
64 Proximal tubule S1, 1 st 2/3 of para convoluta S2, last 1/3 of para convoluta & much of para recta S3, remainder of para recta Loop of Henle Thin descending limb Thin ascending limb Distal tubule Medullary thick ascending limb Cortical thick ascending limb Distal convoluted tubule Connecting tubule Collecting tubule or duct Cortical collecting tubule Outer medullary collecting tubule Inner medullary collecting tubule
65
66 S1 S3 S2 S1 Cortical nephron JM nephron S2 S3
67
68
69 PROXIMAL TUBULE I First part of renal tubule Drains the urinary space Pars convoluta = PCT Pars recta = straight PT = DTkLH Divides into three segments: S1;1 st 2/3 of pars convoluta S2; last 1/3 of PC & much of PR S3; remainder of pars recta
70 PROXIMAL TUBULE II Confined to renal cortex Is longer than DCT therefore more numerous on histological cross section It is surrounded by peritubular capillaries Composed of single layer of cuboidal epithelial cells
71 PROXIMAL TUBULE III Have brush border of microvilli & apical canaliculi in between These canaliculi help in formation of pinocytosis to absorb macromolecules as proteins
72
73 PROXIMAL TUBULE IV Rich in mitochondria and it is highly metabolically active,mainly S1 Because basolateral membranes have abundant Na-K pump which responsible for active reabsorption of Na ions back into peritubular capillaries
74
75 HENLE S LOOP A U-shaped structure starts as continuation of PR & ends as ATkLHL Consists of three (or 5) parts: Descending thick LHL Descending thin LHL Loop or turn of Henle Ascending thin LHL Ascending thick LHL composed of single squamous
76 HENLE S LOOP
77 HENLE S LOOP 1/7 are JM nephrons Consists of four types of cells: l Type I only in midcortical & superficial nephrons l Type II,III,IV in JM nephrons JM nephrons have long LHL Cortical nephrons have short LHL
78
79
80
81 DISTAL TUBULE Starts as continuation of ATnLHL Subdivided into three parts: Pars recta = ATkLHL (part of HL) Macula densa Pars convoluta = DCT DT has single cuboidal epithelial cells, no brush border, no canaliculi ATkLHL is highly metabolic
82
83 Shorter than PCT, ratio 1:7 DISTAL TUBULE Macula densa At junction of ATkLHL & DCT It is part of juxtaglomerular apparatus DCT From MD to connecting tubule Cudoidal cells, No brush border
84 Macula densa Is a part of DT at junction of ATkLHL & DCT Also part of juxtaglomerular apparatus Consists of modified columnar cells with closely packed nuclei Sensitive to ionic content & water of tubular fluid
85 Juxtaglomerular apparatus
86
87 CONNECTING TUBULE It is a short segment of renal tubules that connects DCT to cortical collecting tubules DCT of several nephrons join to form short connecting tubule Several connecting tubules join to form collecting tubule
88 S1 S3 S2 S1 Cortical nephron JM nephron S2 S3
89 COLLECTING TUBULE Consists of three parts: CCT IMCT OMCT (papillary duct, Bellini ducts) It is not part of the nephron embryologicaly different The epithelium of CT is sensitive to vasopressin or ADH to water reabsorption
90
91
92 Development of the renal pelvis, calyces, collecting tubules A: at 6 weeks, B: at the end of the 6 th wk, C: 7 weeks & D: newborn
93 COLLECTING TUBULE CCT consists of two types of cells: Principal cells (P cells), Na reabsorption & water reabsorption 2ndary to ADH Intercalated cells (I cells); AB balance MCT formed by union of several CCT; has same cells as CCT Papillary CT or ducts of Bellini formed by union of several MCT & open at area cribosa; has only principal cells
94
95
96
97 Prof. Dr. Peter AGRE Nobel Laureate Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2003
98
99
100 RENAL INTERSTITIUM It is the space between uriniferous tubules & blood & lymphatic vessels Composed of: scanty loose CT; collagen & elastic fibers in both cortex & medulla Three types of cells; fibroblast; macrophages & interstitial cells
101 RENAL INTERSTITIUM Interstitial cells have numerous lipid droplets & synthesize & secrete medullipin I Medullipin I is converted (liver) to medullipin II; a potent vasodialtor which lowers BP Also secrete PGs (E2), prostcyclin
102 JUXTAGLOMERULAR APPARATUS Is a combination of specialized tubular & vascular cells located at vascular pole of glomerulus Consists of: Juxtaglomerular cells of the AGA Macula densa of the distal tubule Extraglomerular mesangial or Lacis cells
103 Juxtaglomerular apparatus
104 Juxtaglomerular apparatus
105 Juxtaglomerular apparatus
106
107 JUXTAGLOMERULAR CELLS Specialized, modified (VSMC) myoepithelaial cells; mainly tunica media of AGA as it enters glomeruls, occasionally EGA Contain secretory granules; renin Renin is a proteolytic enzyme that converts angoitensinogen into angiotensin I to regulate BP
108 JUXTAGLOMERULAR CELLS JGCs receive sympathetic nerve via 1 adrenergic receptors Acts as a baroreceptor (BP) Sensitive to change of BP So regulate arterial blood pressure
109 MACULA DENSA Is a speciliazed short segment of DT, as ATkLHL passes near its own corpuscle Located at vascular pole between AGA & EGA Composed of modified epithelial cells that are tall, narrow & have dense closely packed nuclei Appears as dark spot by LM
110
111 MACULA DENSA They are not innervated Act as chemoreceptors (Na&Cl) Sensitive to Na & Cl load in DT The JG cells & MD cells are in intimate contact, because no basal lamina between them
112 LACIS CELLS Extraglomerular mesangial cells Polkissen or polar cushions Are one type of mesangial cells forming interstitium of JGA Located between AGA, EGA & MD Are in intimate contact with intramesangial cells Function is unknown (renin)
113
114 Bladder & Urinary passages Conduct & store urine till excreted to exterior Mucosa of calyces, renal pelvis, ureters, UB consists of transitional epit with basal lamina Muscle fibers of UB run in every direction until reach bladder neck then arranged into 3 layers Adventia covers them externally
115 Bladder & Urinary passages Internal long layer becomes circular around prostatic urethra, true involuntary urethral sphincter It extends to external meatus in Middle layer ends at bladder neck Outer layer ends at prostate in & at external meatus
116 THANKS FOR ATTENTION
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal
 Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
THE RENAL / URINARY SYSTEM
 1 THE RENAL / URINARY SYSTEM Definition/Description: The Renal/Urinary system is the body system, which plays a vital role in the maintenance of homeostasis by the following processes: 1. Production of
1 THE RENAL / URINARY SYSTEM Definition/Description: The Renal/Urinary system is the body system, which plays a vital role in the maintenance of homeostasis by the following processes: 1. Production of
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Histology / First stage The Urinary System: Introduction. Kidneys
 The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system By the end of the topic the learner should be able to: Describe the histological structure of the kidney. Illustrate the ultrastructure of the blood renal barrier. Illustrate the
Histology Urinary system By the end of the topic the learner should be able to: Describe the histological structure of the kidney. Illustrate the ultrastructure of the blood renal barrier. Illustrate the
Urinary system. Aleš Hampl
 Urinary system Aleš Hampl Functions of urinary system 1. Regulating blood volume and pressure 2. Regulating plasma concentrations of sodium, potassium, chloride and other ions 3. Stabilising blood ph 4.
Urinary system Aleš Hampl Functions of urinary system 1. Regulating blood volume and pressure 2. Regulating plasma concentrations of sodium, potassium, chloride and other ions 3. Stabilising blood ph 4.
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Chapter 25: Urinary System
 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology
 Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Dr. Mahmud Abuauba MBChB, DCH, MD, PhD Consultant Pediatrician & pediatric Nephrologist Assistant Professor of Pediatrician
 RENAL BLOOD SUPPLY & FLOW Dr. Mahmud Abuauba MBChB, DCH, MD, PhD Consultant Pediatrician & pediatric Nephrologist Assistant Professor of Pediatrician Zawia Kidney Center 5 th May 2018 برعاية مركز عالج
RENAL BLOOD SUPPLY & FLOW Dr. Mahmud Abuauba MBChB, DCH, MD, PhD Consultant Pediatrician & pediatric Nephrologist Assistant Professor of Pediatrician Zawia Kidney Center 5 th May 2018 برعاية مركز عالج
H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY GROSS ANATOMY Location *Bean-shaped *Retroperitoneal *At level of T12 L1 vertebrae. *The right kidney lies slightly inferior to left
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY GROSS ANATOMY Location *Bean-shaped *Retroperitoneal *At level of T12 L1 vertebrae. *The right kidney lies slightly inferior to left
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Frontal section of human kidney. (Scheme).
 15 Urinary system 15-001 Kidney Cortex Medulla Papilla renalis Medial Lateral Medullary ray Labyrinth Columna renalis Pelvis renalis Calix renalis Ureter Capsula fibrosa Lobus renalis Columna renalis 15-01.
15 Urinary system 15-001 Kidney Cortex Medulla Papilla renalis Medial Lateral Medullary ray Labyrinth Columna renalis Pelvis renalis Calix renalis Ureter Capsula fibrosa Lobus renalis Columna renalis 15-01.
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology)
 Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran The Urinary System
Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran The Urinary System
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a.
 I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
بسن هلال الرحون الرحين
 1 P a g e 3 بسن هلال الرحون الرحين Today we will continue talking about the histology of the kidney, but before we start we will go over a quick review of what we took yesterday which s about the different
1 P a g e 3 بسن هلال الرحون الرحين Today we will continue talking about the histology of the kidney, but before we start we will go over a quick review of what we took yesterday which s about the different
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced
 Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
convoluted tubule. The proximal straight tubule is located in the medulla and dives down towards the pelvis.. [3] The Distal Straight Tubule receive
![convoluted tubule. The proximal straight tubule is located in the medulla and dives down towards the pelvis.. [3] The Distal Straight Tubule receive convoluted tubule. The proximal straight tubule is located in the medulla and dives down towards the pelvis.. [3] The Distal Straight Tubule receive](/thumbs/75/72965530.jpg) Chapter 16 Urinary System 16.1. Introduction The urinary system includes the: kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys regulate the composition and volume of body fluids by constantly
Chapter 16 Urinary System 16.1. Introduction The urinary system includes the: kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys regulate the composition and volume of body fluids by constantly
Waste. Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8. Urinary System. Urinary System. Nitrogenous Wastes. Nitrogenous Wastes 4/22/2016
 Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
Chapter 26. The Urinary System. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden
 Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Urinary System. BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
Collin College. BIOL Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12. Urinary System INTRODUCTION. Main functions of the kidneys are
 Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 INTRODUCTION Main functions of the kidneys are regulate blood volume, water content regulate blood composition e..g. Na, Cl, K, ph
Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 INTRODUCTION Main functions of the kidneys are regulate blood volume, water content regulate blood composition e..g. Na, Cl, K, ph
General Human Histology. The Urinary System
 General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Chapter 24: The Urinary System
 Chapter 24: The Urinary System Overview of kidney functions n Regulation of blood ionic composition n Regulation of blood ph n Regulation of blood volume n Regulation of blood pressure n Maintenance of
Chapter 24: The Urinary System Overview of kidney functions n Regulation of blood ionic composition n Regulation of blood ph n Regulation of blood volume n Regulation of blood pressure n Maintenance of
Urinary System Review Questions:
 Urinary System Review Questions: 1. This system would be lined with what type of membrane? 2. What type of epithelial tissue would line the opening of the urethra (the exit of the tract)? 3. What type
Urinary System Review Questions: 1. This system would be lined with what type of membrane? 2. What type of epithelial tissue would line the opening of the urethra (the exit of the tract)? 3. What type
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM
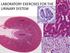 LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM cortex Medulla DEMO SLIDE BOX 172 (450-E001-H-76). Kidney, horse. the inner medulla medullary rays, Uriniferous tubules expand both the cortex and medulla corticomedullary
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM cortex Medulla DEMO SLIDE BOX 172 (450-E001-H-76). Kidney, horse. the inner medulla medullary rays, Uriniferous tubules expand both the cortex and medulla corticomedullary
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Basic Functions of the Kidneys
 Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
Urinary system. Urinary system
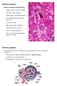 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
5.Which part of the nephron removes water, ions and nutrients from the blood?
 Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
URINARY SYSTEM. Urinary System
 URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY
 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Urinary Anatomy. Lab 40. Kidneys. Nephrons. Renal Corpuscle
 Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Waste Products & Kidney Function
 Waste Products & Kidney Function urinary system principal means of metabolic waste removal urinary system is closely associated with reproductive system urogenital system share embryonic development share
Waste Products & Kidney Function urinary system principal means of metabolic waste removal urinary system is closely associated with reproductive system urogenital system share embryonic development share
1. The Fibrous Capsule covers the outside of the kidney. It is made of fat and fibers.
 Slide 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is the excretion of toxic metabolic waste through urine production. The kidneys filter blood plasma and as a result of filtering blood, the kidneys help
Slide 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is the excretion of toxic metabolic waste through urine production. The kidneys filter blood plasma and as a result of filtering blood, the kidneys help
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Urinary System
 Urinary System What are the organs that comprise the urinary system? Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder Ureters Urethra Hepatic veins (cut) Esophagus (cut) Inferior vena cava Adrenal gland Aorta
Urinary System What are the organs that comprise the urinary system? Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder Ureters Urethra Hepatic veins (cut) Esophagus (cut) Inferior vena cava Adrenal gland Aorta
UNIT II HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 UNIT II HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II B--EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATION Very Short Answer Questions 1. Name the blood vessels that enter and exit the kidney? A. Renal artery enters kidney and
UNIT II HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II B--EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATION Very Short Answer Questions 1. Name the blood vessels that enter and exit the kidney? A. Renal artery enters kidney and
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM
 AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - ANATOMY Glomerulus + renal tubule Each kidney has 1.3 million nephrons Cortical nephrons (85%) have shorter Loop of Henle than Juxtamedullary nephrons
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - ANATOMY Glomerulus + renal tubule Each kidney has 1.3 million nephrons Cortical nephrons (85%) have shorter Loop of Henle than Juxtamedullary nephrons
Histotopography of nephron
 THE URINARY SYSTEM Microscopic structure and development of urinary systém Kidney: nephron structure and function Urinary passages: ureter, urinary bladder, urethra Development of urinary system THE URINARY
THE URINARY SYSTEM Microscopic structure and development of urinary systém Kidney: nephron structure and function Urinary passages: ureter, urinary bladder, urethra Development of urinary system THE URINARY
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Chapter 25 The Urinary System
 Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
LECTURE ON THE URINARY SYSTEM
 LECTURE ON THE URINARY SYSTEM (Uropoetic System) AN OVERVIEW Dr HAMIADJI THE URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance
LECTURE ON THE URINARY SYSTEM (Uropoetic System) AN OVERVIEW Dr HAMIADJI THE URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance
Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate
 Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily.
 1 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily. Next, the kidneys filter blood. As a result of filtering blood, the kidneys
1 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily. Next, the kidneys filter blood. As a result of filtering blood, the kidneys
Func%ons of the Urinary System
 Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Regula%on of blood volume Regula%on of blood pressure Regula%on of blood- solute concentra%on Regula%on of ph of extracellular fluid Regula%on of erythropoiesis
Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Regula%on of blood volume Regula%on of blood pressure Regula%on of blood- solute concentra%on Regula%on of ph of extracellular fluid Regula%on of erythropoiesis
Chapter 17: Urinary System
 Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
11/8/2017. Urinary System Functions. Organs and Vessels of the Urinary System Hepatic veins (cut)
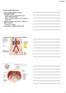 Urinary System Functions Major excretory pathway for wastes transported by blood Filtration, secretion, and reabsorption by the kidney s microscopic tubules Includes wastes from metabolism, excess water
Urinary System Functions Major excretory pathway for wastes transported by blood Filtration, secretion, and reabsorption by the kidney s microscopic tubules Includes wastes from metabolism, excess water
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
The Urinary System: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Mr. Barrow @ BEHS C H A P T E R 25 The Urinary System: Part A INTRODUCTION Introduction All organisms within Kingdom Animalia, including humans (homo sapiens), need
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Mr. Barrow @ BEHS C H A P T E R 25 The Urinary System: Part A INTRODUCTION Introduction All organisms within Kingdom Animalia, including humans (homo sapiens), need
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note
![Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note](/thumbs/77/75431210.jpg) Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
active transport of! Na. C. Tubular Reabsorption of Nutrients, Water, and Ions (p. 979; Fig )
 The Urinary System Outline 25.1 The kidneys have three distinct regions and a rich blood supply (pp. 963 965; Figs. 25.1 25.5) A. Location and External Anatomy (p. 963; Figs. 25.1 25.3) 1. The kidneys
The Urinary System Outline 25.1 The kidneys have three distinct regions and a rich blood supply (pp. 963 965; Figs. 25.1 25.5) A. Location and External Anatomy (p. 963; Figs. 25.1 25.3) 1. The kidneys
Chapter 26 The Urinary System. Overview of Kidney Functions. External Anatomy of Kidney. External Anatomy of Kidney
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Collin County Community College RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp , Chapter 19: pp ,
 P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART
 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART 1 DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Urinary System Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body Regulates water, electrolyte, and ph
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART 1 DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Urinary System Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body Regulates water, electrolyte, and ph
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
