Warrior Initiation & Circumcison in the Maasai. Lecture 10: Sexuality and Orgasm
|
|
|
- Shannon Reynolds
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 10: Sexuality and Orgasm Primate Sexuality where do we come from? Concealed ovulation Hormones & Sexual behavior Human Female Orgasm > Physiology > Explanations adaptation or artifact? Warrior Initiation & Circumcison in the Maasai Behavioral Biology of Women
2 Circumcision Found especially in strongly patrilineal and patriarchial societies Symbolizes belonging to a male kin group. Ritual circumcision -- at puberty or after birth Why the penis? Non-religious circumcision developed in English speaking countries at the end of 19th century as cure for masturbation Medical foundation for circumcision debated. US only country in world with routine non-religious circumcision 80% of men in world not circumcised By 1984, 40% of US babies not circumcised. 2
3 Circumcision Functions of Foreskin Protects the glans of the penis Shield glans and urinary opening from irritation due to feces and urine (newborn) and friction Functions of Foreskin Protects the glans of the penis Shield glans and urinary opening from irritation due to feces and urine (newborn) and friction Smegma - produced by Tyson s s glands of Glans Protects the glans Lubricates the glans during intercourse. Changes with Circumcision Cornification of the Glans: Increased thickness (10x) in outer cell layer Free nerve endings disappear Surface cells covered with a layer of dead cells Smega no longer produced for lubrication Skin on penile shaft is tighter Cost & Benefits of Non-Religious Circumcision Costs Benefits Risk of non-essential surgical Possible slight procedure. mutilation or decrease in rates of damage - 1-3% penile cancer and Emotional stress on baby STD s, but study Ulcerations formed around results are equivocal urinary opening 1% risk of urinary Decreased sensitivity of glans tract infection during 1st year of life without Lack of smega production for circumcision lubrication May decrease AIDS Increased tightening of skin risk of shaft 3
4 Examples of Primate Sexuality Examples of Primate Sexuality Primate Sexuality Non-reproductive sexuality is NOT uniquely human Primate Sexuality Sexuality can be situation dependent Mating confined to a few days around ovulation Slight sexual swelling Females solicit mating from silverback male Gorilla Sexuality Chimpanzee Sexuality Promiscuous mating Estrus chimp may copulate x per day Concentration of mating with dominant male(s) mid- cycle 4
5 Function of Estrus Swellings? Attraction of many males to avoid infanticide Incite male-male competition Ensure mating with the dominant male Advertise fecundity Select males with particular genotypes Orangutan Sexuality Females do not show signs of ovulation Variety of sexual behaviors and positions Long periods of mating (3-17 minutes) Forced copulations Mating during periods of high energy balance/hormonal levels Nadler Nadler Nadler Nadler 5
6 A high degree of non-procreative sexual activity Bonobo Sexuality A high degree of non-procreative sexual activity Regular occurrence of female-female sexual behavior Bonobo Sexuality Bonobos Explanations for G-G G G Rubbing Reconciliation Mate attraction Tension Regulation Expression of social status Social bonding/alliance formation Bonobo Testosterone Levels and G-G G Rubbing By Cycle Phase Jurke et al., 2000 Orgasm in Female Primates Rhesus macaques Stumptail macaques Japanese macaques Orangutans Chimpanzees Bonobos All involved manual stimulation, not during intercourse What is our Sexual Inheritance? Primate females are much more actively sexual than previously thought 6
7 What is our Sexual Inheritance? Primate females are much more actively sexual than previously thought Primates engage in sex for other reasons besides procreation What is our Sexual Inheritance? Primate females are much more actively sexual than previously thought Primates engage in sex for other reasons besides procreation Some evidence for orgasm in female primates through manual stimulation Concealed Ovulation in Humans Continuous receptivity in humans strengthened the pair-bond and increased paternal investment in offspring through frequent copulations Concealed Ovulation in Humans Continuous receptivity in humans strengthened the pair-bond and increase paternal investment in offspring through frequent copulations Weakened by: Evidence of high, non-reproductive sexual behavior in non pair-bonding primates (Morris, 1967) Low rates of sexual activity in other pairbonded species (Morris, 1967) Concealed Ovulation in Humans Concealed Ovulation in Humans Force desirable males into consort relationships long enough to ensure paternity and not seek other matings (Alexander and Noonan) Force desirable males into consort relationships long enough to ensure paternity and not seek other matings Raised paternity confidence because other males don t know female is ovulating (Alexander and Noonan) 7
8 Concealed Ovulation in Humans Prevention of women themselves limiting the number of their children because of pain of childbirth. Concealed Ovulation in Humans Prevention of women themselves limiting the number of their children because of pain of childbirth. No evidence modern women do this Concealed ovulation may have evolved before the increase in brain size and thus painful childbirth Concealed Ovulation in Humans Energetically more efficient if humans not living in a multi- male mating system Hormonal Influence on Sexual Behavior Slight rise in testosterone around time of ovulation - some studies show increase in sexual behavior (female initiated) Testosterone and Female Sexual Behavior Western Populations Female Sexuality in!kung Peak in sexual behavior at mid- cycle Husbands and lovers (Worthman, Ph.D. thesis) 8
9 Female Sexuality in!kung Orgasm and Symmetry Peak in sexual behavior at mid- cycle Husbands and lovers Increase in peak rate of orgasm at mid-cycle (Worthman, Ph.D. thesis) Ovulation and Extra-pair copulations Corpus cavernosa Ischiocavernosus muscles Sexual Response Cycle Excitation Vaginal lubrication > Transudation - vasocongestion in walls of vagina lead to moisture Inner 2/3 of vagina expands Cervix and uterus pulled upwards Labia majora flatten and move apart Labia minor and clitoris enlarge Contraction of small muscle fibers in nipples Breast size may increase Veins on breast more visible 9
10 Sexual Response Cycle Excitation Plateau Prominent vasocongestion in outer 2/3 of vagina cause tissue to swell Vagina narrows by 30% or more Clitoris pulled back against pubic bone (hides and protects it from direct touch) Labia minora may double or triple in size Color changes develop Sexual Response Cycle Excitation Plateau Orgasm Through intercourse alone= indirectly from penile shaft distention (manual traction) of labia minora at opening of vagina. Or through direct manual stimulation Contractions at 0.8 second intervals Average time = 4 minutes (masturbation) and 10 minutes (intercourse) Sexual Response Cycle Excitation Plateau Orgasm Resolution Return to pre-orgasmic state % Frequency of Orgasm Frequency of Female Orgasm (western populations) Always Frequently Sometimes Rarely Never How do women achieve orgasm? 95% women said could orgasm easily with masturbation Women masturbate through manual stimulation of clitoris 1.5% through vaginal insertion alone Multiple Orgasms? Women 14% of women Return to the plateau phase, rather than resolution after orgasm Little cross-cultural cultural information 10
11 Multiple Orgasms? Men Pattern seen in pre-pubescent pubescent boys (55%) 8-15% of younger adult males and 3% of adult men Ejaculation seems to prevent return to plateau stage Is The Female Orgasm Adaptive? Female orgasm as non-adaptive Females have low variance in reproductive success (RS) Female orgasm as non-adaptive Females have low variance in reproductive success (RS) Variance in sexual behavior does not effect a woman s s RS (Symons 1979; Gould 1991) (Symons 1979; Gould 1991) Female orgasm as non-adaptive Females have low variance in reproductive success (RS) Variance in sexual behavior does not effect a woman s s RS Female orgasm is a by-product of mammalian bi-sexual potential. Orgasm is possible because it is adaptive for males. Female orgasm as non-adaptive Females have low variance in reproductive success (RS) Variance in sexual behavior does not effect a woman s s RS Female orgasm is a by-product of mammalian bi-sexual potential. Orgasm is possible because it is adaptive for males. Can t t be adaptive because it doesn t t always happen. (Symons 1979; Gould 1991) (Symons 1979; Gould 1991) 11
12 Problems with Non-adaptive Hypothesis Assumes that females in a natural state unlike males breed at or near their reproductive capacity, and that there is little room for natural selection to operate on females Blaffer-Hrdy, 1981 Problems with Non-adaptive Hypothesis Assumes that females in a natural state unlike males breed at or near their reproductive capacity, and that there is little room for natural selection to operate on females Assumption that copulation serves no function other than insemination Blaffer-Hrdy, 1981 Adaptive Hypothesis: Intermittent Reinforcement Female orgasm has been selected to be irregular Increases likelihood of mating Encourage Extra-Pair Copulations (EPC) Non-human primates have orgasms Intermittent Reinforcement Female orgasm has been selected to be irregular Increases likelihood of mating Encourage Extra-Pair Copulations (EPC) Little evidence that human females engaged in closely spaced repeated copulations with multiple males Non-human primates have orgasms But, not during intercourse Blaffer-Hrdy, 1979/1981; Diamond 1980 Blaffer-Hrdy, 1979/1981; Diamond 1980 Is The Female Orgasm Adaptive? Problem with debate: Assumes female orgasm = Female sexuality It is difficult to see how expending time and energy pursuing the will-o-the wisp of sexual satiation, endlessly and fruitlessly attempting to make a bottomless cup run over, could conceivably contribute to a female s reproductive success. On the contrary, insatiability would markedly interfere with the adaptively significant activities of food gathering and preparing and child care. Symons, The Evolution of Human Sexuality,
13 Questions about female sexuality: (1) Is the female orgasm adaptive? (2) Is the clitoris a product of natural selection? (3) Is female sexual response adaptive? Is female orgasm adaptive? Capacity for orgasm may be a universal although not universally realized (Masters & Johnson) but not necessarily from intercourse Non-human primate females appear capable of orgasm (not during intercourse) Orgasm probably not frequent in many cultures Orgasm during intercourse occurs about 1/4 of the time in some studies of western women (should go to fixation if adaptive for intercourse) Problems with adaptive argument Probably does not qualify as a physiological adaptation per se Has the clitoris evolved through natural selection? Function of the clitoris: transmits pleasure upon stimulation that may or may not culminate in orgasm. Has the clitoris evolved through natural selection? Function of the clitoris: transmits pleasure upon stimulation that may or may not culminate in orgasm. The size and position of the clitoris shows variation between primate species Has the clitoris evolved through natural selection? Function of the clitoris: transmits pleasure upon stimulation that may or may not culminate in orgasm. The size and position of the clitoris shows variation between primate species In humans, the clitoris is sometimes removed as a way to control/remove female sexual pleasure. Is female sexual pleasure adaptive? Does the potential for female sexual pleasure affect her behavior and ultimately her reproductive success? 13
14 Is female sexual pleasure adaptive? Does the potential for female sexual pleasure affect her behavior and ultimately her reproductive success? > Increase the probability of seeking extra-pair copulations, which under some circumstances may lead to: _ Improved genetic quality of offspring _ Confusion of paternity and investment from more than one male Is female sexual pleasure adaptive? Does the potential for female sexual pleasure effect her behavior and ultimately her reproductive success? > Increase the probability of seeking extra-pair copulations, which under some circumstances may lead to: _ Improved genetic quality of offspring _ Paternity confusion and investment from more than one male > Strengthen the duration of pair-bond with an investing male influencing offspring survival Is female sexual pleasure adaptive? Does female arousability (or orgasm) increase the probability of conception? > Arousability facilitates copulation Orgasm & Sperm Retention > Orgasm and sperm retention Baker & Bellis, 1993 Orgasm & Sperm Retention Female Orgasm and Male Ejaculation 35% sperm ejected by female within 30 minutes Sperm retention influenced by female orgasm Orgasm more than 1 minute before male ejaculation led to highest level of sperm retention Sperm from one copulation hindered retention of sperm at next copulation up to 8 days Baker & Bellis, 1993 Baker & Bellis,
15 Female Orgasm and Male Ejaculation Intercourse and oxytocin release Timing isn t t right Don t t know how much ejaculated, thus hard to measure flow-back accurately Small sample size, certain individuals over sampled Hasn t t been replicated Intercourse alone causes release of oxytocin Oxytocin may increase sperm uptake Is female sexual pleasure adaptive? Does female arousability (or orgasm) increase the probability of conception? > Arousability facilitates copulation > Orgasm and sperm retention >Evidence not good for orgasm and sperm retention >IS evidence for a role of intercourse in oxytocin release and sperm retention Female Sexual Adaptations: (1) Is the female orgasm adaptive? No, Probably has not been selected for independently (2) Is the clitoris a product of natural selection? Yes, shows evidence of this. (3) Is female sexual response adaptive? Yes, there is evidence of this Next Time Male Reproductive Strategies Male Reproductive Strategies Control of Females & Female Sexuality Evolution of Patriarchy Fathering 15
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
Sexual Anatomy. Monday, 30 March 2009
 Sexual Anatomy 1 2 3 Fallopian Tube Ovary Uterus Bladder Cervix Pubic bone Clitoris Urethra Rectum Vagina Anus G Spot 4 Variety of Vulvae 5 Bladder Corpus Cavernosum Rectum Seminal Vesicle Prostate Glans
Sexual Anatomy 1 2 3 Fallopian Tube Ovary Uterus Bladder Cervix Pubic bone Clitoris Urethra Rectum Vagina Anus G Spot 4 Variety of Vulvae 5 Bladder Corpus Cavernosum Rectum Seminal Vesicle Prostate Glans
Level I - Lesson 8: Know Your Body
 Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Friday, 11 January 13. Sexual Anatomy
 Friday, 11 January 13 Sexual Anatomy Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Fallopian Tube Ovary Uterus Bladder Cervix Pubic bone Clitoris Urethra Rectum
Friday, 11 January 13 Sexual Anatomy Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Friday, 11 January 13 Fallopian Tube Ovary Uterus Bladder Cervix Pubic bone Clitoris Urethra Rectum
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM ~::> bladder penis prostate gland scrotum seminal vesicle testicle urethra vas deferens ;:; . l0\ OJ IQ) I"- ...
 MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Sex Organs - Student Edition (Human Biology)
 Sex Organs - Student Edition (Human Biology) The Program in Human Biology, Stanford Univ- ersity, (HumBio) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access
Sex Organs - Student Edition (Human Biology) The Program in Human Biology, Stanford Univ- ersity, (HumBio) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access
Types of Mating Systems
 The Human Mating System Note: this is the stereotypical EP view (e.g., Buss) Types of Mating Systems Random Monogamy Polygyny: variance in male reproductive success > variance in female reproductive success
The Human Mating System Note: this is the stereotypical EP view (e.g., Buss) Types of Mating Systems Random Monogamy Polygyny: variance in male reproductive success > variance in female reproductive success
The bell is gently and slowly removed (the foreskin may naturally form an adhesion to
 Circumcision Definition: The removal of the foreskin anatomy of the penis; to cut off the clitoris and sometimes the labia of a female. This document only covers male circumcision. Male Anatomy: The foreskin,
Circumcision Definition: The removal of the foreskin anatomy of the penis; to cut off the clitoris and sometimes the labia of a female. This document only covers male circumcision. Male Anatomy: The foreskin,
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Grade 6 Reproduction Review
 Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Taking Care of Your Sexual Health
 Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Word list of symbols and signs in Sex Education
 Word list of symbols and signs in Sex Education Abbreviations Key: CV Core Vocabulary * Signs Only + Symbols Only Abortion / Termination Abuse, to (2) / Physical Abuse Abuse, to (3) / Verbal Abuse* Adolescence
Word list of symbols and signs in Sex Education Abbreviations Key: CV Core Vocabulary * Signs Only + Symbols Only Abortion / Termination Abuse, to (2) / Physical Abuse Abuse, to (3) / Verbal Abuse* Adolescence
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Test Bank. Chapter 2. Abrams, Sexuality and Its Disorders SAGE Publishing, 2017
 Test Bank Chapter 2 1. Is the male female dichotomy an appropriate mode of defining gender? Why, or why not? Ans: The male female dichotomy is strongly embodied in most of cultures, religions, and even
Test Bank Chapter 2 1. Is the male female dichotomy an appropriate mode of defining gender? Why, or why not? Ans: The male female dichotomy is strongly embodied in most of cultures, religions, and even
Intersexual Competition
 (in press, October 2012). In P. Whelan & A. Bolin (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Human Sexuality. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley Blackwell. Intersexual Competition Valerie G. Starratt, Nova Southeastern University, valerie.starratt@nova.edu
(in press, October 2012). In P. Whelan & A. Bolin (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Human Sexuality. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley Blackwell. Intersexual Competition Valerie G. Starratt, Nova Southeastern University, valerie.starratt@nova.edu
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Chapter 2: Female Sexual Anatomy and Physiology
 Human Sexuality in a Changing World 10th Edition Rathus TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/human-sexuality-in-a-changing-world- 10th-edition-rathus-test-bank/
Human Sexuality in a Changing World 10th Edition Rathus TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/human-sexuality-in-a-changing-world- 10th-edition-rathus-test-bank/
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
Why Sex? Mating. Disadvantages of Sex. Advantages of Sex. What Would We Expect? Sex Differences in Parental Investment
 Mating Cost of males Red Queen hypothesis Reproductive value Waist-hip ratio (WHR) Body mass index (BMI) Parental investment (PI) Why Sex? Most genes have a 5% chance of being replicated in sexually produced
Mating Cost of males Red Queen hypothesis Reproductive value Waist-hip ratio (WHR) Body mass index (BMI) Parental investment (PI) Why Sex? Most genes have a 5% chance of being replicated in sexually produced
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems. Male Reproductive Organs. Male Reproductive Organs. Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm)
 Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Healthy Boys POWERFUL BOYS
 Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Sexuality. Chapter 4
 Sexuality Chapter 4 Meaning of Sex Sex is social and biological Most people are heterosexual, preferring malefemale sexual relations A small minority of people are homosexual, preferring only those of
Sexuality Chapter 4 Meaning of Sex Sex is social and biological Most people are heterosexual, preferring malefemale sexual relations A small minority of people are homosexual, preferring only those of
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE INTACT PENIS
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE INTACT PENIS Contains diagrams and photographs of penile anatomy for educational purposes only. THE INTACT PENIS: NOT JUST A FLAP OF SKIN The foreskin is not a flap of skin,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE INTACT PENIS Contains diagrams and photographs of penile anatomy for educational purposes only. THE INTACT PENIS: NOT JUST A FLAP OF SKIN The foreskin is not a flap of skin,
List of Equipment, Tools, Supplies, and Facilities:
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6: Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the
Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6: Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the
Sexuality in Later Life
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Sexuality in Later Life Many people want and need to be close to others as they grow older. This includes the desire to continue an active, satisfying sex life. But,
National Institute on Aging AgePage Sexuality in Later Life Many people want and need to be close to others as they grow older. This includes the desire to continue an active, satisfying sex life. But,
Appropriate and Inappropriate Sexual Behavior of Children
 Appropriate and Inappropriate Sexual Behavior of Children Sexual Knowledge Birth to 2 years Origins of gender identity Learns labels for body parts including genitals Uses slang labels for body parts Sexual
Appropriate and Inappropriate Sexual Behavior of Children Sexual Knowledge Birth to 2 years Origins of gender identity Learns labels for body parts including genitals Uses slang labels for body parts Sexual
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Circumcision Excerpted from Gentle Baby Care by Elizabeth Pantley
 Male Circumcision Circumcision Dr. Morris Elstein is the only doctor (that we are aware of) who will perform this surgery on your homebirthed son. He is not only a doctor but also, a special religious
Male Circumcision Circumcision Dr. Morris Elstein is the only doctor (that we are aware of) who will perform this surgery on your homebirthed son. He is not only a doctor but also, a special religious
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 2 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 2 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 2 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 2 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas. Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N
 Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Gender and Sexuality. Chapter 4 6/30/2010. Gender Development. Gender Differences in Aggression
 Gender and Sexuality Chapter 4 Gender Development Based on genetic makeup, males and females are alike, since the majority of our inherited genes (45 chromosomes are unisex) are similar. Males and females
Gender and Sexuality Chapter 4 Gender Development Based on genetic makeup, males and females are alike, since the majority of our inherited genes (45 chromosomes are unisex) are similar. Males and females
Understanding Sexual Response
 Porterbrook Clinic Sheffield Care Trust Getting the Most out of Psychosexual Therapy Understanding Sexual Response Information for Users of our service Dr Kevan Wylie Clinical Lead Porterbrook Clinic 75
Porterbrook Clinic Sheffield Care Trust Getting the Most out of Psychosexual Therapy Understanding Sexual Response Information for Users of our service Dr Kevan Wylie Clinical Lead Porterbrook Clinic 75
-There are 2 aspects of sex: genetic sex and anatomical sex. In women, the sex chromosomes are XX. In men, the sex chromosomes are XY.
 111 Chapter 7 Gender Sex vs. Gender sex -refers to biological maleness or femaleness -There are 2 aspects of sex: genetic sex and anatomical sex 1. genetic sex -determined by the sex chromosomes In women,
111 Chapter 7 Gender Sex vs. Gender sex -refers to biological maleness or femaleness -There are 2 aspects of sex: genetic sex and anatomical sex 1. genetic sex -determined by the sex chromosomes In women,
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Growth and Development 6 th Grade
 Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Defining Sex and Gender & The Biology of Sex
 Defining Sex and Gender & The Biology of Sex Today: -Defining Sex and Gender -Conception of a Child -Chromosomes -Defects in Chromosomes Often we hear the terms sex and gender used in our society interchangeably,
Defining Sex and Gender & The Biology of Sex Today: -Defining Sex and Gender -Conception of a Child -Chromosomes -Defects in Chromosomes Often we hear the terms sex and gender used in our society interchangeably,
The Female Reproductive System
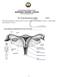 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Reproductive Systems. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Human Sexuality Overview of Sexuality
 Human Sexuality Today: -Overview of Sexuality -Sexual Intercourse/Sexual Response -Sexual Values -Sexual Deviance -Sexual Orientation Overview of Sexuality Human sexuality has always been a taboo to discuss
Human Sexuality Today: -Overview of Sexuality -Sexual Intercourse/Sexual Response -Sexual Values -Sexual Deviance -Sexual Orientation Overview of Sexuality Human sexuality has always been a taboo to discuss
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Lecture Series: Puberty
 Lecture Series: Puberty Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will explain the basics of what your
Lecture Series: Puberty Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will explain the basics of what your
Human Reproduction. Male & Female Systems & Menstration
 Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception
 PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
SEXUALITY AND DIABETES
 SEXUALITY AND DIABETES Sexuality is one of the greatest gifts we have as humans. When it works it can be wonderful and when it doesn t work it can be confusing and tremendously frustrating. WHAT DOES DIABETES
SEXUALITY AND DIABETES Sexuality is one of the greatest gifts we have as humans. When it works it can be wonderful and when it doesn t work it can be confusing and tremendously frustrating. WHAT DOES DIABETES
WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES?
 CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
Female Genital Mutilation. Key facts
 Female Genital Mutilation Key facts Female genital mutilation (FGM) includes procedures that intentionally alter or cause injury to the female genital organs for non-medical reasons. The procedure has
Female Genital Mutilation Key facts Female genital mutilation (FGM) includes procedures that intentionally alter or cause injury to the female genital organs for non-medical reasons. The procedure has
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that
 The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
Interactive Questions & Exercises
 Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Handouts for Stepping Stones with Children
 Handouts for Stepping Stones with Children This Handout for Stepping Stones with Children is to be used with the Stepping Stones with Children training manual published by Practical Action Publishing,
Handouts for Stepping Stones with Children This Handout for Stepping Stones with Children is to be used with the Stepping Stones with Children training manual published by Practical Action Publishing,
When cancer joins you in the bedroom...sexuality and intimacy
 Meeting of the Waters 22/7/2017 When cancer joins you in the bedroom...sexuality and intimacy Gay Corbett Prostate Cancer Specialist nurse Continence Nurses Society Australia Vic Tas (CoNSAVT) Victorian
Meeting of the Waters 22/7/2017 When cancer joins you in the bedroom...sexuality and intimacy Gay Corbett Prostate Cancer Specialist nurse Continence Nurses Society Australia Vic Tas (CoNSAVT) Victorian
Quick Study: Sex Therapy
 Quick Study: Sex Therapy Sexual Dysfunction: Difficulty experienced by an individual or couple during the stages of normal sexual activity including physical pleasure, desire, arousal, or orgasm. Assessing
Quick Study: Sex Therapy Sexual Dysfunction: Difficulty experienced by an individual or couple during the stages of normal sexual activity including physical pleasure, desire, arousal, or orgasm. Assessing
ESRM 350 Reproduction and Mating Systems
 ESRM 350 Reproduction and Mating Systems Autumn 2013 Life s but a walking shadow, a poor player That struts and frets his hour upon the stage And then is heard no more. - Macbeth, William Shakespeare Reproduction
ESRM 350 Reproduction and Mating Systems Autumn 2013 Life s but a walking shadow, a poor player That struts and frets his hour upon the stage And then is heard no more. - Macbeth, William Shakespeare Reproduction
Short-Term Sexual Strategies
 Short-Term Sexual Strategies Theories of Men s Short-Term Mating Primary reproductive benefit: Direct increase in number of offspring Competition (usually Males) Sperm are cheap RS with # of matings Potential
Short-Term Sexual Strategies Theories of Men s Short-Term Mating Primary reproductive benefit: Direct increase in number of offspring Competition (usually Males) Sperm are cheap RS with # of matings Potential
CHAPTER 2: Sexual Anatomy Total Assessment Guide (T.A.G.)
 CHAPTER 2: Sexual Anatomy Total Assessment Guide (T.A.G.) Topic Introduction to Chapter Question Type Remember the Facts Multiple Choice 1 Understand the Concepts Apply What You Know Essay Historical Perspectives
CHAPTER 2: Sexual Anatomy Total Assessment Guide (T.A.G.) Topic Introduction to Chapter Question Type Remember the Facts Multiple Choice 1 Understand the Concepts Apply What You Know Essay Historical Perspectives
Let s Talk About Hormones!
 Let s Talk About Hormones! This lesson was created by Serena Reves and Nichelle Penney, with materials from the BCTF and The Pride Education Network. Hormones are responsible for the regulation of many
Let s Talk About Hormones! This lesson was created by Serena Reves and Nichelle Penney, with materials from the BCTF and The Pride Education Network. Hormones are responsible for the regulation of many
Human Reproductive Anatomy The female anatomy first just the reproductive parts:
 Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Learner Outcomes. Classroom Activities & Timing
 Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
Year Five. God loves me in my changing and development. 1 A Journey in Love - Year 5
 Year Five God loves me in my changing and development 1 A Journey in Love - Year 5 Objectives * Know that as we grow we will become different in our bodies feelings love of God 2 A Journey in Love - Year
Year Five God loves me in my changing and development 1 A Journey in Love - Year 5 Objectives * Know that as we grow we will become different in our bodies feelings love of God 2 A Journey in Love - Year
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections Storytelling Activity
 Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections Storytelling Activity Trainer s Tips Make the context and characters in the story culturally relevant.» Choose culturally relevant girls and boys names for the
Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections Storytelling Activity Trainer s Tips Make the context and characters in the story culturally relevant.» Choose culturally relevant girls and boys names for the
Physiology of the Reproductive System
 Physiology of the Reproductive System Lector: MD Ganna Pola Reproductive system Embryologically, the human reproductive system is one of the last systems to begin formation, and hence one of the last to
Physiology of the Reproductive System Lector: MD Ganna Pola Reproductive system Embryologically, the human reproductive system is one of the last systems to begin formation, and hence one of the last to
The Reproductive System Responsibility: Continue the species Structure: Pair of Gonads Accessory organs, ducts, hormones, etc.
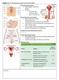 Chapter 11: The Reproductive System and Sexual Health The Reproductive System Responsibility: Continue the species Structure: Pair of Gonads Accessory organs, ducts, hormones, etc. Sexual Autonomy and
Chapter 11: The Reproductive System and Sexual Health The Reproductive System Responsibility: Continue the species Structure: Pair of Gonads Accessory organs, ducts, hormones, etc. Sexual Autonomy and
Name: Grade 6 Sexual Health Workbook
 Name: Grade 6 Sexual Health Workbook Vocabulary Review Anatomy Bingo Exploring Fetal Development Promoting Fetal Development BBI Decision Making Ask an Adult Contents Grade 6 Reproduction Review Vocabulary
Name: Grade 6 Sexual Health Workbook Vocabulary Review Anatomy Bingo Exploring Fetal Development Promoting Fetal Development BBI Decision Making Ask an Adult Contents Grade 6 Reproduction Review Vocabulary
Lecture Series: Pregnancy
 Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Female Genital Mutilation. Guidance on Best Practice
 Female Genital Mutilation Guidance on Best Practice Contents Page 1 Definition 3 2 Who is at Risk? 3 3 No Health Benefits, only harm 4 4 The legal position 4 5 Issues for Inverclyde 6 6 Child protection
Female Genital Mutilation Guidance on Best Practice Contents Page 1 Definition 3 2 Who is at Risk? 3 3 No Health Benefits, only harm 4 4 The legal position 4 5 Issues for Inverclyde 6 6 Child protection
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction
 Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
AP Biology Ch ANIMAL REPRODUCTION. Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below.
 AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
What to do about infertility?
 What to do about infertility? Dr. M.A. Fischer Section Head, Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton,
What to do about infertility? Dr. M.A. Fischer Section Head, Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton,
 Table of Contents 1) What exactly is a virgin?.............................................1 2) Does the term virgin apply for girls only, and what is the term used for boys?..2 3) How can a boy know whether
Table of Contents 1) What exactly is a virgin?.............................................1 2) Does the term virgin apply for girls only, and what is the term used for boys?..2 3) How can a boy know whether
Male circumcision decreases
 Male circumcision decreases penile sensitivity Justine Schober MD University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hamot Hospital, Erie PA Rockefeller University, New York, NY Anatomy is not destiny but a little
Male circumcision decreases penile sensitivity Justine Schober MD University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Hamot Hospital, Erie PA Rockefeller University, New York, NY Anatomy is not destiny but a little
Special Parts: Gender. Why Have Sex?
 Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
The Happiness Class. October 29, 2017 afternoon session: sexual sensations
 The Happiness Class October 29, 2017 afternoon session: sexual sensations Sunday Oct 29th 10:30am 11:00am 11:00am 12:00pm 12:00pm 1:00pm 1:00pm 2:30pm questions about last week jealousy, heartbreak lunch
The Happiness Class October 29, 2017 afternoon session: sexual sensations Sunday Oct 29th 10:30am 11:00am 11:00am 12:00pm 12:00pm 1:00pm 1:00pm 2:30pm questions about last week jealousy, heartbreak lunch
PUBERTY: MY CHANGING BODY Lesson 2
 PUBERTY: MY CHANGING BODY Lesson 2 DIFFERING ABILITIES LEARNER OUTCOME Identify, label and discuss human reproductive body parts. MATERIALS: 1. Public Parts Illustrations (unlabelled &labelled) 2. Private
PUBERTY: MY CHANGING BODY Lesson 2 DIFFERING ABILITIES LEARNER OUTCOME Identify, label and discuss human reproductive body parts. MATERIALS: 1. Public Parts Illustrations (unlabelled &labelled) 2. Private
Lecture 4: Sexual Selection & Female Choice. Differential Investment. Differential Investment in Mammals. Triver s Hypothesis.
 Lecture 4: Sexual Selection & Female Choice Differential investment Classic views of male-female behavioral differences Natural Selection Sexual Selection Inter-sexual choice Intra-sexual competition Inter-sexual
Lecture 4: Sexual Selection & Female Choice Differential investment Classic views of male-female behavioral differences Natural Selection Sexual Selection Inter-sexual choice Intra-sexual competition Inter-sexual
Anatomy of Reproductive System
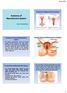 Anatomy of Reproductive System Anatomy of Reproductive System Lector: MD Ganna Pola Anatomy of Female Reproductive System The female reproductive system (or female genital system) contains two main parts:
Anatomy of Reproductive System Anatomy of Reproductive System Lector: MD Ganna Pola Anatomy of Female Reproductive System The female reproductive system (or female genital system) contains two main parts:
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
A Teacher s Guide Sexually
 sue 3. Grades 9-12 : Issue 3. milk. ed every year. ow stopthesilence TeenZine ol, even once, can Grades 9-12 : Issue 3. men who don't use me pregnant. s. chlamydia.,ghest can among 15 to Contraceptives
sue 3. Grades 9-12 : Issue 3. milk. ed every year. ow stopthesilence TeenZine ol, even once, can Grades 9-12 : Issue 3. men who don't use me pregnant. s. chlamydia.,ghest can among 15 to Contraceptives
