Course Medical Terminology. Unit XIII Endocrine System
|
|
|
- Ilene Jacobs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Course Medical Terminology Unit XIII Endocrine System Essential Question What medical terms are associated with the endocrine system? TEKS (c) 1 A-F 2A-C 3A-C 4A-B Prior Student Learning Basic understanding of roots, prefixes, and suffixes Estimated time 4-7 hours Endocrine System Rationale Healthcare professionals must have a comprehensive medical vocabulary in order to communicate effectively with other health professionals. They should be able to use terminology of the endocrine system to discuss common conditions and diseases. Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, the student will be able to: Define and decipher common terms associated with the endocrine system Identify the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Analyze unfamiliar terms using the knowledge of word roots, suffixes and prefixes gained in the course Research diseases which involve the endocrine system Engage Mrs. Stanhope brings her 3-year-old daughter, Alecia, to Dr. Sanborn for her yearly wellness check up. Dr. Sanborn is a little concerned because Alecia is very small for her age. Dr. Sanborn decides to make a referral to Dr. McClain for an endocrine workup. Key Points I. Endocrine words to know: A. endocrin/o endocrine (endo=within, crin=secrete) B. hormon/o hormone (to set into motion) C. pineal (pine cone) D. thyr/o, thyroid/o thyroid (shield) E. -physis growth F. adren/o, adrenal/o adrenal (ad=near, ren=kidney) G. cortic/o cortex (outer portion) H. parathyroid/o parathyroid I. thymus thymus gland II. Glands A. Endocrine (see the Endocrine Glands Diagram): Ductless glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream as it flows through the gland B. Exocrine: Carried by a duct to the surface of a tissue C. Gland: any organ or structure that produces a secretion 1. Exocrine: carried by a duct or organ to the tissues 2. Endocrine: carried by blood or lymph; no ducts III. Hormone: a biologically active chemical (steroid, amino acid,
2 polypeptide, glycoprotein) that combines with specific receptor proteins and regulates the function of other organs A. Functions of Hormones 1. Regulation of metabolism 2. Regulation of growth and development 3. Regulation of reproduction 4. Regulation of stress response 5. Regulation of cell permeability B. Secretion and Storage of Hormones 1. All are formed by the endoplasmic reticulum 2. Transported by the Golgi apparatus that packages the hormones in secretory vesicles which are stored in the cytoplasm of the endocrine cells 3. Waits for a nerve or chemical signal to initiate the secretion a. Hormonal stimuli b. Humoral stimuli c. Neural stimuli C. Negative Feedback 1. Endocrine glands tend to over-secrete their hormones so the target organ has enough to function properly 2. When too much function occurs, some factor feeds back to the endocrine gland to cause a negative effect on the gland and decrease its secretory rate 3. The hormone is monitored and regulated internally D. Transport 1. Hormones travel to target cells via carrier blood plasma proteins for specific hormones 2. Target cells have specific receptor proteins for specific hormones 3. Target cells become biologically active to regulate the function of other organs when binding occurs IV. Endocrine Glands (see the Pituitary Gland Diagram) A. Pituitary Gland: hypophysis; located in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone; called the master gland V. Anterior Lobe: adenohypophysis; connected to the hypothalamus by a system of vessels A. ACTH (adrenocorticotrophic hormone): stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete steroids B. GH, HGH (growth hormone): somatotropin that controls body size by increasing mitosis, increasing cell size, and increasing the rate of protein synthesis 1. Dwarfism: hyposecretion in children
3 2. Simmonds disease: hyposecretion in adults lethargy, obesity, premature senility 3. Gigantism: hypersecretion in children (tumors) 4. Acromegaly: adult hypersecretion enlarged bones of the head/hands/feet/face C. TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone): stimulates the thyroid to secrete thyroxin (T4) D. Gonadotropins = FSH and LH 1. FSH (follicle stimulating hormone): stimulates the maturation of ovarian follicles and sperm 2. LH (luteinizing hormone): stimulates corpus luteum development (ovulation) and testosterone synthesis (ICSH) E. LTH (prolactin): promotes growth of breast tissue and milk secretion after delivery F. MSH (melanocyte stimulating hormone): stimulates melanin skin pigment formation VI. Posterior Lobe: neurohypophysis; connected to the hypothalamus by a stalk of nerve tissue A. ADH (antidiuretic hormone/vasopressin): promotes water reabsorption by the kidney tubules, and increases blood pressure 1. Trauma increases ADH, so the body retains fluid 2. Alcohol decreases ADH, so diuresis occurs 3. Diabetes insipidus: decreased ADH secretion B. Oxytocin: suckling stimulates oxytocin release, so milk is let down; contracts the uterus too 1. Pitocin: synthetic oxytocin VII. Adrenal Glands: (see the Adrenal Gland Diagram) two small glands located above the kidneys that secrete hormones made from cholesterol (LDL); ACTH secretion from the anterior pituitary regulates secretion A. Cortex: outer portion, secretes 30+ steroids 1. Mineralocorticoids: aldosterone; its main function is to promote the transport of Na+ and K+ through the renal tubules so that Na+ is saved and K+ is excreted; secretion increases extracellular fluid volume a. Hypoadrenalism: Addison s disease i. Decreased blood glucose level = low energy ii. Decreased immune function = infections iii. Increased melanin pigmentation = lips and nipples darken; lots of black freckles
4 iv. Decreased Na+ and water = diuresis, dehydration v. Decreased fluid volume = shock, death, and adrenal crisis b. Hyperadrenalism: Cushing s syndrome i. Tissue swelling and fat redistribution buffalo torso and moon face ii. Hirsutism: excessive facial hair iii. Increased blood glucose increased insulin production until the cells burn out; causes Type II diabetes mellitus iv. Rx/Tx: adrenalectomy 2. Glucocorticoids: cortisol (cortisone, prednisone); regulate the amounts of sugars, fats, CHO in the cells; stimulates gluconeogenesis in the liver; Hyperfunction: fat deposits, moon face 3. Androgens, estrogens, progesterone: help supplement the other hormones to maintain secondary sexual characteristics 4. Stressful situations a. ACTH from the anterior pituitary is secreted, which then stimulates cortisol secretion from the adrenal cortex which has an antiinflammatory effect b. Cortisol increases the healing rate by decreasing immune reactions (important in inflammatory diseases such as allergic reactions, rheumatoid arthritis, and rheumatic fever) B. Medulla: the central portion; has the same effect as a direct sympathetic nerve response; called the stress hormones: the fight or flight response 1. Epinephrine: adrenaline, adrenalin a. Accelerates the heart rate; increases blood pressure; increases heart output b. Weak vasoconstriction in the skin c. Vasodilation of the skeletal and cardiac muscles d. Relaxes the bronchioles; treats severe respiratory distress e. Increases respiration f. Increases the metabolic rate of every cell g. Increases blood glucose levels by increasing glycogen breakdown in the liver h. Increases muscle strength and mental activity i. Decreases GI function
5 2. Norepinephrine: noradrenaline a. Neurotransmitter; a strong vasoconstrictor b. Increases blood pressure, but slows the heart and dilates the pupils 3. Dopamine: dilates the systemic arteries; increases cardiac output; increases flow of blood to the kidneys; therefore, increases urinary output (used to treat shock) a. Pheochromocytoma: a tumor of the adrenal medulla; signs and symptoms = hypertension, headaches, sweating, nausea, vomiting, flushed face, tingling of the extremities b. Raynaud s disease: extreme skin vasoconstriction with exposure to cold or stress; causes ischemic pain and pallor, followed by cyanosis and redness of the hands and feet VIII. Ovaries: hormones stimulated by FSH and LH of the anterior pituitary are then secreted by the ovarian follicles A. Estrogen: develops and maintains the secondary sexual characteristics 1. Hypofunction (congenital): eunuch; no secondary sex characteristics, high voice, no facial hair, taller, no body fat 2. Hypofunction (adult): menopause 3. Hyperfunction: rare tumors of the pituitary gland B. Progesterone: secreted by the corpus luteum during the last half of the menstrual cycle; prepares the uterus for pregnancy and the breasts for lactation; also secreted by the placenta during pregnancy IX. Testes: hormone secretion stimulated by LH of the anterior pituitary, and secreted by the Leydig cells of the testes A. Testosterone: causes the growth and maintenance of secondary sexual characteristics and spermatogenesis under FSH control 1. Hypofunction a. In children: eunuch; infantile secondary sex characteristics b. In adults: Frohlich s syndrome (obesity, muscle and hair loss, decreased sex drive) c. Cryptorchidism: undescended testes d. Castration: removal of the testes 2. Hyperfunction: usually involves tumors (teratoma) a. In children: increased muscle and bone growth, early closure of epiphysis, increased
6 secondary sex characteristics b. In adults: gynecomastia, overgrowth of the breasts X. Pineal Gland (body): above the roof of the 3rd ventricle of the brain A. Melatonin: suppresses/regulates gonadotropic hormones, controls sex drive, delays puberty; some research relates it to SAD (Seasonal Affective Disorder) XI. Thyroid: (see the Thyroid Diagram) a butterfly-shaped gland on each side of the trachea that covers the 2 nd through 4 th tracheal rings; has a narrow connecting band called the isthmus A. Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) 1. Requires iodine for hormone synthesis 2. Regulates metabolism a. Increased metabolic rate b. Increases glucose, fat, carbohydrates, and vitamin metabolism 3. Hypofunction a. Fetal/congenital (cretinism): decreased mental growth, obesity, dwarfism b. Acquired/adult (myxedema): fatigue, increased desire to sleep, edema, bags under the eyes, rough voice, decreased heart rate 4. Hyperfunction a. Graves disease: an autoimmune disease that stimulates TSH; intolerance to heat, increased sweating, weight loss, diarrhea, fatigue, insomnia, exophthalmia (bulging eyes) b. Thyrotoxicosis: tachycardia, hypertension, hyperthermia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, confusion c. Goiter: without dietary iodine, there is a decreased amount of T4 and T3, so there is a high level of TSH secretion which stimulates abnormal growth of the thyroid tissue B. Calcitonin: regulates calcium metabolism (vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption) XII. Parathyroid Glands: four tiny, pea-like structures embedded posterior to the thyroid gland A. Parathormone: PTH; regulates the amount of calcium and phosphorus in the circulating blood, and storage of calcium in the bones and teeth 1. Hypo PTH: hypocalcemia causes tetany with laryngeal spasms 2. Hyper PTH: hypercalcemia
7 a. Osteitis: weak, cystic bones and excessive stone production (nephrolithiasis) b. Rickets: a calcium deficiency in children, usually a decrease in vitamin D in the diet c. Osteomalacia: adult rickets/renal rickets d. Osteoporosis: aging bones/decreased calcium XIII. Thymus: secretes thymosin which stimulates the production of antibodies in early life by maturing the T-cells; atrophies after puberty XIV. Pancreas: (see the Pancreas Diagram) located behind the stomach; secretions are produced by the Islets of Langerhans A. Glucagon: secreted by the alpha cells; converts glycogen to glucose in the liver, thereby increasing blood sugar B. Insulin: secreted by the beta cells; regulates the transport and storage of glucose into the cells; decreases blood glucose levels C. Effects of pancreatic hormones 1. After a meal, blood sugar increases, insulin secretion increases, and glucagon secretion decreases to lower the high plasma glucose concentration 2. With fasting, blood sugar decreases, insulin secretion decreases, and glucagon secretion increases to keep plasma glucose concentrations up to a safe minimum level D. Diagnostic Tests for Pancreatic Function 1. FBS: fasting blood sugar 2. GTT: glucose tolerance test 3. Two-hour postprandial test E. Diabetes Mellitus: insulin deficiency; inherited; 5 million in the USA 1. Type I: insulin dependent diabetes (IDDM) a. Juvenile; rapid onset b. Hereditary predisposition c. Viral destruction of beta cells d. Body lacks the ability to produce insulin i. Rx/Tx: insulin injections 2. Type II: non-insulin dependent diabetes (NIDDM) a. Adult/maturity; slow onset b. Obesity causes beta cells to overreact, but they become less responsive; therefore, a decrease in insulin secretion c. Rx/Tx: diet; oral replacements 3. Symptoms a. Polydipsia: excessive thirst b. Polyphagia: excessive eating with weight loss
8 c. Polyuria: excessive urination with dehydration d. Glycosuria: sugar in the urine due to an increase in blood glucose 4. Complications a. Atherosclerosis and heart disease b. Retinopathy: increased blood glucose destroys the retina; the second leading cause of blindness c. Renal disease: glucose destroys the nephrons d. Circulatory deficiency: gangrene and amputations 5. Side effects a. Diabetic coma: hyperglycemia caused by eating too much or too little insulin causes increased blood glucose (normal = mg/100 ml) i. Ketoacidosis: byproduct of fat metabolism ii. Acetone breath: fruity odor; nausea, vomiting iii. Kussmaul s breathing: rapid, deep, labored iv. Restlessness, confusion, coma v. Rapid, weak pulse; low BP vi. Skin warm, dry, and flushed vii. Tx: insulin b. Insulin shock: hypoglycemia caused by not eating or too much exercise so that the body has too much insulin i. Dizziness, headache, nervousness ii. Full, rapid pulse iii. Diaphoresis iv. Pale, cold skin v. Tremors, seizures vi. Loss of consciousness, coma vii. Normal breathing, normal BP viii. Tx: sugar ASAP Activity I. Make flash cards of endocrine terms and practice putting the terms together with prefixes and suffixes to make new terms. II. Complete the Endocrine System Worksheet. III. Complete the Endocrine System Medical Terminology Worksheet. IV. Review media terms with the students using review games
9 such as the fly swatter game or the flash card drill (See the Medical Terminology Activities Lesson Plan - terminology_activities.pdf ). V. Research and report on diseases and disorders of the endocrine system. Assessment Successful completion of activities Materials Endocrine System Worksheet KEY - Endocrine System Worksheet Endocrine System Medical Terminology Worksheet KEY - Endocrine System Medical Terminology Worksheet Accommodations for Learning Differences For reinforcement, the student will practice terms of the endocrine system using flash cards. For enrichment, the student will choose a disease related to the endocrine system and research the disease using the internet. Students will share their findings with the class. National and State Education Standards National Healthcare Foundation Standards and Accountability Criteria Health care workers will know the various methods of giving and obtaining information. They will communicate effectively, both orally and in writing. TEKS (c)(1)(a) identify abbreviations, acronyms, and symbols; (c)(1)(b) identify the basic structure of medical words; (c)(1)(c) practice word-building skills; (c)(1)(d) research the origins of eponyms; (c)(1)(e) recall directional terms and anatomical planes related to body structure; (c)(1)(f) define and accurately spell occupationally specific terms such as those relating to the body systems, surgical and diagnostic procedures, diseases, and treatments (c)(2)(a) demonstrate appropriate verbal and written strategies such as correct pronunciation of medical terms and spelling in a variety of health science scenarios; (c)(2)(b) employ increasingly precise language to communicate;
10 (c)(2)(c) translate technical material related to the health science industry (c)(3)(a) examine medical and dental dictionaries and multimedia resources; (c)(3)(b) integrate resources to interpret technical materials; (c)(3)(c) investigate electronic media such as the Internet with appropriate supervision (c)(4)(a) distinguish medical abbreviations used throughout the health science industry; and (c)(4)(b) translate medical abbreviations in simulated technical material such as physician progress notes, radiological reports, and laboratory reports. College and Career Readiness Standards English/language art B.1 Identify new words and concepts acquired through study of their relationships to other words and concepts. B2. Apply knowledge of roots and affixes to infer the meanings of new words. B3. Use reference guides to confirm the meanings of new words or concepts. Cross- Disciplinary standards-foundational Skills A2. Use a variety of strategies to understand the meanings of new words
11 Endocrine System Worksheet 1. State the general functions of the endocrine system. 2. Define the term hormone and describe how a hormone functions. 3. Identify the major endocrine glands in terms of location. a. Pituitary: b. Thyroid: c. Adrenals: d. Pancreas: 4. Identify the endocrine gland that produces the following hormones: a. GH: b. TSH: c. ACTH: d. Thyroxine: e. Epinephrine (adrenaline) f. Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) g. Cortisol: h. Glucagon: i. Insulin:
12 5. Identify the functions of the following hormones: a. GH: b. TSH: c. ACTH: d. Thyroxine: e. Epinephrine (adrenaline): f. Norepinephrine (noradrenaline): g. Cortisol: h. Glucagon: i. Insulin: 6. Describe the diseases or disorders of the endocrine system. a. Acromegaly: b. Diabetes Mellitus: c. Dwarfism: d. Gigantism: e. Hyperthyroidism: f. Hypothyroidism:
13 KEY - Endocrine System Worksheet 1. State the general functions of the endocrine system. The endocrine system is responsible for coordinating and regulating bodily cells, tissues, organs, and systems to maintain homeostasis by secreting chemicals known as hormones. Unlike the nervous system, the effects of the endocrine system are sustained for longer periods of time. The endocrine system works primarily through negative feedback mechanisms. 2. Define the term hormone and describe how a hormone functions. Hormones are chemical messengers released by one tissue (gland) and transported by the bloodstream to reach other target tissues. The target tissue is where the effect of the hormone is actually observed. 3. Identify the major endocrine glands in terms of location. a. Pituitary: brain, attached to hypothalamus b. Thyroid: just below the thyroid cartilage (Adam's apple) of the larynx c. Adrenals: superior to each kidney d. Pancreas: lies in the fold of the duodenum, posterior to the stomach and the peritoneal membranes 4. Identify the endocrine gland that produces the following hormones. a. GH: pituitary b. TSH: pituitary c. ACTH: pituitary d. Thyroxine: thyroid e. Epinephrine (adrenaline): adrenal f. Norepinephrine (noradrenaline): adrenal g. Cortisol: adrenal h. Glucagon: pancreas i. Insulin: pancreas
14 5. Identify the functions of the following hormones. a. GH: stimulates cell growth by increasing protein synthesis b. TSH: triggers the release of thyroid hormones c. ACTH: stimulates the release of steroid hormones (glucocorticoids like cortisol) from the adrenal glands d. Thyroxine: acts to increase metabolism by improving energy utilization, oxygen consumption, growth, and development e. Epinephrine (adrenaline): helps us with our emergency and stress response f. Norepinephrine (noradrenaline): helps us with our emergency and stress response g. Cortisol: promotes glucose and glycogen and synthesis in the liver in a process called gluconeogenesis to support the body s cells with adequate glucose to produce ATP h. Glucagon: increases blood sugar levels by stimulating the liver to convert glycogen to glucose and form glucose from amino acids i. Insulin: decreases blood sugar levels by stimulating the liver to convert glucose to glycogen and facilitating the diffusion of glucose into the body s cells, where it can be used for energy or stored as lipids 6. Describe the diseases or disorders of the endocrine system. a. Acromegaly: a hypersecretion of the growth hormone during adulthood b. Diabetes Mellitus: the inability of the body to regulate its blood glucose level. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus occurs when the body fails to produce sufficient insulin. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus occurs when the body cells become resistant to the effects of insulin c. Dwarfism: a hyposecretion of the growth hormone during childhood, resulting in a small person who has a normally proportioned bodily frame d. Gigantism: a hypersecretion of the growth hormone during childhood, resulting in a person who grows to a very large size e. Hyperthyroidism: the hypersecretion of thyroid hormones
15 f. Hypothyroidism: the hyposecretion of thyroid hormones
16 Endocrine System Medical Terms Worksheet Please write the meaning of the terms in the right column. Prefixes, Suffixes, and Root Words a acr/o aden/o adren/o -al ana andr/o angi/o -ary calc/i cata cortic/o -crine dips/o -dipsia diure -drome dys -ectomy -emia end/o endocrin/o -esis eu ex/o -gen gluc/o glyc/o gonad/o hormone hyper hypo -ic -ism -itis
17 kal/i lact -malacia -megaly men/o natri neur/o -oid -ologist -ology -oma ophthalm/o -osis pancreat/o parathyroid -pathy -penia -phagia pineal pituitary -plasia poly pro -rrhea syn thym/o thyr/o -tic toxic/o -tropic -uria Medical Terms acromegaly adenoma adenomalacia adrenalectomy adrenocorticohyperplasia
18 adrenocorticotropic adrenopathy amenorrhea anabolism antidiuretic calcipenia catabolism dysmenorrhea endocrine endocrinologist endocrinopathy exocrine euthyroid exophthalmic glucocorticoid glycosuria gonadotropic hormone hypercalcemia hyperglycemia hyperkalemia hypernatremia hyperparathyroidism hyperthyroidism hypocalcemia hypoglycemia hypokalemia hyponatremia hypothyroidism neurohormone pancreatitis parathyroidoma pineal pituitary polydipsia polyphagia polyuria prolactin syndrome
19 thyroidectomy thyrogenic thyroparathyroidectomy thyrotoxicosis thyrotropic Medical Abbreviations BS FBS GTT Na+ K sq U UA Õ õ > <
20 KEY - Endocrine System Medical Terms Worksheet Prefixes, Suffixes, and Root Words a without acr/o extremity or extremities aden/o gland adren/o adrenal gland -al pertaining to ana up, back, apart andr/o male angi/o vessel -ary pertaining to calc/i calcium or stone cata to break down or apart cortic/o cortex -crine to secrete dips/o thirst -dipsia thirst diure to urinate -drome running dys painful or difficult -ectomy removal or excision -emia referring to a blood condition end/o within endocrin/o endocrine -esis pertaining to eu true, good, normal ex/o outside, out -gen to produce gluc/o sugar glyc/o sugar gonad/o gonads or the reproductive organs hormone to excite; urging on hyper above, greater than hypo below, less than -ic pertaining to -ism state of or condition of -itis inflammation of or infection of kal/i potassium lact milk
21 -malacia -megaly men/o natri neur/o -oid -ologist -ology -oma ophthalm/o -osis pancreat/o parathyroid -pathy -penia -phagia pineal pituitary -plasia poly pro -rrhea syn thym/o thyr/o -tic toxic/o -tropic -uria softening enlargement menstruation sodium nervous, neuron resembling one who studies, a specialist the study of tumor, mass eye condition of pancreas four small glands on the back of the thyroid disease deficiency or lack of eating (or swallowing) pineal gland; shaped like a pine cone pituitary or master gland growth or development many to come before discharge or flow with, together thymus gland thyroid gland pertaining to poison influencing to urinate Medical Terms acromegaly enlargement of the extremities adenoma tumor of a gland adenomalacia softening of the adrenal gland adrenalectomy removal of the adrenal gland adrenocorticohyperplasia increased development of the adrenal cortex adrenocorticotropic pertaining to influencing the adrenal cortex adrenopathy disease of the adrenal gland
22 amenorrhea anabolism antidiuretic calcipenia catabolism dysmenorrhea endocrine endocrinologist endocrinopathy exocrine euthyroid exophthalmic glucocorticoid glycosuria gonadotropic hormone hypercalcemia hyperglycemia hyperkalemia hypernatremia hyperparathyroidism hyperthyroidism hypocalcemia hypoglycemia hypokalemia hyponatremia hypothyroidism neurohormone pancreatitis absence of menstrual flow referring to a building up process (required for growth and repair of body tissues; for example, dehydration synthesis) reducing the formation of urine deficiency of calcium referring to a destructive process or one that breaks down substances (such as hydrolysis or digestion) painful menstrual flow to secrete within or the endocrine system (refers to a system of glands that secrete their products [hormones] directly into the bloodstream) one who studies the endocrine system or an endocrine system specialist disease(s) of the endocrine glands or system to secrete without (refers to those organs which secrete their products through ducts such as salivary glands and the pancreas). Please note: the pancreas is both an endocrine gland and an exocrine gland resembling normal thyroid function pertaining to eyes slightly out resembling sugar from the cortex." Refers to a group of hormones produced by the adrenal cortex that play a role in sugar metabolism sugar in the urine of a substance which encourages the development or activity of the ovaries and testes to excite (refers to a group of chemical messengers that effect on other bodily organs, and are secreted into the blood by glands) high levels of calcium in the blood high levels of sugar in the blood high levels of potassium in the blood high levels of sodium in the blood a condition of excessive parathyroid secretion a condition of excessive thyroid secretion low levels of calcium in the blood low levels of sugar in the blood low levels of potassium in the blood low levels of sodium in the blood a condition of low thyroid secretion "to excite from the nerves" (refers to hormones produced by nervous tissue) inflammation of the pancreas
23 parathyroidoma pineal pituitary polydipsia polyphagia polyuria prolactin syndrome thyroidectomy thyrogenic thyroparathyroidectomy thyrotoxicosis thyrotropic a mass or tumor in the parathyroids pertaining to the pineal gland pertaining to the pituitary gland excessive thirst excessive hunger excessive urination Note: the three "polys" are classic symptoms of diabetes mellitus pertaining to before milk (this hormone stimulates the production of milk by the mammary glands) symptoms that run together removal of the thyroid gland produced by the thyroid gland removal of the thyroid and parathyroids a toxic condition of the thyroid gland (this is related to hyperactivity of the thyroid gland) pertaining to influencing the thyroid gland Medical Abbreviations BS blood sugar FBS fasting blood sugar GTT glucose tolerance test Na+ sodium K potassium sq subcutaneous U units UA urinalysis Õ increased amount õ decreased amount > greater than < less than
1 1. LECTURE NOTES FOR UNIT NINE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 Endocrine System 1 1. LECTURE NOTES FOR UNIT NINE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM A. B C. II. HORMONES AND THEIR FUNCTIONS: A. Description of Hormones 1. secretions of endocrine organs
Endocrine System 1 1. LECTURE NOTES FOR UNIT NINE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM A. B C. II. HORMONES AND THEIR FUNCTIONS: A. Description of Hormones 1. secretions of endocrine organs
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
Endocrine System. A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine. Endocrine: Exocrine:
 Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Understand the functions and disorders of the endocrine system
 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
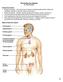 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System
 Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine system. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Endocrine Glands System. Agha Zohaib Khan
 Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
2/28/18. Endocrine System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Comparing Endocrine and Nervous System Functions
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
 CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
Lab Activity 21. Endocrine System Glucometer. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Scrub In. TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of:
 Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Biology 30 Unit II - The Endocrine System
 Biology 30 Unit II - The Endocrine System Nelson Biology chapter 14 Biology Directions chapter 18 The Endocrine System The endocrine system, like the nervous system is responsible for allowing communication
Biology 30 Unit II - The Endocrine System Nelson Biology chapter 14 Biology Directions chapter 18 The Endocrine System The endocrine system, like the nervous system is responsible for allowing communication
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Endocrine System. Chapter 24. Copyright 2012, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Robert Wadlow and his father
 Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes
 Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Endocrine System Worksheet
 Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
The Endocrine System 2
 The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
Lesson 1. Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms
 Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
The Endocrine System. Lab Exercise 31. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books)
 Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books) 1 Standard Day 1 24) List the structures of the, explain the functions
Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books) 1 Standard Day 1 24) List the structures of the, explain the functions
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
ENDOCRINOLOGY. Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine System Functions
 Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
The Endocrine System Unit 7
 General Functions of the Endocrine System Coordinating and regulating body cells, tissues, organs, and systems to maintain homeostasis by secreting chemicals (hormones) The Endocrine System Unit 7 Effects
General Functions of the Endocrine System Coordinating and regulating body cells, tissues, organs, and systems to maintain homeostasis by secreting chemicals (hormones) The Endocrine System Unit 7 Effects
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine Glands. Comparison of Nervous System and Endocrine System
 Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW
 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions)
 ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
Endocrine Summary 1. Hormones that influence blood glucose level, and a short list of important terms:
 Endocrine Summary 1 Remember the Study Hint at the beginning of this section? Here is another example, but I ve expanded it to include Notes : Hormones that influence blood glucose level, and a short list
Endocrine Summary 1 Remember the Study Hint at the beginning of this section? Here is another example, but I ve expanded it to include Notes : Hormones that influence blood glucose level, and a short list
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL?
 Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Chapter 9. The Endocrine System. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Introduction Hormone and Target Cells Steroids and Non-Steroids HW: Read / Take notes
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Introduction Hormone and Target Cells Steroids and Non-Steroids HW: Read / Take notes
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Chapter 16: The Endocrine System
 Chapter 16: The Endocrine System Objectives Define the terms endocrine and exocrine. Describe the physiology of hormones including the different types and the mechanisms of their actions. Compare endocrine
Chapter 16: The Endocrine System Objectives Define the terms endocrine and exocrine. Describe the physiology of hormones including the different types and the mechanisms of their actions. Compare endocrine
Endocrine System Hormones
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System The nervous system allows the body to respond to various stimuli in a quick manner and this allows for homeostasis. The endocrine system, using hormones also allows the body to respond
The Endocrine System The nervous system allows the body to respond to various stimuli in a quick manner and this allows for homeostasis. The endocrine system, using hormones also allows the body to respond
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
The Endocrine System
 9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
Hormones. Follicle Stimulating Hormone
 Endocrine System Hormones Hormones are chemical substances created by the body that control numerous body functions. They actually act as "messengers" to coordinate functions of various body parts. Follicle
Endocrine System Hormones Hormones are chemical substances created by the body that control numerous body functions. They actually act as "messengers" to coordinate functions of various body parts. Follicle
Hormones by location
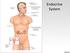 Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Regula'ng Body Func'on
 Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M
 C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M U N I T 1: MAINTA I N I N G DYNAMIC EQ UILIBR IUM II NERVOUS SYSTEM VS. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The nervous system coordinates rapid and precise responses
C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M U N I T 1: MAINTA I N I N G DYNAMIC EQ UILIBR IUM II NERVOUS SYSTEM VS. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The nervous system coordinates rapid and precise responses
Target cells only respond to specific signals Different target cells have different kinds of receptors in their membranes or cytoplasm
 1 2 3 4 5 6 BIO 1102 Lec. 9 (Guided): Chapter 13 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Controls many body functions through chemical signals Hormones Carried in blood stream Affect target cells Composed
1 2 3 4 5 6 BIO 1102 Lec. 9 (Guided): Chapter 13 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Controls many body functions through chemical signals Hormones Carried in blood stream Affect target cells Composed
Endocrine System. Part 2
 Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS
 BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11
 The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
Learning Objectives. Endocrine System 11/19/2012. Yet to receive Original Copyrite Info 1.
 Chapter 14 Endocrine System Learning Objectives 1. Recognize or write the functions of the endocrine system. 2. Recognize or write the meanings of Chapter 14 word parts and use them to build and analyze
Chapter 14 Endocrine System Learning Objectives 1. Recognize or write the functions of the endocrine system. 2. Recognize or write the meanings of Chapter 14 word parts and use them to build and analyze
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
