Supplementary Figure 1: Imaging T-ALL progression and growth in transplanted
|
|
|
- Felix Stevens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1: Imaging T-ALL progression and growth in transplanted rag2e450fs fish. Monoclonal T-ALLs were serially passaged in strain fish and then used as donors (left panel). Cells were transplanted intra-peritoneally into rag2e450fs, rag2e450fs (AB), and unconditioned, casper-strain recipient fish (1.0x105 cells per recipient animal). Merged brightfield and fluorescent images are shown at 10, 20 and 30 dpt. Scale bars equal 5 mm.
2 Supplementary Figure 2: Emergence of clonal dominance can result from inherent functional differences between T-ALL clones. (a) Donor animals engrafted with monoclonal T-ALL arising in the background. (b-c) Monoclonal T-ALLs were implanted into syngeneic strain fish and assessed for LPC frequency by limiting dilution cell transplantation (b) or latency of regrowth (c). T-ALLs have significantly different LPC frequency and latency, with p-values noted on each panel. (d-e) Confocal imaging of engrafted rag2e450fs fish at 14 dpt (d) and 25 dpt (e). White arrow denotes site of injection and imaging. Pie chart shows the relative proportion of each fluorescent clone contained within the imaging panel shown. Scale bars equal 5 mm in whole animal images and 50 µm in confocal images.
3 Supplementary Figure 3: Emergence of clonal dominance among three similar T- ALL clones. (a) Donor animals engrafted with monoclonal T-ALL arising in the background. (b-c) Monoclonal T-ALLs were implanted into syngeneic strain fish and assessed for LPC frequency by limiting dilution cell transplantation (b) or latency of regrowth (c). T-ALLs have similar LPC frequency and latency, with p-values noted on each panel. (d-e) Confocal imaging of engrafted fish at 15 dpt (d) and 21 dpt (e). White arrow denotes site of injection and imaging. (f-g) Relative proportions of each fluorescent clone contained within individual engrafted animals quantified by
4 fluorescence area within confocal images (f) and manual cell counts (g). Scale bars equal 5 mm in whole animal images and 50 µm in confocal images.
5 Supplementary Figure 4: Visualising neuroblastoma and ERMS metastasis in transplanted fish. (a) Retro-orbital transplantation of a GFP-labelled neuroblastoma. White arrow indicates the site of injection; yellow arrow indicates metastasis to a region near the liver. (b) Intra-muscular transplantation of ERMS into recipient fish. White arrow indicates the site of injection; yellow arrows indicate the site of metastasis. Note that metastasis can be directly visualised by epifluorescence microscopy in the recipients (yellow arrow) but not the (AB) (open yellow arrow). H&E and anti-gfp staining on sections of the recipient animals confirmed the location of metastasis. Scale bars equal 5 mm for whole animal images, 2 mm in images of heads, 1 mm in 40x histological images; 300 µm in 100x histological images; and 100 µm in 400x histological images.
6 Supplementary Figure 5: Serial passaging did not result in increased metastatic potential or growth in one melanoma. (a-b) Serial imaging of engraftment of a pigmented melanoma into recipient fish. 1 transplant (a) and 8 transplant (b). White arrow indicates the site of injection. (c) Quantification of tumour growth within individual engrafted fish. Scale bar equals 5 mm.
7 Supplementary Table 1: Transplantations performed in this study Tumour type Transgenics Donor Total transplanted Background Fluorescent marker Donor animal Recipient Age of recipients (months) Method of transplantation Number of tumour cells transplanted per recipient Recipients engrafted AmCyan Monoclonal in Fig. 1) Wild-type (AB) ZsYellow Monoclonal in (Fig. 1a; Supplementary Fig. 1) intra-peritoneal (i.p.) 1.0x10 5 cells in 5 µl Wild-type (AB) T-cell lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL) (rag2:cmyc) mcherry Monoclonal in Fig. 1) Wild-type (AB) AmCyan + ZsYellow + mcherry Monoclonal in (Fig. 4) AmCyan + ZsYellow + DsRED AmCyan + ZsYellow + mcherry Monoclonal in Fig. 2) Monoclonal in Fig. 3) 2 3.3x10 4 of each 3 16 clone, 1.0x10 5 cells intra-muscular (i.m.) in total per recipient animal, in 2 µl (repeat) primary (AB) 3 intra-peritoneal (i.p.) 5.0x10 5 cells in 5 µl 7 7 (AB) (AB) 3 intra-peritoneal (i.p.) 1.0x10 6 cells in 5 µl 4 4 Neuroblastoma (dβh:egfp- MYCN; dβh:alk F1174L ) AB EGFP 2 transplant in (AB) (Fig. 1b) (AB) 3.25 intra-peritoneal (i.p.) 1.0x10 6 cells in 5 µl intra-peritoneal (i.p.) 3.75 retro-orbital (r.o.) Fig. 4a) 5.0x10 5 cells in 2.5 µl x10 5 cells in 2 µl Wild-type 3.75 retro-orbital (r.o.) 4.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl 0 15
8 4 5 6 Wild-type 4 intra-peritoneal (i.p.) 5.0x10 5 cells in 5 µl 0 7 (rag2:kras G12D ; ICN) myf5:gfp; mylpfa:mcherry 3 transplant in (AB) intra-muscular (i.m.) Wild-type 4 (Fig. 1c; Supplementary Fig. 3.0x10 5 cells in 3 µl 0 9 (AB) 3 4b) 6 6 Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) AB myf5:gfp; mylpfa:mcherry myf5:gfp; myogenin- H2b:mRFP; mylpfa:lyn-cyan 4 transplant in primary (Fig. 3), (tp53 +/- ) 2 rag2:gfp (AB) 3 intra-muscular (i.m.) intra-muscular (i.m.) 3.3x10 5 cells in 2 µl retro-orbital (r.o.) intra-peritoneal (i.p.) 2.0x10 4 cells in 5 µl intra-muscular (i.m.) 4.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl intra-muscular (i.m.) intra-muscular (i.m.) 8.0x10 4 cells in 2 µl intra-muscular (i.m.) (rag2:kras G12D ) rag2:gfp primary rag2:gfp primary 2.5 intra-muscular (i.m.) 1.6x10 5 cells in 2 µl 2.5 intra-muscular (i.m.) 2.5 intra-muscular (i.m.) 2.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl 2.5 intra-muscular (i.m.) rag2:gfp 2 transplant in (Fig. 2c,d) 4 intra-muscular (i.m.) 5.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl 4 intra-muscular (i.m.) (mitfa:braf V600E ); tp53 -/- ; mitfa -/- nacre (MiniCoopR:GFP) primary 3 intra-peritoneal (i.p.) 1.5x10 5 cells in 5 µl intra-muscular (i.m.) 5.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl 8 8 Melanoma (mitfa:braf V600E ); tp53 -/- ; mitfa -/- nacre (MiniCoopR:GFP) primary 3 intra-peritoneal (i.p.) 8.0x10 5 cells in 5 µl intra-muscular (i.m.) 5.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl 7 8 (mitfa:braf V600E ); tp53 -/- ; mitfa -/- nacre (MiniCoopR:GFP) primary 3 intra-peritoneal (i.p.) 1.8x10 6 cells in 5 µl intra-muscular (i.m.) 5.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl 7 8
9 primary 4 intra-peritoneal (i.p.) x10 5 cells in 5 µl (AB) 1.5 intra-peritoneal (i.p.) intra-muscular (i.m.) (Fig. 5c-e) 1.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl retro-orbital (r.o.) (mitfa:braf V600E ); tp53 -/- ; mitfa -/- ; alb -/- nacre (MiniCoopR:GFP) 4 transplant in 6 transplant in 3 intra-muscular (i.m.) 5.0x10 5 cells in 3 µl 3 3 (Fig. 2b) (Fig. 2a) 2.5 intra-muscular (i.m.) 5.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl 3 intra-muscular (i.m.) 1.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl transplant in 2 intra-muscular (i.m.) 5.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl 2 intra-muscular (i.m.) primary 4 intra-peritoneal (i.p.) 3.5x10 5 cells in 5 µl (mitfa:braf V600E ); tp53 -/- ; mitfa -/- nacre (MiniCoopR:GFP) 5 transplant in 4 intra-muscular (i.m.) (Fig. 6a) 5.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl retro-orbital (r.o.) intra-muscular (i.m.) 5.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl transplant in 3 intra-muscular (i.m.) (Fig. 6b,d) 5.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl 4 4 Primary (Fig. 1d) 4 intra-peritoneal (i.p.) 4.5x10 5 cells in 5 µl (mitfa:braf V600E ); tp53 -/- ; mitfa -/- nacre (MiniCoopR:GFP) 4 4 intra-muscular (i.m.) Fig. 5a) retro-orbital (r.o.) (Fig. 5a) 3.5x10 5 cells in 2 µl transplant in 3 intra-muscular (i.m.) 5.0x10 5 cells in 3 µl transplant in 4 intra-muscular (i.m.) Fig. 5b) 5.0x10 5 cells in 2 µl
10 Supplementary Table 2: Metastasis assessments in this study Tumour type ERMS Transgenics Neuroblastoma (dβh:egfp- MYCN; dβh:alk F1174L ) (rag2:kras G12D ;ICN) (rag2:kras G12D ;ICN) Donor Total transplanted Background AB Fluorescence marker dβh:egfp myf5:gfp; mylpfa:mcherry myf5:gfp; mylpfa:mcherry (rag2:kras G12D ) rag2:gfp Donor animal 2 transplant in (AB) 3 transplant in 4 transplant in 2 transplant in (mitfa:braf V600E ); tp53 -/- ; mitfa -/- nacre MiniCoopR:GFP (mitfa:braf V600E ); tp53 -/- ; mitfa -/- nacre MiniCoopR:GFP Recipients (AB) (AB) Method of Transplantation Dosage per recipient (cells) Local engraftment only Engraftment and Metastasis Invasion r.o. 4.0x i.m. 3.0x i.m i.m. Distal Metastasis 1 (near liver) Fig. 4a) 1 (muscle tissue adjacent to thymus) Fig. 4b) 1 (muscle tissue adjacent to thymus) Fig. 4b) Total engrafted i.m. 3.3x (trunk kidney) (invasion into r.o. 8 cranial cavity, no kidney 1 (head kidney) involvement) i.m. 5.0x (whole kidney) 0 i.m. 5.0x i.m. 5.0x i.m. 5.0x (trunk and head kidney) 7 8 (mitfa:braf V600E ); tp53 -/- ; mitfa -/- nacre MiniCoopR:GFP i.m. 5.0x10 1 (invasion along the spinal cord) 2 (trunk kidney) 8 8 Melanoma (mitfa:braf V600E ); tp53 -/- ; mitfa -/- ; alb -/- nacre MiniCoopR:GFP i.m. 1.0x10 5 r.o [2 (tumour invades through the cranial cavity to spread into 2 [1 (muscle tissue adjacent to thymus); 1 (thymus)] (Fig. 5c-e)
11 (mitfa:braf V600E ); tp53 -/- -/- nacre MiniCoopR:GFP ; mitfa 6 transplant in 7 transplant in 5 transplant in 7 transplant in i.m. gills, further reaching to head and trunk kidney); 1(thymus)] 1.0x x (trunk kidney) i.m. 5.0x i.m. 5.0x i.m. 5.0x r.o. 5.0x (invasion along the spinal cord) 1 (invasion along the spinal cord) 1 (invasion along the spinal cord, involving mesonephros) 12 [11 (tumour invades through the cranial cavity and spread into gills, further reaching to pronephros and mesonephros); 1 (tumour invades into the optic tectum/brain region)] i.m. 5.0x i.m. 5.0x [1 (head kidney); 1 (region above the trunk kidney); 1 (scattered throughout the whole body)] 0 3 [1 (head kidney); 1 (trunk and head kidney); 1 (thymus)] 0 (Fig. 6a) [2 (head kidney); 1 (muscle tissue beneath trunk kidney )] 4 [2 (kidney, then disseminate to whole body); 1 (trunk kidney); 1 (region above
12 the trunk kidney)] (Fig. 6b,d) (mitfa:braf V600E ); tp53 -/- -/- nacre MiniCoopR:GFP ; mitfa 4 transplant in 8 transplant in i.m. 3.5x r.o. 3.5x (region above the trunk kidney) 10 [5 (invasion into cranial cavity); 1 (invasion into cranial cavity, spreading into the gills); 3 (tumour invades through the cranial cavity to spread into gills, further reaching to head and trunk kidney); 1 (tumour invades into the optic tectum (brain) region)] (Fig. 5a) 0 Fig. 5a) i.m. 5.0x i.m. 5.0x (whole kidney) 0 Fig. 5b)
Imaging tumour cell heterogeneity following cell transplantation into optically clear immunedeficient
 Received 20 Apr 2015 Accepted 2 Dec 2015 Published 21 Jan 2016 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10358 OPEN Imaging tumour cell heterogeneity following cell transplantation into optically clear immunedeficient zebrafish
Received 20 Apr 2015 Accepted 2 Dec 2015 Published 21 Jan 2016 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10358 OPEN Imaging tumour cell heterogeneity following cell transplantation into optically clear immunedeficient zebrafish
Correspondence: mirna regulation of Sdf1 chemokine signaling provides genetic robustness to germ cell migration
 Correspondence: mirna regulation of Sdf1 chemokine signaling provides genetic robustness to germ cell migration Alison A. Staton, Holger Knaut, and Antonio J. Giraldez Supplementary Note Materials and
Correspondence: mirna regulation of Sdf1 chemokine signaling provides genetic robustness to germ cell migration Alison A. Staton, Holger Knaut, and Antonio J. Giraldez Supplementary Note Materials and
Supplementary Information. Tissue-wide immunity against Leishmania. through collective production of nitric oxide
 Supplementary Information Tissue-wide immunity against Leishmania through collective production of nitric oxide Romain Olekhnovitch, Bernhard Ryffel, Andreas J. Müller and Philippe Bousso Supplementary
Supplementary Information Tissue-wide immunity against Leishmania through collective production of nitric oxide Romain Olekhnovitch, Bernhard Ryffel, Andreas J. Müller and Philippe Bousso Supplementary
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
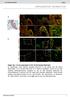 Suppl. Fig. 1 in vivo expression of ISL1 in the human fetal heart. a, Hematoxylin eosin staining showing structures of left atrium and left atrium appendage (*) of a human fetal heart at 11 weeks of gestation.
Suppl. Fig. 1 in vivo expression of ISL1 in the human fetal heart. a, Hematoxylin eosin staining showing structures of left atrium and left atrium appendage (*) of a human fetal heart at 11 weeks of gestation.
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material Supplementary Fig. 1. EETs stimulate primary tumor growth. a) Schematic presentation of genetic and pharmacological tools used to manipulate endogenous EET levels. b) Endothelial
Supplemental Material Supplementary Fig. 1. EETs stimulate primary tumor growth. a) Schematic presentation of genetic and pharmacological tools used to manipulate endogenous EET levels. b) Endothelial
Pearson r = P (one-tailed) = n = 9
 8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
Supplemental Information. Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes. Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain. and Regulates Ventricular Development
 Current Biology, Volume Supplemental Information Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain and Regulates Ventricular Development Emilie W. Olstad, Christa Ringers, Jan N.
Current Biology, Volume Supplemental Information Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain and Regulates Ventricular Development Emilie W. Olstad, Christa Ringers, Jan N.
(A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC,
 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure S1 (a) (b)
 Supplementary Figure S1: IC87114 does not affect basal Ca 2+ level nor nicotineinduced Ca 2+ influx. (a) Bovine chromaffin cells were loaded with Fluo-4AM (1 μm) in buffer A containing 0.02% of pluronic
Supplementary Figure S1: IC87114 does not affect basal Ca 2+ level nor nicotineinduced Ca 2+ influx. (a) Bovine chromaffin cells were loaded with Fluo-4AM (1 μm) in buffer A containing 0.02% of pluronic
Parvathi Haridas 1,2, Jacqui A McGovern 1, D L Sean McElwain 1,2, Matthew J Simpson 1,2. Brisbane, Australia. Corresponding Author:
 Supplemental Information Quantitative comparison of the spreading and invasion of radial growth phase and metastatic melanoma cells in a three-dimensional human skin equivalent model Parvathi Haridas 1,2,
Supplemental Information Quantitative comparison of the spreading and invasion of radial growth phase and metastatic melanoma cells in a three-dimensional human skin equivalent model Parvathi Haridas 1,2,
Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r
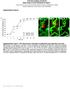 Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r Yvonne Kienast, Louisa von Baumgarten, Martin Fuhrmann, Wolfgang E.F. Klinkert, Roland Goldbrunner, Jochen Herms and Frank Winkler
Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r Yvonne Kienast, Louisa von Baumgarten, Martin Fuhrmann, Wolfgang E.F. Klinkert, Roland Goldbrunner, Jochen Herms and Frank Winkler
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
F-actin VWF Vinculin. F-actin. Vinculin VWF
 a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast
 Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Through the Looking Glass: Visualizing Leukemia Growth, Migration, and Engraftment Using Fluorescent Transgenic Zebrafish
 Through the Looking Glass: Visualizing Leukemia Growth, Migration, and Engraftment Using Fluorescent Transgenic Zebrafish The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how
Through the Looking Glass: Visualizing Leukemia Growth, Migration, and Engraftment Using Fluorescent Transgenic Zebrafish The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how
Supplementary information
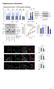 Supplementary information 1 Supplementary Figure 1. CALM regulates autophagy. (a). Quantification of LC3 levels in the experiment described in Figure 1A. Data are mean +/- SD (n > 3 experiments for each
Supplementary information 1 Supplementary Figure 1. CALM regulates autophagy. (a). Quantification of LC3 levels in the experiment described in Figure 1A. Data are mean +/- SD (n > 3 experiments for each
In Vivo Imaging of Tumor-Propagating Cells, Regional Tumor Heterogeneity, and Dynamic Cell Movements in Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma
 Article In Vivo Imaging of Tumor-Propagating Cells, Regional Tumor Heterogeneity, and Dynamic Cell Movements in Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma Myron S. Ignatius, 1,3 Eleanor Chen, 1,3,4 Natalie M. Elpek, 2
Article In Vivo Imaging of Tumor-Propagating Cells, Regional Tumor Heterogeneity, and Dynamic Cell Movements in Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma Myron S. Ignatius, 1,3 Eleanor Chen, 1,3,4 Natalie M. Elpek, 2
Diabetic pdx1-mutant zebrafish show conserved responses to nutrient overload and anti-glycemic treatment
 Supplementary Information Diabetic pdx1-mutant zebrafish show conserved responses to nutrient overload and anti-glycemic treatment Robin A. Kimmel, Stefan Dobler, Nicole Schmitner, Tanja Walsen, Julia
Supplementary Information Diabetic pdx1-mutant zebrafish show conserved responses to nutrient overload and anti-glycemic treatment Robin A. Kimmel, Stefan Dobler, Nicole Schmitner, Tanja Walsen, Julia
activation with anti-cd3/cd28 beads and 3d following transduction. Supplemental Figure 2 shows
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1 compares CXCR4 expression in untreated CD8 + T cells, following activation with anti-cd3/cd28 beads and 3d following transduction. Supplemental Figure 2 shows the
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1 compares CXCR4 expression in untreated CD8 + T cells, following activation with anti-cd3/cd28 beads and 3d following transduction. Supplemental Figure 2 shows the
Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a)
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Supplemental Information. Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo
 Supplemental Information Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo viability Satoshi Tsukamoto*, Taichi Hara, Atsushi Yamamoto, Seiji Kito, Naojiro Minami, Toshiro Kubota,
Supplemental Information Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo viability Satoshi Tsukamoto*, Taichi Hara, Atsushi Yamamoto, Seiji Kito, Naojiro Minami, Toshiro Kubota,
Beverly A. Teicher, PhD DCTD/NCI. The content reflects my professional opinions, not an NCI policy statement.
 Beverly A. Teicher, PhD DCTD/NCI The content reflects my professional opinions, not an NCI policy statement. Outline 1. Transplantable Syngeneic Tumors 2. Human Tumor Xenografts 3. Disseminated Disease
Beverly A. Teicher, PhD DCTD/NCI The content reflects my professional opinions, not an NCI policy statement. Outline 1. Transplantable Syngeneic Tumors 2. Human Tumor Xenografts 3. Disseminated Disease
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed
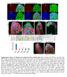 Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a. Smo+/+ b. Smo+/+ 5.63 5.48 c. Lin- d. e. 6 5 4 3 Ter119 Mac B T Sca1 Smo+/+ 25 15 2 o BMT 2 1 5 * Supplementary Figure 1: Deletion of Smoothened does not alter the frequency of hematopoietic lineages
a. Smo+/+ b. Smo+/+ 5.63 5.48 c. Lin- d. e. 6 5 4 3 Ter119 Mac B T Sca1 Smo+/+ 25 15 2 o BMT 2 1 5 * Supplementary Figure 1: Deletion of Smoothened does not alter the frequency of hematopoietic lineages
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3412
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gata1 expression in heamatopoietic stem and progenitor populations. (a) Unsupervised clustering according to 100 top variable genes across single pre-gm cells. The two main cell
Supplementary Figure 1 Gata1 expression in heamatopoietic stem and progenitor populations. (a) Unsupervised clustering according to 100 top variable genes across single pre-gm cells. The two main cell
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma.
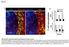 Fig S1 CD4 Fibronectin EpCM CD8 CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma. Fluorescently-labeled CD4 (CMFD, green) and CD8 (Hoechst, yellow) T cells were added to a human lung
Fig S1 CD4 Fibronectin EpCM CD8 CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma. Fluorescently-labeled CD4 (CMFD, green) and CD8 (Hoechst, yellow) T cells were added to a human lung
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted
 Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Supplementary Figure 1. Chimeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) Chimeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears.
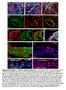 Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
genome edited transient transfection, CMV promoter
 Supplementary Figure 1. In the absence of new protein translation, overexpressed caveolin-1-gfp is degraded faster than caveolin-1-gfp expressed from the endogenous caveolin 1 locus % loss of total caveolin-1-gfp
Supplementary Figure 1. In the absence of new protein translation, overexpressed caveolin-1-gfp is degraded faster than caveolin-1-gfp expressed from the endogenous caveolin 1 locus % loss of total caveolin-1-gfp
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and
 Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Ahtiainen et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
Differential neuronal vulnerability identifies IGF-2 as a protective factor in
 Supplementary Information Differential neuronal vulnerability identifies IGF-2 as a protective factor in ALS Ilary Allodi 1,3, Laura Comley 1,3, Susanne Nichterwitz 1,3, Monica Nizzardo 2, Chiara Simone
Supplementary Information Differential neuronal vulnerability identifies IGF-2 as a protective factor in ALS Ilary Allodi 1,3, Laura Comley 1,3, Susanne Nichterwitz 1,3, Monica Nizzardo 2, Chiara Simone
293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell extracts were subjected
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
CHMP Oncology Working Party Workshop on: Histology Independent Indications in Oncology. Non-clinical models: Tumour Models - Proof of Concept
 CHMP Oncology Working Party Workshop on: Histology Independent Indications in Oncology Non-clinical models: Tumour Models - Proof of Concept Edward C. Rosfjord Pfizer Worldwide R. & D. 14 December 2017
CHMP Oncology Working Party Workshop on: Histology Independent Indications in Oncology Non-clinical models: Tumour Models - Proof of Concept Edward C. Rosfjord Pfizer Worldwide R. & D. 14 December 2017
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
Lai et al 2008 JCI RG-Revision 2
 Lai et al 2008 JCI 36612-RG-Revision 2 Suppmentary Table 1. Epitope specific dystrophin antibodies Name Epitope Dilution Source Dys-3* Hinge 1 1:20 Novocastra Dys-1 Repeats 6-8 1:100 Novocastra Mandys8
Lai et al 2008 JCI 36612-RG-Revision 2 Suppmentary Table 1. Epitope specific dystrophin antibodies Name Epitope Dilution Source Dys-3* Hinge 1 1:20 Novocastra Dys-1 Repeats 6-8 1:100 Novocastra Mandys8
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
Supplemental Data. Hao et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Confocal Images and VA-TIRFM Analysis of GFP-RbohD in Arabidopsis Seedlings. (A) RbohD expression in whole Arabidopsis seedlings. RbohD was expressed in the leaves, hypocotyl, and
Supplemental Figure 1. Confocal Images and VA-TIRFM Analysis of GFP-RbohD in Arabidopsis Seedlings. (A) RbohD expression in whole Arabidopsis seedlings. RbohD was expressed in the leaves, hypocotyl, and
Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC
 Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC Supplementary Table 2. Drug content and loading efficiency estimated with F-NMR and UV- Vis Supplementary Table 3. Complete
Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC Supplementary Table 2. Drug content and loading efficiency estimated with F-NMR and UV- Vis Supplementary Table 3. Complete
Supplementary Figure 1. Gene schematics of hyls-1, gasr-8 and k10g6.4, and TEM analysis of TFs in WT and hyls-1 cilia. (a) Gene structure of hyls-1,
 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene schematics of hyls-1, gasr-8 and k10g6.4, and TEM analysis of TFs in WT and hyls-1 cilia. (a) Gene structure of hyls-1, gasr-8 and k10g6.4 based on WormBase (http://wormbase.org),
Supplementary Figure 1. Gene schematics of hyls-1, gasr-8 and k10g6.4, and TEM analysis of TFs in WT and hyls-1 cilia. (a) Gene structure of hyls-1, gasr-8 and k10g6.4 based on WormBase (http://wormbase.org),
ASSESSMENT OF CELLULAR OXYGEN GRADIENTS WITH A PANEL OF PHOSPHORESCENT OXYGEN-SENSITIVE PROBES
 ASSESSMENT OF CELLULAR OXYGEN GRADIENTS WITH A PANEL OF PHOSPHORESCENT OXYGEN-SENSITIVE PROBES Ruslan I. Dmitriev, Alexander V. Zhdanov, Greg Jasionek, Dmitri B. Papkovsky Biochemistry Department, University
ASSESSMENT OF CELLULAR OXYGEN GRADIENTS WITH A PANEL OF PHOSPHORESCENT OXYGEN-SENSITIVE PROBES Ruslan I. Dmitriev, Alexander V. Zhdanov, Greg Jasionek, Dmitri B. Papkovsky Biochemistry Department, University
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Ras V12 expression in the entire eye-antennal disc does not cause invasive tumours. a, Eye-antennal discs expressing Ras V12 in all cells (marked with GFP, green) overgrow moderately
Supplementary Figure 1. Ras V12 expression in the entire eye-antennal disc does not cause invasive tumours. a, Eye-antennal discs expressing Ras V12 in all cells (marked with GFP, green) overgrow moderately
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death
 www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death Supplementary
www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death Supplementary
Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells. a. Schematic of the V-ATPase proton pump macro-complex structure. The V1 complex is composed of
Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells. a. Schematic of the V-ATPase proton pump macro-complex structure. The V1 complex is composed of
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
Germ Cell Transplantation in Fish
 Larvi 2009 Germ Cell Transplantation in Fish Goro Yoshizaki (Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology, SORST/JST) Tuna Mackerel Body weight; 300 kg 300 g Body length; 3 m 30 cm Scombridae family
Larvi 2009 Germ Cell Transplantation in Fish Goro Yoshizaki (Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology, SORST/JST) Tuna Mackerel Body weight; 300 kg 300 g Body length; 3 m 30 cm Scombridae family
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the
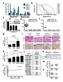 Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Afferent lymph-derived T cells and dendritic cells use different CCR7-dependent routes for lymph node entry and intranodal migration
 Braun et al. Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Information Afferent lymph-derived T cells and dendritic cells use different CCR7-dependent routes for lymph node entry and intranodal migration Asolina
Braun et al. Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Information Afferent lymph-derived T cells and dendritic cells use different CCR7-dependent routes for lymph node entry and intranodal migration Asolina
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Luminal localization of CCM-3. (a) The CCM-3::GFP fusion protein localizes along the apical (luminal) surface of the pharynx (b) as well as the lumen of
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Luminal localization of CCM-3. (a) The CCM-3::GFP fusion protein localizes along the apical (luminal) surface of the pharynx (b) as well as the lumen of
Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia
 General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 3 Rate of growth, local invasion, and metastasis. Molecular basis of cancer (normal cell-cycle and cellular proliferation). Enrique
General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 3 Rate of growth, local invasion, and metastasis. Molecular basis of cancer (normal cell-cycle and cellular proliferation). Enrique
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS. atypical adenomatous hyperplasias (AAH); Grade II: adenomas; Grade III: adenocarcinomas;
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure S1: Tumor grades in Ras G12D ; p53 / lung tumors. Representative histology (H&E) of K-Ras G12D ; p53 / lung tumors 13 weeks after tumor initiation. Grade
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure S1: Tumor grades in Ras G12D ; p53 / lung tumors. Representative histology (H&E) of K-Ras G12D ; p53 / lung tumors 13 weeks after tumor initiation. Grade
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
BMT for Cystinosis? K30 Journal Club Jan 26, 2009
 BMT for Cystinosis? K30 Journal Club Jan 26, 2009 Cystine Cystine is a dimeric amino acid formed by the oxidation of two cysteine residues Cystinosis is a lysosomal storage disorder QuickTime and a TIFF
BMT for Cystinosis? K30 Journal Club Jan 26, 2009 Cystine Cystine is a dimeric amino acid formed by the oxidation of two cysteine residues Cystinosis is a lysosomal storage disorder QuickTime and a TIFF
Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al
 Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread
 Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin
 Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Supplementary information. The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic. Spindle Orientation
 Supplementary information The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic Spindle Orientation Running title: Dynein LICs distribute mitotic functions. Sagar Mahale a, d, *, Megha
Supplementary information The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic Spindle Orientation Running title: Dynein LICs distribute mitotic functions. Sagar Mahale a, d, *, Megha
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the
 Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
In vitro bactericidal assay Fig. S8 Gentamicin protection assay Phagocytosis assay
 In vitro bactericidal assay Mouse bone marrow was isolated from the femur and the tibia. Cells were suspended in phosphate buffered saline containing.5% BSA and 2 mm EDTA and filtered through a cell strainer.
In vitro bactericidal assay Mouse bone marrow was isolated from the femur and the tibia. Cells were suspended in phosphate buffered saline containing.5% BSA and 2 mm EDTA and filtered through a cell strainer.
Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo. SI Figures and Legend
 Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo Authors: *Faith H. Barnett, *Mauricio Rosenfeld, Malcolm Wood, William Kiosses, Yoshihiko Usui, Valentina Marchetti, Edith Aguilar, and Martin
Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo Authors: *Faith H. Barnett, *Mauricio Rosenfeld, Malcolm Wood, William Kiosses, Yoshihiko Usui, Valentina Marchetti, Edith Aguilar, and Martin
effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of ε j2b10 show no
 Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic labeling of microglia Male and female 2-3 month-old CreERT2;R26-tdTomato mice or CreERT2;R26-tdTomato;Iba1-eGFP transgenic mice were treated with 1x, 2x (48 h apart), or
Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic labeling of microglia Male and female 2-3 month-old CreERT2;R26-tdTomato mice or CreERT2;R26-tdTomato;Iba1-eGFP transgenic mice were treated with 1x, 2x (48 h apart), or
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Representative images of an in vitro comparison of several AAV serotypes regarding egfp expression in cochlear explants of CBA/CaJ mice. (A-F): Results after incubation at equal
Supplementary Figure 1 Representative images of an in vitro comparison of several AAV serotypes regarding egfp expression in cochlear explants of CBA/CaJ mice. (A-F): Results after incubation at equal
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Supplemental Material. Results
 Supplemental Material Results Fractionation of mouse plasma by high-resolution SEC. APOA1 eluted as a single major peak in fractions 16 of plasma (the apparent size of mature, lipidated HDL) when it was
Supplemental Material Results Fractionation of mouse plasma by high-resolution SEC. APOA1 eluted as a single major peak in fractions 16 of plasma (the apparent size of mature, lipidated HDL) when it was
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1. Galectin-3 is present within tumors. (A) mrna expression levels of Lgals3 (galectin-3) and Lgals8 (galectin-8) in the four classes of cell lines as determined
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1. Galectin-3 is present within tumors. (A) mrna expression levels of Lgals3 (galectin-3) and Lgals8 (galectin-8) in the four classes of cell lines as determined
In Vivo Imaging of Virological Synapses
 In Vivo Imaging of Virological Synapses Xaver Sewald 1, David G. Gonzalez 2, Ann M. Haberman 2, and Walther Mothes 1 * 1 Department of Microbial Pathogenesis, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven,
In Vivo Imaging of Virological Synapses Xaver Sewald 1, David G. Gonzalez 2, Ann M. Haberman 2, and Walther Mothes 1 * 1 Department of Microbial Pathogenesis, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven,
Extracellular vesicles are transferred from melanocytes to keratinocytes after UVA irradiation
 Supplementary material; Title; Extracellular vesicles are transferred from melanocytes to keratinocytes after UVA irradiation Authors; Petra Wäster 1, Ida Eriksson 1, Linda Vainikka 1, Inger Rosdahl 2,
Supplementary material; Title; Extracellular vesicles are transferred from melanocytes to keratinocytes after UVA irradiation Authors; Petra Wäster 1, Ida Eriksson 1, Linda Vainikka 1, Inger Rosdahl 2,
Supplemental Table S1
 Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of the AA5x. a, Camera lucida drawing of embryo at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf, modified from Kimmel et al. Dev Dyn. 1995 203:253-310). b, Confocal microangiogram
Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of the AA5x. a, Camera lucida drawing of embryo at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf, modified from Kimmel et al. Dev Dyn. 1995 203:253-310). b, Confocal microangiogram
PHENOTYPIC DYNAMICS OF MICROGLIAL AND MONOCYTE-DERIVED CELLS IN GLIOBLASTOMA-BEARING MICE.
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, TABLES AND VIDEOS PHENOTYPIC DYNAMICS OF MICROGLIAL AND MONOCYTE-DERIVED CELLS IN GLIOBLASTOMA-BEARING MICE. Clément Ricard 1,2,3,4, Aurélie Tchoghandjian 2,4, Hervé Luche 5, Pierre
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, TABLES AND VIDEOS PHENOTYPIC DYNAMICS OF MICROGLIAL AND MONOCYTE-DERIVED CELLS IN GLIOBLASTOMA-BEARING MICE. Clément Ricard 1,2,3,4, Aurélie Tchoghandjian 2,4, Hervé Luche 5, Pierre
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Therapeutic implications of cancer stem cells. Cédric Blanpain, MD, PhD Laboratory of stem cells and cancer WELBIO, Université Libre de Bruxelles
 Therapeutic implications of cancer stem cells Cédric Blanpain, MD, PhD Laboratory of stem cells and cancer WELBIO, Université Libre de Bruxelles Stem cell properties Differentiation Self-renewal Tumor
Therapeutic implications of cancer stem cells Cédric Blanpain, MD, PhD Laboratory of stem cells and cancer WELBIO, Université Libre de Bruxelles Stem cell properties Differentiation Self-renewal Tumor
