Academic Achievement Center 524 Cook Library (p)
|
|
|
- Daniel Gaines
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 READING STRATEGIES TO INCREASE COMPREHENSION Academic Achievement Center 524 Cook Library (p)
2 After reading a chapter in your textbook Has this ever happened to you? I don t understand what I just read. I don t remember what I just read. This chapter is so boring that I just don t get it.
3 Help you study Why are Reading Strategies Important? Help you understand your material more easily Help to improve your reading ability
4 Good Readers Monitor their understanding as they read; recognize when things are or are not making sense. Activate background knowledge and make connections between new and old information Self-question the text to clarify uncertainty and deepen understanding.
5 Good Readers Draw inferences from the text use background knowledge and clues from the text. Determine importance in text to separate details from main ideas. Use sensory images to enhance comprehension and visualize reading. Synthesizing and extending thinking.
6 Factors that Influence Reading Sociocultural Text Activity Reader Context
7 Preview what you are reading: Look at pictures, text boxes, sides notes, etc. Basic Reading Strategies Sticky Notes: Identify important information Chunk the Reading Focus on smaller sections. Underlining Chunk areas that are important, identify areas that you have questions, look at areas that you can connect with, etc. Cornell Notes Study strategy using note taking and reading skills at the same time.
8 The Cueing System 5 main aspects of cueing Graphics Semantics Syntax Experiential Background Text Structure
9 Graphics Would you rather read this? Microspores and megaspores are formed on sporophylls in male and female cones respectively. Each scale in the male cone has two sporangia in which meiosis occurs to produce tetrads of spores, just as in a fern sporangium. Male gametophyte development starts in the microspore (or pollen grain) before it is shed. Mitotic divisions result in two prothallial cells, a tube cell and a generative cell. The sporangium breaks open to shed the immature gametophytes which are carried on the wind and may chance to arrive at a sporophyll on a female cone. In the female cone each scale bears two megasporangia - ovules in which a single mother cell undergoes meiosis to produce four megaspores. One megaspore develops into the female gametophyte which contains thousands of cells and is considerably larger than the male gametophyte. Male gametophyte development has to wait up to a year for the female gametophyte to mature and produce two or three archegonia with egg cells. The pollen tube grows slowly through a pore in the integument of the megasporangium and eventually the generative cell divides to produce two sperm cells. One of these fertilizes an egg cell to produce a zygote. Usually only one archegonium will produce a zygote in each megagametophyte so that there is only one embryo per seed. The mature seed consists of three generations of tissues: maternal sporophyte tissue (seed coat and nucellus), gametophyte and daughter sporophyte (embryo) - After about two years the mature seeds are shed. Conifer seedlings have several needlelike cotyledons in a whorl and the seedlings produce scattered leaves until adult foliage develops.
10 Graphics Or look at this?
11 Semantics The meaning General vocabulary - one general definition pencil - 1. A narrow, generally cylindrical implement for writing, drawing, or marking, consisting of a thin rod of graphite, colored wax, or similar substance encased in wood or held in a mechanical holder. Nonspecific vocabulary multiple meanings based on content/context Radical in Math? Social Studies? English? Chemistry? Technical vocabulary content specific Metaphor in English, photosynthesis in Science
12 How it s written Syntax Often, textbooks are confusing. But you have it break it down. Identify important information
13 Syntax Professor Bernard Wasserstein of Brandeis University is shortly to publish a new biography of Herbert Samuel, who was, in effect, leader of the Liberal party for the crucial months of 1931, during Lloyd George's illness, and a central figure in the crisis. Professor Wassertein is shortly to publish a new biography. Professor Wassertein works at Brandeis University. Herbert Samuel was leader of the Liberal party in Lloyd George was ill. Herbert Samuel was leader of the Liberal party during the illness. Herbert Samuel was a central figure in the crisis.
14 Comprehension of text is dependent on your past experiences and background knowledge Experiential Background The flat-pattern method begins with the creation of a sloper or block, a basic pattern for a fitted, jewel-neck bodice and narrow skirt, made to the wearer's measurements. The sloper is usually made of lightweight cardboard or tagboard, without seam allowances or style details. Once the shape of the sloper has been refined by making a series of mock-up garments called toiles (UK) or muslins (US), the final sloper can be used in turn to create patterns for many styles of garments with varying necklines, sleeves, dart placements, and so on.
15 Experiential Background Did you understand the text? Why or why not? You could read the words, and the syntax was not difficult to decipher, so why could this have been a complicated text to comprehend?
16 Text How is the text set up? Problem/solution Compare/contrast Main idea/supporting detail? Sequentially Structure Does this affect how you read the text? YES! Steps in a process? Scientific journal article? Cause and effect in Social Studies?
17 During Reading strategy. Text Rendering (AKA Annotation) Creates interactivity between the reader and the text.
18 Text Rendering (AKA Annotation) Using a code to simplify the process, make connections, etc.! * Making notes Highlighting
19 Text Rendering (AKA Annotation) It is beneficial: Individualized Easy to implement Easy to read
20 Text Rendering (AKA Annotation)
21 If lack of knowledge is caused by forgetting a technical term Write the term and definition in the margins and try re-reading Things to Keep in Mind Do not merely re-read material again Avoid dull repetition because it doesn t led to deep thinking and memory building Know the main idea Look for supporting details to the main idea Subheadings and related topics Purpose of the text Argument? Information? What is the tone of the text? Why do you need to know this information?
22 Try It Out! Using the information from the presentation, utilize the reading strategies to decode the following passages!
23 What We Have to Offer: Workshops Tutoring Academic Coaching Contact Us! Call: Academic Achievement Center at TU AACTowson
24 Resources Scott, M SCED560, Towson University. PPT.
Reproduction in Plants
 23 Reproduction in Plants section 1 Introduction to Plant Reproduction Before You Read On the lines below, describe the characteristics you use to recognize friends and family members in old photos. In
23 Reproduction in Plants section 1 Introduction to Plant Reproduction Before You Read On the lines below, describe the characteristics you use to recognize friends and family members in old photos. In
Botany: An introduction to plant biology, 5 ed. Mauseth. Chapter 22
 63 UNIT 5: GYMNOSPERMS th Botany: An introduction to plant biology, 5 ed. Mauseth. Chapter 22 OBJECTIVES This lab considers the gymnosperms, vascular plants that produce seeds but lack flowers and fruits.
63 UNIT 5: GYMNOSPERMS th Botany: An introduction to plant biology, 5 ed. Mauseth. Chapter 22 OBJECTIVES This lab considers the gymnosperms, vascular plants that produce seeds but lack flowers and fruits.
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land
 Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Be able to describe/illustrate the evolutionary relationships of embryophytes. Be able to map major events in the evolution of plant reproduction
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Be able to describe/illustrate the evolutionary relationships of embryophytes. Be able to map major events in the evolution of plant reproduction
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land
 Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Understand the evolutionary relationships between plants and algae. Know the features that distinguish plants from algae. Understand the
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Understand the evolutionary relationships between plants and algae. Know the features that distinguish plants from algae. Understand the
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
plant reproduction Alternation of Generations chapter 38
 Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction
 Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
plant reproduction chapter 40 Alternation of Generations
 Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Name: Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back and
Name: Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back and
Alternation of generations
 Plant Life Cycles Allplants alternate between two phases in their life cycles Alternation of generations Sporophyte (diploid) Begins when sperm fertilizes egg (zygote) Diploid zygote divides by mitosis
Plant Life Cycles Allplants alternate between two phases in their life cycles Alternation of generations Sporophyte (diploid) Begins when sperm fertilizes egg (zygote) Diploid zygote divides by mitosis
Unit 16.3: Variation in Plant Life Cycles
 Unit 16.3: Variation in Plant Life Cycles Lesson Objectives Describe a general plant life cycle. Outline the life cycle of nonvascular plants. Describe the life cycle of seedless vascular plants. Summarize
Unit 16.3: Variation in Plant Life Cycles Lesson Objectives Describe a general plant life cycle. Outline the life cycle of nonvascular plants. Describe the life cycle of seedless vascular plants. Summarize
Ontwikkeling; bevruchting
 Ontwikkeling; bevruchting http://www.lima.ohiostate.edu/biology/archive/flowers. html Young Lily anther x40. Four pollen sacs and a cross section of the fillament are visible. Diploid (2N chromosomes)
Ontwikkeling; bevruchting http://www.lima.ohiostate.edu/biology/archive/flowers. html Young Lily anther x40. Four pollen sacs and a cross section of the fillament are visible. Diploid (2N chromosomes)
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Four main events must occur in order for sexual reproduction to take place. 1. The organism must be developed and mature sexually. 2. Gametogenesis; production of
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Four main events must occur in order for sexual reproduction to take place. 1. The organism must be developed and mature sexually. 2. Gametogenesis; production of
Reproductive Development and Structure
 Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
Chapter 12. Biology of Non-Flowering Plants
 BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 12 Chapter 12 Biology of Non-Flowering Plants Objectives Overview of Non-Flowering Plants. Know the distinguishing characteristics of plants. Know the plant
BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 12 Chapter 12 Biology of Non-Flowering Plants Objectives Overview of Non-Flowering Plants. Know the distinguishing characteristics of plants. Know the plant
Angiosperm Reproduction
 Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
Plant Reproduction fertilization
 Plant Reproduction In the plant kingdom, both sexual and asexual reproduction occur. Recall from Chapter 3 that plants reproduce sexually by sporic reproduction, which is also called alternation of generations.
Plant Reproduction In the plant kingdom, both sexual and asexual reproduction occur. Recall from Chapter 3 that plants reproduce sexually by sporic reproduction, which is also called alternation of generations.
Seed Plants: An Overview of Terms
 Topic 25. Introduction to the Seed Plants: The Gymnosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Conifers Genus Pinus The Cycads The Ginkgoes Gnetophyes (The Vessel Bearing Gymnosperms) Seed Plants: An Overview
Topic 25. Introduction to the Seed Plants: The Gymnosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Conifers Genus Pinus The Cycads The Ginkgoes Gnetophyes (The Vessel Bearing Gymnosperms) Seed Plants: An Overview
CHAPTER 2 Reproduction of Flowering Plants. Bui Tan Anh College of Natural Sciences
 CHAPTER 2 Reproduction of Flowering Plants Bui Tan Anh College of Natural Sciences Rafflesiaarnoldii in Indonesia Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Seeds and Fruits Flower Plant Reproduction Many
CHAPTER 2 Reproduction of Flowering Plants Bui Tan Anh College of Natural Sciences Rafflesiaarnoldii in Indonesia Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Seeds and Fruits Flower Plant Reproduction Many
BIOLOGY 3201 REPRODUCTION
 BIOLOGY 3201 REPRODUCTION Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction MODES OF REPRODUCTION (1) Asexual one parent cell divides into two by mitosis to produce 2 identical cells which are clones of the parent (2) Sexual
BIOLOGY 3201 REPRODUCTION Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction MODES OF REPRODUCTION (1) Asexual one parent cell divides into two by mitosis to produce 2 identical cells which are clones of the parent (2) Sexual
PRESENT
 Chapter 29 Plants 29.1 Evolutionary History of Plants Domain Eukarya, kingdom Plantae Plants evolved from freshwater green algae 450 million years ago Both contain chlorophyll a and b and accessory pigments
Chapter 29 Plants 29.1 Evolutionary History of Plants Domain Eukarya, kingdom Plantae Plants evolved from freshwater green algae 450 million years ago Both contain chlorophyll a and b and accessory pigments
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 9 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for
Seed Plants Lab. Learning Objectives. Procedure and Questions
 Seed Plants Lab Learning Objectives Define the terms (meanings of the names) angiosperm and gymnosperm State what type of cells create eggs and what type of cells create sperm in gymnosperms and angiosperms
Seed Plants Lab Learning Objectives Define the terms (meanings of the names) angiosperm and gymnosperm State what type of cells create eggs and what type of cells create sperm in gymnosperms and angiosperms
30 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 30 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Transforming
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 30 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Transforming
Plant Reproduction. In a nutshell
 Plant Reproduction In a nutshell 2007-2008 Plant Diversity mosses ferns conifers flowering plants Bryophytes non-vascular land plants Pteridophytes seedless vascular plants Gymnosperm pollen & naked seeds
Plant Reproduction In a nutshell 2007-2008 Plant Diversity mosses ferns conifers flowering plants Bryophytes non-vascular land plants Pteridophytes seedless vascular plants Gymnosperm pollen & naked seeds
Chapter 17. Part 1 Plants. Plants, Fungi, and the Colonization of Land. Lecture by Dr. Prince
 Chapter 17 Plants, Fungi, and the Colonization of Land Part 1 Plants Lecture by Dr. Prince Plants and Fungi A Beneficial Partnership Plants and fungi colonized land together Mycorrhizae, mutually beneficial
Chapter 17 Plants, Fungi, and the Colonization of Land Part 1 Plants Lecture by Dr. Prince Plants and Fungi A Beneficial Partnership Plants and fungi colonized land together Mycorrhizae, mutually beneficial
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. 1
 1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida
 Kingdom Plantae The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida The closest living relative of plants are in the green algae are charophytes. At one time the had a common
Kingdom Plantae The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida The closest living relative of plants are in the green algae are charophytes. At one time the had a common
seed embryo microscopic gametophytes Gymnospermes Angiosperms
 Gymnosperms Spermatophytes It is the group that includes seed-producing plants. The seed contains embryo, protects it during adverse conditions and contains all nutrients needed for the seedling development.
Gymnosperms Spermatophytes It is the group that includes seed-producing plants. The seed contains embryo, protects it during adverse conditions and contains all nutrients needed for the seedling development.
Plant Life Cycles. Plant life cycles alternate between. producing gametes. Life cycle phases look different among various
 Plant Life Cycles Plant life cycles alternate between two cycles: Producing spores and producing gametes A two phase life cycle is called alternation of generations Diploid phase Haploid phase Alternates
Plant Life Cycles Plant life cycles alternate between two cycles: Producing spores and producing gametes A two phase life cycle is called alternation of generations Diploid phase Haploid phase Alternates
The Land Plants. Chapter 23 Part 2
 The Land Plants Chapter 23 Part 2 23.5 Ancient Carbon Treasures In the Carboniferous, plants with ligninreinforced tissues flourished, died, and became compacted into coal, a nonrenewable fossil fuel Lepidodendron,
The Land Plants Chapter 23 Part 2 23.5 Ancient Carbon Treasures In the Carboniferous, plants with ligninreinforced tissues flourished, died, and became compacted into coal, a nonrenewable fossil fuel Lepidodendron,
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: To Seed or Not to Seed
 Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: To Seed or Not to Seed The parasitic plant Rafflesia arnoldi produces huge flowers that produce up to 4 million seeds Many angiosperms reproduce sexually
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: To Seed or Not to Seed The parasitic plant Rafflesia arnoldi produces huge flowers that produce up to 4 million seeds Many angiosperms reproduce sexually
Flowering plants can be pollinated by wind or animals.
 Wed 4/5 Activities Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Describe the reproductive organs and fertilization of flowering plants.
Wed 4/5 Activities Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Describe the reproductive organs and fertilization of flowering plants.
ANGIOSPERM L.S. POLLEN GRAIN
 ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
Chapter 22 The Land Plants. Cengage Learning 2016
 Chapter 22 The Land Plants 22.2 Plant Ancestry and Diversity Plants Multicelled Photosynthetic eukaryotes Adapted to life on land Close relatives of red algae and green algae Contain cellulose cell walls
Chapter 22 The Land Plants 22.2 Plant Ancestry and Diversity Plants Multicelled Photosynthetic eukaryotes Adapted to life on land Close relatives of red algae and green algae Contain cellulose cell walls
BIOLOGI UMUM Priyambodo, M.Sc.
 BIOLOGI UMUM Priyambodo, M.Sc. KONSEP REPRODUKSI TUMBUHAN KONSEP REPRODUKSI TUMBUHAN Vegetatif vs generatif VEGETATIF VS GENERATIF Menurut pendapat Anda, makanah jenis reproduksi yang lebih baik bagi tumbuhan?
BIOLOGI UMUM Priyambodo, M.Sc. KONSEP REPRODUKSI TUMBUHAN KONSEP REPRODUKSI TUMBUHAN Vegetatif vs generatif VEGETATIF VS GENERATIF Menurut pendapat Anda, makanah jenis reproduksi yang lebih baik bagi tumbuhan?
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2
 NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Exercise Solutions Exercise : Solutions of Questions on
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Exercise Solutions Exercise : Solutions of Questions on
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question 1: Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male and female gametophyte take place. Answer :- The male gametophyte or the pollen grain
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question 1: Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male and female gametophyte take place. Answer :- The male gametophyte or the pollen grain
Biology Class 12 th NCERT Solutions
 Chapter.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class XII Subject Biology 1. Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male and female gametophyte take place. Answer 1. Pollen grains
Chapter.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class XII Subject Biology 1. Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male and female gametophyte take place. Answer 1. Pollen grains
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants
 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants Overview: Feeding the World Seeds changed the course of plant evolution Enabling their bearers to become the dominant producers in most terrestrial ecosystems
Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants Overview: Feeding the World Seeds changed the course of plant evolution Enabling their bearers to become the dominant producers in most terrestrial ecosystems
A GLAUCA (MOENCH) VOSS EMBRYOLOGY OF PIC. R. M. Rauter 2/ and J. L. Farrar INTRODUCTION
 2/ EMBRYOLOGY OF PIC A GLAUCA (MOENCH) VOSS R. M. Rauter 2/ and J. L. Farrar INTRODUCTION In a tree improvement program, it is important to understand the morphological and physiological development of
2/ EMBRYOLOGY OF PIC A GLAUCA (MOENCH) VOSS R. M. Rauter 2/ and J. L. Farrar INTRODUCTION In a tree improvement program, it is important to understand the morphological and physiological development of
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Mastery. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter Content CHAPTER 3 LESSON 1. Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions.
 Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction
 NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL
 SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL LIFE SCIENCES DEPARTMENT LIFE SCIENCES CONTROL TEST 2-2017 EXAMINER: T. GABRIELS MODERATOR: Z. SHADE GRADE 11 TIME: 1 HOUR MARKS: 60 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION Read the following
SPINE ROAD HIGH SCHOOL LIFE SCIENCES DEPARTMENT LIFE SCIENCES CONTROL TEST 2-2017 EXAMINER: T. GABRIELS MODERATOR: Z. SHADE GRADE 11 TIME: 1 HOUR MARKS: 60 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION Read the following
2. When and where does reduction division take place in the life cycle of a liverwort, a moss, a fern, a gymnosperm and an angiosperm?
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Plant Kingdom 1. What is the basis of classification of algae? Answer: The main basis of classification of algae has been done on the basis of presence or absence of pigments, which impart
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Plant Kingdom 1. What is the basis of classification of algae? Answer: The main basis of classification of algae has been done on the basis of presence or absence of pigments, which impart
Chapter 40 Flowering Plant Sexual Reproduction
 3.6 Reproduction & Growth 3.6.1 Reproduction of The Flowering Plant Chapter 40 Flowering Plant Sexual Reproduction Learning Objectives 1. Give the structure and function of the floral parts. 2. Outline
3.6 Reproduction & Growth 3.6.1 Reproduction of The Flowering Plant Chapter 40 Flowering Plant Sexual Reproduction Learning Objectives 1. Give the structure and function of the floral parts. 2. Outline
On the Use of Some Common Botanical Terms
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 2, Issue 5 (March, 1902) 1902-03 On the Use of Some Common Botanical
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 2, Issue 5 (March, 1902) 1902-03 On the Use of Some Common Botanical
Overview: Transforming the World
 Chapter 30 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with
Chapter 30 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with
STROBILUS HOMOSPOROUS LYCOPODIUM
 STROBILUS HOMOSPOROUS LYCOPODIUM I SPORES HOMOSPOROUS LYCOPODIUM EUSPORANGIUM L.S. ISOSPORES HOMOSPOROUS LYCOPODIUM EUSPORANGIUM L.S. SPOROPHYTE STROBILUS LYCOPODIUM ISOSPORE M ISOSPORES SPOROPHYLL L.S.
STROBILUS HOMOSPOROUS LYCOPODIUM I SPORES HOMOSPOROUS LYCOPODIUM EUSPORANGIUM L.S. ISOSPORES HOMOSPOROUS LYCOPODIUM EUSPORANGIUM L.S. SPOROPHYTE STROBILUS LYCOPODIUM ISOSPORE M ISOSPORES SPOROPHYLL L.S.
Reproduction 19/02/2016. Asexual Reproduction. Budding: Types of asexual reproduction: SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL
 Asexual Reproduction Reproduction SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL One parent cell divides by mitosis to produce 2 daughter cells which are clones of the parent Types of asexual reproduction: Budding: 1. Budding 2.
Asexual Reproduction Reproduction SEXUAL VS. ASEXUAL One parent cell divides by mitosis to produce 2 daughter cells which are clones of the parent Types of asexual reproduction: Budding: 1. Budding 2.
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure
 wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
Flowering Plant Reproduction
 Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Downloaded from CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS POINTS TO REMEMBER
 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS POINTS TO REMEMBER Autogamy : When pollen grains of a flower are transferred from anther to stigma of the same flower. Coleorhiza : A protective sheath
CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS POINTS TO REMEMBER Autogamy : When pollen grains of a flower are transferred from anther to stigma of the same flower. Coleorhiza : A protective sheath
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination
 BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Difference between self-pollination & cross pollination Self -Pollination 1. It is transfer of pollen grains from
13.3. Sexual Reproduction in Seed Plants. Seed Function and Structure
 Sexual Reproduction in Seed Plants In the previous section you saw that plants can reproduce by asexual reproduction, which can quickly establish a population of plants. However, asexual reproduction cannot
Sexual Reproduction in Seed Plants In the previous section you saw that plants can reproduce by asexual reproduction, which can quickly establish a population of plants. However, asexual reproduction cannot
Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
kingdom Plantae multicellular most with photosynthesis cell walls (cellulose) movement by growth, some w/ flagellated sperm sporic meiosis
 kingdom Plantae multicellular most with photosynthesis cell walls (cellulose) movement by growth, some w/ flagellated sperm sporic meiosis (alternation of generations) Since we re talking about plants
kingdom Plantae multicellular most with photosynthesis cell walls (cellulose) movement by growth, some w/ flagellated sperm sporic meiosis (alternation of generations) Since we re talking about plants
GENES AND CHROMOSOMES CHAPTER 5
 CHAPTER 5 GENES AND CHROMOSOMES For many years the standard authority on the chromosomes was Wilson s The Cell in Development and Inheritance. The second edition of this work was published in 1900; it
CHAPTER 5 GENES AND CHROMOSOMES For many years the standard authority on the chromosomes was Wilson s The Cell in Development and Inheritance. The second edition of this work was published in 1900; it
sporophyte (2n) DIPLOID GENERATION
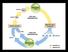 Figure 21-1 Alternation of generations in plants embryo 2n sporophyte (2n) zygote 2n DIPLOID GENERATION FERTILIZATION MEIOTIC CELL DIVISION n sperm n egg HAPLOID GENERATION n n n n spores gametophyte (n)
Figure 21-1 Alternation of generations in plants embryo 2n sporophyte (2n) zygote 2n DIPLOID GENERATION FERTILIZATION MEIOTIC CELL DIVISION n sperm n egg HAPLOID GENERATION n n n n spores gametophyte (n)
PLANT REPRODUCTION CHAPTER. SECTION 1 Plant Life Cycles. SECTION 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants. SECTION 3 Dispersal and Propagation
 CHAPTER 30 PLANT REPRODUCTION Two pollen grains (yellow) have been deposited on the stigma of a goose-grass (Galium aparine) flower. A pollen tube can be seen growing from the pollen grain on the right.
CHAPTER 30 PLANT REPRODUCTION Two pollen grains (yellow) have been deposited on the stigma of a goose-grass (Galium aparine) flower. A pollen tube can be seen growing from the pollen grain on the right.
Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from
 Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Modes of Reproduction
 Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
"Our Flowering World" PRE-TEST. Directions: Write a definition for each of the terms listed below:
 1 PRE-TEST Directions: Write a definition for each of the terms listed below: 1. fertilization 2. embryo 3. pollen 4. anther 5. pistil 6. stamen 7. ovule 8. nectar 9. ovary 10. style Directions: Use the
1 PRE-TEST Directions: Write a definition for each of the terms listed below: 1. fertilization 2. embryo 3. pollen 4. anther 5. pistil 6. stamen 7. ovule 8. nectar 9. ovary 10. style Directions: Use the
Plants Provision for Life. Chapter 2 7 th Grade
 Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
Angiosperm Reproduction (Ch.24) (Ch. 38)
 Angiosperm Reproduction (Ch.24) (Ch. 38) Charophyceans Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Seedless vascular plants Gymnosperms Angiosperms Rafflesia arnoldii, monster flower of Indonesia Orchid (Lemboglossum
Angiosperm Reproduction (Ch.24) (Ch. 38) Charophyceans Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Seedless vascular plants Gymnosperms Angiosperms Rafflesia arnoldii, monster flower of Indonesia Orchid (Lemboglossum
o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into 2
 Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants.
 CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
CHAPTER 2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 8 1 7 CHAPTER 2 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTS FLOWERS Site of sexual Reproduction. Male and female reproductive organs are borne on flowers. PARTS
A2 WJEC BIOLOGY UNIT 4 Sexual reproduction in plants
 A2 WJEC BIOLOGY UNIT 4 Sexual reproduction in plants Biology Department - Gower College Swansea The generalised structure of flowers to be able to compare wind and insect pollinated flowers Learners should
A2 WJEC BIOLOGY UNIT 4 Sexual reproduction in plants Biology Department - Gower College Swansea The generalised structure of flowers to be able to compare wind and insect pollinated flowers Learners should
BIO-BOTANY important questions to discuss for NEET 2018/Matric Exam HOPE ACADEMY HOSUR
 Questions = 45 REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 1 1. Which is the characteristics for ornithophily (1) Scented flowers (2) Bright red colored flowers and infloresnce (3) White colored funnel shaped large
Questions = 45 REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS 1 1. Which is the characteristics for ornithophily (1) Scented flowers (2) Bright red colored flowers and infloresnce (3) White colored funnel shaped large
 CHAPTER 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. Reproduction ensured continuity of life on earth. Reproduction
CHAPTER 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. Reproduction ensured continuity of life on earth. Reproduction
Unit -VI Chapter-2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
 Unit -VI Chapter-2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants IMPORTANT POINTS - Reproduction is the most important feature of living organisms. - It is a process of producing offspring, ie., the next generation,
Unit -VI Chapter-2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants IMPORTANT POINTS - Reproduction is the most important feature of living organisms. - It is a process of producing offspring, ie., the next generation,
Unit 1 Biological Diversity Topic 1.1 Examining Diversity. Text p. 3-15
 Topic 1.1 Examining Diversity. Text p. 3-15 Variation to the MAX! Biologists have identified over species of animals and over species of plants. The most successful life form is What is Biodiversity? The
Topic 1.1 Examining Diversity. Text p. 3-15 Variation to the MAX! Biologists have identified over species of animals and over species of plants. The most successful life form is What is Biodiversity? The
Introduction 1. INTRODUCTION
 1. INTRODUCTION Early in their evolution, plants have acquired a life cycle that alternates between a multicellular haploid organism, the gametophyte and a multicellular diploid organism, the sporophyte.
1. INTRODUCTION Early in their evolution, plants have acquired a life cycle that alternates between a multicellular haploid organism, the gametophyte and a multicellular diploid organism, the sporophyte.
Chapter-4 Plant Kingdom
 Chapter-4 Plant Kingdom Very Short Answer Questions 1. What is the basis of classification of Algae? A: Pigments and types of stored food. 2. When and where does reduction division takes place in the life
Chapter-4 Plant Kingdom Very Short Answer Questions 1. What is the basis of classification of Algae? A: Pigments and types of stored food. 2. When and where does reduction division takes place in the life
Unit E: Plant Propagation. Lesson 1: Understanding Sexual Reproduction
 Unit E: Plant Propagation Lesson 1: Understanding Sexual Reproduction 1 Vocabulary Cross-pollination Diploid Endosperm Fertilization Gametes Genes Haploid Hybrids Pollination Seed Self-pollination Sexual
Unit E: Plant Propagation Lesson 1: Understanding Sexual Reproduction 1 Vocabulary Cross-pollination Diploid Endosperm Fertilization Gametes Genes Haploid Hybrids Pollination Seed Self-pollination Sexual
The Chromosomes of a Frimpanzee: An Imaginary Animal
 The Chromosomes of a Frimpanzee: An Imaginary Animal Introduction By now, you have heard the terms chromosome, mitosis, and meiosis. You probably also know that chromosomes contain genetic information
The Chromosomes of a Frimpanzee: An Imaginary Animal Introduction By now, you have heard the terms chromosome, mitosis, and meiosis. You probably also know that chromosomes contain genetic information
Plant Reproduction. More Exciting Than You Think
 Plant Reproduction More Exciting Than You Think Ever seen Silence of the Lambs?? Fava beans anyone? Check this. Now for Chapter 4 of Survival of the Sickest. Fig. 38.1 2. Flowers are specialized leaves
Plant Reproduction More Exciting Than You Think Ever seen Silence of the Lambs?? Fava beans anyone? Check this. Now for Chapter 4 of Survival of the Sickest. Fig. 38.1 2. Flowers are specialized leaves
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Science Question 1: What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction? DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which
Class X Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Science Question 1: What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction? DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which
Chapter 8: How do Organisms Reproduce? 1 What is the primary importance of DNA copying in reproduction? SOLUTION:
 Chapter 8: How do Organisms Reproduce? 1 What is the primary importance of DNA copying in reproduction? DNA copying in reproduction is important for maintenance of body designs and features. It is also
Chapter 8: How do Organisms Reproduce? 1 What is the primary importance of DNA copying in reproduction? DNA copying in reproduction is important for maintenance of body designs and features. It is also
b. What is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction?
 Unit 4: Reproduction 1. Reproduction function 2. Reproduction in animals 2.1. Asexual reproduction 2.2. Sexual reproduction 3. Reproduction in plants 3.1. Asexual reproduction 3.2. Sexual reproduction
Unit 4: Reproduction 1. Reproduction function 2. Reproduction in animals 2.1. Asexual reproduction 2.2. Sexual reproduction 3. Reproduction in plants 3.1. Asexual reproduction 3.2. Sexual reproduction
MICROSPORANGIA, MICROSPORES, MALE GAMETOPHYTES
 LAB 06: Seed Plant Synapomorphies Introduction to non-flowering seed plants (Gymnosperms) A seed is a highly modified megasporangium, so seed plants are heterosporous. We will review important differences
LAB 06: Seed Plant Synapomorphies Introduction to non-flowering seed plants (Gymnosperms) A seed is a highly modified megasporangium, so seed plants are heterosporous. We will review important differences
WILLIAM CLIFFORD MORSE.
 Nov., 1907.] Life History of Cornuz Florida. 197 CONTRIBUTION TO THE LIFE HISTORY OF CORNUS FLORIDA.* WILLIAM CLIFFORD MORSE. This study of the Flowering Dogwood was undertaken at the suggestion of Professor
Nov., 1907.] Life History of Cornuz Florida. 197 CONTRIBUTION TO THE LIFE HISTORY OF CORNUS FLORIDA.* WILLIAM CLIFFORD MORSE. This study of the Flowering Dogwood was undertaken at the suggestion of Professor
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants
 Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure. Name
 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction
 Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
Reproduction in plants
 Reproduction in plants No individual organism can live forever, but reproduction makes sure that organisms do not become extinct. Organisms reproduce sexually or asexually and some organisms, such as angiosperms
Reproduction in plants No individual organism can live forever, but reproduction makes sure that organisms do not become extinct. Organisms reproduce sexually or asexually and some organisms, such as angiosperms
PLANT SEXUAL REPRODUCTION: ASPECTS OF INTERACTION, HISTORY AND REGULATION
 ACTA BIOLOGICA CRACOVIENSIA Series Botanica 45/1: 19 26 2003 PLANT SEXUAL REPRODUCTION: ASPECTS OF INTERACTION, HISTORY AND REGULATION MICHIEL T. M. WILLEMSE * Laboratory of Plant Cell Biology, Wageningen
ACTA BIOLOGICA CRACOVIENSIA Series Botanica 45/1: 19 26 2003 PLANT SEXUAL REPRODUCTION: ASPECTS OF INTERACTION, HISTORY AND REGULATION MICHIEL T. M. WILLEMSE * Laboratory of Plant Cell Biology, Wageningen
Topic 2.1 A Closer Look At Variation
 1 UNIT A SECTION 2.0 As species reproduce, characteristics are passed from parents to offspring. 2 Topic 2.1 A Closer Look At Variation Textbook Pages 27 29 1 Variation in a species 3 Not all variations
1 UNIT A SECTION 2.0 As species reproduce, characteristics are passed from parents to offspring. 2 Topic 2.1 A Closer Look At Variation Textbook Pages 27 29 1 Variation in a species 3 Not all variations
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Pre Fertilisation Events Several hormonal and structural changes result in the development of a flower. Inflorescences bear the flower buds, and then the flowers.
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Pre Fertilisation Events Several hormonal and structural changes result in the development of a flower. Inflorescences bear the flower buds, and then the flowers.
Sexual Reproduction. Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction BC Science Probe 9 pages
 Sexual Reproduction Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction BC Science Probe 9 pages 72-105 Why Sex? Textbook Read pages 74 77 Sexual Reproduction Is reproduction involving two parents Each parent contributes equal
Sexual Reproduction Chapter 3 Sexual Reproduction BC Science Probe 9 pages 72-105 Why Sex? Textbook Read pages 74 77 Sexual Reproduction Is reproduction involving two parents Each parent contributes equal
Types of Reproduction
 Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. It ensures continuity of life on earth. Nucleus of the cell contains DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid)
Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. It ensures continuity of life on earth. Nucleus of the cell contains DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid)
To produce its kind is a
 12 Reproduction in Plants To produce its kind is a characteristic of all living organisms. You have already learnt this in Class VI. The production of new individuals from their parents is known as reproduction.
12 Reproduction in Plants To produce its kind is a characteristic of all living organisms. You have already learnt this in Class VI. The production of new individuals from their parents is known as reproduction.
Chapter 17. Plants, Fungi, and the Colonization of Land. Lecture by Joan Sharp
 Chapter 17 Plants, Fungi, and the Colonization of Land PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Chapter 17 Plants, Fungi, and the Colonization of Land PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Downloaded from Organisms Reproduce
 Organisms Reproduce Question 1: What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction? Answer: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which are present in the nucleus
Organisms Reproduce Question 1: What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction? Answer: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which are present in the nucleus
