HYPERTELORISM: An Unilateral Case.' BY
|
|
|
- David Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HYPERTELORISM: An Unilateral Case.' BY R. C. LIGHTWOOD, M.D., M.R.C.P. and W. P. H. SHELDON, M.D., M.R.C.P. (From the Children's Department, King's College Hospital, London). Ocular hypertelorism has been defined by D. M. Greig,1 who was the first to differentiate this condition, as a congenital cranio-facial deformity produced by abnormal development of the portion of the sphenoid which is laid down in cartilage. This mal-development results in the formation of great wings which are under-sized, while the lesser wings are as big as, or bigger than, the great wings. The facial appearances are characteristic. They consist in wide separation of the orbits, a broad nasal bridge, and external strabismus. The head is brachycephalic with flattening of the occiput and bulging of the temporal regions. Mental deficiency is a feature of the cases, at any rate of the severe ones. Greig was prepared to admit the possibility of ocular hypertelorism occurring as a unilateral deformity and in an addendum to his paper he writes as follows: Perhaps the following may not be irrelevant. In 1890, as a variety of plagiocephaly, Fridolin2 described the skull of a boy aged 3 months. It was asymmetrical, high and short, and the right side flatter than the left. The frontal and parietal eminences were absent from the right side, and the upper two-thirds of the right half of the coronal suture were synostosed. In my opinion the partial synostosis and the absence of the right parietal and frontal eminences are related to each other, the synostosis having prevented their development, and, an unwonted strain being thrown on the anterior fontanelle, a large inter-sutural bone has been the result. This part of the deformity is not uncommon, and has no particular relation to hypertelorism, but the other part of the deformity present has; and the presence of two defects in the skull need excite surprise no more than the co-existence or multiplicity of congenital defects elsewhere. The right orbital cavity is higher and narrower than the left, and the distance between the eyes ig in consequence increased. The right orbital index is 155, the left is 84. In the right temporal region the great wing of the sphenoid is much narrower than in the left, the measureiiients being respectively 3 mm. and 11 mm. The right zygomatic bone is higher than the left, and the zygomatic arch is shorter. The right side of the root of the nose is 54 mm. from the acoustic meatus, the left is 69 mm. from the corresponding point on the left side... It is obvious that synostosis of part of the right side of the coronal suture could not explain all these defects which are entirely unilateral. It is not difficult from what we have seen in liypertelorism to visualize the right side of the skull Fridolin so minutely describes. Further, if one can imagine the deformity as bilateral, the similarity to hypertelorism will be at once recognised and the fault ascribed to the sphenoid, especially that portion of its greater wings which is developed in cartilage. The explanation I have given of hypertelorism makes a unilateral affection not only possible but probable. Enough has been quoted to show how completely D. M. Greig anticipated the existence of unilateral hypertelorism, and Fridolin's description can be compared with the features of the case of unilateral hypertelorism described in this paper.
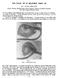
2 iiypeuitelorism: AN UNILATERAL CASE DESCRIPTION OF CASE. Winifred B., aged eight years, is the last child in a family of five. The other four children are of normal appearance. The first is a girl of twenty-three; the next is a boy of twenty-one, said to be the subject of renal trouble; the third (a girl) died of pneumonia; the fourth, a girl of fifteen, is of small stature but otherwise normal. Winifred was born when her mother was forty-two. Although labour was prolonged no instruments were employed. There have been no miscarriages. Both mother and father come of normal families. Winifred was brought to the Children's Department at King's College Hospital because she held her head on one side, and it was found that she had a torticollis, probably of ocular origin. Facial Appearance. The general facial appearance is shown by the photograph (Fig. 1). The upper part of the face on the right side is flattened and the right supra-orbital margin is underdeveloped. The right eyebrow is somewhat higher than the left, and the right palpebral fissure is wider than its fellow. It appears on close examination that the right orbit is displaced outwards and a little upwards. In consequence, the nasal bridge is wide; the distance between the inner canthi is 34 mm. The inter-pupillary measurement could not be taken accurately on account of an alternating strabismus, but an approximate measurement of 60 mm. was made. The distance between the external canthi is 86 mm. With the object of demonstrating more fully this facial asymmetry the photograph reproduced in Figure 1 was enlarged and two right halves made into one picture (Fig. 2) and two left halves into another (Fig. 3). Figure 2 gives the appearance of separation of the eyes and breadth of the nasal bridge characteristic of hypertelorism, while Figure 3 would pass for the photograph of a normal child. Description and Measurements of Head. The presence of hair made accurate head measurements difficult. The maximum horizontal circumference (measuring round the most prominent parts of the glabella and occiput) is 514mm. (20X"). The greatest length (from the most prominent part of the glabella to the most prominent part of the occiput) is 197 mm. (73"). The greatest parietal breadth is 168 mm.-(") but a longer measurement was taken from a point above and in front of the left ear to a point above and behind the right ear (63"). These measurements give a cephalic index of 85 and the skull is brachycephalic. There is very well marked flattening of the occipital region on the right side but none on the left. Orbits and Eyes. That the orbital measurements differ on the two sides is beyond doubt but such accuracy as is obtainable in the macerated skull, is not possible. On the right the orbital height is 34 mm. and the greatest width 33 mm., giving an orbital index of 103. On the left the orbital height is 31 mm., and the width 37 mm. giving an orbital index of 84. Dr. Whittington, who has examined her eyes, reports, " Compound hypermetropic astig. matism for which she wears glasses. Has alternating concomitant external strabismus and does not fix a near object with both eyes. The right eye tends to diverge most with the screen test and turns a little upwards as well as outwards, but the right eye is the fixing eye of choice under ordinary circumstances. The vision of the left eye is the worse of the two, and the tendency to turn the face to the left and to tilt the head to the left is probably associated with faulty vision and defective muscle balance. Discs normal." General Condition. This little girl is a healthy and not unattractive child. Examination of the nervous system and visceral organs yields no abnormality. There is slight webbing of the second and third digits on each foot. There is the slightest suggestion of incurving of the little fingers but neither the hands nor feet are mongolian in character. There is no acrocyanosis. 160
3 170 ARCHIVES OF DISEASE IN CHILDHOOD Mental Condition. Her mental condition is reported on by her teachers in the following words: (Infants School): " She was admitted at the age of five. During her first year her general progress was rather slow owing to timidity, but later she attained a good average degree of proficiency." (Girls' School): "She is below average in ability, but she has made great progress in reading and writing. Arithmetic she finds very difficult. She is a quiet little girl but is very interested in all school work." On examination by the Binet-Simon tests I)r. N. H. M. Burke says of her: " This child is bright and intelligent in manner. She shows failure in tests requiring understanding of imagery and relationships. Ob3ervation, attention, and memory are good, and the gereral intelligernce I Fig. 1.-Unilateral hypertelorism. is vell above the average. Her mental age is 9. years, giving an Initelligence Quotient of 117%." Thus the slight backwardniess reported by the school teachers is not confirmed by the Binet. Simon tests. Radiological Examination. The radiological appearances are, in our opinion, inconclusive. The two sides of the skull arc obviously not symmetrical, and there is definite bulging of the temporal region on the right side. The sella turcica is normal. DiscussION. In the case of Winifred B., we have an unusual ophthalmological condition to explain, namely, the occurrence of hypermetropia with external strabismus. It is well known that hypermetropia is usually associated with internal
4 HYFtYPEIT'EELO( lisix: ANK UNXILATERAL CASE strabismus. For an exception to this rule there are two theoretical explanations forthcoming. First, that a lesion of part of the third nerve nucleus may cause weakness of convergence. This, for example, is what occurs in the postencephalitic state following encephalitis lethargica. Thus, Dr. T. H. Whittington found that among 100 post-encephalitic children there were eighteen cases of external strabismus and no cases of internal strabismus, although among unselected children internal strabismus is the commoner type of squint. It is reasonable to assume a partial lesion of the third nerve nucleus in these post-encephlalitic children. Secondly, that a developmental defect of binocular Fig. 2. Fig. 3. 'ltwo riilit (hyperteloric) halves made iilto Two left (ilon-liypeiteloric) halves made into one picture. Note the w%-idely separatcel eyes one picture. and width of nasal bridge. vision and the fusion centre* inay occur. This is the explanlation which seems more probable in the case under discussion. If hypertelorism is atavistic it would be expected that, together with the lateral displacement of the eyes, binocular vision would be absent. This, in fact, is the rule in hypertelorism and explains the ocular conldition in the present case. Greig describes one of his cases in the following words: " Her eyes did not converge on near objects. Like a hare, she could not see objects directly in front of her so readily or so well as when they were placed laterally or when she turined her head away e A fusion centre has been postulated by Worth but proof of its existerice is wanting. -171
5 172 ARCHIVES OF DISEASE IN CHILDHOOD from them." Binocular vision is a recently acquired characteristic of man. Birds and many quadrupeds have laterally placed eyes. The horse is in an intermediate position; the ape with its arboreal agility is in need of binocular vision-a function which reaches its highest development in man. Another point in the case here related is interesting. Her hypertelorism is right-sided. Although her right eye is the fixing eye of choice and the one which is more nearly emmetropic, yet it is the right eye which deviates more widely. The turning of her head to the left is an effort to bring objects into line with the right eye, and this explains her torticollis. Ocular hypertelorism by derivation implies wide-apartness of the eyes (i'relp, too much; 1-9AE, apart; OEIs,, to separate). To describe a case as " unilateral ocular hypertelorism" is perhaps, somewhat contradictory, but the term " ocular hypertelorism " is established and has such merit that it should be retained. CONCLUSION. A case of right-sided (unilateral) ocular hypertelorism is described. External deviation of the fixing (right) eye is probably responsible for an associated torticollis. There is no mental defect. In preparing this paper valuable help has been received from Dr. H. Graham Hodgson, who took the radiograms, from l)r. T. H. Whittington, who made the ophthalmological examination, from Dr. N. H. M. Burke, who carried out the Binet-Simon tests, and from Mr. E. G. Parfitt, who prepared the photographs. To all these our thanks are due. REFERENCES. 1. Greig, D. M., Edin. Med. J., Edin., 1924, XXXI, Fridolin, J., Virchow Archiv., Berlin, 1890, (XX1I, 528. Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 June Downloaded from on 17 September 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Craniosynostosis. Diagnosis and Treatment
 Craniosynostosis Diagnosis and Treatment 2015 For more information about the Weill Cornell Craniofacial Program ABOUT The Weill Cornell Craniofacial Program takes a multidisciplinary approach to treating
Craniosynostosis Diagnosis and Treatment 2015 For more information about the Weill Cornell Craniofacial Program ABOUT The Weill Cornell Craniofacial Program takes a multidisciplinary approach to treating
T HERE is an unusual and interesting variety of craniosynostosis in
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
"A" AND "V" PHENOMENA*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 718 "A" AND "V" PHENOMENA*t DHANWANT SINGH, GURBUX SINGH, L. P. AGGARWAL, AND PREM CHANDRA BY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Government Medical College, Patiala, and
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 718 "A" AND "V" PHENOMENA*t DHANWANT SINGH, GURBUX SINGH, L. P. AGGARWAL, AND PREM CHANDRA BY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Government Medical College, Patiala, and
Congenital ocular palsy
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (1972) 56, 356 Congenital ocular palsy C. G. KEITH Queen Elizabeth Hospitalfor Children, Hackney Road, London Three patients with severe restriction of the ocular movements in one eye
Brit. j. Ophthal. (1972) 56, 356 Congenital ocular palsy C. G. KEITH Queen Elizabeth Hospitalfor Children, Hackney Road, London Three patients with severe restriction of the ocular movements in one eye
HEAD TO FOOT EXAMINATION DR JP,ASST. PROF.ICH,GOVT MEDICAL COLLEGE KOTTAYAM
 HEAD TO FOOT EXAMINATION DR JP,ASST. PROF.ICH,GOVT MEDICAL COLLEGE KOTTAYAM 1.CRANIUM Is the size of head normal.?(measure ofc).is the skull shape abnormal( LOOK FROM ABOVE)? Are there any swellings on
HEAD TO FOOT EXAMINATION DR JP,ASST. PROF.ICH,GOVT MEDICAL COLLEGE KOTTAYAM 1.CRANIUM Is the size of head normal.?(measure ofc).is the skull shape abnormal( LOOK FROM ABOVE)? Are there any swellings on
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Abnormal Facies, Myopia, and Short Stature
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1972, 47, 787. Abnormal Facies, Myopia, and Short Stature C. G. KEITH, R. H. DOBBS, D. G. SHAW, and K. COTTRALL From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital for Children, London
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1972, 47, 787. Abnormal Facies, Myopia, and Short Stature C. G. KEITH, R. H. DOBBS, D. G. SHAW, and K. COTTRALL From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital for Children, London
NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM
 LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
sheath syndrome Bilateral superior oblique tendon of uniovular twins Occurrence and spontaneous recovery in one Brit. J. Ophthal.
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I969) 53, 466 Bilateral superior oblique tendon sheath syndrome Occurrence and spontaneous recovery in one of uniovular twins RONALD F. LOWE Melbourne, Australia Brown (I950) defined
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I969) 53, 466 Bilateral superior oblique tendon sheath syndrome Occurrence and spontaneous recovery in one of uniovular twins RONALD F. LOWE Melbourne, Australia Brown (I950) defined
Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board
 THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
Prevention Diagnosis
 Prevention and Management of Positional Skull Deformities in Infants John Persing, MD, Hector James, MD, Jack Swanson, MD, John Kattwinkel, MD, Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on
Prevention and Management of Positional Skull Deformities in Infants John Persing, MD, Hector James, MD, Jack Swanson, MD, John Kattwinkel, MD, Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions
 Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
WITH REPORT OF A PEDIGREE*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955), 39, 374. HEREDITARY POSTERIOR POLAR CATARACT WITH REPORT OF A PEDIGREE* BY C. G. TULLOH London K HEREDITARY, developmental, posterior polar cataract has been encountered in a
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955), 39, 374. HEREDITARY POSTERIOR POLAR CATARACT WITH REPORT OF A PEDIGREE* BY C. G. TULLOH London K HEREDITARY, developmental, posterior polar cataract has been encountered in a
OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY
 OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY By Sir HAROLD GILLIES, C.B.E., F.R.C.S., and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S., R.C.S. From the Plastic
OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY By Sir HAROLD GILLIES, C.B.E., F.R.C.S., and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S., R.C.S. From the Plastic
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses
 J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
Coding For Craniosynostosis. Peggy Feeley RHIA, CCS, CCS-P, COC AHIMA Approved ICD-10-CM/PCS Trainer
 Coding For Craniosynostosis Peggy Feeley RHIA, CCS, CCS-P, COC AHIMA Approved ICD-10-CM/PCS Trainer Cranial sagittal Synostosis Cranium job is to protect the brain The top portion of the skull, which protects
Coding For Craniosynostosis Peggy Feeley RHIA, CCS, CCS-P, COC AHIMA Approved ICD-10-CM/PCS Trainer Cranial sagittal Synostosis Cranium job is to protect the brain The top portion of the skull, which protects
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Klinefelter syndrome ( 47, XXY )
 Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
Craniosynostosis and Plagiocephaly
 Craniosynostosis and Plagiocephaly Andrew Jea MD MHA FAAP Professor and Chief Section of Pediatric Neurosurgery Riley Hospital for Children Department of Neurosurgery Indiana University School of Medicine
Craniosynostosis and Plagiocephaly Andrew Jea MD MHA FAAP Professor and Chief Section of Pediatric Neurosurgery Riley Hospital for Children Department of Neurosurgery Indiana University School of Medicine
Dysmorphology. Sue White. Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase. Victorian Clinical Genetics Services
 Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Skeletal System: Skull.
 Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
 SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
BIO 137 AXIAL SKELETON BONE STUDY THE HUMAN SKELETON
 BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
BINOCULAR MECHANISMS IN SMALL-ANGLE
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 648. BINOCULAR MECHANISMS IN SMALL-ANGLE STRABISMUS* BY A. STANWORTH AND DAPHNE DA CUNHA University of Manchester and Manchester Royal Eye Hospital THE purpose of treatment
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 648. BINOCULAR MECHANISMS IN SMALL-ANGLE STRABISMUS* BY A. STANWORTH AND DAPHNE DA CUNHA University of Manchester and Manchester Royal Eye Hospital THE purpose of treatment
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 51. UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE* BY FROMA SOMERVILLE London APLASIA of the optic nerve occurring as an isolated abnormality in an eye of normal external appearance
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 51. UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE* BY FROMA SOMERVILLE London APLASIA of the optic nerve occurring as an isolated abnormality in an eye of normal external appearance
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
HYPERTELORISM. With Reports of Cases."
 SCAPHOCEPHALY, OXYCEPHALY AND HYPERTELORISM. With Reports of Cases." BY A. G. OGILVIE, M.B., B.S., and M. M. POSEL, L.R.C.P., M.R.C.S. From the East London Hospital for Children. The congenital abnormalities
SCAPHOCEPHALY, OXYCEPHALY AND HYPERTELORISM. With Reports of Cases." BY A. G. OGILVIE, M.B., B.S., and M. M. POSEL, L.R.C.P., M.R.C.S. From the East London Hospital for Children. The congenital abnormalities
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of Anatomy
 5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
The Future of Exercise
 The Future of Exercise (1997 and Beyond) ArthurJonesExercise.com 9 Requirements for Proper Exercise (con t) The relatively poor strength increases that were produced in the unworked range of movement during
The Future of Exercise (1997 and Beyond) ArthurJonesExercise.com 9 Requirements for Proper Exercise (con t) The relatively poor strength increases that were produced in the unworked range of movement during
Anatomy Made Easy MSS
 Anatomy Made Easy MSS part #1 هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة الثانية لعون بدءا من الصفحة 11 وحتى األخير Done By :MohamedA. Diabat Edited by Awn Academic team The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton consist
Anatomy Made Easy MSS part #1 هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة الثانية لعون بدءا من الصفحة 11 وحتى األخير Done By :MohamedA. Diabat Edited by Awn Academic team The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton consist
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Esotropia - Exotropia. Carlos Eduardo Solarte MD. MPH Assistant Clinical Professor Director Residency Program Ophthalmology
 Esotropia - Exotropia Carlos Eduardo Solarte MD. MPH Assistant Clinical Professor Director Residency Program Ophthalmology Financial Disclosure and Source I have no actual or potential financial interest
Esotropia - Exotropia Carlos Eduardo Solarte MD. MPH Assistant Clinical Professor Director Residency Program Ophthalmology Financial Disclosure and Source I have no actual or potential financial interest
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Bone Flashcards for 10a
 Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Blair Radiology Exam Examination Packet
 Blair Radiology Exam Examination Packet This packet is made of up five sections: Examiner s Instructions, Applicant Requirements, Analysis Rubric, Overall Result and Comments and Exam Form. The Exam Form
Blair Radiology Exam Examination Packet This packet is made of up five sections: Examiner s Instructions, Applicant Requirements, Analysis Rubric, Overall Result and Comments and Exam Form. The Exam Form
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
BINOCULAR DEPTH PERCEPTION IN SMALL-ANGLE
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 662. BINOCULAR DEPTH PERCEPTION IN SMALL-ANGLE STRABISMUS* BY E. J. NAYLOR AND A. STANWORTH Department of Ophthalmology, University of Manchester MEASUREMENTS of the binocular
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 662. BINOCULAR DEPTH PERCEPTION IN SMALL-ANGLE STRABISMUS* BY E. J. NAYLOR AND A. STANWORTH Department of Ophthalmology, University of Manchester MEASUREMENTS of the binocular
HEAD CIRCUMFERENCE OF INFANTS RELATED TO BODY WEIGHT
 Arch Dis Childh 1965 40 672 HEAD CRCUMFERENCE OF NFANTS RELATED TO BODY WEGHT BY R S LLNGWORTH and W LUTZ From the Department of Child Health and the Department of Statistics the University of Sheffield
Arch Dis Childh 1965 40 672 HEAD CRCUMFERENCE OF NFANTS RELATED TO BODY WEGHT BY R S LLNGWORTH and W LUTZ From the Department of Child Health and the Department of Statistics the University of Sheffield
Cleidocranial Dysplasia
 BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Forensic Anthropology
 Forensic Anthropology a type of applied anthropology that specializes in the changes and variations in the human skeleton for the purpose of legal inquiry A forensic anthropologist may provide basic identification
Forensic Anthropology a type of applied anthropology that specializes in the changes and variations in the human skeleton for the purpose of legal inquiry A forensic anthropologist may provide basic identification
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera
 PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSIALIS MULTIPLEX IN THREE SISTERS
 DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Terms: Structures of Bones Articulations: Contacts with other bones Landmarks (Bone
An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Terms: Structures of Bones Articulations: Contacts with other bones Landmarks (Bone
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7
 TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
o Diaphysis o Area where red marrow is found o Area where yellow marrow is found o Epiphyseal plate AXIAL SKELETON Skull
 64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
Skeletal System -Axial System. Chapter 7 Part A
 Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Facial measurements in the newborn (towards syndrome delineation)
 358 3 Med Genet 1990; 27: 358-362 Facial measurements in the newborn (towards syndrome delineation) 0 0 Omotade Abstract Inner and outer canthal distances, palpebral fissure length, occipitofrontal circumference,
358 3 Med Genet 1990; 27: 358-362 Facial measurements in the newborn (towards syndrome delineation) 0 0 Omotade Abstract Inner and outer canthal distances, palpebral fissure length, occipitofrontal circumference,
Important Parts of Bones
 Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Forensic Anthropology. What can it tell us?
 Forensic Anthropology What can it tell us? History 1800s scientists began using skull measurements to differentiate human bodies 1897 Luetgert murder case; man killed his wife and boiled down her remains
Forensic Anthropology What can it tell us? History 1800s scientists began using skull measurements to differentiate human bodies 1897 Luetgert murder case; man killed his wife and boiled down her remains
Skeletal System. Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section
 Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci. Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D Tuesday
 View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
ESD 113 Sound to Harbor Head Start/ECEAP Procedure 620 Page 1 of 6 HEALTH SCREENINGS PROCEDURE. Health Section
 Page 1 of 6 HEALTH SCREENINGS PROCEDURE 1. Head Start children will be screened within 45 days of enrollment and ECEAP children will be screened within 90 days of enrollment. ECEAP children at Head Start
Page 1 of 6 HEALTH SCREENINGS PROCEDURE 1. Head Start children will be screened within 45 days of enrollment and ECEAP children will be screened within 90 days of enrollment. ECEAP children at Head Start
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
Department of Neurosurgery. Differentiating Craniosynostosis from Positional Plagiocephaly
 Department of Neurosurgery Differentiating Craniosynostosis from Positional Plagiocephaly The number of infants with head shape deformities has risen over the past several years, likely due to increased
Department of Neurosurgery Differentiating Craniosynostosis from Positional Plagiocephaly The number of infants with head shape deformities has risen over the past several years, likely due to increased
Bones of the Skull Lateral View
 Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
The University Hospital/ 90! Twenty-Third.Street, N.IV./ Washington, D.C Representatives Select Committee on Assassinations Staff Member
 222 ADDENDUM D REPORT OF DAVID O. DAVIS, M.D., CONCERNING THE EXAMINATION OF THE AUTOPSY X-RAYS OF PRESIDENT JOHN F. KENNEDY, DATED AUGUST 23, 1975 REPORT OF DAVID 0. DAVIS, M.D., CONCERNING THE EXAMINATION
222 ADDENDUM D REPORT OF DAVID O. DAVIS, M.D., CONCERNING THE EXAMINATION OF THE AUTOPSY X-RAYS OF PRESIDENT JOHN F. KENNEDY, DATED AUGUST 23, 1975 REPORT OF DAVID 0. DAVIS, M.D., CONCERNING THE EXAMINATION
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
a guide to understanding craniosynostosis a publication of children s craniofacial association
 a guide to understanding craniosynostosis a publication of children s craniofacial association 1 a guide to understanding craniosynostosis this parent s guide to craniosynostosis is designed to answer
a guide to understanding craniosynostosis a publication of children s craniofacial association 1 a guide to understanding craniosynostosis this parent s guide to craniosynostosis is designed to answer
THE INCIDENCE OF INCOMPLETE DESCENT OF THE TESTICLE AT BIRTH
 THE INCIDENCE OF INCOMPLETE DESCENT OF THE TESTICLE AT BIRTH BY C. G. SCORER From Hillingdon Hospital, Uxbridge (RECEIo-ED FOR PUBUCATION JANUARY 17. 19) Descent of the testicle from the abdomen into meaning
THE INCIDENCE OF INCOMPLETE DESCENT OF THE TESTICLE AT BIRTH BY C. G. SCORER From Hillingdon Hospital, Uxbridge (RECEIo-ED FOR PUBUCATION JANUARY 17. 19) Descent of the testicle from the abdomen into meaning
Skull basic structures. Neurocranium
 Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
MICROTIA. The condition is a complex mix of cosmetic, functional, and often psychological difficulties. Microtia: Not only the ear.
 MICROTIA Underdevelopment /deformity of the auricle (pinna) varies from subtle deformities and small pre-auricular rudiments to gross developmental failure, distortion or malpositioned remnants. The external
MICROTIA Underdevelopment /deformity of the auricle (pinna) varies from subtle deformities and small pre-auricular rudiments to gross developmental failure, distortion or malpositioned remnants. The external
Autism Cutting Edge Discoveries By Dr. Roger L. Turner D.C. Would you like to hear about the cause missed by most treatment protocols?
 Autism Cutting Edge Discoveries By Dr. Roger L. Turner D.C. Do you feel there must be an answer to the causes of Autism? Would you like to hear about the cause missed by most treatment protocols? A cutting
Autism Cutting Edge Discoveries By Dr. Roger L. Turner D.C. Do you feel there must be an answer to the causes of Autism? Would you like to hear about the cause missed by most treatment protocols? A cutting
Human, Male, Single gunshot wound
 Human, Male, Single gunshot wound Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-152 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium - left inferior nasal concha absent - middle nasal conchae absent 1
Human, Male, Single gunshot wound Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-152 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium - left inferior nasal concha absent - middle nasal conchae absent 1
ADDENDUM C DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY. THE HOSPITAk..O,Is THR ;GOIDD SAMARITAN T.- --T dnjfopnaa sooty
 217 ADDENDUM C REPORT OF G, M. MCDONNEL, M.D., CONCERNING THE OBSERVATIONS, ANALYSIS, AND CONCLUSIONS IN CONNECTION WITH THE RADIOGRAPHIC IMAGES AND EN- HANCED IMAGES OF X-RAYS ATTRIBUTED TO PRESIDENT
217 ADDENDUM C REPORT OF G, M. MCDONNEL, M.D., CONCERNING THE OBSERVATIONS, ANALYSIS, AND CONCLUSIONS IN CONNECTION WITH THE RADIOGRAPHIC IMAGES AND EN- HANCED IMAGES OF X-RAYS ATTRIBUTED TO PRESIDENT
frontalis muscle while the patient makes an attempt to open the eye. With the first and third classes I am not now concerned, except
 OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIs 741 AN OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIS* BY R. AFFLECK GREEVES LONDON CASES of congenital ptosis may be conveniently divided, clinically, into
OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIs 741 AN OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIS* BY R. AFFLECK GREEVES LONDON CASES of congenital ptosis may be conveniently divided, clinically, into
External Acoustic Meatus. Mastoid Process. Zygomatic Process. Temporal Bone
 Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Quantitative Determination of
 The Application of 3D Images for Quantitative Determination of Zygoma in an Asian Population Shih-Hsuan Mao, Yu-Hsuan Hsieh, Chih-Hao Chen, Chien-Tzung Chen Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
The Application of 3D Images for Quantitative Determination of Zygoma in an Asian Population Shih-Hsuan Mao, Yu-Hsuan Hsieh, Chih-Hao Chen, Chien-Tzung Chen Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
New Patient Information Form
 New Patient Information Form Patient Identification Prenatal Alcohol & Drug Exposure Clinic FASD CLINIC Patient s OHIP N. Female Male Race Patient s Name Birth Date Age First Middle Last Patient s Address
New Patient Information Form Patient Identification Prenatal Alcohol & Drug Exposure Clinic FASD CLINIC Patient s OHIP N. Female Male Race Patient s Name Birth Date Age First Middle Last Patient s Address
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations The outline form
 Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Anatomy of. External NOSE. By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC
 Anatomy of External NOSE By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 24 th Nov. 2017 The External Nose Descriptions of the nose always begin with that part of it which is covered by the skin, i.e., the EXPOSED PART
Anatomy of External NOSE By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 24 th Nov. 2017 The External Nose Descriptions of the nose always begin with that part of it which is covered by the skin, i.e., the EXPOSED PART
INGUINAL HERNIA IN FEMALE TWINS
 INGUINAL HERNIA IN FEMALE TWINS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO THE IDENTIFICATION OF MONOZYGOTISM BY C. E. KELLETT, M.D., M.R.C.P. It has long been common knowledge that certain twins resemble one another in
INGUINAL HERNIA IN FEMALE TWINS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO THE IDENTIFICATION OF MONOZYGOTISM BY C. E. KELLETT, M.D., M.R.C.P. It has long been common knowledge that certain twins resemble one another in
Reassessment of Sphenoid Dysplasia Associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 1
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:644 648, April 2002 Reassessment of Sphenoid Dysplasia Associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Claude Jacquemin, Thomas M. Bosley, Don Liu, Helena Svedberg, and Amal Buhaliqa
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:644 648, April 2002 Reassessment of Sphenoid Dysplasia Associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Claude Jacquemin, Thomas M. Bosley, Don Liu, Helena Svedberg, and Amal Buhaliqa
Facing the Facts: Craniofacial Asymmetry and Developmental Pathology in LB1 from Liang Bua, Flores, Indonesia
 Facing the Facts: Craniofacial Asymmetry and Developmental Pathology in LB1 from Liang Bua, Flores, Indonesia Robert B. Eckhardt Professor of Developmental Genetics and Evolutionary Morphology Laboratory
Facing the Facts: Craniofacial Asymmetry and Developmental Pathology in LB1 from Liang Bua, Flores, Indonesia Robert B. Eckhardt Professor of Developmental Genetics and Evolutionary Morphology Laboratory
INFANTILE EXOTROPIA. Lionel Kowal
 INFANTILE EXOTROPIA Lionel Kowal INFANTILE XT Usage often imprecise Variation in definitions number of investigators? onset day 1 of life? constant / intermittent Any / large angle? Associated systemic
INFANTILE EXOTROPIA Lionel Kowal INFANTILE XT Usage often imprecise Variation in definitions number of investigators? onset day 1 of life? constant / intermittent Any / large angle? Associated systemic
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
Human Male Asian Skeleton, Robust
 Human Male Asian Skeleton, Robust Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: SC-287 Original Specimen Near-complete human skeleton with 28 teeth. Osteological Observations: This is a clean,
Human Male Asian Skeleton, Robust Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: SC-287 Original Specimen Near-complete human skeleton with 28 teeth. Osteological Observations: This is a clean,
What is Craniosynostosis?
 What is Craniosynostosis? Craniosynostosis is defined as the premature closure of the cranial sutures (what some people refer to as soft spots). This results in restricted and abnormal growth of the head.
What is Craniosynostosis? Craniosynostosis is defined as the premature closure of the cranial sutures (what some people refer to as soft spots). This results in restricted and abnormal growth of the head.
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview. Functions
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Forensic Anthropology Open Notes Practice Test
 Name: Date: 1/2/18 Section Broughton High School 1 Section 1: - True or False Forensic Anthropology Open Notes Practice Test 1. The number of bones in the body increases from the time of birth to adulthood.
Name: Date: 1/2/18 Section Broughton High School 1 Section 1: - True or False Forensic Anthropology Open Notes Practice Test 1. The number of bones in the body increases from the time of birth to adulthood.
