CALICUT UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
|
|
|
- Emerald Hunt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CALICUT UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY II Core course of BSc. COUNSELLING PSYCHOLOGY V semester CUCBCSS 2014 Admn onwards MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. is best known for his research on conformity Asch d) Zimbardo b) Rubin 2. c) Schachter 3. During the Stanford Prison study, guards did not take their roles seriously b) guards readily assumed their roles as agents of force c) the prisoners and the guards quickly became friendly towards one another d) three prisoners were so severely beaten they had to be hospitalized 4. During research in a simulated prison situation three prisoners were so severely beaten they had to be hospitalized b) guards did not take their roles seriously c) prisoners quickly became passive and dehumanized d) the prisoners and the guards quickly became friendly towards one another 5. The degree of attraction among group members relates to the dimension of b) Compatibility c) Structure
2 d) Cohesiveness 6. e) Conformity 7. You are walking into a store when a man rudely cuts in front of you, almost shoving you, so that he may enter the store first. "What a jerk!" you think to yourself. As you enter the store, you see the same man performing an emergency tracheotomy on a women with a collapsed windpipe. You have just discounted a person's actions due to situational demands b) self-handicapped c) overemphasized the object in this action sequence d) made the fundamental attribution error 8. According to evolutionary psychologists, women tend to be concerned with whether mates will devote time and resources to a relationship. b) men place less emphasis on physical attractiveness c) women place more emphasis on sexual fidelity d) men are biologically driven to have multiple partners 9. Which statement about physical attractiveness is FALSE? Beauty is a factor mainly in initial acquaintances b) Looks are less related to dating frequency for men than for women c) For men, there is little relationship between attractiveness and the achievement of status d) For marriage partners there is a tendency for attractive men to be paired with highly educated women with high incomes 10.Moderate self-disclosure typically leads to b) competence matching e) reciprocity c) rejection 11. d) romantic attraction 12.When subjects in Milgram's obedience experiments received their orders over the phone, they
3 conformed more completely due to the formality of the telephoned instructions b) completely refused to participate c) were only slightly more obedient than they were in face-to-face conditions d) were far less obedient 13.Solomon Asch's classic experiment (in which subjects judged a standard line and comparison lines) was arranged to test the limits of b) social perception e) conformity c) indoctrination 14. d) coercive power 15.The person who agrees to a small request initially is more likely later to comply with a larger demand. This describes the b) door-in-the-face-effect e) high-ball technique. c) foot-in-the-door effect 16. d) low-ball technique 17.For most American adults, an invisible spatial envelope defining their most intimate space 18. b) extends four feet from their body c) extends an "arm's reach" from their body d) is reserved for comfortable interactions with friends e) extends about 18 inches out from their body 19.Which theory holds that a relationship must be profitable to endure? b) complementary need theory c) social exchange theory d) gain-loss theory e) social comparison theory
4 You are asked by a close friend to outline a complete text to aid her studying for a final exam. You refuse to help. Later, your friend asks if you would at least outline two chapters. Feeling guilty, you now agree to help. Your behavior is predicted by the b) foot-in-the-face technique e) door-in-the-face effect c) high-ball effect 22. d) low-ball technique 23. attachment style is marked by conflicting feelings of affection, anger, and emotional turmoil b) Mutual e) Ambivalent c) Secure 24. d) Avoidant 25.Zimbardo interpreted the results of his simulated prison study as an indication of the b) powerful influence of roles on people c) tendency to show compassion to people in need d) weakness of social pressure in some situations e) tendency to displace aggression 27.Subjects in Milgram's experiment who gave large shocks rationalized that they were NOT personally responsible for their actions. This raises questions about our willingness to commit inhumane acts as a result of 26. b) coercive power c) obedience to a legitimate authority 28. d) expert power e) conformity to group pressure
5 29.The process of changing your behavior to match that of others in a group is b) Norming e) standardization c) forming a social contract 30. d) conformity 31.If everyone leaves five minutes before the game is over to avoid a traffic jam, the resulting traffic jam would be an example of b) social impregnation e) self-handicapping c) a social trap 32. d) groupthink 33.People's invisible "spatial envelope" defines their, and extends "I" or "me" boundaries past the skin b) spatial role e) proximal location c) personal space 34. d) ego location 35.Physical proximity increases attraction because it b) increases frequency of contact e) reduces development of incompatible roles c) enhances social comparisons 36. d) establishes common norms 37.The study of unspoken rules for the use of interpersonal space is called b) Kinesics c) Psychoecology
6 d) Proxemics 38. e) Territoriality 39.Someone asks you to bring dip to a party and you agree. Later the person asks you to also bring popcorn, chips, and sodas. The person has used which compliance strategy? b) the low-ball technique c) the over-commitment strategy 41.The real danger of "groupthink" is that it b) is contagious c) occurs in cohesive groups 40. d) the whole-part technique e) the passive obedience method d) disrupts coordinated efforts at group problem solving e) leads to a suspension of critical thinking The organization of roles, patterns of communication, and power in a group defines the group's b) Status e) Norms c) Structure 45. d) Cohesiveness 46.Those roles which one attains voluntarily are called b) ascribed roles c) achieved roles d) positions e) social selves
7 Social traps can be dismantled by changing b) rewards and costs c) supply and demand d) compliance and assertiveness 49. e) the tendency toward groupthink 50.A learned disposition to respond to people, objects, or institutions in a positive or negative way defines b) cognitive dissonance e) stereotypes c) socialization 51. d) attitudes 52.In general, helping behavior in emergency situations is discouraged by the presence of a large number of persons b) low costs associated with helping c) smaller social distance between the helper and the victim d) fear of cognitive dissonance 53.When a person with little or no authority makes a direct request to another person, the situation involves b) Compliance e) Conformity c) Obedience 54. d) Coercion 55.The fact that physically attractive people also tend to be rated more highly on traits such as intelligence and honesty is an example of
8 b) social magnetism e) the halo effect c) role modeling 56. d) social comparisons 57.Negative attitudes that are tinged with fear, hatred, or suspicion is a definition of b) Prejudice e) Displaced aggression c) Authoritarianism 58. d) Discrimination 59.Interpersonal attraction is encouraged by which one of the following? b) personal space e) similarity c) proxemics 60. d) competition 61.Janis recommends ways to prevent groupthink, which include focusing on subjective evaluation and interpretation b) having the leader state personal preferences before discussion c) focusing on the decision, as opposed to the process d) encouraging someone to play devil's advocate 62.In an experiment in which a "student" simulated a seizure, helping was inhibited by b) conditions employing smaller groups c) diffusion of responsibility d) group discussion e) reference cognitive dissonance 63.
9 64.Sharing your own private thoughts and feelings is called b) self-talk e) introspection c) autonomy 65. d) self-disclosure 66.Which of the following was a significant factor in determining the degree of obedience in Milgram's series of experiments? the tone of voice used by the experimenter b) whether the experimenter was male or female c) amount of complaining, shouting, and crying by the learner d) the setting in which the experiment was conducted 67.You do not want a large, unattractive political sign in your yard. However, if you initially agree to put a small sign in your window, later you are more likely to allow the large sign in your yard. This course of events is described by the b) foot-in-the-face technique e) foot-in-the-door effect c) low-ball technique 68. d) door-in-the-face effect 69.In his classic studies of conformity, Asch demonstrated that size of the majority does not influence how many people will conform b) a majority of one produces about as much conformity as a majority of eight c) lack of unanimity greatly reduces the pressure to conform d) obedience to authority was determined by the authority's perceived referent power 70.Expected behavior patterns associated with particular social positions are called b) Roles c) Culture
10 d) Stereotypes 71. e) Mannerisms 72.As part of an experiment, two young women stroll down a busy sidewalk with their arms around each other. They get a variety of reactions from passersby, including disapproving looks and comments. These reactions demonstrate the existence of b) Norms e) achieved roles c) ascribed roles 73. d) group structures 74.How individuals are affected by the presence of others is the focus of study in the field of b) Sociology e) Sociobiology c) Social psychology 75. d) Experimental psychology 76.Groups reward members with and for comformity. b) unanimity; power e) approval; acceptance c) power; authority 77. d) legitimacy; power 78.Stanley Milgram's experiment in which a "teacher" gave shocks to a "learner" was designed to test the limits of b) expert power e) conformity to a majority c) coercive power 79. d) obedience 80.Milgram's shock study showed people to be surprisingly
11 b) Rebellious e) Obedient c) Intelligent 81. d) Sexist 82.A reference group is one with which a person has face-to-face contact b) any group in which one plays an active role or has membership c) any group outside one's social distance boundaries d) any group whose values and attitudes are seen as relevant to one's own 83.Studies of conformity indicate that people are more apt to be influenced by others if they are concerned about the approval of others b) have low needs for certainty and structure c) are in temporary rather than established groups d) are in very large groups 84.In-group bias is the Tendency to favor one's group and see this group as correct b) Tendency to see other members of a group as similar c) Tendency to perform worse when others are watching d) Tendency to conform to the social harmony of a group 85.People who are less likely to help someone because there are a lot of people present would be exhibiting: b) Groupthink e) Mere exposure effect c) Group polarization 86. d) Diffusion of responsibility 87.If you have a friend who is reluctant to help you clean your entire room, you maybe successful through asking him to simply help you move one item in your room. this approach is referred to as: b) Cognitive dissonance c) Altruism d) Foot-in-the-door Which of these is not a principle of great man theory? Leaders are born not made. b) Great men rise up in times of crisis c) We can learn from the biographies of great leaders e) Door-in-the-foot
12 d) A great leader is only great in certain situations 90.In leadership trait theory what is a trait? A list of the things that make leaders different to everyone else b) A list of the key things that a leader should do to be great c) The list of key behaviours a leader exhibits d) A list of key characteristics that makes a leader great 91.For the Ohio State leadership studies the perfect leader: Combines a focus on the task and the employee b) Focuses on the task and getting things done c) Inspires workers to aim higher and achieve more d) Is concerned about the small details and how to increase productivity 92.Contingency theory is based on the assumption that the ideal leader: Shapes their leadership style depending on the situation b) Provides clear instructions to the followers so that they know what they are doing c) Knows what their strengths are and makes the most out of them d) Spends time with their followers and therefore listens and responds to their needs 93.A transactional leader is one who: Inspires people and has strong interactions with them b) Does deals with people in order to get them to do things the leader wants c) Is the ideal form of leadership d) Works for long-term goals of the organization 94.What is a transformational leader? Someone who is involved in organizational change b) A leader, like Taylor, who provided new ways of carrying out management c) A leader who inspires the workers to new levels by offering them a vision of a better future d) leader who tries to transform their staff by giving them rewards for what they do 95.What is post-heroic leadership theory? A theory which states that there is too much emphasis on leaders and more attention should be placed on followers b) A theory looking beyond current leadership styles to new, more creative ways of leading c) A theory which tries to create new organizations which do not need leaders d) A theory which tries to find the ideal form of leadership 96.What is the social construction of leadership? The view that all leadership is social and what matters is how leaders interact with others b) Leadership is a made up idea that therefore we should pay more attention to more significant aspects of the organization c) What counts as good leadership is a construction of the perceptions of the followers d) Leadership is something that the leader constructs as they meet with others 97.What is the 'glass ceiling'? A barrier which prevents women from passing through to more senior positions in the company
13 b) An old fashioned idea that suggests that women should not make it to the boardroom in organizations c) The effect where men can pass by women in women dominated professions d) An approach which seeks to get more women in senior positions in organizations 98.Jimmy is very quiet at school, but later that night at a party Jimmy gets 'crazy' and starts to cut the rug on the dance floor. Jimmy's classmates are stunned at this displayed behavior. Jimmy is experiencing: b) Group polarization e) Groupthink c) The power of SSRI's 99. d) Deindividuation 100. set up an experiment, known as the Stanford Prison experiment, where people plaed the role of a prison guard. The goal was to observe if this authority position would cause them to act differently. b) Stanley Milgram c) Philip Zimbardo d) Soloman Ache e) MuzaferSherif 101. Social Facilitation occurs: To the tendency for people to do less in a group setting b) To the tendency to keep personal opinions to themselves for fear of upsetting the group c) When the presence of other people watching improves a person s performance d) When the presence of other people watching hinders a person's performance 102. Groupthink is defined as: When an attitude becomes stronger in group presence b) Thinking that revolves around keeping harmony within a group through not disagreeing with group opinion c) The tendency to do less in a group situation d) Improved performance when people are watching 103. In Stanley Migram's experiment on the role of obedience, the was the person who worked with Milgram and played the part of an authority figure. b) Teacher e) Doctor c) Learner 104. d) Experimenter 105. According to Soloman Ache, in his experiment on conformity % of the subjects gave the wrong answer because the group unanimously also gave the wrong answer. b) 76 c) 48 d) 32 e) In Stanley Milgram's experiment on the role of obedience, the was the subject who was being observed and did not know what the experiment was about or what was being studied.
14 b) Learner e) Milgram c) Experimenter 108. d) Teacher 109. is a change in behavior or belief as a result of group pressure. b) Cohesiveness c) Conformity d) Compliance 110. e) Obedience 111. Publicly acting in accord with social pressure while privately disagreeing is called b) Acceptance d) Reactance c) Compliance e) Interaction Both acting and believing in accord with social pressure is called b) Acceptance e) Interaction c) Reactance 114. d) Compliance 115. An important difference between Asch's experiment in which participants judged the length of lines and Sherif's experiment in which participants judged the movement of light was that Asch's participants were older than were Sherif's b) there was an obviously correct answer in judging the length of lines but that was not so in judging the movement of light c) Asch's participants made their judgments privately whereas Sherif's participants made their judgments publicly d) Asch's participants were all male whereas Sherif's participants were both male and female 116. In Asch's study of perceptual judgment involving the length of lines, naive participants conformed of the time to the false judgments of the confederates. b) 10 percent e) 92 percent c) 37 percent 117. d) 68 percent 118. Participants' tendencies to obey the experimenter's commands to shock a victim were highest when the experimenter was and the victim was. b) close; distant c) close; close d) distant; distant e) distant; close
15 To believe that Asch's compliant participants were particularly spineless people is to forget that behavior shapes belief b) overlook other personality characteristics that determine conformity c) make the fundamental attribution error d) ignore how the status of the experimenter shapes behavior 121. How social pressure may lead us to perform immoral acts is best illustrated by studies of b) psychological reactance e) informational influence c) spontaneous self-concept 122. d) obedience to authority 123. The effect of group size on conformity has been explained by theory. b) cognitive dissonance c) social norm d) psychological reactance 124. e) social impact 125. Milgram reported that a participant's tendency to obey the experimenter decreased dramatically when two other participants defied the experimenter b) when the participant could not hear the responses of the learner c) when the experimenter was a female d) when the experimenter was younger than the participant 126. Philip hates to attend concerts but goes because his wife wants to. After three years Philip comes to genuinely enjoy concerts. This is an example of a. how acceptance can lead to compliance b. how compliance can lead to acceptance c. the "boomerang effect" d. how psychological reactance can lead to acceptance 127. Commitment without intimacy or passion is b) Romantic love e) Consummate love c) Empty love 128. d) Non love 129. Decibel (db) is the unit of b) Temperature e) Density c) Noise d) Pressure 130. Depressive disorder connected to a specific season is b) Bipolar Disorder c) SAD
16 d) Mania 131. e) Hallucination 132. A person s domicile is an example of territory b) Primary e) None of the above c) Secondary 133. d) Tertiary 134. Waiting room is a kind of territory b) Primary e) None of the above c) Secondary 135. d) Tertiary 136. One s preferred chair in a class is b) Primary territory e) None of the above c) Secondary territory 137. d) Tertiary territory 138. Crowding is a: b) Psychological phenomena e) All of the above c) Subjective feeling 139. d) Potential source of stress 140. Everyone has the right to access is: b) Primary territory e) Both b & c c) Secondary territory 141. d) Tertiary territory 142. According to Hall, intimate distance is b) 6 18 inches e) feet c) feet 143. d) 4 12 feet 144. Personal distance is b) 6 18 inches e) feet c) feet d) 4 12 feet 145. Public distance can be b) 6 18 inches e) feet c) feet 146. d) 4 12 feet 147. A distance of is social distance b) 6 18 inches d) 4 12 feet c) feet e) feet
17 The highest level of physical distance is in b) Intimate relations e) Social relations c) Public relations 150. d) Personal relations 151. Personal space first defined by b) Hall e) Sheriff c) Sommer 152. d) Katz 153. Correct Sequence of prosocial behaviour Notice what is happening > Interpret the event as an emergency > Experience feelings of responsibility > Believe that they have the skills to help > Make a conscious choice to offer assistance b) Interpret the event as an emergency >Notice what is happening >Experience feelings of responsibility > Believe that they have the skills to help > Make a conscious choice to offer assistance c) Believe that they have the skills to help > Experience feelings of responsibility > Notice what is happening > Interpret the event as an emergency > Make a conscious choice to offer assistance d) Experience feelings of responsibility > Believe that they have the skills to help > Notice what is happening > Interpret the event as an emergency > Make a conscious choice to offer assistance 154. Unselfish concern for other people is b) Prosocial behaviour c) Bystander effect d) Altruism The Negative Affect Escape Model explained by b) Baron c) Baron & Bell d) Bell e) None of the above 157. Negative Affect Escape Model links to: b) Inverted S hypothesis c) Inverted U hypothesis d) Parabola 159. Population is effected by b) Birth & death c) immigration d) emigration e) Volunteering e) S curve 161. Technical term used for the study of human population e) all of the above
18 b) Biography e) Census c) Demography 162. d) Bibliography 163. Kin selection is an evolutionary theory that explains of Altruism b) Biological reasons e) Social norms c) Neurological reasons 164. d) Cognitive reasons 165. Emergency observed -> Empathy aroused -> Help provided to the victim as it gave good feeling to the helper is; b) Negative state relief model c) Genetic determinism model 166. Who is more likely to help? b) A person with a handicap c) A person with an altruistic personality ANSWER KEY d) Empathy-altruism hypothesis e) Empathy-joy hypothesis d) A stranger to the victim e) A person in a crowd of strangers No Answer No Answe r No Answe r No Answer 1 A 26 B 51 D 76 A 2 B 27 A 52 D 77 B 3 C 28 C 53 A 78 B 4 C 29 A 54 A 79 B 5 D 30 A 55 B 80 B 6 A 31 D 56 C 81 A 7 D 32 A 57 A 82 C 8 D 33 D 58 C 83 B 9 D 34 D 59 A 84 D 10 D 35 B 60 C 85 C 11 B 36 C 61 B 86 A 12 D 37 D 62 C 87 B 13 B 38 D 63 B 88 D
19 14 D 39 C 64 C 89 C 15 D 40 A 65 A 90 B 16 A 41 A 66 C 91 C 17 B 42 B 67 B 92 A 18 C 43 D 68 B 93 C 19 B 44 C 69 A 94 B 20 B 45 D 70 B 95 B 21 A 46 D 71 B 96 D 22 C 47 A 72 A 97 B 23 A 48 A 73 C 98 A 24 D 49 C 74 C 99 C 25 B 50 C 75 D 10 0 B Prepared By: Sri. Vishnu Sidharthan T, Research Scholar, Dept. of Psychology, University of Calicut
CHAPTER 15. Social Psychology. Lecture Overview. Introductory Definition PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY. Social Cognition.
 Social Psychology CHAPTER 15 Social Cognition Lecture Overview Social Influence Social Relations Applying Social Psychology to Social Problems Introductory Definition Social Psychology: scientific study
Social Psychology CHAPTER 15 Social Cognition Lecture Overview Social Influence Social Relations Applying Social Psychology to Social Problems Introductory Definition Social Psychology: scientific study
Social Psychology Terms and Vocabulary. How one tends to act toward the object of an attitude.
 Psychology Terms and Vocabulary Action component Actor observer bias Attitude Attitude scale Attribution Autokinetic effect Belief component Brainwashing Coercion How one tends to act toward the object
Psychology Terms and Vocabulary Action component Actor observer bias Attitude Attitude scale Attribution Autokinetic effect Belief component Brainwashing Coercion How one tends to act toward the object
Chapter 13. Social Psychology
 Social Psychology Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Social Psychology Interpreting the Behavior of Others Behaving in the Presence of Others Establishing Relations With Others Social
Social Psychology Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Social Psychology Interpreting the Behavior of Others Behaving in the Presence of Others Establishing Relations With Others Social
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY. Social Influences on the Self. Self Concept. How do we see ourselves? How do we see others?
 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY Social Cognition and Influence (how we think about ourselves) Social Influences on the Self How do we see ourselves? How do we see others? How do we compare ourselves with others? Self
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY Social Cognition and Influence (how we think about ourselves) Social Influences on the Self How do we see ourselves? How do we see others? How do we compare ourselves with others? Self
Review Sheet Social Psych (8-10%)
 Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet Social Psych (8-10%) 1) social psychology Social Thinking 1) attribution theory 2) fundamental attribution error 3) foot-in-the-door
Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet Social Psych (8-10%) 1) social psychology Social Thinking 1) attribution theory 2) fundamental attribution error 3) foot-in-the-door
Chapter 14. Social Psychology. How Does the Social Situation Affect our Behavior? Social Psychology
 Chapter 14 Social Psychology This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: Any public performance or display, including transmission of
Chapter 14 Social Psychology This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: Any public performance or display, including transmission of
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 16: Social Psychology. 4. What cultures do not make the fundamental attribution error as much?
 Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 16: Social Psychology Attribution, Attitudes, and Actions (pg. 673-679) 1. Social Psychologists: 2. Attribution Theory (Fritz Heider): 3. Fundamental Attribution Error:
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 16: Social Psychology Attribution, Attitudes, and Actions (pg. 673-679) 1. Social Psychologists: 2. Attribution Theory (Fritz Heider): 3. Fundamental Attribution Error:
Social Psychology. Social Thinking Social Influence Social Relations.
 Social Psychology Social Thinking Social Influence Social Relations http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Social Thinking Social Psychology scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to
Social Psychology Social Thinking Social Influence Social Relations http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Social Thinking Social Psychology scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to
Conformity ASCH S STUDY 12/8/2010 ASCH S STUDY. Social Psychology (581, ) Others Focus on Social Influences on Our Behavior
 Social Psychology (581, 592-598) Study of how people behave, think, and feel in social situations Relatively recent addition to psychology Research influenced by current social problems Researchers in
Social Psychology (581, 592-598) Study of how people behave, think, and feel in social situations Relatively recent addition to psychology Research influenced by current social problems Researchers in
Factors that affect interpersonal attraction:
 Introduction: You are a member of a social world on a planet containing about 7 billion people. Our behaviors differ in different settings (like if we are in the college, market, or at home). Human behavior
Introduction: You are a member of a social world on a planet containing about 7 billion people. Our behaviors differ in different settings (like if we are in the college, market, or at home). Human behavior
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY SOCIAL INFLUENCE TYPES OF NORMS. Chapter 18
 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 18 SOCIAL INFLUENCE Social Norms- learned, socially-based rules of behavior Generally they create orderly social behavior TYPES OF NORMS Injunctive Norms Shows what actions are
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 18 SOCIAL INFLUENCE Social Norms- learned, socially-based rules of behavior Generally they create orderly social behavior TYPES OF NORMS Injunctive Norms Shows what actions are
AP Psychology Guided Reading Chapter 16 Social Psychology
 Name: Period: AP Psychology Guided Reading Chapter 16 Social Psychology Social Thinking 1. Define social psychology: 2. Define attribution theory. How does dispositional attribution differ from situational
Name: Period: AP Psychology Guided Reading Chapter 16 Social Psychology Social Thinking 1. Define social psychology: 2. Define attribution theory. How does dispositional attribution differ from situational
Are they formed through education or is it just part of being a human being?
 Social Behavior ~ Social Psychology Altruism; Conformity; Obedience; Compliance Are they formed through education or is it just part of being a human being? YouTube: Referee Helps Girl Finish Anthem YouTube:
Social Behavior ~ Social Psychology Altruism; Conformity; Obedience; Compliance Are they formed through education or is it just part of being a human being? YouTube: Referee Helps Girl Finish Anthem YouTube:
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 12 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 12 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY PowerPoint Image Slideshow Social Psychology? What s that? The scientific study of how one s behavior, thoughts or feelings are influenced by the situation, or the
PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 12 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY PowerPoint Image Slideshow Social Psychology? What s that? The scientific study of how one s behavior, thoughts or feelings are influenced by the situation, or the
Psychology chapter 16 Test Notes Social Psychology Altruistic Behavior - helping behavior that is not linked to personal gain; recognition and reward
 Psychology chapter 16 Test Notes Social Psychology Altruistic Behavior - helping behavior that is not linked to personal gain; recognition and reward are not expected Attitude - relatively stable organization
Psychology chapter 16 Test Notes Social Psychology Altruistic Behavior - helping behavior that is not linked to personal gain; recognition and reward are not expected Attitude - relatively stable organization
Introduction to Psychology Social Psychology Quiz
 MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. We usually adapt our behavior to the demands of the social situation, and in ambiguous situations: A) We take our cues from the behavior of others. B) We will do the same thing that
MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. We usually adapt our behavior to the demands of the social situation, and in ambiguous situations: A) We take our cues from the behavior of others. B) We will do the same thing that
attitude the theory that we explain someone's behavior by crediting the situation or the person's disposition attribution theory
 attitude feelings, often influenced by our beliefs, that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events attribution theory the theory that we explain someone's behavior by
attitude feelings, often influenced by our beliefs, that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events attribution theory the theory that we explain someone's behavior by
Defining Social Psychology. informal definition: the study of how people think about, influence, and relate to other people
 Social Psychology Defining Social Psychology informal definition: the study of how people think about, influence, and relate to other people formal definition: the study of how a person s thoughts, feelings,
Social Psychology Defining Social Psychology informal definition: the study of how people think about, influence, and relate to other people formal definition: the study of how a person s thoughts, feelings,
Chapter 15 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions PERSON PERCEPTION: FORMING IMPRESSIONS OF OTHERS
 Chapter 15 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions PERSON PERCEPTION: FORMING IMPRESSIONS OF OTHERS #1) Explain how schemas, stereotypes, and other factors contribute to subjectivity in person perception
Chapter 15 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions PERSON PERCEPTION: FORMING IMPRESSIONS OF OTHERS #1) Explain how schemas, stereotypes, and other factors contribute to subjectivity in person perception
PSYC 210 Social Psychology
 South Central College PSYC 210 Social Psychology Course Information Description Total Credits 4.00 Pre/Corequisites PSYC100 or consent of instructor. Course Competencies Social Psychology introduces the
South Central College PSYC 210 Social Psychology Course Information Description Total Credits 4.00 Pre/Corequisites PSYC100 or consent of instructor. Course Competencies Social Psychology introduces the
-Attitude- Abdullah Nimer
 -Attitude- Abdullah Nimer Attitude refers to evaluation of things. The things can be concrete objects like cars or ideas like Marxism. Attitudes have: an affective component a cognitive component a behavioral
-Attitude- Abdullah Nimer Attitude refers to evaluation of things. The things can be concrete objects like cars or ideas like Marxism. Attitudes have: an affective component a cognitive component a behavioral
10 Norms and behavior. What s it about?
 10 Norms and behavior What s it about? (Social Psychology pp. 351 395) Norms are effective guides for social behavior. Norms must be activated before they can guide behavior. When individuals are in a
10 Norms and behavior What s it about? (Social Psychology pp. 351 395) Norms are effective guides for social behavior. Norms must be activated before they can guide behavior. When individuals are in a
Name: Period: Score /95. Unit 14 Study Assignment Social Psychology. 1. Social behavior arises from our social. 2. Who proposed attribution theory?
 Name: Period: Score /95 Unit 14 Study Assignment Social Psychology 1. Social behavior arises from our social. 2. Who proposed attribution theory? 3. Create an example of the fundamental attribution error.
Name: Period: Score /95 Unit 14 Study Assignment Social Psychology 1. Social behavior arises from our social. 2. Who proposed attribution theory? 3. Create an example of the fundamental attribution error.
What is Social Psychology
 The Social World What is Social Psychology An attempt to understand and explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behavior of individuals are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others
The Social World What is Social Psychology An attempt to understand and explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behavior of individuals are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others
CHAPTER 16 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY OBEDIENCE ATTITUDES & ATTITUDE CHANGE GROUP INFLUENCES PREJUDICE AGGRESSION ATTRACTION ALTRUISM
 CHAPTER 16 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY OBEDIENCE ATTITUDES & ATTITUDE CHANGE GROUP INFLUENCES PREJUDICE AGGRESSION ATTRACTION ALTRUISM ~ Professor Fazakas-deHoog lfazakas@uwo.ca AFFECT (Feelings) BEHAVIOR (Actions
CHAPTER 16 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY OBEDIENCE ATTITUDES & ATTITUDE CHANGE GROUP INFLUENCES PREJUDICE AGGRESSION ATTRACTION ALTRUISM ~ Professor Fazakas-deHoog lfazakas@uwo.ca AFFECT (Feelings) BEHAVIOR (Actions
What is Social Cognition?
 Social Cognition What is Social Cognition? Social Psychology scientific study of how people s thoughts, feelings, and actions are influenced by social environment Cognitive Psychology scientific study
Social Cognition What is Social Cognition? Social Psychology scientific study of how people s thoughts, feelings, and actions are influenced by social environment Cognitive Psychology scientific study
8 Diffusion of Responsibility
 Ruggerio Chapter : The Basic Problem: Mine is Better Aronson & Tavris Book- Chapter 1 & Self- Justification Norms Rules that regulate human life, including social conventions, explicit laws, and implicit
Ruggerio Chapter : The Basic Problem: Mine is Better Aronson & Tavris Book- Chapter 1 & Self- Justification Norms Rules that regulate human life, including social conventions, explicit laws, and implicit
Social Psychology. An Overview By Halford Fairchild September 3, 2013
 Social Psychology An Overview By Halford Fairchild September 3, 2013 Areas of interest Social influence - real or imagined presence of others Social cognition - how we think about social situations Attitudes
Social Psychology An Overview By Halford Fairchild September 3, 2013 Areas of interest Social influence - real or imagined presence of others Social cognition - how we think about social situations Attitudes
I DON T WANT TO BE CONFUSED! Social Psych topics that could be easily mixed up!
 I DON T WANT TO BE CONFUSED! Social Psych topics that could be easily mixed up! Groupthink vs. Group Polarization Both are effects the larger group has on an individual s behavior within that group Groupthink
I DON T WANT TO BE CONFUSED! Social Psych topics that could be easily mixed up! Groupthink vs. Group Polarization Both are effects the larger group has on an individual s behavior within that group Groupthink
CHAPTER 16 - SOCIAL BEHAVIOR - EXAM
 CHAPTER 16 - SOCIAL BEHAVIOR - EXAM Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Jill assumes her new biology professor is probably studious
CHAPTER 16 - SOCIAL BEHAVIOR - EXAM Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Jill assumes her new biology professor is probably studious
Social Psychology. Social Psychology
 Term Explanation Application/Example/Extension Social psychology is the study of how people think, act, are influenced, and relate to one another in social situations Implicit personality theory- quick
Term Explanation Application/Example/Extension Social psychology is the study of how people think, act, are influenced, and relate to one another in social situations Implicit personality theory- quick
FARMINGDALE STATE COLLEGE DATE: FALL 2017
 FARMINGDALE STATE COLLEGE DEPARTMENT: PSYCHOLOGY PREPARED BY: PSYCHOLOGY DEPT. DATE: FALL 2017 COURSE TITLE: Social Psychology COURSE CODE: PSY 234 CREDITS: 3 CONTACT HOURS: 45 CATALOG DESCRIPTION: This
FARMINGDALE STATE COLLEGE DEPARTMENT: PSYCHOLOGY PREPARED BY: PSYCHOLOGY DEPT. DATE: FALL 2017 COURSE TITLE: Social Psychology COURSE CODE: PSY 234 CREDITS: 3 CONTACT HOURS: 45 CATALOG DESCRIPTION: This
Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience
 Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience Objectives 1) knowledge about various forms of social influence, such as social facilitation, social loafing, conformity, compliance, and obedience. 2) An
Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience Objectives 1) knowledge about various forms of social influence, such as social facilitation, social loafing, conformity, compliance, and obedience. 2) An
Estimated Distribution of Items for the Exams
 Estimated Distribution of Items for the Exams The current plan is that there are 5 exams with 50 multiple choice items that will cover two chapters. Each chapter is planned to have 25 multiple choice items.
Estimated Distribution of Items for the Exams The current plan is that there are 5 exams with 50 multiple choice items that will cover two chapters. Each chapter is planned to have 25 multiple choice items.
Psychology study guide Chapter 14
 Psychology study guide Chapter 14 Attribution Attribution a conclusion about the cause of an observed behavior / event Attribution theory we explain other s behaviors with two types of attributions Situational
Psychology study guide Chapter 14 Attribution Attribution a conclusion about the cause of an observed behavior / event Attribution theory we explain other s behaviors with two types of attributions Situational
Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience
 Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience Objectives 1) knowledge about various forms of social influence, such as social facilitation, social loafing, conformity, compliance, and obedience. 2) An
Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience Objectives 1) knowledge about various forms of social influence, such as social facilitation, social loafing, conformity, compliance, and obedience. 2) An
Defining Psychology Behaviorism: Social Psychology: Milgram s Obedience Studies Bystander Non-intervention Cognitive Psychology:
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Defining Psychology Behaviorism: The scientific study of how rewards and punishment in the environment affect human and non-human behavior Empirical approach: vary contingencies of
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Defining Psychology Behaviorism: The scientific study of how rewards and punishment in the environment affect human and non-human behavior Empirical approach: vary contingencies of
Cambridge Public Schools SEL Benchmarks K-12
 Cambridge Public Schools SEL Benchmarks K-12 OVERVIEW SEL Competencies Goal I: Develop selfawareness Goal II: Develop and Goal III: Develop social Goal IV: Demonstrate Goal V: Demonstrate skills to demonstrate
Cambridge Public Schools SEL Benchmarks K-12 OVERVIEW SEL Competencies Goal I: Develop selfawareness Goal II: Develop and Goal III: Develop social Goal IV: Demonstrate Goal V: Demonstrate skills to demonstrate
Unit 5: Individual and. Group Behaviour
 Group Behaviour Unit 5: Individual and Group Behaviour What are groups? Groups are collections of people who have shared goals, a degree of interdependence, and some amount of communication. Groups serve
Group Behaviour Unit 5: Individual and Group Behaviour What are groups? Groups are collections of people who have shared goals, a degree of interdependence, and some amount of communication. Groups serve
Conformity Asch study (1951) Which of the lines below is the same as the line to the right?
 a change in a belief or behavior with the intent to follow a perceived social norm May lead to positive or negative behaviors E.g., conforming to a norm of volunteering versus conforming to a norm of cheating
a change in a belief or behavior with the intent to follow a perceived social norm May lead to positive or negative behaviors E.g., conforming to a norm of volunteering versus conforming to a norm of cheating
Social Psychology. Studying the way people relate to others. Attitude. Group Behavior. Attraction Aggression
 Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Studying the way people relate to others. Attitudes A set of beliefs and feelings. Attitudes predispose our reactions to people, issues,
Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Studying the way people relate to others. Attitudes A set of beliefs and feelings. Attitudes predispose our reactions to people, issues,
Social Biases and Pressures. Critical Thinking
 Social Biases and Pressures Critical Thinking Humans are Social Animals We are very sensitive to what others do and think. Most of our deep-rooted beliefs and values come from family and society we grow
Social Biases and Pressures Critical Thinking Humans are Social Animals We are very sensitive to what others do and think. Most of our deep-rooted beliefs and values come from family and society we grow
Note:- Receptors are the person who receives any images from outer environment.
 Concept According to Oxford Advanced Learner s Dictionary, Perception means the way you notice things especially with the senses. Perception is the process of organizing and attempting to understand the
Concept According to Oxford Advanced Learner s Dictionary, Perception means the way you notice things especially with the senses. Perception is the process of organizing and attempting to understand the
Conformity & Obedience
 Higher Psychology Conformity & Obedience Exam Revision 1 This is the mandatory topic in the Social Behaviour unit. This means it will probably come up in the exam. What to revise: - Types of conformity
Higher Psychology Conformity & Obedience Exam Revision 1 This is the mandatory topic in the Social Behaviour unit. This means it will probably come up in the exam. What to revise: - Types of conformity
AQA A-level Psychology Unit 1 (7182/1) SOCIAL INFLUENCE. Questions + Answers SAMPLE MATERIAL
 AQA A-level Psychology Unit 1 (7182/1) SOCIAL INFLUENCE Questions + Answers SAMPLE MATERIAL Copyright 2017, StudyLogic. All rights reserved. UNIQUE PRODUCT IDENTIFIER: DOCUMENT #4534478 SOCIAL INFLUENCE
AQA A-level Psychology Unit 1 (7182/1) SOCIAL INFLUENCE Questions + Answers SAMPLE MATERIAL Copyright 2017, StudyLogic. All rights reserved. UNIQUE PRODUCT IDENTIFIER: DOCUMENT #4534478 SOCIAL INFLUENCE
Social Psychology 10 (14)
 Social Psychology 10 (14) KEY TERMS Attitude False-consensus effect Pluralistic ignorance Mere exposure effect Self-serving bias Attraction research Central versus peripheral Just-world bias Social facilitation
Social Psychology 10 (14) KEY TERMS Attitude False-consensus effect Pluralistic ignorance Mere exposure effect Self-serving bias Attraction research Central versus peripheral Just-world bias Social facilitation
Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being
 Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being expressed by others. The task in Asch s studies involved judging
Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being expressed by others. The task in Asch s studies involved judging
Social Psychology. What We Will Cover in This Section. Roles. PDF Created with deskpdf PDF Writer - Trial ::
 Social Psychology Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney What We Will Cover in This Section Conformity Attitudes Group Behavior Prejudice Roles Socially defined expectations that we expect individuals to fulfill in a given
Social Psychology Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney What We Will Cover in This Section Conformity Attitudes Group Behavior Prejudice Roles Socially defined expectations that we expect individuals to fulfill in a given
Interpersonal Communication in a Changing World: Culture and Social Networking 28
 Brief Contents PREFACE xix PART ONE: FOUNDATIONS OF INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION CHAPTER 1: Interpersonal Process 1 CHAPTER 2: Interpersonal Communication in a Changing World: Culture and Social Networking
Brief Contents PREFACE xix PART ONE: FOUNDATIONS OF INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION CHAPTER 1: Interpersonal Process 1 CHAPTER 2: Interpersonal Communication in a Changing World: Culture and Social Networking
Being liked. Attraction. Research results. Reward theory. Includes a wide range of situations:
 Attraction Includes a wide range of situations: People we find appealing to work with People we enjoy hanging out with Friends Serious love attachments Being liked Americans are deeply concerned about
Attraction Includes a wide range of situations: People we find appealing to work with People we enjoy hanging out with Friends Serious love attachments Being liked Americans are deeply concerned about
PERSON PERCEPTION AND INTERPERSONAL ATTRACTION
 Person Perception and Interpersonal Attraction MODULE-V 22 PERSON PERCEPTION AND INTERPERSONAL ATTRACTION We have already noted, achieving a sense of self is an important achievement. A neonate may not
Person Perception and Interpersonal Attraction MODULE-V 22 PERSON PERCEPTION AND INTERPERSONAL ATTRACTION We have already noted, achieving a sense of self is an important achievement. A neonate may not
SOCIAL INFLUENCE: OBEDIENCE. Attitudes beliefs tinged with emotion cognitive dissonance
 Term Test 4 Thursday March 9 in class, 12:00-1:50 40 multiple choice questions 10% of course grade Topics covered class material: Feb 7 - Mar 2 assigned readings: see lectures web page Language and Nonverbal
Term Test 4 Thursday March 9 in class, 12:00-1:50 40 multiple choice questions 10% of course grade Topics covered class material: Feb 7 - Mar 2 assigned readings: see lectures web page Language and Nonverbal
Milgram Experiment. Harlow s Attachment Studies
 Milgram Experiment Hypothesis: that humans obey other people who are in a position of authority. Obedience Design: a shock generator that the teacher would use to shock the learner in the study if the
Milgram Experiment Hypothesis: that humans obey other people who are in a position of authority. Obedience Design: a shock generator that the teacher would use to shock the learner in the study if the
A B C. Copyright Allyn and Bacon 2005
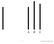 A B C 1 A B C 2 A B C 3 A B C 4 Asch, 1951 How many of you own something from one of these companies? 5 Fads 6 Lecture 10 Social Influence 7 Social Influence Have you ever: Asked a friend what was appropriate
A B C 1 A B C 2 A B C 3 A B C 4 Asch, 1951 How many of you own something from one of these companies? 5 Fads 6 Lecture 10 Social Influence 7 Social Influence Have you ever: Asked a friend what was appropriate
Psychology Ciccarelli and White
 1 Psychology Ciccarelli and White C H A P T E R 12: S O C I A L P S Y C H O L O G Y What is social psychology? It is the scientific study of how the individual functions as a result of being a part of
1 Psychology Ciccarelli and White C H A P T E R 12: S O C I A L P S Y C H O L O G Y What is social psychology? It is the scientific study of how the individual functions as a result of being a part of
Ronald B. Adler, Lawrence B. Rosenfeld, Russell F. Proctor II Interplay : the process of interpersonal communication
 Ronald B. Adler, Lawrence B. Rosenfeld, Russell F. Proctor II Interplay : the process of interpersonal communication Brief Contents PREFACE PART ONE: FOUNDATIONS OF INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION CHAPTER
Ronald B. Adler, Lawrence B. Rosenfeld, Russell F. Proctor II Interplay : the process of interpersonal communication Brief Contents PREFACE PART ONE: FOUNDATIONS OF INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION CHAPTER
Assertive Communication
 Assertive Communication Listed below are some of the key features of the three main communication styles: Passive Aggressive Assertive Apologetic You statements I statements Overly soft or tentative voice
Assertive Communication Listed below are some of the key features of the three main communication styles: Passive Aggressive Assertive Apologetic You statements I statements Overly soft or tentative voice
CHAPTER 16 Social Psychology
 CHAPTER 16 Social Psychology INTRODUCTION Please watch this short clip: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bohgujn2gk8 How do you describe the driver s behavior? What if the adjacent white car or red car belonged
CHAPTER 16 Social Psychology INTRODUCTION Please watch this short clip: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bohgujn2gk8 How do you describe the driver s behavior? What if the adjacent white car or red car belonged
Values. A principle, standard, or quality considered worthwhile or desirable
 Values A principle, standard, or quality considered worthwhile or desirable What s more important to you: Alaska s environment or money you could save if we drilled for oil there? Values indicate what
Values A principle, standard, or quality considered worthwhile or desirable What s more important to you: Alaska s environment or money you could save if we drilled for oil there? Values indicate what
Introduction to Social Psychology p. 1 Introduction p. 2 What Is Social Psychology? p. 3 A Formal Definition p. 3 Core Concerns of Social Psychology
 Preface p. xv Introduction to Social Psychology p. 1 Introduction p. 2 What Is Social Psychology? p. 3 A Formal Definition p. 3 Core Concerns of Social Psychology p. 3 Sociology, Psychology, or Both? p.
Preface p. xv Introduction to Social Psychology p. 1 Introduction p. 2 What Is Social Psychology? p. 3 A Formal Definition p. 3 Core Concerns of Social Psychology p. 3 Sociology, Psychology, or Both? p.
Social Cognition and Social Perception
 Social Cognition and Social Perception Gathered & Prepared By: Maha Wasfi Mobasher Professor of Psychiatry-Faculty of Medicine Cairo University December-2011 www.mahawmobasher.com Social Psychology -Introduction:
Social Cognition and Social Perception Gathered & Prepared By: Maha Wasfi Mobasher Professor of Psychiatry-Faculty of Medicine Cairo University December-2011 www.mahawmobasher.com Social Psychology -Introduction:
TRACOM Sneak Peek Excerpts from. Self-Perception Guide
 TRACOM Sneak Peek Excerpts from Self-Perception Guide Self-perception GUIDE Table of Contents Introduction...1 The SOCIAL STYLE MODEL TM............................................. 1 Where Did Your Style
TRACOM Sneak Peek Excerpts from Self-Perception Guide Self-perception GUIDE Table of Contents Introduction...1 The SOCIAL STYLE MODEL TM............................................. 1 Where Did Your Style
4/30 Lecture 23 Social psychology: Practice Question. PSYC 120 General Psychology. Social Psychology: Social Cognition Social Behavior
 4/30 Lecture 23 Social psychology: PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 23: Social Psychology 2 Social Psychology: Social Cognition Social Behavior Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office
4/30 Lecture 23 Social psychology: PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 23: Social Psychology 2 Social Psychology: Social Cognition Social Behavior Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office
Improving Personal Effectiveness With Versatility
 CONCEPTS GUIDE TRACOM Sneak Peek Excerpts from Improving Personal Effectiveness With Versatility Concepts Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Introduction...1 The SOCIAL STYLE MODEL TM...1 Where Did Your Style
CONCEPTS GUIDE TRACOM Sneak Peek Excerpts from Improving Personal Effectiveness With Versatility Concepts Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Introduction...1 The SOCIAL STYLE MODEL TM...1 Where Did Your Style
What is Social Psychology
 What is Social Psychology Social psychology is a scientific concept that seeks to explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of individuals are influenced by the presence of others, or lack of others.
What is Social Psychology Social psychology is a scientific concept that seeks to explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of individuals are influenced by the presence of others, or lack of others.
Social Influence. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Social Psychology. Module 56. Social influence
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Social Influence Module 56 2 Social Psychology Social influence Conformity
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Social Influence Module 56 2 Social Psychology Social influence Conformity
c) Potential sources of error in social cognition A Basic Tilt in Social Thought, Situation-Specific Sources of Error in Social Cognition
 ANNEXURE-II Syllabi for Psychology Core Courses (Major Elective) at the S.Y.B.A. Forthe academic year 2017-2018 Code Semester Course Title Credits Marks UAPSY301 1 Social Psychology: Part I 3 100 ( 75
ANNEXURE-II Syllabi for Psychology Core Courses (Major Elective) at the S.Y.B.A. Forthe academic year 2017-2018 Code Semester Course Title Credits Marks UAPSY301 1 Social Psychology: Part I 3 100 ( 75
Chapter 3 Perceiving Ourselves and Others in Organizations
 Chapter 3 Perceiving Ourselves and Others in Organizations Changing Perceptions at Camp FFIT - Camp FFIT is part of the Ottawa Fire Service s campaign to recruit more female firefighters - Aligning their
Chapter 3 Perceiving Ourselves and Others in Organizations Changing Perceptions at Camp FFIT - Camp FFIT is part of the Ottawa Fire Service s campaign to recruit more female firefighters - Aligning their
Social Psychology CHAPTER 14 CHAPTER OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 14 Social Psychology CHAPTER OUTLINE Social psychology is the scientific study of how people s thoughts and feelings influence their behavior toward others and how the behavior of others influences
CHAPTER 14 Social Psychology CHAPTER OUTLINE Social psychology is the scientific study of how people s thoughts and feelings influence their behavior toward others and how the behavior of others influences
TTI Personal Talent Skills Inventory Coaching Report
 TTI Personal Talent Skills Inventory Coaching Report "He who knows others is learned. He who knows himself is wise." Lao Tse Mason Roberts District Manager YMCA 8-1-2008 Copyright 2003-2008. Performance
TTI Personal Talent Skills Inventory Coaching Report "He who knows others is learned. He who knows himself is wise." Lao Tse Mason Roberts District Manager YMCA 8-1-2008 Copyright 2003-2008. Performance
INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIPS (IR)
 Discussion Questions The concept of IR INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIPS (IR) 1. Define interpersonal relationship. 2. List types of interpersonal relationship. 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of
Discussion Questions The concept of IR INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIPS (IR) 1. Define interpersonal relationship. 2. List types of interpersonal relationship. 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of
PROSOCIAL BEHAVIOR. What is Prosocial Behavior? Prosocial Behavior is voluntary behavior that is carried out to benefit another person
 PROSOCIAL BEHAVIOR 1 What is Prosocial Behavior? Prosocial Behavior is voluntary behavior that is carried out to benefit another person 2 There are 2 basic forms of helping 1. Egoistic helping A form of
PROSOCIAL BEHAVIOR 1 What is Prosocial Behavior? Prosocial Behavior is voluntary behavior that is carried out to benefit another person 2 There are 2 basic forms of helping 1. Egoistic helping A form of
Ms. Berdelle AP Psychology UNIT 2 EXAM: SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY
 UNIT 2 EXAM: SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY 1. Which of the following is considered an explanation of why bystander intervention is less likely to occur if there is a large number of witnesses to a crime? a. prejudice
UNIT 2 EXAM: SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY 1. Which of the following is considered an explanation of why bystander intervention is less likely to occur if there is a large number of witnesses to a crime? a. prejudice
Lesson 12. Understanding and Managing Individual Behavior
 Lesson 12 Understanding and Managing Individual Behavior Learning Objectives 1. Identify the focus and goals of individual behavior within organizations. 2. Explain the role that attitudes play in job
Lesson 12 Understanding and Managing Individual Behavior Learning Objectives 1. Identify the focus and goals of individual behavior within organizations. 2. Explain the role that attitudes play in job
43. Can subliminal messages affect behavior? o Subliminal messages have NO effect on behavior - but people perceive that their behavior changed.
 34. How does the idea of mindlessness relate to persuasion? What is the Elaboration Likelihood Model? What are two routes of the ELM? What is the differences between the two routes? Many decisions are
34. How does the idea of mindlessness relate to persuasion? What is the Elaboration Likelihood Model? What are two routes of the ELM? What is the differences between the two routes? Many decisions are
Groups in Organizations. Overview of topics
 Groups in Organizations Overview of topics 1 Plan of today s lecture Groups general aspects Links with individual behavior Cohesion & conformity Decision making in groups 2 Characteristics of Groups Groups
Groups in Organizations Overview of topics 1 Plan of today s lecture Groups general aspects Links with individual behavior Cohesion & conformity Decision making in groups 2 Characteristics of Groups Groups
AP Psych Unit 14 REVIEW
 Name: Date: 1. Research on physical attractiveness indicates that men are more likely than women to A) be attracted to dating partners whose hips are narrower than their waists. B) judge members of the
Name: Date: 1. Research on physical attractiveness indicates that men are more likely than women to A) be attracted to dating partners whose hips are narrower than their waists. B) judge members of the
Introduction to Social Psychology
 Introduction to Social Psychology Instructor: Edward (Ed) Royzman, Ph.D Time and place: T-TH, 5:30 9:30 pm, B-35, Psych Lab Building. e-mail: royzman@psych.upenn.edu edwardroyzman@yahoo.com tele: 917 292
Introduction to Social Psychology Instructor: Edward (Ed) Royzman, Ph.D Time and place: T-TH, 5:30 9:30 pm, B-35, Psych Lab Building. e-mail: royzman@psych.upenn.edu edwardroyzman@yahoo.com tele: 917 292
COACH WORKPLACE REPORT. Jane Doe. Sample Report July 18, Copyright 2011 Multi-Health Systems Inc. All rights reserved.
 COACH WORKPLACE REPORT Jane Doe Sample Report July 8, 0 Copyright 0 Multi-Health Systems Inc. All rights reserved. Response Style Explained Indicates the need for further examination possible validity
COACH WORKPLACE REPORT Jane Doe Sample Report July 8, 0 Copyright 0 Multi-Health Systems Inc. All rights reserved. Response Style Explained Indicates the need for further examination possible validity
8/17/2012. Self-Concept Video. Cultural Differences in Defining the Self. Chapter 5. The Self: Understanding Ourselves in a Social Context
 Chapter 5 The Self: Understanding Ourselves in a Social Context Slides prepared by JoNell Strough, Ph.D. & Philip Lemaster, M.A. West Virginia University Self-Concept Video Click on the screenshot and
Chapter 5 The Self: Understanding Ourselves in a Social Context Slides prepared by JoNell Strough, Ph.D. & Philip Lemaster, M.A. West Virginia University Self-Concept Video Click on the screenshot and
Introducing Social Psychology
 Introducing Social Psychology Colin Fraser and Brendan Burchell Dale Hay and Gerard Duveen Polity Contents List of Contributors xix Preface xxi Acknowledgements xxiii I A Brief I SodaHmJivMual 2 Personality
Introducing Social Psychology Colin Fraser and Brendan Burchell Dale Hay and Gerard Duveen Polity Contents List of Contributors xix Preface xxi Acknowledgements xxiii I A Brief I SodaHmJivMual 2 Personality
The Power of Feedback
 The Power of Feedback 35 Principles for Turning Feedback from Others into Personal and Professional Change By Joseph R. Folkman The Big Idea The process of review and feedback is common in most organizations.
The Power of Feedback 35 Principles for Turning Feedback from Others into Personal and Professional Change By Joseph R. Folkman The Big Idea The process of review and feedback is common in most organizations.
Ones Way of Thinking. Every day, people make decisions that determine where the next step we take in life will
 Guerrero 1 Ypani Guerrero Prof Serpas Exp 389 11/28/12 Ones Way of Thinking Every day, people make decisions that determine where the next step we take in life will be. We often don t know whether those
Guerrero 1 Ypani Guerrero Prof Serpas Exp 389 11/28/12 Ones Way of Thinking Every day, people make decisions that determine where the next step we take in life will be. We often don t know whether those
Addressing Provider Bias and Needs
 From Counseling and Communicating with Men 2003 EngenderHealth 2 Addressing Provider Bias and Needs This chapter reviews the anxieties and/or negative feelings that health care workers may have about providing
From Counseling and Communicating with Men 2003 EngenderHealth 2 Addressing Provider Bias and Needs This chapter reviews the anxieties and/or negative feelings that health care workers may have about providing
Chapter 7: Cognitive Aspects of Personality. Copyright Allyn & Bacon (2009)
 Chapter 7: Cognitive Aspects of Personality Roots in Gestalt Psychology Human beings seek meaning in their environments We organize the sensations we receive into meaningful perceptions Complex stimuli
Chapter 7: Cognitive Aspects of Personality Roots in Gestalt Psychology Human beings seek meaning in their environments We organize the sensations we receive into meaningful perceptions Complex stimuli
Resistance to Change 7/17/2010. Paper exercise. Essence of Resistance. Grief Cycle death of the past. Phases of Change Acceptance
 Paper exercise Resistance to Change Ross A. Wirth, Ph.D. Change Leadership Symposium June 8, 2010 Jot down change initiatives where you observed resistance Symptoms of the resistance Reasons behind the
Paper exercise Resistance to Change Ross A. Wirth, Ph.D. Change Leadership Symposium June 8, 2010 Jot down change initiatives where you observed resistance Symptoms of the resistance Reasons behind the
Warm-Up. Read the story of Kody on pages in your textbook. 1. What makes someone join a group such as a gang or peer group?
 Warm-Up Read the story of Kody on pages 147-148 in your textbook. 1. What makes someone join a group such as a gang or peer group? 2. Why do people feel the need to join groups within society? Objectives
Warm-Up Read the story of Kody on pages 147-148 in your textbook. 1. What makes someone join a group such as a gang or peer group? 2. Why do people feel the need to join groups within society? Objectives
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE TEST-R
 We thank you for taking the test and for your support and participation. Your report is presented in multiple sections as given below: Menu Indicators Indicators specific to the test Personalized analysis
We thank you for taking the test and for your support and participation. Your report is presented in multiple sections as given below: Menu Indicators Indicators specific to the test Personalized analysis
Attribution Theory: we explain others behaviors by crediting the situation or the person s disposition/personality
 Social Psychology CB Learning Objective: Apply attribution theory to explain motives. Attribution Theory: we explain others behaviors by crediting the situation or the person s disposition/personality
Social Psychology CB Learning Objective: Apply attribution theory to explain motives. Attribution Theory: we explain others behaviors by crediting the situation or the person s disposition/personality
TTI Success Insights Emotional Quotient Version
 TTI Success Insights Emotional Quotient Version 2-2-2011 Scottsdale, Arizona INTRODUCTION The Emotional Quotient report looks at a person's emotional intelligence, which is the ability to sense, understand
TTI Success Insights Emotional Quotient Version 2-2-2011 Scottsdale, Arizona INTRODUCTION The Emotional Quotient report looks at a person's emotional intelligence, which is the ability to sense, understand
12 The biology of love
 The biology of love Motivation Neurological origins of passionate love begin in infancy when infants attach to mother. Certain neurotransmitters and hormones involved in pleasure and reward are activated
The biology of love Motivation Neurological origins of passionate love begin in infancy when infants attach to mother. Certain neurotransmitters and hormones involved in pleasure and reward are activated
Introduction. The focus is on spatial relations between humans and their environments Often called The Big Four
 Introduction The focus is on spatial relations between humans and their environments Often called The Big Four 1. Personal Space 2. Territoriality 3. Crowding 4. Privacy History of Personal Space 1966:
Introduction The focus is on spatial relations between humans and their environments Often called The Big Four 1. Personal Space 2. Territoriality 3. Crowding 4. Privacy History of Personal Space 1966:
Peer Support Meeting COMMUNICATION STRATEGIES
 Peer Support Meeting COMMUNICATION STRATEGIES Communication Think of a situation where you missed out on an opportunity because of lack of communication. What communication skills in particular could have
Peer Support Meeting COMMUNICATION STRATEGIES Communication Think of a situation where you missed out on an opportunity because of lack of communication. What communication skills in particular could have
Relationship Contexts. COMO 101 Lectures. Person to Person Relationships in Context. Chapter 9
 COMO 101 Lectures 9/28/06 Person to Person Relationships in Context Chapter 9 1 Relationship Contexts Acquaintanceships Friendships Romantic relationships Family relationships Work relationships Relationships
COMO 101 Lectures 9/28/06 Person to Person Relationships in Context Chapter 9 1 Relationship Contexts Acquaintanceships Friendships Romantic relationships Family relationships Work relationships Relationships
Social Psychology. The scientific study of how we think about, influence and relate to one another.
 Social Psychology The scientific study of how we think about, influence and relate to one another. Attribution Theory Suggests how we explain someone s behavior We credit that behavior either to the situation
Social Psychology The scientific study of how we think about, influence and relate to one another. Attribution Theory Suggests how we explain someone s behavior We credit that behavior either to the situation
CONCEPTS GUIDE. Improving Personal Effectiveness With Versatility
 CONCEPTS GUIDE Improving Personal Effectiveness With Versatility TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Introduction...1 The SOCIAL STYLE MODEL TM...1 Where Did Your Style Come From?...1 SOCIAL STYLE and Versatility Work...
CONCEPTS GUIDE Improving Personal Effectiveness With Versatility TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Introduction...1 The SOCIAL STYLE MODEL TM...1 Where Did Your Style Come From?...1 SOCIAL STYLE and Versatility Work...
Social Psychology. The scientific study of how we think about, influence and relate to one another.
 Social Psychology The scientific study of how we think about, influence and relate to one another. 1 Attribution Theory Suggests how we explain someone s behavior We credit that behavior either to the
Social Psychology The scientific study of how we think about, influence and relate to one another. 1 Attribution Theory Suggests how we explain someone s behavior We credit that behavior either to the
Social Psychology. Social Identity theory our beliefs about the groups to which we belong; our social identity is thus part of our self-concept
 Social Psychology Social Construction of the Self Social Comparison Theory social comparison (Festinger) - people evaluate themselves in relation to others reference groups - the categories of people to
Social Psychology Social Construction of the Self Social Comparison Theory social comparison (Festinger) - people evaluate themselves in relation to others reference groups - the categories of people to
