SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D.
|
|
|
- Esmond Cook
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Divisions of Somatosensory Systems The pathways that convey sensory modalities from the body to consciousness are divided into two groups: the anterolateral system (ALS) and the dorsal column system. These systems are named after the locations of their tracts in the spinal cord. These two systems provide a basis for the classical notion of a division of somatic sensation into protopathic (anterolateral) and epicritic (dorsal column) systems. The protopathic system has been thought to be a more primitive system subserving gross, diffuse recognition of stimuli (low spatial resolution) and functioning in an attention-provoking capacity with the activation of withdrawal, autonomic, and emotive reflexes. By contrast, the epicritic system has been considered to be more recently evolved, transmits information faster, and functions in the fine discrimination (high resolution) of sensory inputs, particularly in regard to the spatial and temporal features of a stimulus. The ALS consists of the lateral spinothalamic and anterior spinothalamic tracts. At the level of the pons, the ALS lies just lateral to the medial lemnsicus, and is called the spinal lemniscus. Another important difference between these two is the level at which the first synapse is made (between the first and second order neurons). For the older, cruder, slower system, the ALS, the synapse is made in the spinal cord. For the faster, more discrete, newer system, the Dorsal Columns, the synapse is made in the medulla. A major contributor to the overall speed of these pathways is the conduction speed of the first order fibers. Speed of conduction in first order fibers is due to the amount of myelination and diameter of the axon, with larger more heavily myelinated fibers being faster. Proprioception is subserved by the fastest fibers (Aα), which are associated with muscle spindles and golgi tendon organs. Fine Discrimination Touch is subserved by the next fastest fibers (Aβ), which are associated primarily with mechanoreceptors and muscle spindles. Fast pain, which can be described as sharp and pricking, is subserved by Aδ fibers, and associated with free nerve endings, and other noci -, thermo-, and mechanoreceptors. The Aδ fibers are small diameter, thinly myelinated fibers. Slow pain, which can be described as a burning type of pain, is subserved by C fibers, associated with free nerve endings, and other noci -, thermo-, and mechano-receptors. The C fibers are very small diameter, unmyelinated fibers. The larger, more heavily myelinated fibers conducting touch and proprioception, that will ascend in the dorsal funiculus before synapsing in the medulla, enter the spinal cord medial to the dorsal horn.
2 The thinner, lightly myelinated and unmyelinated axons enter the spinal cord more laterally, just over the gray matter of the dorsal horn, where they are about to synapse. Touch from the body - DORSAL COLUMN - MEDIAL LEMNISCUS SYSTEM Subserves fine discrimination touch, deep touch (pressure), proprioception, and vibration sensitivity. A. Receptors. Mechanoreceptors and proprioceptors: Meissner s Corpuscles, Pacinian Corpuscles, Merkel s discs, Ruffini end organs, muscle spindles, GTO) B. First-Order Neurons. Pseudounipolar neurons in the dorsal root ganglia. Central processes enter the spinal cord in the medial division of the dorsal root. At levels below mid-thoracic (T7 and below) the fibers enter the posterior funiculus and form the fasciculus gracilis, thus this conveys information about the lower body. In the upper thoracic and cervical segments (T6 and above) they occupy the fasciculus cuneatus. The posterior intermediate sulcus separates the gracile and cuneate fasciculi in the upper thoracic and cervical spinal cord regions. A lesion eliminating only the fasciculus cuneatus would therefore eliminate fine discrimination touch from the ipsilateral arms and upper body. C. Second-Order Neurons. The ascending primary afferent fibers terminate upon second-order neurons in the nucleus gracilis (lower body representation) and nucleus cuneatus (upper body representation) in the caudal medulla. Neurons in the gracile and cuneate nuclei give rise to axons known as internal arcuate fibers. These fibers course ventromedially, cross the midline (sensory decussation), and form the medial lemniscus on the contralateral side. Within the medial lemniscus, the lower body is represented more ventrally than the upper body. D. Third-Order Neurons. In the diencephalon, fibers of the medial lemniscus terminate in the ventral posterolateral (VPL) nucleus of the thalamus. Fibers from the VPL of the thalamus enter the posterior limb of the internal capsule and terminate in somatotopic register along the dorsomedial aspect of the postcentral gyrus in Brodmann s areas 3, 1, and 2. Brodmann s area 3 is Primary Somatosensory Cortex, in the post central gyrus. E. Fourth-Order Neurons. Cells within layer IV of the Primary Somatosensory Cortex are the fourth order neurons. Key Questions: a) Where are the cell bodies of origin for the Medial Lemniscus? Answer: Contralateral nucleus gracilius (lower body) and nucleus cuneatus (upper body).
3 b) Where does the Medial Lemniscus terminate? Answer: Ipsilateral VPL of the thalamus. c) Where does the crossing occur for this pathway? Answer: In the brainstem (lower medulla). d) What symptoms are associated with a lesion of the medial lemniscus? Answer: Loss of Fine Discrimination Touch in the contralateral Body. Figure 1: Dorsal Columns Pathway subserving fine discrimination touch. Figure from Fix,JD, 2000, High-Yield Neuroanatomy, Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
4 Clinical Syndromes 1. Tabes Dorsalis Degeneration of myelinated, large diameter axons in the dorsal columns. This occurs in late stages of Syphilis. Because the lesion is bilateral, the deficits are bilateral. The symptoms are bilateral loss of Fine Discrimination Touch, while pain and temperature sensations remain intact (unaltered). 2. Brown Sequard Syndrome incomplete spinal cord lesion characterized by a clinical picture reflecting hemisection of the spinal cord, often in the cervical cord region. It is rare for the entire hemisection of the cord to be affected, but does occur in some cases. More often incomplete hemisection is found. The size of the lesion will affect what symptoms are observed. A small dorsal lesion will destroy the dorsal columns, resulting in loss of fine discrimination touch ipsilaterally at the level of the lesion and below. A larger lesion that includes lateral funiculus, will affect the lateral spinothalamic tract, resulting in loss of contralateral pain and temperature sensation from the level of the lesion and below. In addition for complete hemisections, there will be a focal region of ipsilateral loss of pain and temperature, due to destruction of Lissauer s tract, incoming fibers, and the fibers crossing the midline. If the lesion includes destruction of the ventral horn, there will be motor effects of ipsilateral spasticity and weakness. Trigeminal Pathways specifically, fine discrimination touch from the head and face. A. Receptors. Free nerve endings, Merkel s discs, hair receptors and receptors with encapsulated endings. B. First-Order Neurons. Pseudounipolar cell bodies in the trigeminal ganglion, located outside the CNS, similar to dorsal root ganglion neurons. Peripheral processes (component of axon that extends from the sensory receptor to the ganglion) come from 3 branches of the trigeminal nerve, the Opthalamic, Maxillary, and Mandibular. The central portion of axons transmitting fine discrimination touch information will be distributed to the Principal (also called the Main, also called the Chief) Trigeminal Nucleus. C. Second Order Neurons. Second order neurons are located in the Trigeminal Nucleus (Principal component). Principal Sensory Nucleus of V (also called the Main or Chief Trigeminal Nucleus) located mid pons. This nucleus and subsequent pathway is similar to the dorsal column system. The axons of the second order neurons project to the thalamus through 2 paths. Most
5 axons from the Main Sensory Nucleus of V cross the midline and then ascend as the Ventral Trigeminothalamic tract (axons) to ultimately synapse in the VPM nucleus of the Thalamus. Some axons project ipsilaterally as the Dorsal Trigeminothalamic Tract, ultimately synapsing in the ventral posterior medial (VPM) nucleus of the ipsilateral Thalamus. NOTE: Remember that below the level of the pons, the ventral trigeminal thalamic tract will contain only pain and temperature information (from the contralateral head and face). The axons of the Principal Trigeminal Nucleus Neurons will be added to this tract at the level of the pons. Therefore at the level of the pons and above, the ventral trigeminal tract will contain information about fine discrimination touch as well as pain and temperature, all from the contralateral head and face. D. Third-Order Neurons. The dorsal and ventral Trigeminothalamic tracts terminate on neurons in the ventral posteromedial (VPM) nucleus of the thalamus. The axons of neurons in VPM project through the posterior limb of the internal capsule to terminate in the ventrolateral portion of the postcentral gyrus of the cerebral cortex, which is primary somatosensory cortex, and can be identified as Brodmann s areas 3, l, and 2. E. Fourth-Order Neurons. Layer IV Neocortical neurons of Primary Somatosensory Cortex (Bordmann s areas 3, 1, and 2). Key Questions: a) Where are the cell bodies of origin for the Ventral Trigeminothalamic tract? Answer: Contralateral Trigeminal Nucleus (Main and Spinal Components). b) Where does the Ventral Trigeminothalamic tract terminate? Answer: Ipsilateral Ventral Posterior Medial Nucleus of the Thalamus. c) What symptoms would result from lesion of the Ventral Trigeminothalamic tract? Answer: Loss of pain, temperature and touch senses in the contralateral face and head. Cerebellar Tracts - Nonconscious Proprioception from the Body The cerebellum is a coordinator of movement, but does not initiate movement. It receives information about limb position, joint angles, muscle length and tension from the same receptor and primary afferent types that subserve conscious proprioception in the dorsal column system. The general
6 rule is that the cerebellum receives information from the ipsilateral side of the body. Four pathways carry proprioceptive information from the body to spinal cord and ultimately the cerebellum. A fifth pathway carries proprioceptive information from the head to the cerebellum. A. Dorsal (Posterior) Spinocerebellar Tract First-order neurons (include groups Ia and II fibers from neuromuscular spindles, group Ib fibers from Golgi tendon organs, touch receptors, and pressure receptors) are pseudounipolar neurons in the dorsal root ganglion and convey coded information from the receptors directly to the second-order neurons in the nucleus dorsalis of Clarke (located in lamina VII of segments T1 to L2 only). The second-order axons from this nucleus ascend ipsilaterally as the uncrossed dorsal spinocerebellar tract. This tract ascends through the posterolateral aspect of the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord, enters the inferior cerebellar peduncle, and terminates in the vermis of the ipsilateral anterior and posterior lobes of the cerebellum. This pathway has a role in the coordination of individual muscles of the lower trunk and lower extremity during postural adjustments and movements. B. Cuneocerebellar Tract This is the upper body equivalent to the dorsal spinocerebellar tract. First-order neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia. Central processes enter the spinal cord, ascend in the ipsilateral fasciculus cuneatus, and terminate upon second-order neurons located in the accessory cuneate nucleus (also called the lateral cuneate nucleus). This nucleus, located in the lower medulla just lateral to the cuneate nucleus, is the rostral equivalent to the nucleus dorsalis of Clarke. Axons of accessory cuneate neurons course ipsilaterally as the cuneocerebellar tract through the inferior cerebellar peduncle and terminate in the ipsilateral cerebellar cortex. This pathway is involved in the coordination of individual muscles in the upper trunk and upper extremity. C. Ventral (Anterior) and Rostral Spinocerebellar Tracts Afferents from the lower extremity have first-order neurons in the dorsal root ganglia and enter the spinal cord via the dorsal roots terminating upon second-order neurons in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord (Rexed s laminae VI and VII) in the lumbosacral (L3-S1) segments. The axons of the second-order neurons cross the midline in the anterior white commissure of the spinal cord and ascend as the ventral spinocerebellar tract located in the anterolateral aspect of the lateral funiculus. Some fibers of this tract are uncrossed. The tract courses through the lateral brainstem and along the dorsal surface of the superior cerebellar peduncle before terminating in the vermis of the anterior lobe of the cerebellum. This pathway has a role
7 in the general coordination of muscles of the lower part of the body during movement (e.g., walking). The counterpart of this pathway for the innervation of the upper extremity is the rostral spinocerebellar tract, which originates from neurons in lamina VII in the cervical enlargement (C4-C8). Figure 2: Spinocerebellar pathways. The Dorsal and Ventral Spinocerebellar tracts carry information from the lower body. The Rostral and Cuneocerebellar tracts carry information from the upper body. Note information from the face is carried in separate trigeminal pathways to the cerebellum. Figure from Haines,DE, 1997, Fundamental Neuroscience, New York, NY, Churchill Livingstone. D. Trigeminocerebellar Fibers Central processes of neurons in the trigeminal ganglion that innervate jaw muscle receptors, periodontal afferents, and the temperomandibular joint course in the spinal trigeminal tract and terminate in the pars interpolaris subdivision of the spinal nucleus of V. It resembles cytoarchitectonically the accessory cuneate nucleus and, like the latter, many of its cells project to the cerebellar cortex via the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Neurons in the
8 mesencephalic nucleus of V also project to the cerebellum through the superior cerebellar peduncle Rostral SpinoCerebellar Tract Lateral Cuneate Nucleus CuneoCerebellar Tract Dorsal SpinoCerebellar Tract Figure 3: Location of Spinocerebellar pathways within the medulla. These pathways convey nonconscious proprioception from the body to the cerebellum. Ventral SpinoCerebellar Tract Figure 4: Pathways that convey nonconscious proprioception from the head to the ipsilateral cerebellum.
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D.
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs
 General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway
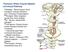 Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Somatosensory System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
Lecturer. Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014
 Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation
 Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS
 SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal.
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
IV. THE SPINAL CORD BLOOD SUPPLY
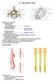 IV. THE SPINAL CORD Spinal cord is covered by o Pia Mater Spinalis Film Teminale Denticulate Ligament ---------------------- Cordotomy o Arachnoid Membrane Subarachnoid Space ----------------------- Lumbar
IV. THE SPINAL CORD Spinal cord is covered by o Pia Mater Spinalis Film Teminale Denticulate Ligament ---------------------- Cordotomy o Arachnoid Membrane Subarachnoid Space ----------------------- Lumbar
Pathways of proprioception
 The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Pain classifications slow and fast
 Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
THE BACK. Dr. Ali Mohsin. Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord THE BACK Dr. Ali Mohsin The spinal cord is the elongated caudal part of the CNS. It starts as the inferior continuation of the medulla oblongata at the level of foramen magnum, & ends as an
Spinal Cord THE BACK Dr. Ali Mohsin The spinal cord is the elongated caudal part of the CNS. It starts as the inferior continuation of the medulla oblongata at the level of foramen magnum, & ends as an
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Unit VIII Problem 1 Physiology: Sensory Pathway
 Unit VIII Problem 1 Physiology: Sensory Pathway - Process of sensation: Sensory receptors: they are specialized cells considered as biologic signal transducers which can detect stimuli and convert them
Unit VIII Problem 1 Physiology: Sensory Pathway - Process of sensation: Sensory receptors: they are specialized cells considered as biologic signal transducers which can detect stimuli and convert them
Spinal Cord Organization. January 12, 2011
 Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007)
 Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
The Spinal Cord. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord. The Spinal Cord 1/2/2016. Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum.
 The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
Skin types: hairy and glabrous (e.g. back vs. palm of hand)
 Lecture 19 revised 03/10 The Somatic Sensory System Skin- the largest sensory organ we have Also protects from evaporation, infection. Skin types: hairy and glabrous (e.g. back vs. palm of hand) 2 major
Lecture 19 revised 03/10 The Somatic Sensory System Skin- the largest sensory organ we have Also protects from evaporation, infection. Skin types: hairy and glabrous (e.g. back vs. palm of hand) 2 major
Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile
 Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile and position sensations (2) Thermoreceptive senses:
Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile and position sensations (2) Thermoreceptive senses:
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? What must sensory systems encode? 9/8/2010. Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination
 Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination What must sensory systems encode? How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? When the brain wants to keep certain types of information distinct,
Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination What must sensory systems encode? How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? When the brain wants to keep certain types of information distinct,
Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination
 Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination What must sensory systems encode? How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? When the brain wants to keep certain types of information distinct,
Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination What must sensory systems encode? How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? When the brain wants to keep certain types of information distinct,
Pain and Temperature Objectives
 Pain and Temperature Objectives 1. Describe the types of sensory receptors that transmit pain and temperature. 2. Understand how axon diameter relates to transmission of pain and temp information. 3. Describe
Pain and Temperature Objectives 1. Describe the types of sensory receptors that transmit pain and temperature. 2. Understand how axon diameter relates to transmission of pain and temp information. 3. Describe
Somatic Sensory System I. Background
 Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To describe the functional divisions of thalamus. II: To state the functions of thalamus and the thalamic syndrome. III: To define the somatic sensory
Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To describe the functional divisions of thalamus. II: To state the functions of thalamus and the thalamic syndrome. III: To define the somatic sensory
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
Chapter 15! Chapter 15 Sensory Pathways, Somatic Nervous System! Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System!
 Chapter 15! Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the SECTION 15-2! Sensory receptors connect our internal and external environments with the nervous system! 2 Sensation and Receptors! Transduction!
Chapter 15! Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the SECTION 15-2! Sensory receptors connect our internal and external environments with the nervous system! 2 Sensation and Receptors! Transduction!
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be?
 Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
The Somatosensory System
 The Somatosensory System Reading: BCP Chapter 12 cerebrovortex.com Divisions of the Somatosensory System Somatosensory System Exteroceptive External stimuli Proprioceptive Body position Interoceptive Body
The Somatosensory System Reading: BCP Chapter 12 cerebrovortex.com Divisions of the Somatosensory System Somatosensory System Exteroceptive External stimuli Proprioceptive Body position Interoceptive Body
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Laurie L. Wellman Ph.D.
 Laurie L. Wellman Ph.D. Theodore Tzavaras MD2015 Eastern Virginia Medical School Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy 1. Discuss -- what is pain? 2. Outline the Anterolateral Quadrant (ALQ) pathway 3. Locate
Laurie L. Wellman Ph.D. Theodore Tzavaras MD2015 Eastern Virginia Medical School Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy 1. Discuss -- what is pain? 2. Outline the Anterolateral Quadrant (ALQ) pathway 3. Locate
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways
 General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
Chapter 16: Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 16: Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems Sensation n Conscious and subconscious awareness of changes in the external or internal environment. n Components of sensation: Stimulation of the sensory
Chapter 16: Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems Sensation n Conscious and subconscious awareness of changes in the external or internal environment. n Components of sensation: Stimulation of the sensory
1. Somatosensory Pathways
 1. Somatosensory Pathways Objectives 1. Describe the general characteristics of sensory pathways 2. Understand the general organization and numbered areas of spinal cord gray matter 3. Understand dermatomes
1. Somatosensory Pathways Objectives 1. Describe the general characteristics of sensory pathways 2. Understand the general organization and numbered areas of spinal cord gray matter 3. Understand dermatomes
*Anteriolateral spinothalamic tract (STT) : a sensory pathway that is positioned anteriorly and laterally in the spinal cord.
 *somatic sensations : PAIN *Anteriolateral spinothalamic tract (STT) : a sensory pathway that is positioned anteriorly and laterally in the spinal cord. *This pathway carries a variety of sensory modalities:
*somatic sensations : PAIN *Anteriolateral spinothalamic tract (STT) : a sensory pathway that is positioned anteriorly and laterally in the spinal cord. *This pathway carries a variety of sensory modalities:
Fig Cervical spinal nerves. Cervical enlargement C7. Dural sheath. Subarachnoid space. Thoracic. Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) spinal nerves
 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation.
 Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem
 Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
V1-ophthalmic. V2-maxillary. V3-mandibular. motor
 4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
Anatomy of the Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Posterior spinal arteries Lateral corticospinal tract Dorsal column Spinothalamic tract Anterior spinal artery Anterior white commissure
Spinal Cord Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Posterior spinal arteries Lateral corticospinal tract Dorsal column Spinothalamic tract Anterior spinal artery Anterior white commissure
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D.
 Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS
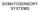 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS Schematic diagram illustrating the neural pathways that convey somatosensory information to the cortex and, subsequently, to the motor system. Double arrows show reciprocal connections.
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS Schematic diagram illustrating the neural pathways that convey somatosensory information to the cortex and, subsequently, to the motor system. Double arrows show reciprocal connections.
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy
 By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
OVERVIEW. Today. Sensory and Motor Neurons. Thursday. Parkinsons Disease. Administra7on. Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online
 OVERVIEW Today Sensory and Motor Neurons Thursday Parkinsons Disease Administra7on Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online 7 major descending motor control pathways from Cerebral Cortex or Brainstem
OVERVIEW Today Sensory and Motor Neurons Thursday Parkinsons Disease Administra7on Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online 7 major descending motor control pathways from Cerebral Cortex or Brainstem
Collin County Community College. BIOL 2401 : Anatomy/ Physiology PNS
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 : Anatomy/ Physiology PNS Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) PNS all neural structures outside the brain and spinal cord Includes sensory receptors, peripheral nerves,
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 : Anatomy/ Physiology PNS Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) PNS all neural structures outside the brain and spinal cord Includes sensory receptors, peripheral nerves,
CHAPTER 16 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 16 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The components of the brain interact to receive sensory input, integrate and store the information, and transmit motor responses. B. To accomplish the primary
CHAPTER 16 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The components of the brain interact to receive sensory input, integrate and store the information, and transmit motor responses. B. To accomplish the primary
1. Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and initiating movements?
 Section: Chapter 10: Multiple Choice 1. Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and initiating movements? p.358 frontal lobe hippocampus basal ganglia cerebellum 2. The prefrontal cortex is
Section: Chapter 10: Multiple Choice 1. Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and initiating movements? p.358 frontal lobe hippocampus basal ganglia cerebellum 2. The prefrontal cortex is
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Chapter 6. Gathering information; the sensory systems
 Chapter 6 Gathering information; the sensory systems Gathering information the sensory systems The parts of the nervous system that receive and process information are termed sensory systems. There are
Chapter 6 Gathering information; the sensory systems Gathering information the sensory systems The parts of the nervous system that receive and process information are termed sensory systems. There are
Lecture VIII. The Spinal Cord, Reflexes and Brain Pathways!
 Reflexes and Brain Bio 3411! Monday!! 1! Readings! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed: Review Chapter 1 pp. 11-21;!!Read Chapter 9 pp. 189-194, 198! THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed:! Read pp. 4-17 on class web site! Look at
Reflexes and Brain Bio 3411! Monday!! 1! Readings! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed: Review Chapter 1 pp. 11-21;!!Read Chapter 9 pp. 189-194, 198! THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed:! Read pp. 4-17 on class web site! Look at
Non-cranial nerve nuclei
 Brainstem Non-cranial nerve nuclei Nucleus Gracile nucleus Cuneate nucleus Infeiro olivary nucleus Pontine nucleus inferior colliculus superior colliculus Red nucleus Substantia nigra Pretectal area Site
Brainstem Non-cranial nerve nuclei Nucleus Gracile nucleus Cuneate nucleus Infeiro olivary nucleus Pontine nucleus inferior colliculus superior colliculus Red nucleus Substantia nigra Pretectal area Site
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
CHAPTER 16: SENSORY, MOTOR, & INTEGRATIVE SYSTEM DR. WELCH
 BIOL 2401 DR. WELCH CHAPTER 16: SENSORY, MOTOR, & INTEGRATIVE SYSTEM I. Sensation conscious or subconscious awareness of internal & external changes. Define perception. Primary function of. Why isn t blood
BIOL 2401 DR. WELCH CHAPTER 16: SENSORY, MOTOR, & INTEGRATIVE SYSTEM I. Sensation conscious or subconscious awareness of internal & external changes. Define perception. Primary function of. Why isn t blood
lecture #2 Done by : Tyma'a Al-zaben
 lecture #2 Done by : Tyma'a Al-zaben ** Hello SERTONIN! note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures in the previous lecture we talk about ascending tract and its
lecture #2 Done by : Tyma'a Al-zaben ** Hello SERTONIN! note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures in the previous lecture we talk about ascending tract and its
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Spinal Cord: Clinical Applications. Dr. Stuart Inglis
 Spinal Cord: Clinical Applications Dr. Stuart Inglis Tabes dorsalis, also known as syphilitic myelopathy, is a slow degeneration (specifically, demyelination) of the nerves in the dorsal funiculus of the
Spinal Cord: Clinical Applications Dr. Stuart Inglis Tabes dorsalis, also known as syphilitic myelopathy, is a slow degeneration (specifically, demyelination) of the nerves in the dorsal funiculus of the
Spinal cord. We have extension of the pia mater below L1-L2 called filum terminale
 Spinal cord Part of the CNS extend from foramen magnum to the level of L1-L2 (it is shorter than the vertebral column) it is covered by spinal meninges. It is cylindrical in shape. It s lower end become
Spinal cord Part of the CNS extend from foramen magnum to the level of L1-L2 (it is shorter than the vertebral column) it is covered by spinal meninges. It is cylindrical in shape. It s lower end become
Sensory information processing, somato-sensory systems
 mm? Sensory information processing, somato-sensory systems Recommended literature 1. Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessel TM (2000) Principles of Neural Science, McGraw-Hill, Ch. xx. 2. Berne EM, Levy MN, Koeppen
mm? Sensory information processing, somato-sensory systems Recommended literature 1. Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessel TM (2000) Principles of Neural Science, McGraw-Hill, Ch. xx. 2. Berne EM, Levy MN, Koeppen
Sensory coding and somatosensory system
 Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve)
 Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity
 Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
Psychophysical laws. Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 )
 Psychophysical laws Legge di Weber: ΔS=K*S Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 ) Sensory receptors Vision Smell Taste Touch Thermal senses Pain Hearing Balance Proprioception Sensory receptors Table 21-1 Classification
Psychophysical laws Legge di Weber: ΔS=K*S Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 ) Sensory receptors Vision Smell Taste Touch Thermal senses Pain Hearing Balance Proprioception Sensory receptors Table 21-1 Classification
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or to the head TA (jcolas).
 Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Developmental sequence of brain
 Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal:
 Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Doctor Osama Asa ad Khader. Mohammad Alsalem
 6 Doctor 2015 Osama Asa ad Khader Mohammad Alsalem A quick revision for the spinal cord blood supply: Arterial Blood supply of spinal cord The spinal cord got its arterial supply by two ways: Longitudinal
6 Doctor 2015 Osama Asa ad Khader Mohammad Alsalem A quick revision for the spinal cord blood supply: Arterial Blood supply of spinal cord The spinal cord got its arterial supply by two ways: Longitudinal
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D.
 Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways.
 Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways. Each higher level will control the level under It. In controlling
Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways. Each higher level will control the level under It. In controlling
Somatosensation. Recording somatosensory responses. Receptive field response to pressure
 Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Fig.1: A, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a
 Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Spinal Column Supports the skull, pectoral girdle, upper limbs and thoracic cage by way of the pelvic girdle. Transmits body weight
Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Spinal Column Supports the skull, pectoral girdle, upper limbs and thoracic cage by way of the pelvic girdle. Transmits body weight
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata
 Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi
 Brainstem &diencephalon Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi Brainstem Functions Ascending and descending tracts Reflex centers Cardiovascular and respiratory centers Coughing, sneezing, swallowing Nuclei of the
Brainstem &diencephalon Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi Brainstem Functions Ascending and descending tracts Reflex centers Cardiovascular and respiratory centers Coughing, sneezing, swallowing Nuclei of the
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum
 Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord
 Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
NERVOUS SYSTEM. Academic Resource Center. Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 Daniel J. Simons, Ph.D. I. Peripheral Nervous System THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM The somatosensory system consists of those components of the peripheral and central nervous systems that mediate sensations
Daniel J. Simons, Ph.D. I. Peripheral Nervous System THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM The somatosensory system consists of those components of the peripheral and central nervous systems that mediate sensations
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Human Anatomy. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Brainstem. Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences
 Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
