Pure motor hemiparesis (PMH) and ataxic hemiparesis
|
|
|
- Nicholas Wilkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Somatosensory Evoked Potentials in Lacunar Syndromes of Pure Motor and Ataxic Hemiparesis 09 Michael A. Kelly, MD, Stuart J. Perlik, MD, and Morris A. Fisher, MD Syndromes of hemlparetic lacunar infarction include pure motor hemiparesis and ataxic hemiparesis. Twelve such patients were evaluated with somatosensory evoked potentials. Potentials were delayed or absent in all patients with ataxic hemiparesis and in of 8 patients with pure motor hemiparesis. Unlike pure motor hemiparesis, ataxic hemiparesis appears to be associated with abnormal somatosensory evoked potentials. These abnormalities suggest that disturbance of afferent pathways are important in ataxic hemiparesis (Stroke 987;8:09-097) Pure motor hemiparesis (PMH) and ataxic hemiparesis (AHP) are lacunar stroke syndromes characterized by hemiparesis in the absence of objective sensory loss or evidence of cortical dysfunction. In AHP, the hemiparesis is combined with a "cerebellar" dysmetria of the affected limbs. It has been suggested that this is caused by injury to corticoponto-cerebellar pathways.' * Somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs) are thought to be generated by impulses traversing the posterior columns and the medial lemnisci reaching the cortex after relay through the thalamus. The more rostral projections of these pathways course through the internal capsule in areas frequently involved in lesions producing PMH and AHP. It has been shown that SSEPs are normal in PMH, 7 presumably because afferent pathways are substantially spared. We sought to evaluate SSEPs in AHP. Abnormalities in SSEPs would suggest greater involvement of afferent pathways in AHP than in PMH and could provide an alternate explanation for the ataxia. Subjects and Methods SSEPs were performed on patients with hemiparetic lacunar infarcts evaluated by the stroke service at Michael Reese Hospital during the period September 98 to June 985. SSEPs were evaluated on the average (range -8) days after the ictus (Table ). The clinical findings were consistent with a diagnosis of PMH in 8 patients or AHP in patients without other evidence of cerebrovascular disease. All patients had computed tomography (CT) scans; an Elscint 00 scanner (Haifa, Israel) was used with a -cm slice thickness. The CT scans showed either evidence consistent with lacunar infarction or no discrete abnormalities. Weakness was graded on a scale of mild to marked. Ataxia was evaluated except where weakness From the Department of eurology, Loyola University Stritch School of Medicine (M.A.K.) and the Department of eurology, Michael Reese Hospital, University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine (S.J.P., M.A.F.), Chicago, Illinois. Address for correspondence: Dr. Morris A. Fisher, Michael Reese Hospital, Lake Shore at st Street, Chicago, IL Received April, 987; accepted June, 987. prohibited adequate voluntary movement. Ataxia was defined as dysmetria on finger-to-nose and heel-toshin testing; dysarthria and gait instability may also have been present. The mean age of the patients was 67 (range -79) years (Table ). SSEPs were recorded with Ag-AgCl 9-mm disk electrodes applied with collodion and filled with electroencephalography gel. Resistances were < 5,000 Q. Electrodes were placed according to the International 0-0 System. Montages included Cz, C, and C referred to Fpz, Cv (cervical spine cm inferior to the inion) also referred to Fpz, bilateral Erb's point (EP) recordings, and recordings between the lumbar spine at LI and the iliac crest (Ll-IC). Stimulation of the median nerves at the wrists and the tibia! nerves at the ankles was percutaneous at Hz, with nerves on the clinically involved and uninvolved sides stimulated separately. Stimulus intensity produced a minimal motor twitch, 5responseswere averaged, and at least sets ofresponseswere obtained to ensure reproducibility. Minimal montages for arm stimulation were contralateral C or C to Fpz, Cv to Fpz, and ipsilateral to contralateral EP; for leg stimulation, Cz to Fpz and LI to IC. Latencies were measured with electronic cursors and labelled as follows: with tibial stimulation onset, P0, 50, P60 (scalp), and LI (lumbar); with median stimulation EP, (cervical), 0, P5, and 5 (scalp). Abnormality was defined as absent or delayed potentials (or interpeak latencies) differing by > SD from laboratory controls (n = 0). For P0 and 0 scalp potentials, these values were 5. and.8 msec, respectively. Results Theresultsare presented in Table, and representative CT scans as well as SSEPs are shown in Figures and. erve conduction studies in the distribution of the median, posterior tibial, and sural nerves were unremarkable except for unobtainable sural nerve action potentials in patients. All patients demonstrated weakness. In general, this weakness was of mild to moderate degree and tended to be more pronounced in those with PMH compared with those with AHP. In most patients, weakness of
2 09 Stroke Vol 8, o 6, ovember-december 987 Table. Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Lacunar Syndromes Patient Age Pure motor hemiparesis Atoxic hemiparesis Weakness Arm Leg Ataxia CT SSEP Day CR AC,BG Absent Absent Weakness:, mild;, moderate;, marked. Ataxia: +, present; -', absent or negative. CT, lacunar infarct: -, negative; CR, corona radiata; AC, anterior capsule; BG, basal ganglia;, posterior capsule. SSEP, somatosensory evoked potential:, within normal limits. Day, days from ictus to SSEP the arm was equal to or slightly greater than that of the leg. Ataxia on finger-to-nose or heel-to-shin testing was present in the patients with AHP. CT scans were abnormal in 5 of the patients. In the 8 patients with PMH, CT scans were unrevealing in 6 and showed evidence of lacunar infarcts in ; in, the lesion was in the corona radiata, whereas in the other patient the infarct involved the anterior limb of the internal capsule and the adjacent basal ganglia. In the patients with AHP, CT scans were abnormal in. In all, the infarct was located in the posterior limb of the internal capsule. SSEPs stimulating either the hemiparetic arm or leg were abnormal in 5 patients: scalp SSEPs were absent in patients; in the remaining, 0 and P0 peaks were delayed. L-P0, EP-0, and Cv-0 interpeak latencies were within normal limits except in the patients with delayed scalp potentials. SSEP abnormalities were found in only of the 8 patients with PMH but were present in all of those with AHP. Discussion PMH is the most common of the clinical syndromes of lacunar infarction. Studies using CT 8 and autopsied cases 90 have shown that the lesion responsible for PMH is most often in the internal capsule or pons. AHP lesions may be similarly located. Fisher demonstrated pontine lesions in pathologically studied cases. Since then, others "*" have shown using CT scans that lesions of the internal capsule may produce an identical syndrome. Localization of lacunes by CT is limited, however, because lesions in the brainstem as well as those smaller than several millimeters in diameter may not be visualized. In our study, of the patients with AHP had lacunar infarcts demonstrated by CT scan in the posterior limb of the internal capsule; the fourth patient had a normal CT scan. The location of these infarcts is similar to that of previous reports in patients with AHP and are therefore thought to be related. Two of the 8 patients with PMH had lacunes demonstrated radiographically: was in the corona radiata, the other in the anterior capsule and basal ganglia. The former Iacune was probably coincidental rather than causative, whereas the latter was similar to lesions previously reported in PMH. 8 The remaining 6 patients with PMH presumably had unrevealing CT scans because of either lacunar location or size. Robinson et al 7 have recently described their experience with SSEPs following median nerve stimulation in pure sensory, pure sensorimotor, and PMH lacunar syndromes. All patients with pure sensory strokes had normal SSEPs; CT scans were normal in all but. Each of patients with sensorimotor stroke had abnormal SSEPs; CT scans in these cases showed infarcts in either the thalamus or in the thalamus and internal capsule. Robinson et al 7 concluded that the size of the infarct was critical in generating abnormal SSEPs and in producing hemiparesis. In their 0 patients with PMH, had abnormal SSEPs and had abnormal CT scans. In our 8 patients with PMH, only had abnormal SSEPs confirming the observation of Robinson et al that SSEP abnormalities are rare in PMH. In the patients with AHP, all had delayed or absent SSEPs on stimulation of the involved limbs. These results suggest that abnormal SSEPs are related to ataxia ( of 5 patients). They also suggest (Table ) that abnormal SSEPs are associated with evidence of infarction on CT scan ( of 5 patients) and therefore possibly with lacunar size. Interruption of descending corticospinal tracts ex-
3 Kelly et al SSEPs in Motor Lacunar Syndromes 095 FIGURE. A: Lacune (arrow) involving posterior limb of the internal capsule (Patient, Table ). B: Somatosensory evoked potentials stimulating left tibial and median nerves were within normal limits. When stimulating on the right, scalp potentials were absent while cervical (Cv), Erb's point (EP), and lumbar (L,) potentials were unremarkable. B C -FPz fljuv L LEFT MEDIA Cv-FPz EP (R-O 8>iv I RIGHT MEDIA Cz-FPz Cz-FPz L-IC L-IC 6AIVL S*JV LEFT TIBIAL RIGHT TIBIAL
4 095 Stroke Vol 8, o 6, ovember-december 987 FIGURE. A: Lacune (arrow) in region of the anterior limb of left internal capsule extending into the basal ganglia (Patient 8, Table ). B: Scalp somatosensory evoked potent tab were asymmetrically delayed when stimulating right median nerve, whereas subcortical potentials were unremarkable bilaterally. P0 potentials were also asymmetrically delayed when stimulating right tibial nerve (P07.6 msec) compared with left (P0=.0 msec). B r r k * d i V :-FPZ [. i LEFT MED. STIMULATIO RIGHT MED. STIMULATIO $K\
5 Kelly et al SSEPs in Motor Lacunar Syndromes 097 plains the hemiparesis in PMH and AHP. The apparent cerebellar ataxia has been somewhat more difficult to understand. Disruption of both cerebellar afferents and efferents has been considered. Corticopontine fibers traverse the internal capsule and pontine nuclei and project to the contralateral cerebellum. Interruption of these pathways has been proposed to explain capsular and pontine AHP. '~ 6 Cerebellar efferents have received less attention 5 but do traverse the internal capsule in passing to and from the ventral lateral nucleus of the thalamus. Lemniscal pathways also deserve consideration. Proprioceptive and kinesthetic information ascends in the dorsal columns of the spinal cord and in the contralateral medial lemniscus of the brainstem to enter the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus. Thalamocortical fibers traverse the posterior limb of the internal capsule en route to the sensory cortex. Sensory loss has been described in AHP with internal capsule lesions, 8 and subclinical sensory deficits could be present. It is possible that disruption of thalamocortical fibers combined with weakness may produce clinical ataxia. SSEPs are thought to reflect the integrity of afferent input, particularly of the large fiber sensory pathways mediated through the posterior column-lemniscal system. Lesions in the posterior limb of the internal capsule might therefore alter SSEPs even if the deficits were subclinical. At the same time, it is clear that the issues are more complex, including the findings in our patient with PMH, infarction in the anterior portion of the internal capsule, and abnormal SSEPs. Although the anatomy has not been defined, there is physiologic evidence that primary afferents from muscle spindles project to the cerebral cortex. These inputs may be the dominant element in SSEPs, and it is of interest that such projections are also prominent in mediating cerebellar function via the spinocerebellar tracts. SSEPs were abnormal in each of our patients with AHP, and of those patients had lesions of the posterior limb of the internal capsule. If ataxia in these patients was due only to interruption of corticopontine fibers, it is unlikely that the SSEPs would have been abnormal. Disruption of afferent fibers would better explain both the ataxia and the abnormal SSEPs. We conclude that SSEPs are characteristically normal in PMH. or absent SSEPs are frequently seen in AHP. The presence of abnormal SSEPs suggests that the ataxia of AHP may be caused by disruption of afferent pathways. References. Fisher CM, Cole M: Homolateral ataxia and crural paresis: A vascular syndrome. J eurol eurosurg Psychiatry 965; 8:8-55. Fisher CM: Ataxic hemiparesis: A pathologic study. Arch eurol 978;5:6-8. Ichikawa K, Tsutsumishita A, Fujioka A: Capsular ataxic hemiparesis: A case report. Arch eurol 98;9: Iragui VJ, McCutchen CB: Capsular ataxic hemiparesis. Arch eurol 98;9: Huang CY, Lui FS: Ataxic-hemiparesis, localization and clinical features. Stroke 98; 5: Sage JI, Lepore FE: Ataxic hemiparesis from lesions of the corona radiata. Arch eurol 98;0: Robinson RK, Richey KT, Kase CS, Mohr JP: Somatosensory evoked potentials in pure sensory stroke and related conditions. Stroke 985; 6: Rascol A, Clanet M, Manelfe C, Guiraud B, Bonafe A: Pure motor hemiplegia: CT study of 0 cases. Stroke 98; : Fisher CM: Capsular infarcts: The underlying vascular lesions. Arch eurol 979;6: Fisher CM, Caplan LR: Basilar branch occlusion: A cause of pontine infarction. eurology 97;: Perman GP, Racy A: Homolateral ataxia and crural paresis: Case report. eurology 980;0:0-05. Carpenter MB, Sutin J: Human euroanatomy, ed B. Baltimore, Williams & Wilkins Co, 98, pp Gandevia SC, Burke D, McKeon B: The projection of muscle afferents from the hand to cerebral cortex in man. Brain 98;07:l- KEY WORDS lacunar infarcts somatosensory evoked potentials
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs
 General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
Stroke School for Internists Part 1
 Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Lecturer. Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014
 Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum
 Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Somatosenory Evoked Potentials. Ronald Emerson, MD Cornell University Hospital for Special Surgery New York
 Somatosenory Evoked Potentials Ronald Emerson, MD Cornell University Hospital for Special Surgery New York Median SSEPs CPc - Ci CPi - Epc SC5 Epc Medial Lemniscus Epi - Epc Spinal Cord Dorsal Gray Tibial
Somatosenory Evoked Potentials Ronald Emerson, MD Cornell University Hospital for Special Surgery New York Median SSEPs CPc - Ci CPi - Epc SC5 Epc Medial Lemniscus Epi - Epc Spinal Cord Dorsal Gray Tibial
Somatosenory Evoked Potentials
 Somatosenory Evoked Potentials Ronald Emerson, MD Cornell University Hospital for Special Surgery New York Median SSEPs CPc - Ci CPi - Epc SC5 Epc Medial Lemniscus Epi - Epc Spinal Cord Dorsal Gray Tibial
Somatosenory Evoked Potentials Ronald Emerson, MD Cornell University Hospital for Special Surgery New York Median SSEPs CPc - Ci CPi - Epc SC5 Epc Medial Lemniscus Epi - Epc Spinal Cord Dorsal Gray Tibial
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway
 Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS
 SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D.
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
8/24/2015. It is divided into an a. Anterior limb b. Posterior limb c. Genu (or knee)
 Joint Commission Technical Advisory Panel (TAP) for Comprehensive Stroke Centers no monetary benefits Debbie Summers, MSN, RN, ACNS-BC, CNRN, SCRN, FAHA, ANVP Evaluates the structures of the internal capsule
Joint Commission Technical Advisory Panel (TAP) for Comprehensive Stroke Centers no monetary benefits Debbie Summers, MSN, RN, ACNS-BC, CNRN, SCRN, FAHA, ANVP Evaluates the structures of the internal capsule
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Pathways of proprioception
 The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D.
 Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal.
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana
 3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana Introduction Ataxia is derived from Greek word a -not, taxis -orderly, (not orderly/ not in order) Ataxia is the inability to make smooth, accurate and coordinated movements
3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana Introduction Ataxia is derived from Greek word a -not, taxis -orderly, (not orderly/ not in order) Ataxia is the inability to make smooth, accurate and coordinated movements
FUNCTION: It COORDINATES movement HOW IT WORKS
 CEREBELLUM Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo Objectives: Describe the anatomy of the cerebellum, its 3 functions and associated regions Describe how the cerebellum influences
CEREBELLUM Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo Objectives: Describe the anatomy of the cerebellum, its 3 functions and associated regions Describe how the cerebellum influences
Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To describe the functional divisions of thalamus. II: To state the functions of thalamus and the thalamic syndrome. III: To define the somatic sensory
Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To describe the functional divisions of thalamus. II: To state the functions of thalamus and the thalamic syndrome. III: To define the somatic sensory
Spinal Cord: Clinical Applications. Dr. Stuart Inglis
 Spinal Cord: Clinical Applications Dr. Stuart Inglis Tabes dorsalis, also known as syphilitic myelopathy, is a slow degeneration (specifically, demyelination) of the nerves in the dorsal funiculus of the
Spinal Cord: Clinical Applications Dr. Stuart Inglis Tabes dorsalis, also known as syphilitic myelopathy, is a slow degeneration (specifically, demyelination) of the nerves in the dorsal funiculus of the
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
The NIHSS score is 4 (considering 2 pts for the ataxia involving upper and lower limbs.
 Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cortical Control of Movement
 Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
THE BACK. Dr. Ali Mohsin. Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord THE BACK Dr. Ali Mohsin The spinal cord is the elongated caudal part of the CNS. It starts as the inferior continuation of the medulla oblongata at the level of foramen magnum, & ends as an
Spinal Cord THE BACK Dr. Ali Mohsin The spinal cord is the elongated caudal part of the CNS. It starts as the inferior continuation of the medulla oblongata at the level of foramen magnum, & ends as an
Spinal Cord Organization. January 12, 2011
 Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
The Spinal Cord. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord. The Spinal Cord 1/2/2016. Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum.
 The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
Abdullah AlZibdeh. Dr. Maha ElBeltagy. Maha ElBeltagy
 19 Abdullah AlZibdeh Dr. Maha ElBeltagy Maha ElBeltagy Introduction In this sheet, we discuss the cerebellum; its lobes, fissures and deep nuclei. We also go into the tracts and connections in which the
19 Abdullah AlZibdeh Dr. Maha ElBeltagy Maha ElBeltagy Introduction In this sheet, we discuss the cerebellum; its lobes, fissures and deep nuclei. We also go into the tracts and connections in which the
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem
 Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Functions. Traditional view: Motor system. Co-ordination of movements Motor learning Eye movements. Modern view: Cognition
 The Cerebellum Involved in motor coordination and timing Is simple and well documented Only has one type of output cell (Purkinje) The cerebellum influences motor activity through inhibition The Cerebellum
The Cerebellum Involved in motor coordination and timing Is simple and well documented Only has one type of output cell (Purkinje) The cerebellum influences motor activity through inhibition The Cerebellum
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy
 By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Brainstem. Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences
 Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
NS201C Anatomy 1: Sensory and Motor Systems
 NS201C Anatomy 1: Sensory and Motor Systems 25th January 2017 Peter Ohara Department of Anatomy peter.ohara@ucsf.edu The Subdivisions and Components of the Central Nervous System Axes and Anatomical Planes
NS201C Anatomy 1: Sensory and Motor Systems 25th January 2017 Peter Ohara Department of Anatomy peter.ohara@ucsf.edu The Subdivisions and Components of the Central Nervous System Axes and Anatomical Planes
Progression of deficit was noted in two of the ischaemic. cases. Two patients had ataxic hemiparesis, with one as the
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1988;51:509-515 Lacunar syndromes due to brainstem infarct and haemorrhage CY HUANG, E WOO, YL YU, FL CHAN* From the University Department of Medicine
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1988;51:509-515 Lacunar syndromes due to brainstem infarct and haemorrhage CY HUANG, E WOO, YL YU, FL CHAN* From the University Department of Medicine
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation.
 Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
At the highest levels of motor control, the brain represents actions as desired trajectories of end-effector
 At the highest levels of motor control, the brain represents actions as desired trajectories of end-effector Normal condition, using fingers and wrist Using elbow as folcrum Using shoulder as folcrum (outstretched
At the highest levels of motor control, the brain represents actions as desired trajectories of end-effector Normal condition, using fingers and wrist Using elbow as folcrum Using shoulder as folcrum (outstretched
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
SEP Monitoring. Outline. Outline 1/22/2015. Development of SEPs Stimulation and recording techniques Predictive value of SEP Uses of SEP monitoring
 SEP Monitoring Andres A Gonzalez, MD Director, Surgical Neurophysiology Keck Medical Center of USC University of Southern California Outline Development of SEPs Stimulation and recording techniques Predictive
SEP Monitoring Andres A Gonzalez, MD Director, Surgical Neurophysiology Keck Medical Center of USC University of Southern California Outline Development of SEPs Stimulation and recording techniques Predictive
Key Clinical Concepts
 Cerebrovascular Review and General Vascular Syndromes, Including Those That Impact Dizziness Key Clinical Concepts Basic Review of Cerebrovascular Circulation Circulation to the brain is divided into anterior
Cerebrovascular Review and General Vascular Syndromes, Including Those That Impact Dizziness Key Clinical Concepts Basic Review of Cerebrovascular Circulation Circulation to the brain is divided into anterior
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function. Dr Z Akbari
 Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Module 5. Ischemia in Vertebral-basilar Territory
 T I Module 5. Ischemia in Vertebral-basilar Territory Introduction and Key Clinical Examples Ischemia in Vertebrobasilar branches Objectives for Module 5 Knowledge! List 4 common symptoms that patients
T I Module 5. Ischemia in Vertebral-basilar Territory Introduction and Key Clinical Examples Ischemia in Vertebrobasilar branches Objectives for Module 5 Knowledge! List 4 common symptoms that patients
1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas:
 DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
SEP Monitoring. Andres A Gonzalez, MD Director, Surgical Neurophysiology Keck Medical Center of USC University of Southern California
 SEP Monitoring Andres A Gonzalez, MD Director, Surgical Neurophysiology Keck Medical Center of USC University of Southern California Outline Development of SEPs Stimulation and recording techniques Predictive
SEP Monitoring Andres A Gonzalez, MD Director, Surgical Neurophysiology Keck Medical Center of USC University of Southern California Outline Development of SEPs Stimulation and recording techniques Predictive
Pain classifications slow and fast
 Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D.
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Divisions of Somatosensory Systems The pathways that convey sensory modalities from the body to consciousness are
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Divisions of Somatosensory Systems The pathways that convey sensory modalities from the body to consciousness are
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
The Cerebellum. The Little Brain. Neuroscience Lecture. PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu
 The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Connection of the cerebellum
 CEREBELLUM Connection of the cerebellum The cerebellum has external layer of gray matter (cerebellar cortex ), & inner white matter In the white matter, there are 3 deep nuclei : (a) dentate nucleus laterally
CEREBELLUM Connection of the cerebellum The cerebellum has external layer of gray matter (cerebellar cortex ), & inner white matter In the white matter, there are 3 deep nuclei : (a) dentate nucleus laterally
Brainstem: Midbrain. 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain:
 Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
Anatomy of the Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Posterior spinal arteries Lateral corticospinal tract Dorsal column Spinothalamic tract Anterior spinal artery Anterior white commissure
Spinal Cord Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Posterior spinal arteries Lateral corticospinal tract Dorsal column Spinothalamic tract Anterior spinal artery Anterior white commissure
Somatosensory System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
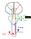 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CASE 48. What part of the cerebellum is responsible for planning and initiation of movement?
 CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system
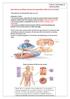 Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Arterial Blood Supply
 Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways
 General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
Motor System Hierarchy
 Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII
 Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Nervous system Cerebellum. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
Audit and Compliance Department 1
 Introduction to Intraoperative Neuromonitoring An intro to those squiggly lines Kunal Patel MS, CNIM None Disclosures Learning Objectives History of Intraoperative Monitoring What is Intraoperative Monitoring
Introduction to Intraoperative Neuromonitoring An intro to those squiggly lines Kunal Patel MS, CNIM None Disclosures Learning Objectives History of Intraoperative Monitoring What is Intraoperative Monitoring
Fig Cervical spinal nerves. Cervical enlargement C7. Dural sheath. Subarachnoid space. Thoracic. Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) spinal nerves
 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve)
 Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere)
 Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF NEUROLOGY- John W. Day, M.D., Ph.D.
 I. TAKE HOME POINTS FOR THIS LECTURE A. Localizing the disease is the first step in diagnosing a neurological disorder. B. Time course of the disease (acute, subacute, or chronic) indicates the pathophysiological
I. TAKE HOME POINTS FOR THIS LECTURE A. Localizing the disease is the first step in diagnosing a neurological disorder. B. Time course of the disease (acute, subacute, or chronic) indicates the pathophysiological
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline.
 The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata
 Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or to the head TA (jcolas).
 Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
IV. THE SPINAL CORD BLOOD SUPPLY
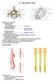 IV. THE SPINAL CORD Spinal cord is covered by o Pia Mater Spinalis Film Teminale Denticulate Ligament ---------------------- Cordotomy o Arachnoid Membrane Subarachnoid Space ----------------------- Lumbar
IV. THE SPINAL CORD Spinal cord is covered by o Pia Mater Spinalis Film Teminale Denticulate Ligament ---------------------- Cordotomy o Arachnoid Membrane Subarachnoid Space ----------------------- Lumbar
Fig.1: A, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a
 Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Somatic Sensory System I. Background
 Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord
 Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Medial View of Cerebellum
 Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
Clarke's Column Neurons as the Focus of a Corticospinal Corollary Circuit. Supplementary Information. Adam W. Hantman and Thomas M.
 Clarke's Column Neurons as the Focus of a Corticospinal Corollary Circuit Supplementary Information Adam W. Hantman and Thomas M. Jessell Supplementary Results Characterizing the origin of primary
Clarke's Column Neurons as the Focus of a Corticospinal Corollary Circuit Supplementary Information Adam W. Hantman and Thomas M. Jessell Supplementary Results Characterizing the origin of primary
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal:
 Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
The Cerebellum. Little Brain. Neuroscience Lecture. Dr. Laura Georgescu
 The Cerebellum Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum- its lobes, their input and output connections and their functions.
The Cerebellum Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum- its lobes, their input and output connections and their functions.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
THE BRAINSTEM. Raymond S. Price, MD University of Pennsylvania
 THE BRAINSTEM Raymond S. Price, MD University of Pennsylvania Overview of Brainstem Functions The brainstem serves numerous crucial neurologic functions. The most clinically relevant functions include:
THE BRAINSTEM Raymond S. Price, MD University of Pennsylvania Overview of Brainstem Functions The brainstem serves numerous crucial neurologic functions. The most clinically relevant functions include:
BASAL GANGLIA. Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY
 BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Histology of the CNS
 Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
CVA. Alison Atwater PA-C
 CVA Alison Atwater PA-C Types of CVAs Ischemic strokes 80% of strokes 2/3 are thrombotic 1/3 are embolic emboli from the heart or arteries feeding the brain such as carotids, vertebral and basilar etc
CVA Alison Atwater PA-C Types of CVAs Ischemic strokes 80% of strokes 2/3 are thrombotic 1/3 are embolic emboli from the heart or arteries feeding the brain such as carotids, vertebral and basilar etc
Voluntary Movement. Ch. 14: Supplemental Images
 Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Electrophysiologic assessment of neurologic injury
 Electrophysiologic assessment of neurologic injury Gregory A Kinney, PhD Dept of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington Seattle, WA Electrophysiologic Monitoring of Spinal Cord Function http://faculty.etsu.edu/currie/images/neuro2.jpg
Electrophysiologic assessment of neurologic injury Gregory A Kinney, PhD Dept of Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington Seattle, WA Electrophysiologic Monitoring of Spinal Cord Function http://faculty.etsu.edu/currie/images/neuro2.jpg
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
