Immunohistochemical analysis of Na + /I symporter distribution in human extra-thyroidal tissues
|
|
|
- Hope Victoria Johnston
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Journal of Endocrinology (1999) ISSN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY Immunohistochemical analysis of Na + /I symporter distribution in human extra-thyroidal tissues Laure Vayre 1, Jean-Christophe Sabourin 2, Bernard Caillou 2, Michel Ducreux 1, Martin Schlumberger 3 and Jean-Michel Bidart 4 Departments of 1 Medicine, 2 Pathology, 3 Nuclear Medicine and 4 Clinical Biology, Institut Gustave-Roussy, Villejuif, France (Correspondence should be addressed to J-M Bidart, Institut Gustave-Roussy, 39 rue Camille Desmoulins, Villejuif, France; bidart@igr.fr) Abstract 131 Iodine concentration has been described in several extra-thyroidal tissues. Recent evidence has shown that iodine uptake is achieved by the recently cloned human Na /I ¹ symporter (hnis) gene. However, conflicting results were observed in the expression of hnis transcripts in extra-thyroidal tissues. In order to document further the distribution of hnis, we investigated its expression using an immunohistochemical method, based on a polyclonal antibody raised against a synthetic peptide. Various extra-thyroidal tissues were examined, particularly from the digestive tract. Our results confirm that the salivary glands and the stomach express hnis protein significantly. In contrast, hnis was undetectable in the colon but the rectal mucosa, which has never been examined, exhibited positive immunohistochemical staining. Other digestive tissues, including the oesophagus, small intestine and appendix, were negative. Weak staining was observed in the mammary gland, indicating that hnis is expressed in this tissue. The pancreas, skin, ovaries, spleen and kidney showed no positive immunostaining. European Journal of Endocrinology Introduction Thyroid-specific iodine concentrating activity is widely applied in clinical practice for the evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of various thyroid diseases (1). Radioactive iodine ( 131 I) is used both to detect and to treat differentiated thyroid carcinomas (2). Despite the high specificity of thyroid uptake, radioiodine accumulation has been reported in both normal and pathological conditions. Indeed, radioiodine concentration has been observed in various normal tissues including the salivary glands, gastric mucosa, mammary gland, ovaries, placenta, choroid plexus and thymus, and in various pathological conditions such as pleuropericardial cysts and thymus hypertrophy; also accumulation of radioiodine is frequently found in the colonic lumen during hypothyroidism (3 5). Iodine uptake is mediated in thyroid follicular cells by the Na /I ¹ symporter (NIS), localized on the basolateral cell membrane (6, 7). The human NIS (hnis) has recently been cloned and it shares a high degree of homology with the Na /glucose-dependent cotransporter family (8 10). Interestingly, in recent studies, hnis expression was detected in extra-thyroidal tissues. NIS immunohistochemical expression was described in salivary gland tissues (11) and in thymus (12). Furthermore, NIS mrna was detected by reverse transcriptase (RT)- PCR and Southern blot in various tissues, including parotid gland, stomach and others, but only thyroid tissue displays a positive signal by Northern blot analysis, suggesting a low level of gene expression in extra-thyroidal tissues (10, 13). In order to understand better the physiological uptake of iodide, we investigated hnis expression in extra-thyroidal tissues, and particularly in those of the digestive tract, where radioiodide accumulation has been reported. A polyclonal antibody, raised against a synthetic peptide mimicking the C-terminal portion of hnis, was used to detect the Na /I ¹ symporter by immunohistochemistry. This antibody has been proven useful for the detection of hnis protein in normal, pathological non-neoplastic thyroid tissues and in papillary and follicular thyroid carcinomas (14). We also demonstrated that immunodetection of hnis could be of value in predicting radioiodine uptake in thyroid cancers. Our present results demonstrate that most tissues and organs purported to take up iodide, do indeed express hnis. Materials and methods Materials The production and the characteristics of the anti-hnis antiserum have been described previously (14). Briefly, 1999 Society of the European Journal of Endocrinology Online version via
2 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (1999) 141 hnis expression in extra-thyroidal tissues 383
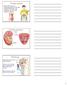
3 384 L Vayre and others EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (1999) 141 a synthetic peptide corresponding to the C-terminal portion of hnis was synthesized by a solid phase method. This peptide was then purified and coupled to the carrier molecule Keyhole Limpet Haemocyanin. The polyclonal antibody was obtained by immunizing rabbits with the peptide-carrier conjugate and the presence of anti-peptide antibodies was verified with an enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay. Immunohistochemistry Normal frozen tissues and paraffin-embedded specimens were retrospectively retrieved from the tissue bank of the Department of Pathology. These normal tissue samples were obtained at a distance from tumour sites during surgical procedures in patients whose disease was diagnosed and followed up at the Institut Gustave- Roussy. The following specimens were collected: normal tissue from the digestive tract including the oesophagus (n = 2), stomach (n = 6), duodenum (n = 4), small intestine (n = 8), ileum (n = 3), caecum (n = 2), colon (n = 5), rectum (n = 3), pancreas (n = 3), appendix (n = 4) and spleen (n = 2); normal tissues known to concentrate radioiodine, namely the salivary glands (n = 2 ), the mammary gland (n = 3), and ovaries (n = 3); and finally tissue from the skin (n = 2) and kidney (n = 2). Normal thyroid tissue was used as a positive control for hnis expression. Specimens, frozen at ¹70 C in isopentane and stored in liquid nitrogen, were cut into serial cryostat tissue sections (5 mm) and fixed in cold acetone for 10 min. The paraffin-embedded tissue sections (5 mm) were fixed in formaldehyde. Before the procedure, the paraffin specimens were deparaffinized, then rehydrated by successive immersion in a xylene bath and an absolute ethanol bath and finally rinsed in distilled water. All sections were incubated with hydrogen peroxide for 5 min to inactivate endogenous peroxidase and then with the anti-hnis antiserum, diluted at 1:500, for one hour. Sections were washed three times in Tris HCl buffer for 5 min each time and then incubated with a biotinylated antibody (K677, Universal LSAB2 kit/ HRP, Dako Corporation, Carpinteria, CA, USA) for 30 min. They were again washed three times and incubated for 30 min with either streptavidin peroxidase (K677, Universal LSAB2 kit/hrp, Dako Corporation) for extra-thyroid tissues or with alkaline phosphataselabelled streptavidin (K674, Universal LSAB2 kit/ap, Dako Corporation) for thyroid tissue. After three further washes, staining was completed after incubation with the corresponding chromogen solutions (K677, Universal LSAB2 kit/hrp or K699, fast red substrate, Dako Corporation). When these conventional procedures failed to detect hnis by immunohistochemical staining, a recent sensitive procedure was applied (Dako EnVision Labelled Polymer, Dako Corporation). Finally, sections were counterstained with haematoxylin. Tissue sections incubated with the preimmune serum or with antibody preabsorbed with the corresponding excess peptide were used as negative controls (14). Results When hnis was detected in non-thyroidal specimens, only epithelial cells were positive; vessels, lymphoid tissue and connective tissue (the lamina propria of the mucous membrane in digestive tissues) never reacted with hnis antibodies. Strong immunostaining was observed in all specimens of the salivary glands and stomach. In the salivary glands, only ductal cells were immunostained by the antiserum (Fig. 1A and B). The hnis protein was diffusely distributed throughout the cytoplasm of the cell. Gastric epithelial cells exhibited a heterogeneous pattern when stained with hnis antibodies (Fig. 1C and D). Approximately 10% of mucinproducing cells were positive for hnis and staining was localized on the basolateral cell membrane. Furthermore, gastric antrum staining was stronger than that observed in the fundus. Positive immunostaining was also observed in the rectum (Fig. 1E and F). In this tissue, hnis appeared to be expressed in approximately 10% of epithelial cells and was localized on their basolateral cell membrane. No hnis immunohistochemical staining was observed in the oesophagus, the small and large intestines, the pancreas, the appendix nor in the spleen, even with the amplification procedure. Using the amplification procedure, hnis protein was detected at a low level in a few epithelial lobular cells of the mammary gland (Fig. 1G). Tissues obtained from the ovaries, skin and kidney did not react with the hnis antibody, even with the amplification procedure. Normal thyroid specimens, used as positive controls, displayed the characteristic heterogeneous staining pattern previously described (14) (Fig. 1H). Discussion Whole body scintigraphy with radioactive iodine ( 131 I) reveals extra-thyroidal 131 I concentration in a significant number of patients. Nuclear physicians need to be alerted to these potential pitfalls so that additional Figure 1 Immunohistochemical detection of hnis protein in human tissues. Frozen tissues: submaxillary gland (A and B), normal thyroid (H); paraffin-embedded tissues: gastric mucosa (C and D), rectum (E and F), and mammary gland (G). (A) and (B) Ductal cells of the salivary gland were stained by anti-hnis. (C) and (D) Gastric epithelial mucin-producing cells exhibited a heterogeneous pattern. (E) and (F) Rectum glandular cells exhibited strong hnis immunostaining. (G) Only a few lobular epithelial mammary cells were stained by anti-hnis (arrows). (H) hnis protein was detected in the basolateral membrane of normal thyroid tissues. The antiserum was diluted 1:500 for panels A and B, C and D, E and F, and G and 1:750 for panel H. Original magnification: panels A, C, E: 10; panels B, F: 200; panels D, G and H: 1000.
4 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (1999) 141 hnis expression in extra-thyroidal tissues 385 costly investigations and/or inappropriate therapies are avoided. This accumulation of 131 I is due to physiological uptake in several tissues, and particularly in the salivary glands and gastrointestinal tract, but also to contamination of physiological fluids such as the saliva, urine, milk and sputum. Recent evidence has shown that, although 131 I uptake is achieved by the specific Na /I ¹ symporter in these extrathyroidal sites, it is not retained because it is not efficiently organified (6). Cloning of the extra-thyroidal hnis gene indicated total identity with the thyroidderived NIS cdna sequence (13). In order to specify the role of the symporter in these extra-thyroidal tissues, we examined extensively the distribution of hnis protein and compared it to data reported on hnis transcripts (Table 1). The salivary glands and stomach exhibited significant hnis protein expression. Iodine accumulation in these tissues is well-known. The genetic alteration in the active transport of iodine that results in impaired iodine concentration in the thyroid, resulting in a hypothyroid goiter, also affects the salivary glands and stomach (15). 131 I uptake in the salivary glands leading to radiation-induced damage is frequent in patients treated with 131 I for thyroid carcinoma (16). hnis has recently been identified in ductal cells of the salivary glands (11). These cells are actively involved in salt reabsorption and secretion. Our results confirm these observations and also indicate that hnis protein is diffusely expressed within cells, suggesting its intervention in multidirectional transfer of iodide. They also confirm the expression of hnis transcripts in the gastric mucosa (13). The stomach and small intestine are areas where the transport of electrolytes and solutes occurs in profusion. In contrast to the location of NIS protein in parietal cells of the rat stomach (17), only gastric mucin-secreting cells were found to express hnis. Furthermore, the gastric antrum showed more intense immunostaining than fundal glands, which is consistent with a greater density of mucin-secreting cells in pyloric antrum glands. This discrepancy in the cellular location of NIS in rat vs human gastric mucosa may be partly related to the different anatomical structure of the stomach in these two species. It remains to be established whether, in human stomach, NIS protein is efficiently matured and functional or not (17). Finally, the presence of hnis in mucin-producing cells of the stomach rules out a recent hypothesis suggesting its potential role as an autoantigen in autoimmune gastritis (13). Conflicting results were observed in the expression of hnis transcripts in colon tissue (10, 13). Our results indicate that hnis protein is undetectable in this tissue, which is not surprising given the absence of transcripts (13). This suggests that the 131 I found in the colon of thyroid cancer patients treated with 131 I while they were hypothyroid is, more likely than not, related to an accumulation in the colonic lumen of 131 I secreted by the gastric mucosa due to its sluggish mobility. The expression of hnis protein in the rectal mucosa was somewhat expected. Indeed, iodine uptake is substantial via the rectal route, which is an effective alternative to sodium iodide administration per os in patients with upper gastrointestinal tract dysfunction (18). Other tissues of the gastrointestinal tract, such as the oesophagus, small intestine and appendix, did not express hnis protein. Our study also showed that hnis protein is expressed at a low level in the mammary gland, which is Table 1 Comparative studies on hnis expression in human thyroid and extra-thyroid tissues. RT-PCR Immunohistochemistry Smanik et al. Spitzweg et al. Caillou et al. Jhiang et al. Tissue (1997) (10) (1998) (13) (1998) (14) (1998) (11) Present study Thyroid gland Submandibular gland Parotid gland Pituitary gland Pancreas ¹ Mammary gland Gastric mucosa Prostate Ovary ¹ Heart Lung Kidney ¹ Oesophagus ¹ Small intestine ¹ Colon ¹ ¹ Rectum Appendix ¹ Spleen ¹
5 386 L Vayre and others EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (1999) 141 consistent with the presence of transcripts (13). It remains to be established whether the degree of expression is dependent or not on the lactotrophic status (19). Breast uptake of 131 I is occasionally seen in young women treated with 131 I for a thyroid carcinoma and iodine concentration in milk is times higher than in blood. Finally, we were unable to detect hnis protein in pancreas, ovary and skin tissue specimens although the presence of hnis transcripts has been reported. This discrepancy may be due to both the low level of hnis protein concentration in these tissues and to the relatively poor sensitivity of the immunohistochemical procedures compared with that of RT-PCR. Acknowledgements This work was supported by grants from the Comité du Val de Marne de la Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer, the FEGEFLUC, LIPHA Santé and Université Paris-Sud (Bonus Qualité Recherche). Laure Vayre is a Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale fellow. The help of Lorna Saint-Ange in editing the manuscript is gratefully acknowledged. References 1 Cavalieri RR. Iodine metabolism and thyroid physiology: current concepts. Thyroid Schlumberger MJ. Papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine McDougall R. Whole-body scintigraphy with radioiodine-131. A comprehensive list of false-positives with some examples. Clinical Nuclear Medicine Francese C, Schlumberger M, Travagli JP, Vera P, Caillou B & Parmentier C. Iodine 131 uptake in a pleuropericardial cyst: case report of a false-positive radioiodine total body scan result in a patient with a thyroid cancer. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine Vermiglio F, Baudin E, Travagli JP, Caillou B, Fragu P, Ricard M et al. Iodine concentration by the thymus in thyroid carcinoma. Journal of Nuclear Medicine Carrasco N. Iodide transport in the thyroid gland. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Dai G, Levy O & Carrasco N. Cloning and characterization of the thyroid iodide transporter. Nature Smanik PA, Liu Q, Furminger L, Ryu K, Xing S, Mazzaferri EL et al. Cloning of the human sodium iodide symporter. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications Turk E, Martin MG & Wright EM. Structure of the human Na / glucose cotransporter gene SGTL1. Journal of Biological Chemistry Smanik PA, Ryu KY, Theil KS, Mazzaferri EL & Jhiang SM. Expression, exon intron organization, and chromosome mapping of the human sodium iodide symporter. Endocrinology Jhiang SM, Cho JY, Ryu KY, De Young BR, Smanik PA, McGaughy VR et al. An immunohistochemical study of Na /I ¹ symporter in human thyroid tissues and salivary gland tissues. Endocrinology Spitzweg C, Joba W & Heufelder AE. Expression of thyroid-related genes in human thymus. Thyroid Spitzweg C, Joba W, Eisenmenger W & Heufelder AE. Analysis of human sodium iodide symporter gene expression in extrathyroidal tissues and cloning of its complementary deoxyribonucleic acids from salivary gland, mammary gland, and gastric mucosa. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism Caillou B, Troalen F, Baudin E, Talbot M, Filetti S, Schlumberger M et al. Na /I ¹ symporter in human thyroid tissues: an immunohistochemical study. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism Pohlenz J, Rosenthal IM, Weiss RE, Jhiang SM, Burant C & Refetoff S. Congenital hypothyroidism due to mutations in the sodium/ iodide symporter. Identification of a nonsense mutation producing a downstream cryptic 3 0 splice site. Journal of Clinical Investigation Alexander C, Bader JB, Schaefer A, Finke C & Kirsch CM. Intermediate and long-term side effects of high-dose radioiodine therapy for thyroid carcinoma. Journal of Nuclear Medicine Kotani T, Ogata Y, Yamamoto I, Aratake Y, Kawano JI, Suganuma T et al. Characterization of gastric Na /I - symporter of the rat. Clinical Immunology and Immunopathology Yeung SC, Go R & Balasubramanyam A. Rectal administration of iodide and propylthiouracil in the treatment of thyroid storm. Thyroid Hammami MM & Bakheet S. Radioiodine breast uptake in nonbreast-feeding women: clinical and scintigraphic characteristics. Clinical and Nuclear Medicine Received 12 February 1999 Accepted 17 May 1999
Differential expression of the Na + /I symporter protein in thyroid cancer and adjacent normal and nodular goiter tissues
 368 Differential expression of the Na + /I symporter protein in thyroid cancer and adjacent normal and nodular goiter tissues SHASHA WANG 1, JUN LIANG 1, YANSONG LIN 2 and RUYONG YAO 3 1 Department of
368 Differential expression of the Na + /I symporter protein in thyroid cancer and adjacent normal and nodular goiter tissues SHASHA WANG 1, JUN LIANG 1, YANSONG LIN 2 and RUYONG YAO 3 1 Department of
Sodium±iodide symporter (NIS) gene expression in lymph-node metastases of papillary thyroid carcinomas
 European Journal of Endocrinology (2000) 143 623±627 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Sodium±iodide symporter (NIS) gene expression in lymph-node metastases of papillary thyroid carcinomas F Arturi, D Russo
European Journal of Endocrinology (2000) 143 623±627 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Sodium±iodide symporter (NIS) gene expression in lymph-node metastases of papillary thyroid carcinomas F Arturi, D Russo
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:!
 LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
Sodium/iodide-symporter: distribution in different mammals and role in entero-thyroid circulation of iodide.
 Sodium/iodide-symporter: distribution in different mammals and role in entero-thyroid circulation of iodide. Josefsson, Malin; Grunditz, Torsten; Ohlsson, Tomas G; Ekblad, Eva Published in: Acta Physiologica
Sodium/iodide-symporter: distribution in different mammals and role in entero-thyroid circulation of iodide. Josefsson, Malin; Grunditz, Torsten; Ohlsson, Tomas G; Ekblad, Eva Published in: Acta Physiologica
BMC Cancer. Open Access. Abstract
 BMC Cancer BioMed Central Research article Expression of the Na + /l - symporter (NIS) is markedly decreased or absent in gastric cancer and intestinal metaplastic mucosa of Barrett esophagus Áron Altorjay
BMC Cancer BioMed Central Research article Expression of the Na + /l - symporter (NIS) is markedly decreased or absent in gastric cancer and intestinal metaplastic mucosa of Barrett esophagus Áron Altorjay
Expression of the Na+/I- symporter (NIS) is markedly decreased or absent in gastric cancer and intestinal metaplastic mucosa of Barrett esophagus
 BMC Cancer This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Copyedited and fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Expression of the
BMC Cancer This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Copyedited and fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Expression of the
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry
 Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Sodium Iodide Symporter (NIS) and Thyroid
 22 CH. HORMONES SPITZWEG, 2002, J.C. 1(1):22-34 MORRIS Sodium Iodide Symporter (NIS) and Thyroid Christine Spitzweg 1, John C. Morris 2 Department of Internal Medicine II, Klinikum Grosshadern, Ludwig-Maximilians-University
22 CH. HORMONES SPITZWEG, 2002, J.C. 1(1):22-34 MORRIS Sodium Iodide Symporter (NIS) and Thyroid Christine Spitzweg 1, John C. Morris 2 Department of Internal Medicine II, Klinikum Grosshadern, Ludwig-Maximilians-University
Research Article Thyroid-Related Protein Expression in the Human Thymus
 Hindawi International Journal of Endocrinology Volume 2017, Article ID 8159892, 10 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8159892 Research Article Thyroid-Related Protein Expression in the Human Thymus Mi
Hindawi International Journal of Endocrinology Volume 2017, Article ID 8159892, 10 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8159892 Research Article Thyroid-Related Protein Expression in the Human Thymus Mi
Imaging Journal of Clinical and Medical Sciences ISSN: DOI CC By
 Clinical Group Imaging Journal of Clinical and Medical Sciences ISSN: 2455-8702 DOI CC By Daniella F Pinho* Department of Radiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Texas, USA Dates: Received:
Clinical Group Imaging Journal of Clinical and Medical Sciences ISSN: 2455-8702 DOI CC By Daniella F Pinho* Department of Radiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Texas, USA Dates: Received:
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Multi-Cytokeratin (4/5/6/8/10/13/18)
 Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Multi-Cytokeratin (4/5/6/8/10/13/18) Product Code: NCL-L-C11 Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Multi-Cytokeratin (4/5/6/8/10/13/18) Product Code: NCL-L-C11 Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW
Assessment Run CK19
 Assessment Run 29 200 CK9 The slide to be stained for CK9 comprised:. Appendix, 2. Thyroid gland, 3. Pancreas, 4. Ductal breast carcinoma, 5. Esophagus, 6. Papillary thyroid carcinoma. All tissues were
Assessment Run 29 200 CK9 The slide to be stained for CK9 comprised:. Appendix, 2. Thyroid gland, 3. Pancreas, 4. Ductal breast carcinoma, 5. Esophagus, 6. Papillary thyroid carcinoma. All tissues were
What location in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract has tight, or impermeable, junctions between the epithelial cells?
 CASE 32 A 17-year-old boy presents to his primary care physician with complaints of diarrhea for the last 2 days. The patient states that he just returned to the United States after visiting relatives
CASE 32 A 17-year-old boy presents to his primary care physician with complaints of diarrhea for the last 2 days. The patient states that he just returned to the United States after visiting relatives
AN INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR MEDICINE
 AN INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR MEDICINE WITH RESPECT TO THYROID DISORDERS By: B.Shafiei MD Nuclear Physician Taleghani Medical Center Radioactive: An element with Unstable Nucleus (Excess Energy), can achieve
AN INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR MEDICINE WITH RESPECT TO THYROID DISORDERS By: B.Shafiei MD Nuclear Physician Taleghani Medical Center Radioactive: An element with Unstable Nucleus (Excess Energy), can achieve
Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC-
 Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
The stomach is formed of three parts: -
 The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
WT1, Estrogen Receptor, and Progesterone Receptor as Markers for Breast or Ovarian Primary Sites in Metastatic Adenocarcinoma to Body Fluids
 Anatomic Pathology / WT1, ESTROGEN RECEPTOR, AND PROGESTERONE RECEPTOR IN CYTOLOGY OF BODY FLUIDS WT1, Estrogen Receptor, and Progesterone Receptor as Markers for Breast or Ovarian Primary Sites in Metastatic
Anatomic Pathology / WT1, ESTROGEN RECEPTOR, AND PROGESTERONE RECEPTOR IN CYTOLOGY OF BODY FLUIDS WT1, Estrogen Receptor, and Progesterone Receptor as Markers for Breast or Ovarian Primary Sites in Metastatic
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
HRP cytochemistry. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, Heidelberg, Germany
 HRP cytochemistry WOLF D. KUHLMANN, M.D. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany A range of substrates is available for the cytochemical staining of peroxidase
HRP cytochemistry WOLF D. KUHLMANN, M.D. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany A range of substrates is available for the cytochemical staining of peroxidase
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
SMH (Myosin, smooth muscle heavy chain)
 Material The slide to be stained for SMH comprised: Assessment Run 50 2017 SMH (Myosin, smooth muscle heavy chain) 1.Tonsil, 2. Esophagus, 3. Breast hyperplasia, 4. Breast ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS),
Material The slide to be stained for SMH comprised: Assessment Run 50 2017 SMH (Myosin, smooth muscle heavy chain) 1.Tonsil, 2. Esophagus, 3. Breast hyperplasia, 4. Breast ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS),
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment
 BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
IMPC phenotyping SOPs in JMC
 IMPC phenotyping SOPs in JMC Tissue Embedding and Block Banking IMPC_BLK_001 Purpose Collect and fix a standard list of tissues from the complete necropsy (see IMPC Gross Pathology & Tissue Collection
IMPC phenotyping SOPs in JMC Tissue Embedding and Block Banking IMPC_BLK_001 Purpose Collect and fix a standard list of tissues from the complete necropsy (see IMPC Gross Pathology & Tissue Collection
Expression of NA/1 symporter (NIS) in endometrial mucosa of fertile, sterile and post-menopausal women
 Histol Histopathol (2008) 23: 549-554 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Expression of NA/1 symporter (NIS) in endometrial mucosa of fertile, sterile and post-menopausal
Histol Histopathol (2008) 23: 549-554 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Expression of NA/1 symporter (NIS) in endometrial mucosa of fertile, sterile and post-menopausal
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody CD71
 Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody CD71 Product Code: NCL-L-CD71-309 Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW United Kingdom ( +44 191
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody CD71 Product Code: NCL-L-CD71-309 Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW United Kingdom ( +44 191
CEA (CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN)
 (CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN) 428 C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle third of esophagus C15.5 Malignant neoplasm of lower third of esophagus C15.8 Malignant
(CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN) 428 C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle third of esophagus C15.5 Malignant neoplasm of lower third of esophagus C15.8 Malignant
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Radioiodine Contamination Artifacts and Unusual Patterns of Accumulation in Whole-body I-131 Imaging: A Case Series
 Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2014 January; 12(1): e9329. Published online 2014 January 1. DOI: 10.5812/jjm.9329 Case Report Radioiodine Contamination Artifacts and Unusual Patterns of Accumulation in Whole-body
Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2014 January; 12(1): e9329. Published online 2014 January 1. DOI: 10.5812/jjm.9329 Case Report Radioiodine Contamination Artifacts and Unusual Patterns of Accumulation in Whole-body
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Cytokeratin (5/6/18)
 Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Cytokeratin (5/6/18) Product Code: NCL-L-LP34 Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW United Kingdom
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Cytokeratin (5/6/18) Product Code: NCL-L-LP34 Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW United Kingdom
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
155.2 Malignant neoplasm of liver not specified as primary or secondary. C22.9 Malignant neoplasm of liver, not specified as primary or secondary
 ICD-9 TO ICD-10 Reference ICD-9 150.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus unspecified site C15.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus, unspecified 151.9 Malignant neoplasm of stomach unspecified site C16.9 Malignant
ICD-9 TO ICD-10 Reference ICD-9 150.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus unspecified site C15.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus, unspecified 151.9 Malignant neoplasm of stomach unspecified site C16.9 Malignant
ROLE OF TTF-1, CK20, AND CK7 IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY FOR DIAGNOSIS OF PRIMARY
 Y.C. Su, Y.C. Hsu, and C.Y. Chai ROLE OF TTF-1, CK20, AND CK7 IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY FOR DIAGNOSIS OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA Yue-Chiu Su 1, Yu-Chang Hsu 2, and Chee-Yin Chai 1,3 Departments
Y.C. Su, Y.C. Hsu, and C.Y. Chai ROLE OF TTF-1, CK20, AND CK7 IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY FOR DIAGNOSIS OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA Yue-Chiu Su 1, Yu-Chang Hsu 2, and Chee-Yin Chai 1,3 Departments
MT09 - Normal Human Tissue Microarray, FDA
 Reveal Biosciences offers Histochemical Staining, Immunohistochemistry (IHC), In Situ Hybridization (ISH), Whole Slide Imaging, and Quantitative Image Analysis on any TMA MT09 - Normal Human Tissue Microarray,
Reveal Biosciences offers Histochemical Staining, Immunohistochemistry (IHC), In Situ Hybridization (ISH), Whole Slide Imaging, and Quantitative Image Analysis on any TMA MT09 - Normal Human Tissue Microarray,
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Myeloperoxidase
 Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Myeloperoxidase Product Code: NCL-L-MYELO Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW United Kingdom (
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Myeloperoxidase Product Code: NCL-L-MYELO Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW United Kingdom (
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
SHN-1 Human Digestive Panel Test results
 SHN-1 Human Digestive Panel Test results HN-30 tongue HN-24 salivary gland HN-12 larynx HN-28 esophagus HN-29 stomach HN-20 pancreas HN-13 liver HN-14 gall bladder HN-27-1 duodenum HN-27-2 ileum HN-27-3
SHN-1 Human Digestive Panel Test results HN-30 tongue HN-24 salivary gland HN-12 larynx HN-28 esophagus HN-29 stomach HN-20 pancreas HN-13 liver HN-14 gall bladder HN-27-1 duodenum HN-27-2 ileum HN-27-3
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
The Human Digestive Tract
 The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
Nordic Immunohistochemical Quality Control
 Nordic Immunohistochemical Quality Control Immunohistochemistry in the classifiation of neoplasias of the alimentary tract & External Quality Assurance of Immunohistochemistry for GI cancer markers Mogens
Nordic Immunohistochemical Quality Control Immunohistochemistry in the classifiation of neoplasias of the alimentary tract & External Quality Assurance of Immunohistochemistry for GI cancer markers Mogens
Thyroid Cancer: Imaging Techniques (Nuclear Medicine)
 Thyroid Cancer: Imaging Techniques (Nuclear Medicine) Andrei Iagaru, MD MIPS Molecular Imaging Program at Stanford Stanford University School of Medicine Department of Radiology Introduction Ø There are
Thyroid Cancer: Imaging Techniques (Nuclear Medicine) Andrei Iagaru, MD MIPS Molecular Imaging Program at Stanford Stanford University School of Medicine Department of Radiology Introduction Ø There are
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
HISTOLOGY. GIT Block 432 Histology Team. Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
Urinary system. Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal. Nephrons
 Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Thyroid Function. Thyroglobulin Analyte Information
 Thyroid Function Thyroglobulin Analyte Information - 1-2011-01-11 Thyroglobulin Introduction Thyroglobulin (Tg) is a big dimeric protein consisting of two identical subunits. It has 2,748 amino acids in
Thyroid Function Thyroglobulin Analyte Information - 1-2011-01-11 Thyroglobulin Introduction Thyroglobulin (Tg) is a big dimeric protein consisting of two identical subunits. It has 2,748 amino acids in
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
Cytokeratin 19 (CK19)
 Assessment Run 34 202 Cytokeratin 9 (CK9) Material The slide to be stained for CK9 comprised:. Thyroid gland, 2. Appendix, 3. Esophagus, 4. Papillary thyroid carcinoma, 5 & 6. Pancreatic neuroendocrine
Assessment Run 34 202 Cytokeratin 9 (CK9) Material The slide to be stained for CK9 comprised:. Thyroid gland, 2. Appendix, 3. Esophagus, 4. Papillary thyroid carcinoma, 5 & 6. Pancreatic neuroendocrine
Estrogen receptor (ER)
 Assessment Run B7 204 Estrogen receptor (ER) Material The slide to be stained for ER comprised: No. Tissue ER-positivity* ER-intensity*. Uterine cervix 80-90% Moderate to strong 2. Breast carcinoma 0%
Assessment Run B7 204 Estrogen receptor (ER) Material The slide to be stained for ER comprised: No. Tissue ER-positivity* ER-intensity*. Uterine cervix 80-90% Moderate to strong 2. Breast carcinoma 0%
Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution. Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to
Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
CS 6824: Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome
 CS 6824: Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome T. M. Murali November 17, 2016 Human Protein Atlas Measure protein and gene expression using tissue microarrays and deep sequencing, respectively. Alternative
CS 6824: Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome T. M. Murali November 17, 2016 Human Protein Atlas Measure protein and gene expression using tissue microarrays and deep sequencing, respectively. Alternative
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody p57 Protein (Kip2)
 Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody p57 Protein (Kip2) Product Code: NCL-L-p57 Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW United Kingdom
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody p57 Protein (Kip2) Product Code: NCL-L-p57 Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW United Kingdom
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody MyoD1 (Rhabdomyosarcoma Marker)
 Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody MyoD1 (Rhabdomyosarcoma Marker) Product Code: NCL-L-MyoD1 Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody MyoD1 (Rhabdomyosarcoma Marker) Product Code: NCL-L-MyoD1 Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Assessment Run GATA3
 Assessment Run 44 2015 GATA3 Material The slide to be stained for GATA3 comprised: 1. Tonsil 2. Kidney, 3. Urothelial carcinoma, 4. Breast ductal carcinoma, 5. Colon adenocarcinoma All tissues were fixed
Assessment Run 44 2015 GATA3 Material The slide to be stained for GATA3 comprised: 1. Tonsil 2. Kidney, 3. Urothelial carcinoma, 4. Breast ductal carcinoma, 5. Colon adenocarcinoma All tissues were fixed
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare
 Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Update of mixed tumours of the GI tract, the pancreas and the liver Introduction to the concept of mixed tumours and clinical implication Jean-Yves SCOAZEC Surgical
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Update of mixed tumours of the GI tract, the pancreas and the liver Introduction to the concept of mixed tumours and clinical implication Jean-Yves SCOAZEC Surgical
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
Chapter 26 Hormones and the
 Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Mouse GLP-2 EIA. Cat. No. KT-374. For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in mouse serum or plasma. For Research Use Only. 1 Rev.
 Mouse GLP-2 EIA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in mouse serum or plasma. Cat. No. KT-374 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 11357374 PRODUCT INFORMATION Mouse GLP-2 EIA Cat. No. KT-374 INTENDED
Mouse GLP-2 EIA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in mouse serum or plasma. Cat. No. KT-374 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 11357374 PRODUCT INFORMATION Mouse GLP-2 EIA Cat. No. KT-374 INTENDED
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma
 Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Expression of the Sodium Iodide Symporter and Thyroglobulin Genes Are Reduced in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
 Expression of the Sodium Iodide Symporter and Thyroglobulin Genes Are Reduced in Papillary Thyroid Cancer Matthew D. Ringel, M.D., Jeffery Anderson, B.S., Suzikelli L. Souza, M.D., Henry B. Burch, M.D.,
Expression of the Sodium Iodide Symporter and Thyroglobulin Genes Are Reduced in Papillary Thyroid Cancer Matthew D. Ringel, M.D., Jeffery Anderson, B.S., Suzikelli L. Souza, M.D., Henry B. Burch, M.D.,
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES, USP DIAGNOSTIC. For Oral Use DESCRIPTION
 DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES, USP DIAGNOSTIC For Oral Use DESCRIPTION Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules, USP are color-coded capsules containing sodium iodide I 131 for diagnostic use by oral administration.
DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES, USP DIAGNOSTIC For Oral Use DESCRIPTION Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules, USP are color-coded capsules containing sodium iodide I 131 for diagnostic use by oral administration.
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Holistic Healing Professional Practitioner Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
 The last phase is called the intestinal phase and takes place about four hours after the gastric phase. The chyme passes through the small intestine, or duodenum, through the pyloric sphincter. This is
The last phase is called the intestinal phase and takes place about four hours after the gastric phase. The chyme passes through the small intestine, or duodenum, through the pyloric sphincter. This is
Carcinoembryonic Antigen
 Other Names/Abbreviations CEA 190.26 - Carcinoembryonic Antigen Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is a protein polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring
Other Names/Abbreviations CEA 190.26 - Carcinoembryonic Antigen Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is a protein polysaccharide found in some carcinomas. It is effective as a biochemical marker for monitoring
Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA)
 Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet on ICD-10 Coding of Neoplasms Introduction The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10 th Revision (ICD-10)
Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet on ICD-10 Coding of Neoplasms Introduction The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10 th Revision (ICD-10)
Chapter 9. The digestive system. Glossary. Louise McErlean
 Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
Stage 4 gastric adenocarcinoma icd 10
 > Stage 4 gastric adenocarcinoma icd 10 stage iii; Carcinoma of colon, stage iv; Colon cancer metastatic to unspecified site; Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer; Malignant tumor of colon; Metastasis.
> Stage 4 gastric adenocarcinoma icd 10 stage iii; Carcinoma of colon, stage iv; Colon cancer metastatic to unspecified site; Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer; Malignant tumor of colon; Metastasis.
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
CD15 and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 8, No., 8 CD and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms AYTEKİN AKYOL, AYŞEGÜL ÜNER Hacettepe University, Department of Pathology, Ankara-Turkey ABSTRACT The aim
Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 8, No., 8 CD and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms AYTEKİN AKYOL, AYŞEGÜL ÜNER Hacettepe University, Department of Pathology, Ankara-Turkey ABSTRACT The aim
Nuclear Medicine Head and Neck Region. Bán Zsuzsanna, MD University of Pécs, Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Nuclear Medicine Head and Neck Region Bán Zsuzsanna, MD University of Pécs, Department of Nuclear Medicine Thyroid scintigraphy Parathyroid scintigraphy F18-FDG PET examinations in head and neck cancer
Nuclear Medicine Head and Neck Region Bán Zsuzsanna, MD University of Pécs, Department of Nuclear Medicine Thyroid scintigraphy Parathyroid scintigraphy F18-FDG PET examinations in head and neck cancer
Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts
 Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 243-247 TÜB TAK CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts Ayla ÖZVEREN 1, Can TUSKAN 3, Mehmet YALTIRIK 3, Belir ATALAY 3, Gülçin
Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 243-247 TÜB TAK CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts Ayla ÖZVEREN 1, Can TUSKAN 3, Mehmet YALTIRIK 3, Belir ATALAY 3, Gülçin
HercepTest for the Dako Autostainer Code K5207
 HercepTest for the Dako Autostainer Code K5207 9th edition For immunocytochemical staining. The kit is for 50 tests (100 slides). (126659-002) P04088US_02_K520721-5/2016.05 p. 1/54 Contents Page Intended
HercepTest for the Dako Autostainer Code K5207 9th edition For immunocytochemical staining. The kit is for 50 tests (100 slides). (126659-002) P04088US_02_K520721-5/2016.05 p. 1/54 Contents Page Intended
Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma
 Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: van Seters M, van Beurden M, ten Kate FJW, et al. Treatment
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: van Seters M, van Beurden M, ten Kate FJW, et al. Treatment
TYPES OF EPITHELIA. Epithelia can be divided into two main groups. A-covering (or lining) epithelia B- Secretory (glandular) epithelia.
 TYPES OF EPITHELIA Epithelia can be divided into two main groups A-covering (or lining) epithelia B- Secretory (glandular) epithelia. Glands Glandular epithelial cells may synthesize, store, and secrete:
TYPES OF EPITHELIA Epithelia can be divided into two main groups A-covering (or lining) epithelia B- Secretory (glandular) epithelia. Glands Glandular epithelial cells may synthesize, store, and secrete:
A. Incorrect! The esophagus connects the pharynx and the stomach.
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 19: Digestive Physiology and Nutrition Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. This organ
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 19: Digestive Physiology and Nutrition Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. This organ
