VISUALIZING. Chapter 15: Social Psychology. Lecture Overview
|
|
|
- Darcy Harvey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VISUALIZING Prepared By: Dawn More, Algonquin College Chapter 15: Social Psychology Media Enhanced PowerPoint Presentation Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 2 Lecture Overview Our Thoughts about Others Our Feelings about Others Others Applying Social Psychology to Social Problems Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 3 1
2 O u r T h o u g h t s a b o u t O t h e r s LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain how attributions and attitudes affect the way we perceive and judge others. 2. Summarize the three components of attitudes. 3. Describe cultural differences in how people explain behaviour. Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 4 Our Thoughts about Others Social Psychology: study of how other people influence our thoughts, feelings, and actions Attribution: explanation for the cause of behaviours or events To determine the cause, we first decide whether the behaviour comes from an: Internal (dispositional) cause, such as personal characteristics, or External (situational) cause, such as situational demands Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 5 Our Thoughts about Others: Mistaken Attributions Fundamental attribution error: misjudging causes of others behaviour and attributing to internal (dispositional) versus external (situational) ones Saliency bias: may explain this focus on dispositional causes. Self Serving Bias: taking credit for our successes and externalizing our failures Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 6 2
3 Our Thoughts about Others Attitude: learned predisposition to respond cognitively, affectively, and behaviourally to a particular object Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 7 Our Thoughts about Others: Cognitive Dissonance Cognitive Dissonance: feeling of discomfort created from a discrepancy between an attitude and a behaviour or between two competing attitudes Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 8 Our Thoughts about Others: Cognitive Dissonance Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 9 3
4 Our Thoughts about Others: Cognitive Dissonance Festinger and Carlsmith s Cognitive Dissonance Study: Participants given VERY boring tasks to complete, and then paid either $1 or $20 to tell next participant the task was very enjoyable and fun. Result: Those paid $1 experienced greater cognitive dissonance, and, therefore changed their attitude more than those paid $20. Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 10 Pause and Reflect: Check & Review 1. What is the fundamental attribution error? 2. According to the theory, people are motivated to change their attitudes because of tension created by a discrepancy between an attitude and a behaviour or between two or more competing attitudes. Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 11 O u r F e e l i n g s a b o u t O t h e r s LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain the difference between prejudice and discrimination. 2. Identify four explanations for why prejudice develops. 3. Summarize the factors that influence interpersonal attraction. 4. Explain how loving is different from liking. Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 12 4
5 Our Feelings about Others: Prejudice and Discrimination Prejudice: learned, generally negative, attitude toward members of a group Discrimination: negative behaviours directed at members of a group Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 13 Our Feelings about Others: Prejudice and Discrimination Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 14 Our Feelings about Others: Prejudice and Discrimination There are three components of prejudice: 1. Cognitive Stereotype: set of beliefs about the characteristics of people in a group generalized to all group members 2. Affective: feelings associated with objects of prejudice 3. Behavioural Discrimination: negative behaviours directed at members of a group Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 15 5
6 Our Feelings about Others: Sources of Prejudice and Discrimination Learned response Mental shortcut Ingroup favouritism: ingroup viewed more positively than outgroup Outgroup homogeneity effect: outgroup judged as less diverse than ingroup Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 16 O u r F e e l i n g s a b o u t O t h e r s : P r e j u d i c e a n d D i s c r i m i n a - t i o n Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 17 Pause and Reflect: Critical Thinking Do you believe you are free of prejudice? Would you date and marry someone of another ethnic group? If you are heterosexual, would you live with a roommate who is gay or lesbian? Why or why not? Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 18 6
7 Our Feelings about Others: Interpersonal Attraction Interpersonal attraction: positive feelings toward another Three key factors: Physical attractiveness Proximity (geographic closeness) Similarity Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 19 Our Feelings about Others: Interpersonal Attraction (Liking and Loving) Liking is a favourable evaluation of another. Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 20 Our Feelings about Others: Interpersonal Attraction Romantic Love: erotic attraction with future expectations Companionate Love: lasting attraction based on trust, caring, tolerance, and friendship Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 21 7
8 Pause and Reflect: Check & Review 1. Briefly explain how prejudice differs from discrimination. 2. How does romantic love differ from companionate love? Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 22 O u r A c t i o n s T o w a r d s O t h e r s LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Identify the factors that contribute to conformity and obedience. 2. Explain how groups affect behaviour and decision-making. 3. Summarize the biological and psychosocial factors believed to be involved in aggression. 4. Compare the egoistic model with the empathy altruism hypothesis. Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 23 Others: Social Influence Conformity: changing behaviour because of real or imagined group pressure Obedience: following direct commands, usually from an authority figure Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 24 8
9 Others: Conformity Asch s Conformity Study Participants were asked to select the line closest in length to X. When confederates gave obviously wrong answers (A or C), more than 1/3 conformed and agreed with the incorrect choices. Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 25 Others: Conformity Why do we conform? Normative social influence: need for approval and acceptance Informational social influence: need for information and direction Reference groups: we conform to people we like and admire because we want to be like them Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 26 Others: Obedience Milgram s obedience study: Participants serving as teachers are ordered to continue shocking someone with a known heart condition who is begging to be released. Result: 65% of teachers delivered highest level of shock (450 volts) to the heart condition learner. Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 27 9
10 Others: Obedience Milgram s Learner & Shock Generator Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 28 Others: Obedience Four major factors affecting obedience: legitimacy and closeness of the authority figure remoteness of the victim assignment of responsibility modeling/imitation Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 29 Others: Obedience Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 30 10
11 Pause and Reflect: Critical Thinking How would you have behaved if you were a teacher in Milgram s obedience studies? Would you have given the highest level of shocks? What about your best friend or parents? Would their behaviour differ from yours? Why and how? Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 31 Others: Group Processes Group membership involves: Roles: set of behavioural patterns connected with particular social positions Deindividuation: anonymity leads to reduced inhibition, self consciousness, and personal responsibility Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 32 Group Processes: Power of the Situation Zimbardo s Stanford Prison Study Students were randomly assigned to play the role of either prisoner or guard. Original study was scheduled for 2 weeks, but it was stopped after 6 days due to serious psychological changes in both prisoners and guards. Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 33 11
12 Group Processes: Problems with Decision Making Group Polarization: group movement toward either a riskier or more conservative decision; result depends on the members initial dominant tendency Groupthink: faulty decision making occurring when a highly cohesive group seeks agreement and avoids inconsistent information Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 34 Our Actions toward Others: Group Processes How Groupthink occurs Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 35 Others: Aggression Aggression: any behaviour intended to harm someone Biological factors in aggression: instincts, genes, brain and nervous system, hormones and neurotransmitters, substance abuse, and other mental disorders Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 36 12
13 Others: Aggression Psychosocial Factors in Aggression: Aversive stimuli Culture and learning Violent media/video games Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 37 Others: Aggression How can we control or reduce aggression? Introduce incompatible responses Improve social and communication skills Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 38 Others: Altruism Altruism: actions designed to help others with no obvious benefit to the helper Why do we help? Egoistic Model: helping motivated by anticipated gain Empathy Altruism Model: helping motivated by empathy Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 39 13
14 Others: Altruism Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 40 Others: Altruism Why don t we help? Diffusion of Responsibility: dilution, or diffusion, of personal responsibility by spreading it among others Ambiguity of the Situation: unclear what help is needed Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 41 Pause and Reflect: Check & Review 1. Briefly explain how groupthink differs from group polarization. 2. What are the best ways to reduce aggression? Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 42 14
15 A p p l y i n g S o c i a l P s y c h o l o g y t o S o c i a l P r o b l e m s LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe four major approaches to reducing prejudice and discrimination. 2. Explain how social changes might create cognitive dissonance and eventually promote a reduction in prejudice. 3. Summarize the principles that explain destructive obedience to authority. Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 43 Applying Social Psychology to Social Problems Prejudice and discrimination How do we reduce prejudice and discrimination? Encourage cooperation and superordinate goals Increased contact Cognitive retraining Employ cognitive dissonance Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 44 Applying Social Psychology to Social Problems: Destructive Obedience How do we reduce destructive obedience? Adjust socialization toward obedience Recognize power of the situation Protect against groupthink Avoid foot in the door technique: making a small request followed by increasingly larger requests Guard against relaxed moral guard Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 45 15
16 Pause and Reflect: Why Study Psychology? Psychology provides scientific research and insight into social problems, like prejudice and destructive obedience. Psychologists also produce concrete suggestions for reducing these problems. Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 46 Pause and Reflect: Critical Thinking Chapter 15 is often the last chapter covered in a general psychology course. If this is true for you, stop and take the time to list the top 5 to 10 concepts or terms that you learned in this course and want to remember for the rest of your life. Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 47 Web Links Social Psychology Network Welcome to Social Psychology Network, one of the largest Internet sites devoted to psychological research and teaching. Mirror Neurons Why do sports fans feel so emotionally invested in the game, reacting almost as if they were part of the game themselves? You Have Found the Prisoner s Dilemma A fiendish cyberspace wizard has locked you and Serendip into a diabolical game with the following rules Locus Of Control & Attributional Style Test Do you control your destiny or are you controlled by it? Project Implicit The demonstration site for the Implicit Association Test (IAT). Multimedia Cognitive Dissonance theory Cognitive Dissonance theory was first developed by Leon Festinger in 1956 after the publication of a book When Prophecy Fails, written with co authors Henry W. Riecken and Stanley Schachter, to explain how members of a UFO doomsday cult increased their commitment to the cult when a prophesised destruction of the Earth did not happen. Cognitive Dissonance Cognitive dissonance is a theory of human motivation that asserts that it is psychologically uncomfortable to hold contradictory cognitions. Festinger and Carlsmith Cognitive consequences of forced compliance Understanding Prejudice Exercises and Demonstrations Justice4Youth Homepage Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 48 16
17 Web Links Kids Help Phone Homepage Virtual Attractiveness A remarkable result of our research project is that faces which have been rated as highly attractive do not exist in reality. How Love Works If you've ever been in love, you've probably at least considered classifying the feeling as an addiction. The Science of Love Poets have been struggling to describe love for centuries. Indecently Exposed Profile: Jane Elliott Stanley Milgram The purpose of this website is to be a source of accurate information about the life and work of one of the most outstanding social scientists of our time, the social psychologist Stanley Milgram. Multimedia Thirty Years Later, Stanford Prison Experiment Lives On Thirty years ago, a group of young men were rounded up by Palo Alto police and dropped off at a new jail in the Stanford Psychology Department. A Simulation Study of the Psychology of Imprisonment Conducted at Stanford University Welcome to the Stanford Prison Experiment web site, which features an extensive slide show and information about this classic psychology experiment, including parallels with the abuse of prisoners at Abu Ghraib. Philip G. Zimbardo Welcome to the website of Philip G. Zimbardo, Professor Emeritus of Psychology at Stanford University, current core faculty at Palo Alto University, two time past president of the Western Psychological Association, and the past president of the American Psychological Association. Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 49 Web Links How Groups can Intensify Decisions People in groups often advocate riskier decisions than individuals Helping Preschoolers Resolve Social Conflicts We can help even the youngest of our girls express their feelings and solve conflicts directly so they don't need to use indirect forms of aggression. Understanding Boy Aggression What did the boys play at recess today? Media Smarts Canada s Centre for Digital and Media Literacy Is it the Media? Does violence in the media contribute to boys' aggressive behavior or does it reflect it? Multimedia International Center for Aggression Replacement Training The International Center for Aggression Replacement Training, ICART, is an organization devoted to the practice and evaluation of Aggression Replacement Training (ART), a cognitive behavioral intervention designed for aggressive children, adolescents, and adults. What We Can Do There are ways we can help support our boys' active impulses and help them work through feelings of aggression. Re Establishing Altruism As A Viable Social Norm What is Altruism? Egoism/Altruism Test Are you the type who will bend over backwards for others until it hurts or do you merely look out for #1? Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 50 Web Links Research Bulletin: Reducing Prejudice with Fiction We have discussed the relation between fiction and empathy extensively in OnFiction, but have not really broached the topic of what the consequences of this empathy might be. Jigsaw Classroom Welcome to the official web site of the jigsaw classroom, a cooperative learning technique that reduces racial conflict among school children, promotes better learning, improves student motivation, and increases enjoyment of the learning experience. Jane Elliot s Blue Eyes Brown Eyes Exercise Jane Elliott, internationally known teacher, lecturer, diversity trainer, and recipient of the National Mental Health Association Award for Excellence in Education, exposes prejudice and bigotry for what it is, an irrational class system based upon purely arbitrary factors. Multimedia Jigsaw Classroom Chapter 1: What Happened at Columbine? Resisting the Effects of Destructive Obedience Obedience is something that everyone must exhibit in one form or another in order to be considered a productive member of society, however, obedience may be taken to a form which in many ways becomes a crime against others (Hamilton, 1978). Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 51 17
18 Videos Gender and Love (1:27) Are men from Mars and women from Venus? As this ScienCentral News video reports, this Valentine's Day, brain scientists offer new evidence for that continuing debate. Multimedia Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 52 Animations Attitudes and Cognitive Dissonance Imagine that after months of searching, you and your spouse have found the home of your dreams a beautiful old house on a tree lined street. You love everything about the house, and you re even more captivated by the old fashioned charm of the neighbourhood. Then and there, you decide to make an offer. Multimedia Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Canada Ltd 53 Copyright Copyright 2013 John Wiley & Sons Canada, Ltd. All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted by Access Copyright (The Canadian Copyright Licensing Agency) is unlawful. Requests for further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons Canada, Ltd. The purchaser may make back-up copies for his or her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The author and the publisher assume no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages caused by the use of these programs or from the use of the information contained herein
CHAPTER 15. Social Psychology. Lecture Overview. Introductory Definition PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY. Social Cognition.
 Social Psychology CHAPTER 15 Social Cognition Lecture Overview Social Influence Social Relations Applying Social Psychology to Social Problems Introductory Definition Social Psychology: scientific study
Social Psychology CHAPTER 15 Social Cognition Lecture Overview Social Influence Social Relations Applying Social Psychology to Social Problems Introductory Definition Social Psychology: scientific study
Social Psychology. Social Thinking Social Influence Social Relations.
 Social Psychology Social Thinking Social Influence Social Relations http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Social Thinking Social Psychology scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to
Social Psychology Social Thinking Social Influence Social Relations http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Social Thinking Social Psychology scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY. Social Influences on the Self. Self Concept. How do we see ourselves? How do we see others?
 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY Social Cognition and Influence (how we think about ourselves) Social Influences on the Self How do we see ourselves? How do we see others? How do we compare ourselves with others? Self
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY Social Cognition and Influence (how we think about ourselves) Social Influences on the Self How do we see ourselves? How do we see others? How do we compare ourselves with others? Self
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 16: Social Psychology. 4. What cultures do not make the fundamental attribution error as much?
 Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 16: Social Psychology Attribution, Attitudes, and Actions (pg. 673-679) 1. Social Psychologists: 2. Attribution Theory (Fritz Heider): 3. Fundamental Attribution Error:
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 16: Social Psychology Attribution, Attitudes, and Actions (pg. 673-679) 1. Social Psychologists: 2. Attribution Theory (Fritz Heider): 3. Fundamental Attribution Error:
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Chapter 13. Social Psychology
 Social Psychology Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Social Psychology Interpreting the Behavior of Others Behaving in the Presence of Others Establishing Relations With Others Social
Social Psychology Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Social Psychology Interpreting the Behavior of Others Behaving in the Presence of Others Establishing Relations With Others Social
Factors that affect interpersonal attraction:
 Introduction: You are a member of a social world on a planet containing about 7 billion people. Our behaviors differ in different settings (like if we are in the college, market, or at home). Human behavior
Introduction: You are a member of a social world on a planet containing about 7 billion people. Our behaviors differ in different settings (like if we are in the college, market, or at home). Human behavior
Chapter 14. Social Psychology. How Does the Social Situation Affect our Behavior? Social Psychology
 Chapter 14 Social Psychology This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: Any public performance or display, including transmission of
Chapter 14 Social Psychology This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: Any public performance or display, including transmission of
AP Psychology Guided Reading Chapter 16 Social Psychology
 Name: Period: AP Psychology Guided Reading Chapter 16 Social Psychology Social Thinking 1. Define social psychology: 2. Define attribution theory. How does dispositional attribution differ from situational
Name: Period: AP Psychology Guided Reading Chapter 16 Social Psychology Social Thinking 1. Define social psychology: 2. Define attribution theory. How does dispositional attribution differ from situational
attitude the theory that we explain someone's behavior by crediting the situation or the person's disposition attribution theory
 attitude feelings, often influenced by our beliefs, that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events attribution theory the theory that we explain someone's behavior by
attitude feelings, often influenced by our beliefs, that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events attribution theory the theory that we explain someone's behavior by
CHAPTER 16 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY OBEDIENCE ATTITUDES & ATTITUDE CHANGE GROUP INFLUENCES PREJUDICE AGGRESSION ATTRACTION ALTRUISM
 CHAPTER 16 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY OBEDIENCE ATTITUDES & ATTITUDE CHANGE GROUP INFLUENCES PREJUDICE AGGRESSION ATTRACTION ALTRUISM ~ Professor Fazakas-deHoog lfazakas@uwo.ca AFFECT (Feelings) BEHAVIOR (Actions
CHAPTER 16 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY OBEDIENCE ATTITUDES & ATTITUDE CHANGE GROUP INFLUENCES PREJUDICE AGGRESSION ATTRACTION ALTRUISM ~ Professor Fazakas-deHoog lfazakas@uwo.ca AFFECT (Feelings) BEHAVIOR (Actions
Defining Social Psychology. informal definition: the study of how people think about, influence, and relate to other people
 Social Psychology Defining Social Psychology informal definition: the study of how people think about, influence, and relate to other people formal definition: the study of how a person s thoughts, feelings,
Social Psychology Defining Social Psychology informal definition: the study of how people think about, influence, and relate to other people formal definition: the study of how a person s thoughts, feelings,
Social Psychology. An Overview By Halford Fairchild September 3, 2013
 Social Psychology An Overview By Halford Fairchild September 3, 2013 Areas of interest Social influence - real or imagined presence of others Social cognition - how we think about social situations Attitudes
Social Psychology An Overview By Halford Fairchild September 3, 2013 Areas of interest Social influence - real or imagined presence of others Social cognition - how we think about social situations Attitudes
PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 12 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 12 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY PowerPoint Image Slideshow Social Psychology? What s that? The scientific study of how one s behavior, thoughts or feelings are influenced by the situation, or the
PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 12 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY PowerPoint Image Slideshow Social Psychology? What s that? The scientific study of how one s behavior, thoughts or feelings are influenced by the situation, or the
Chapter 15 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions PERSON PERCEPTION: FORMING IMPRESSIONS OF OTHERS
 Chapter 15 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions PERSON PERCEPTION: FORMING IMPRESSIONS OF OTHERS #1) Explain how schemas, stereotypes, and other factors contribute to subjectivity in person perception
Chapter 15 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions PERSON PERCEPTION: FORMING IMPRESSIONS OF OTHERS #1) Explain how schemas, stereotypes, and other factors contribute to subjectivity in person perception
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY SOCIAL INFLUENCE TYPES OF NORMS. Chapter 18
 SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 18 SOCIAL INFLUENCE Social Norms- learned, socially-based rules of behavior Generally they create orderly social behavior TYPES OF NORMS Injunctive Norms Shows what actions are
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 18 SOCIAL INFLUENCE Social Norms- learned, socially-based rules of behavior Generally they create orderly social behavior TYPES OF NORMS Injunctive Norms Shows what actions are
Conformity ASCH S STUDY 12/8/2010 ASCH S STUDY. Social Psychology (581, ) Others Focus on Social Influences on Our Behavior
 Social Psychology (581, 592-598) Study of how people behave, think, and feel in social situations Relatively recent addition to psychology Research influenced by current social problems Researchers in
Social Psychology (581, 592-598) Study of how people behave, think, and feel in social situations Relatively recent addition to psychology Research influenced by current social problems Researchers in
Are they formed through education or is it just part of being a human being?
 Social Behavior ~ Social Psychology Altruism; Conformity; Obedience; Compliance Are they formed through education or is it just part of being a human being? YouTube: Referee Helps Girl Finish Anthem YouTube:
Social Behavior ~ Social Psychology Altruism; Conformity; Obedience; Compliance Are they formed through education or is it just part of being a human being? YouTube: Referee Helps Girl Finish Anthem YouTube:
Social Psychology. An Overview By Halford Fairchild January 22, 2015
 Social Psychology An Overview By Halford Fairchild January 22, 2015 What is Social Psychology? From our text: Social Psychology is the scientific study of how we feel about, think about, and behave toward
Social Psychology An Overview By Halford Fairchild January 22, 2015 What is Social Psychology? From our text: Social Psychology is the scientific study of how we feel about, think about, and behave toward
Review Sheet Social Psych (8-10%)
 Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet Social Psych (8-10%) 1) social psychology Social Thinking 1) attribution theory 2) fundamental attribution error 3) foot-in-the-door
Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet Social Psych (8-10%) 1) social psychology Social Thinking 1) attribution theory 2) fundamental attribution error 3) foot-in-the-door
Name: Period: Score /95. Unit 14 Study Assignment Social Psychology. 1. Social behavior arises from our social. 2. Who proposed attribution theory?
 Name: Period: Score /95 Unit 14 Study Assignment Social Psychology 1. Social behavior arises from our social. 2. Who proposed attribution theory? 3. Create an example of the fundamental attribution error.
Name: Period: Score /95 Unit 14 Study Assignment Social Psychology 1. Social behavior arises from our social. 2. Who proposed attribution theory? 3. Create an example of the fundamental attribution error.
Estimated Distribution of Items for the Exams
 Estimated Distribution of Items for the Exams The current plan is that there are 5 exams with 50 multiple choice items that will cover two chapters. Each chapter is planned to have 25 multiple choice items.
Estimated Distribution of Items for the Exams The current plan is that there are 5 exams with 50 multiple choice items that will cover two chapters. Each chapter is planned to have 25 multiple choice items.
What is Social Cognition?
 Social Cognition What is Social Cognition? Social Psychology scientific study of how people s thoughts, feelings, and actions are influenced by social environment Cognitive Psychology scientific study
Social Cognition What is Social Cognition? Social Psychology scientific study of how people s thoughts, feelings, and actions are influenced by social environment Cognitive Psychology scientific study
Social Psychology. Studying the way people relate to others. Attitude. Group Behavior. Attraction Aggression
 Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Studying the way people relate to others. Attitudes A set of beliefs and feelings. Attitudes predispose our reactions to people, issues,
Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Studying the way people relate to others. Attitudes A set of beliefs and feelings. Attitudes predispose our reactions to people, issues,
8 Diffusion of Responsibility
 Ruggerio Chapter : The Basic Problem: Mine is Better Aronson & Tavris Book- Chapter 1 & Self- Justification Norms Rules that regulate human life, including social conventions, explicit laws, and implicit
Ruggerio Chapter : The Basic Problem: Mine is Better Aronson & Tavris Book- Chapter 1 & Self- Justification Norms Rules that regulate human life, including social conventions, explicit laws, and implicit
What is Social Psychology
 The Social World What is Social Psychology An attempt to understand and explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behavior of individuals are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others
The Social World What is Social Psychology An attempt to understand and explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behavior of individuals are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others
Social Psychology. What We Will Cover in This Section. Roles. PDF Created with deskpdf PDF Writer - Trial ::
 Social Psychology Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney What We Will Cover in This Section Conformity Attitudes Group Behavior Prejudice Roles Socially defined expectations that we expect individuals to fulfill in a given
Social Psychology Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney What We Will Cover in This Section Conformity Attitudes Group Behavior Prejudice Roles Socially defined expectations that we expect individuals to fulfill in a given
Informational influence. External validity. Asch. Sherif Agentic Social conflict. Informed consent. Internalisation
 Internalisation Snowball effect Autonomous Moscovici Obedience Zimbardo Agentic Social conflict Internalisation Legitimacy Laboratory Hospital Conformity Social conflict Laboratory Moscovici Obedience
Internalisation Snowball effect Autonomous Moscovici Obedience Zimbardo Agentic Social conflict Internalisation Legitimacy Laboratory Hospital Conformity Social conflict Laboratory Moscovici Obedience
Introduction to Psychology Social Psychology Quiz
 MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. We usually adapt our behavior to the demands of the social situation, and in ambiguous situations: A) We take our cues from the behavior of others. B) We will do the same thing that
MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. We usually adapt our behavior to the demands of the social situation, and in ambiguous situations: A) We take our cues from the behavior of others. B) We will do the same thing that
Topics for today Ethics Bias
 HCI and Design Topics for today Ethics Bias What are ethics? The study of moral standards and how they affect conduct Moral standards are A system of principles governing the appropriate conduct of an
HCI and Design Topics for today Ethics Bias What are ethics? The study of moral standards and how they affect conduct Moral standards are A system of principles governing the appropriate conduct of an
Conformity Asch study (1951) Which of the lines below is the same as the line to the right?
 a change in a belief or behavior with the intent to follow a perceived social norm May lead to positive or negative behaviors E.g., conforming to a norm of volunteering versus conforming to a norm of cheating
a change in a belief or behavior with the intent to follow a perceived social norm May lead to positive or negative behaviors E.g., conforming to a norm of volunteering versus conforming to a norm of cheating
Defining Psychology Behaviorism: Social Psychology: Milgram s Obedience Studies Bystander Non-intervention Cognitive Psychology:
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Defining Psychology Behaviorism: The scientific study of how rewards and punishment in the environment affect human and non-human behavior Empirical approach: vary contingencies of
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Defining Psychology Behaviorism: The scientific study of how rewards and punishment in the environment affect human and non-human behavior Empirical approach: vary contingencies of
-Attitude- Abdullah Nimer
 -Attitude- Abdullah Nimer Attitude refers to evaluation of things. The things can be concrete objects like cars or ideas like Marxism. Attitudes have: an affective component a cognitive component a behavioral
-Attitude- Abdullah Nimer Attitude refers to evaluation of things. The things can be concrete objects like cars or ideas like Marxism. Attitudes have: an affective component a cognitive component a behavioral
Psychology UNIT 1: PSYCHOLOGY AS A SCIENCE. Core
 Core provides a solid overview of the field's major domains: methods, biopsychology, cognitive and developmental psychology, and variations in individual and group behavior. By focusing on significant
Core provides a solid overview of the field's major domains: methods, biopsychology, cognitive and developmental psychology, and variations in individual and group behavior. By focusing on significant
Social Psychology 10 (14)
 Social Psychology 10 (14) KEY TERMS Attitude False-consensus effect Pluralistic ignorance Mere exposure effect Self-serving bias Attraction research Central versus peripheral Just-world bias Social facilitation
Social Psychology 10 (14) KEY TERMS Attitude False-consensus effect Pluralistic ignorance Mere exposure effect Self-serving bias Attraction research Central versus peripheral Just-world bias Social facilitation
AP Psych Unit 14 REVIEW
 Name: Date: 1. Research on physical attractiveness indicates that men are more likely than women to A) be attracted to dating partners whose hips are narrower than their waists. B) judge members of the
Name: Date: 1. Research on physical attractiveness indicates that men are more likely than women to A) be attracted to dating partners whose hips are narrower than their waists. B) judge members of the
Groups in Organizations. Overview of topics
 Groups in Organizations Overview of topics 1 Plan of today s lecture Groups general aspects Links with individual behavior Cohesion & conformity Decision making in groups 2 Characteristics of Groups Groups
Groups in Organizations Overview of topics 1 Plan of today s lecture Groups general aspects Links with individual behavior Cohesion & conformity Decision making in groups 2 Characteristics of Groups Groups
PSYC 210 Social Psychology
 South Central College PSYC 210 Social Psychology Course Information Description Total Credits 4.00 Pre/Corequisites PSYC100 or consent of instructor. Course Competencies Social Psychology introduces the
South Central College PSYC 210 Social Psychology Course Information Description Total Credits 4.00 Pre/Corequisites PSYC100 or consent of instructor. Course Competencies Social Psychology introduces the
A B C. Copyright Allyn and Bacon 2005
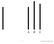 A B C 1 A B C 2 A B C 3 A B C 4 Asch, 1951 How many of you own something from one of these companies? 5 Fads 6 Lecture 10 Social Influence 7 Social Influence Have you ever: Asked a friend what was appropriate
A B C 1 A B C 2 A B C 3 A B C 4 Asch, 1951 How many of you own something from one of these companies? 5 Fads 6 Lecture 10 Social Influence 7 Social Influence Have you ever: Asked a friend what was appropriate
Cognitive Dissonance. by Saul McLeod published 2008, updated
 Cognitive Dissonance by Saul McLeod published 2008, updated Cognitive dissonance refers to a situation involving conflicting attitudes, beliefs or behaviors. This produces a feeling of discomfort leading
Cognitive Dissonance by Saul McLeod published 2008, updated Cognitive dissonance refers to a situation involving conflicting attitudes, beliefs or behaviors. This produces a feeling of discomfort leading
Social Psychology Terms and Vocabulary. How one tends to act toward the object of an attitude.
 Psychology Terms and Vocabulary Action component Actor observer bias Attitude Attitude scale Attribution Autokinetic effect Belief component Brainwashing Coercion How one tends to act toward the object
Psychology Terms and Vocabulary Action component Actor observer bias Attitude Attitude scale Attribution Autokinetic effect Belief component Brainwashing Coercion How one tends to act toward the object
Attribution Theory: we explain others behaviors by crediting the situation or the person s disposition/personality
 Social Psychology CB Learning Objective: Apply attribution theory to explain motives. Attribution Theory: we explain others behaviors by crediting the situation or the person s disposition/personality
Social Psychology CB Learning Objective: Apply attribution theory to explain motives. Attribution Theory: we explain others behaviors by crediting the situation or the person s disposition/personality
CHAPTER 16 Social Psychology
 CHAPTER 16 Social Psychology INTRODUCTION Please watch this short clip: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bohgujn2gk8 How do you describe the driver s behavior? What if the adjacent white car or red car belonged
CHAPTER 16 Social Psychology INTRODUCTION Please watch this short clip: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bohgujn2gk8 How do you describe the driver s behavior? What if the adjacent white car or red car belonged
Thinking About Psychology
 Thinking About Psychology Charles T. Blair-Broeker & Randal M. Ernst PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2012 Social Context Domain Jason Doly/istockphoto
Thinking About Psychology Charles T. Blair-Broeker & Randal M. Ernst PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2012 Social Context Domain Jason Doly/istockphoto
SOCIAL INFLUENCE: CONFORMITY
 SOCIAL INFLUENCE: CONFORMITY IB SYLLABUS SAYS: Evaluate research on conformity to group norms. Discuss factors influencing conformity. Textbook pages: 119-123 WHAT IS CONFORMITY? One of the key ways that
SOCIAL INFLUENCE: CONFORMITY IB SYLLABUS SAYS: Evaluate research on conformity to group norms. Discuss factors influencing conformity. Textbook pages: 119-123 WHAT IS CONFORMITY? One of the key ways that
The Power of the Situation! Essentials of Effective Management! Business (XP)! Nicholas Epley!
 The Power of the Situation! Essentials of Effective Management! Business 38811 (XP)! Nicholas Epley! Two foundational insights:" Experimental Psychology" 1. Thought and behavior is profoundly influenced
The Power of the Situation! Essentials of Effective Management! Business 38811 (XP)! Nicholas Epley! Two foundational insights:" Experimental Psychology" 1. Thought and behavior is profoundly influenced
SOCIAL INFLUENCE: OBEDIENCE. Attitudes beliefs tinged with emotion cognitive dissonance
 Term Test 4 Thursday March 9 in class, 12:00-1:50 40 multiple choice questions 10% of course grade Topics covered class material: Feb 7 - Mar 2 assigned readings: see lectures web page Language and Nonverbal
Term Test 4 Thursday March 9 in class, 12:00-1:50 40 multiple choice questions 10% of course grade Topics covered class material: Feb 7 - Mar 2 assigned readings: see lectures web page Language and Nonverbal
Psychology study guide Chapter 14
 Psychology study guide Chapter 14 Attribution Attribution a conclusion about the cause of an observed behavior / event Attribution theory we explain other s behaviors with two types of attributions Situational
Psychology study guide Chapter 14 Attribution Attribution a conclusion about the cause of an observed behavior / event Attribution theory we explain other s behaviors with two types of attributions Situational
Psychology chapter 16 Test Notes Social Psychology Altruistic Behavior - helping behavior that is not linked to personal gain; recognition and reward
 Psychology chapter 16 Test Notes Social Psychology Altruistic Behavior - helping behavior that is not linked to personal gain; recognition and reward are not expected Attitude - relatively stable organization
Psychology chapter 16 Test Notes Social Psychology Altruistic Behavior - helping behavior that is not linked to personal gain; recognition and reward are not expected Attitude - relatively stable organization
What is Social Psychology
 What is Social Psychology Social psychology is a scientific concept that seeks to explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of individuals are influenced by the presence of others, or lack of others.
What is Social Psychology Social psychology is a scientific concept that seeks to explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of individuals are influenced by the presence of others, or lack of others.
4/30 Lecture 23 Social psychology: Practice Question. PSYC 120 General Psychology. Social Psychology: Social Cognition Social Behavior
 4/30 Lecture 23 Social psychology: PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 23: Social Psychology 2 Social Psychology: Social Cognition Social Behavior Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office
4/30 Lecture 23 Social psychology: PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 23: Social Psychology 2 Social Psychology: Social Cognition Social Behavior Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office
Focuses in Social Psychology
 Focuses in Social Psychology We cannot live for ourselves alone. Herman Melville Social psychology scientifically studies how we think about, influence, and relate to one another. Social Thinking 1. Does
Focuses in Social Psychology We cannot live for ourselves alone. Herman Melville Social psychology scientifically studies how we think about, influence, and relate to one another. Social Thinking 1. Does
Social Biases and Pressures. Critical Thinking
 Social Biases and Pressures Critical Thinking Humans are Social Animals We are very sensitive to what others do and think. Most of our deep-rooted beliefs and values come from family and society we grow
Social Biases and Pressures Critical Thinking Humans are Social Animals We are very sensitive to what others do and think. Most of our deep-rooted beliefs and values come from family and society we grow
Power Benchmarks. Advanced Psychology
 Power Benchmarks Social Studies Standard: Students investigate the development of society and the influence of history, geography, government, human behavior, and economics on individuals and cultures.
Power Benchmarks Social Studies Standard: Students investigate the development of society and the influence of history, geography, government, human behavior, and economics on individuals and cultures.
Social Structure: underlying patterns of relationships in a group. October 23 rd, 2017
 Social Structure: underlying patterns of relationships in a group October 23 rd, 2017 Social Structure Social Structure refers to the underlying patterns of relationships in a group Aspects of Social Structure:
Social Structure: underlying patterns of relationships in a group October 23 rd, 2017 Social Structure Social Structure refers to the underlying patterns of relationships in a group Aspects of Social Structure:
Psychology. What is Psychology? The Biological Approach
 Psychology What is Psychology? The Biological Approach This approach argues that all human behaviour is determined by biology, this includes the role of the brain, nervous system, neurotransmitters, hormones
Psychology What is Psychology? The Biological Approach This approach argues that all human behaviour is determined by biology, this includes the role of the brain, nervous system, neurotransmitters, hormones
Emotion. I. What is Emotion II. Theories of Emotion III. The Physiology of Emotion IV. Emotional Expression
 Emotion I. What is Emotion II. Theories of Emotion III. The Physiology of Emotion IV. Emotional Expression Emotion Defined: Positive & negative feeling states consisting of patterns of: physiological arousal
Emotion I. What is Emotion II. Theories of Emotion III. The Physiology of Emotion IV. Emotional Expression Emotion Defined: Positive & negative feeling states consisting of patterns of: physiological arousal
Page 1 of 10 Saylor URL:
 This text was adapted by The Saylor Foundation under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work s original creator or licensee. Page
This text was adapted by The Saylor Foundation under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work s original creator or licensee. Page
Values. A principle, standard, or quality considered worthwhile or desirable
 Values A principle, standard, or quality considered worthwhile or desirable What s more important to you: Alaska s environment or money you could save if we drilled for oil there? Values indicate what
Values A principle, standard, or quality considered worthwhile or desirable What s more important to you: Alaska s environment or money you could save if we drilled for oil there? Values indicate what
Milgram Experiment. Harlow s Attachment Studies
 Milgram Experiment Hypothesis: that humans obey other people who are in a position of authority. Obedience Design: a shock generator that the teacher would use to shock the learner in the study if the
Milgram Experiment Hypothesis: that humans obey other people who are in a position of authority. Obedience Design: a shock generator that the teacher would use to shock the learner in the study if the
10 Norms and behavior. What s it about?
 10 Norms and behavior What s it about? (Social Psychology pp. 351 395) Norms are effective guides for social behavior. Norms must be activated before they can guide behavior. When individuals are in a
10 Norms and behavior What s it about? (Social Psychology pp. 351 395) Norms are effective guides for social behavior. Norms must be activated before they can guide behavior. When individuals are in a
Introduction to Social Psychology p. 1 Introduction p. 2 What Is Social Psychology? p. 3 A Formal Definition p. 3 Core Concerns of Social Psychology
 Preface p. xv Introduction to Social Psychology p. 1 Introduction p. 2 What Is Social Psychology? p. 3 A Formal Definition p. 3 Core Concerns of Social Psychology p. 3 Sociology, Psychology, or Both? p.
Preface p. xv Introduction to Social Psychology p. 1 Introduction p. 2 What Is Social Psychology? p. 3 A Formal Definition p. 3 Core Concerns of Social Psychology p. 3 Sociology, Psychology, or Both? p.
I DON T WANT TO BE CONFUSED! Social Psych topics that could be easily mixed up!
 I DON T WANT TO BE CONFUSED! Social Psych topics that could be easily mixed up! Groupthink vs. Group Polarization Both are effects the larger group has on an individual s behavior within that group Groupthink
I DON T WANT TO BE CONFUSED! Social Psych topics that could be easily mixed up! Groupthink vs. Group Polarization Both are effects the larger group has on an individual s behavior within that group Groupthink
Scientific Method. Five Steps To Conducting A Study Formulate a hypothesis Design a study Conduct study Analyse/evaluate data Report findings
 Contents Lectures 1 & 2: Scientific Method Lecture 3: Attitudes Lecture 4: Persuasion Tutorial 3 & 4: The Bystander Effect Lecture 5: Aggression and Prosocial Behaviour Lecture 6: Assignment (not included)
Contents Lectures 1 & 2: Scientific Method Lecture 3: Attitudes Lecture 4: Persuasion Tutorial 3 & 4: The Bystander Effect Lecture 5: Aggression and Prosocial Behaviour Lecture 6: Assignment (not included)
Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience
 Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience Objectives 1) knowledge about various forms of social influence, such as social facilitation, social loafing, conformity, compliance, and obedience. 2) An
Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience Objectives 1) knowledge about various forms of social influence, such as social facilitation, social loafing, conformity, compliance, and obedience. 2) An
FARMINGDALE STATE COLLEGE DATE: FALL 2017
 FARMINGDALE STATE COLLEGE DEPARTMENT: PSYCHOLOGY PREPARED BY: PSYCHOLOGY DEPT. DATE: FALL 2017 COURSE TITLE: Social Psychology COURSE CODE: PSY 234 CREDITS: 3 CONTACT HOURS: 45 CATALOG DESCRIPTION: This
FARMINGDALE STATE COLLEGE DEPARTMENT: PSYCHOLOGY PREPARED BY: PSYCHOLOGY DEPT. DATE: FALL 2017 COURSE TITLE: Social Psychology COURSE CODE: PSY 234 CREDITS: 3 CONTACT HOURS: 45 CATALOG DESCRIPTION: This
LP 12A Attribution and Stereotypes 1 04/13/15. Social Psychology
 Social Psychology LP 12A Attribution and Stereotypes 1 12.1 How Do We Form Our Impressions of Others? Nonverbal Actions and Expressions Affect our First Impressions We Make Attributions about Others Stereotypes
Social Psychology LP 12A Attribution and Stereotypes 1 12.1 How Do We Form Our Impressions of Others? Nonverbal Actions and Expressions Affect our First Impressions We Make Attributions about Others Stereotypes
Introduction to Psychology: Gateways to Mind and Behavior 13 th ed. Introduction: The Psychology of Studying Reflective Learning.
 Introduction to Psychology: Gateways to Mind and Behavior 13 th ed. Introduction: The Psychology of Studying Reflective Learning I.1 What is the best way to read a textbook? I.2 How can learning in class
Introduction to Psychology: Gateways to Mind and Behavior 13 th ed. Introduction: The Psychology of Studying Reflective Learning I.1 What is the best way to read a textbook? I.2 How can learning in class
Conformity & Obedience
 Higher Psychology Conformity & Obedience Exam Revision 1 This is the mandatory topic in the Social Behaviour unit. This means it will probably come up in the exam. What to revise: - Types of conformity
Higher Psychology Conformity & Obedience Exam Revision 1 This is the mandatory topic in the Social Behaviour unit. This means it will probably come up in the exam. What to revise: - Types of conformity
Self-Handicapping Variables and Students' Performance
 Georgia Southern University Digital Commons@Georgia Southern SoTL Commons Conference SoTL Commons Conference Mar 12th, 4:00 PM - 5:45 PM Self-Handicapping Variables and Students' Performance Lugenia Dixon
Georgia Southern University Digital Commons@Georgia Southern SoTL Commons Conference SoTL Commons Conference Mar 12th, 4:00 PM - 5:45 PM Self-Handicapping Variables and Students' Performance Lugenia Dixon
Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being
 Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being expressed by others. The task in Asch s studies involved judging
Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being expressed by others. The task in Asch s studies involved judging
C) Use of "credible" sources (experts, authority figures)
 Traditional Persuasion Techniques A) Greater rewards lead to more responses B) Greater punishment leads to less responses C) Use of "credible" sources (experts, authority figures) D) Use of conformity
Traditional Persuasion Techniques A) Greater rewards lead to more responses B) Greater punishment leads to less responses C) Use of "credible" sources (experts, authority figures) D) Use of conformity
CHAPTER 16 - SOCIAL BEHAVIOR - EXAM
 CHAPTER 16 - SOCIAL BEHAVIOR - EXAM Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Jill assumes her new biology professor is probably studious
CHAPTER 16 - SOCIAL BEHAVIOR - EXAM Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Jill assumes her new biology professor is probably studious
9. A woman named Kitty Genovese was murdered while a number of New Yorkers watched from their apartments. The onlookers did not call the cops right aw
 1. A long time smoker reads an article how smoking leads to cancer. The smoker then says to himself "I exercise a lot, so it doesn't matter if I smoke." This smoker's reasoning illustrates which of the
1. A long time smoker reads an article how smoking leads to cancer. The smoker then says to himself "I exercise a lot, so it doesn't matter if I smoke." This smoker's reasoning illustrates which of the
Don t allow fans to wear team football shirts
 Don t allow fans to wear team football shirts HTTPS://WWW.JIGSAW.ORG/#OVER VIEW What do you think we are learning about today? LEARNING OBJECTIVE We are learning about the use of psychological knowledge
Don t allow fans to wear team football shirts HTTPS://WWW.JIGSAW.ORG/#OVER VIEW What do you think we are learning about today? LEARNING OBJECTIVE We are learning about the use of psychological knowledge
PELLISSIPPI STATE COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY PSYC 2120
 PELLISSIPPI STATE COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY PSYC 2120 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 3.0 Laboratory Hours: 0.0 Date Revised: Fall 2016 Catalog Course Description: Theories, methods
PELLISSIPPI STATE COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY PSYC 2120 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 3.0 Laboratory Hours: 0.0 Date Revised: Fall 2016 Catalog Course Description: Theories, methods
Social Psychology. Social Psychology
 Term Explanation Application/Example/Extension Social psychology is the study of how people think, act, are influenced, and relate to one another in social situations Implicit personality theory- quick
Term Explanation Application/Example/Extension Social psychology is the study of how people think, act, are influenced, and relate to one another in social situations Implicit personality theory- quick
Interpersonal Communication in a Changing World: Culture and Social Networking 28
 Brief Contents PREFACE xix PART ONE: FOUNDATIONS OF INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION CHAPTER 1: Interpersonal Process 1 CHAPTER 2: Interpersonal Communication in a Changing World: Culture and Social Networking
Brief Contents PREFACE xix PART ONE: FOUNDATIONS OF INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION CHAPTER 1: Interpersonal Process 1 CHAPTER 2: Interpersonal Communication in a Changing World: Culture and Social Networking
Organizational Behaviour
 Bachelor of Commerce Programme Organizational Behaviour Individual Behaviour Perception The Da Vinci Institute for Technology Management (Pty) Ltd Registered with the Department of Education as a private
Bachelor of Commerce Programme Organizational Behaviour Individual Behaviour Perception The Da Vinci Institute for Technology Management (Pty) Ltd Registered with the Department of Education as a private
c) Potential sources of error in social cognition A Basic Tilt in Social Thought, Situation-Specific Sources of Error in Social Cognition
 ANNEXURE-II Syllabi for Psychology Core Courses (Major Elective) at the S.Y.B.A. Forthe academic year 2017-2018 Code Semester Course Title Credits Marks UAPSY301 1 Social Psychology: Part I 3 100 ( 75
ANNEXURE-II Syllabi for Psychology Core Courses (Major Elective) at the S.Y.B.A. Forthe academic year 2017-2018 Code Semester Course Title Credits Marks UAPSY301 1 Social Psychology: Part I 3 100 ( 75
Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience
 Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience Objectives 1) knowledge about various forms of social influence, such as social facilitation, social loafing, conformity, compliance, and obedience. 2) An
Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience Objectives 1) knowledge about various forms of social influence, such as social facilitation, social loafing, conformity, compliance, and obedience. 2) An
Prentice Hall. Psychology North Carolina Advanced Placement for Psychology
 Prentice Hall Psychology 2007 C O R R E L A T E D T O North Carolina ADVANCED PLACEMENT PSYCHOLOGY Advanced Placement Psychology is designed to introduce students to the systematic and scientific study
Prentice Hall Psychology 2007 C O R R E L A T E D T O North Carolina ADVANCED PLACEMENT PSYCHOLOGY Advanced Placement Psychology is designed to introduce students to the systematic and scientific study
Describe how social influence research has contributed to our understanding of social change.
 1 Describe how social influence research has contributed to our understanding of social change. Extra space (Total 6 marks) Page 1 of 15 2 Explain what is meant by locus of control. Extra space (Total
1 Describe how social influence research has contributed to our understanding of social change. Extra space (Total 6 marks) Page 1 of 15 2 Explain what is meant by locus of control. Extra space (Total
Social Psychology. Social Psychology (study of how other people influence our thoughts, feelings, and actions)
 Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Social Psychology (study of how other people influence our thoughts, feelings, and actions) Attribution Theory Tries to explain how people
Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Social Psychology (study of how other people influence our thoughts, feelings, and actions) Attribution Theory Tries to explain how people
Obediance and conformity
 Obediance and conformity PSY 268 Contemporary Issues in Psychology Fall 2012 Mgr. Zuzana Petrovicova QUIZ Briefly summarize main findings of Milgram s experiment ( do not describe the experiment itself)
Obediance and conformity PSY 268 Contemporary Issues in Psychology Fall 2012 Mgr. Zuzana Petrovicova QUIZ Briefly summarize main findings of Milgram s experiment ( do not describe the experiment itself)
Social Psychology. Course Syllabus
 Course Syllabus (3 Credits) Lecturers: Dr. ZHANG Zhongyuan zhangzhongyuan@zju.edu.cn Dr. LV Jiaying Jiaying_lu@zju.edu.cn Dr. ZHOU Xinhong zxhzheda@zju.edu.cn Office Hours: Friday, 1330-1700, 805-01 central
Course Syllabus (3 Credits) Lecturers: Dr. ZHANG Zhongyuan zhangzhongyuan@zju.edu.cn Dr. LV Jiaying Jiaying_lu@zju.edu.cn Dr. ZHOU Xinhong zxhzheda@zju.edu.cn Office Hours: Friday, 1330-1700, 805-01 central
Content Area: Social Studies Course: Introduction to Psychology Grade Level: R14 The Seven Cs of Learning
 Content Area: Social Studies Course: Introduction to Psychology Grade Level: 10-12 R14 The Seven Cs of Learning Collaboration Character Communication Citizenship Critical Thinking Creativity Curiosity
Content Area: Social Studies Course: Introduction to Psychology Grade Level: 10-12 R14 The Seven Cs of Learning Collaboration Character Communication Citizenship Critical Thinking Creativity Curiosity
Why do Psychologists Perform Research?
 PSY 102 1 PSY 102 Understanding and Thinking Critically About Psychological Research Thinking critically about research means knowing the right questions to ask to assess the validity or accuracy of a
PSY 102 1 PSY 102 Understanding and Thinking Critically About Psychological Research Thinking critically about research means knowing the right questions to ask to assess the validity or accuracy of a
Social Psychology. Social Psychology. Friends agree that person is: Friends agree that person is:
 Social Psychology Social Psychology Chapter 13 Impression formation and Attribution theory Study of the ways in which thoughts, feelings, perceptions, motives, and behavior are influenced by interactions
Social Psychology Social Psychology Chapter 13 Impression formation and Attribution theory Study of the ways in which thoughts, feelings, perceptions, motives, and behavior are influenced by interactions
Ones Way of Thinking. Every day, people make decisions that determine where the next step we take in life will
 Guerrero 1 Ypani Guerrero Prof Serpas Exp 389 11/28/12 Ones Way of Thinking Every day, people make decisions that determine where the next step we take in life will be. We often don t know whether those
Guerrero 1 Ypani Guerrero Prof Serpas Exp 389 11/28/12 Ones Way of Thinking Every day, people make decisions that determine where the next step we take in life will be. We often don t know whether those
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology
 PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 10 Social and community Psychology Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 10 Social and community Psychology Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Sample Psy 300 Test. You will need a Scantron form for each test (#882).
 Sample Psy 300 Test This sample test is presented to show you the types of questions that you can expect on the tests you take in my Psychology 300 classes. I will not post other sample tests that cover
Sample Psy 300 Test This sample test is presented to show you the types of questions that you can expect on the tests you take in my Psychology 300 classes. I will not post other sample tests that cover
Social Psychology. Preview
 CHAPTER 13 Social Psychology Preview Social psychology is the scientific study of how people think about, influence, and relate to one another. In thinking about others behavior and its possible causes,
CHAPTER 13 Social Psychology Preview Social psychology is the scientific study of how people think about, influence, and relate to one another. In thinking about others behavior and its possible causes,
Question: I m worried my child is using illegal drugs, what should I do about it?
 Question: I m worried my child is using illegal drugs, what should I do about it? Answer: Many parents worry about whether their son or daughter is using illegal drugs and what they should do about it.
Question: I m worried my child is using illegal drugs, what should I do about it? Answer: Many parents worry about whether their son or daughter is using illegal drugs and what they should do about it.
SAMPLE. Social Psychology. Authoritarian Personality.
 Social Psychology Authoritarian Personality tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint This tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint is copyrighted and may not be reproduced or shared without permission from the author. All
Social Psychology Authoritarian Personality tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint This tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint is copyrighted and may not be reproduced or shared without permission from the author. All
Social Psychology CHAPTER 14 CHAPTER OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 14 Social Psychology CHAPTER OUTLINE Social psychology is the scientific study of how people s thoughts and feelings influence their behavior toward others and how the behavior of others influences
CHAPTER 14 Social Psychology CHAPTER OUTLINE Social psychology is the scientific study of how people s thoughts and feelings influence their behavior toward others and how the behavior of others influences
Social Psychology. Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior. Studying the way people relate to others.
 Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Studying the way people relate to others. Attitudes A set of beliefs and feelings. Attitudes predispose our reactions to people, issues,
Social Psychology Attitude Attraction Aggression Group Behavior Studying the way people relate to others. Attitudes A set of beliefs and feelings. Attitudes predispose our reactions to people, issues,
Module 30. Learning by Observation
 Module 30 Learning by Observation 1 Module 30 Describe the process of observational learning, and explain how some scientists believe it is enabled by mirror neurons. Discuss the impact of prosocial modeling
Module 30 Learning by Observation 1 Module 30 Describe the process of observational learning, and explain how some scientists believe it is enabled by mirror neurons. Discuss the impact of prosocial modeling
8/17/2012. Self-Concept Video. Cultural Differences in Defining the Self. Chapter 5. The Self: Understanding Ourselves in a Social Context
 Chapter 5 The Self: Understanding Ourselves in a Social Context Slides prepared by JoNell Strough, Ph.D. & Philip Lemaster, M.A. West Virginia University Self-Concept Video Click on the screenshot and
Chapter 5 The Self: Understanding Ourselves in a Social Context Slides prepared by JoNell Strough, Ph.D. & Philip Lemaster, M.A. West Virginia University Self-Concept Video Click on the screenshot and
