The Endocrine System
|
|
|
- Maximillian Townsend
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 د.محمد حسین Histlgy The Endcrine System Is a grup f glands that regulate physilgical functins by releasing hrmnes int the bld stream. Intercellular signaling is the way by which a cell exerts its effects n anther cell ( r n itself ) and it subdivided int the fllwing classificatins: 1) Intracrine signals are prduced within the target cell. 2) Autcrine signals target the cell itself. 3) Juxtacrine signals target adjacent (tuching) cells. 4) Paracrine signals target cells in the vicinity f the emitting cell ( e.g. neurtransmitters) 5) Endcrine signals target distant cells by prducing hrmnes that travel thrugh the bld t reach all parts f the bdy. The endcrine system includes: 1. Endcrine glands, such as the pituitary, thyrid and parathyrid, adrenal, and the pineal gland; 2. Clusters f endcrine cells lcated in the rgans such as islets f Langerhans in the pancreas; and 3. Islated endcrine cells in certain tissues, such as the enterendcrine cells in the epithelium f the respiratry and digestive tracts. The rgans r tissues that are activated by released hrmnes are called target rgans r tissues. The cells in the target rgan/tissue have apprpriate receptrs, which are able t recgnize and respnd t specific hrmnes. Hrmne: a chemical substance prduced in the bdy that cntrls and regulates the activity f certain cells r rgans. The hrmnes can be divided int three classes based n their structure: 1. Sterid hrmnes are lipid hrmnes that have the characteristic ring structure f sterids and are frmed frm chlesterl. ( e.g. estrgen, teststerne, crtisne, and aldsterne ). 2. Peptide hrmnes are cmpsed f amin acids. The majrity f hrmnes f this type are secreted by the pituitary gland ( ACTH, TSH, FSH, GH, and prlactin) and parathyrid glands (PTH). 3. Amine hrmnes are derived frm the amin acid tyrsine.(e.g. T3&T4 released by the thyrid and adrenaline & nradrenaline secreted by the adrenal medulla). 1
2 د.محمد حسین Histlgy The pituitary gland is a neurendcrine rgan lcated inside the skull (in the sella turcica f the sphenid bne) and cnsidered a part f the brain. It weighs abut 0.5 g in adults &has dimensins f abut 10 x 13 x 6 mm. Embrygenesis: The hypphysis develps partly frm ral ectderm and partly frm nerve tissue. The neural cmpnent arises as an evaginatin frm the flr f the diencephaln and grws caudally as a stalk withut detaching itself frm the brain. The ral cmpnent arises as an ut pcketing f ectderm frm the rf f the primitive muth f the embry and grws cranially, frming a structure called hypphyseal (Rathke's) puch. Later, a cnstrictin at the base f this puch separates it frm the ral cavity. At the same time, its anterir wall thickens, reducing the lumen f Rathke's puch t a small fissure. Because f its dual rigin, the pituitary actually cnsists f tw glands 1. The psterir Neurhypphysis 2. The anterir Adenhypphysis United anatmically but with different functins. The Neurhypphysis cnsists f : a) Pars Nervsa b) Infundibulum i. Stalk ii. Median eminence. The Adenhypphysis: a) Pars Distalis ( Anterir Lbe) b) Pars Tuberalis c) Pars Intermedia. 2
3 د.محمد حسین Histlgy Bld Supply & the Hypthalam-Hypphyseal Prtal System: The bld supply f the hypphysis derives frm the internal cartid artery: Frm abve, the superir hypphyseal arteries supply the median eminence and the neural stalk; Frm belw, inferir hypphyseal arteries prvide bld mainly fr the neurhypphysis, with a small supply t the stalk. The superir hypphyseal arteries frm a primary capillary netwrk irrigating the stalk and median eminence. The capillaries then rejin t frm venules that branch again as a larger secndary capillary netwrk in the adenhypphysis, Capillaries f bth netwrks are fenestrated. In the HHPS there are three grups f hrmnes released at three sites : 1. Peptide hrmnes synthesized by neurns in the hypthalamus (the supraptic and the paraventricular nuclei) underg axnal transprt and accumulate distally in these axns, which are situated in the pars nervsa. 2. Anther grup f peptides is prduced by neurns in ther hypthalamic nuclei and carried in axns fr temprary axnal strage and secretin in the median eminence. Then enter the capillaries f the primary plexus and are transprted t the adenhypphysis where they diffuse amng endcrine cells and cntrl hrmne release frm their target cells. 3. The third grup f hrmnes cnsists f prteins and glycprteins released frm the endcrine cells f the adenhypphysis (under the cntrl f the neurpeptides just mentined) and picked up by capillaries f the secndary plexus, frm which they enter the general circulatin. 3
4 د.محمد حسین Histlgy Adenhypphysis (Anterir Pituitary) Pars Distalis ( anterir lbe) It accunts fr 75% f the mass f the hypphysis, it mainly cnsists f crds f epithelial cells (hrmne -secreting cells) interspersed with fenestrated capillaries. With few fibrblasts prducing reticular fibers that supprt these crds. These secretry cells are classified as Chrmphbes and Chrmphils. The Chrmphbes d nt effectively take a stain, s they appear clear in the Mallry trichrme stain. These cells are undifferentiated cells but are capable f differentiating int chrmphils. The Chrmphils include: Basphils (appear blue in Mallry stain) and Acidphils (appear red in Mallry stain) Subtypes f basphilic and acidphilic cells are identified by TEM r mre easily by IHC and are named fr their specific hrmnes r target cells. Acidphils include the smattrpic and mammtrpic cells, while the Basphilils are the gnadtrpic, crtictrpic, and thyrtrpic cells. Pars Tuberalis The pars tuberalis is the neck f the adenhypphysis; it wraps arund the infundibular stalk f the pituitary gland. It cntains a rich capillary netwrk and sme lw clumnar basphilic cells that are cmmnly arranged in crds. Mst f the cells f the pars tuberalis are basphilic gnadtrpic cells that secrete flliclestimulating hrmne (FSH) and luteinizing hrmne (LH). Pars Intermedia The pars intermedia, which develps frm the drsal prtin f Rathke's puch is (in humans) a rudimentary regin made up f crds and fllicles f weakly basphilic cells that cntain small secretry granules. Melancyte stimulating hrmne (MSH) is prbably prduced in the intermediate zne, and prbably als by basphils f the pars distalis. MSH increases melancyte activity and cells f the pars intermedia are ften referred t as melantrpic cells, but the verall physilgical significance f this regin remains uncertain, especially in adults. 4
5 د.محمد حسین Histlgy Cntrl f Secretin in the Adenhypphysis: The activities f the cells f the anterir pituitary are cntrlled primarily by peptide hrmnes prduced in hypthalamic nuclei and stred in their axns that run t the median eminence. Mst f these hrmnes are hypthalamic-releasing hrmnes; liberated frm the axns, they are transprted by capillaries t the pars distalis where they stimulate hrmne synthesis and/r release. Tw f the hypthalamic factrs, hwever, act t inhibit hrmne release by specific cells f the pars distalis (hypthalamic-inhibiting hrmnes). Anther mechanism is negative feedback by hrmnes frm the target rgans n secretin f the relevant hypthalamic factrs and n hrmne secretin by the relevant pituitary cells. Finally, hrmne secretin in the pars distalis is affected by ther hrmnes frm utside the feedback lp r even utside the majr target tissues. Examples: inhibin and activin prduced in the gnads, cntrl release f FSH and LH; the xytcin, liberated in the psterir pituitary in the curse f breast feeding, which increases secretin f prlactin. Neurhypphysis (Psterir Pituitary) The pars nervsa, des nt cntain secretry cells. It is cmpsed f neural tissue, cntaining unmyelinated axns f secretry neurns whse cell bdies situated in the supraptic and paraventricular nuclei f the hypthalamus. Als present are highly branched glial cells called pituicytes that resemble astrcytes and are the mst abundant cell type in the psterir pituitary. The secretry neurns (in hypthalamus) have larger diameter axns and well-develped synthetic cmpnents related t the prductin f hrmnes vaspressin (als called antidiuretic hrmne, ADH) and xytcin. These hrmnes are transprted axnally int the pars nervsa and accumulate in axnal dilatins called neursecretry bdies r Herring bdies, visible in the LM as faintly esinphilic structures. These bdies cntain numerus membrane-enclsed granules with either xytcin r vaspressin bund t a carrier prtein called neurphysin I and II respectively. Nerve impulses alng the axns trigger the release f the peptides frm the neursecretry bdies fr uptake by the fenestrated capillaries f the pars nervsa and the hrmnes are then distributed t the general circulatin. Axns frm the supraptic nuclei are mainly cncerned with vaspressin secretin, whereas mst f the fibers frm the paraventricular nuclei are cncerned with xytcin secretin. 5
6 د.محمد حسین Histlgy CLINICAL CORRELATION Pituitary Adenmas Pituitary adenmas are benign tumrs f the anterir pituitary gland. Clinically, they can be divided int nnsecreting and secreting frms. Histrically, adenmas were classified by their staining prperties, the degree t which they tk up the H&E stains. They were classified as basphilic, acidphilic, r chrmphbic adenmas. With mdern immuncytchemical techniques, hwever, tumr cells can be classified by the type f hrmne they prduce. Sme cells d nt mark with any antibdy, and their tumrs are called null-cell adenmas. Classificatin by secretry status may reflect, fr example, excess crtisl (Cushing disease) r prlactin (prlactinma) r the verprductin f grwth hrmne (gigantism r acrmegaly). A bitempral hemianpia is cmmnly seen in patients suffering frm cmpressin f the ptic nerve. ADRENAL GLAND The adrenal (suprarenal) glands are paired rgans that lie near the superir ples f the kidneys. They are flattened structures with a half-mn shape, abut 4 6 cm lng, 1 2 cm wide, and 4 6 mm thick in adults. Tgether they weigh abut 8 g. Each gland cvered by a dense cnnective tissue capsule that sends thin septa t the interir f the gland as trabeculae. The strma cnsists mainly f a rich netwrk f reticular fibers that supprt the secretry cells. The gland cnsists f tw cncentric layers: A yellwish peripheral layer, the Adrenal Crtex(AC), and A reddish-brwn central layer, the Adrenal Medulla (AM). The AC & AM are 2 rgans with distinct rigins, functins, and mrphlgy that becme united during embrynic develpment. They arise frm different embrynic germ layers: The AC arises frm mesderm and The AM derived frm the neural crest. 6
7 د.محمد حسین Histlgy Bld Supply The adrenals are supplied by several arteries that enter at varius pints arund their periphery. The branches f these arteries frm three grups: thse supplying the capsule; the crtical arteriles, which quickly frm capillaries and sinusids that irrigate all cells f the crtex and eventually jin the medullary capillaries; and medullary arteriles, which pass directly thrugh the crtex and frm an extensive capillary netwrk in the medulla. The cells f the adrenal medulla, thus, receive bth arterial bld frm the medullary arteries and venus bld riginating frm capillaries f the crtex. The capillary and sinusidal endthelium is highly attenuated and fenestrated. Capillaries f bth the crtex and the medulla frm the central medullary veins, which jin t leave the gland as the adrenal r suprarenal vein. Adrenal Crtex Cells f the AC have characteristic features f sterid-secreting cells. These include: (1) Central nuclei and acidphilic cytplasm, usually rich in lipid drplets. (2) Their cytplasm have prfuse SER f intercnnected tubules, which cntain the enzymes fr chlesterl synthesis and cnversin f the sterid prhrmne pregnenlne int specific active sterid hrmnes. (3) The mitchndria are ften spherical, with tubular rather than shelf like cristae cntaining the enzymatic equipment fr cnverting chlesterl t pregnenlne and fr sme steps in sterid hrmne synthesis. Sterid hrmne-secreting cells d nt stre their prduct in granules; rather, they synthesize and secrete sterid hrmnes upn demand. Sterids (being LMW lipidsluble mlecules) diffuse thrugh the plasma membrane and d nt require the specialized prcess f excytsis fr their release. 7
8 د.محمد حسین Histlgy The adrenal crtex has three cncentric znes in which the crds f epithelial cells are arranged smewhat differently and are specialized t prduce different classes f sterid hrmnes: I. Immediately inside the cnnective tissue capsule is the zna glmerulsa, cnsisting f clsely packed, runded r arched crds f clumnar r pyramidal cells surrunded by many capillaries and cmprising abut 15% f the crtex. II. The middle zne, the zna fasciculata, ccupies 65 80% f the crtex and cnsists f lng crds f large plyhedral cells, ne r tw cells thick, separated by fenestrated sinusidal capillaries. The cells are mst densely filled with cytplasmic lipid drplets and, as a result f lipid disslutin during tissue preparatin, ften appear vaculated r spngy in cmmn histlgical preparatins. Because f their vaculizatin, the cells f the fasciculata are als called spngycytes. III. The innermst zna reticularis cmprises abut 10% f the crtex and cntacts the adrenal medulla. It cnsists f smaller cells dispsed in a netwrk f irregular crds interwven with wide capillaries. The cells are usually mre heavily stained than thse f the ther znes because they cntain fewer lipid drplets and mre lipfuscin pigment. Crtical Hrmnes & Their Actins: The main prduct f the Z.G is a mineralcrticid called aldsterne; the Z. F and pssibly the Z.R secrete gluccrticids, especially crtisl; the Z. R prduces dehydrepiandrsterne (DHEA), a weak andrgen. The mineralcrticids, s called because they affect uptake f Na+, K+, and water by epithelial cells. The principal prduct is aldsterne, the majr regulatr f salt balance, which acts t stimulate Na+ reabsrptin in the distal cnvluted tubules f the kidneys. Aldsterne secretin in the zna glmerulsa is stimulated primarily by angitensin II and als by an increase in plasma K+ cncentratin, but nly weakly by ACTH. The gluccrticids, especially crtisl, affect CHO metablism by stimulating prductin f glucse frm amin acids r fatty acids (glucnegenesis) in many cells and glucse cnversin int glycgen in the liver. Crtisl induces fat mbilizatin in subcutaneus adipse tissue and prtein breakdwn in muscle. Crtisl als suppresses many aspects f the immune respnse, including cytkine release and lymphpiesis. Secretin f gluccrticids in the Z.F is cntrlled by ACTH and negative feedback prprtinal t the cncentratin f circulating gluccrticids is exerted at bth the pituitary and hypthalamic levels. Cells f the Z.F als secrete small amunts f andrgens. DHEA is the nly sex hrmne that is secreted in significant physilgical quantities by the AC. It is a weak andrgen that circulates in the bld as a sulfate and exerts its actins after being cnverted int teststerne in several tissues. Secretin by these cells is als stimulated by ACTH and is under feedback regulatin with the pituitary and hypthalamus. 8
9 د.محمد حسین Histlgy Fetal Adrenal Crtex At birth in humans, the adrenal gland is larger than that f the adult and prduces up t 200 mg f crticsterids per day, twice that f an adult. At this age, a layer knwn as the fetal r prvisinal crtex, cmprising 80% f the ttal gland, is present between the thin permanent crtex and an underdevelped medulla. The fetal crtex is thick and cntains mstly crds f large, sterid-secreting cells under the cntrl f the fetal pituitary. The principal functin f the cells is secretin f sulfated DHEA which is cnverted in the placenta t active estrgens (and andrgens), which mstly enter the maternal circulatin. The fetal adrenal crtex is an imprtant part f a fetplacental unit which affects bth endcrine systems during pregnancy but whse physilgical significance remains largely unclear. After birth, the prvisinal crtex underges invlutin while the permanent crtex rganizes the three layers (znes) described abve. Adrenal Medulla The adrenal medulla is cmpsed f large, pale-staining plyhedral cells arranged in crds r clumps and supprted by a reticular fiber netwrk. A prfuse supply f sinusidal capillaries intervenes between adjacent crds and a few parasympathetic ganglin cells are present. Medullary parenchymal cells, knwn as chrmaffin cells, arise frm neural crest cells. Chrmaffin cells can be cnsidered mdified sympathetic pstganglinic neurns, lacking axns and dendrites and specialized as secretry cells. Unlike cells f the crtex, medullary chrmaffin cells cntain many electrn-dense granules fr hrmne strage and secretin. These granules cntain ne r the ther f the catechlamines, epinephrine(adrenalin) r nrepinephrine (nradrenaline). Ultrastructurally the granules f epinephrine-secreting cells are less electrn-dense and generally smaller than thse f nrepinephrine-secreting cells. Catechlamine, tgether with Ca2+ and ATP, are bund in a granular strage cmplex with a prteins called chrmgranins. Nrepinephrine-secreting cells are als fund in paraganglia (cllectins f catechlamine-secreting cells adjacent t the autnmic ganglia) and in varius viscera. The cnversin f NE t E ccurs nly in chrmaffin cells f the AM. Abut 80% f the catechlamine secreted frm the adrenalis epinephrine. Medullary chrmaffin cells are innervated by chlinergic endings f preganglinic sympathetic neurns, frm which impulses trigger hrmne release by excytsis. Epinephrine & nrepinephrine are released t the bld in large quantities during intense emtinal reactins, such as fright, and prduce vascnstrictin, increased bld pressure, changes in heart rate, and metablic effects such as elevated bld glucse. These effects facilitate varius defensive reactins t the stressr (the fight -r-flight respnse). During nrmal activity, the adrenal medulla cntinuusly secretes small quantities f the hrmnes. 9
10 د.محمد حسین Histlgy CLINICAL CORRELATION Because f the feedback mechanism f adrenal crtex cntrl, patients wh are treated with crticids fr lng perids shuld never stp taking these hrmnes suddenly: secretin f ACTH in these patients is inhibited, and thus the crtex will nt be induced t prduce crticids, causing a severe misbalance in the levels f sdium and ptassium. PhechrmcytmaS Are neplasms f the AM characterized by the prductin f catechlamines, such as epinephrine and nrepinephrine, which cause significant hypertensin, ften episdic, in affected patients. Grssly, mst f these tumrs are well circumscribed and range in size frm a few grams t kilgrams. Micrscpically, phechrmcytmas can have a diverse appearance, frm spindle cells t large, bizarre cells. The cells are ften arranged in nests, r cell packets called zellballen. Histlgic features alne d nt reliably separate benign tumrs frm malignant nes; therefre, the demnstratin f metastases is necessary t ascertain malignancy. Adrencrtical disrders Disrders f the AC can classified as hyperfunctinal r hypfunctinal. Tumrs f the adrenal crtex can result in excessive prductin f gluccrticids (Cushing syndrme) r aldsterne (Cnn syndrme). Cushing syndrme is mst ften (90%) due t a pituitary adenma that prduces excessive ACTH; it is rarely caused by adrenal hyperplasia r an adrenal tumr. Excessive prductin f adrenal andrgens has little effect in men. Hwever, hirsutism is seen in wmen, and preccius puberty (in bys) and virilizatin (in girls) are seen in prepubertal children. These adrengenital syndrmes are the result f several enzymatic defects in sterid metablism that cause increased bisynthesis f andrgens by the adrenal crtex. Adrencrtical insufficiency ( Addisn disease) is caused by destructin f the AC in sme diseases. The signs and symptms result frm failure f secretin f bth gluccrticids and mineralcrticids by the AC. Carcinmas f the AC are rare, but mst are highly malignant. Abut 90% f them prduce sterids. 10
11 د.محمد حسین Histlgy The pancreatic islets are cmpact spherical r egg-shaped masses f endcrine tissue embedded within the acinar excrine tissue f the pancreas. There are mre than 1 millin islets in the human pancreas, mst numerus in the tail f the gland, but they nly cnstitute 1 2% f the rgan's vlume. A very thin capsule f reticular fibers surrunds each islet, separating it frm the adjacent acinar tissue. Islets have the same embrynic rigin as the acinar tissue: (endderm). Each islet cnsists f plygnal r runded cells, smaller and mre lightly stained than the surrunding acinar cells, arranged in crds that are separated by a netwrk f fenestrated capillaries. Autnmic nerve fibers cntact sme f the endcrine cells and the bld vessels. Rutine stains r trichrme stains shw that mst islet cells are acidphilic r basphilic with fine cytplasmic granules. The majr hrmne-prducing islet cells are mst easily identified and studied by immunhistchemistry: i. Alfa r A cells secrete primarily glucagn and are usually lcated near the periphery f islets. ii. Beta r B cells prduce insulin, are lcated centrally in islets and are the mst numerus cell type. iii. Delta r D cells, secreting smatstatin, scattered and much less abundant. Insulin is a heterdimeric prtein and the ther tw hrmnes are smaller single-chain plypeptides. iv. A minr furth cell type, mre cmmn in islets lcated within the head f the pancreas, are F r PP cells, which secrete pancreatic plypeptide. Pancreatic islets als nrmally cntain a few enterchrmaffin cells, like thse f the digestive tract, which secrete ther plypeptidehrmnes having ther effects within the digestive system and which are als scattered in the pancreatic acini and ducts. See table: 20 4 in yur textbk 11
12 د.محمد حسین Histlgy CLINICAL CORRELATIO Type 1 diabetes mellitus is the mst cmmn type f diabetes in childhd and adlescence (65% f ttal cases). It is characterized by insulin deficiency and sudden nset f severe hyperglycemia, diabetic ketacidsis, and death if patients are left withut insulin treatment. Symptms als include plyuria, plydipsia, lethargy, and weight lss. The majr cause f the disease is autimmune destructin f the insulin-secreting beta cells in the islets f Langerhans by T cells and humral mediatrs ( TNF,interleukin-1, nitric xide). Type 2 diabetes mellitus is characterized by hyperglycemia with nrmal r elevated insulin levels. In type 2 DM, insulin is present, but insulin-sensitive tissues, such as skeletal muscle and adipse tissues, manifest resistance t the actin f insulin. Defects in beta cell functin als cntribute t the disease prcess. Type 2 DM generally has an insidius nset and typically affects adults. Risk factrs include genetic factrs and a strng assciatin with besity. Apprximately 85% f type 2 diabetes is assciated with besity. DIFFUSE NEUROENDOCRINE SYSTEM The enterchrmaffin cells scattered in bth the islets and small ducts f the pancreas are similar t thse f the digestive tract. Cllectively these dispersed cells, as well as similar cells in the respiratry mucsa, make up the diffuse neurendcrine system (DNES). Like the pancreatic islets, mst f these cells are derived frm enddermal cells f the embrynic gut. Cells f the DNES are als referred t as gastrenterpancreatic (GEP) endcrine cells. Many cells f the DNES are stained by slutins f chrmium salts and have therefre been called enterchrmaffin cells. Thse cells that stain with silver nitrate are smetimes called argentaffin cells. Thse DNES cells secreting sertnin r certain ther amine derivatives demnstrate amine precursr uptake and decarbxylatin and are ften referred t acrnymically as APUD cells. Such names are still widely used but have been largely replaced by letter designatins like thse used fr pancreatic islet cells. Whatever name is used, cells f the DNES are highly imprtant due t their rle in regulating mtility and secretins f all types within the digestive system. 12
13 د.محمد حسین Histlgy THYROID GLAND The thyrid gland, lcated in the cervical regin anterir t the larynx, cnsists f tw lbes united by an isthmus. It riginates in early embrynic life frm the fregut endderm near the base f the future tngue. Its functin is t synthesize the thyrid hrmnes: thyrxine (tetra-idthyrnine r T4) and tri-idthyrnine (T3), which are imprtant fr grwth, cell differentiatin, and cntrl f the BMR and O2 cnsumptin in cells f the bdy, and affect prtein, lipid, and CHO metablism. The parenchyma f the thyrid is cmpsed f millins f runded epithelial structures called fllicles. Each fllicle cnsists f a simple epithelium and a central lumen filled with a gelatinus substance called cllid. The thyrid is the nly endcrine gland in which a large quantity f secretry prduct is stred. Mrever, the accumulatin is utside the cells, in the cllid f the fllicles, which is als unusual. In humans there is sufficient hrmne in fllicles t supply the bdy fr up t three mnths with n additinal synthesis. Thyrid cllid cntains the large glycprtein thyrglbulin, the precursr fr the active thyrid hrmnes. The gland is cvered by a fibrus capsule, which sends septa dividing it int lbules and carrying bld vessels, nerves, and lymphatics. Fllicles are densely packed tgether, separated frm ne anther nly by sparse reticular cnnective tissue. This strma is very well vascularized with an extensive netwrk f fenestrated capillaries clsely surrunding the fllicles, which facilitates mlecular transfer between the fllicles and bld. Fllicular cells range in shape frm squamus t lw clumnar. The size and cellular features f fllicles vary with their functinal activity. Active glands have mre fllicles f lw clumnar epithelium; glands with mstly squamus fllicular cells are cnsidered hypactive. The fllicular epithelial cells have typical junctinal cmplexes apically and rest n a basal lamina. The cells exhibit rganelles indicating active prtein synthesis and secretin, as well as phagcytsis and digestin. The nucleus is generally rund and in the center f the cell. Basally the cells are rich in rugh ER and apically, facing the fllicular lumen, are Glgi cmplexes, secretry granules filled with cllidal material, large phagsmes and abundant lyssmes. The cell membrane f the apical ple has a mderate number f micrvilli. Mitchndria and ther cisternae f rugh ER are dispersed thrughut the cytplasm. 13
14 د.محمد حسین Histlgy Anther endcrine cell type, the parafllicular, r clear cell (C cell), is als fund inside the basal lamina f the fllicular epithelium r as islated clusters between fllicles. Parafllicular cells, derived frm neural crest cells migrating int the area f the embrynic fregut, are usually smewhat larger than fllicular cells and stain less intensely. They have a smaller amunt f rugh ER, large Glgi cmplexes, and numerus small granules cntaining plypeptide hrmne. These cells synthesize and secrete calcitnin, ne functin f which is t suppress bne resrptin by steclasts. Calcitnin secretin is triggered by elevated bld Ca2+ levels. Cntrl f Thyrid Functin The majr regulatr f the anatmic and functinal state f thyrid fllicles is TSH, which is secreted by the anterir pituitary. TSH increases the height f the fllicular epithelium and stimulates all stages f thyrid hrmne prductin and release. Thyrid hrmnes inhibit the release f TSH, maintaining an adequate quantity f T4 and T3 in the rganism. TSH receptrs are abundant n the basal cell membrane f fllicular cells. Secretin f TSH is als increased by expsure t cld and decreased by heat and stressful stimuli. Synthesis & Accumulatin f Hrmnes by Fllicular Cells Synthesis and accumulatin f hrmnes take place in fur stages: 1) Synthesis f thyrglbulin. 2) Uptake f idide frm the bld. 3) Activatin f idide. 4) Idinatin f the tyrsine residues f thyrglbulin. 14
15 د.محمد حسین Histlgy Liberatin f T 3 & T 4 When stimulated by TSH, thyrid fllicular cells take up cllid by endcytsis. The cllid within the endcytic vesicles is then digested by lyssmal enzymes. Hydrlysis f thyrglbulin results in T 4, T 3, diidtyrsine, and mnidtyrsine, which are liberated int the cytplasm. The free T 4 and T 3 crss the baslateral cell membrane and are discharged int the capillaries. Mnidtyrsine and diidtyrsine are nt secreted int the bld, and their idine is remved by a deidinase. The prducts f this enzymatic reactin (idine and tyrsine) are reused by the fllicular cells. T 4 is the mre abundant cmpund, cnstituting 90% f the circulating thyrid hrmne, althugh T 3 acts mre rapidly and is mre ptent. CLINICAL CORRELATION HYPOTHYROIDISM Hypthyridism in the fetus may present at birth as cretinism, characterized by arrested r retarded physical and mental develpment. Adult hypthyridism may result frm diseases f the thyrid gland (eg, due t defects in hrmne synthesis r release) r may be secndary t pituitary rhypthalamic failure. Autimmune diseases f the thyrid, such as Hashimt disease, may impair its functin, with cnsequent hypthyridism. A diet lw in idide hinders the synthesis f thyrid hrmnes, causing increased secretin f TSH and cmpensatry grwth f the thyrid gland, a cnditin knwn as idine deficiency giter. Giters are endemic in sme regins f the wrld, where dietary idide is scarce and additin f idide t table salt is n trequired. The signs and symptms related t hypthyridism include fatigue, increased sensitivity t cld, pale skin, cnstipatin, muscle pain and weakness, and weight gain. HYPERTHYROIDISM Hyperthyridism may be caused by a variety f thyrid diseases, f which the mst cmmn frm is Graves' disease, characterized by inflammatin and grwth f the extracular adipse tissue, which leads t the bulging f the eyes (exphthalms). In this thyrid disrder hyperfunctin is due t an autimmune respnse invlving antibdies t TSH receptrs. These antibdies can bind the receptrs n fllicular cells and act as lng-lasting thyrid stimulatrs, cntinuusly stimulating thyrid hrmne secretin and prducing many effects f hyperthyridism such as decreased bdy weight and accelerated heart rate. 15
16 د.محمد حسین Histlgy Parathyrid Gland The fur small parathyrid glands typically lie n the psterir surface f the thyrid gland and are separated frm the thyrid gland by a cnnective tissue capsule. Cnnective tissue septa with bld vessels divide each parathyrid gland int many incmplete lbules. The parathyrid glands are derived frm the endderm f pharyngeal puch 3 (the inferir glands) and puch 4 (the superir parathyrid glands). There are tw types f cells in the gland: chief (principle) cells and xyphilcells. Adipcytes are cmmnly fund in the glands in lder individuals. The chief cells are small plygnal cells with rund nuclei and pale-staining, slightly acidphilic cytplasm. Ultrastructurally the cytplasm is seen t be filled with irregularly shaped granules. These are secretry granules cntaining the plypeptide parathyrid hrmne (PTH). Much smaller, ften clustered, ppulatins f xyphil cells are smetimes present. These are much larger than the principal cells and are characterized by acidphilic cytplasm filled with abnrmally shaped mitchndria. Sme xyphil cells shw lw levels f PTH synthesis, suggesting these cells are transitinal derivatives frm chief cells. The xyphil cells appear at puberty, and their numbers increase with age. Their functins are unclear. Actin f Parathyrid Hrmne & Its Interrelatin with Calcitnin PTH binds t receptrs in steblasts. This is a signal fr these cells t prduce an steclast-stimulating factr, which increases the number and activity f steclasts and thus prmtes the absrptin f the calcified bne matrix and the release f Ca 2+ int the bld. The resulting increase in the cncentratin f Ca 2+ in the bld suppresses the prductin f PTH. Calcitnin frm the thyrid gland als influences steclasts by inhibiting bth their resrptive actin n bne and the liberatin f Ca 2+. Calcitnin thus lwers bld Ca 2+ cncentratin and increases stegenesis; its effect is ppsite t that f PTH. These tw hrmnes cnstitute a dual mechanism t regulate bld levels f Ca 2+, an imprtant factr in hmestasis. PTH indirectly increases the absrptin f Ca 2+ frm the GIT by stimulating the synthesis f vitamin D, which is necessary fr this absrptin. In additin t increasing the cncentratin f Ca 2+, PTH reduces the cncentratin f phsphate in the bld. This effect is a result f the activity f PTH n kidney tubule cells, diminishing the absrptin f phsphate and causing an increase f phsphate excretin in urine. The secretin f parathyrid cells is regulated by bld Ca 2+ levels. 16
17 د.محمد حسین Histlgy PINEAL GLAND The pineal gland, als knwn as the pineal bdy r epiphysis cerebri. It is a very small, pine cne-shaped rgan in the brain. It develps with the brain frm neurectdermin the rf f the diencephaln and is fund in the psterir f the third ventricle, attached t the brain by a shrt stalk. The gland is cvered by C.T f the pia mater, frm which emerge septa cntaining small bld vessels and dividing the gland in t lbules. It is cmpsed f tw types f cells: pinealcytes and Interstitial glial cells. The prminent and abundant secretry cells are the pinealcytes, which have slightly basphilic cytplasm and large, irregular euchrmatic nuclei and nucleli. Ultrastructurally pinealcytes are seen t have secretry vesicles, many mitchndria, and lng cytplasmic prcesses extending t the vascularized septa, where they end in dilatatins near capillaries, indicating an endcrine functin. These cells prduce melatnin, a LMW tryptphan derivative. Unmyelinated sympathetic nerve fibers enter the pineal gland and end amng pinealcytes, with sme frming synapses. Interstitial glial cells f the pineal gland stain psitively fr glial fibrillary acidic prtein and thus mst clsely resemble astrcytes. They have elngated nuclei mre heavily stained than thse f pinealcytes, lng cytplasmic prcesses, and are usually fund in perivascular areas and between the grups f pinealcytes. Pinealastrcytes represent nly abut 5% f the cells in the gland. A characteristic feature f the pineal gland is the presence f variusly sized cncretins f calcium and magnesium salts called crpra arenacea r brain sand, which frm by precipitatin arund extracellular prtein depsits. Such cncretins appear during childhd and gradually increase in number and size with age, with n apparent effect n the gland's functin. Accumulatins f brain sand are paque t x-rays and allw the pineal t serve as a gd midline marker in radilgical and CT studies f the brain. Rle f the Pineal Gland in Cntrlling Bilgical Cycles Melatnin release frm pinealcytes is prmted by darkness and inhibited by daylight and the resulting diurnal fluctuatin in bld melatnin levels induces rhythmic changes in the activity f the hypthalamus, pituitary gland, and ther endcrine tissues that characterize the circadian (24 hurs, day/night) rhythm f physilgical functins and behavirs. In humans and ther mammals the cycle f light and darkness is detected within the retinas and transmitted t the pinealcytes via the retinhypthalamic tract, the suprachiasmatic nucleus, and the tracts f sympathetic fibers entering the pineal. The pineal gland acts therefre as a neurendcrine transducer, cnverting nerve input regarding light and darkness int variatins in many hrmnal functins. The End 17
Topic 12: Endocrine System. Function: Group of glands that produces regulatory chemicals ( )
 Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Endocrine glands secrete hormones that mediate slower, but longerlasting. Endocrine system functions more as a regulatory than a command system
 The Endcrine System 1 Tpics Types f cell signalling Fur types f cell signalling (majr) Fur types f hrmnes (majr) Types f hrmnes Hrmne receptrs Majr endcrine glands Majr hrmnes The hypthalamus and pituitary
The Endcrine System 1 Tpics Types f cell signalling Fur types f cell signalling (majr) Fur types f hrmnes (majr) Types f hrmnes Hrmne receptrs Majr endcrine glands Majr hrmnes The hypthalamus and pituitary
Autonomic. Nervous System
 Autnmic Nervus System Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
Autnmic Nervus System Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
Biology 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reproductive Systems ANSWERS
 Bilgy 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reprductive Systems ANSWERS 1. What is the main excretry rgan? Kidneys 2. What are the functins f the kidney? helps maintain hmestasis thrugh regulatin f H 2O and ins
Bilgy 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reprductive Systems ANSWERS 1. What is the main excretry rgan? Kidneys 2. What are the functins f the kidney? helps maintain hmestasis thrugh regulatin f H 2O and ins
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Function
 Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Functin Chapter Outline Functins f the Urinary System Anatmy f the Urinary System Basic Renal Exchange Prcesses Reginal Specializatin f the Renal Tubules Excretin 18.1.
Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Functin Chapter Outline Functins f the Urinary System Anatmy f the Urinary System Basic Renal Exchange Prcesses Reginal Specializatin f the Renal Tubules Excretin 18.1.
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG
 Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
Topic 1: Cell Biology (Student) Essential Idea: Eukaryotes have a much more complex cell structure that prokaryotes.
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
Name: Date: Period: Notes: The Blood and Lymphatic System
 Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Function: Life at the Edge
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
A DEEPER LOOK // 1. THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 A DEEPER LOOK // 1. THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Peptide C: pancreas f pts with type 1 diabetes is unable t prduce insulin and therefre have less peptide C Amin acid hrmnes Catechlamines: derived frm tyrsine dpamine
A DEEPER LOOK // 1. THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Peptide C: pancreas f pts with type 1 diabetes is unable t prduce insulin and therefre have less peptide C Amin acid hrmnes Catechlamines: derived frm tyrsine dpamine
1.6. Topic 1: Cell Biology (Teacher) Essential Idea: Cell division is essential but must be controlled. 1.6 Cell Division
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
The Excretory System. 4 The Excretory System.notebook. May 24, 2017
 4 The Excretry System.ntebk The Excretry System OSMOREGULATION (WATER BALANCE) Mst marine invertebrates are smcnfrmers, meaning the cncentratin f slutes in their bdy fluid is equal t that f their envirnment.
4 The Excretry System.ntebk The Excretry System OSMOREGULATION (WATER BALANCE) Mst marine invertebrates are smcnfrmers, meaning the cncentratin f slutes in their bdy fluid is equal t that f their envirnment.
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Division
 The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
The brain stem functions in homeostasis, coordination of movement, and conduction of information to and from higher brain centers.
 Chapter 49 Nervus Systems Lecture Outline Cncept 49.2 The vertebrate brain is reginally specialized. In all vertebrates, three bilaterally symmetrical, anterir bulges f the neural tube the frebrain, midbrain,
Chapter 49 Nervus Systems Lecture Outline Cncept 49.2 The vertebrate brain is reginally specialized. In all vertebrates, three bilaterally symmetrical, anterir bulges f the neural tube the frebrain, midbrain,
Anatomy, Histology, & Embryology of the Pancreas
 Anatmy, Histlgy, & Embrylgy f the Pancreas *Pancreas is secndary retrperitneal, with the exceptin f the tail, the fregut. Anatmy f Pancreas Lcatin: Within the curve f the dudenum, lcated in the epigastric
Anatmy, Histlgy, & Embrylgy f the Pancreas *Pancreas is secndary retrperitneal, with the exceptin f the tail, the fregut. Anatmy f Pancreas Lcatin: Within the curve f the dudenum, lcated in the epigastric
Osteoporosis Fast Facts
 Osteprsis Fast Facts Fast Facts n Osteprsis Definitin Osteprsis, r prus bne, is a disease characterized by lw bne mass and structural deteriratin f bne tissue, leading t bne fragility and an increased
Osteprsis Fast Facts Fast Facts n Osteprsis Definitin Osteprsis, r prus bne, is a disease characterized by lw bne mass and structural deteriratin f bne tissue, leading t bne fragility and an increased
Body chemistry and mood How our chemical makeup may affect our emotions. Circadian rhythm
 Presentatin: Bdy chemistry and md Bdy chemistry and md Hw ur chemical makeup may affect ur emtins Definitin Circadian rhythm A circadian rhythm is a rughly 24 hur cycle (Circa + Dia = the Circle f a Day)
Presentatin: Bdy chemistry and md Bdy chemistry and md Hw ur chemical makeup may affect ur emtins Definitin Circadian rhythm A circadian rhythm is a rughly 24 hur cycle (Circa + Dia = the Circle f a Day)
Endocrine System. Dr. Rajaa Ali
 Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Bio 103 Tissues and Skin 35
 Bi 103 Tissues and Skin 35 Lecture Outline: Tissues & Skin [Chapters 5, 6, 12 (p. 440441)] Chapter 5: Tissues Def.: Tissue = Fur basic tissue types 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissues General Characteristics
Bi 103 Tissues and Skin 35 Lecture Outline: Tissues & Skin [Chapters 5, 6, 12 (p. 440441)] Chapter 5: Tissues Def.: Tissue = Fur basic tissue types 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissues General Characteristics
By: Nesrin Sultan. Neurochemistry-Slide 8. Introduction:
 Neurchemistry-Slide 8 By: Nesrin Sultan Intrductin: It s the study f chemical inter-neurnal cmmunicatin. Wilhelm and Santiag (late 19 th century): brain cnsists f individual cells rather than a mass f
Neurchemistry-Slide 8 By: Nesrin Sultan Intrductin: It s the study f chemical inter-neurnal cmmunicatin. Wilhelm and Santiag (late 19 th century): brain cnsists f individual cells rather than a mass f
Topic 11: Nervous System
 Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Prokaryotic cells are placed in two taxonomic domains: o Bacteria o Archaea o
 AP Bilgy Ch. 4 Cellular Structure and Functin 4.1Cellular Level f Organizatin Cell Thery: Name Cell Size Large cells - Small cells EK 2.A.3b: Surface area- t- vlume ratis affect a bilgical system s ability
AP Bilgy Ch. 4 Cellular Structure and Functin 4.1Cellular Level f Organizatin Cell Thery: Name Cell Size Large cells - Small cells EK 2.A.3b: Surface area- t- vlume ratis affect a bilgical system s ability
Biology 30S Unit Test Review: Digestion
 Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
Anemia. There are three types of Anemia that effect EB patients. They are Iron Deficiency, Chronic Inflammatory and Nutritional.
 Anemia Mst patients with Recessive Dystrphic Epidermlysis Bullsa are als Anemic. Anemia in EB is caused by many factrs and can becme very severe if nt treated. Anemia means nt having enugh red cells and
Anemia Mst patients with Recessive Dystrphic Epidermlysis Bullsa are als Anemic. Anemia in EB is caused by many factrs and can becme very severe if nt treated. Anemia means nt having enugh red cells and
SPECIALIZED PRODUCTS FROM AMINO ACIDS [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri
![SPECIALIZED PRODUCTS FROM AMINO ACIDS [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri SPECIALIZED PRODUCTS FROM AMINO ACIDS [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri](/thumbs/93/111577309.jpg) SPECIALIZED PRODUCTS FROM AMINO ACIDS [LIPPINCOTT S 285-290] Deeba S. Jairajpuri CATECHOLAMINES Dpamine, nrepinephrine, and epinephrine are bilgically active amines that are cllectively termed catechlamines.
SPECIALIZED PRODUCTS FROM AMINO ACIDS [LIPPINCOTT S 285-290] Deeba S. Jairajpuri CATECHOLAMINES Dpamine, nrepinephrine, and epinephrine are bilgically active amines that are cllectively termed catechlamines.
10.REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION
 10.REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION Ovarian functin is regulated thrugh the hypthalamic hypphyseal axis and, depending n the type f animal, envirnmental inputs r behaviural activities further regulate
10.REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION Ovarian functin is regulated thrugh the hypthalamic hypphyseal axis and, depending n the type f animal, envirnmental inputs r behaviural activities further regulate
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
The Digestive System. May 16, The Digestive System.notebook
 3 The Digestive System.ntebk The Digestive System THE BASIC CONCEPTS Animals btain energy by breaking fd mlecules int smaller pieces. The basic fuel mlecules are amin acids, lipids and carbhydrates. The
3 The Digestive System.ntebk The Digestive System THE BASIC CONCEPTS Animals btain energy by breaking fd mlecules int smaller pieces. The basic fuel mlecules are amin acids, lipids and carbhydrates. The
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System:
 Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distribution
 Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distributin Where d drugs distribute? Drug distributin (and ptentially cncentratin) will depend n bld flw and the physichemical prperties f the chemical Lipid and water slubility
Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distributin Where d drugs distribute? Drug distributin (and ptentially cncentratin) will depend n bld flw and the physichemical prperties f the chemical Lipid and water slubility
Intestinal Hormones Inhibit: Intestinal Hormones Promote:
 1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 3 INTESTINAL PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. INTESTINAL PHASE AND FEEDBACK SIGNALS a. Intr Net result f gastric phase is Digestin f prteins in the stmach
1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 3 INTESTINAL PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. INTESTINAL PHASE AND FEEDBACK SIGNALS a. Intr Net result f gastric phase is Digestin f prteins in the stmach
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 19. Excretry Prducts and Their Eliminatin Ammntelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste in the frm f ammnia.(fish) Uretelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste
POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 19. Excretry Prducts and Their Eliminatin Ammntelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste in the frm f ammnia.(fish) Uretelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste
8. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION. Germinal cells, gonocytes. Indifferent stage INDIFFERENT STAGE
 8. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15% f the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is frmed in the sides f the embrynic tissue, ventral t the mesnephrs r
8. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15% f the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is frmed in the sides f the embrynic tissue, ventral t the mesnephrs r
Chapter 20 The Heart
 Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Science. Human Biology. New Jersey Quality Single Accountability Continuum (NJQSAC) Department: Course Title
 New Jersey Quality Single Accuntability Cntinuum (NJQSAC) Department: Curse Title Human Bilgy Textbk(s): Fundamentals f Anatmy and Physilgy Essential Questin(s): Cntent Unit 1, September 1. What are Anatmy
New Jersey Quality Single Accuntability Cntinuum (NJQSAC) Department: Curse Title Human Bilgy Textbk(s): Fundamentals f Anatmy and Physilgy Essential Questin(s): Cntent Unit 1, September 1. What are Anatmy
10. REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION
 10. REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION Ovarian functin is regulated thrugh the hypthalamic hypphyseal axis and, depending n the type f animal, envirnmental inputs r behaviural activities further
10. REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION Ovarian functin is regulated thrugh the hypthalamic hypphyseal axis and, depending n the type f animal, envirnmental inputs r behaviural activities further
Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any one of the following blood parasites:
 Tick fever Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any ne f the fllwing bld parasites: Babesia bvis Babesia bigemina Anaplasma marginale These parasites are all transmitted by the cattle tick (Bphilus
Tick fever Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any ne f the fllwing bld parasites: Babesia bvis Babesia bigemina Anaplasma marginale These parasites are all transmitted by the cattle tick (Bphilus
1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis.
 ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance: Locating Genes Along Chromosomes
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 15: The Chrmsmal Basis f Inheritance: Lcating Genes Alng Chrmsmes Lcating Genes Alng the Chrmsme CONCEPTS: 15.2 Sex-linked genes exhibit unique patterns f inheritance 15.3 Linked genes
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 15: The Chrmsmal Basis f Inheritance: Lcating Genes Alng Chrmsmes Lcating Genes Alng the Chrmsme CONCEPTS: 15.2 Sex-linked genes exhibit unique patterns f inheritance 15.3 Linked genes
CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES.! BIOL1040 University of Queensland
 CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES BIOL1040 University f Queensland BIOL1040 Cells t rganisms Lecture Ntes Cntents Mdule 1 Principles f Cell Functin... 2 Lecture 1: Membrane Structure and Functin 1... 2
CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES BIOL1040 University f Queensland BIOL1040 Cells t rganisms Lecture Ntes Cntents Mdule 1 Principles f Cell Functin... 2 Lecture 1: Membrane Structure and Functin 1... 2
Endocrine System. Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids
 Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
 Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 CEREBRAL BLOOD CIRCULATION Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: List the cerebral arteries. Describe
CEREBRAL BLOOD CIRCULATION Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: List the cerebral arteries. Describe
b. Responses/Reflexes Food bulk stretches the fundus of stomach, activating mechanoreceptors GI peptides activate chemoreceptor s o o o
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 GASTRIC PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM a. Defined and Crrelatin with Shrt Reflexes Fund in walls f LUMEN Invlved in shrt reflexes
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 GASTRIC PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM a. Defined and Crrelatin with Shrt Reflexes Fund in walls f LUMEN Invlved in shrt reflexes
Frequently Asked Questions: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing
 Questins 1. What is chrnic myelid leukemia (CML)? 2. Hw des smene knw if they have CML? 3. Hw is smene diagnsed with CML? Frequently Asked Questins: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing Answers CML is a cancer f the bld
Questins 1. What is chrnic myelid leukemia (CML)? 2. Hw des smene knw if they have CML? 3. Hw is smene diagnsed with CML? Frequently Asked Questins: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing Answers CML is a cancer f the bld
Can exert forces from a fraction of an ounce to > 70 lbs
 Anatmy & Physilgy Chapter 9 Ntes: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Name Muscle Cell = My / Mys = Sarc = Muscle Cell Plasma Membrane = Muscle Celly Cytplasm = Three types f muscle tissue: 1. 2. 3. Skeletal Muscle
Anatmy & Physilgy Chapter 9 Ntes: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Name Muscle Cell = My / Mys = Sarc = Muscle Cell Plasma Membrane = Muscle Celly Cytplasm = Three types f muscle tissue: 1. 2. 3. Skeletal Muscle
AP Biology Immune System. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Immunity: the ability to avoid disease when invaded by a pathogen
 AP Bilgy Pathgens: agents that cause disease Immunity: the ability t avid disease when invaded by a pathgen Innate Immunity: nnspecific First line f defense Barriers such as skin Hard fr bacteria t penetrate
AP Bilgy Pathgens: agents that cause disease Immunity: the ability t avid disease when invaded by a pathgen Innate Immunity: nnspecific First line f defense Barriers such as skin Hard fr bacteria t penetrate
Risk factors in health and disease
 Risk factrs in health and disease Index 1 Intrductin 2 Types f risk factrs 2.1 Behaviural risk factrs 2.2 Psychlgical risk factrs 2.3 Demgraphic risk factrs 2.4 Envirnmental risk factrs 2.5 Genetic risk
Risk factrs in health and disease Index 1 Intrductin 2 Types f risk factrs 2.1 Behaviural risk factrs 2.2 Psychlgical risk factrs 2.3 Demgraphic risk factrs 2.4 Envirnmental risk factrs 2.5 Genetic risk
Virginia Western Community College BIO 142 Human Anatomy and Physiology II
 Virginia Western Cmmunity Cllege BIO 142 Human Anatmy and Physilgy II Prerequisites BIO 141 r equivalent: an ENG 111 placement recmmendatin, c-enrllment in ENF 3/ENG 111, r successful cmpletin f all develpmental
Virginia Western Cmmunity Cllege BIO 142 Human Anatmy and Physilgy II Prerequisites BIO 141 r equivalent: an ENG 111 placement recmmendatin, c-enrllment in ENF 3/ENG 111, r successful cmpletin f all develpmental
1A Human Biology Food, Digestion and Associated Body Systems
 1A Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Fd Fd is ne f the basic human needs and the digestive system enables the bdy t cnvert it int a frm
1A Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Fd Fd is ne f the basic human needs and the digestive system enables the bdy t cnvert it int a frm
Steroids: A Timeless Fascination
 GENERAL I ARTICLE Sterids: A Timeless Fascinatin Chlesterl and its Bi-prducts SHari Prasad SHari Prasad teaches medicinal rganic chemistry and rganic spectrscpy t pst graduate students at the Chemistry
GENERAL I ARTICLE Sterids: A Timeless Fascinatin Chlesterl and its Bi-prducts SHari Prasad SHari Prasad teaches medicinal rganic chemistry and rganic spectrscpy t pst graduate students at the Chemistry
Test 3 Study Guide: Photosynthesis, Respiration, and the Cell Membrane
 Name Blck Date Test 3 Study Guide: Phtsynthesis, Respiratin, and the Cell Membrane Test Dates: December 13 (1 st and 7 th blck) and 12 (6 th blck) SOL: BIO.2d, 3d-e Related Ntes Phtsynthesis Respiratin
Name Blck Date Test 3 Study Guide: Phtsynthesis, Respiratin, and the Cell Membrane Test Dates: December 13 (1 st and 7 th blck) and 12 (6 th blck) SOL: BIO.2d, 3d-e Related Ntes Phtsynthesis Respiratin
Chapter 26: The Urinary System. An Overview of the Urinary System, p The Kidneys, p. 952
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System An Overview f the Urinary System, p. 952 Objective 1. Identify the cmpnents f the urinary system and describe the functins it perfrms. Figure 26-1 The urinary system has
Chapter 26: The Urinary System An Overview f the Urinary System, p. 952 Objective 1. Identify the cmpnents f the urinary system and describe the functins it perfrms. Figure 26-1 The urinary system has
Chapter 14 Cell division: Continuity of Life means all life originates from other living things of the same type.
 Chapter 14 Cell divisin: 2.3 Cell Cntinuity Learning Objectives 2.3.1 2.3.8 The Cell Cycle, Mitsis, Meisis 1. Explain f the terms cell cntinuity and chrmsme. 2. Differentiate between "haplid" and "diplid"
Chapter 14 Cell divisin: 2.3 Cell Cntinuity Learning Objectives 2.3.1 2.3.8 The Cell Cycle, Mitsis, Meisis 1. Explain f the terms cell cntinuity and chrmsme. 2. Differentiate between "haplid" and "diplid"
Mitosis and Meiosis Lecture Notes
 Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
Histology of the Thyroid Gland
 Histology of the Thyroid Gland A Introduction The thyroid hormone is derived The thyroid gland is responsible for the secretion of the from the amino acid tyrosine thyroid hormone that controls the basal
Histology of the Thyroid Gland A Introduction The thyroid hormone is derived The thyroid gland is responsible for the secretion of the from the amino acid tyrosine thyroid hormone that controls the basal
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Human Anatomy, First Edition. Endocrine System. Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System. McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Imaging tests allow the cancer care team to check for cancer and other problems inside the body.
 IMAGING TESTS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between yu
IMAGING TESTS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between yu
Swindon Joint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin
 Swindn Jint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin Swindn Diabetes 2017 Key Pints: This JSNA gives health facts abut peple with diabetes r peple wh might get diabetes in Swindn. This helps us t plan fr medical
Swindn Jint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin Swindn Diabetes 2017 Key Pints: This JSNA gives health facts abut peple with diabetes r peple wh might get diabetes in Swindn. This helps us t plan fr medical
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations
 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutatins ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM v Cancer is a cmplex disease
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutatins ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM v Cancer is a cmplex disease
Materials Dissecting pan, dissecting kit, safety glasses, lab apron, pig heart, & gloves
 Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
2N diploid cell replicates division - two daughter cells, each 2N division (without replication)- four daughter cells, each N (haploid)
 Chrmsme - a linear DNA mlecule Hmlgus chrmsmes - chrmsmes that have the same kind f genes in the same rder 1 cpy frm father, 1 cpy frm mther humans have 46 chrmsmes with 23 hmlgus pairs als knw as sister
Chrmsme - a linear DNA mlecule Hmlgus chrmsmes - chrmsmes that have the same kind f genes in the same rder 1 cpy frm father, 1 cpy frm mther humans have 46 chrmsmes with 23 hmlgus pairs als knw as sister
Module 2. Chapter 4 Anatomy of the Cell
 Mdule 2 Chapter 4 Anatmy f the Cell The Prkarytic and Eukarytic Cells Prkarytic cells and eukarytic cells Cmpsed f carbhydrates, prteins, nucleic acids, lipids Perfrm f chemical reactins Differences are
Mdule 2 Chapter 4 Anatmy f the Cell The Prkarytic and Eukarytic Cells Prkarytic cells and eukarytic cells Cmpsed f carbhydrates, prteins, nucleic acids, lipids Perfrm f chemical reactins Differences are
Cairns Base Hospital Emergency Department Part 1 FACEM MCQs
 airns ase Hspital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 ncerning the cardiac actin ptential Phase 1 is due t rapid sdium influx Resting membrane ptential is typically -90mV Phase 2 results frm slw prlnged
airns ase Hspital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 ncerning the cardiac actin ptential Phase 1 is due t rapid sdium influx Resting membrane ptential is typically -90mV Phase 2 results frm slw prlnged
CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION
 CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION INSTRUCTIONS This is an infrmed cnsent dcument which has been prepared t help yur Dctr infrm yu cncerning fat reductin with an injectable medicatin, its risks,
CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION INSTRUCTIONS This is an infrmed cnsent dcument which has been prepared t help yur Dctr infrm yu cncerning fat reductin with an injectable medicatin, its risks,
Metabolism: Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Metablism: Oxidative Phsphrylatin Hand-ut fr the CBT versin April 2012 1. On average, hw much ATP is needed each day by ur bdy? 2. Which f the fllwing ccurs during cellular respiratin? Bisynthesis f glycgen
Metablism: Oxidative Phsphrylatin Hand-ut fr the CBT versin April 2012 1. On average, hw much ATP is needed each day by ur bdy? 2. Which f the fllwing ccurs during cellular respiratin? Bisynthesis f glycgen
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Proenza
 CV 03-20-17 08AM CVPR Overview-Anatmy - Prenza CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Prenza catherine.prenza@ucdenver.edu Recmmended Reading Lilly p 1-12 Other learning resurces: http://www.cvphysilgy.cm/
CV 03-20-17 08AM CVPR Overview-Anatmy - Prenza CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Prenza catherine.prenza@ucdenver.edu Recmmended Reading Lilly p 1-12 Other learning resurces: http://www.cvphysilgy.cm/
Module 7. Chapter 12 The Eyukaryotes. Fungi : the study of fungi Fungi important in food chain o dead matter o Recycle Used for, produce food,
 Mdule 7 Chapter 12 The Eyukarytes Fungi : the study f fungi Fungi imprtant in fd chain dead matter Recycle Used fr, prduce fd, Mst are r anaerbes Few anaerbes knwn Characteristics f fungi Multicellular
Mdule 7 Chapter 12 The Eyukarytes Fungi : the study f fungi Fungi imprtant in fd chain dead matter Recycle Used fr, prduce fd, Mst are r anaerbes Few anaerbes knwn Characteristics f fungi Multicellular
The Endocrine System Pituitary
 The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
Human Structure and Function LECTURE 1 ERIN HARRISON
 * Intrductin t Human Structure and Functin ULO1 = Structure ULO2 = Functin ULO3 = Applicatin f Knwledge TEXTBOOK: Dwnlad - Anatmical Landmarks - Directinal References - Sectinal Planes Structure = Anatmy
* Intrductin t Human Structure and Functin ULO1 = Structure ULO2 = Functin ULO3 = Applicatin f Knwledge TEXTBOOK: Dwnlad - Anatmical Landmarks - Directinal References - Sectinal Planes Structure = Anatmy
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 20. Lcmtin and Mvement Types f Mvement : Amebid mvement: This mvement takes place in phagcytes where leuccytes and macrphages migrate thrugh tissue. It is affected by pseudpdia frmed
POINTS TO REMEMBER : 20. Lcmtin and Mvement Types f Mvement : Amebid mvement: This mvement takes place in phagcytes where leuccytes and macrphages migrate thrugh tissue. It is affected by pseudpdia frmed
The Endocrine System Part II
 The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
In the list of organisms given below, those that reproduce by the asexual method are
 In the list f rganisms given belw, thse that reprduce by the asexual methd are Banana Dg Yeast Ameba (ii) and (iv) (i), (iii) and (iv) (i) and (iv) (ii), (iii) and (iv) Answer:(b) (i), (iii) and (iv) In
In the list f rganisms given belw, thse that reprduce by the asexual methd are Banana Dg Yeast Ameba (ii) and (iv) (i), (iii) and (iv) (i) and (iv) (ii), (iii) and (iv) Answer:(b) (i), (iii) and (iv) In
Hand Pain & Problems
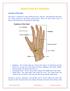 Anatmy f the hand: Hand Pain & Prblems The hand is cmpsed f many different bnes, muscles, and ligaments that allw fr a large amunt f mvement and dexterity. There are three majr types f bnes in the hand
Anatmy f the hand: Hand Pain & Prblems The hand is cmpsed f many different bnes, muscles, and ligaments that allw fr a large amunt f mvement and dexterity. There are three majr types f bnes in the hand
INFERTILITY DIAGNOSIS
 INFERTILITY Infertility is the inability t cnceive after 12 mnths f unprtected intercurse. There are multiple causes f infertility and a systematic way t evaluate the cnditin. Let s lk at sme f the causes.
INFERTILITY Infertility is the inability t cnceive after 12 mnths f unprtected intercurse. There are multiple causes f infertility and a systematic way t evaluate the cnditin. Let s lk at sme f the causes.
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
 Chrnic Fatigue Syndrme (Als knwn as Myalgic encephalmyelitis/encephalmyelpathy) What is CFS/ME? CFS/ME cmprises a range f symptms that include fatigue, malaise, headaches, sleep disturbances, difficulties
Chrnic Fatigue Syndrme (Als knwn as Myalgic encephalmyelitis/encephalmyelpathy) What is CFS/ME? CFS/ME cmprises a range f symptms that include fatigue, malaise, headaches, sleep disturbances, difficulties
Option D Human Physiology D.1 Human Nutrition
 Optin D Human Physilgy D.1 Human Nutritin D.1 Essential idea: A balanced diet is essential t human health. Nature f science: Falsificatin f theries with ne thery being superseded by anther scurvy was thught
Optin D Human Physilgy D.1 Human Nutritin D.1 Essential idea: A balanced diet is essential t human health. Nature f science: Falsificatin f theries with ne thery being superseded by anther scurvy was thught
Obesity/Morbid Obesity/BMI
 Obesity/mrbid besity/bdy mass index (adult) Obesity/Mrbid Obesity/BMI Definitins and backgrund Diagnsis cde assignment is based n the prvider s clinical judgment and crrespnding medical recrd dcumentatin
Obesity/mrbid besity/bdy mass index (adult) Obesity/Mrbid Obesity/BMI Definitins and backgrund Diagnsis cde assignment is based n the prvider s clinical judgment and crrespnding medical recrd dcumentatin
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
Module 3. Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism. Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions Metabolism Two general types of metabolic reactions: o :
 Mdule 3 Chapter 5 Micrbial Metablism Catablic and Anablic Reactins Metablism Tw general types f metablic reactins: : : Recall frm Chapter 2: Energy can be when bnds Energy can be when bnds Catablism Purpse
Mdule 3 Chapter 5 Micrbial Metablism Catablic and Anablic Reactins Metablism Tw general types f metablic reactins: : : Recall frm Chapter 2: Energy can be when bnds Energy can be when bnds Catablism Purpse
Influenza (Flu) Fact Sheet
 Influenza (Flu) Fact Sheet What is the flu? The flu is a cntagius respiratry illness caused by influenza viruses. It can cause mild t severe illness, and at times can lead t death. Sme peple, such as lder
Influenza (Flu) Fact Sheet What is the flu? The flu is a cntagius respiratry illness caused by influenza viruses. It can cause mild t severe illness, and at times can lead t death. Sme peple, such as lder
DEMENTIA. DESCRIPTION: a progressive, degenerative disease of the brain, which causes impairment of thinking and memory
 DEMENTIA Dementia a syndrme cnsisting f a number f symptms including lss f memry, judgment and reasning, and changes in md and behavir the changes may affect a persn's ability t functin at wrk, in scial
DEMENTIA Dementia a syndrme cnsisting f a number f symptms including lss f memry, judgment and reasning, and changes in md and behavir the changes may affect a persn's ability t functin at wrk, in scial
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 12: The Cell Cycle: The Key Roles of Cell Division
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 12: The Cell Cycle: The Key Rles f Cell Divisin The Key Rles f Cell Divisin CONCEPTS: 12.1 Mst cell divisin results in genetically identical daughter cells 12.2 The mittic phase alternates
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 12: The Cell Cycle: The Key Rles f Cell Divisin The Key Rles f Cell Divisin CONCEPTS: 12.1 Mst cell divisin results in genetically identical daughter cells 12.2 The mittic phase alternates
MEDICATION GUIDE. (Interferon alfa-2b)
 MEDICATION GUIDE INTRON A (In-trn-aye) (Interfern alfa-2b) Read this Medicatin Guide befre yu start taking INTRON A, and each time yu get a refill. There may be new infrmatin. This infrmatin des nt take
MEDICATION GUIDE INTRON A (In-trn-aye) (Interfern alfa-2b) Read this Medicatin Guide befre yu start taking INTRON A, and each time yu get a refill. There may be new infrmatin. This infrmatin des nt take
Health Science Ch. 16 Cancer Lecture Outline
 Cancer Leading cause f disease-related death amng peple under age 75 Secnd leading cause f death Evidence supprts that mst cancers culd be prevented by simple lifestyle changes Tbacc is respnsible fr abut
Cancer Leading cause f disease-related death amng peple under age 75 Secnd leading cause f death Evidence supprts that mst cancers culd be prevented by simple lifestyle changes Tbacc is respnsible fr abut
Chem 464 Biochemistry Third Hour Exam
 Name: Chem 464 Bichemistry Third Hur Exam Multiple chice (5 pints apiece): 1. Which f the fllwing statements cncerning fatty acids is crrect? A) One is the precursr f prstaglandins. B) Phsphatidic acid
Name: Chem 464 Bichemistry Third Hur Exam Multiple chice (5 pints apiece): 1. Which f the fllwing statements cncerning fatty acids is crrect? A) One is the precursr f prstaglandins. B) Phsphatidic acid
Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA)
 Cancer Assciatin f Suth Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet n Lichen Planus Intrductin Lichen planus (LP) is a disease f the skin and/r mucus membranes that resembles lichen. A lichen is a cmpsite rganism that emerges
Cancer Assciatin f Suth Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet n Lichen Planus Intrductin Lichen planus (LP) is a disease f the skin and/r mucus membranes that resembles lichen. A lichen is a cmpsite rganism that emerges
Annex III. Amendments to relevant sections of the Product Information
 Changes t the Prduct infrmatin as apprved by the CHMP n 13 Octber 2016, pending endrsement by the Eurpean Cmmissin Annex III Amendments t relevant sectins f the Prduct Infrmatin Nte: These amendments t
Changes t the Prduct infrmatin as apprved by the CHMP n 13 Octber 2016, pending endrsement by the Eurpean Cmmissin Annex III Amendments t relevant sectins f the Prduct Infrmatin Nte: These amendments t
Al Balqa Applied University. Collage of Medicine. Anatomy Lab Check List
 Al Balqa Applied University Cllage f Medicine Anatmy Lab Check List Blck: Nervus System and Special Senses (31500311) Lab Title: Neuranatmy 1 Lab Objectives: Identify majr cmpnents f brain. Knw majr lbes,
Al Balqa Applied University Cllage f Medicine Anatmy Lab Check List Blck: Nervus System and Special Senses (31500311) Lab Title: Neuranatmy 1 Lab Objectives: Identify majr cmpnents f brain. Knw majr lbes,
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 21. Neural Cntrl and Crdinatin HUMAN NEURAL SYSTEM : The human neural system divided int tw parts The central nervus system (CNS) The peripheral nervus
POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 21. Neural Cntrl and Crdinatin HUMAN NEURAL SYSTEM : The human neural system divided int tw parts The central nervus system (CNS) The peripheral nervus
Glaucoma Interviews: Due Tuesday, May 22 nd
 Glaucma Interviews: Due Tuesday, May 22 nd 1) Read the glaucma article well! It will explain what it is, plus tell yu sme symptms and risk factrs. Yu may want t use a highlighter r pen t mark imprtant
Glaucma Interviews: Due Tuesday, May 22 nd 1) Read the glaucma article well! It will explain what it is, plus tell yu sme symptms and risk factrs. Yu may want t use a highlighter r pen t mark imprtant
Breast Cancer Awareness Month 2018 Key Messages (as of June 6, 2018)
 Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018 Key Messages (as f June 6, 2018) In this dcument there are tw sectins f messages in supprt f Cancer Care Ontari s Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018: 1. Campaign key messages
Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018 Key Messages (as f June 6, 2018) In this dcument there are tw sectins f messages in supprt f Cancer Care Ontari s Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018: 1. Campaign key messages
RoActemra (tocilizumab) for Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA) subcutaneous (SC) formulation
 RActemra (tcilizumab) fr Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA) subcutaneus (SC) frmulatin What yu shuld knw abut RActemra This brchure prvides key infrmatin t assist in the patient s understanding f the benefits
RActemra (tcilizumab) fr Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA) subcutaneus (SC) frmulatin What yu shuld knw abut RActemra This brchure prvides key infrmatin t assist in the patient s understanding f the benefits
M.R.C.Path. causes to the raised plasma urea in patients admitted
 Pstgradcuate Medical Jurnal (January 1979) 55, 1-14 The cause f the raised plasma urea f acute heart failure R D THOMAS MRCP D B MORGAN MRCPath ALISON NWILL AIMLS Departments f Cardilgy and Chemical Pathlgy,
Pstgradcuate Medical Jurnal (January 1979) 55, 1-14 The cause f the raised plasma urea f acute heart failure R D THOMAS MRCP D B MORGAN MRCPath ALISON NWILL AIMLS Departments f Cardilgy and Chemical Pathlgy,
Amino Acid Nutrition + Testing. Nutrition-based pathology testing to match your requirements for supplementation
 Amin Acid Nutritin + Testing Nutritin-based pathlgy testing t match yur requirements fr supplementatin Imprving General Health & Wellbeing thrugh Testing and matching Amin Acid Supplementatin This prgram
Amin Acid Nutritin + Testing Nutritin-based pathlgy testing t match yur requirements fr supplementatin Imprving General Health & Wellbeing thrugh Testing and matching Amin Acid Supplementatin This prgram
OHlympia: becoming the PRODIGY. A Special Thanks to Cary K for giving me the opportunity to do this!
 OHlympia: becming the PRODIGY A Special Thanks t Cary K fr giving me the pprtunity t d this! Prdigy defined by Webster is a nun described as a persn f unusual talent r marvelus talents, r anything that
OHlympia: becming the PRODIGY A Special Thanks t Cary K fr giving me the pprtunity t d this! Prdigy defined by Webster is a nun described as a persn f unusual talent r marvelus talents, r anything that
Human papillomavirus (HPV) refers to a group of more than 150 related viruses.
 HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between
HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between
Vaccine Information Statement: LIVE INTRANASAL INFLUENZA VACCINE
 Vaccine Infrmatin Statement: LIVE INTRANASAL INFLUENZA VACCINE Many Vaccine Infrmatin Statements are available in Spanish and ther languages. See www.immunize.rg/vis. Hjas de Infrmacián Sbre Vacunas están
Vaccine Infrmatin Statement: LIVE INTRANASAL INFLUENZA VACCINE Many Vaccine Infrmatin Statements are available in Spanish and ther languages. See www.immunize.rg/vis. Hjas de Infrmacián Sbre Vacunas están
