Sensation Perception
|
|
|
- Miles Ray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sensation Perception THIRD EDITION Jeremy M. Wolfe Harvard University Medical School Keith R. Kluender Purdue University Dennis M. Levi University of California, Berkeley Linda M. Bartoshuk University of Florida Rachel S. Herz Brown University Roberta Klatzky Carnegie Mellon University Susan J. Lederman Queen s University Daniel M. Merfeld Harvard University Medical School Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts U.S.A.
2 Brief Contents CHAPTER 1 Introduction 3 CHAPTER 2 The First Steps in Vision: From Light to Neural Signals 31 CHAPTER 3 Spatial Vision: From Spots to Stripes 55 CHAPTER 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects 85 CHAPTER 5 The Perception of Color 117 CHAPTER 6 Space Perception and Binocular Vision 149 CHAPTER 7 Attention and Scene Perception 187 CHAPTER 8 Motion Perception 221 CHAPTER 9 Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics 243 CHAPTER 10 Hearing in the Environment 275 CHAPTER 11 Music and Speech Perception 303 CHAPTER 12 Spatial Orientation and the Vestibular System 329 CHAPTER 13 Touch 363 CHAPTER 14 Olfaction 399 CHAPTER 15 Taste 433
3 Contents CHAPTER 1 Introduction 3 Welcome to Our World 3 Sensation and Perception 3 Method 1: Thresholds 4 Method 2: Scaling Measuring Private Experience 4 Method 3: Signal Detection Theory Measuring Difficult Decisions 4 Method 4: Sensory Neuroscience 4 Method 5: Neuroimaging An Image of the Mind 5 Thresholds and the Dawn of Psychophysics 5 Psychophysical Methods 7 Scaling Methods and Supertasters 9 Signal Detection Theory 11 Fourier Analysis 15 Sensory Neuroscience and the Biology of Perception 17 Neuronal Connections 21 Neural Firing: The Action Potential 22 Neural Firing: Populations of Neurons 24 CHAPTER 2 The First Steps in Vision: From Light to Neural Signals 31 A Little Light Physics 31 Eyes That See Light 32 Focusing Light onto the Retina 34 The Retina 35 Retinal Information Processing 38 Light Transduction by Rod and Cone Photoreceptors 38 The Man Who Could Not Read 42 Lateral Inhibition through Horizontal and Amacrine Cells 43 Convergence and Divergence of Information via Bipolar Cells 43 Communicating to the Brain via Ganglion Cells 44 Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation 48 The Man Who Could Not See Stars 50 CHAPTER 3 Spatial Vision: From Spots to Stripes 55 Visual Acuity: Oh Say, Can You See? 55 A Visit to the Eye Doctor 58 Acuity for Low-Contrast Stripes 59 Why Sine Wave Gratings? 61 Retinal Ganglion Cells and Stripes 61 The Lateral Geniculate Nucleus 62 Striate Cortex 64 Topography of the Human Cortex 66 Some Perceptual Consequences of Cortical Magnification 67 Receptive Fields in Striate Cortex 68 Orientation Selectivity 68 Other Receptive-Field Properties 69 Simple and Complex Cells 70 Further Complications 71
4 x CONTENTS Columns and Hypercolumns 72 Selective Adaptation: The Psychologist s Electrode 75 The Site of Selective Adaptation Effects 78 Spatial Frequency Tuned Pattern Analyzers in Human Vision 78 The Development of Spatial Vision 80 Development of the Contrast Sensitivity Function 81 The Girl Who Almost Couldn t See Stripes 82 CHAPTER 4 Perceiving and Recognizing Objects 85 What and Where Pathways 85 The Problems of Perceiving and Recognizing Objects 91 Middle Vision 93 Finding Edges 93 Texture Segmentation and Grouping 96 Perceptual Committees Revisited 99 Figure and Ground 101 Dealing with Occlusion 103 CHAPTER 5 The Perception of Color 117 Basic Principles of Color Perception 117 Three Steps to Color Perception 117 Step 1: Color Detection 118 Step 2: Color Discrimination 118 The Problem of Univariance 118 The Trichromatic Solution 120 Metamers 120 The History of Trichromatic Theory 122 A Brief Digression into Lights, Filters, and Finger Paints 123 From Retina to Brain: Repackaging the Information 124 Cone-Opponent Cells in the Retina and LGN 125 Step 3: Color Appearance 125 Three Numbers, Many Colors 125 Parts and Wholes 104 Summarizing Middle Vision 104 From Metaphor to Formal Model 105 Object Recognition 106 Templates versus Structural Descriptions 108 Problems with Structural-Description Theories 110 Multiple Recognition Committees? 111 Faces: An Illustrative Special Case 112 The Pathway Runs in Both Directions: Feedback and Reentrant Processing 113 Opponent Colors 128 Color in the Visual Cortex 131 Adaptation and Afterimages 133 Does Everyone See Colors the Same Way? 134 Does Everyone See Colors the Same Way? Yes 134 Does Everyone See Colors the Same Way? No 135 Does Everyone See Colors the Same Way? Maybe 136 From the Color of Lights to a World of Color 138 CHAPTER 6 Space Perception and Binocular Vision 149 Color Constancy 139 The Problem with the Illuminant 139 Physical Constraints Make Constancy Possible 141 Color Vision in Animals 143 Monocular Cues to Three-Dimensional Binocular Vision and Stereopsis 162 Space 152 Stereoscopes and Stereograms 166 Occlusion 152 Random Dot Stereograms 168 Size and Position Cues 153 Stereo Movies, TV, and Video Games 169 Aerial Perspective 157 Using Stereopsis 170 Linear Perspective 158 Stereoscopic Correspondence 171 Pictorial Depth Cues and Pictures 158 The Physiological Basis of Stereopsis 173 Motion Cues 160 Accommodation and Convergence 162
5 CONTENTS xi Combining Depth Cues 174 The Bayesian Approach Revisited 175 Illusions and the Construction of Space 176 Binocular Rivalry and Suppression 178 Development of Binocular Vision and Stereopsis 180 Abnormal Visual Experience Can Disrupt Binocular Vision 183 CHAPTER 7 Attention and Scene Perception 187 Selection in Space 189 The Spotlight of Attention 190 Visual Search 191 Feature Searches Are Efficient 192 Many Searches Are Inefficient 193 In Real-World Searches, Basic Features Guide Visual Search 194 In Real-World Searches, the Real World Guides Visual Search 194 The Binding Problem in Visual Search 196 Attending in Time: RSVP and the Attentional Blink 197 The Physiological Basis of Attention 200 Attention Could Enhance Neural Activity 200 Attention Could Enhance the Processing of a Specific Type of Stimulus 201 Attention and Single Cells 202 Disorders of Visual Attention 204 Neglect 204 Extinction 205 Balint Syndrome 206 Perceiving and Understanding Scenes 206 Two Pathways to Scene Perception 206 The Nonselective Pathway Computes Ensemble Statistics 207 The Nonselective Pathway Computes Scene Gist and Layout Very Quickly 208 Memory for Objects and Scenes Is Amazingly Good 210 Memory for Objects and Scenes Is Amazingly Bad: Change Blindness 210 What Do We Actually See? 214 CHAPTER 8 Motion Perception 221 Computation of Visual Motion 222 Apparent Motion 224 The Correspondence Problem 225 The Aperture Problem 226 Detection of Global Motion in Area MT 227 Motion Aftereffects Revisited 229 Second-Order Motion 230 Using Motion Information 231 Going with the Flow: Using Motion Information to Navigate 232 Something in the Way You Move: Using Motion Information to Identify Objects 233 Avoiding Imminent Collision: The Tao of Tau 234 Eye Movements 235 Physiology and Types of Eye Movements 236 Eye Movements and Reading 238 Saccadic Suppression and the Comparator 238 Development of Motion Perception 239 The Man Who Couldn t See Motion 240 CHAPTER 9 Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics 243 The Function of Hearing 243 What Is Sound? 244 Basic Qualities of Sound Waves: Frequency and Amplitude 244 Sine Waves and Complex Sounds 246 Basic Structure of the Mammalian Auditory System 249 Outer Ear 249 Middle Ear 249 Inner Ear 250 The Auditory Nerve 256 Auditory Brain Structures 261 Basic Operating Characteristics of the Auditory System 264 Intensity and Loudness 264 Frequency and Pitch 266 Hearing Loss 268
6 xii CONTENTS CHAPTER 10 Hearing in the Environment 275 Sound Localization 275 Interaural Time Difference 276 Interaural Level Difference 279 Cones of Confusion 281 Pinna and Head Cues 282 Auditory Distance Perception 285 Complex Sounds 286 Harmonics 287 Timbre 288 CHAPTER 11 Music and Speech Perception 303 Music 303 Music and Emotion 303 Musical Notes 304 Making Music 307 Modalities and Qualities of Spatial Orientation 331 Sensing Angular Motion, Linear Motion, and Tilt 331 Basic Qualities of Spatial Orientation: Amplitude and Direction 332 The Mammalian Vestibular System 334 Hair Cells: Mechanical Transducers 334 Semicircular Canals 336 Otolith Organs 340 Spatial Orientation Perception 344 Rotation Perception 345 Translation Perception 346 Tilt Perception 347 Auditory Color Constancy 289 Attack and Decay 291 Auditory Scene Analysis 292 Spatial, Spectral, and Temporal Segregation 292 Grouping by Timbre 294 Grouping by Onset 296 When Sounds Become Familiar 297 Continuity and Restoration Effects 298 Restoration of Complex Sounds 299 Speech 309 Speech Production 310 Speech Perception 314 Learning to Listen 319 Speech in the Brain 323 CHAPTER 12 Spatial Orientation and the Vestibular System 329 CHAPTER 13 Touch 363 Touch Physiology 364 The Skin and Its Tactile Receptors 364 From Skin to Brain 369 Pain 373 Pleasant Touch 376 Tactile Sensitivity and Acuity 377 How Sensitive Are We to Mechanical Pressure? 377 How Finely Can We Resolve Spatial Details? 379 How Finely Can We Resolve Temporal Details? 380 Sensory Integration 348 Visual-Vestibular Integration 348 Reflexive Vestibular Responses 350 Vestibulo-Ocular Responses 350 Vestibulo-Autonomic Responses 354 Vestibulo-Spinal Responses 354 Spatial Orientation Cortex 357 Vestibular Thalamocortical Pathways 358 Cortical Influences 358 When the Vestibular System Goes Bad 359 Mal de Debarquement Syndrome 360 Ménière s Syndrome 360 Haptic Perception 380 Perception for Action 381 Action for Perception 381 Role of Fingerprints in Perception and Action 383 The What System of Touch: Perceiving Objects and Their Properties 384 The Where System of Touch: Locating Objects 387 Tactile Spatial Attention 390 Social Touch 391 Interactions between Touch and Other Modalities 392 Haptic Virtual Environments 394
7 CONTENTS xiii CHAPTER 14 Olfaction 399 Olfactory Physiology 399 Odors and Odorants 399 The Human Olfactory Apparatus 400 The Genetic Basis of Olfactory Receptors 406 The Feel of Scent 407 From Chemicals to Smells 407 Theories of Olfactory Perception 407 The Importance of Patterns 410 Odor Mixtures 411 The Power of Sniffing 413 Odor Imagery 413 Olfactory Psychophysics, Identification, and Adaptation 414 Detection, Discrimination, and Recognition 414 Psychophysical Methods for Detection and Discrimination 415 Identification 416 Adaptation 417 Cognitive Habituation 419 Olfactory Hedonics 420 Familiarity and Intensity 420 Nature or Nurture? 420 An Evolutionary Argument 422 Caveats 423 Olfaction, Memory, and Emotion 423 Neuroanatomical and Evolutionary Connections between Odor and Emotion 425 The Vomeronasal Organ, Human Pheromones, and Chemosignals 426 CHAPTER 15 Taste 433 Taste versus Flavor 433 Localizing Flavor Sensations 434 Anatomy and Physiology of the Gustatory System 435 Papillae 436 Taste Buds and Taste Receptor Cells 437 Taste Processing in the Central Nervous System 438 The Four Basic Tastes 439 Salty 439 Sour 440 Bitter 441 Sweet 442 The Survival Value of Taste 444 The Pleasures of Taste 445 Specific Hungers 446 The Special Case of Umami 447 The Special Case of Fat 448 Coding of Taste Quality 449 Taste Adaptation and Cross-Adaptation 450 Genetic Variation in Taste Experience 450 Supertasters 451 Health Consequences of Taste Sensation 453 Pleasure and Retronasal versus Orthonasal Olfaction 453 Chili Peppers 453 Glossary 457 References 473 Photo Credits 489 Index 491
Sensing and Perceiving Our World
 PSYCHOLOGY: Perspectives & Connections 2 nd Edition GREGORY J. FEIST ERIKA L. ROSENBERG Sensing and Perceiving Our World Chapter Four Chapter Preview The Long Strange Trip From Sensation to Perception
PSYCHOLOGY: Perspectives & Connections 2 nd Edition GREGORY J. FEIST ERIKA L. ROSENBERG Sensing and Perceiving Our World Chapter Four Chapter Preview The Long Strange Trip From Sensation to Perception
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
The Perceptual Experience
 Dikran J. Martin Introduction to Psychology Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Pages: 35 TEXT: Lefton, Lester A. and Brannon, Linda (2003). PSYCHOLOGY. (Eighth Edition.) Needham
Dikran J. Martin Introduction to Psychology Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Pages: 35 TEXT: Lefton, Lester A. and Brannon, Linda (2003). PSYCHOLOGY. (Eighth Edition.) Needham
Dikran J. Martin. Psychology 110. Name: Date: Making Contact with the World around Us. Principal Features
 Dikran J. Martin Psychology 110 Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 3 Sensation and Perception: Pages: 31 Making Contact with the World around Us TEXT: Baron, Robert A. (2001). Psychology (Fifth Edition).
Dikran J. Martin Psychology 110 Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 3 Sensation and Perception: Pages: 31 Making Contact with the World around Us TEXT: Baron, Robert A. (2001). Psychology (Fifth Edition).
Review Sheet: Sensation and Perception (6-8%) Sensation. Date Period. 1) sensation. 2) perception. 3) bottom-up processing. 4) top-down processing
 Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet: Sensation and Perception (6-8%) Sensation 1) sensation 2) perception 3) bottom-up processing 4) top-down processing Thresholds 5) psychophysics
Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet: Sensation and Perception (6-8%) Sensation 1) sensation 2) perception 3) bottom-up processing 4) top-down processing Thresholds 5) psychophysics
Answer: B difficulty: 2 conceptual Goal 3: Critical Thinking Skills in Psychology
 Chapter Test 1. The concepts of sensation and perception are different because a. perception is something that happens to your sense organs and neurons; sensation is something that happens to you b. sensation
Chapter Test 1. The concepts of sensation and perception are different because a. perception is something that happens to your sense organs and neurons; sensation is something that happens to you b. sensation
Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction
 Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction Sarah L. Chollar University of California, Riverside sarah.chollar@gmail.com Sensory Systems How the brain allows us to see, hear,
Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction Sarah L. Chollar University of California, Riverside sarah.chollar@gmail.com Sensory Systems How the brain allows us to see, hear,
Psychology Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception. Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed!
 Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
l3;~~?~~~,'0~'~~t~t:~:~~~~~~~~~~!,1
 112 Sensation and Perception Line A should look longer, even though both lines are actually the same length. People who come from noncarpentered cultures that do not use right angles and corners often
112 Sensation and Perception Line A should look longer, even though both lines are actually the same length. People who come from noncarpentered cultures that do not use right angles and corners often
Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds. Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor
 Chapter 8 Sensation and Perception Sec 1: Sensation Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor Perception
Chapter 8 Sensation and Perception Sec 1: Sensation Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor Perception
Practice Test Questions
 Practice Test Questions Multiple Choice 1. Which term is most descriptive of the process of sensation? a. transportation c. selection b. interpretation d. transduction 2. Which terms are most descriptive
Practice Test Questions Multiple Choice 1. Which term is most descriptive of the process of sensation? a. transportation c. selection b. interpretation d. transduction 2. Which terms are most descriptive
Vision Seeing is in the mind
 1 Vision Seeing is in the mind Stimulus: Light 2 Light Characteristics 1. Wavelength (hue) 2. Intensity (brightness) 3. Saturation (purity) 3 4 Hue (color): dimension of color determined by wavelength
1 Vision Seeing is in the mind Stimulus: Light 2 Light Characteristics 1. Wavelength (hue) 2. Intensity (brightness) 3. Saturation (purity) 3 4 Hue (color): dimension of color determined by wavelength
Sensation and Perception: How the World Enters the Mind
 Sensation and Perception: How the World Enters the Mind Copyright Allyn & Bacon 2007 Sensation and Perception Sensation The awareness of properties of an object or event when a sensory receptor is stimulated
Sensation and Perception: How the World Enters the Mind Copyright Allyn & Bacon 2007 Sensation and Perception Sensation The awareness of properties of an object or event when a sensory receptor is stimulated
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
A. Acuity B. Adaptation C. Awareness D. Reception E. Overload
 Unit 4 Review #1 The longer an individual is exposed to a strong odor, the less aware of the odor the individual becomes. This phenomenon is known as sensory A. Acuity B. Adaptation C. Awareness D. Reception
Unit 4 Review #1 The longer an individual is exposed to a strong odor, the less aware of the odor the individual becomes. This phenomenon is known as sensory A. Acuity B. Adaptation C. Awareness D. Reception
Sensory Physiology. Sensory Range Varies. Introduction to the Special Senses. How do we sense the world around us?
 Sensory Physiology How do we sense the world around us? We do not see things as they are; we see things as we are. --Anais Nin Anais Nin, French author 1903-1977 Sensory Range Varies Introduction to the
Sensory Physiology How do we sense the world around us? We do not see things as they are; we see things as we are. --Anais Nin Anais Nin, French author 1903-1977 Sensory Range Varies Introduction to the
Sensation and Perception. 8.2 The Senses
 Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
3. Sensory and Perception
 3. Sensory and Perception Now we will discuss the topics of sensation and perception. This section will cover the different perceptual processes as well as its development. It will also cover the components
3. Sensory and Perception Now we will discuss the topics of sensation and perception. This section will cover the different perceptual processes as well as its development. It will also cover the components
Definition Slides. Sensation. Perception. Bottom-up processing. Selective attention. Top-down processing 11/3/2013
 Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
= add definition here. Definition Slide
 = add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
= add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 5 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 5 1 Chapter in Review 1. Sensing is the process by which our sense organs receive raw physical or chemical energy from the natural world; perception occurs when our brains organize
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 5 1 Chapter in Review 1. Sensing is the process by which our sense organs receive raw physical or chemical energy from the natural world; perception occurs when our brains organize
Sensation and Perception. A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations
 I. Overview Sensation and Perception A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations C. Top-Down vs Bottom-up Processing D. Psychophysics -- thresholds 1.
I. Overview Sensation and Perception A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations C. Top-Down vs Bottom-up Processing D. Psychophysics -- thresholds 1.
Taste buds Gustatory cells extend taste hairs through a narrow taste pore
 The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8. Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017
 V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Topography: mapping of objects in space onto the visual cortex contralateral representation
V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Topography: mapping of objects in space onto the visual cortex contralateral representation
7. Sharp perception or vision 8. The process of transferring genetic material from one cell to another by a plasmid or bacteriophage
 1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 6: Vision
 Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 6: Vision This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 6: Vision This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect. absolute threshold. Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information.
 absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception
 Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation
 Module 19 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions
Module 19 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions
Our Senses & the World CHAPTER 4. Sensations & Senses. Characteristics (continued) Characteristics (continued) Characteristics of All Senses
 CHAPTER 4 Sensations & Senses Our Senses & the World Characteristics of All Senses RECEPTION: Accessory Structures-modify the energy created by something in the person s environment Characteristics TRANSDUCTION:
CHAPTER 4 Sensations & Senses Our Senses & the World Characteristics of All Senses RECEPTION: Accessory Structures-modify the energy created by something in the person s environment Characteristics TRANSDUCTION:
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
AP Psychology Review Chapter 04: Sensation and Perception
 AP Psychology Review Chapter 04: Sensation and Perception 1. What is perception? The process by which the brain organizes and interprets sensation 2. Which senses allow for sensation at a distance? Vision
AP Psychology Review Chapter 04: Sensation and Perception 1. What is perception? The process by which the brain organizes and interprets sensation 2. Which senses allow for sensation at a distance? Vision
Biological Bases of Behavior. 6: Vision
 Biological Bases of Behavior 6: Vision Sensory Systems The brain detects events in the external environment and directs the contractions of the muscles Afferent neurons carry sensory messages to brain
Biological Bases of Behavior 6: Vision Sensory Systems The brain detects events in the external environment and directs the contractions of the muscles Afferent neurons carry sensory messages to brain
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Unit 4 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. Kinesthesis refers to the A) process of organizing and interpreting sensory information. B) diminished sensitivity to an unchanging stimulus. C) quivering eye movements that enable the retina
Name: Date: 1. Kinesthesis refers to the A) process of organizing and interpreting sensory information. B) diminished sensitivity to an unchanging stimulus. C) quivering eye movements that enable the retina
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION
 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION CHAPTER 5 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe transduction, sensation, and perception for the following sensory systems: Vision Audition (hearing) Skin and body Touch Pain Chemical
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION CHAPTER 5 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe transduction, sensation, and perception for the following sensory systems: Vision Audition (hearing) Skin and body Touch Pain Chemical
Chapter 18. The Senses SENSORY RECEPTION. Introduction: Superhuman Senses. Introduction: Superhuman Senses
 Introduction: Superhuman Senses Chapter 18 The Senses! Three senses found in some animals but not humans Echolocation locating objects by detecting echoes of emitted sound waves Electroreception ability
Introduction: Superhuman Senses Chapter 18 The Senses! Three senses found in some animals but not humans Echolocation locating objects by detecting echoes of emitted sound waves Electroreception ability
the human 1 of 3 Lecture 6 chapter 1 Remember to start on your paper prototyping
 Lecture 6 chapter 1 the human 1 of 3 Remember to start on your paper prototyping Use the Tutorials Bring coloured pencil, felts etc Scissor, cello tape, glue Imagination Lecture 6 the human 1 1 Lecture
Lecture 6 chapter 1 the human 1 of 3 Remember to start on your paper prototyping Use the Tutorials Bring coloured pencil, felts etc Scissor, cello tape, glue Imagination Lecture 6 the human 1 1 Lecture
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
Sensation and Perception
 Term Explanation Application/Example/Extension Sensation is the process of using senses to detect or sense information from the environment Your eyes detect light waves, your ears detect sound waves, your
Term Explanation Application/Example/Extension Sensation is the process of using senses to detect or sense information from the environment Your eyes detect light waves, your ears detect sound waves, your
Chapter 5 Test Review. Try the practice questions in the Study Guide and on line
 Chapter 5 Test Review Try the practice questions in the Study Guide and on line Printing game plan Put six slides on a page Select pure black and white as the printing option Okay, now wade into the answers>>>>
Chapter 5 Test Review Try the practice questions in the Study Guide and on line Printing game plan Put six slides on a page Select pure black and white as the printing option Okay, now wade into the answers>>>>
Sense system. Introduction The visual system Hearing. Introduction to sensory mechanisms
 Sense system Introduction The visual system Hearing Introduction to sensory mechanisms Sensory receptors & sense organs Sensory neurons & Receptor cells Adequate stimulus threshold Transduction Receptor
Sense system Introduction The visual system Hearing Introduction to sensory mechanisms Sensory receptors & sense organs Sensory neurons & Receptor cells Adequate stimulus threshold Transduction Receptor
SENSES: VISION. Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014
 SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
Sensation and Perception
 1 Sensation and Perception DR. ARNEL BANAGA SALGADO, Doctor of Psychology (USA) FPM (Ph.D.) Psychology (India) Doctor of Education (Phl) Master of Arts in Nursing (Phl) Master of Arts in Teaching Psychology
1 Sensation and Perception DR. ARNEL BANAGA SALGADO, Doctor of Psychology (USA) FPM (Ph.D.) Psychology (India) Doctor of Education (Phl) Master of Arts in Nursing (Phl) Master of Arts in Teaching Psychology
Introduction to Physiological Psychology
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html This class n Sensation vs. Perception n How light is translated into what we see n Structure
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html This class n Sensation vs. Perception n How light is translated into what we see n Structure
Sensation occurs when external information is picked up by sensory receptors (what your 5 senses do) Perception how your brain interprets the
 Sensory and Perceptual Development Sensation occurs when external information is picked up by sensory receptors (what your 5 senses do) Perception how your brain interprets the information fromyour 5 senses
Sensory and Perceptual Development Sensation occurs when external information is picked up by sensory receptors (what your 5 senses do) Perception how your brain interprets the information fromyour 5 senses
Unit Two: Biopsychology Domain Chapter 3: Senation and Perception. Module 7: Sensation; Module 8: Perception
 Unit Two: Biopsychology Domain Chapter 3: Senation and Perception Module 7: Sensation; Module 8: Perception SENSORY PROCESSES: How Do We Perceive The World? ThEcOwgAvecOla..rat eht saw tac eht The quick
Unit Two: Biopsychology Domain Chapter 3: Senation and Perception Module 7: Sensation; Module 8: Perception SENSORY PROCESSES: How Do We Perceive The World? ThEcOwgAvecOla..rat eht saw tac eht The quick
Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 3 Chapter Overview I. Worksheets II. Introduction III. Sensation III. Perception IV. Pass in your Work Sheets V. Review I. Worksheets: See Handout Packet II. Introduction A. Define sensation B.
Chapter 3 Chapter Overview I. Worksheets II. Introduction III. Sensation III. Perception IV. Pass in your Work Sheets V. Review I. Worksheets: See Handout Packet II. Introduction A. Define sensation B.
Sensation and Perception. Chapter 6
 Sensation and Perception Chapter 6 1 Sensation & Perception How do we construct our representations of the external world? Text To represent the world, we must detect physical energy (a stimulus) from
Sensation and Perception Chapter 6 1 Sensation & Perception How do we construct our representations of the external world? Text To represent the world, we must detect physical energy (a stimulus) from
Sensation and Perception Chapter 6
 Sensation and Perception Chapter 6 Basic Principles Basic Principles Sensation- how sensory receptors and your nervous system receive stimuli I hear, I see Perception- the process of organizing and interpreting
Sensation and Perception Chapter 6 Basic Principles Basic Principles Sensation- how sensory receptors and your nervous system receive stimuli I hear, I see Perception- the process of organizing and interpreting
c. finding it difficult to maintain your balance when you have an ear infection
 Sensory and Perception Quiz- Reynolds Fall 2015 1. The inner ear contains receptors for: a. audition and kinesthesis. b. kinesthesis and the vestibular sense. c. audition and the vestibular sense. d. audition,
Sensory and Perception Quiz- Reynolds Fall 2015 1. The inner ear contains receptors for: a. audition and kinesthesis. b. kinesthesis and the vestibular sense. c. audition and the vestibular sense. d. audition,
14 Taste. 14 Taste versus Flavor. Chapter 14
 14 Taste Chapter 14 14 Taste Taste versus Flavor Anatomy and Physiology The Four Basic Tastes Coding of Taste Quality Genetic Variation in Taste Experience The Pleasures of Taste 14 Taste versus Flavor
14 Taste Chapter 14 14 Taste Taste versus Flavor Anatomy and Physiology The Four Basic Tastes Coding of Taste Quality Genetic Variation in Taste Experience The Pleasures of Taste 14 Taste versus Flavor
Sensation Outline Chapter 5, Psychology, David G Meyers, 7 th Edition
 Sensation Outline Chapter 5, Psychology, David G Meyers, 7 th Edition Sensation the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment
Sensation Outline Chapter 5, Psychology, David G Meyers, 7 th Edition Sensation the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment
Livingston American School Quarterly Lesson Plan
 Livingston American School Quarterly Lesson Plan Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Concept / Topic To Teach: VISION & HEARING OTHER IMPORTANT SENSES & PERCEPTUAL ORGANIZATION Standards Addressed: PERCEPTUAL
Livingston American School Quarterly Lesson Plan Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Concept / Topic To Teach: VISION & HEARING OTHER IMPORTANT SENSES & PERCEPTUAL ORGANIZATION Standards Addressed: PERCEPTUAL
Unit 4 Practice. PSYCHOLOGY SECTION I Time-- Minutes Questions, Unit 4 Practice/Quiz
 PSYCHOLOGY SECTION I Time-- Minutes Questions, Unit 4 Practice/Quiz Unit 4 Practice Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions.
PSYCHOLOGY SECTION I Time-- Minutes Questions, Unit 4 Practice/Quiz Unit 4 Practice Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions.
BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences
 BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences General Psychology: PSY100-1405 & 1708 Prof. Charles Alexander Zorn, Adjunct Lecturer-FALL 2017 Quiz 3 mt,
BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences General Psychology: PSY100-1405 & 1708 Prof. Charles Alexander Zorn, Adjunct Lecturer-FALL 2017 Quiz 3 mt,
Ch 5. Perception and Encoding
 Ch 5. Perception and Encoding Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by Y.-J. Park, M.-H. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang
Ch 5. Perception and Encoding Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by Y.-J. Park, M.-H. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus
 THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. Hue: the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color)
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. Hue: the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color)
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2003
 ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2003 Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Pay careful attention to the point value of questions so that you allocate your time appropriately (1 point = 1 minute).
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2003 Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Pay careful attention to the point value of questions so that you allocate your time appropriately (1 point = 1 minute).
Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II
 Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South AP Psychology Name: Date: Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II Psychophysics study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological
Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South AP Psychology Name: Date: Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II Psychophysics study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological
Special Senses. Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others
 Special Senses Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others Recall our receptor types Chemically regulated: Respond to particular chemicals Voltage regulated: respond to changing membrane potential
Special Senses Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others Recall our receptor types Chemically regulated: Respond to particular chemicals Voltage regulated: respond to changing membrane potential
Senses Other Than Vision. Hearing (Audition) Transmission of Vibrations
 Senses Other Than Vision Hearing The Kinesthetic Senses Touch The Chemical Senses Hearing (Audition) Sound begins as pressure waves in a medium (usually air). The frequency of the pressure waves corresponds
Senses Other Than Vision Hearing The Kinesthetic Senses Touch The Chemical Senses Hearing (Audition) Sound begins as pressure waves in a medium (usually air). The frequency of the pressure waves corresponds
Ch 5. Perception and Encoding
 Ch 5. Perception and Encoding Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by Y.-J. Park, M.-H. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang
Ch 5. Perception and Encoding Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by Y.-J. Park, M.-H. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang
Sensation & Perception Unit Guide
 ΨAP METEA VALLEY PSYCHOLOGY Sensation & Perception Unit Guide Essential Questions What is the difference between sensation and perception, and how are they related? What are the basic sensory concepts
ΨAP METEA VALLEY PSYCHOLOGY Sensation & Perception Unit Guide Essential Questions What is the difference between sensation and perception, and how are they related? What are the basic sensory concepts
Consciousness and Blindsight
 Consciousness and Blindsight Blindsight: The ability to respond appropriately to visual inputs while lacking the feeling of having seen them These patients are unable to see, but are able to reach for
Consciousness and Blindsight Blindsight: The ability to respond appropriately to visual inputs while lacking the feeling of having seen them These patients are unable to see, but are able to reach for
SMELL 2
 SENSORY SYSTEMS 1 SMELL 2 TASTE 3 HEARING 4 TOUCH EQUILIBRIUM 5 PAIN 6 OTHER SENSES 7 HOW DO SENSORY CELLS CONVERT STIMULI INTO ACTION POTENTIALS? HOW DO SENSORY SYSTEMS DETECT CHEMICAL STIMULI? HOW DO
SENSORY SYSTEMS 1 SMELL 2 TASTE 3 HEARING 4 TOUCH EQUILIBRIUM 5 PAIN 6 OTHER SENSES 7 HOW DO SENSORY CELLS CONVERT STIMULI INTO ACTION POTENTIALS? HOW DO SENSORY SYSTEMS DETECT CHEMICAL STIMULI? HOW DO
First Exam. Sensation and Perception. Process of Forming Sensations. Sensation and Perception. The Eye. Our perceptual experience. Mean = 57.
 First Exam Sensation and Perception Mean = 57.5 SD = 11 Source of human knowledge Could we know anything without our senses? Empiricists - John Locke (1632-1704), all knowledge comes from sensory experience
First Exam Sensation and Perception Mean = 57.5 SD = 11 Source of human knowledge Could we know anything without our senses? Empiricists - John Locke (1632-1704), all knowledge comes from sensory experience
PSYC& Lilienfeld et al. - Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception: How We Sense and Conceptualize the World Study Guide
 Many first time college students struggle adjusting to expectations of college-level courses. One reason for this is that college-level courses require students to learn new content and apply that content
Many first time college students struggle adjusting to expectations of college-level courses. One reason for this is that college-level courses require students to learn new content and apply that content
Myers Psychology for AP, 2e David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2014
 Myers Psychology for AP, 2e David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2014 AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP, 2e David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2014 AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
SENSATION & PERCEPTION
 SENSATION & PERCEPTION Sensation and perception result from a symphony of sensory receptors and the neurons those receptors communicate with. The receptors and neurons fire in different combinations and
SENSATION & PERCEPTION Sensation and perception result from a symphony of sensory receptors and the neurons those receptors communicate with. The receptors and neurons fire in different combinations and
Chapter 18 Senses SENSORY RECEPTION 10/21/2011. Sensory Receptors and Sensations. Sensory Receptors and Sensations. Sensory Receptors and Sensations
 SENSORY RECEPTION Chapter 18 Senses s convert stimulus energy to action potentials s 1. Are specialized cells, or 2. Specialized endings that detect stimuli All stimuli are forms of energy s in eyes detect
SENSORY RECEPTION Chapter 18 Senses s convert stimulus energy to action potentials s 1. Are specialized cells, or 2. Specialized endings that detect stimuli All stimuli are forms of energy s in eyes detect
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus
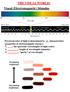 THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. : the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color) 2.
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. : the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color) 2.
Hearing in the Environment
 10 Hearing in the Environment Click Chapter to edit 10 Master Hearing title in the style Environment Sound Localization Complex Sounds Auditory Scene Analysis Continuity and Restoration Effects Auditory
10 Hearing in the Environment Click Chapter to edit 10 Master Hearing title in the style Environment Sound Localization Complex Sounds Auditory Scene Analysis Continuity and Restoration Effects Auditory
Study Guide Chapter 5
 Name: Date: 1. Superman's eyes used, while his brain used. A) perception; sensation B) top-down processing; bottom-up processing C) bottom-up processing; top-down processing D) sensory adaptation; subliminal
Name: Date: 1. Superman's eyes used, while his brain used. A) perception; sensation B) top-down processing; bottom-up processing C) bottom-up processing; top-down processing D) sensory adaptation; subliminal
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
2 Sensing the Environment
 CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
Chapter 29 The Senses
 Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Reading Assignments: Lecture 5: Introduction to Vision. None. Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence
 Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence Lecture 5:. Reading Assignments: None 1 Projection 2 Projection 3 Convention: Visual Angle Rather than reporting two numbers (size of object and distance to observer),
Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence Lecture 5:. Reading Assignments: None 1 Projection 2 Projection 3 Convention: Visual Angle Rather than reporting two numbers (size of object and distance to observer),
BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY I (2012) MIDTERM EXAM 2
 BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY I (2012) MIDTERM EXAM 2 Mark the ONE BEST letter choice (either A, B, C, D, or E) on the computer-graded sheet in NUMBER TWO PENCIL. If you need to erase, do so completely! You MUST
BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY I (2012) MIDTERM EXAM 2 Mark the ONE BEST letter choice (either A, B, C, D, or E) on the computer-graded sheet in NUMBER TWO PENCIL. If you need to erase, do so completely! You MUST
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2007
 ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2007 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, which you ll acknowledge when you turn in your exam. Each multiple-choice question is worth 1 point and the value of the other
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2007 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, which you ll acknowledge when you turn in your exam. Each multiple-choice question is worth 1 point and the value of the other
Construction of the Visual Image
 Construction of the Visual Image Anne L. van de Ven 8 Sept 2003 BioE 492/592 Sensory Neuroengineering Lecture 3 Visual Perception Light Photoreceptors Interneurons Visual Processing Ganglion Neurons Optic
Construction of the Visual Image Anne L. van de Ven 8 Sept 2003 BioE 492/592 Sensory Neuroengineering Lecture 3 Visual Perception Light Photoreceptors Interneurons Visual Processing Ganglion Neurons Optic
4. Which letter in figure 9.1 points to the fovea centralis? Ans: b
 Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
PROGRESS TEST 1. Multiple-Choice Questions. a. wavelength; loudness b. amplitude; loudness c. wavelength; intensity d. amplitude; intensity
 136 Chapter 5 Sensation The receptors for this sense are located in the and --------------~ --------------~ of the inner ear. PROGRESS TEST 1 Multiple-Choice Questions Circle your answers to the following
136 Chapter 5 Sensation The receptors for this sense are located in the and --------------~ --------------~ of the inner ear. PROGRESS TEST 1 Multiple-Choice Questions Circle your answers to the following
Rods vs Cones 3/10/2014. Example 1: Light Sensitive Visual Receptors. Turning Light Waves Into Electrical Messages (Transduction)
 Example 1: Light Sensitive Visual Receptors The typical neuron is designed to receive neurotransmitter messages from other neurons. Sensory receptors, on the other hand, are specialized to receive sensory
Example 1: Light Sensitive Visual Receptors The typical neuron is designed to receive neurotransmitter messages from other neurons. Sensory receptors, on the other hand, are specialized to receive sensory
Nervous System. Made of two parts. Central Peripheral
 Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception 1 Chapters 4 of the required textbook Introduction to Psychology International Edition bv James Kalat (2010) 9 th Edition EXPECTED LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this chapter,
Sensation and Perception 1 Chapters 4 of the required textbook Introduction to Psychology International Edition bv James Kalat (2010) 9 th Edition EXPECTED LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this chapter,
Biology. Slide 1 of 49. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221
 BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Sensation is the conversion of energy from the environment into a pattern of response by the nervous system. Perception is the interpretation of that information. Sensing
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Sensation is the conversion of energy from the environment into a pattern of response by the nervous system. Perception is the interpretation of that information. Sensing
Senses and Sense Organs
 Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Sensation Sensation bottom-down processing Perception top-down processing Psychophysics absolute threshold signal detection theory subliminal
 1 Sensation To represent the world in our heads we must detect physical energy from the environment and encode it as neural signals (sensation) and we must select, organize and interpret our sensations
1 Sensation To represent the world in our heads we must detect physical energy from the environment and encode it as neural signals (sensation) and we must select, organize and interpret our sensations
PHGY 210,2,4 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY. Martin Paré
 PHGY 210,2,4 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Martin Paré Associate Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare PHGY 210,2,4 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
PHGY 210,2,4 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Martin Paré Associate Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare PHGY 210,2,4 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
Prof. Greg Francis 7/7/08
 Perceptual development IIE 366: Developmental Psychology Chapter 5: Perceptual and Motor Development Module 5.1 Basic Sensory and Perceptual Processes Greg Francis Lecture 11 Children and Their Development,
Perceptual development IIE 366: Developmental Psychology Chapter 5: Perceptual and Motor Development Module 5.1 Basic Sensory and Perceptual Processes Greg Francis Lecture 11 Children and Their Development,
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 7. Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses. Copyright Allyn & Bacon 2004
 Chapter 7 Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Chapter 7 Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
JEOPARDY How do Human Sensors Work? Center for Computational Neurobiology, University of Missouri
 JEOPARDY How do Human Sensors Work? Center for Computational Neurobiology, University of Missouri Robot Router Sensors Modes Touch Human WAN WAN Router Sight Sound & Sensors Encapsulation Services Basics
JEOPARDY How do Human Sensors Work? Center for Computational Neurobiology, University of Missouri Robot Router Sensors Modes Touch Human WAN WAN Router Sight Sound & Sensors Encapsulation Services Basics
