MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY. Copyright: Judy Adams, CME. COPYRIGHT NOTICE Copyright 2017 by Judy Adams. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
|
|
|
- Aron Summers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Copyright: Judy Adams, CME COPYRIGHT NOTICE Copyright 2017 by Judy Adams. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED No part of this publication may be copied or distributed, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any human or computer language, in any form, or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, manual, or otherwise, or disclosed to third parties without the express written permission of Judy Adams, 213 Highway 17 South, Suite B, East Palatka, FL 32131
2 Preview Goals and Objectives: As allied health professionals we have moved into a more medical realm, and our need for a strong medical vocabulary has become greater. Since it would be impossible to memorize all of the terms with which you must become familiar, it will be an easier task to master if you understand more about the way medical terms are combined or put together. Smaller pieces of words are joined together to build a meaning. If you can understand the basics of the small parts, then it will be easier to decipher the meaning of words that are unfamiliar to you. This home study unit will concentrate on medical terms that you will commonly use when communicating with other professionals in the health care industry. When you complete this study unit you will be able to: Identify many of the common roots, prefixes, and suffixes that are used in the hair removal profession Determine the meaning of medical terms by analyzing their component parts Familiarize yourself with medical specialties Learn the correct pronunciation of medical words 2
3 Using this study unit: So you will be able to learn the correct pronunciation of these medical terms, a phonetic spelling of each new word will be included in the material. You will find this phonetic spelling in parenthesis after the term. This method spells the word as it actually sounds. Always say the word out loud as you read and learn new terms. The basic rules are fairly simple. 1. Vowel sounds that are marked with a straight line above them are called long vowel sounds. For example the phonetic spelling of mate is māt, the phonetic spelling of bite is bīt, the phonetic spelling of home is hōm, and so on. 2. Short vowel sounds are marked with a breve ( ) over them. Therefore, the phonetic spelling of bat is băt, the phonetic spelling of met is mĕt, the phonetic spelling of bit is bĭt, and so on. 3. The primary stress in a word is indicated by a single boldface accent ( ) and the secondary stress is indicated by a double lightface accent ( ). ă as in măp ě as in bět ĭ as in lĭp ŏ as in hŏt ŭ as in hŭg ā as in lāke ē as in rēflex ī as in pīe ō as in nō ū as in ūnion oo as in booth oy as in boy 3
4 Contents: Section 1: Preview Goals and Objectives Using this Study Unit Introduction Word Analysis Suffixes Prefixes Root Words and Their Combining Forms Lists of commonly used prefixes and suffixes Check your Knowledge Answers Examination 4
5 Introduction HOW MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY IS USED Medical vocabulary originates from Greek and Latin. Much of our medical language comes from Hippocrates, the Father of Medicine. He was a Greek physician in the fourth century B.C. and was the author of the Hippocratic oath. Since most medical terms are compound English derivatives of Latin and Greek it is impossible to always achieve a word for word translation. Although medical terminology is primarily compiled from dead languages, it is as much a living language as English! Hundreds of new words are born into it and hundreds die of disuse in each medical generation. New medical words are always being created, and it should come as no surprise that learning medical technology is very similar to learning a foreign language. Medical words are not monotonous. Each separate syllable holds a meaning. A mixture of roots from both languages, or a Greek prefix to a Latin stem is common. These words are called hybrids. EPILEPTIFORM ENDOCERVICITIS EXTRASYSTOLE (Gr. Epileptos, L. forma) (Gr. Endon, L. cervix, Gr. itis) (L. extra, Gr. systole) Listed below are some common body parts, with their Latin and Greek terms. PART LATIN GREEK DISEASE Skin Cutis Derma Dermatitis Gland Glandula Aden Adenitis Breast Mamma Mastos Mastitis Muscle Musculus Mys Myositis Stomach Stomachus Gaster Gastritis Womb Uterus Metra Metritis To accurately interpret a medical term, you may need to consult a good medical dictionary. Learning another language is not just a matter of memorizing the new words, but of learning the rules that govern it. The order in which a word is constructed will affect its meaning. Take a look at the following English sentences and you will see how important order can be. 5
6 The ball hit John Hit John the ball. Hit the ball, John. Now, take a look at how much punctuation can change the meaning of the following sentence. John hit the ball. John, hit the ball! Words and groups of words all have specific meanings. If you change the order of these words, then you change their meaning. There are some rules for the language of medical terminology, but they are not that hard to learn. If you know the meaning of the word parts, then you can usually analyze most of the words that you come across. WORD ANALYSIS Analysis is the separation of a whole into its component parts. To understand a word, you must separate the word into its component parts, establish the meaning of those parts, and add those meanings together in the right order! Here are the component parts that you will be working with when you are learning a new medical word or term. Prefix a unit of meaning attached to the front (or beginning) of a word. For example, the prefix ENDO- means within, so ENDO-carditis is within the heart. Root the core or foundation of the word s meaning. You may also find the root referred to as the stem. The root of endo-cardi-tis is CARDI, which means heart. Suffix a unit of meaning attached to the end of the word. The ITIS in endocard-itis is a suffix meaning inflammation. Combining Vowel a vowel (usually o) added to the end of the root, without changing the meaning. A combining vowel is positioned between two roots, or between a root and a suffix that begins with a consonant, to help make the newly combined word easier to pronounce. Combining form the root and the combining vowel together, as in CARDI/O Not all words have a prefix or a suffix, so don t develop the habit of thinking that the beginning of all words is a prefix or the endings of all words are a suffix. Sometimes words can begin or end with a root and often do! 6
7 Let s take a word that we are all familiar with and analyze its component parts. We all know that the word diagnosis means something like the process of finding out what is causing a patient s illness. We would consider that our plain English version or translation of the word. Let s take a look at the true scientific analysis of the word diagnosis. DIA- GNOS/O -SIS Prefix Root + Combining Vowel Suffix = Combining Form (complete) (knowledge) (process) We have just translated this to mean complete knowledge process, but that seems awkward. It would sound much better if we described this as process of complete knowledge. We have just learned from this example that we must begin reading medical words from the right, instead of from the left like we are accustomed to when reading English. The most important rule in analyzing medical terminology is to begin at the end! To determine the meaning of a term, look at the parts in this order: 1. Suffix 2. Prefix 3. Root(s) Some commonly used prefixes and suffixes, and their meanings. Prefix A-, AN- ANTE- ANTI- AUTO- ECTO- ENDO- EPI- EX- HYPER- HYPO- INTER- INTRA- PARA- PERI- PER- PRO- RE- RETRO- SUB- SUPER- SUPRA- Meaning no, not, without before against self outside within above, upon out above, excessive below, deficient between within beside around through before back, backward, again behind below, under above, beyond above, beyond Suffix -ALGIA -CYTE -ECTOMY -EMIA -GRAM -IST -LOGY -POIESIS -PTOSIS -PTYSIS -RRHAGIA -RRHAGE -RRHAPHY -RRHEA -RRHEXIS -SCOPE -SCOPY -TOME -TOMY -TRIPSY -TROPHY Meaning pain cell excision, removal blood condition record specialist study of formation prolapse, drooping spitting bursting forth bursting forth suture flow rupture instrument to view, examine instrument to cut incision crushing nourishment 7
8 PRACTICE TEST (1) Give a brief definition to each of the following terms: 1. Root 2. Prefix 3. Suffix 4. Combining vowel 5. Combining form 6. Analysis When translating a medical term you should look at the parts in this order:
9 SUFFIXES The word suffix comes from the Latin word suffigere, to fasten underneath. When a suffix is attached to a medical term, it usually denotes a diagnosis or medical procedure. Here are some common suffixes: -ITIS inflammation tonsillitis inflammation of the tonsils bronchitis sinusitis inflammation of the bronchial walls inflammation of the sinuses -ECTOMY removal tonsillectomy removal of the tonsils appendectomy hysterectomy removal of the appendix removal of the uterus Common Diagnostic Suffixes -ALGIA pain neuralgia (nū-ră jē-ah) nerve pain -DYNIA pain gastrodynia (găs trō-dĭn e-ah) pain in the stomach -EMIA blood condition leukemia (loo-kē mēah) cancer of white blood cells -GENIC producing, forming carcinogenic (kar sĭ-nō-jĕn ĭk) cancer forming -IA condition, disease polyuria (pŏl ē-ū rē-ah) excessive urination -ITIS inflammation laryngitis (lar ĭn-jī tĭs) inflammation of the larynx -OMA tumor, mass sarcoma (sar-kō mah) cancerous tissue of connective tissue -OSIS condition tuberculosis (too-ber kū-lō sĭs) infectious disease commonly caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis 9
10 COMMON ADJECTIVE SUFFIXES Suffix Meaning Example -AC, -IAC pertaining to the heart cardiac -AL, -EAL, -IAL pertaining to conditions present at birth congenital -AR pertaining to ventricles of heart or brain ventricular -ARY pertaining to lungs pulmonary -IC, ICAL pertaining to time chronic -OUS pertaining to mucus mucous PRACTICE TEST (2) The combining form GASTR/O means stomach, or belly. ENTER/O means small intestine. Using the tools that you have learned for combining forms and suffixes, define the following words. 1. Gastritis 2. Gastralgia 3. Gastroenteritis 4. Enteritis 5. Gastrectomy 6. Gastrostomy 7. Gastric 10
11 PREFIXES The word prefix begins with a prefix! Pre- means before, in front of. The root FIX means attach, fasten. So a prefix is something that is attached to the front of something. Not all medical words have a prefix, but the prefix is always at the beginning of a word. A prefix is usually very short, and it always changes the meaning of the root word in some way! Prefixes most often refer to location or amount. Prefix Root Location SUB- + COSTAL = SUBCOSTAL (under, below) (pertaining to rib) (below the rib) SUPRA- + COSTAL = SUPRACOSTAL (above, beyond) (pertaining to rib) (above the rib) As you can see in the example above, just one or two letters can make a large difference in the meaning of a word! The same holds true for root words and suffixes. Many times a medical word will begin with a root word, and does not have a prefix. So be careful not to mistake a root word for a prefix because it could cause you to completely misconstrue the meaning of the word! Root words are always nouns or verbs, or the strongest point in the meaning. Prefixes are used as adjectives or prepositions, and are used to describe things rather than naming them. 11
12 ROOT WORDS & THEIR COMBINING FORMS The foundation of a plant is its root, and the foundation or origin of a medical term is its root word. When you attach other meanings in the form of prefixes or suffixes to a root word, it changes the meaning of the root word as well. Usually the only part of a word that can stand alone is its root word. It needs no prefix or suffix to make it a complete word. Although, some root words cannot stand alone. Any time that you see the letter o in a medical term, you should first suspect that it means that there is a root word in front of it. It does not always indicate that it is a combing form for the root word, but it is so commonly used in this way, that you should try that first. It is easy to get confused, but since we are not studying to become brain surgeons, we only need to grasp the basics. There are always exceptions to the rules, but a basic understanding of how words are put together can help you at least get a grasp of the meaning of a medical word or phrase. Learning to turn a singular word into a plural carries its own set of rules. You will find the chart below to be of value. Singular Plural a in vertebra becomes ae in vertebrae ax in thorax becomes axes (aces) in thoraxes (thoraces) en in foramen becomes ina in foramina is in diagnosis becomes es in diagnoses is in femoris becomes a in femora is in metastasis becomes es in metastases ix in appendix becomes ixes (ices) in appendixes (appendices) ex in apex becomes ices in apices nx in phalanx becomes ges in phalanges on in spermatozoon becomes a in spermatozoa um in bacterium becomes a in bacteria us in nucleus becomes I in nuclei y in artery becomes ies in arteries 12
13 Roots commonly used for medical specialties Roots Meaning Specialist ESTHESI/O feeling, anesthesiologist dealing with the administration sensation of anesthetic agents prior to and during surgery CARDI/O heart cardiologist dealing with abnormalities, functions, diseases, & disorders of the heart CHIR/O hand chiropractor by means of manual manipulation, treats disorders originating from misalignment of the spinal vertebrae DENT/O tooth dentist diagnoses & treats diseases & disorders of teeth & tissues of the oral cavity DERMAT/O skin dermatologist dealing with diseases & disorders of the skin CRIN/O secrete endocrinologist dealing with diseases & malfunctions of the glands of internal secretion DEM/O people epidemiologist the study of sudden outbreaks of disease, or epidemics, in a population group GASTER/O stomach gasteroenterologist diagnoses & treats disorders ENTER/O intestine of the stomach & intestines GERONT/O old age gerontologist dealing with the diseases, disorders, & hygiene of old age GYNEC/O female gynecologist diagnoses & treats diseases & disorders of the female reproductive system HEMAT/O blood hematologist diagnoses & treats diseases & disorders of the blood & blood-forming tissues IMMUN/O protected immunologist studies the immune system INTER/O within, internist diagnoses & treats diseases & disorders inner of the internal organs LARYNG/O throat laryngologist specialist dealing with the throat & its diseases 13
14 Roots Meaning Specialist NAT/O birth neonatologist diagnoses & treats disorders of the new born NEPHR/O kidney nephrologist diagnoses & treats diseases & disorders of the kidneys NEUR/O nerve neurologist diagnoses & treats diseases & disorders of the nervous system including the brain OBSTETR/O midwife obstetrician provides medical care to women during & immediately after pregnancy ONC/O tumor oncologist diagnoses & treats malignant disorders OPHTHALMO/O eye ophthalmologist diagnoses & treats diseases & disorders of the eye OPT/O eye, optometrist measures accuracy of vision & vision prescribes corrective lenses or eyeglasses ORTH/O straight, orthopedist diagnoses & treats diseases & normal disorders involving the bones, joints, & muscles OSTE/O bone osteopathic physician diagnoses & treats health problems by manipulation, & also by traditional forms of treatment OT/O ear otorhinolaryngologist diagnoses & treats diseases RHIN/O nose & disorders of the ear, nose, and throat LARYNG/O larynx, throat PATH/O disease, pathologist analyzes tissue samples to confirm suffering diagnoses & performs autopsies PED/O child pediatrician diagnoses, treats, & prevents PEDI/A disorders & diseases of children POD/O foot podiatrist diagnoses, treats, & corrects disorders PED/I of the foot PROCT/O anus, proctologist diagnoses & treats disorders of the rectum anus & rectum 14
15 Roots Meaning Specialist PSYCH/O mind psychiatrist concerned with the treatment & prevention of the disorders of the mind RADI/O radiation radiologist dealing with x-rays and other forms of energy for x-raying body parts & treating diseases RHIN/O nose rhinologist dealing with the nose & its diseases UR/O urine, urologist diagnoses & treats diseases & urinary disorders of the system of females & the organs genitourinary system of males PRACTICE TEST (3) Name the field of specialty for each term: 1. Cardiology 2. Endocrinology 3. Gastroenterology 4. Gerontology 5. Hematology 6. Nephrology 7. Neurology 8. Oncology 9. Radiology 10. Urology 15
16 Common Prefixes Prefix Meaning Example A- no, not, apnea (ǎp-nē ah) (before consonant) without without breath AN- no, not, analgesic (ăn ăl-jē sĭk) (before vowel) without drug for pain relief without affecting consciousness AB- away from abductor (ăb-dŭk tor) muscle that moves a body part away from the midline AD- toward, near adductor (ah-dŭk tor) muscle that moves a part toward the midline ANA- up, apart anaphoria (ǎn-ah-fō rē-ah) tendency of the eyes to turn upward when at rest ANTE- before, forward anteversion (ǎn tē-ver zhǔn) abnormal tipping forward of an organ (such as the uterus) AUTO- self, own autoimmune (aw tō-ĭ-mŭn ) production of antibodies against one s tissues BI- two, both biceps (bī sĕps) muscle that has two heads or points of origin CO- with, together coenzyme (kō-ĕn zīm) (before h or a vowel) substance that binds with a protein to form an enzyme COL- with, together collapse (kō-lǎps ) (before l) Falling together of a structure s wall COM- with, together compression (kŏm-presh ŭn) (before h, m, or p) squeezing together 16
17 Prefix Meaning Example COM- with, together contraction (kǒn-trǎk shǔn) (before h or a vowel) drawing together COR- with, together corrugator (kǒr u-gā ter) (before r) a muscle that wrinkles the skin DE- down, lack of dehydration (dē hī-drā shŭn) lack of water DIA- through, diarrhea (dī-ah-rē ah) complete rapid discharge of fecal matter DIS- apart, away from dissect (dī-sĕct ) cut apart DYS- bad, painful dysfunction (dĭs-fŭnk shŭn) abnormal function E- out elution (ē-lū shŭn) separation of a chemical substance EC-, ECTO- outer, outside ectopic (ĕk-tŏp ĭk) located away from normal position EN- in encapsulation (ĕn-kăp sū-lā shŭn) enclosure in a capsule ENDO- within, inner endometrium (ĕn-dō-mē trē-ŭm) membrane lining the uterus EPI- above, upon epidermis (ĕp ĭ-der mĭs) outermost layer of the skin EX- out excision (ĕk-sĭzh ŭn) removal by cutting out EXTRA- outside of extrapulmonary (ĕks tra-pŭl mĭn-ē rē) not connected with the lungs HEMI- half hemilateral (hĕm ē-lăt er-ăl) affecting one side of the body HYPER- excessive, above hypertension (hī per-tĕn shŭn) persistently high blood pressure 17
18 Prefix Meaning Example HYPO- below, deficient hypoglycemia (hī pō-glī-sēmē-ah) abnormally low level of sugar in blood IN- in, into incision (ĭn-sĭzh ŭn) cutting into INFRA- below, beneath infraclavicular (ĭin frah-klah-vĭik ū-lăr) below the clavicle INTER- between interosseous (ĭn ter-ŏs ē-ŭs) between two bones INTRA- within intravenous (ĭn trah-vē nŭs) within a vein MACRO- large macronutrient (măk rō-nū trē-ĕnt) nutrient with a large daily requirement MAL- bad malignant (mah-lĭg nant) cancerous META- change metabolism (mĕ-tăb ō-lĭzm) process of changing food to a form used by the body beyond metacarpal (mĕt ah-kăr pal) bones beyond the wrist MICRO- small microscope (mī krō-skōp) instrument used to obtain a large image of small objects NEO- new neonatal (nē ō-nā tăl) newborn PAN- all panhysterectomy (păn hĭs-ter-ĕk tō-mē) total hysterectomy PARA- near, along the parametric (par ah-mĕt rĭk) side of near the uterus PERI- surrounding peritoneum (per ĭ-tō-nē ŭm) membrane surrounding the abdominal and pelvic cavities 18
19 Prefix Meaning Example POLY- many, much polydipsia (pŏl ē-dĭp sē-ah) excessive thirst POST- after, behind posttraumatic (pōst traw-măt ĭk) following injury PRE- before prenatal (prē-nā tăl) before birth PRO- before, forward prognosis (prŏg-nō sĭs) forecast of probable outcome of disease and treatment PROS- before, forward prosencephalon (prōs ĕn-sef ah-lŏn) the forebrain PSEUDO- false pseudoparalysis (soo dō-pah-răl ĭ-sĭs) loss of muscular power without real paralysis RE- back, again relapse (rē lăps ) symptoms of disease returned RETRO- behind, backward retrodisplacement (rĕ trō-dĭs-plās mĕnt) backward displacement SUB- beneath, less than subcutaneous (sŭb kū-tā nē-ŭs) under the skin SUPRA- above, upper supraclavicular (soo prah-klah-vĭk ū lăr) above the clavicle SYN- with, together syndrome (sĭn drōm) groups of symptoms that occur together TRANS- across, through transverse (trăns-vers ) extending through a structure from side to side TRI- three triceps (trī sĕps) muscle formed from three divisions ULTRA- beyond ultrasonic (ŭl trah-sŏn ĭk) beyond the audible range 19
20 PRACTICE TEST (4) Circle the correct prefix for each meaning: 1. Toward AD- AB- ANA- ANTE- ANTI- 2. Two TRI- BI- UNI- HEMI- DIA- 3. Excessive, HYPO- DYS- PARA- PAN- HYPERabove 4. False RETRO- POST- PSEUDO- MAL- META- 5. Out, outside ENDO- ECTO- EX- ULTRA- SUB- PRACTICE TEST (5) Add the correct hyphen (-) to each term to identify each suffix (s) and prefix (p). Briefly define each term. -DYNIA S pain AB- P away from 1. MACRO 2. STOMY 3. ALGIA 4. HYPO 5. RRHAGE 6. NEO 20
21 PRACTICE TEST ANSWERS (1) Page 8 1. Core meaning of a word; stem 2. Unit of meaning attached to the beginning of a word 3. Unit of meaning attached to the end of a word 4. Vowel added to the end of a root, without changing the meaning of the root 5. Root plus combining vowel (usually o ) 6. Separation of a whole into parts 1. Suffix 2. Prefix 3. Root (2) Page Inflammation of the stomach 2. A stomachache 3. Inflammation of the stomach and small intestine 4. Inflammation of the small intestine 5. Surgical removal of the stomach 6. Cutting an opening into the stomach 7. Pertaining to the stomach 21
22 PRACTICE TEST ANSWERS (3) Page Study of the heart 2. Study of internal secretion 3. Study of stomach and secretions 4. Study of old age 5. Study of the kidney 6. Study of blood 7. Study of the kidney 8. Study of tumors 9. Study of x-rays 10. Study of the urinary system (4) Page AD- 2. BI- 3. HYPER- 4. PSEUDO- 5. ECTO- (5) Page MACRO- P large 2. -STOMY S opening 3. -ALGIA S pain 4. HYPO- P below, under, deficient 5. -RRHAGE S bursting forth of blood 6. NEO- P new 22
23 References Chabner, Davi-Ellen. The Language of Medicine. 2 nd Edition. W.B.Saunders Company 1981 Dorland s Pocket Medical Dictionary, 25 th Edition Harcourt Learning Direct, Introduction to Medical Terminology JeHarned. Medical Terminology Made Easy. Physicians Record Company Tortora, Gerard J., & Grabowski, Sandra Reynolds. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition. Harper Collin College Publishers, 1996 Vaughn, Dean. Medical Terminology 350 Learning Guide. DCM/Instructional Systems
24 INSTRUCTIONS FOR SUBMITTING EXAMINATION ANSWERS You can only take the final exam on line! Use the same link that took you to the page that was ed to you to access the course. You can also use the back arrow on the top left corner of the PDF page to go back to the home page to take the exam. At the bottom of that page is a start exam now button for you to click for taking the exam on the When prompted, be sure to spell your name exactly the way you want it to appear on your certificate of completion. When prompted, enter your EO license number correctly to ensure that your credits are entered properly into CEBroker. As soon as you have completed the exam, you will be sent an with a link to a PDF file so you can print your certificate. You can also save that PDF file for your reference. You can also forward your with this certificate to the SCMHR for credit towards your CME renewal. Judy Adams Training Center of America will enter your hours into the mandatory CEBroker system. Thank you! 24
CHAPTER 1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY BUILDING BLOCKS
 CHAPTER 1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY BUILDING BLOCKS COMPLETION 1. An enlarged stomach is known as. gastromegaly 2. Inflammation of the joints is known as. arthritis 3. Pertaining to the stomach is known as.
CHAPTER 1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY BUILDING BLOCKS COMPLETION 1. An enlarged stomach is known as. gastromegaly 2. Inflammation of the joints is known as. arthritis 3. Pertaining to the stomach is known as.
Upon completion of this continuing education course, the professional should be able to:
 COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is designed for individuals working in medical support services (e.g., billing, insurance, transcription, records, medical assisting, etc.) to review, refine, and expand
COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is designed for individuals working in medical support services (e.g., billing, insurance, transcription, records, medical assisting, etc.) to review, refine, and expand
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. All answers to questions asking for a combining form must be written in the combining form style,
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. All answers to questions asking for a combining form must be written in the combining form style,
Medical Terminology made easy...
 Medical Terminology made easy... well, sort of... What is medical terminology? describes parts of the body locations in the body bodily functions (physiology) diseases procedures instruments Why so complicated?
Medical Terminology made easy... well, sort of... What is medical terminology? describes parts of the body locations in the body bodily functions (physiology) diseases procedures instruments Why so complicated?
Chapter 5 Medical Terminology Health Care Science Technology
 Chapter 5 Medical Terminology Health Care Science Technology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Objectives 2 Identify the 4 medical technology word parts. Build and break apart medical terms to
Chapter 5 Medical Terminology Health Care Science Technology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Objectives 2 Identify the 4 medical technology word parts. Build and break apart medical terms to
FAQ: Foundations of Medical Terminology
 Question 1: What is the purpose of a root? A root in a medical term is the basic meaning of the term. Roots refer to body parts or systems of the body. Body systems include skin, muscular, digestive, nervous,
Question 1: What is the purpose of a root? A root in a medical term is the basic meaning of the term. Roots refer to body parts or systems of the body. Body systems include skin, muscular, digestive, nervous,
List as many as you can think of Go To --Student Worksheet Med Terms I am going to start you off
 Medical Terminology You may fear learning medical terminology thinking of it as a whole new language. Actually it is just a combination of terms many of which you are familiar with. Each student needs
Medical Terminology You may fear learning medical terminology thinking of it as a whole new language. Actually it is just a combination of terms many of which you are familiar with. Each student needs
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY. Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER. Understanding Suffixes. Content Review Slides
 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 2 Understanding Suffixes Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the suffixes often used in medical terminology. Identify suffixes
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 2 Understanding Suffixes Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the suffixes often used in medical terminology. Identify suffixes
Medical Terminology The Fun in Deciphering Words. Julie A. Shay, RHIA Santa Fe HIT Program Director AAPC Conference September 29, 2012
 Julie A. Shay, RHIA Santa Fe HIT Program Director AAPC Conference September 29, 2012 Back to the Basics Pieces, Parts, Whole Body Systems Musculoskeletal Cardiovascular Solve the Puzzle 1. Word roots
Julie A. Shay, RHIA Santa Fe HIT Program Director AAPC Conference September 29, 2012 Back to the Basics Pieces, Parts, Whole Body Systems Musculoskeletal Cardiovascular Solve the Puzzle 1. Word roots
Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 10 Cardiovascular and atic Systems Cardiology The medical specialty of cardiology encompasses the treatment of heart disease. Generally, three types of cardiology specialists provide medical care: the
10 Cardiovascular and atic Systems Cardiology The medical specialty of cardiology encompasses the treatment of heart disease. Generally, three types of cardiology specialists provide medical care: the
Suffix can mean a condition, procedure, surgery, treatment. ia/ism/sis/y condition or status
 Chapter 2 suffix Outline: condition suffix specialty suffix surgical suffix diagnostic suffix disease suffix Adjective suffix Introduction about suffix suffix are always at the word ending When added to
Chapter 2 suffix Outline: condition suffix specialty suffix surgical suffix diagnostic suffix disease suffix Adjective suffix Introduction about suffix suffix are always at the word ending When added to
Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Terminology
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Terminology MATCHING Match each definition with the correct word part. a. abnormal condition b. deficient c. excessive d. pain e. surgical removal 1. -algia 2. -ectomy
Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Terminology MATCHING Match each definition with the correct word part. a. abnormal condition b. deficient c. excessive d. pain e. surgical removal 1. -algia 2. -ectomy
Respiratory System. Anatomy and Physiology Overview. Pulmonology
 Respiratory System 9 Pulmonology The medical specialty of pulmonology, also called pulmonary medicine, is the branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases involving the structures
Respiratory System 9 Pulmonology The medical specialty of pulmonology, also called pulmonary medicine, is the branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases involving the structures
Chapter 1: Basic Word Structure Test Bank
 Chapter 1: Basic Word Structure Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Gastrectomy: a. Gastric resection b. Intestinal incision c. Tumor of the stomach d. Incision of the stomach e. Resection of the intestine A
Chapter 1: Basic Word Structure Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Gastrectomy: a. Gastric resection b. Intestinal incision c. Tumor of the stomach d. Incision of the stomach e. Resection of the intestine A
TYPES OF DOCTORS. Dermatologist - This is a doctor that treats any ailment related to the skin and its appendages such as hair, nails etc.
 Cardiologist - A cardiologist is certified to treat any problem dealing with heart diseases and cardiovascular diseases. Dentist - Any dental problem from tooth decay to dentures to retainers are handled
Cardiologist - A cardiologist is certified to treat any problem dealing with heart diseases and cardiovascular diseases. Dentist - Any dental problem from tooth decay to dentures to retainers are handled
1-Choose the correct answer
 Course No: DSEC 1201 Course Title: Medical Terminology Date: 16/1/2017 No. of Questions: (5) Time: 2 hour final Exam2016/2017 Total Grade: ------------- Instructor Name: Dr. Fuad M. Nijim Student No.:
Course No: DSEC 1201 Course Title: Medical Terminology Date: 16/1/2017 No. of Questions: (5) Time: 2 hour final Exam2016/2017 Total Grade: ------------- Instructor Name: Dr. Fuad M. Nijim Student No.:
Spelling & Pronunciation
 Spelling & Pronunciation Question 1: What are examples of medical terms with silent and differently pronounced letters? Examples of silent and differently pronounced letters (Leonard, 2000): pneumonia
Spelling & Pronunciation Question 1: What are examples of medical terms with silent and differently pronounced letters? Examples of silent and differently pronounced letters (Leonard, 2000): pneumonia
This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system
 SECTION 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system that allows blood to travel through the body. The heart works as a pump to keep
SECTION 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system that allows blood to travel through the body. The heart works as a pump to keep
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY LANGUAGE FOR HEALTH CARE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY LANGUAGE FOR HEALTH CARE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 medical terminology language for health care medical terminology language for pdf medical terminology language
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY LANGUAGE FOR HEALTH CARE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 medical terminology language for health care medical terminology language for pdf medical terminology language
Title: Pamela Chandler M.Ed, RHIT, CDIP Academic Complex 411F
 Course Number and Title: Instructor: Credit Hours: Course Description: Due Dates: Required Textbook: AH 290 Medical Terminology Pamela Chandler M.Ed, RHIT, CDIP Academic Complex 411F pamela.skipworth@wku.edu
Course Number and Title: Instructor: Credit Hours: Course Description: Due Dates: Required Textbook: AH 290 Medical Terminology Pamela Chandler M.Ed, RHIT, CDIP Academic Complex 411F pamela.skipworth@wku.edu
PHYSICIAN (MD/DO) Varies by specialty: $150,000-$700,000. University of Kentucky, University of Louisville, University of Pikeville
 PHYSICIAN (MD/DO) Description A physician diagnoses and treats patients as part of the health care team. There are many different specialties in the career. Education Required Doctorate 8yr + Residency
PHYSICIAN (MD/DO) Description A physician diagnoses and treats patients as part of the health care team. There are many different specialties in the career. Education Required Doctorate 8yr + Residency
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine
 Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
UW- Extensions provides equal opportunities in employment and programming including Title IX and ADA. 1
 Chapter 4 gives us the beginning of talking about prefixes. We've done the roots and the basic word analysis and suffixes. So now we go to the prefixes. And there's a variety of mixed slides here that
Chapter 4 gives us the beginning of talking about prefixes. We've done the roots and the basic word analysis and suffixes. So now we go to the prefixes. And there's a variety of mixed slides here that
list of speciality types
 Descriptions of Speciality Types GENERAL PRACTITIONER GENERAL PRACTITIONER GP or family practitioner (FP) Family doctor A medical practitioner whose practice is not limited to any specific branch of medicine
Descriptions of Speciality Types GENERAL PRACTITIONER GENERAL PRACTITIONER GP or family practitioner (FP) Family doctor A medical practitioner whose practice is not limited to any specific branch of medicine
A Sound Track to Reading
 A Sound Track to Reading Blending Flashcards Prepared by Donald L Potter June 1, 2018 Mr. Potter prepared these cards to be used with Sister Monica Foltzer s advanced intensive phonics program and reader,
A Sound Track to Reading Blending Flashcards Prepared by Donald L Potter June 1, 2018 Mr. Potter prepared these cards to be used with Sister Monica Foltzer s advanced intensive phonics program and reader,
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Combining Forms Append/o appendix Hepat/o liver Appendic/o appendix Lingu/o tongue Col/o colon Myc/o fungus Dent/o teeth Odont/o teeth Enter/o intestine Or/o mouth Esophag/o esophagus
The Digestive System Combining Forms Append/o appendix Hepat/o liver Appendic/o appendix Lingu/o tongue Col/o colon Myc/o fungus Dent/o teeth Odont/o teeth Enter/o intestine Or/o mouth Esophag/o esophagus
EHS Benchmark 1. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 EHS Benchmark 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The horizontal plane that divides the body into a top half and a bottom half is the. a.
EHS Benchmark 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The horizontal plane that divides the body into a top half and a bottom half is the. a.
Health Education (HLED) 1541 Medical Terminology (3 Units) CSU [formerly Health Education 41] Prerequisite: None. Total Hours: 48 hours lecture
![Health Education (HLED) 1541 Medical Terminology (3 Units) CSU [formerly Health Education 41] Prerequisite: None. Total Hours: 48 hours lecture Health Education (HLED) 1541 Medical Terminology (3 Units) CSU [formerly Health Education 41] Prerequisite: None. Total Hours: 48 hours lecture](/thumbs/94/120119998.jpg) Health Education (HLED) 1541 Medical Terminology (3 Units) CSU [formerly Health Education 41] Prerequisite: None Total Hours: 48 hours lecture Prepared by: D. Headrick Reviewed by: G. Golling Date prepared:
Health Education (HLED) 1541 Medical Terminology (3 Units) CSU [formerly Health Education 41] Prerequisite: None Total Hours: 48 hours lecture Prepared by: D. Headrick Reviewed by: G. Golling Date prepared:
Latin Language course
 Latin Language course The main aim of the Latin language course is to form the fundamentals of terminological competence of health professionals capable of using medical terms of Greek and Latin origin
Latin Language course The main aim of the Latin language course is to form the fundamentals of terminological competence of health professionals capable of using medical terms of Greek and Latin origin
CORE MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Course Syllabus
 Course Syllabus Course Number: HLTH-0342 OHLAP Credit: No OCAS Code: None Course Length: 45 Hours Career Cluster: Health Science Career Pathway: Therapeutic Services Career Major(s): Pre-requisite(s):
Course Syllabus Course Number: HLTH-0342 OHLAP Credit: No OCAS Code: None Course Length: 45 Hours Career Cluster: Health Science Career Pathway: Therapeutic Services Career Major(s): Pre-requisite(s):
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
Directions: For each of the following terms, select the best definition from the options provided.
 CC306M: Medical Terminology Quiz 1 June 4, 2012 Section 1: Defining Terms Directions: For each of the following terms, select the best definition from the options provided. 1. carcinophobia a. cancer-eating
CC306M: Medical Terminology Quiz 1 June 4, 2012 Section 1: Defining Terms Directions: For each of the following terms, select the best definition from the options provided. 1. carcinophobia a. cancer-eating
study of body structure & Physiology study of body function
 study of body structure & Physiology study of body function Medical Words Made up of Latin, Greek, French, German, Dutch, Scandinavian, Italian, English, etc.. Common Medical Roots, Prefixes & Suffixes
study of body structure & Physiology study of body function Medical Words Made up of Latin, Greek, French, German, Dutch, Scandinavian, Italian, English, etc.. Common Medical Roots, Prefixes & Suffixes
If You Have Head or Neck Cancer
 EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
Medical Terminology. 1 P a g e
 Medical Terminology 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Medical Terminology Assignment Guidelines When terms are assigned, primarily the Latin or Greek word parts will be given; however, combined forms of the word parts
Medical Terminology 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Medical Terminology Assignment Guidelines When terms are assigned, primarily the Latin or Greek word parts will be given; however, combined forms of the word parts
Premium Specialty: Pediatrics
 Premium Specialty: Pediatrics Credentialed Specialties include: Adolescent Medicine, Pediatric Adolescent, and Pediatrics This document is designed to be used in conjunction with the UnitedHealth Premium
Premium Specialty: Pediatrics Credentialed Specialties include: Adolescent Medicine, Pediatric Adolescent, and Pediatrics This document is designed to be used in conjunction with the UnitedHealth Premium
An Interview with a Chiropractor
 An Interview with a Chiropractor Doctor Scott Warner took the time out of his busy schedule to talk to us about chiropractic medicine what it is, what it isn t, and why he chose it as a profession. What
An Interview with a Chiropractor Doctor Scott Warner took the time out of his busy schedule to talk to us about chiropractic medicine what it is, what it isn t, and why he chose it as a profession. What
Assignments for SUM Program Beginning Medical Transcription, 2nd edition
 Assignments for SUM Program Beginning, 2nd edition SECTION 1 Introduction, Dermatology/ Plastics Body () Unit 1, Body as a Whole, Ch. 1, Organization of the Body; Ch. 4, Tissues, Glands, etc., Ch. 5, Integumentary
Assignments for SUM Program Beginning, 2nd edition SECTION 1 Introduction, Dermatology/ Plastics Body () Unit 1, Body as a Whole, Ch. 1, Organization of the Body; Ch. 4, Tissues, Glands, etc., Ch. 5, Integumentary
The Language of Science and Medicine
 The Language of Science and Medicine Why do scientists seem to speak a foreign language (in any language)? Model 1: Common root words and their meaning Root word Meaning Example Example Definition arthr-
The Language of Science and Medicine Why do scientists seem to speak a foreign language (in any language)? Model 1: Common root words and their meaning Root word Meaning Example Example Definition arthr-
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Sinus Surgery. Middle Meatus
 Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
The University of Jordan. Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center. COURSE Syllabus
 The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center COURSE Syllabus 1 Course title Medical terminology 2 Course number 1203102 3 Credit hours (theory, practical) Contact hours (theory, practical)
The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center COURSE Syllabus 1 Course title Medical terminology 2 Course number 1203102 3 Credit hours (theory, practical) Contact hours (theory, practical)
Step 1: Salivary Structures
 (Slide1) Step 1: Salivary Structures Remove the skin, fat and connective fascia to view the salivary glands and ducts. The submaxillary salivary gland is just behind the masseter muscle and pretty easy
(Slide1) Step 1: Salivary Structures Remove the skin, fat and connective fascia to view the salivary glands and ducts. The submaxillary salivary gland is just behind the masseter muscle and pretty easy
8 Digestive System. Anatomy and Physiology Overview
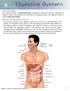 8 Digestive System Gastroenterology The medical practice of gastroenterology encompasses treatment of diseases affecting the digestive system. The physician who specializes in treating disorders of the
8 Digestive System Gastroenterology The medical practice of gastroenterology encompasses treatment of diseases affecting the digestive system. The physician who specializes in treating disorders of the
2. Important Pharmacy Abbreviations A. Routes (p 8) B. Forms (p 8) C. Times (p 9) D. Measurements (p 9) E. Other (p 10) F. Sample Questions (p 11)
 Module Three Pharmacology, Medical and Pharmacy Abbreviations Table of Contents 1. Basic Pharmacology A. Pharmacology i. The Object of Drug Delivery (p 3) ii. Drug Receptors (p 3) iii. Concentration to
Module Three Pharmacology, Medical and Pharmacy Abbreviations Table of Contents 1. Basic Pharmacology A. Pharmacology i. The Object of Drug Delivery (p 3) ii. Drug Receptors (p 3) iii. Concentration to
Body Science: Cell Theory (3 rd -5 th Grades) Pre-Visit Activities
 Body Science: Cell Theory (3 rd -5 th Grades) Pre-Visit Activities Vocabulary List and Student Definitions (elementary level): Cell: basic unit of life, too small to see with the naked eye Tissue: group
Body Science: Cell Theory (3 rd -5 th Grades) Pre-Visit Activities Vocabulary List and Student Definitions (elementary level): Cell: basic unit of life, too small to see with the naked eye Tissue: group
Medical Terminology EMED1201/ Mid- Term Exam. PART I: Multiple Choice Questions - Select the one best answer:
 Question One: Medical Terminology EMED1201/ Mid- Term Exam PART I: Multiple Choice Questions - Select the one best answer: 1. The main part of a medical term is the A. prefix B. combining form. C. root.
Question One: Medical Terminology EMED1201/ Mid- Term Exam PART I: Multiple Choice Questions - Select the one best answer: 1. The main part of a medical term is the A. prefix B. combining form. C. root.
Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224 Lama Alzamil Email: lalzamil1@ksu.edu.sa 3 rd floor/ office #119 Lecture 1: The Human Body (an orientation) 1. An overview of anatomy and physiology. 2. Levels of structural
Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224 Lama Alzamil Email: lalzamil1@ksu.edu.sa 3 rd floor/ office #119 Lecture 1: The Human Body (an orientation) 1. An overview of anatomy and physiology. 2. Levels of structural
Pelvic Support Problems
 AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
Patient Care: Dental
 C H A PTER 05 Patient Care: Dental CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Af t e r c a re f u l s t u dy of t h i s c h a p ter, you should be able to: 1. State the education, training, and legal requirements for becoming
C H A PTER 05 Patient Care: Dental CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Af t e r c a re f u l s t u dy of t h i s c h a p ter, you should be able to: 1. State the education, training, and legal requirements for becoming
UNIT 1. Introduction
 UNIT 1 Introduction Grading A grade is an inadequate report of an inaccurate judgment by a biased and variable judge of the extent to which a student has attained an undefined level of mastery of an unknown
UNIT 1 Introduction Grading A grade is an inadequate report of an inaccurate judgment by a biased and variable judge of the extent to which a student has attained an undefined level of mastery of an unknown
Listen to Arshia talking to Dr. Davis. Fill in the missing words. Dr. Davis: All, right we re all set, you can get.
 Listen to Arshia talking to Dr. Davis. Fill in the missing words. Dr. Davis: All, right we re all set, you can get. Arshia: Can I ask you a before you go? Dr. Davis: Sure Arshia: Just to make sure I, what
Listen to Arshia talking to Dr. Davis. Fill in the missing words. Dr. Davis: All, right we re all set, you can get. Arshia: Can I ask you a before you go? Dr. Davis: Sure Arshia: Just to make sure I, what
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
DeltaScience. Content Readers. Summary. Science Background. Objectives. Reading Comprehension Skills. Supporting English Learners
 DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe cells, the basic units of all living things. List the four main kinds of tissue
DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe cells, the basic units of all living things. List the four main kinds of tissue
How Is Lupus Diagnosed?
 Fever with no known cause Red rashes, most often on the face Chest pain when taking a deep breath Hair loss Pale or purple fingers or toes Sensitivity to the sun Swelling in legs or around eyes Mouth ulcers
Fever with no known cause Red rashes, most often on the face Chest pain when taking a deep breath Hair loss Pale or purple fingers or toes Sensitivity to the sun Swelling in legs or around eyes Mouth ulcers
Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia
 Patient and Family Education Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia What is tracheoesophageal fistula? The word fistula means abnormal connection. Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a condition
Patient and Family Education Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia What is tracheoesophageal fistula? The word fistula means abnormal connection. Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a condition
The Body s Organization
 Chapter 4 The Body s Organization CHAPTER CONTENTS Introduction The Major Body Cavities The Anatomic Position and Directional Terms Body Systems Exercises Pre-Quiz Checklist Chapter Quiz 28 CHAPTER 4 THE
Chapter 4 The Body s Organization CHAPTER CONTENTS Introduction The Major Body Cavities The Anatomic Position and Directional Terms Body Systems Exercises Pre-Quiz Checklist Chapter Quiz 28 CHAPTER 4 THE
Introduction. Study detail of structure - - Gross Anatomy. Study all structures in one part of body Study of internal structures as relate to skin
 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
9 Review. Labeling Exercise. Blood high in oxygen. Blood low in oxygen. Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195
 Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195 Chapter 9 Review Labeling Exercise THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer
Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195 Chapter 9 Review Labeling Exercise THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer
[A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
![[A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE] [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]](/thumbs/88/117127924.jpg) 2013 COLORECTAL SURGERY GROUP Dr. Carl J. Brown Dr. Ahmer A. Karimuddin Dr. P. Terry Phang Dr. Manoj J. Raval Authored by Jennifer Lee A cartoon about colonoscopies. 1 [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
2013 COLORECTAL SURGERY GROUP Dr. Carl J. Brown Dr. Ahmer A. Karimuddin Dr. P. Terry Phang Dr. Manoj J. Raval Authored by Jennifer Lee A cartoon about colonoscopies. 1 [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
Chapter 22. Body Organization & Structure
 Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Dissection: The Fetal Pig
 Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Presenting the Read-Aloud
 Organs Presenting the Read-Aloud 4A 15 minutes Organs Show image 4A-1: Nick Nutri showing photos of the progression of cells, tissues, and? 1 1 [Review the progression with students and ask them to predict
Organs Presenting the Read-Aloud 4A 15 minutes Organs Show image 4A-1: Nick Nutri showing photos of the progression of cells, tissues, and? 1 1 [Review the progression with students and ask them to predict
Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer
 Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Medical Terminology & Transcription Editor Online
 Education & Training Plan Medical Terminology & Transcription Editor Online MyCAA Information Tuition: $3200 (RMT-AHDI exam included) MyCAA Course Code: LIT-MTE2 Course Contact Hours: 400 Hours Program
Education & Training Plan Medical Terminology & Transcription Editor Online MyCAA Information Tuition: $3200 (RMT-AHDI exam included) MyCAA Course Code: LIT-MTE2 Course Contact Hours: 400 Hours Program
Introduction to Body Systems
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
Introduction to Human Anatomy. Prepared by:- Mohammad Zmaili
 Introduction to Human Anatomy 1 Prepared by:- Mohammad Zmaili Definitions Anatomy: the science of the structure and shape of living organisms and their parts. Physiology: the science that deals with the
Introduction to Human Anatomy 1 Prepared by:- Mohammad Zmaili Definitions Anatomy: the science of the structure and shape of living organisms and their parts. Physiology: the science that deals with the
Lab Report Sheet. Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did)
 Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
University of Palestine. Final Exam 1 nd Semester 2014/2015 Total Grade: 120. Medical Terminology
 Course No: UNI1305 Course Title:Medical Terminology Date: 21/1/2015 No. of Questions: (9) Time: 2 hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Final Exam 1 nd Semester 2014/2015 Total Grade: 120
Course No: UNI1305 Course Title:Medical Terminology Date: 21/1/2015 No. of Questions: (9) Time: 2 hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Final Exam 1 nd Semester 2014/2015 Total Grade: 120
Contents. Section 1: The Circulatory System. Section 2: The Digestive System. Section 3: The Excretory System. Section 4: The Endocrine System
 Contents Section 1: The Circulatory System 1. The Heart... 2 2. The Blood Vessels.... 6 3. The Blood.... 10 4. Quiz 1.... 14 Section 2: The Digestive System 5. The Mouth and Esophagus.... 15 6. The Stomach....
Contents Section 1: The Circulatory System 1. The Heart... 2 2. The Blood Vessels.... 6 3. The Blood.... 10 4. Quiz 1.... 14 Section 2: The Digestive System 5. The Mouth and Esophagus.... 15 6. The Stomach....
Contact us! Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 4200 Nashville, TN
 Contact us! Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 4200 Nashville, TN 37232-8774 615-343-9430 This information is intended for education of the reader about medical conditions
Contact us! Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 4200 Nashville, TN 37232-8774 615-343-9430 This information is intended for education of the reader about medical conditions
New Hope Clinic Weekly Reports March Weekly Report March 2-6, 2015
 New Hope Clinic Weekly Reports March 2015 Weekly Report March 2-6, 2015 This week we saw a total of 100 patients, 30 of whom were unable to pay because of limited financial I sent a 4 year old girl to
New Hope Clinic Weekly Reports March 2015 Weekly Report March 2-6, 2015 This week we saw a total of 100 patients, 30 of whom were unable to pay because of limited financial I sent a 4 year old girl to
Body System: Team Members: Body System Project
 Body System: Team Members: Body System Project Working with your team, you will research an assigned body system, create a slide presentation, draw a diagram of the system, and present to the class. You
Body System: Team Members: Body System Project Working with your team, you will research an assigned body system, create a slide presentation, draw a diagram of the system, and present to the class. You
Surgery for vaginal vault prolapse. Patient decision aid
 Surgery for vaginal vault prolapse Patient decision aid? i What is vaginal vault prolapse? Vaginal vault prolapse happens when the top of the vagina (the vault) slips from its normal position and sags
Surgery for vaginal vault prolapse Patient decision aid? i What is vaginal vault prolapse? Vaginal vault prolapse happens when the top of the vagina (the vault) slips from its normal position and sags
Integrated General Biology
 Integrated General Biology A Contextualized Approach FIRST EDITION Jason E. Banks Julianna L. Johns Diane K. Vorbroker, PhD Chapter 13 Life, Organization, Anatomy & Physiology Section 13.1 The Facts of
Integrated General Biology A Contextualized Approach FIRST EDITION Jason E. Banks Julianna L. Johns Diane K. Vorbroker, PhD Chapter 13 Life, Organization, Anatomy & Physiology Section 13.1 The Facts of
KEY TO LIFE CHIROPRACTIC
 KEY TO LIFE CHIROPRACTIC REGISTRATION FORM Date Home Phone Cell Phone Email Last Name First Name Middle Initial Street Address City State Zip Sex M F Birth Date Occupation How did you hear about this office?
KEY TO LIFE CHIROPRACTIC REGISTRATION FORM Date Home Phone Cell Phone Email Last Name First Name Middle Initial Street Address City State Zip Sex M F Birth Date Occupation How did you hear about this office?
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
Understanding Epilepsy Lapbook
 Understanding Epilepsy Lapbook Designed for 2 nd - 8 th Grades L-EPIL Designed by Cyndi Kinney & Amy Moses Understanding Epilepsy Lapbook Copyright 2014 Knowledge Box Central www.knowledgeboxcentral.com
Understanding Epilepsy Lapbook Designed for 2 nd - 8 th Grades L-EPIL Designed by Cyndi Kinney & Amy Moses Understanding Epilepsy Lapbook Copyright 2014 Knowledge Box Central www.knowledgeboxcentral.com
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Strands & Standards MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
 Strands & Standards MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY COURSE DESCRIPTION A one-semester course that helps students understand the Greek- and Latin-based language of medicine and healthcare. Emphasis is placed upon word
Strands & Standards MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY COURSE DESCRIPTION A one-semester course that helps students understand the Greek- and Latin-based language of medicine and healthcare. Emphasis is placed upon word
KEY TO LIFE CHIROPRACTIC
 KEY TO LIFE CHIROPRACTIC REGISTRATION FORM Date Home Phone Cell Phone Email Last Name First Name Middle Initial Street Address City State Zip Sex M F Birth Date Occupation How did you hear about this office?
KEY TO LIFE CHIROPRACTIC REGISTRATION FORM Date Home Phone Cell Phone Email Last Name First Name Middle Initial Street Address City State Zip Sex M F Birth Date Occupation How did you hear about this office?
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N
 Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Appendicitis. Diagnosis and Surgery
 Appendicitis Diagnosis and Surgery What Is Appendicitis? Your side may hurt so much that you called your doctor. Or maybe you went straight to the hospital emergency room. If the symptoms came on quickly,
Appendicitis Diagnosis and Surgery What Is Appendicitis? Your side may hurt so much that you called your doctor. Or maybe you went straight to the hospital emergency room. If the symptoms came on quickly,
Contents. Section 1: Life s Building Blocks. Section 2: The Human Framework. Section 3: The Senses and the Respiratory System
 Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig Integrated Science 4 Honors
 Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig Integrated Science 4 Honors Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig Integrated Science 4 Honors Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
Chapter One Study Guide Answers
 Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Your Home Exercise Plan
 A Home Exercise Plan is designed for people who are unable to attend Pulmonary Rehabilitation classes in a community setting. This may be for a number of reasons such as travelling difficulties, personal
A Home Exercise Plan is designed for people who are unable to attend Pulmonary Rehabilitation classes in a community setting. This may be for a number of reasons such as travelling difficulties, personal
Welcome to Biology! 1. Watch the videos below and answer the corresponding questions. These videos will provide a visual for your learning.
 Welcome to Biology! What s In your Summer Assignment Packet? 1. Directions Page 2. Video Worksheets that must be completed for your binder a. Cell Membrane b. Cell Organelles c. Cells Alive (3) i. Animal
Welcome to Biology! What s In your Summer Assignment Packet? 1. Directions Page 2. Video Worksheets that must be completed for your binder a. Cell Membrane b. Cell Organelles c. Cells Alive (3) i. Animal
7 weeks: 28 mm 8 weeks: 40 mm 15 weeks: 220 mm 17 weeks: 300 mm
 Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Honduras New Hope Clinic Weekly Reports, August Weekly Report August 3-7, 2015
 Honduras New Hope Clinic Weekly Reports, August 2015 Weekly Report August 3-7, 2015 This week we saw a total of 82 patients, 35 of whom were unable to pay because of limited financial This a 32 year old
Honduras New Hope Clinic Weekly Reports, August 2015 Weekly Report August 3-7, 2015 This week we saw a total of 82 patients, 35 of whom were unable to pay because of limited financial This a 32 year old
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Testing Services and School of Allied Health & Communicative Disorders HSCI 318 Proficiency Examination Medical Terminology COURSE DESCRIPTION: A study of the basic language
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Testing Services and School of Allied Health & Communicative Disorders HSCI 318 Proficiency Examination Medical Terminology COURSE DESCRIPTION: A study of the basic language
Chapter 12. Eye. Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 12 Eye Chapter 12 Objective 1: Pronounce organs and anatomic structures of the eye. Anatomy of the Eye Visible Surface of the Eye Lacrimal Apparatus of the Eye Select the pronunciation of the anatomic
Chapter 12 Eye Chapter 12 Objective 1: Pronounce organs and anatomic structures of the eye. Anatomy of the Eye Visible Surface of the Eye Lacrimal Apparatus of the Eye Select the pronunciation of the anatomic
This nonfiction book
 This nonfiction book presents basic facts about ears and hearing in both people and animals. Diagrams help simplify challenging concepts. Interesting details about animals ears are supported by photos
This nonfiction book presents basic facts about ears and hearing in both people and animals. Diagrams help simplify challenging concepts. Interesting details about animals ears are supported by photos
A. Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow.
 JAZAN UNIVERSITY ENGLISH LANGUAGE CENTER Medical Colleges 2nd Progress Test Name in Arabic Name in English االسم بالعربية االسم باإلنجليزية Marking Profile Skill READING WRITING GRAMMAR 1st Check 2nd Check
JAZAN UNIVERSITY ENGLISH LANGUAGE CENTER Medical Colleges 2nd Progress Test Name in Arabic Name in English االسم بالعربية االسم باإلنجليزية Marking Profile Skill READING WRITING GRAMMAR 1st Check 2nd Check
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
