Did I Have a Daddy? A Parthenogenic Problem
|
|
|
- Jasmine Riley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Did I Have a Daddy? A Parthenogenic Problem What Is Parthenogenesis? Parthenogenic species have the ability to reproduce asexually, without need of a male, mating or pollination. Parthenogenesis comes from the Greek words parthenos meaning maiden or virgin and genesis meaning origin or birth. In parthenogenic animals, the offspring are usually all the same sex, and in certain species like whiptail lizards, the entire species is female. Parthenogenesis often happens where there are few or no males of a species in the area. In some cases, should males make a reappearance, the species can still make use of sexual reproduction. Recently in zoos, reptiles like komodo dragons and file snakes were discovered to be capable of this reproductive back-up plan. Q1: Why is parthenogenesis considered an adaptation?: Bdelloid Rotifers Rotifers are a group of microscopic aquatic animals that have evolved into many separate species over the past 40 million years without sexual reproduction. The research has focused on bdelloid rotifers, which live in ponds, rivers, and occasionally wet habitats like soils, mosses, and lichens. Biologists Ridego Fontaneto from the University of Milan and Timothy Barraclough from Imperial College London found evidence of distinct species of the bdelloid rotifers by comparing DNA sequencing and jaw measurements of animals living across the U.K., Italy, and other parts of the world. Asexual animals can evolve and mutate over time, but usually do not diversify or last long. However, records of the bdelloid rotifers show they have been around for more than 40 million years and they have evolved into hundreds of species individually adapted the their environments allowing some to now live in hot springs or the Antarctic waters. Komodo Dragons Komodo dragons, the largest of the lizards, are under threat as wild populations become smaller. Two female Komodo dragons have been kept at separate zoos and have produced offspring, having always been isolated from males. One of these females then produced additional offspring sexually after being introduced to a male. This indicates that Komodo dragons can switch between asexual and sexual reproduction. One of the dragons had never been kept with a male but has produced a clutch of 25 eggs, of which 11 seemed to be viable. Three of the eggs collapsed but the remaining eight eggs developed normally. The parthenogenic adaptation creates homozygous populations in zoos and drastically decreases genetic diversity in these populations. 123
2 Whiptail Lizards Whiptail lizards (genus Aspidoscelis) from Mexico and southwestern U.S. are made up entirely of females and manage to produce well-bred offspring without the aid of male fertilization. The new research by Peter Baumann of Stowers Medical Research Institute reveals that these lizards maintain genetic richness by starting the reproductive process with twice the number of chromosomes as their sexually reproducing cousins. This asexual species resulted from the hybridization of different sexual species, a process that instills the parthenogenic lizards with a great amount of genetic diversity at the beginning. And the researchers found that these species could maintain their genetic diversity by never pairing their homologous chromosomes (as sexual species do by taking one set of chromosomes from each parent during meiosis) but rather by combining their own sister chromosomes instead through fusing two of their own reproductive cells together. Bonnethead Sharks (and other shark species) Female sharks of several species have been observed producing young in institutions like Chicago s Shedd Aquarium where no males were present. Shark pups have been analyzed genetically and the results of these findings heave led scientists to believe that this process occurs more often in the wild than many have thought. Parthenogenesis in sharks raises concerns for shark scientists and researchers. With increased fishing and capture of sharks, the male population has decreased over recent years. Sharks have XY and XX sex chromosomes and females can only produce XX (females) with parthenogenesis. This means that sharks cannot restore the depleted male population with parthenogenesis alone, and must use sexual reproduction to produce more males. Q2: Which species discussed above can produce through either sexual or asexual means? How does having these options benefit these species? Why One Sex? Since species have differences in sex chromosomes, it impacts the sex of the offspring if produced asexually. For example, like humans and other mammals, a female shark is XX and males are XY. Since a female only has a pair of X chromosomes, she can only produce XX offspring (female). Not all species follow the XX/XY design. Reptiles, for example, are the opposite of mammals. Females are XY (called ZW) and males are XX (called ZZ). A female komodo dragon is ZW so she can produce ZZ zygotes and WW zygotes after her chromosome pairs divide in meiosis. Since all organisms need a Z chromosome (or an X chromosome), then zygotes that are WW do not develop. Therefore, all offspring produced by a female (ZW) komodo dragon through parthenogenesis will be male (ZZ). Thus, female reptiles produce male offspring. 124
3 A Cartilagenous Conundrum Sharks and rays are different from other fish as their skeletons are composed of cartilage, not bone. They live in many different types of aquatic ecosystems around the world and have adapted to a host of different environmental conditions. These organisms have been kept in zoos and aquaria and studied but still continue to surprise researchers, especially when it comes to how they reproduce. Zebra sharks are long and sleek, allowing them to wriggle into reef crevices and caves to hunt for their food. Barbels (fleshy feelers) on their snouts help them search for their prey. Zebra sharks hunt at night; in the daytime they usually rest quietly on the bottom, standing on their pectoral (side) fins. To reproduce, male sharks use claspers (modifications of the pelvic fins) to transfer sperm into the female s reproductive tract. The zebra female lays fertilized eggs in tough capsules covered with tufts of filaments, which attach the eggs to the seafloor. But these eggs are certainly not like the eggs most recognize! These are opaque and in a tough casing that protects the shark embryo and its yolk during development. Pictured left: Researcher performing ultrasound on shark egg. Pictured right: Developing shark embryo with yolk within egg. Lise Watson, species coordinator and record keeper for all zebra sharks in North American institutions, must always be mindful of maintaining a healthy, genetically diverse population. Recently, three shark pups were produced and their parents were known. Blood samples from all individuals that inhabit the tank were sent to the laboratory for genetic analysis to determine who produced these pups. In the data provided below, there are individuals from the F1 generation and their offspring, F2 individuals. Be sure to take note of the gender of each individual. Seven (7) genes were genotyped and numbers were assigned. Observe the genotypes below. ID Number Name Sex Generation Gene 1 Gene 2 Gene 3 Gene 4 Gene 5 Gene 6 Gene 7 SF03-07 Yin F F1 191/ / / / / / /196 SF03-06 Yang F F1 177/ / / / / / /182 SF06-10 Ping F F1 199/ / / / / / /160 SF97-02 Pong F F1 189/ / / / / / /196 SF06-11 Jaws M F1 197/ / / / / / /202 SF12-12 Quinn F F2 197/ / / / / / /196 SF Grace F F2 199/ / / / / / /182 SF Ariel F F2 189/ / / / / / /194 The goal of this aquarium is to produce sharks through sexual reproduction so that the gene pool is diverse and each individual has a different complement of genes to pass on to their own offspring. It is their hope that their male, Jaws, fathers offspring that contain some of his unique genes. Q3: What does heterozygous mean? 125
4 Write one heterozygous genotype from Individual SF06-10 here: Q4: What does homozygous mean? Write one homozygous genotype from Individual SF06-10 here: Determining Parentage To determine the parents of each of the F2 individuals, their genotypes must match with ALL of the genotypes of the parent. For Quinn, Grace and Ariel, look at F1 individuals anhhd find the mother first. Then determine if the father contributed any alleles to the offspring. Q5: Who is the mother of Quinn? How do you know? Q6: Is Jaws the father of Quinn? YES NO (Circle one) How do you know? Q7: Who is the mother of Grace? How do you know? Q8: Is Jaws the father of Grace? YES NO (Circle one) How do you know? Q9: Who is the mother of Ariel? How do you know? Q10: Is Jaws the father of Ariel? YES NO (Circle one) How do you know? Q11: Look at the F2 shark pups in the data table. What do all of the F2 individuals have in common? Q12: Based on your answer to the last question, what does this trend tell us? 126
5 Q13: What could this trend do to the gene pool? Q14: What would the researchers want the F2 generation to look like? Q15: Would the gene pool of the sharks be more or less diverse if parthenogenesis was the main form of reproduction? Why? Q16: How might this affect the fitness of the species? Q17: How would meiosis look in a species like the whiptail lizards since the homologous chromosomes never pair and the sister chromosomes instead fuse? Draw a picture here to show how this might work. Science always leads to more questions As you consider your results, write some questions below that you would need answers to in order to improve the chances of sexual reproduction. A) What information would you need in order to answer this question? B) What information would you need in order to answer this question? 127
6 Shedd ing Some Light on Paternity At Chicago s Shedd Aquarium, many successful shark offspring have been produced. However, in an effort to limit inbreeding and maintain genetic diversity in the managed population, paternity and maternity must be known so that relatedness can be determined. The data below came from the population of zebra sharks to determine (1) if the sharks were produced through sexual reproduction or parthenogenesis (asexual), and (2) who the father was if sexual reproduction occurred. Also, pay careful attention to the hatch dates and determine if there were any changes in parentage over time. What could this tell us? Possible Parent Sharks (F1 generation) ID# Dam/Sire Sex Gen Gene 1 Gene 2 Gene 3 Gene 4 Gene 5 Gene 6 Gene Possible dam F F1 191/ / / / / / / Possible dam F F1 187/ / / / / / / Possible F F1 179/ / / / / / /180 dam 254 Possible M F1 187/ / / / / / /196 sire 395 Possible sire M F1 179/ / / / / / / Possible sire 346 Possible sire M F1 199/ / / / / / /188 M F1 187/ / / / / / /182 F2 Offspring ID# Date of Hatch Sex Gen Gene 1 Gene 2 Gene 3 Gene 4 Gene 5 Gene 6 Gene /14/13? F2 187/ / / / / / / /16/13? F2 187/ / / / / / / /17/13? F2 187/ / / / / / / /20/13? F2 187/ / / / / / / /21/13? F2 187/ / / / / / / /24/13? F2 187/ / / / / / / /26/13? F2 187/ / / / / / / /11/13? F2 187/ / / / / / / /14/13? F2 187/ / / / / / / /17/13? F2 193/ / / / / / / /19/13? F2 187/ / / / / / / /30/13? F2 191/ /247 Test fail Test fail 291/ / / /01/13 F F2 179/ / / / / / /182 Sexual or Asexual? 128
7 Q18) What was the more favorable form of reproduction used in this population of sharks How do you know? Q19) Why is this is an advantage? Q20) Propose a hypothesis as to why some offspring my be produced through sexual reproduction Using the genotypes provided in the table above, determine which parent gave each allele to the offspring. In the table below, write the identification numbers for each parent. If there was no father, put ABSENT in the box. ID# Mother ID# Father ID# Q21) Based on current reproductive technologies that are available today, what could be used with the sharks in order to increase the chances of having offspring through sexual reproduction? Explain what would be needed in order for this to be successful: 129
8 Design a Breeding Plan: Describe a plan in order to breed the F2 sharks above below. Who would you pair with whom? Which individuals would you breed? Of these chosen individuals, how many different aquaria would you need to ensure that each individual produces offspring to maintain genetic diversity? You can draw out or explain your breeding plan here: 130
9 131
Biology 321 QUIZ#3 W2010 Total points: 20 NAME
 Biology 321 QUIZ#3 W2010 Total points: 20 NAME 1. (5 pts.) Examine the pedigree shown above. For each mode of inheritance listed below indicate: E = this mode of inheritance is excluded by the data C =
Biology 321 QUIZ#3 W2010 Total points: 20 NAME 1. (5 pts.) Examine the pedigree shown above. For each mode of inheritance listed below indicate: E = this mode of inheritance is excluded by the data C =
Reproduction Review YOU ARE EXPECTED TO KNOW THE MEANING OF ALL THE FOLLOWING TERMS:
 Reproduction Review YOU ARE EXPECTED TO KNOW THE MEANING OF ALL THE FOLLOWING TERMS: CHROMOSOME GENE DNA TRAIT HEREDITY INTERPHASE MITOSIS CYTOKINESIS ASEXUAL BINARY FISSION CELL CYCLE GENETIC DIVERSITY
Reproduction Review YOU ARE EXPECTED TO KNOW THE MEANING OF ALL THE FOLLOWING TERMS: CHROMOSOME GENE DNA TRAIT HEREDITY INTERPHASE MITOSIS CYTOKINESIS ASEXUAL BINARY FISSION CELL CYCLE GENETIC DIVERSITY
This is an extension piece to the lesson, The
 Biology The Amazing Sperm Race Lone Parents: Parthenogenesis in Sharks MATERIALS AND RESOURCES ABOUT THIS EXTENSION None This is an extension piece to the lesson, The Amazing Sperm Race. It includes an
Biology The Amazing Sperm Race Lone Parents: Parthenogenesis in Sharks MATERIALS AND RESOURCES ABOUT THIS EXTENSION None This is an extension piece to the lesson, The Amazing Sperm Race. It includes an
Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7
 Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 20 Q. Cystic fibrosis is a disease which affects in 600 babies. (a) What are the symptoms of cystic fibrosis? (3) Two parents with normal
Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 20 Q. Cystic fibrosis is a disease which affects in 600 babies. (a) What are the symptoms of cystic fibrosis? (3) Two parents with normal
Evolution of gender Sex ratio how many males and females? Sex determination how did they get to be male/female? Some truly weird animals
 1 Roadmap Finishing up inbreeding Evolution of gender Sex ratio how many males and females? Sex determination how did they get to be male/female? Some truly weird animals 2 Midterm Mean 72.6 Range 35-92
1 Roadmap Finishing up inbreeding Evolution of gender Sex ratio how many males and females? Sex determination how did they get to be male/female? Some truly weird animals 2 Midterm Mean 72.6 Range 35-92
Unit 1 Biological Diversity Topic 1.1 Examining Diversity. Text p. 3-15
 Topic 1.1 Examining Diversity. Text p. 3-15 Variation to the MAX! Biologists have identified over species of animals and over species of plants. The most successful life form is What is Biodiversity? The
Topic 1.1 Examining Diversity. Text p. 3-15 Variation to the MAX! Biologists have identified over species of animals and over species of plants. The most successful life form is What is Biodiversity? The
Genetic Variation Junior Science
 2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
Normal enzyme makes melanin (dark pigment in skin and hair) Defective enzyme does not make melanin
 Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with suggestions for implementation are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with suggestions for implementation are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
Mrs. Fanek Asexual/Sexual Reproduction Date
 Name Period Mrs. Fanek Asexual/Sexual Reproduction Date 1. An organism that reproduces asexually will have offspring that have A) the same as both of its parents B) different from either of its parents
Name Period Mrs. Fanek Asexual/Sexual Reproduction Date 1. An organism that reproduces asexually will have offspring that have A) the same as both of its parents B) different from either of its parents
Answers to Questions from old quizzes and exams Problem 1A (i). a (ii) c (iii) a (iv) d
 BIOLOGY 321 SPRING 2013 ANSWERS TO ASSIGNMENT SET #2 Answers to text questions: Chapter 2 http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/iga_10e_sm_chapter_02.pdf Chapter 3 http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/iga_10e_sm_chapter_03.pdf
BIOLOGY 321 SPRING 2013 ANSWERS TO ASSIGNMENT SET #2 Answers to text questions: Chapter 2 http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/iga_10e_sm_chapter_02.pdf Chapter 3 http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/iga_10e_sm_chapter_03.pdf
What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results?
 CHAPTER 5 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results? National
CHAPTER 5 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results? National
Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction. Part 1of 3
 Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction Part 1of 3 UNIT QUESTION: What new information has modern day biology been able to uncover about planarian stem cells and regeneration and what do these findings tell us
Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction Part 1of 3 UNIT QUESTION: What new information has modern day biology been able to uncover about planarian stem cells and regeneration and what do these findings tell us
Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares
 Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares 1 OUTCOME QUESTION(S): S1-1-12: How are the features of the parents inherited to create unique offspring? Vocabulary & Concepts Allele Dominant Recessive Genotype
Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares 1 OUTCOME QUESTION(S): S1-1-12: How are the features of the parents inherited to create unique offspring? Vocabulary & Concepts Allele Dominant Recessive Genotype
2. Circle the genotypes in the table that are homozygous. Explain how the two different homozygous genotypes result in different phenotypes.
 Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with background information are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
Genetics Supplement (These supplementary modules, a Genetics Student Handout, and Teacher Preparation Notes with background information are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/#genetics.
What would happen if organisms in a species did not reproduce?
 Do Now Jan 2, 2019 1. Think about: a. If you could be any living organism for a day, what would you be and why? b. What organism(s) other than Homo sapiens did you notice over break? 2. Make a Name Card
Do Now Jan 2, 2019 1. Think about: a. If you could be any living organism for a day, what would you be and why? b. What organism(s) other than Homo sapiens did you notice over break? 2. Make a Name Card
Page 2. Q1.Figure 1 shows a human body cell. Figure 1. Which part in Figure 1 contains chromosomes? Tick one box. A B C
 Q1.Figure 1 shows a human body cell. Figure 1 (a) Which part in Figure 1 contains chromosomes? Tick one box. A B C (b) Humans have pairs of chromosomes in their body cells. Draw one line from each type
Q1.Figure 1 shows a human body cell. Figure 1 (a) Which part in Figure 1 contains chromosomes? Tick one box. A B C (b) Humans have pairs of chromosomes in their body cells. Draw one line from each type
Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next.
 Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next. Section 1 Mendel and His Peas Key Concept The work of Gregor Mendel explains the
Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next. Section 1 Mendel and His Peas Key Concept The work of Gregor Mendel explains the
The Discovery of Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Traits
 The Discovery of Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Traits Outcomes: 1. Compare the pattern of inheritance produced by genes on the sex chromosomes to that produced by genes on autosomes, as investigated by Morgan.
The Discovery of Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Traits Outcomes: 1. Compare the pattern of inheritance produced by genes on the sex chromosomes to that produced by genes on autosomes, as investigated by Morgan.
Biology Unit III Exam» Form C
 Directions: For each of the following questions, decide which of the choices is best and fill in the corresponding space on the answer document. 1. Which of these sets of chromosomes is found in a single
Directions: For each of the following questions, decide which of the choices is best and fill in the corresponding space on the answer document. 1. Which of these sets of chromosomes is found in a single
3.1 Meiosis
 3.1 Meiosis Chromosome Number Individuals of the same species have the same number of chromosomes. Meiosis is used to half the number of chromosomes passed to the offspring. What is meiosis Meiosis happens
3.1 Meiosis Chromosome Number Individuals of the same species have the same number of chromosomes. Meiosis is used to half the number of chromosomes passed to the offspring. What is meiosis Meiosis happens
Sexual Reproduction. Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction BC Science Probe 9 pages
 Sexual Reproduction Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction BC Science Probe 9 pages 72-105 Why Sex? Textbook Read pages 74 77 Sexual Reproduction Is reproduction involving two parents Each parent contributes equal
Sexual Reproduction Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction BC Science Probe 9 pages 72-105 Why Sex? Textbook Read pages 74 77 Sexual Reproduction Is reproduction involving two parents Each parent contributes equal
TEST NAME:review TEST ID: GRADE:07 Seventh Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom
 TEST NAME:review TEST ID:1070005 GRADE:07 Seventh Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom review Page 1 of 18 Student: Class: Date: 1. There are four blood types: A, B, AB,
TEST NAME:review TEST ID:1070005 GRADE:07 Seventh Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom review Page 1 of 18 Student: Class: Date: 1. There are four blood types: A, B, AB,
Some observations. Some traits are difficult to view as adaptations, because they appear to provide a disadvantage to the organism
 Some traits are difficult to view as adaptations, because they appear to provide a disadvantage to the organism Darwin asked: Can natural selection explain these differences? Structural traits: cumbersome
Some traits are difficult to view as adaptations, because they appear to provide a disadvantage to the organism Darwin asked: Can natural selection explain these differences? Structural traits: cumbersome
Section 8.1 Studying inheritance
 Section 8.1 Studying inheritance Genotype and phenotype Genotype is the genetic constitution of an organism that describes all the alleles that an organism contains The genotype sets the limits to which
Section 8.1 Studying inheritance Genotype and phenotype Genotype is the genetic constitution of an organism that describes all the alleles that an organism contains The genotype sets the limits to which
Objectives. ! Describe the contributions of Gregor Mendel to the science of genetics. ! Explain the Law of Segregation.
 Objectives! Describe the contributions of Gregor Mendel to the science of genetics.! Explain the Law of Segregation.! Explain the Law of Independent Assortment.! Explain the concept of dominance.! Define
Objectives! Describe the contributions of Gregor Mendel to the science of genetics.! Explain the Law of Segregation.! Explain the Law of Independent Assortment.! Explain the concept of dominance.! Define
Genetics & Heredity 11/16/2017
 Genetics & Heredity Biology I Turner College & Career High School 2017 Fertilization is the fusion of an egg and a sperm. Purebred (True breeding plants) are plants that were allowed to selfpollinate and
Genetics & Heredity Biology I Turner College & Career High School 2017 Fertilization is the fusion of an egg and a sperm. Purebred (True breeding plants) are plants that were allowed to selfpollinate and
SEX DETERMINATION AND SEX CHROMOSOMES
 Klug et al. 2006, 2009 Concepts of Genetics Chapter 7 STUDY UNIT 5 SEX DETERMINATION AND SEX CHROMOSOMES Some species reproduce asexually Most diploid eukaryotes reproduce sexually Parent (2n) Parent (2n)
Klug et al. 2006, 2009 Concepts of Genetics Chapter 7 STUDY UNIT 5 SEX DETERMINATION AND SEX CHROMOSOMES Some species reproduce asexually Most diploid eukaryotes reproduce sexually Parent (2n) Parent (2n)
Genetics 1 by Drs. Scott Poethig, Ingrid Waldron, and. Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, Copyright, 2011
 Genetics 1 by Drs. Scott Poethig, Ingrid Waldron, and. Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, Copyright, 2011 We all know that children tend to resemble their parents in appearance.
Genetics 1 by Drs. Scott Poethig, Ingrid Waldron, and. Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, Copyright, 2011 We all know that children tend to resemble their parents in appearance.
This document is a required reading assignment covering chapter 4 in your textbook.
 This document is a required reading assignment covering chapter 4 in your textbook. Chromosomal basis of genes and linkage The majority of chapter 4 deals with the details of mitosis and meiosis. This
This document is a required reading assignment covering chapter 4 in your textbook. Chromosomal basis of genes and linkage The majority of chapter 4 deals with the details of mitosis and meiosis. This
Name: Date: Period: Unit 1 Test: Microevolution (Original Test) Ms. OK, AP Biology,
 Name: Date: Period: Unit 1 Test: Microevolution (Original Test) Ms. OK, AP Biology, 2014-2015 General Directions: Use your time effectively, working as quickly as you can without losing accuracy. Do not
Name: Date: Period: Unit 1 Test: Microevolution (Original Test) Ms. OK, AP Biology, 2014-2015 General Directions: Use your time effectively, working as quickly as you can without losing accuracy. Do not
VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid homologous chromosome sexual reproduction meiosis
 SECTION 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid
SECTION 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid
Q: Do platypus have more functional genes on their Y s than other mammals?
 One minute responses Q: Do platypus have more functional genes on their Y s than other mammals? A: I wasn t able to find out I did learn that the platypus X s and Y s are not homologous to normal mammal
One minute responses Q: Do platypus have more functional genes on their Y s than other mammals? A: I wasn t able to find out I did learn that the platypus X s and Y s are not homologous to normal mammal
4-6 Inheritance Biology
 4-6 Inheritance Biology.0 Figure shows a cell from the small intestine. Figure. Which part of the cell contains chromosomes? Circle one part from the list. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria.2
4-6 Inheritance Biology.0 Figure shows a cell from the small intestine. Figure. Which part of the cell contains chromosomes? Circle one part from the list. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria.2
EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663]
![EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663]](/thumbs/87/96059079.jpg) EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] Student Class Date 1. A particular peach tree produces peaches that are more resistant to disease than other peaches. What method would reproduce these EXACT
EOG Practice:,Evolution & Genetics [126663] Student Class Date 1. A particular peach tree produces peaches that are more resistant to disease than other peaches. What method would reproduce these EXACT
c. Relate Mendelian principles to modern-day practice of plant and animal breeding.
 Course: Biology Agricultural Science & Technology Unit: Genetics in Agriculture STATE STANDARD IV: Students will understand that genetic information coded in DNA is passed from parents to offspring by
Course: Biology Agricultural Science & Technology Unit: Genetics in Agriculture STATE STANDARD IV: Students will understand that genetic information coded in DNA is passed from parents to offspring by
How do living things Sexually Reproduce?
 How do living things Sexually Reproduce? Besides animals, what other things reproduce sexually? Think of a family that has both biological parents and has 2 or more children #1 Consider what the parents
How do living things Sexually Reproduce? Besides animals, what other things reproduce sexually? Think of a family that has both biological parents and has 2 or more children #1 Consider what the parents
Genetics: field of biology that studies heredity, or the passing of traits from parents to offspring Trait: an inherited characteristic, such as eye
 Genetics: field of biology that studies heredity, or the passing of traits from parents to offspring Trait: an inherited characteristic, such as eye colour or hair colour Gregor Mendel discovered how traits
Genetics: field of biology that studies heredity, or the passing of traits from parents to offspring Trait: an inherited characteristic, such as eye colour or hair colour Gregor Mendel discovered how traits
SEX. Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection. Sex: Sources of Genotypic Variation. Genetic Variation
 Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection Sex: Sources of Genotypic Variation Dr. Carol E. Lee, University of Wisconsin Genetic Variation If there is no genetic variation, neither
Genetic Variation: The genetic substrate for natural selection Sex: Sources of Genotypic Variation Dr. Carol E. Lee, University of Wisconsin Genetic Variation If there is no genetic variation, neither
Section 4 Genetics and heredity
 1 Section 4 Genetics and heredity Chapter 21 Cell division, chromosomes and genes Page 182 1. a Gametes are reproductive cells. (i) Plants. The male gametes are the pollen nuclei and are produced in the
1 Section 4 Genetics and heredity Chapter 21 Cell division, chromosomes and genes Page 182 1. a Gametes are reproductive cells. (i) Plants. The male gametes are the pollen nuclei and are produced in the
Lectures 7 & 8 Wednesday, October 12, 2011 & Friday, October 14, 2011
 Lectures 7 & 8 Wednesday, October 12, 2011 & Friday, October 14, 2011 Recombination Diploid organisms: The first step in sexual reproduction is the production of gametes, each of which has half the chromosomes
Lectures 7 & 8 Wednesday, October 12, 2011 & Friday, October 14, 2011 Recombination Diploid organisms: The first step in sexual reproduction is the production of gametes, each of which has half the chromosomes
2017 Version. Key Question types NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948
 2017 Version Key Question types NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948 Linking DNA, Alleles and Chromosomes Chromosomes are made up of DNA. DNA is a large molecule that is coiled into a double helix
2017 Version Key Question types NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948 Linking DNA, Alleles and Chromosomes Chromosomes are made up of DNA. DNA is a large molecule that is coiled into a double helix
The bases on complementary strands of DNA bond with each other in a specific way A-T and G-C
 1 Bio 1101 Lecture 6 (Guided Notes) Ch. 8: Cellular Basis of Reproduction 2 3 4 5 6 Cellular Basis of Reproduction & Inheritance In order for an organism to replace dead cells or to grow and produce new
1 Bio 1101 Lecture 6 (Guided Notes) Ch. 8: Cellular Basis of Reproduction 2 3 4 5 6 Cellular Basis of Reproduction & Inheritance In order for an organism to replace dead cells or to grow and produce new
Mastery. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter Content CHAPTER 3 LESSON 1. Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions.
 Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
The Experiments of Gregor Mendel
 11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel 11.2 Applying Mendel s Principles The Experiments of Gregor Mendel Every living thing (plant or animal, microbe or human being) has a set of characteristics inherited from
11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel 11.2 Applying Mendel s Principles The Experiments of Gregor Mendel Every living thing (plant or animal, microbe or human being) has a set of characteristics inherited from
CADASIL is an inherited disorder caused by a dominant allele. CADASIL leads to weakening of blood vessels in the brain.
 REPRODUCTION PART II Q1. CADASIL is an inherited disorder caused by a dominant allele. CADASIL leads to weakening of blood vessels in the brain. The diagram shows the inheritance of CADASIL in one family.
REPRODUCTION PART II Q1. CADASIL is an inherited disorder caused by a dominant allele. CADASIL leads to weakening of blood vessels in the brain. The diagram shows the inheritance of CADASIL in one family.
The Evolution of Sex. Or, why do we even need males?
 The Evolution of Sex Or, why do we even need males? Sexual VS Asexual reproduction Sexual Fewer offspring/individual Only half of genes passed on Good genotypes are lost Offspring are variable Asexual
The Evolution of Sex Or, why do we even need males? Sexual VS Asexual reproduction Sexual Fewer offspring/individual Only half of genes passed on Good genotypes are lost Offspring are variable Asexual
Chapter 12 Multiple Choice
 Chapter 12 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What did Gregor Mendel do to study different characteristics in his genetics experiments? a.
Chapter 12 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What did Gregor Mendel do to study different characteristics in his genetics experiments? a.
Sexual Reproduction: Adding Variety
 4.3 gamete a sex cell; includes sperm cells in males and egg cells in females fertilization the formation of a zygote by the joining together, or fusion, of two gametes zygote a cell produced by the fusion
4.3 gamete a sex cell; includes sperm cells in males and egg cells in females fertilization the formation of a zygote by the joining together, or fusion, of two gametes zygote a cell produced by the fusion
By Mir Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' CHAPTER CONCEPT NOTES
 Chapter Notes- Genetics By Mir Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' 1 CHAPTER CONCEPT NOTES Relationship between genes and chromosome of diploid organism and the terms used to describe them Know the terms Terms
Chapter Notes- Genetics By Mir Mohammed Abbas II PCMB 'A' 1 CHAPTER CONCEPT NOTES Relationship between genes and chromosome of diploid organism and the terms used to describe them Know the terms Terms
Reproduction. Asexual vs Sexual
 Reproduction Asexual vs Sexual Why is Reproduction Important? The means by which an organism produces offspring Biologically and evolutionarily speaking, reproduction is what has made the continuation
Reproduction Asexual vs Sexual Why is Reproduction Important? The means by which an organism produces offspring Biologically and evolutionarily speaking, reproduction is what has made the continuation
The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Chromosomes
 & Karyotypes The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Homologous Chromosomes Pair of chromosomes (maternal and paternal) that are similar in shape,
& Karyotypes The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Homologous Chromosomes Pair of chromosomes (maternal and paternal) that are similar in shape,
The Living Environment
 Name: Class: 1. Asexual reproduction primarily involves the process of 1) pollination 3) spermatogenesis 2) mitosis 4) ovulation The Living Environment Ms. Fazio Base your answers to questions 4 and 5
Name: Class: 1. Asexual reproduction primarily involves the process of 1) pollination 3) spermatogenesis 2) mitosis 4) ovulation The Living Environment Ms. Fazio Base your answers to questions 4 and 5
Even before he began his experiments on pea plants in the 1860s,
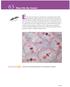 63 Show Me the Genes! The History of the Germ Theory of Disease Activity 37 r e a d i n g Even before he began his experiments on pea plants in the 1860s, Mendel knew that the genes had to be in the male
63 Show Me the Genes! The History of the Germ Theory of Disease Activity 37 r e a d i n g Even before he began his experiments on pea plants in the 1860s, Mendel knew that the genes had to be in the male
Genetics. by their offspring. The study of the inheritance of traits is called.
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Semi-Meiotic hypothesis: Producing new species
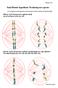 Semi-Meiotic hypothesis: Producing new species Let us begin by reviewing the crucial moment in which mitosis and meiosis differ. Mitosis: Each chromosome replicates itself; one of each goes to the new
Semi-Meiotic hypothesis: Producing new species Let us begin by reviewing the crucial moment in which mitosis and meiosis differ. Mitosis: Each chromosome replicates itself; one of each goes to the new
MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis. (Sections 11-3,11-4;)
 MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis (Sections 11-3,11-4;) RECALL: Mitosis and Meiosis differ in several key ways: MITOSIS: MEIOSIS: 1 round of cell division 2 rounds of cell division Produces
MEIOSIS: Genetic Variation / Mistakes in Meiosis (Sections 11-3,11-4;) RECALL: Mitosis and Meiosis differ in several key ways: MITOSIS: MEIOSIS: 1 round of cell division 2 rounds of cell division Produces
Cross-Dressing or Crossing-Over: Sex Testing of Women Athletes
 Cross-Dressing or Crossing-Over: Sex Testing of Women Athletes Maureen Knabb, Department of Biology, West Chester University, and Joan Sharp, Biological Sciences, Simon Fraser University Caster s Story
Cross-Dressing or Crossing-Over: Sex Testing of Women Athletes Maureen Knabb, Department of Biology, West Chester University, and Joan Sharp, Biological Sciences, Simon Fraser University Caster s Story
12 Biology Revision Notes - Term 3
 QCE Biology Year 2016 Mark 0.00 Pages 21 Published Jan 24, 2017 Revision Notes - Term 3 By Sophie (1 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Sophie. Sophie achieved an ATAR of 1 in 2016
QCE Biology Year 2016 Mark 0.00 Pages 21 Published Jan 24, 2017 Revision Notes - Term 3 By Sophie (1 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Sophie. Sophie achieved an ATAR of 1 in 2016
XY CHROMOSOME MAKES WHAT EPUB
 31 March, 2018 XY CHROMOSOME MAKES WHAT EPUB Document Filetype: PDF 244.84 KB 0 XY CHROMOSOME MAKES WHAT EPUB Is there really scientific evidence that everyone alive descended from one woman? In women,
31 March, 2018 XY CHROMOSOME MAKES WHAT EPUB Document Filetype: PDF 244.84 KB 0 XY CHROMOSOME MAKES WHAT EPUB Is there really scientific evidence that everyone alive descended from one woman? In women,
GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION SENIOR SECONDARY INTERVENTION PROGRAMME LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 SESSION 3 (LEARNER NOTES)
 TOPIC 1: MENDEL S 1 ST LAW, SEX AND BLOOD GROUP DETERMINATION Learner Note: Mendel s Laws are very important and you must understand the basic concepts of Genetics. You must understand the concepts of
TOPIC 1: MENDEL S 1 ST LAW, SEX AND BLOOD GROUP DETERMINATION Learner Note: Mendel s Laws are very important and you must understand the basic concepts of Genetics. You must understand the concepts of
Laws of Inheritance. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The seven characteristics that Mendel evaluated in his pea plants were each expressed as one of two versions, or traits. Mendel deduced from his results that each individual had two
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The seven characteristics that Mendel evaluated in his pea plants were each expressed as one of two versions, or traits. Mendel deduced from his results that each individual had two
Lab 5: Testing Hypotheses about Patterns of Inheritance
 Lab 5: Testing Hypotheses about Patterns of Inheritance How do we talk about genetic information? Each cell in living organisms contains DNA. DNA is made of nucleotide subunits arranged in very long strands.
Lab 5: Testing Hypotheses about Patterns of Inheritance How do we talk about genetic information? Each cell in living organisms contains DNA. DNA is made of nucleotide subunits arranged in very long strands.
The Chromosomes of a Frimpanzee: An Imaginary Animal
 The Chromosomes of a Frimpanzee: An Imaginary Animal Introduction By now, you have heard the terms chromosome, mitosis, and meiosis. You probably also know that chromosomes contain genetic information
The Chromosomes of a Frimpanzee: An Imaginary Animal Introduction By now, you have heard the terms chromosome, mitosis, and meiosis. You probably also know that chromosomes contain genetic information
Human Molecular Genetics Prof. S. Ganesh Department of Biological Sciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Human Molecular Genetics Prof. S. Ganesh Department of Biological Sciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 02 Lecture - 06 Let us test your understanding of Pedigree
Human Molecular Genetics Prof. S. Ganesh Department of Biological Sciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 02 Lecture - 06 Let us test your understanding of Pedigree
15/12/2011. You and your genes (OCR)
 You and your genes (OCR) Variation Variation is the name given to differences between individuals of the SAME species. Variation is due to GENETIC or ENVIRONMENTAL causes. For example, consider dogs: 1)
You and your genes (OCR) Variation Variation is the name given to differences between individuals of the SAME species. Variation is due to GENETIC or ENVIRONMENTAL causes. For example, consider dogs: 1)
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Factors and Genes Mendel s model of inheritance was based on the idea of factors that were independently assorted and segregated into gametes We now know that these
The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Factors and Genes Mendel s model of inheritance was based on the idea of factors that were independently assorted and segregated into gametes We now know that these
Genetic basis of inheritance and variation. Dr. Amjad Mahasneh. Jordan University of Science and Technology
 Genetic basis of inheritance and variation Dr. Amjad Mahasneh Jordan University of Science and Technology Segment 1 Hello and welcome everyone. My name is Amjad Mahasneh. I teach molecular biology at Jordan
Genetic basis of inheritance and variation Dr. Amjad Mahasneh Jordan University of Science and Technology Segment 1 Hello and welcome everyone. My name is Amjad Mahasneh. I teach molecular biology at Jordan
See pedigree info on extra sheet 1. ( 6 pts)
 Biol 321 Quiz #2 Spring 2010 40 pts NAME See pedigree info on extra sheet 1. ( 6 pts) Examine the pedigree shown above. For each mode of inheritance listed below indicate: E = this mode of inheritance
Biol 321 Quiz #2 Spring 2010 40 pts NAME See pedigree info on extra sheet 1. ( 6 pts) Examine the pedigree shown above. For each mode of inheritance listed below indicate: E = this mode of inheritance
For a long time, people have observed that offspring look like their parents.
 Chapter 10 For a long time, people have observed that offspring look like their parents. Even before we knew about genes, people were breeding livestock to get certain traits in the offspring. They knew
Chapter 10 For a long time, people have observed that offspring look like their parents. Even before we knew about genes, people were breeding livestock to get certain traits in the offspring. They knew
Unit D Notebook Directions
 DO NOT PUT THIS FIRST PAGE IN YOUR NOTEBOOK!! Unit D Notebook Directions Immediately following the last page of Unit C, do the following: (Page numbers are not important, but the order needs to be exact)
DO NOT PUT THIS FIRST PAGE IN YOUR NOTEBOOK!! Unit D Notebook Directions Immediately following the last page of Unit C, do the following: (Page numbers are not important, but the order needs to be exact)
Genetics. *** Reading Packet
 Genetics *** Reading Packet 5.4 Mendel and His Peas Learning Objectives Describe Mendel's first genetics experiments. Introduction Why do you look like your family? For a long time people understood that
Genetics *** Reading Packet 5.4 Mendel and His Peas Learning Objectives Describe Mendel's first genetics experiments. Introduction Why do you look like your family? For a long time people understood that
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Meiosis sexual reproduction! Meiosis makes the cells that are responsible for sexual reproduction Sexual Reproduction Producing a new organism by combining chromosomes from
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Meiosis sexual reproduction! Meiosis makes the cells that are responsible for sexual reproduction Sexual Reproduction Producing a new organism by combining chromosomes from
Answers. Reproduction. Year 8 Science Chapter 4
 Answers Reproduction Year 8 Science Chapter 4 p89 1 Asexual reproduction is a method of reproduction by which a single parent produces offspring. The offspring is a clone of the parent (The offspring have
Answers Reproduction Year 8 Science Chapter 4 p89 1 Asexual reproduction is a method of reproduction by which a single parent produces offspring. The offspring is a clone of the parent (The offspring have
GENETICS PREDICTING HEREDITY
 GENETICS PREDICTING HEREDITY INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS Genetics is the scientific study of heredity Heredity is essentially the study of how traits are passed from parents to their offspring. GREGOR MENDEL
GENETICS PREDICTING HEREDITY INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS Genetics is the scientific study of heredity Heredity is essentially the study of how traits are passed from parents to their offspring. GREGOR MENDEL
Genetics. the of an organism. The traits of that organism can then be passed on to, on
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
The bases on complementary strands of DNA bond with each other in a specific way A-T and G-C
 1 Bio 1101 Lecture 6 Ch. 8: Cellular Basis of Reproduction 2 3 4 5 6 Cellular Basis of Reproduction & Inheritance In order for an organism to replace dead cells or to grow and produce new cells, existing
1 Bio 1101 Lecture 6 Ch. 8: Cellular Basis of Reproduction 2 3 4 5 6 Cellular Basis of Reproduction & Inheritance In order for an organism to replace dead cells or to grow and produce new cells, existing
Trait characteristic (hair color) Gene segment of DNA Allele a variety of a trait (brown hair or blonde hair)
 Evolution Change in DNA to favor certain traits over multiple generations Adaptations happen within a single generations Evolution is the result of adding adaptations together Evolution doesn t have a
Evolution Change in DNA to favor certain traits over multiple generations Adaptations happen within a single generations Evolution is the result of adding adaptations together Evolution doesn t have a
.the science that studies how genes are transmitted from one generation to the next.
 Genetics .the science that studies how genes are transmitted from one generation to the next. The chromosomes are contained in the nucleus of the cell. Genes and Chromosomes Chromosomes are made of: Gene:
Genetics .the science that studies how genes are transmitted from one generation to the next. The chromosomes are contained in the nucleus of the cell. Genes and Chromosomes Chromosomes are made of: Gene:
Untitled Document. A. The foxes will eat more wolves. B. The foxes will eat fewer wolves.
 Name: Date: 1. The picture below shows an energy pyramid. What will most likely happen to the foxes and the wolves if the rabbits are removed? A. The foxes will eat more wolves. B. The foxes will eat fewer
Name: Date: 1. The picture below shows an energy pyramid. What will most likely happen to the foxes and the wolves if the rabbits are removed? A. The foxes will eat more wolves. B. The foxes will eat fewer
Name Date Per. Vocabulary Crossword - Chapter 6: Genetics and Heredity M 2 3 D S 11 L P Y 30 L 38 E 45
 Name Date Per. Vocabulary Crossword - Chapter 6: enetics and Heredity 1 2 3 D 5 6 7 4 8 9 10 S 11 12 D 13 16 19 20 21 14 X 17 18 15 P E 22 H D 23 24 25 N 31 32 33 29 26 C B Z 28 I P Y 30 34 V 27 38 T 41
Name Date Per. Vocabulary Crossword - Chapter 6: enetics and Heredity 1 2 3 D 5 6 7 4 8 9 10 S 11 12 D 13 16 19 20 21 14 X 17 18 15 P E 22 H D 23 24 25 N 31 32 33 29 26 C B Z 28 I P Y 30 34 V 27 38 T 41
Period Biology Blizzard Bag #1
 Name Date Period Biology Blizzard Bag #1 Directions: Complete the two OGT review tests from the concepts we covered in the 1 st semester in the spaces provided on the following pages. You may print out
Name Date Period Biology Blizzard Bag #1 Directions: Complete the two OGT review tests from the concepts we covered in the 1 st semester in the spaces provided on the following pages. You may print out
LIFE SCIENCES: PAPER I ANSWER BOOKLET. There are eleven (xi) pages in this Answer Booklet. Please write your examination number in the spaces above.
 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION NOVEMBER 2016 LIFE SCIENCES: PAPER I EXAMINATION NUMBER ANSWER BOOKLET There are eleven (xi) pages in this Answer Booklet. Please write your examination number in
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION NOVEMBER 2016 LIFE SCIENCES: PAPER I EXAMINATION NUMBER ANSWER BOOKLET There are eleven (xi) pages in this Answer Booklet. Please write your examination number in
How Organisms Evolve Chapters The Theory of Evolution. The Theory of Evolution. Evolution can be traced through the fossil record.
 How Organisms Evolve Chapters 14-15 The Theory of Evolution Evolution is the process of change in the inherited traits of a population of organisms from one generation to the next. The inherited traits
How Organisms Evolve Chapters 14-15 The Theory of Evolution Evolution is the process of change in the inherited traits of a population of organisms from one generation to the next. The inherited traits
Cell Division Questions. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Cell Division Questions Mitosis and Meiosis 1 10 Do not write outside the box 5 Figure 3 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 3 E E e e F F f f 5 (a)
Cell Division Questions Mitosis and Meiosis 1 10 Do not write outside the box 5 Figure 3 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 3 E E e e F F f f 5 (a)
Sexual Reproduction & Inheritance
 Sexual Reproduction & Sexual Reproduction & Overview Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Meiosis Genetic Diversity Mendel & The Laws of Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Prokaryotes
Sexual Reproduction & Sexual Reproduction & Overview Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Meiosis Genetic Diversity Mendel & The Laws of Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Prokaryotes
GENETICS - NOTES-
 GENETICS - NOTES- Warm Up Exercise Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. Use the genotype that you came
GENETICS - NOTES- Warm Up Exercise Using your previous knowledge of genetics, determine what maternal genotype would most likely yield offspring with such characteristics. Use the genotype that you came
QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT
 Eighth Grade Science 1 2 3 4 QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT Zanesville City Schools 1 1. [LS 1] [R3] Scientists found fish fossils in the desert. What do the fossils tell about this environment when the fish were
Eighth Grade Science 1 2 3 4 QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT Zanesville City Schools 1 1. [LS 1] [R3] Scientists found fish fossils in the desert. What do the fossils tell about this environment when the fish were
NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948
 NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948 Achievement Criteria Biological ideas relating to genetic variation are limited to concepts and processes connected with: the continuity of life based on the
NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948 Achievement Criteria Biological ideas relating to genetic variation are limited to concepts and processes connected with: the continuity of life based on the
Unit B2, B2.7. Cell division and inheritance. Stage 1. Ovary. Cell Q. Cell P. Cell R. Cell S. 7 Embryo A B C
 Cell division and inheritance 1. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released from the ovary at the same time.
Cell division and inheritance 1. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released from the ovary at the same time.
B. male gametes that may be carried by the wind
 1. Which characteristic of sexual reproduction has specifically favored the survival of animals that live on land? A. fusion of gametes in the outside environment B. male gametes that may be carried by
1. Which characteristic of sexual reproduction has specifically favored the survival of animals that live on land? A. fusion of gametes in the outside environment B. male gametes that may be carried by
4-6 Inheritance Trilogy
 4-6 Inheritance Trilogy.0 Figure shows a cell from the small intestine. Figure. Which part of the cell contains chromosomes? Choose one part from the list. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria.2
4-6 Inheritance Trilogy.0 Figure shows a cell from the small intestine. Figure. Which part of the cell contains chromosomes? Choose one part from the list. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria.2
Mendelian Genetics. 7.3 Gene Linkage and Mapping Genes can be mapped to specific locations on chromosomes.
 7 Extending CHAPTER Mendelian Genetics GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. 7.2 Complex
7 Extending CHAPTER Mendelian Genetics GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. 7.2 Complex
Fertilization. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Fertilization Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction starts with the combination of a sperm and an egg in a process called fertilization. This can occur either inside (internal fertilization) or outside
Fertilization Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction starts with the combination of a sperm and an egg in a process called fertilization. This can occur either inside (internal fertilization) or outside
What creates variation in the offspring of sexually reproducing organisms?
 What creates variation in the offspring of sexually reproducing organisms? 1. genetic recombination during fertilization 2. mitotic division in body cells 62% 3. crossing over in mitosis 4. homologous
What creates variation in the offspring of sexually reproducing organisms? 1. genetic recombination during fertilization 2. mitotic division in body cells 62% 3. crossing over in mitosis 4. homologous
What You ll Learn. Genetics Since Mendel. ! Explain how traits are inherited by incomplete dominance
 Genetics Since Mendel GLE 0707.4.4 Predict the probable appearance of offspring based on the genetic characteristics of the parents. What You ll Learn! Explain how traits are inherited by incomplete dominance!
Genetics Since Mendel GLE 0707.4.4 Predict the probable appearance of offspring based on the genetic characteristics of the parents. What You ll Learn! Explain how traits are inherited by incomplete dominance!
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 4734-1 - Page 1 Warts result when certain viruses cause skin cells to reproduce at a high rate. This rapid reproduction of skin cells is due to the viruses stimulating cellular digestion mitotic
Name: 4734-1 - Page 1 Warts result when certain viruses cause skin cells to reproduce at a high rate. This rapid reproduction of skin cells is due to the viruses stimulating cellular digestion mitotic
3. What law of heredity explains that traits, like texture and color, are inherited independently of each other?
 Section 2: Genetics Chapter 11 pg. 308-329 Part 1: Refer to the table of pea plant traits on the right. Then complete the table on the left by filling in the missing information for each cross. 6. What
Section 2: Genetics Chapter 11 pg. 308-329 Part 1: Refer to the table of pea plant traits on the right. Then complete the table on the left by filling in the missing information for each cross. 6. What
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.2 MENDEL'S LAWS OF INHERITANCE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MENDELS EXPERIMENTS AND LAWS Mendel s Experiments Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk who studied Genetics using pea plants Mendel used pure lines meaning that all offspring
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MENDELS EXPERIMENTS AND LAWS Mendel s Experiments Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk who studied Genetics using pea plants Mendel used pure lines meaning that all offspring
Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Meiosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Mitosis & 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Mitosis Form of cell division that leads to identical daughter cells with the full complement of DNA Occurs in somatic cells Cells of body
Mitosis & 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Mitosis Form of cell division that leads to identical daughter cells with the full complement of DNA Occurs in somatic cells Cells of body
Evidence for evolution in Darwin s time came from several sources: 1. Fossils 2. Geography 3. Embryology 4. Anatomy
 Evidence for evolution in Darwin s time came from several sources: 1. Fossils 2. Geography 3. Embryology 4. Anatomy 1 Fossils in different layers of rock (sedimentary rock strata) have shown: Evidence
Evidence for evolution in Darwin s time came from several sources: 1. Fossils 2. Geography 3. Embryology 4. Anatomy 1 Fossils in different layers of rock (sedimentary rock strata) have shown: Evidence
