Animal Behavior. AP Biology. meerkats
|
|
|
- Mary Hunter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Animal Behavior meerkats
2 What is behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate inherited, instinctive automatic & consistent learned QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ability to learn is inherited, but the behavior develops during animal s lifetime variable & flexible change with experience & environment
3 are needed to see this picture. QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor Why study behavior? Evolutionary perspective part of phenotype acted upon by natural selection lead to greater fitness? lead to greater survival? lead to greater reproductive success? QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture.
4 What questions can we ask? Proximate causes immediate stimulus & mechanism how & what questions Ultimate causes evolutionary significance how does behavior contribute to survival & reproduction adaptive value why questions male songbird what triggers singing? how does he sing? why does he sing? Courtship behavior in cranes what how & why questions how does daylength influence breeding? why do cranes breed in spring?
5 Evolutionary perspective Adaptive advantage? innate behaviors automatic, fixed, built-in, no learning curve despite different environments, all individuals exhibit the behavior ex. early survival, reproduction, kinesis, taxis learned behaviors modified by experience variable, changeable flexible with a complex & changing environment
6 Ethology pioneers in the study of animal behavior Karl von Frisch Niko Tinbergen Konrad Lorenz
7 Innate behaviors Fixed action patterns (FAP) sequence of behaviors essentially unchangeable & usually conducted to completion once started sign stimulus the releaser that triggers a FAP male sticklebacks exhibit aggressive territoriality attack on red belly stimulus court on swollen belly stimulus
8 Fixed Action Patterns (FAP) Digger wasp egg rolling in geese Do humans exhibit Fixed Action Patterns? The eyebrow-flash
9 Supernormal Stimulus Responding more to a larger sign stimulus adaptation or experimental artifact? does lipstick create a supernormal stimulus in humans
10 Innate: Directed movements Taxis change in direction automatic movement toward (positive taxis) or away from (negative taxis) a stimulus phototaxis chemotaxis Kinesis change in rate of movement in response to a stimulus
11 Complex Innate behaviors Migration migratory restlessness seen in birds bred & raised in captivity navigate by sun, stars, Earth magnetic fields Sandpiper Monarch migration Bobolink ancient flyways Golden plover
12 Innate & Learning: Imprinting Learning to form social attachments at a specific critical period both learning & innate components Konrad Lorenz
13 Conservation Conservation biologists have taken advantage of imprinting by young whooping cranes as a means to teach the birds a migration route. A pilot wearing a crane suit in an Ultralight plane acts as a surrogate parent. teaching cranes to migrate Wattled crane conservation
14 Critical period Sensitive phase for optimal imprinting some behavior must be learned during a receptive time period As a brood parasite, the Cuckoo never learn the song of their species as a nestling. Song development is totally innate. imprinting/critical period in humans?
15 Learned behavior Associative learning learning to associate a stimulus with a consequence operant conditioning trial & error learning associate behavior with reward or punishment ex: learning what to eat classical conditioning Pavlovian conditioning associate a neutral QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. stimulus with a significant stimulus QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture.
16 Operant conditioning Skinner box B. F. Skinner QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. mouse learns to associate behavior (pressing lever) with reward (food pellet)
17 Classical conditioning Ivan Pavlov s dogs connect reflex behavior (salivating at sight of food) to associated stimulus (ringing bell)
18 Learning: Habituation Loss of response to stimulus cry-wolf effect decrease in response to repeated occurrences of stimulus enables animals to disregard unimportant stimuli ex: falling leaves not triggering fear response in baby birds QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture.
19 Learning: Problem-solving Do other animals reason? chimpanzee problem-solving tool use crow sea otter
20 Social behaviors Interactions between individuals develop as evolutionary adaptations communication / language agonistic behaviors dominance hierarchy cooperation altruistic behavior
21 Language Honey bee communication dance to communicate location of food source waggle dance Let s go to the videotape!
22 Communication by song Bird song species identification & mating ritual mixed learned & innate critical learning period Insect song mating ritual & song innate, genetically controlled Red-winged blackbird
23 Social behaviors Agonistic behaviors threatening & submissive rituals symbolic, usually no harm done ex: territoriality, competitor aggression Let s go to the videotape!
24 Social behaviors Dominance hierarchy social ranking within a group pecking order
25 Social behaviors Cooperation working together in coordination Pack of African dogs hunting wildebeest cooperatively White pelicans herding school of fish
26 Social behaviors Altruistic behavior reduces individual fitness but increases fitness of recipient kin selection increasing survival of close relatives passes these genes on to the next generation I would lay down my life for 2 brothers or 8 cousins! How can this be of adaptive value? Belding ground squirrel
27 Social interaction requires communication Pheromones chemical signal that stimulates a response from other individuals alarm pheromones sex pheromones
28 human sex pheromone? Pheromones Female mosquito use CO 2 concentrations to locate victims marking territory Spider using moth sex pheromones, as allomones, to lure its prey The female lion lures male by spreading sex pheromones, but also by posture & movements
29 Colonial mammals Naked mole rats underground colony, tunnels queen, breeding males, non-breeding workers hairless, blind Picture a hot dog that's been left in a microwave a little too long add some buck teeth at one end, and you've got a fairly good idea of what a Naked Mole Rat looks like. convergent evolution: bees, ants, termites mole rats
30 Any Questions??
31 EXTRA SLIDES
32 Mating & parental behavior Genetic influences changes in behavior at different stages of mating pair bonding competitor aggression Environmental influences modifies behavior quality of diet social interactions learning opportunities
33 Pheromones Human pheromones?
AP Biology. What is behavior? Behavioral Ecology. Why study behavior? What questions can we ask? Evolutionary perspective.
 Behavioral Ecology What is behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate inherited, instinctive automatic & consistent learned ability to learn
Behavioral Ecology What is behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate inherited, instinctive automatic & consistent learned ability to learn
3/30/17. Animal Behavior. What is behavior? Why study behavior?
 Animal Behavior meerkat s What is behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate inherited, instinctive automatic & consistent learned ability
Animal Behavior meerkat s What is behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate inherited, instinctive automatic & consistent learned ability
AP Biology. What is behavior & Why study it? Animal Behavior. Ethology. What questions do we ask? Innate behavior. Types of behaviors
 Animal Behavior What is behavior & Why study it? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate = inherited or developmentally fixed learned = develop
Animal Behavior What is behavior & Why study it? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate = inherited or developmentally fixed learned = develop
Chapter 51 Behavioral Biology
 Chapter 51 Behavioral Biology Essential Knowledge 2.C.2 Organisms respond to changes in their external environments 2.E.2 Timing and coordination of physiological events are regulated by multiple mechanisms
Chapter 51 Behavioral Biology Essential Knowledge 2.C.2 Organisms respond to changes in their external environments 2.E.2 Timing and coordination of physiological events are regulated by multiple mechanisms
Animal Behavior 2/21/2017. What is Behavior? Understanding Behavior. Types of Behavior. Types of Behavior
 What is Behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment Animal Behavior Why Study Behavior? Evolutionary perspective part of phenotype acted upon by
What is Behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment Animal Behavior Why Study Behavior? Evolutionary perspective part of phenotype acted upon by
Animal Behavior. Types of Communication 4/22/2013
 Animal Behavior A behavior is the nervous system s response to a stimulus and is carried out by the muscular or the hormonal system Behavior is subject to natural selection Behaviors have an impact on
Animal Behavior A behavior is the nervous system s response to a stimulus and is carried out by the muscular or the hormonal system Behavior is subject to natural selection Behaviors have an impact on
Introduction to Neuroscience: Behavioral Neuroscience Lecture 1: Introduction to Animal Behavior
 Introduction to Neuroscience: Behavioral Neuroscience Lecture 1: Introduction to Animal Behavior Tali Kimchi Department of Neurobiology Tali.kimchi@weizmann.ac.il Jakob von Uexküll (1864-1944) Umwelt
Introduction to Neuroscience: Behavioral Neuroscience Lecture 1: Introduction to Animal Behavior Tali Kimchi Department of Neurobiology Tali.kimchi@weizmann.ac.il Jakob von Uexküll (1864-1944) Umwelt
Animal Behavior. Chapter 51. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 51 Animal Behavior PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 51 Animal Behavior PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
8. 4 types of communication signals: visual, sound, chemical, electrical
 Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 35 BEHAVIORAL ADAPTATIONS TO THE ENVIRONMENT 1. stimulus vs. response 2. nature vs. nurture 3. fixed action pattern, innate behaviors 4. imprinting vs. learning 5. types of
Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 35 BEHAVIORAL ADAPTATIONS TO THE ENVIRONMENT 1. stimulus vs. response 2. nature vs. nurture 3. fixed action pattern, innate behaviors 4. imprinting vs. learning 5. types of
Behavior. What causes behavior? Chapter 35: Behavioral Adaptations. Honors Biology Wide range of activities
 Chapter 35: Behavioral Adaptations Honors Biology 2013 1 Behavior Wide range of activities Both observable actions and chemical communication Response to internal and external environmental stimuli (environmental
Chapter 35: Behavioral Adaptations Honors Biology 2013 1 Behavior Wide range of activities Both observable actions and chemical communication Response to internal and external environmental stimuli (environmental
Introduction to Neuroscience: Behavioral Neuroscience
 Introduction to Neuroscience: Behavioral Neuroscience Lecture 1: Introduction to Animal Behavior Tali Kimchi tali.kimchi@weizmann.ac.il * Presentation Materials for Personal Use ONLY Introduction Humans
Introduction to Neuroscience: Behavioral Neuroscience Lecture 1: Introduction to Animal Behavior Tali Kimchi tali.kimchi@weizmann.ac.il * Presentation Materials for Personal Use ONLY Introduction Humans
(A) Drive (B) Innate behavior (C) Learning, based on experience (D) A & B (E) None of the above
 CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 24: Behavior No. 1 of 10 1. Habituation is a type of. (A) Drive (B) Innate behavior (C) Learning, based on experience (D) A & B (E) None of the above Having a certain drive
CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 24: Behavior No. 1 of 10 1. Habituation is a type of. (A) Drive (B) Innate behavior (C) Learning, based on experience (D) A & B (E) None of the above Having a certain drive
What Is Behavior? Behavioral Biology: Ethology. Behavioral Ecology. Behavioral Biology: Experimental
 What Is Behavior? Behavior: change in activity in response to stimuli Is what an animal does and how it does it Includes muscular and non-muscular activity Cognition: the ability of an animal s nervous
What Is Behavior? Behavior: change in activity in response to stimuli Is what an animal does and how it does it Includes muscular and non-muscular activity Cognition: the ability of an animal s nervous
Animal Behavior. How can we explain behavior? Behavior. Innate or instinctive behavior. Instinctive behavior. Instinctive behavior 11/26/2017
 Animal Behavior Chapter 51 How can we explain behavior? How it works physiologically Proximate answer The adaptive value of the behavior Ultimate answer So, behavioral scientists study what behavior an
Animal Behavior Chapter 51 How can we explain behavior? How it works physiologically Proximate answer The adaptive value of the behavior Ultimate answer So, behavioral scientists study what behavior an
PSY 2364 Animal Communication. Tinbergen s four questions. Niko Tinbergen ( ) Niko Tinbergen ( ) Niko Tinbergen ( )
 PSY 2364 Animal Communication The curious naturalist noninvasive field experiments Studies of herring gull behavior, spatial learning in insects Tinbergen s four questions 1) What is the mechanism? 2)
PSY 2364 Animal Communication The curious naturalist noninvasive field experiments Studies of herring gull behavior, spatial learning in insects Tinbergen s four questions 1) What is the mechanism? 2)
AP Biology. Behavioral Biology
 AP Biology Behavioral Biology Day 1 Objectives Describe how organisms get innate behaviors Explain how learning occurs Explain how living organisms regulate behavior Analyze how environmental factors can
AP Biology Behavioral Biology Day 1 Objectives Describe how organisms get innate behaviors Explain how learning occurs Explain how living organisms regulate behavior Analyze how environmental factors can
Animal Behavior. meerkats
 Animal Behavior meerkats AP Biology 2006-2007 What is behavior & Why study it? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment Why study behavior? part of phenotype
Animal Behavior meerkats AP Biology 2006-2007 What is behavior & Why study it? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment Why study behavior? part of phenotype
Behavioral Animal Adaptations. Survival of organisms
 Behavioral Animal Adaptations Survival of organisms ANIMAL BEHAVIOR BEHAVIOR = anything an animal does in response to a stimulus in its environment What is a stimulus for bears beginning to hibernate?
Behavioral Animal Adaptations Survival of organisms ANIMAL BEHAVIOR BEHAVIOR = anything an animal does in response to a stimulus in its environment What is a stimulus for bears beginning to hibernate?
Animal Behavior. Chapter 51. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 51 Animal Behavior PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Chapter 51 Animal Behavior PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Animal Behavior. Thur March 24: Animal Behavior: outline. Questions: What, How, and Why. Behavior is shaped partly by inheritance
 Thur March 24: Animal Behavior Animal Behavior: outline Animal Behavior Questions Behavior is partly shaped by Inheritance Behavior is partly shaped by Learning Hormones and Behavior The Genetics of Behavior
Thur March 24: Animal Behavior Animal Behavior: outline Animal Behavior Questions Behavior is partly shaped by Inheritance Behavior is partly shaped by Learning Hormones and Behavior The Genetics of Behavior
Behavioural Ecology. This subdiscipline studies the behaviour of individuals in an ecological context.
 Behavioural Ecology This subdiscipline studies the behaviour of individuals in an ecological context. In general, the behaviours studies are directed toward food, habitat, and mates. In all three, genetics
Behavioural Ecology This subdiscipline studies the behaviour of individuals in an ecological context. In general, the behaviours studies are directed toward food, habitat, and mates. In all three, genetics
The How and Why of Animal Activity
 The How and Why of Animal Activity Fiddler crabs feed with their small claw and wave their large claw Why do male fiddler crabs engage in claw waving behavior? Claw waving is used to repel other males
The How and Why of Animal Activity Fiddler crabs feed with their small claw and wave their large claw Why do male fiddler crabs engage in claw waving behavior? Claw waving is used to repel other males
Chapter 51. Behavioral Ecology. PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition. Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 51 Behavioral Ecology PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Overview: Studying Behavior Humans have probably studied animal behavior for as long as we have
Chapter 51 Behavioral Ecology PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Overview: Studying Behavior Humans have probably studied animal behavior for as long as we have
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Animal Behavior
 Animal Behavior Answer Key SECTION 1. ADAPTIVE VALUE OF BEHAVIOR 1. stimulus; behavior 2. Internal; body 3. External; surroundings 4. b, c, a 5. constant; stimuli 6. increase; particular 7. internal; external
Animal Behavior Answer Key SECTION 1. ADAPTIVE VALUE OF BEHAVIOR 1. stimulus; behavior 2. Internal; body 3. External; surroundings 4. b, c, a 5. constant; stimuli 6. increase; particular 7. internal; external
Types of behaviors that are elicited in response to simple stimuli
 Lecture 19: Animal Behavior I. Background A. Animal behavior reflects and arises from biological properties 1. Exhibited behavior defends on the physiological systems and processes unique to a given organism
Lecture 19: Animal Behavior I. Background A. Animal behavior reflects and arises from biological properties 1. Exhibited behavior defends on the physiological systems and processes unique to a given organism
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 51 Animal Behavior Lectures by
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 51 Animal Behavior Lectures by
BIOLOGY. Animal Behavior CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 51 Animal Behavior Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The How and Why of Animal Activity Fiddler
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 51 Animal Behavior Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The How and Why of Animal Activity Fiddler
Chapter 51: Animal Behavior
 Chapter 51: Animal Behavior AP Biology Lindemulder 2013 1 Behavior Behavior - the nervous system s response to a stimulus and is carried out by the muscular system or the hormonal system Behavior is subject
Chapter 51: Animal Behavior AP Biology Lindemulder 2013 1 Behavior Behavior - the nervous system s response to a stimulus and is carried out by the muscular system or the hormonal system Behavior is subject
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 14: Animals
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 14: Animals NC Essential Standard: 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish life functions 2.1.3 Explain various ways organisms interact with each other Did you
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 14: Animals NC Essential Standard: 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish life functions 2.1.3 Explain various ways organisms interact with each other Did you
SY 2017/ nd Final Term Revision. Student s Name: Grade: 11A. Subject: Biology. Teacher Signature
 SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 11A Subject: Biology Teacher Signature Grade 11 Biology A/B Revision Work Sheet Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or
SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 11A Subject: Biology Teacher Signature Grade 11 Biology A/B Revision Work Sheet Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or
Innate behavior & Learning
 & & has a fixed, genetic component. Despite differing environments, the behavior develops in all individuals. Learned behavior is acquired and modified over development. s can be triggered or enhanced
& & has a fixed, genetic component. Despite differing environments, the behavior develops in all individuals. Learned behavior is acquired and modified over development. s can be triggered or enhanced
Erick Sepulveda. Genetic basis. Life experiences. Nature vs. Nuture (it s a tie!)
 http://light.simanonok.com/euglenaphototaxis.jpg Erick Sepulveda A set of activities that orient an animal to its environment Most notable are observable reactions Internal responses also occur Taxes Simple
http://light.simanonok.com/euglenaphototaxis.jpg Erick Sepulveda A set of activities that orient an animal to its environment Most notable are observable reactions Internal responses also occur Taxes Simple
Writing Assignment 1
 Writing Assignment 1 Writing Assignment #1 Due Wednesday October 15th at the beginning of lecture To read: A Tephritid Fly Mimics the Territorial Displays of its Jumping Spider Predators Erick Greene;
Writing Assignment 1 Writing Assignment #1 Due Wednesday October 15th at the beginning of lecture To read: A Tephritid Fly Mimics the Territorial Displays of its Jumping Spider Predators Erick Greene;
Chapter 4 The Control of Behavior
 Chapter 4 Opener: Woodhouse s toad Chapter 4 The Control of Behavior Water toad (Bufo stejnegeri) Bull frog (Japanese) 4.1 A complex response to simple stimuli 4.2 A simple rule of thumb governs this beetle
Chapter 4 Opener: Woodhouse s toad Chapter 4 The Control of Behavior Water toad (Bufo stejnegeri) Bull frog (Japanese) 4.1 A complex response to simple stimuli 4.2 A simple rule of thumb governs this beetle
10/6/14. Writing Assignment 1. Writing Assignment 1. How to test hypotheses in behavioral ecology. Niko Tinbergen s Four Questions
 Writing Assignment 1 Writing Assignment #1 Due Wednesday October 15th at the beginning of lecture To read: A Tephritid Fly Mimics the Territorial Displays of its Jumping Spider Predators Erick Greene;
Writing Assignment 1 Writing Assignment #1 Due Wednesday October 15th at the beginning of lecture To read: A Tephritid Fly Mimics the Territorial Displays of its Jumping Spider Predators Erick Greene;
Bi412/512 Animal Behavior, Exam 1 Practice Page 1
 Bi412/512 Animal Behavior, Exam 1 Practice Page 1 1. Suppose you observe that song sparrows sing more at dawn than at other times of the day. Hmm, maybe singing early in the morning communicates to female
Bi412/512 Animal Behavior, Exam 1 Practice Page 1 1. Suppose you observe that song sparrows sing more at dawn than at other times of the day. Hmm, maybe singing early in the morning communicates to female
Name Date Class. Innate Behavior. SC.F The student knows that organisms respond to internal and external stimuli.
 Innate Behavior Before You Read SC.F.1.4.7 The student knows that organisms respond to internal and external stimuli. You may live in an area where you can observe animals migrating. Have you seen flocks
Innate Behavior Before You Read SC.F.1.4.7 The student knows that organisms respond to internal and external stimuli. You may live in an area where you can observe animals migrating. Have you seen flocks
 4.11 Noctuid moth ears http://www.panda.org.cn/english/index.htm 2010. 9. 27 2010. 9. 27 Chapter 4 Opener: Woodhouse s toad Chapter 4 The Control of Behavior Water toad (Bufo stejnegeri) Bull frog (Japanese)
4.11 Noctuid moth ears http://www.panda.org.cn/english/index.htm 2010. 9. 27 2010. 9. 27 Chapter 4 Opener: Woodhouse s toad Chapter 4 The Control of Behavior Water toad (Bufo stejnegeri) Bull frog (Japanese)
thebiotutor.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F215: Control, genomes and environment Module 4.3 Animal behaviour Notes & Questions
 thebiotutor.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F215: Control, genomes and environment Module 4.3 Animal behaviour Notes & Questions Andy Todd 1 Explain the advantages to organisms of innate behaviour. Behaviour o
thebiotutor.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F215: Control, genomes and environment Module 4.3 Animal behaviour Notes & Questions Andy Todd 1 Explain the advantages to organisms of innate behaviour. Behaviour o
Lecture 6 Behavior ethology Communication
 Lecture 6 Behavior ethology Communication Rich history of behavioral studies of birds Birds display a wide range of innate and learned behavior patterns Overview - Behavior Chapter 8 (Gill) Vocalizations
Lecture 6 Behavior ethology Communication Rich history of behavioral studies of birds Birds display a wide range of innate and learned behavior patterns Overview - Behavior Chapter 8 (Gill) Vocalizations
The Gene Propagation Game
 The Gene Propagation Game Social Living has Costs and Benefits Competition, Territoriality and Dominance Altruism in the Animal Kingdom Genetic Relatedness and Inclusive Fitness Mating Behavior Depends
The Gene Propagation Game Social Living has Costs and Benefits Competition, Territoriality and Dominance Altruism in the Animal Kingdom Genetic Relatedness and Inclusive Fitness Mating Behavior Depends
Launch Lab. How do scientists observe animal behavior in the field? Video. WebQuest. Assessment. Audio. Concepts in Motion. Review.
 CHAPTER 31 Animal Behavior Your one-stop online resource connected.mcgraw-hill.com Video WebQuest Audio Assessment Review Concepts in Motion? Inquiry g Multilingual eglossary Launch Lab How do scientists
CHAPTER 31 Animal Behavior Your one-stop online resource connected.mcgraw-hill.com Video WebQuest Audio Assessment Review Concepts in Motion? Inquiry g Multilingual eglossary Launch Lab How do scientists
Behavioral Biology: Proximate and Ultimate Causes of Behavior *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44879 1 Behavioral Biology: Proximate and Ultimate Causes of Behavior * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
OpenStax-CNX module: m44879 1 Behavioral Biology: Proximate and Ultimate Causes of Behavior * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Exercise 13: Behavior of the House Cricket (Acheta domesticus)
 Exercise 13: Behavior of the House Cricket (Acheta domesticus) 1 Animal Behavior Why do praying mantises display a unique mating system, called sexual cannibalism, where a member of a male-female pair
Exercise 13: Behavior of the House Cricket (Acheta domesticus) 1 Animal Behavior Why do praying mantises display a unique mating system, called sexual cannibalism, where a member of a male-female pair
The function or adaptive value of signals has been broken down into the following classes:
 Communication notes.doc 1 Communication and signals an action on the part of one animal that alters the behavior of another (Wilson 1975). The essence of communication is the relationship between signaler
Communication notes.doc 1 Communication and signals an action on the part of one animal that alters the behavior of another (Wilson 1975). The essence of communication is the relationship between signaler
Lecture #4 Ethology, continued Konrad Lorenz jackdaws
 9.20 M.I.T. 2013 Lecture #4 Ethology, continued Konrad Lorenz jackdaws 1 Konrad Lorenz Ethology: The Jackdaws of Altenberg, Austria Reading: King Solomon s Ring (1952), Chapter 11, The Perennial Retainers
9.20 M.I.T. 2013 Lecture #4 Ethology, continued Konrad Lorenz jackdaws 1 Konrad Lorenz Ethology: The Jackdaws of Altenberg, Austria Reading: King Solomon s Ring (1952), Chapter 11, The Perennial Retainers
The organism s problem: Avoid predation and injury so you can reproduce
 Learning Chapter 7 Design a Brain The organism s problem: Avoid predation and injury so you can reproduce What characteristics are needed to behave adaptively and reproduce successfully? Consider: nearly
Learning Chapter 7 Design a Brain The organism s problem: Avoid predation and injury so you can reproduce What characteristics are needed to behave adaptively and reproduce successfully? Consider: nearly
Operant Condi-oning. Cogni-on and Problem Solving. Cogni-on and Problem Solving. Cogni-on. a process of knowing
 Operant condi-oning a type of associa,ve learning in which an animal learns to associate one of its behaviors with a reward or punishment It is also called trial- and- error learning Example a rat that
Operant condi-oning a type of associa,ve learning in which an animal learns to associate one of its behaviors with a reward or punishment It is also called trial- and- error learning Example a rat that
Animal Behavior Introduction Behavior has Proximate vs. Ultimate Causes Innate vs. Learned Behavior fixed action pattern sign stimulus.
 Animal Behavior Introduction Behavior as most people understand it, is a directed response of an organism to the environment. The response may be chemical, or a physical movement. Bacteria, fungi, and
Animal Behavior Introduction Behavior as most people understand it, is a directed response of an organism to the environment. The response may be chemical, or a physical movement. Bacteria, fungi, and
Name Date Class. As you read Chapter 13, which begins on page 302 of your textbook, answer the following questions.
 CHAPTER 13 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Animals and Behavior As you read Chapter 13, which begins on page 302 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 302) 1a. What did
CHAPTER 13 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Animals and Behavior As you read Chapter 13, which begins on page 302 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 302) 1a. What did
1. Distinguish between releaser and modifier hormones. 2. Give and example of a reflex, a fixed action pattern and a stimulus response chain.
 1 Study Guide 1. Distinguish between releaser and modifier hormones. 2. Give and example of a reflex, a fixed action pattern and a stimulus response chain. 3. Explain how the results presented in the Figure
1 Study Guide 1. Distinguish between releaser and modifier hormones. 2. Give and example of a reflex, a fixed action pattern and a stimulus response chain. 3. Explain how the results presented in the Figure
Animal Behavior Discrete sensory inputs can stimulate both simple and complex behaviors
 51 Animal Behavior KEY CONCEPTS 51.1 Discrete sensory inputs can stimulate both simple and complex behaviors 51.2 Learning establishes specific links between experience and behavior 51.3 Selection for
51 Animal Behavior KEY CONCEPTS 51.1 Discrete sensory inputs can stimulate both simple and complex behaviors 51.2 Learning establishes specific links between experience and behavior 51.3 Selection for
FILM SESSIONS. Film session I - Behaviour of Communication (September 30)
 FILM SESSIONS Film session I - Behaviour of Communication (September 30) 1. Talking to Strangers (60 min.) 1 This film surveys some of the general communication signals used by animals from diverse taxa,
FILM SESSIONS Film session I - Behaviour of Communication (September 30) 1. Talking to Strangers (60 min.) 1 This film surveys some of the general communication signals used by animals from diverse taxa,
Vibration volleys. Standard repeating unit. crossed with. Chrysoperla johnsoni parent: Volley period RESULTS
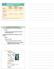 Table 51 1 Regulatory Genes and Behavior A master regulatory gene can control many behaviors Example a single gene controls many behaviors of the male fruit fly courtship ritual Mul:ple independent genes
Table 51 1 Regulatory Genes and Behavior A master regulatory gene can control many behaviors Example a single gene controls many behaviors of the male fruit fly courtship ritual Mul:ple independent genes
I. Ethology of Insects II. Patterns of Behavior III. Modifications IV. Operation V. Genetic Basis VI. Life History
 Insect Behavior I. Ethology of Insects II. Patterns of Behavior III. Modifications IV. Operation V. Genetic Basis VI. Life History I. Ethology of Insects Ethology is the comparative study of behavior We
Insect Behavior I. Ethology of Insects II. Patterns of Behavior III. Modifications IV. Operation V. Genetic Basis VI. Life History I. Ethology of Insects Ethology is the comparative study of behavior We
We know that humans can learn
 We know that humans can learn Learning in Animals Which animals are able to learn? (Hint: all animals have nervous systems) Reasonable guess: All animals can learn!! (Def.) Learning is a relatively long-lasting
We know that humans can learn Learning in Animals Which animals are able to learn? (Hint: all animals have nervous systems) Reasonable guess: All animals can learn!! (Def.) Learning is a relatively long-lasting
Sensory Worlds: The neural basis of animal behaviour. Dr. Katie Lucas Learning in Retirement Winter 2018
 Sensory Worlds: The neural basis of animal behaviour Dr. Katie Lucas Learning in Retirement Winter 2018 The Field of Neuroethology The neural basis of natural adaptive behaviour Environmental Signal Stimulus
Sensory Worlds: The neural basis of animal behaviour Dr. Katie Lucas Learning in Retirement Winter 2018 The Field of Neuroethology The neural basis of natural adaptive behaviour Environmental Signal Stimulus
Chapter 40 Animal Behavior
 40 Animal Behavior Chapter 40 Animal Behavior Key Concepts 40.1 Behavior Is Controlled by the Nervous System but Is Not Necessarily Deterministic 40.2 Behavior Is Influenced by Development and Learning
40 Animal Behavior Chapter 40 Animal Behavior Key Concepts 40.1 Behavior Is Controlled by the Nervous System but Is Not Necessarily Deterministic 40.2 Behavior Is Influenced by Development and Learning
Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning - a type of learning in which one learns to link two stimuli and anticipate events.
 Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning - a type of learning in which one learns to link two stimuli and anticipate events. behaviorism - the view that psychology (1) should be an objective science
Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning - a type of learning in which one learns to link two stimuli and anticipate events. behaviorism - the view that psychology (1) should be an objective science
Outline 3/12/2013. Practice Question. Practice Question. PSYC 120 General Psychology. Spring 2013 Lecture 13: Learning & Memory
 Outline 3/12/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 13: Learning & Memory Learning Observational learning Associative learning Memory? Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays
Outline 3/12/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 13: Learning & Memory Learning Observational learning Associative learning Memory? Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays
Chapter 3. Outline for this lecture
 Chapter 3 Elicited Behaviors and Classical Conditioning Outline for this lecture Elicited Behaviors Reflexes Fixed Action Patterns Opponent Process Theory of Emotion Classical Conditioning Characteristics
Chapter 3 Elicited Behaviors and Classical Conditioning Outline for this lecture Elicited Behaviors Reflexes Fixed Action Patterns Opponent Process Theory of Emotion Classical Conditioning Characteristics
Animal Behavior. Hormones and Neurons Organize Behavior
 Animal Behavior Hormones and Neurons Organize Behavior Controlling Neural Responses What controls neurons? Ganglia -clusters of neuron cell bodies. Brain-greatest concentration of cell bodies. Praying
Animal Behavior Hormones and Neurons Organize Behavior Controlling Neural Responses What controls neurons? Ganglia -clusters of neuron cell bodies. Brain-greatest concentration of cell bodies. Praying
BLY 122 Lecture Notes (O Brien) Chapter 47 Behavior
 BLY 122 Lecture Notes (O Brien) 2005 Chapter 47 Behavior I. Causes of Behavior A. PROXIMAL CAUSATION 1. Describes how actions occur in terms of the neurological, hormonal, and skeletomuscular mechanisms
BLY 122 Lecture Notes (O Brien) 2005 Chapter 47 Behavior I. Causes of Behavior A. PROXIMAL CAUSATION 1. Describes how actions occur in terms of the neurological, hormonal, and skeletomuscular mechanisms
Classical Conditioning & Operant Conditioning
 Classical Conditioning & Operant Conditioning What is Classical Conditioning? Learning Objective: Students will be able to describe the difference between Classical and Operant Conditioning. How Do We
Classical Conditioning & Operant Conditioning What is Classical Conditioning? Learning Objective: Students will be able to describe the difference between Classical and Operant Conditioning. How Do We
Classical Conditioning. Learning. Classical conditioning terms. Classical Conditioning Procedure. Procedure, cont. Important concepts
 Learning Classical Conditioning Pavlov study of digestion dogs salivate before getting food learning as signal detection: emphasis on what happens before a given behavior Classical conditioning terms Stimulus:
Learning Classical Conditioning Pavlov study of digestion dogs salivate before getting food learning as signal detection: emphasis on what happens before a given behavior Classical conditioning terms Stimulus:
Unit 06 - Overview. Click on the any of the above hyperlinks to go to that section in the presentation.
 Unit 06 - Overview How We Learn and Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning s Applications, and Comparison to Classical Conditioning Biology, Cognition, and Learning Learning By
Unit 06 - Overview How We Learn and Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning s Applications, and Comparison to Classical Conditioning Biology, Cognition, and Learning Learning By
Bronze statue of Pavlov and one of his dogs located on the grounds of his laboratory at Koltushi Photo taken by Jackie D. Wood, June 2004.
 Ivan Pavlov http://physiologyonline.physiology.org/ cgi/content/full/19/6/326 Bronze statue of Pavlov and one of his dogs located on the grounds of his laboratory at Koltushi Photo taken by Jackie D. Wood,
Ivan Pavlov http://physiologyonline.physiology.org/ cgi/content/full/19/6/326 Bronze statue of Pavlov and one of his dogs located on the grounds of his laboratory at Koltushi Photo taken by Jackie D. Wood,
Chapter 6. Learning: The Behavioral Perspective
 Chapter 6 Learning: The Behavioral Perspective 1 Can someone have an asthma attack without any particles in the air to trigger it? Can an addict die of a heroin overdose even if they ve taken the same
Chapter 6 Learning: The Behavioral Perspective 1 Can someone have an asthma attack without any particles in the air to trigger it? Can an addict die of a heroin overdose even if they ve taken the same
Psychological Hodgepodge. Mr. Mattingly Psychology
 Psychological Hodgepodge Mr. Mattingly Psychology The Number: Eight What is conditioning? Conditioning = learned or trained Classical Conditioning = learning procedure where associations are made Usually
Psychological Hodgepodge Mr. Mattingly Psychology The Number: Eight What is conditioning? Conditioning = learned or trained Classical Conditioning = learning procedure where associations are made Usually
Associative Learning
 Learning Learning Associative Learning Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Biological Components of Learning Cognitive Components of Learning Behavioral Therapies Associative
Learning Learning Associative Learning Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Biological Components of Learning Cognitive Components of Learning Behavioral Therapies Associative
AP PSYCH Unit 6.1 Learning & Classical Conditioning. Before ever opening this book, what did you think learning meant?
 AP PSYCH Unit 6.1 Learning & Classical Conditioning Before ever opening this book, what did you think learning meant? Learning We are not born with a genetic plan that gets us through our entire life Much
AP PSYCH Unit 6.1 Learning & Classical Conditioning Before ever opening this book, what did you think learning meant? Learning We are not born with a genetic plan that gets us through our entire life Much
Learning Ashrakat & Roukaya. For reference open pages 50-57
 Learning Ashrakat & Roukaya For reference open pages 50-57 Learning Objectives 1. What learning is 2. the different types of learning 3. Learn about each type a. Conditioned Learning (Classical & Operant)
Learning Ashrakat & Roukaya For reference open pages 50-57 Learning Objectives 1. What learning is 2. the different types of learning 3. Learn about each type a. Conditioned Learning (Classical & Operant)
Evolution of Mating Systems. Chapter 8
 Evolution of Mating Systems Chapter 8 Mating Systems-Chapter 8 1 Monogamy 2 Polyandry 3 Polygyny And the many combinations within! Why should a male be monogamous? 1 extension of guarding, little chance
Evolution of Mating Systems Chapter 8 Mating Systems-Chapter 8 1 Monogamy 2 Polyandry 3 Polygyny And the many combinations within! Why should a male be monogamous? 1 extension of guarding, little chance
9.20 Midterm review notes, questions, topics
 9.20 Midterm review notes, questions, topics TOPICS FOR REVIEW Class 1: Introduction 1. What is the blank slate? In what fields did this idea flourish? 2. Contrast the attitudes about this idea in America
9.20 Midterm review notes, questions, topics TOPICS FOR REVIEW Class 1: Introduction 1. What is the blank slate? In what fields did this idea flourish? 2. Contrast the attitudes about this idea in America
Ecological benefits of cooperation. Life Insurance. Life Insurance. Fortress defense
 Ecological benefits of cooperation 1. For cooperation and eusociality to evolve it also is required that ecological conditions lead to a high enough benefit/cost ratio to favor cooperation a. Need B/C
Ecological benefits of cooperation 1. For cooperation and eusociality to evolve it also is required that ecological conditions lead to a high enough benefit/cost ratio to favor cooperation a. Need B/C
Animal Behavior. Unlike most animals, male fiddler crabs (genus Uca) are highly asymmetrical: The How and Why of Animal Activity KEY CONC EPTS
 51 Animal Behavior KEY CONC EPTS 51.1 Discrete sensory inputs can stimulate both simple and complex behaviors 51.2 Learning establishes specific links between experience and behavior 51.3 Selection for
51 Animal Behavior KEY CONC EPTS 51.1 Discrete sensory inputs can stimulate both simple and complex behaviors 51.2 Learning establishes specific links between experience and behavior 51.3 Selection for
Effect of act on fitness of recipient
 Kin selection (inclusive fitness) and social behavior These worker ants are sterile, and they differ greatly from their queens and males. Darwin was troubled by social-insect workers, because they have
Kin selection (inclusive fitness) and social behavior These worker ants are sterile, and they differ greatly from their queens and males. Darwin was troubled by social-insect workers, because they have
PSY 2364 Animal Communication. Pied Butcherbird. Why defend a territory? Why defend a territory? What determines territory size?
 PSY 2364 Animal Communication Pied Butcherbird http://www.piedbutcherbird.net/5-songs.html http://www.piedbutcherbird.net/6-musicality.html Birdsong has inspired humans for centuries: is it music? Is Birdsong
PSY 2364 Animal Communication Pied Butcherbird http://www.piedbutcherbird.net/5-songs.html http://www.piedbutcherbird.net/6-musicality.html Birdsong has inspired humans for centuries: is it music? Is Birdsong
Unit code: M/503/1683 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15
 Unit 11: Animal Behaviour Unit code: M/503/1683 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit aims to develop learner understanding of the relationship between environmental and evolutionary pressures on
Unit 11: Animal Behaviour Unit code: M/503/1683 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit aims to develop learner understanding of the relationship between environmental and evolutionary pressures on
4. Compare and contrast and give specific examples of kinesis and taxis. 5. What is the relationship between migration and genetic control?
 AP Biology Chapter 51 Guided Reading Name 1. How do behavioral ecologists define behavior? 2. What is the focus of: a. Proximate questions of behavior? b. Ultimate questions of behavior? 3. Define the
AP Biology Chapter 51 Guided Reading Name 1. How do behavioral ecologists define behavior? 2. What is the focus of: a. Proximate questions of behavior? b. Ultimate questions of behavior? 3. Define the
Chapter 7. Learning From Experience
 Learning From Experience Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Learning From Experience Noticing and Ignoring Learning What Events Signal Learning About the Consequences of Our Behavior
Learning From Experience Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Learning From Experience Noticing and Ignoring Learning What Events Signal Learning About the Consequences of Our Behavior
An Introduction to Behavioural Ecology
 An Introduction to Behavioural Ecology J.R. Krebs FRS Royal Society Research Professor at the Edward Grey Institute of Field Ornithology Department of Zoology University of Oxford and Fellow of Pembroke
An Introduction to Behavioural Ecology J.R. Krebs FRS Royal Society Research Professor at the Edward Grey Institute of Field Ornithology Department of Zoology University of Oxford and Fellow of Pembroke
PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 6 LEARNING PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 6 LEARNING PowerPoint Image Slideshow Learning? What s that? A relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience or practice. Note that learning is NOT the same as
PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 6 LEARNING PowerPoint Image Slideshow Learning? What s that? A relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience or practice. Note that learning is NOT the same as
Parental Care. External vs. Internal Fertilization. Likelihood of paternal care depends on. Paternal certainty Fertilization mode
 Parental Care Likelihood of paternal care depends on Who should care? How much care? External vs. Internal Fertilization Paternal certainty Fertilization mode Degree to which male can contribute State
Parental Care Likelihood of paternal care depends on Who should care? How much care? External vs. Internal Fertilization Paternal certainty Fertilization mode Degree to which male can contribute State
Whiptail Lizard Sexual Selection
 Whiptail Lizard Sexual Selection Charles Darwin and Alfred Russell Wallace Noticed that males of many species have highly elaborated traits that seem maladaptive (secondary sexual characters) 1 2 Antlers
Whiptail Lizard Sexual Selection Charles Darwin and Alfred Russell Wallace Noticed that males of many species have highly elaborated traits that seem maladaptive (secondary sexual characters) 1 2 Antlers
Evolution of Populations. AP Biology
 Evolution of Populations 2007-2008 Doonesbury - Sunday February 8, 2004 Review of Darwin s Influence Geology Thomas Hutton Charles Lyll - Biology Jean Baptist Lamark - Tendency toward Perfection - Use
Evolution of Populations 2007-2008 Doonesbury - Sunday February 8, 2004 Review of Darwin s Influence Geology Thomas Hutton Charles Lyll - Biology Jean Baptist Lamark - Tendency toward Perfection - Use
Animal Science. Study of animal behaviour Involves observations of animals actions and reactions to different stimuli
 Animal Science Contents: 1. Behaviour 2. Reproductive systems 3. Growth and maturity 4. Lactation system 5. Sensory system 6. Integumentary system 7. Endocrine system 8. Nervous system 9. Immune system
Animal Science Contents: 1. Behaviour 2. Reproductive systems 3. Growth and maturity 4. Lactation system 5. Sensory system 6. Integumentary system 7. Endocrine system 8. Nervous system 9. Immune system
Learning. Learning is the relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience.
 Chapter 7 Learning Learning Learning is the relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience. Learning The Mexican Gray wolves had problems after being released back into the wild,
Chapter 7 Learning Learning Learning is the relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience. Learning The Mexican Gray wolves had problems after being released back into the wild,
Cooperation and conflict: How insects interact with each other and their environment
 Cooperation and conflict: How insects interact with each other and their environment Overview Five examples of cooperation and conflict in insects (and its consequences) Cooperation requires communication:
Cooperation and conflict: How insects interact with each other and their environment Overview Five examples of cooperation and conflict in insects (and its consequences) Cooperation requires communication:
Learning. AP PSYCHOLOGY Unit 5
 Learning AP PSYCHOLOGY Unit 5 Learning Learning is a lasting change in behavior or mental process as the result of an experience. There are two important parts: a lasting change a simple reflexive reaction
Learning AP PSYCHOLOGY Unit 5 Learning Learning is a lasting change in behavior or mental process as the result of an experience. There are two important parts: a lasting change a simple reflexive reaction
Friday Lecture: HUM 15 Deep Time Radiometric Dating Google Map Exercise. Friday Lab: Faculty Lounge Animals in Cinema
 Friday Lecture: HUM 15 Deep Time Radiometric Dating Google Map Exercise https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rdk3it29uoq Friday Lab: Faculty Lounge Animals in Cinema (Tomorrow afternoon practice) - Natural
Friday Lecture: HUM 15 Deep Time Radiometric Dating Google Map Exercise https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rdk3it29uoq Friday Lab: Faculty Lounge Animals in Cinema (Tomorrow afternoon practice) - Natural
THEORETICAL PERSPECTIVES I. Lecturer: Dr. Paul Narh Doku Contact: Department of Psychology, University of Ghana
 THEORETICAL PERSPECTIVES I Lecturer: Dr. Paul Narh Doku Contact: pndoku@ug.edu.gh Department of Psychology, University of Ghana Session Overview This session will deal with the meaning and scope of psychology,
THEORETICAL PERSPECTIVES I Lecturer: Dr. Paul Narh Doku Contact: pndoku@ug.edu.gh Department of Psychology, University of Ghana Session Overview This session will deal with the meaning and scope of psychology,
survival value causation development evolutionary history
 The focus of ethology is observing animal behavior under natural conditions; animal behavior is how an animal responds to the environment that surrounds it and to conditions within its body. Considering
The focus of ethology is observing animal behavior under natural conditions; animal behavior is how an animal responds to the environment that surrounds it and to conditions within its body. Considering
Chapter 7 - Learning
 Chapter 7 - Learning How Do We Learn Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Defining Learning Learning a relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience.
Chapter 7 - Learning How Do We Learn Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Defining Learning Learning a relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience.
DEFINITION. Learning is the process of acquiring knowledge (INFORMATIN ) and new responses. It is a change in behavior as a result of experience
 LEARNING DEFINITION Learning is the process of acquiring knowledge (INFORMATIN ) and new responses. It is a change in behavior as a result of experience WHAT DO WE LEARN? 1. Object :we learn objects with
LEARNING DEFINITION Learning is the process of acquiring knowledge (INFORMATIN ) and new responses. It is a change in behavior as a result of experience WHAT DO WE LEARN? 1. Object :we learn objects with
Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience
 Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience Does NOT include temporary changes due to disease, fatigue, injury, maturation, or drugs, since these do NOT qualify as learning, even
Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience Does NOT include temporary changes due to disease, fatigue, injury, maturation, or drugs, since these do NOT qualify as learning, even
Understanding Evolution (http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/evo_25)
 1 Understanding Evolution (http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/evo_25) Natural selection Natural selection is one of the basic mechanisms of evolution, along with mutation, migration, and
1 Understanding Evolution (http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/evo_25) Natural selection Natural selection is one of the basic mechanisms of evolution, along with mutation, migration, and
Learning Habituation Associative learning Classical conditioning Operant conditioning Observational learning. Classical Conditioning Introduction
 1 2 3 4 5 Myers Psychology for AP* Unit 6: Learning Unit Overview How Do We Learn? Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Learning by Observation How Do We Learn? Introduction Learning Habituation
1 2 3 4 5 Myers Psychology for AP* Unit 6: Learning Unit Overview How Do We Learn? Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Learning by Observation How Do We Learn? Introduction Learning Habituation
Learning. Innate: Advantage of speed, no mistakes. Less need for parental care.
 Learning Innate vs learned behaviors Innate: Advantage of speed, no mistakes. Less need for parental care. Learned: Adaptability, Flexibility If learning is advantageous, will selection inevitably lead
Learning Innate vs learned behaviors Innate: Advantage of speed, no mistakes. Less need for parental care. Learned: Adaptability, Flexibility If learning is advantageous, will selection inevitably lead
