Variations in Foramen Transversarium of Cervical Vertebrae-An Observational Study
|
|
|
- Douglas Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
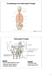
1 DOI: /IJARS/2018/37022:2406 Anatomy Section Original Article Variations in Foramen Transversarium Cervical Vertebrae-An Observational Study Thimmaraju Sumalaa, Bei Manasa ABSTRACT Introduction: Knowledge e anatomical variations e human body is important for us clinically bo for diagnosis and treatment diseases. Vertebral region also presents many variations. Foramen transversarium (FT) is e identification feature cervical vertebrae and give way to neurovascular bundle, vertebral vessels and sympaetic plexus around em. Knowledge e anatomical and surgical variations e FT is very important for radiologists and neurosurgeons for reporting and planning for surgeries on cervical spine as ignorance ese may lead to injury vertebral vessels at may cause headache, migraine, fainting and hearing disturbances. Aim: To observe e incidence double foramina transversarium in e cervical vertebrae and oer variations foramina transversarium. Also to make a note on it s clinical and morphological importance. Materials and Meods: This was a retrospectively designed, single-center study. Total 148 human dried cervical vertebrae (80 typical and 68 atypical) were collected from e Osteology section Department Anatomy, Osmania Medical College, Telangana, India, during e year The collected vertebrae were observed for e presence double FT and also for e oer variations FT. The descriptive statistics were calculated to define e sample. Results: Out 148 human dried cervical vertebrae 80 typical and 68 atypical vertebrae observed for variations in FT. Out 148 human dried cervical vertebrae 17 (11.48%) vertebrae showed e accessory foramina. Out 80 typical cervical vertebrae 13(16.25%) vertebrae showed e accessory foramina and out 68 atypical cervical vertebrae 4(5.88%) vertebrae showed e accessory foramina. Conclusion: These variations may be helpful for planning during neurosurgery for posterior approaches e cervical vertebrae and to avoid post-operative complications. For e radiologist, e anropologist and e anatomist, ese variations are importance and helpful in interpretation e radiological films and also for e academic purpose. Keywords: : foramen, Transverse foramen, Vertebral artery Introduction The cervical spine is formed by e first seven cervical vertebrae in e spine. Cervical spine extends between e base e skull and e oracic spine. Cervical vertebrae are e smallest movable vertebrae and are characterised by e FT, a foramen in each transverse process and a large vertebral canal to accommodate e cervical enlargement e spinal cord. The first (atlas), second (axis) and seven (vertebra prominens) cervical vertebrae are atypical. A typical cervical vertebra has a small, relatively broad vertebral body and a large roughly triangular vertebral foramen. The spinous process is short and bifid. The transverse process cervical vertebrae has dorsal and ventral bars around e FT which terminate laterally as corresponding tubercles. These are connected lateral to e FT by costal or intertubercular lamella. The dorsal and ventral tubercles and e intertubercular lamella represent morphologically e capitellum, tubercle and neck a cervical costal element. The morphological transverse process is represented by e attachment e dorsal bar to e pediculolaminar junction [1]. The presence a FT in e transverse process is e identification feature for cervical vertebrae. In all cervical vertebrae, e FT normally transmits e vertebral artery and vein and a branch from cervicooracic ganglion (vertebral nerve) except seven cervical vertebra where we do not see vertebral artery [1]. Normally, ere is one FT on eier side. Occasionally, it is eier absent or duplicated unilaterally or bilaterally. Cervical spine also presents maximum mobility in contrast wi dorsal and International Journal Anatomy, Radiology and Surgery Jul, Vol-7(3): AO13-AO17 13
2 lumbar segments. Variations e FT cervical vertebrae cause clinical conditions related wi e compression e vertebral arteries which lead to vertebrobasilar insufficiency during neck movements and may cause headache, migraine, fainting attacks and hearing disturbances [2]. The aim e study is to identify e frequency duplication e FT in cervical vertebrae and oer variations foramina transversarium and to discuss e clinical importance ese variations. Materials and Meods This was a retrospectively designed, single-center study. This study was conducted in Department Anatomy, Osmania Medical College, Hyderabad, India, during e year 2016 from March to December around 10 mons. 148 dried human cervical vertebrae were collected from e osteology section e department; among em 80 were typical cervical vertebrae (C3, C4, C5, and C6) and 68 were atypical cervical vertebrae (C1, C2 and C7). The cervical vertebrae collected were from different skeletons not segregated according to age and gender. The broken vertebrae were excluded from e study. Each cervical vertebra was en segregated into typical and atypical group; among atypical again atlas, axis and seven cervical vertebrae were separated. Then from each group all e cervical vertebrae were observed macroscopically for e variations e FT-absence FT, duplication FT and also for e asymmetry FT on bo e sides. Vertebrae wi variations FT were photographed. Statistical Analysis The data was compiled and descriptive analysis was done using Microst Excel stware. Results Out 148 human dried cervical vertebrae 80 typical and 68 atypical vertebrae observed for variations in FT. Out 80 typical cervical vertebrae 13 (16.25%) vertebrae showed e accessory foramina. Among em unilateral duplication was found in 5 (6.25%) cervical vertebrae. Out em right unilateral duplication was found in 3 (3.75%) and left duplication was found in 2 (2.5%) cervical vertebrae. While bilateral duplication was found in 8 (10%) cervical vertebrae. Thus, incidence bilateral double FT was more common an e unilateral one. And asymmetrical FT found in 10 typical cervical vertebrae. In present study, out 148, cervical vertebrae 68 were atypical- 38 C7, 15 C1 and 15 C2 vertebrae. Out 38, C7 vertebrae unilateral FT found in 6 (15.78%), bilateral absent FT in 1 (2.63%), incomplete FT in 1 (2.63%), bilateral accessory FT in 1 (2.63%) and asymmetrical FT in 2 (5.26%). Out 15 C1 vertebrae accessory FT found in 3 (20%) unilateral, incomplete FT in 1(6.66%), asymmetrical FT in 9 (60%), non union costal element/transverse element in 1 (6.66%), retroarticular FT in 1 (6.66%) [Table/Fig-1]. Out 15 C2 vertebrae asymmetrical FT found in 7 (46.66%) vertebrae. Thus, e incidence absence FT was higher in C7 vertebrae. [Table/Fig-2,3]. Illustrates e variations FTaccessory FT, asymmetry FT and absence FT. [Table/Fig-1]: Points to accessory foramen transversarium points to absence foramen transversarium 1, 3, 4 unilateral, 2 bilateral foramen transversarium in cervical vertebrae. [Table/Fig-2]: Cervical vertebrae showing asymmetrical foramena transversaria. In a & b-l>r, in c-r>l Variations FT in Typical Cervical Vertebrae No. Vertebrae FT 13 Asymmetrical FT 10 Total Typical Cervical Vertebrae Showing Variations 23 [Table/Fig-3]: Prevalence variations FT in typical cervical vertebrae. Discussion Vertebrae are formed from e sclerotome portions e somites, which are derived from paraxial mesoderm. A typical vertebra has a body, vertebral arch and a foramen, a transverse process and a spinous process [3]. In e cervical vertebrae vestigial costal element fused to e body and e true transverse process e vertebra to form FT. The vertical part (second part) e vertebral artery lying in e FT is formed from e post-costal anastomosis between e 1 st to 6 cervical inter-segmental arteries [4]. This study dealt wi e variations FT-its presence, absence, asymmetry and presence accessory FT wheer unilateral or bilateral in typical and atypical cervical vertebrae. Among atypical 14 International Journal Anatomy, Radiology and Surgery Jul, Vol-7(3): AO13-AO17
3 Variations FT in C7 Vertebrae No. Vertebrae Unilateral FT 6 Bilateral absent FT 1 Incomplete FT 1 FT-Bilaterally 1 Asymmetrical FT 2 Total C7 Vertebrae Showing Variations 11 [Table/Fig-4]: Prevalence variations FT in C7 vertebrae. Variations FT in C1 Vertebrae No. Vertebrae FT 3 Incomplete FT 1 Asymmetrical FT 9 Non union CE/TE 1 Retro articular FT 1 Total C1 Vertebrae Showing Variations 15 [Table/Fig-5]: Prevalence variations FT in C1 vertebrae. CE-Costal Element; TE Transverse Element Variations FT in C2 Vertebrae No. Vertebrae Asymmetrical FT 7 Total C2 Vertebrae Showing Variations 7 [Table/Fig-6]: Prevalence variations FT in C2 vertebrae. vertebrae atlas, axis and seven cervical vertebrae were observed separately. These were depicted in e [Table/Fig- 4-6]. In typical cervical vertebrae presence or absence accessory FT and asymmetry FT bo sides observed. This can be explained by e variations on e development and course e vertebral artery according to Das S et al., [5]. In seven cervical vertebrae we have observed absence FT unilateral and bilateral, incomplete FT, accessory FT and asymmetrical FT. Usually vertebral artery enters FT C6 vertebra, sometimes FT C7 vertebra. During its course vertebral artery does not have constant caliber wiin FT. FT C7 cervical vertebra may be smaller or absent. Vertebral artery usually does not pass rough e FT C7 vertebra in at case it has vertebral vein and nerve or sometimes fibrous or adipose tissue may be present, which may be e cause for small FT [6]. Sometimes FT can be wider as compared to oer side. This may be due to e tortuosity vertebral artery. Tortuosity reported to cause erosion and enlargement FT and so widening FT [7]. The duplication e vertebral artery could account for e variations e FT [8]. In e first cervical vertebrae we have observed e presence accessory FT, incomplete FT, asymmetrical FT and also nonunion costal element and transverse element. In e second cervical vertebrae we have observed only asymmetrical FT. In e present study e overall prevalence accessory FT was 11.48%. These results [Table/Fig-7]: Atlas showing retroarticular foramen. coincide wi e results Murugan M et al.,, who observed 150 cervical vertebrae and found 12.6% e vertebrae wi accessory FT [9]. In previous studies e overall prevalence accessory FT varied from 1.5% to 23.75% as shown in [Table/Fig-7]. In many studies e prevalence accessory FT was higher an e present study [10-15]. The oer auors had lesser prevalence accessory FT as compared wi e present study [5,16-23]. Chaudhari ML et al., reported had highest prevalence 23.75% [10] and Das S et al., had least prevalence 1.5% [5]. The discrepancy among ese studies could be caused by diverse enic origin e samples studied and by e different meodologies used by e different auors. The C3-C6 segment had a higher Study Chaudhari ML et al., [10] Kaya S et al., [11] Patra A et al., [12] Sharma A et al., [18] Pretty R et al., [19] Chandravadiya L et al., [21 ] Katikireddi RS et al., [22] Muralimanju BV et al., [23] Number vertebrae Foramen Foramen- Unilateral Foramen- Bilateral Present Study [Table/Fig-8]: Prevalence variations FT in different studies. International Journal Anatomy, Radiology and Surgery Jul, Vol-7(3): AO13-AO17 15
4 Study frequency accessory FT, wi a 16.25%, similar to e results El Shaarawy EA et al., who observed e incidence accessory FT as being more common in e lower cervical spine (C5, C6 and C7) [24]. Regarding e laterality e accessory FT, in e present study we have observed a higher unilateral presentation, consistent wi e findings oer auors [10,21,22]. There were many auors who worked on variations accessory FT in cervical vertebrae. A comparison e results ose studies is depicted in [Table/Fig-8,9]. Limitation The sample size was limited and collected from different skeletons and concentrated only on e presence or absence FT. Conclusion The knowledge is variation FT is clinically important in many ways, due to e variations at can be present in e vertebral artery paway. The compression e vertebral artery can produce neurological symptoms, such as headache, migraine, fainting and hearing disturbance. Eier way, it is crucial to know e variations e FT, particularly for e surgeons and neurosurgeons, prior to a posterior cervical surgery. For e radiologist, e importance lies on e interpretation e medical images, such as Computed Tomography (CT scan), Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), and e right presentation e information. This study provides e information about e variations e FT. References Total Das S et al.,[5] (2005) 1.5% Murugan M et al., [9] (2014) 12.6% Kaya S et al.,[11] (2011) 22.7% Patra A et al.,[12] (2015) 22.0% Gupta RV et al.,[13] (2014) 16.5% Shah ST et al.,[14] (2014) 16.1% Ramachandran K et al.,[15] (2014) 15.8% Kumari M et al.,[16] (2015) 9.8% Nagar Y et al.,[17] (1999) 8.6% Sharma A et al.,[18] (2010) 8.0% Pretty R et al.,[19] (2013) 5.7% Patil NP et al.,[20] (2014) 5.7% Chandravadiya L et al.,[21] (2013) 4.7% Katikireddi RS et al., [22] (2014) 3.0% Present Study 11.48% [Table/Fig-9]: Prevalence accessory FT in different studies. [1] Standring S, Gray H. Gray s anatomy. 40 ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; Pp: [2] Caovilla HH, Gananca MM, Munhoz MS, Silva ML, Gananca FF, Silva ML. Cervical syndrome. Most Common Otoneurological Clinical Frames. Sao Paulo: Aeneu Pp: [3] Sadler T, Langman J. Langman s medical embryology. 13 ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Heal/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Pp: 152. [4] Singh I. Human embryology. 10 ed. Jaypee Broers Medical Publishers Pp:262. [5] Das S, Suri R, Kapur V. Double foramen transversaria: An osteological study wi clinical implications. Int Med J. 2005;12: [6] Jovanovic MS. A comparative study e foramen transversarium e six and seven cervical vertebrae. Surg Radiol Anat. 1990;12(3): [7] Brahec DD. Tortuosity Vertebral artery resulting vertebral erosion. J. Manipullative Physiol in Ther. 2000;23: [8] Molinet GM, Robles FP, Roa I. Anatomical variations e foramen transversarium in cervical vertebrae. Int J Morphol. 2017;35(2): [9] Murugan M, Verma S. A study on variations foramen transversarium cer-vical vertebrae. Natl J Clin Anat. (NJCA). 2014;3: [10] Chaudhari ML, Maheria PB, Bachuwar SP. Double foramen transversarium in cervical vertebra: Morphology and clinical importance. IJBAMR. 2013;2: [11] Kaya S, Yilmaz ND, Pusat S, Kural C, Kirik A, Izci Y. Double foramen transversarium variation in ancient Byzantine cervical vertebrae: Preliminary report an anropological study. Turk Neurosurg. 2011;21(4): [12] Patra A, Kaur H, Chhabra U, Kaushal S, Kumar U. Double foramen transversarium in dried cervical vertebra: An osteological study wi its clinical implications. Indian J Oral Sci. 2015;6(1): [13] Gupta RP, Rai A, Gupta N. A study anatomical variations in foramen transversarium and its clinical importance. International Journal Contemporary Surgery. 2014;2: [14] Shah ST, Arora K, Shah KP. Study accessory foramen transversarium in cervical vertebrae. GCSMC (Gujarat Cancer Society Medical College). J Med Sci. 2014;3: [15] Ramachandran K, Ravikumar PC, Manavalan MS. A study on e foramen transversarium in cervical vertebrae. Int J Heal Sci Res. 2014;4: [16] Kumari M, Omar S, Deb S, Alam K. An osteological study on accessory transverse foramina in cervical vertebrae and eir clinical significance. Int J Recent Sci Res. 2015;6: [17] Nagar Y, Taitz C, Reich R. What can we make ese fragments? Excavation at Mamilla cave, byzantine period, Jerusalem. Int J Osteoarchaeol. 1999;9: [18] Sharma A, Kuldeep S, Gupta V, Srivastava S. Double foramen transversarium in cervical vertebra an osteological study. J Anat Soc India. 2010;59(2): [19] Pretty R, Swai RK. Study accessory foramen transversaria in cervical vertebrae. Nitte Univ J Heal Sci. 2013;3(4): [20] Patil NP, Dhapate SS, Porwal S, Bhagwat VB. The study incidence accessory foramen transversaria in e cervical vertebrae. J Dent Med Sci. 2014;13: [21] Chandravadiya L, Shailesh P, Goda J, Chavda V, Ruparelia S, Shamin P. Double foramen transversarium in cervical vertebra: morphology and clinical importance. Int J Res Med. 2013;2(1): [22] Katikireddi RS, Setty SNRS. A study double foramen transversarium in dried cervical vertebra. Int J Heal Sci Res. 2014; 4(1): [23] Murlimanju BV, Prabhu LV, Shilpa K, Rai R, Dhananjaya KV, Jiji PJ. transverse foramina in e cervical spine: incidence, embryological basis, morphology and surgical importance. 16 International Journal Anatomy, Radiology and Surgery Jul, Vol-7(3): AO13-AO17
5 [24] Turkish Neurosurg. 2011; 21(3): El Shaarawy EA, Sabry SM, El Gammaroy T, Nasr LE. Morphology and morphometry e foramina transversaria cervical vertebrae: A correlation wi e position e vertebral artery. Kasr El Aini Medical Journal. 2010:10. AUTHOR(S): 1. Dr. Thimmaraju Sumalaa 2. Dr. Bei Manasa PARTICULARS OF CONTRIBUTORS: 1. Associate Pressor, Department Anatomy, Government Medical College, Mahabubnagar, Hyderabad, Telangana, India. 2. Assistant Pressor, Department Anatomy, Mallareddy Medical College for women, Hyderabad, Telangana, India. NAME, ADDRESS, ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Dr. Bei Manasa, /5, Plot No. 3, Road No. 1, Vijayapuri Colony, Koapet, Hyderabad , Telangana, India. beimanasa@yahoo.co.in Financial OR OTHER COMPETING INTERESTS: None. Date Publishing: Jul 01, 2018 International Journal Anatomy, Radiology and Surgery Jul, Vol-7(3): AO13-AO17 17
THE STUDY OF CERVICAL VERTEBRAE SHOWING VARIATIONAL PRESENTATION OF FORAMEN TRANSVERSARIUM
 Original Article THE STUDY OF CERVICAL VERTEBRAE SHOWING VARIATIONAL PRESENTATION OF FORAMEN TRANSVERSARIUM M.Y Dofe * 1, A.P Kasote 2, M.M Meshram 3. *1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor
Original Article THE STUDY OF CERVICAL VERTEBRAE SHOWING VARIATIONAL PRESENTATION OF FORAMEN TRANSVERSARIUM M.Y Dofe * 1, A.P Kasote 2, M.M Meshram 3. *1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Study on the Foramen Transversarium in Cervical Vertebrae Kalpana Ramachandran 1, Parvathavarthine
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Study on the Foramen Transversarium in Cervical Vertebrae Kalpana Ramachandran 1, Parvathavarthine
AN OSTEOLOGICAL STUDY OF FORAMEN TRASVERSARIUM: VARIATIONS AND CLINICAL ASPECTS Yogesh Yadav 1, Preeti Goswami 2, Veena Bharihoke 3
 AN OSTEOLOGICAL STUDY OF FORAMEN TRASVERSARIUM: VARIATIONS AND CLINICAL ASPECTS Yogesh Yadav 1, Preeti Goswami 2, Veena Bharihoke 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Yogesh Yadav, Preeti Goswami, Veena Bharihoke.
AN OSTEOLOGICAL STUDY OF FORAMEN TRASVERSARIUM: VARIATIONS AND CLINICAL ASPECTS Yogesh Yadav 1, Preeti Goswami 2, Veena Bharihoke 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Yogesh Yadav, Preeti Goswami, Veena Bharihoke.
Analysis of the cervical double transverse foramen in present Spanish population
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Eur. J. Anat. 20 (4): 337-346 (2016) Analysis of the cervical double transverse foramen in present Spanish population Laura Quiles-Guiñau 1, Azucena Gomez-Cabrero 2, Marcos Miquel-Feucht
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Eur. J. Anat. 20 (4): 337-346 (2016) Analysis of the cervical double transverse foramen in present Spanish population Laura Quiles-Guiñau 1, Azucena Gomez-Cabrero 2, Marcos Miquel-Feucht
Original article: Variations in morphometry of foramina transversaria and vertebral artery in subaxial cervical region and its Surgical implications
 Original article: Variations in morphometry of foramina transversaria and vertebral artery in subaxial cervical region and its Surgical implications Dr. Richa Gupta*, Dr. KanchanKapoor**, Dr. SumanKochhar
Original article: Variations in morphometry of foramina transversaria and vertebral artery in subaxial cervical region and its Surgical implications Dr. Richa Gupta*, Dr. KanchanKapoor**, Dr. SumanKochhar
Department of Anatomy and Human Embryology. School of Medicine. University of Valencia (Spain) 2
 IJAE Vol. 122, n. 1: 27-38, 2017 ITALIAN JOURNAL OF ANATOMY AND EMBRYOLOGY Research article - Basic and applied anatomy Double transverse foramen in cervical vertebrae in a Spanish rural population of
IJAE Vol. 122, n. 1: 27-38, 2017 ITALIAN JOURNAL OF ANATOMY AND EMBRYOLOGY Research article - Basic and applied anatomy Double transverse foramen in cervical vertebrae in a Spanish rural population of
Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of th
 Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of the fact that they support the least load. In humans,
Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of the fact that they support the least load. In humans,
Series of vertebral synostosis-clinically implied
 Original article: Series of vertebral synostosis-clinically implied Dr. Somanath Deepa, Dr. Rajasekar SS Department of Anatomy, Sri Manakula Vinayagar Medical College and Hospital, Puducherry (U.T.), India.
Original article: Series of vertebral synostosis-clinically implied Dr. Somanath Deepa, Dr. Rajasekar SS Department of Anatomy, Sri Manakula Vinayagar Medical College and Hospital, Puducherry (U.T.), India.
human anatomy 2015 lecture four Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW
 INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
Fusion of axis with third cervical vertebra: a case report
 284 Saba et al - Fusion of axis with third cervical vertebra Fusion of axis with third cervical vertebra: a case report N. Saba 1, A. Rani 1, G. Sehgal 1, Rk Verma 1, Ak Srivastava 1, M. Faheem 2 1 Department
284 Saba et al - Fusion of axis with third cervical vertebra Fusion of axis with third cervical vertebra: a case report N. Saba 1, A. Rani 1, G. Sehgal 1, Rk Verma 1, Ak Srivastava 1, M. Faheem 2 1 Department
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
OCCIPITO-CERVICAL SYNOSTOSIS: ITS OCCURANCE AND EMBRYOLOGICAL BASIS
 Original Research Article OCCIPITO-CERVICAL SYNOSTOSIS: ITS OCCURANCE AND EMBRYOLOGICAL BASIS Rakesh Kumar Diwan *, Deepshikha Kori, R.K Verma, A.K Pankaj, Garima Sehgal, Sushma Tomar. ABSTRACT Introduction:
Original Research Article OCCIPITO-CERVICAL SYNOSTOSIS: ITS OCCURANCE AND EMBRYOLOGICAL BASIS Rakesh Kumar Diwan *, Deepshikha Kori, R.K Verma, A.K Pankaj, Garima Sehgal, Sushma Tomar. ABSTRACT Introduction:
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE
 THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
STUDY OF PLEUROAPOPHYSEAL MALFORMATION OF HUMAN ATLAS VERTEBRAE AND ITS CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE IN WESTERN MAHARASHTRA REGION
 Original Research Article STUDY OF PLEUROAPOPHYSEAL MALFORMATION OF HUMAN ATLAS VERTEBRAE AND ITS CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE IN WESTERN MAHARASHTRA REGION Shaikh Jasmeen Vajir * 1, Shaikh Shirin Vajir 2. ABSTRACT
Original Research Article STUDY OF PLEUROAPOPHYSEAL MALFORMATION OF HUMAN ATLAS VERTEBRAE AND ITS CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE IN WESTERN MAHARASHTRA REGION Shaikh Jasmeen Vajir * 1, Shaikh Shirin Vajir 2. ABSTRACT
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN. Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms.
 THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
You have 24 vertebrae in your spinal column. Two are special enough to be individually named.
 You have 24 vertebrae in your spinal column. Two are special enough to be individually named. Your atlas (C01) and axis (C02) are very important vertebrae. Without them, head and neck movement would be
You have 24 vertebrae in your spinal column. Two are special enough to be individually named. Your atlas (C01) and axis (C02) are very important vertebrae. Without them, head and neck movement would be
Anatomy and Physiology II. Spine
 Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Morphometric Study of Atlas Vertebrae in South Indian Population Yogesh M 1, Hemanth Raj M
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Morphometric Study of Atlas Vertebrae in South Indian Population Yogesh M 1, Hemanth Raj M
Gross Anatomy Faculty: Gross Anatomy Faculty: Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Melissa McGinn. Welcome to Gross and Developmental Anatomy
 Welcome to Gross and Developmental Anatomy M1 Anatomy Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Richard Krieg Dr. Milton Sholley Dr. David Simpson 1 2 Gross Anatomy Faculty: Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Steve Gudas Dr.
Welcome to Gross and Developmental Anatomy M1 Anatomy Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Richard Krieg Dr. Milton Sholley Dr. David Simpson 1 2 Gross Anatomy Faculty: Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Steve Gudas Dr.
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Sectioned spinous process. Interspinous.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
Radiological Analysis of Ponticulus Posticus in Koreans
 Yonsei Med J 50(1):45-49, 2009 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.1.45 Radiological Analysis of Ponticulus Posticus in Koreans Department of Neurosurgery, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Yonsei Med J 50(1):45-49, 2009 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.1.45 Radiological Analysis of Ponticulus Posticus in Koreans Department of Neurosurgery, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Synostosis of First and Second Ribs: A Case Report
 Synostosis of First and Second Ribs: A Case Report VIDYA K. SHIVAKUMAR 1 & PRIYA RANGANATH 2 Department of Anatomy, Bangalore Medical College & Research Institute, Bangalore 560002, Karnataka E-mail: priya_ranganath@rediffmail.com
Synostosis of First and Second Ribs: A Case Report VIDYA K. SHIVAKUMAR 1 & PRIYA RANGANATH 2 Department of Anatomy, Bangalore Medical College & Research Institute, Bangalore 560002, Karnataka E-mail: priya_ranganath@rediffmail.com
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Case Report Spina Bifida of fifth lumbar vertebrae associated with absence of spinous process, laminae and inferior articular processes A case report
 Case Report Spina Bifida of fifth lumbar vertebrae associated with absence of spinous process, laminae and inferior articular processes A case report Dr. Dona Saha, Dr. Madhushree Pal Demonstrator, Department
Case Report Spina Bifida of fifth lumbar vertebrae associated with absence of spinous process, laminae and inferior articular processes A case report Dr. Dona Saha, Dr. Madhushree Pal Demonstrator, Department
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM
 AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
Incidence of Ponticles in Human Atlas Vertebrae - A Study from South Gujarat Population
 Original Research Incidence of Ponticles in Human Atlas Vertebrae - A Study from South Gujarat Population Nitixa P. Patel 1,*, Deepa S.Gupta 2, Nisha D. Parmar 3 1 3 rd Year Resident, 2 Professor & Head,
Original Research Incidence of Ponticles in Human Atlas Vertebrae - A Study from South Gujarat Population Nitixa P. Patel 1,*, Deepa S.Gupta 2, Nisha D. Parmar 3 1 3 rd Year Resident, 2 Professor & Head,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls
 Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls Presenters Dr. Rob Donkin Functional Anatomy Current research Cervical Radiculopathy Dr. Gert Ferreira Red flags Case Study Kinesio Taping Chris Neethling Gonstead adjusting
Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls Presenters Dr. Rob Donkin Functional Anatomy Current research Cervical Radiculopathy Dr. Gert Ferreira Red flags Case Study Kinesio Taping Chris Neethling Gonstead adjusting
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY. Department of human anatomy
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline дисципліна HUMAN ANATOMY Module 1 Content module 2 The theme of the lesson Sacrum. Coccyx. Ribs. Chest.
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline дисципліна HUMAN ANATOMY Module 1 Content module 2 The theme of the lesson Sacrum. Coccyx. Ribs. Chest.
Morphometric analysis of the mental foramen in adult human mandible in saurashtra region
 International Scholars Journals International Journal of Anatomy and Physiology ISSN 2326-7275 Vol. 4 (6) pp. 081-084, September, 2015. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International
International Scholars Journals International Journal of Anatomy and Physiology ISSN 2326-7275 Vol. 4 (6) pp. 081-084, September, 2015. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International
Morphometric study of the Axis vertebra
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Eur J Anat, 16 (2): 98-103 (2012) Morphometric study of the Axis vertebra Shilpa Gosavi 1, Vatsala Swamy 2 1- Dept. of Anatomy, Padmashree Dr.Vitthalrao Vikhe Patil Foundation s Medical
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Eur J Anat, 16 (2): 98-103 (2012) Morphometric study of the Axis vertebra Shilpa Gosavi 1, Vatsala Swamy 2 1- Dept. of Anatomy, Padmashree Dr.Vitthalrao Vikhe Patil Foundation s Medical
Cervical Cooled RF Training Presentation
 Cervical Cooled RF Training Presentation Agenda Patient Selection Considerations Diagnostic Block General Considerations COOLIEF* Cooled RF Technique Posterior Lateral Precautions Summary Appendix 2 Disclaimer
Cervical Cooled RF Training Presentation Agenda Patient Selection Considerations Diagnostic Block General Considerations COOLIEF* Cooled RF Technique Posterior Lateral Precautions Summary Appendix 2 Disclaimer
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
Journal of Biological and Chemical Research An International Peer Reviewed / Refereed Journal of Life Sciences and Chemistry
 Atlanto-Occipital Synostosis: Embryological Basis By Deepshikha Kori, Archana Rani, R.K. Diwan and Ganpat Prasad ISSN 0970-4973 Print ISSN 2319-3077 Online/Electronic Journal Impact Factor: 4.275 Global
Atlanto-Occipital Synostosis: Embryological Basis By Deepshikha Kori, Archana Rani, R.K. Diwan and Ganpat Prasad ISSN 0970-4973 Print ISSN 2319-3077 Online/Electronic Journal Impact Factor: 4.275 Global
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta.
 Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
CALCULATION OF CANAL/BODY RATIO FOR LUMBAR SPINAL CANAL IN DRIED VERTEBRAE IN GUJARAT.
 CALCULATION OF CANAL/BODY RATIO FOR LUMBAR SPINAL CANAL IN DRIED VERTEBRAE IN GUJARAT. Author(s): Kanani SD, Nirvan AB, Patel JP, Shah RK, Dave RV Kanani SD, Nirvan AB*, Patel JP**, Shah RK***, Dave RV
CALCULATION OF CANAL/BODY RATIO FOR LUMBAR SPINAL CANAL IN DRIED VERTEBRAE IN GUJARAT. Author(s): Kanani SD, Nirvan AB, Patel JP, Shah RK, Dave RV Kanani SD, Nirvan AB*, Patel JP**, Shah RK***, Dave RV
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
Vertebral Column. Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions. Cervical
 Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
A morphometric study of the Pedicles of dry human typical lumbar vertebrae
 Original article: A morphometric of the Pedicles of dry human typical lumbar vertebrae Dhaval K. Patil 1 *, Pritha S. Bhuiyan 2 1Resident, Department of Anatomy, Seth G S Medical College, Parel, Mumbai-400012,
Original article: A morphometric of the Pedicles of dry human typical lumbar vertebrae Dhaval K. Patil 1 *, Pritha S. Bhuiyan 2 1Resident, Department of Anatomy, Seth G S Medical College, Parel, Mumbai-400012,
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
Spinal Column. Anatomy Of The Spine
 Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
Skeletal System. Axial Division
 Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings
 Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics. Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6. Typical Cervical Vertebra Anterior 10/5/2017
 Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine. Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University
 Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
Spur on posterior arch of atlas with fatal spinal cord compression - a case report
 CASE REPORT Eur. J. Anat. 20 (1): 87-91 (2016) Spur on posterior arch of atlas with fatal spinal cord compression - a case report Asit K. Sikary 1, Tony G. Jacob 2, Mohan S. Meena 1 1 Department of Forensic
CASE REPORT Eur. J. Anat. 20 (1): 87-91 (2016) Spur on posterior arch of atlas with fatal spinal cord compression - a case report Asit K. Sikary 1, Tony G. Jacob 2, Mohan S. Meena 1 1 Department of Forensic
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics. Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003
 Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
PONTICULUS POSTICUS: ITS INCIDENCE AND IMPLICATIONS FOR SCREW INSERTION INTO LATERAL MASS OF ATLAS: USING PLAIN CERVICAL RADIOGRAPH
 Original Research Article PONTICULUS POSTICUS: ITS INCIDENCE AND IMPLICATIONS FOR SCREW INSERTION INTO LATERAL MASS OF ATLAS: USING PLAIN CERVICAL RADIOGRAPH Hiroli WF * 1, Kasegaonkar MS 2, Gosavi AG
Original Research Article PONTICULUS POSTICUS: ITS INCIDENCE AND IMPLICATIONS FOR SCREW INSERTION INTO LATERAL MASS OF ATLAS: USING PLAIN CERVICAL RADIOGRAPH Hiroli WF * 1, Kasegaonkar MS 2, Gosavi AG
Bony framework of the vertebral column Structure of the vertebral column
 5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
The Thoracic Cage ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process
ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences POSITION OF MANDIBULAR FORAMEN AND INCIDENCE OF ACCESSORY MANDIBULAR FORAMEN IN DRY MANDIBLES
 Research Article Anatomy International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 POSITION OF MANDIBULAR FORAMEN AND INCIDENCE OF ACCESSORY MANDIBULAR FORAMEN IN DRY MANDIBLES RAGHAVENDRA V. P.
Research Article Anatomy International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 POSITION OF MANDIBULAR FORAMEN AND INCIDENCE OF ACCESSORY MANDIBULAR FORAMEN IN DRY MANDIBLES RAGHAVENDRA V. P.
A morphometric study of foramen ovale and foramen spinosum of the human sphenoid bone in the southern Nigerian population
 Journal of Applied Biosciences 26: 1631-1635 ISSN 1997 5902 A morphometric study of foramen ovale and foramen spinosum of the human sphenoid bone in the southern Nigerian population *Osunwoke E.A, Mbadugha
Journal of Applied Biosciences 26: 1631-1635 ISSN 1997 5902 A morphometric study of foramen ovale and foramen spinosum of the human sphenoid bone in the southern Nigerian population *Osunwoke E.A, Mbadugha
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D.
 Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D. Chest cavity - bony structures Chest cavity- bony structures Sternum Ribs True ribs: first seven pairs connect
Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D. Chest cavity - bony structures Chest cavity- bony structures Sternum Ribs True ribs: first seven pairs connect
Anatomy notes-thorax.
 Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
Anatomical study of the sacral hiatus
 Original article Anatomical study of the sacral hiatus Dr. Somanath Deepa, Dr. Rajasekar SS Department of Anatomy, Sri Manakula Vinayagar Medical College and Hospital, Puducherry (U.T.), India. Corresponding
Original article Anatomical study of the sacral hiatus Dr. Somanath Deepa, Dr. Rajasekar SS Department of Anatomy, Sri Manakula Vinayagar Medical College and Hospital, Puducherry (U.T.), India. Corresponding
SUPERIOR AND INFERIOR POLAR ARTERIES TO LEFT KIDNEY N. Shakuntala Rao 1, K. Manivannan 2, Gangadhara 3, H. R Krishna Rao 4
 SUPERIOR AND INFERIOR POLAR ARTERIES TO LEFT KIDNEY N. Shakuntala Rao 1, K. Manivannan 2, Gangadhara 3, H. R Krishna Rao 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: N. Shakuntala Rao, K. Manivannan, Gangadhara, H. R Krishna
SUPERIOR AND INFERIOR POLAR ARTERIES TO LEFT KIDNEY N. Shakuntala Rao 1, K. Manivannan 2, Gangadhara 3, H. R Krishna Rao 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: N. Shakuntala Rao, K. Manivannan, Gangadhara, H. R Krishna
A rare bilateral varaiation in renal vascular pedicle
 Case Report: A rare bilateral varaiation in renal vascular pedicle *Anshu Mishra, *Parmatma Prasad Mishra, **Gyan Prakash Mishra *Department of Anatomy, Integral Institute of Medical Sciences and Research,
Case Report: A rare bilateral varaiation in renal vascular pedicle *Anshu Mishra, *Parmatma Prasad Mishra, **Gyan Prakash Mishra *Department of Anatomy, Integral Institute of Medical Sciences and Research,
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of orthopaedic conditions must be made in conjunction with
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage orthopaedic health. All decisions about the management of orthopaedic conditions must be made in conjunction with
Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report
 SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE
 MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE Vertebrae are your friends Matthew Harper MS-IV LECTURE OBJECTIVES INTRODUCE THE MOST COMMON MODALITIES OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND BASIC TECHNIQUES FOR READING THESE IMAGES
MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE Vertebrae are your friends Matthew Harper MS-IV LECTURE OBJECTIVES INTRODUCE THE MOST COMMON MODALITIES OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND BASIC TECHNIQUES FOR READING THESE IMAGES
Poonam Verma, Anterpreet K. Arora*, Punita Sharma, Anupama Mahajan
 IJAE Vol. 117, n. 2: 118-122, 2012 ITALIAN JOURNAL OF ANATOMY AND EMBRYOLOGY Research Article: Human Anatomy Case Report Variations in branching pattern of renal artery and arrangement of hilar structures
IJAE Vol. 117, n. 2: 118-122, 2012 ITALIAN JOURNAL OF ANATOMY AND EMBRYOLOGY Research Article: Human Anatomy Case Report Variations in branching pattern of renal artery and arrangement of hilar structures
Anatomy of the Nervous System. Brain Components
 Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Inferior view of the skull showing foramina (Atlas of Human Anatomy, 5th edition, Plate 12)
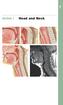 Section 1 Head and Neck Skull, Basal View Incisive foramen Choanae Foramen ovale Foramen lacerum Foramen spinosum Carotid canal Jugular fossa Mastoid process Inferior view of the skull showing foramina
Section 1 Head and Neck Skull, Basal View Incisive foramen Choanae Foramen ovale Foramen lacerum Foramen spinosum Carotid canal Jugular fossa Mastoid process Inferior view of the skull showing foramina
1TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE
 TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
Muscle Action Origin Insertion Nerve Innervation Chapter Page. Deltoid. Trapezius. Latissimus Dorsi
 Muscle Action Origin Insertion Nerve Innervation Chapter Page All Fibers Abduct the shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid Anterior Fibers Flex the shoulder (G/H joint) Horizontally adduct the shoulder
Muscle Action Origin Insertion Nerve Innervation Chapter Page All Fibers Abduct the shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid Anterior Fibers Flex the shoulder (G/H joint) Horizontally adduct the shoulder
The sacrum is a complex anatomical structure.
 A Review Paper Rongming Xu, MD, Nabil A. Ebraheim, MD, and Nicholas K. Gove, MD Abstract Treatment in spinal disorders, sacroiliac joint disruption, and sacral fractures may involve instrumentation of
A Review Paper Rongming Xu, MD, Nabil A. Ebraheim, MD, and Nicholas K. Gove, MD Abstract Treatment in spinal disorders, sacroiliac joint disruption, and sacral fractures may involve instrumentation of
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
A STUDY OF MORPHOMETRY OF SUPERIOR ARTICULAR FACET OF ATLAS AND ITS CLINICAL IMPLICATION IN CENTRAL INDIA
 Original Research Article A STUDY OF MORPHOMETRY OF SUPERIOR ARTICULAR FACET OF ATLAS AND ITS CLINICAL IMPLICATION IN CENTRAL INDIA Ashita Kaore * 1, Ashish U Kamdi 2, A.P. Kasote 3, N.Y.Kamdi 4, M.P.Fulpatil
Original Research Article A STUDY OF MORPHOMETRY OF SUPERIOR ARTICULAR FACET OF ATLAS AND ITS CLINICAL IMPLICATION IN CENTRAL INDIA Ashita Kaore * 1, Ashish U Kamdi 2, A.P. Kasote 3, N.Y.Kamdi 4, M.P.Fulpatil
The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1803.004 The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra Yusof MI, MMed Orth, Hassan
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1803.004 The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra Yusof MI, MMed Orth, Hassan
Variations of Lung Fissures: A Cadaveric Study
 JKIMSU, Vol. 3, No. 1, JanJune 2014 ISSN 22314261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Variations of Lung Fissures: A Cadaveric Study Ambali Manoj P 1*, Jadhav Surekha D 2, Doshi Medha 1, Patil Raosaheb 1 Roy Priya 1, Desai
JKIMSU, Vol. 3, No. 1, JanJune 2014 ISSN 22314261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Variations of Lung Fissures: A Cadaveric Study Ambali Manoj P 1*, Jadhav Surekha D 2, Doshi Medha 1, Patil Raosaheb 1 Roy Priya 1, Desai
Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh. Razi kittaneh. Maher hadidi
 1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
The Thoracic Cage. Role of the Thoracic Cage 2/13/2019. Anatomy 2: Thoracic Cage and Vertebral Column
 PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Anatomy 2: Thoracic Cage and Column The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process 12 thoracic
PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Anatomy 2: Thoracic Cage and Column The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process 12 thoracic
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
DETERMINATION OF SEX USING DRY ADULT HUMAN SACRUM- A MORPHOMETRIC STUDY
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Research Article DETERMINATION OF SEX USING DRY ADULT HUMAN SACRUM- A MORPHOMETRIC STUDY Nisha Yadav 1, Kopal Saini 1, Kalpana Patil 2 1 Department
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Research Article DETERMINATION OF SEX USING DRY ADULT HUMAN SACRUM- A MORPHOMETRIC STUDY Nisha Yadav 1, Kopal Saini 1, Kalpana Patil 2 1 Department
Transitioning to the Suboccipital Triangle. Suboccipital Triangle
 Transitioning to the Suboccipital Triangle Syllabus p. 14-15 Suboccipital Triangle Borders -Rectus capitis posterior major -Obliquus capitis superior -Obliquus capitis inferior Contents -Vertebral artery
Transitioning to the Suboccipital Triangle Syllabus p. 14-15 Suboccipital Triangle Borders -Rectus capitis posterior major -Obliquus capitis superior -Obliquus capitis inferior Contents -Vertebral artery
Sports Medicine Part I : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX
 Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part I : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan 2008 Anatomy of the Upper Body In this section of the
Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part I : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan 2008 Anatomy of the Upper Body In this section of the
Shape and Size of the Transverse Foramina in Japanese. Kunihiko KIMURA, Masayoshi KONISHI and HU Sheng Yu
 Okajimas Foria Anat. Jpn. 62 (2): 123-132, August 1985 Shape and Size of the Transverse Foramina in Japanese By Kunihiko KIMURA, Masayoshi KONISHI and HU Sheng Yu Department of Anatomy, National Defense
Okajimas Foria Anat. Jpn. 62 (2): 123-132, August 1985 Shape and Size of the Transverse Foramina in Japanese By Kunihiko KIMURA, Masayoshi KONISHI and HU Sheng Yu Department of Anatomy, National Defense
CLINICAL EXAM IMAGING AND TREATMENT OF THE NECK
 Arbeitsgruppe Pferd Advanced applications of ultrasound imaging in horses Bonn Germany sept.2010 CLINICAL EXAM IMAGING AND TREATMENT OF THE NECK Philippe HEILES DVM MSc Les Bréviaires France philippeheiles@equineclinic.fr
Arbeitsgruppe Pferd Advanced applications of ultrasound imaging in horses Bonn Germany sept.2010 CLINICAL EXAM IMAGING AND TREATMENT OF THE NECK Philippe HEILES DVM MSc Les Bréviaires France philippeheiles@equineclinic.fr
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D.
 Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
DEFICIENT SACRAL HIATUS CAUSE MECHANICAL LOW BACK PAIN: A RADIOLOGICAL STUDY
 Original Research Article DEFICIENT SACRAL HIATUS CAUSE MECHANICAL LOW BACK PAIN: A RADIOLOGICAL STUDY Ganesh Elumalai * 1, Malarvani Thangamani, Sanjoy Sanyal 1, Palani Kanagarajan 3. ABSTRACT International
Original Research Article DEFICIENT SACRAL HIATUS CAUSE MECHANICAL LOW BACK PAIN: A RADIOLOGICAL STUDY Ganesh Elumalai * 1, Malarvani Thangamani, Sanjoy Sanyal 1, Palani Kanagarajan 3. ABSTRACT International
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives
 Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
The Back. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
Exercise 10. The Axial Skeleton
 Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
