Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.3967
|
|
|
- Marilynn Newman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Network clustering. (a) Clustering performance as a function of inflation factor. The grey curve shows the median weighted Silhouette widths for varying inflation factors (f [1.6, 10]). The red circle indicates the optimal inflation factor of 3.8, which yields the highest average weighted Silhouette width. Representative consensus matrices for 3 (f = 1.6), 4 (f = 3.8) and 5 (f = 10) clusters are shown in the heatmaps in (b), (c) and (d), respectively.
2 Supplementary Figure 2. Distribution of unlabeled samples as percent of data set size from the consensus subtype labeling. Median unlabeled percentage is 20%. The outlier data set (GSE20916) with the corresponding large percentage of unlabeled samples is a study comprised of multiple tissue types, including micro and macro dissected normal mucosa, adenoma, colonic crypt, carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma. Adenocarcinoma samples were extracted for the analysis in our study.
3 Supplementary Figure 3. Classifier performance metrics. (a) Performance metrics for all validation samples (sensitivity, specificity accuracy). (b) Performance metrics on all validation samples, reported per data set. (c) Performance metrics for validation samples (sensitivity, specificity accuracy) in data sets profiled on the Affymetrix and RNAseq expression platforms. (d) Performance metrics on validation samples, reported per data sets in data sets profiled on the Affymetrix and RNAseq expression platforms. (e) Performance metrics for validation samples (sensitivity, specificity accuracy) in data sets profiled on the Agilent expression platform. (f) Performance metrics on validation samples, reported per data sets in data sets profiled on the Agilent expression platform. (g) Performance metrics measured on 3 holdout data sets (GSE39582, GSE17536, TCGA). (h) Summary of performance metrics. Classifier was trained using all fresh-frozen samples (Affymetrix/RNAseq) and validated on the PETACC3 (FFPE) samples.
4 Supplementary Figure 4. Classifier specificity analysis. Relationship between posterior probability threshold on percentage of unclassified samples (solid grey line) and specificity (CMS colored dash lines), where specificity is measured from the validation data split.
5 a b c d Supplementary Figure 5 Unlabeled sample analysis. (a) Principal components analysis of labeled (CMS classified) and unclassified samples. Labeled CMS samples are represented with centroid (colored dot) and 1 standard deviation (colored dashed line). Unclassified samples are represented as black dots. (b) Projected data in three-dimensional latent space using factor analysis model. Black dots represent all four CMS classified samples and red dots represent unclassified samples. (c) Clustering of Random Forest posterior probabilities of unclassified samples. Posterior probabilities less than 0.2 are thresholded to 0; (d) Distribution of mixed subtypes in unclassified samples.
6 Supplementary Figure 6. TCGA methylation analysis. (a) Hierarchical clustering plot for the TCGA 450K DNA methylation data set. Labels for batch and tissue source site (TSS) are plotted below. (b) Heatmap of TCGA DNA methylation 450K data set. Shown is heatmap representation of DNA methylation β-values of 1,486 most variable probes (among probes present in the 27K beadchip) (standard deviation >0.18, 10% of the probes) across 301 tumor samples and 38 normal samples (NT) with dark blue indicating low DNA methylation and yellow indicating high DNA methylation. The RPMM-based cluster assignments are indicated above the heatmap: light green cluster 1/CIMP-H (n = 51); green cluster 2/CIMP-L (n = 65); light blue cluster 3 (n = 115) and blue, cluster 4 (n = 70). (c) Heatmap of differentially methylated genes between the four CMS groups. The heatmap was produced with gene-level methylation data standardized per gene across all samples. Differentially methylated genes were ordered based on hierarchical clustering with Ward s linkage.
7 c WNT TP53 RTK/MAPK PI3K TGF beta d 1.00 Integrative analysis - mutation, copy number (n=168) e purity 0.50 purity Classified Unclassified CMS1 CMS2 CMS3 CMS4 Supplementary Figure 7. TCGA integrative analysis. (a) Key genomic/epigenomic markers in TCGA data set: SCNA high (>Q1 for non-zero GISTIC score events); hypermutation (>180 events in exome sequencing); MSI and CIMP cluster. (b) Distribution of targeted mutations in TCGA data set. (c) Activation of canonical signaling pathways in CRC from integrative mutation, copy number events (high-level focal amplifications, homozygous deletions), and significant up- or down-regulation of gene expression (TCGA data set). RTK/MAPK: receptor tyrosine kinase/ mitogen activated protein kinase. (d) ABSOLUTE purity estimates from the TCGA samples, comparing the CMS classified and unclassified sample. (e) Distribution of ABSOLUTE scores across the CMS groups in the TCGA cohort.
8 Supplementary Figure 8. TCGA microrna analysis. (a) Analysis of batch-effect in TCGA microrna data using hierarchical clustering. Labels for batch and tissue source site (TSS) are plotted below. (b) Comparison of differentially expressed CMS micrornas in TCGA data set 1 (n = 197) and TCGA data set 2 (n = 200): top left (CMS1), top right (CMS2), bottom left (CMS3), bottom right (CMS4). (c) Heatmap of top 110 differentially expressed mirnas across all CMS groups in TCGA.
9 Supplementary Figure 9. Tumor vs. normal comparison. (a) Principal component analysis including unmatched normal samples from the GSE39582 cohort (n = 19, black dots). Dashed blue line is optimal hyperplane separating tumor from normal samples. (b) Corresponding distribution (by CMS + normal) of samples from separating hyperplane. (c) Principal component analysis including unmatched normal samples from the PETACC-3 cohort (n = 64, black dots). Dashed blue line is optimal hyperplane separating tumor from normal samples. (d) Corresponding distribution (by CMS + normal) of samples from separating hyperplane.
10 Supplementary Figure 10. Distribution of CMS groups across different tumor sites. Right colon from cecum to transverse, left colon from splenic flexure to sigmoid, and rectum (n = 2,651).
11 Supplementary Figure 11. Analysis of clinical outcomes. (a) Kaplan-Meier analysis on the PETACC-3 data set: overall-survival (left), Relapse- free survival (center), and survival after recurrence (right). (b) Timedependent AUC analysis, comparing the clinical + molecular model (MSI/BRAF mutations/kras mutations) with the clinical + molecular + CMS model. See Supplementary Table 13 for details.
12 Supplementary Figure 12. Distribution of subtype labels as reported in original subtyping publication and in consortium samples. Overall, the same distribution of subtype labels is seen in individual subtyping efforts (green) and aggregated consortium data (orange).
13 Supplementary Figure 13. Data aggregation workflow. All data sets are combined into a single, normalized gene expression matrix. This matrix is used in the development of a consensus subtype classifier.
Journal: Nature Methods
 Journal: Nature Methods Article Title: Network-based stratification of tumor mutations Corresponding Author: Trey Ideker Supplementary Item Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure
Journal: Nature Methods Article Title: Network-based stratification of tumor mutations Corresponding Author: Trey Ideker Supplementary Item Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure
underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Patient cohorts and study design. To define and interrogate the genetic alterations underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Patient cohorts and study design. To define and interrogate the genetic alterations underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.2995
 Supplementary Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier survival curves of patients with brainstem tumors. (a) Comparison of patients with PPM1D mutation versus wild-type PPM1D. (b) Comparison of patients with PPM1D mutation
Supplementary Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier survival curves of patients with brainstem tumors. (a) Comparison of patients with PPM1D mutation versus wild-type PPM1D. (b) Comparison of patients with PPM1D mutation
Expert-guided Visual Exploration (EVE) for patient stratification. Hamid Bolouri, Lue-Ping Zhao, Eric C. Holland
 Expert-guided Visual Exploration (EVE) for patient stratification Hamid Bolouri, Lue-Ping Zhao, Eric C. Holland Oncoscape.sttrcancer.org Paul Lisa Ken Jenny Desert Eric The challenge Given - patient clinical
Expert-guided Visual Exploration (EVE) for patient stratification Hamid Bolouri, Lue-Ping Zhao, Eric C. Holland Oncoscape.sttrcancer.org Paul Lisa Ken Jenny Desert Eric The challenge Given - patient clinical
Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded
 Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded from TCGA and differentially expressed metabolic genes
Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded from TCGA and differentially expressed metabolic genes
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Glioblastoma 5hmC quantified by paired BS and oxbs treated DNA hybridized to Infinium DNA methylation arrays. Workflow depicts analytic
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Glioblastoma 5hmC quantified by paired BS and oxbs treated DNA hybridized to Infinium DNA methylation arrays. Workflow depicts analytic
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3115
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Biomarker development in the era of precision medicine. Bei Li, Interdisciplinary Technical Journal Club
 Biomarker development in the era of precision medicine Bei Li, 23.08.2016 Interdisciplinary Technical Journal Club The top ten highest-grossing drugs in the United States help between 1 in 25 and 1 in
Biomarker development in the era of precision medicine Bei Li, 23.08.2016 Interdisciplinary Technical Journal Club The top ten highest-grossing drugs in the United States help between 1 in 25 and 1 in
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1: Quality assessment of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE)-derived DNA and nuclei. (a) Multiplex PCR analysis of unrepaired and repaired bulk FFPE gdna from
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1: Quality assessment of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE)-derived DNA and nuclei. (a) Multiplex PCR analysis of unrepaired and repaired bulk FFPE gdna from
Agilent GeneSpring/MPP Metadata Analysis Framework
 Agilent GeneSpring/MPP Metadata Analysis Framework Technical Overview Authors Srikanthi R., Pritha Aggarwal, Durairaj R., Maria Kammerer, and Pramila Tata Strand Life Sciences Bangalore, India Michael
Agilent GeneSpring/MPP Metadata Analysis Framework Technical Overview Authors Srikanthi R., Pritha Aggarwal, Durairaj R., Maria Kammerer, and Pramila Tata Strand Life Sciences Bangalore, India Michael
Supplemental Information. Molecular, Pathological, Radiological, and Immune. Profiling of Non-brainstem Pediatric High-Grade
 Cancer Cell, Volume 33 Supplemental Information Molecular, Pathological, Radiological, and Immune Profiling of Non-brainstem Pediatric High-Grade Glioma from the HERBY Phase II Randomized Trial Alan Mackay,
Cancer Cell, Volume 33 Supplemental Information Molecular, Pathological, Radiological, and Immune Profiling of Non-brainstem Pediatric High-Grade Glioma from the HERBY Phase II Randomized Trial Alan Mackay,
Introduction to Gene Sets Analysis
 Introduction to Svitlana Tyekucheva Dana-Farber Cancer Institute May 15, 2012 Introduction Various measurements: gene expression, copy number variation, methylation status, mutation profile, etc. Main
Introduction to Svitlana Tyekucheva Dana-Farber Cancer Institute May 15, 2012 Introduction Various measurements: gene expression, copy number variation, methylation status, mutation profile, etc. Main
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kaminski MF, Regula J, Kraszewska E, et al. Quality indicators
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Kaminski MF, Regula J, Kraszewska E, et al. Quality indicators
Supplementary Tables. Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Files for Zehir, Benayed et al. Mutational Landscape of Metastatic Cancer Revealed from Prospective Clinical Sequencing of 10,000 Patients Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: Sample
Supplementary Files for Zehir, Benayed et al. Mutational Landscape of Metastatic Cancer Revealed from Prospective Clinical Sequencing of 10,000 Patients Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: Sample
Supplementary Table S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort. Chr. # of Gene 2. Chr. # of Gene 1
 Supplementary Tale S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort TCGA Case ID Gene-1 Gene-2 Chr. # of Gene 1 Chr. # of Gene 2 Genomic coordiante of Gene 1 at fusion junction Genomic
Supplementary Tale S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort TCGA Case ID Gene-1 Gene-2 Chr. # of Gene 1 Chr. # of Gene 2 Genomic coordiante of Gene 1 at fusion junction Genomic
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Somatic coding mutations identified by WES/WGS for 83 ATL cases.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Somatic coding mutations identified by WES/WGS for 83 ATL cases. (a) The percentage of targeted bases covered by at least 2, 10, 20 and 30 sequencing reads (top) and average read
Supplementary Figure 1 Somatic coding mutations identified by WES/WGS for 83 ATL cases. (a) The percentage of targeted bases covered by at least 2, 10, 20 and 30 sequencing reads (top) and average read
The use of diagnostic FFPE material in cancer epidemiology research
 The use of diagnostic FFPE material in cancer epidemiology research Neil O Callaghan Genetic Epidemiology Laboratory Department of Pathology The University of Melbourne www.pedigree.org.au Overview Who
The use of diagnostic FFPE material in cancer epidemiology research Neil O Callaghan Genetic Epidemiology Laboratory Department of Pathology The University of Melbourne www.pedigree.org.au Overview Who
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
ncounter Assay Automated Process Immobilize and align reporter for image collecting and barcode counting ncounter Prep Station
 ncounter Assay ncounter Prep Station Automated Process Hybridize Reporter to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes Immobilize and
ncounter Assay ncounter Prep Station Automated Process Hybridize Reporter to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes Immobilize and
Patient characteristics of training and validation set. Patient selection and inclusion overview can be found in Supp Data 9. Training set (103)
 Roepman P, et al. An immune response enriched 72-gene prognostic profile for early stage Non-Small- Supplementary Data 1. Patient characteristics of training and validation set. Patient selection and inclusion
Roepman P, et al. An immune response enriched 72-gene prognostic profile for early stage Non-Small- Supplementary Data 1. Patient characteristics of training and validation set. Patient selection and inclusion
Molecular subtyping: how useful is it?
 Molecular subtyping: how useful is it? Daniela E. Aust, Institute for Pathology, University Hospital Dresden, Germany Center for Molecular Tumor Diagnostics at the NCT-Partner Site Dresden CMTD Disclosure
Molecular subtyping: how useful is it? Daniela E. Aust, Institute for Pathology, University Hospital Dresden, Germany Center for Molecular Tumor Diagnostics at the NCT-Partner Site Dresden CMTD Disclosure
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis
 The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
Table S2 Study group sample sizes for CEA, CYFRA21-1 and CA125 determinations.
 Supplementary Data Table S Clinico-pathological data associated with malignant and benign cases Primary site Early stage Late stage Caecum 3 (5%) 4 (20%) (5%) Ascending colon 6 (30%) 2 (0%) 0 (0%) Transverse
Supplementary Data Table S Clinico-pathological data associated with malignant and benign cases Primary site Early stage Late stage Caecum 3 (5%) 4 (20%) (5%) Ascending colon 6 (30%) 2 (0%) 0 (0%) Transverse
Biology of cancer development in the GI tract
 1 Genesis and progression of GI cancer a genetic disease Colorectal cancer Fearon and Vogelstein proposed a genetic model to explain the stepwise formation of colorectal cancer (CRC) from normal colonic
1 Genesis and progression of GI cancer a genetic disease Colorectal cancer Fearon and Vogelstein proposed a genetic model to explain the stepwise formation of colorectal cancer (CRC) from normal colonic
Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well
 Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well plate at cell densities ranging from 25-225 cells in
Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well plate at cell densities ranging from 25-225 cells in
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX
 SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
Colon cancer subtypes from gene expression data
 Colon cancer subtypes from gene expression data Nathan Cunningham Giuseppe Di Benedetto Sherman Ip Leon Law Module 6: Applied Statistics 26th February 2016 Aim Replicate findings of Felipe De Sousa et
Colon cancer subtypes from gene expression data Nathan Cunningham Giuseppe Di Benedetto Sherman Ip Leon Law Module 6: Applied Statistics 26th February 2016 Aim Replicate findings of Felipe De Sousa et
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Guided Visual Exploration of Genomic Stratifications in Cancer Marc Streit 1,6, Alexander Lex 2,6, Samuel Gratzl¹, Christian Partl³, Dieter Schmalstieg³, Hanspeter Pfister², Peter
Supplementary Information Guided Visual Exploration of Genomic Stratifications in Cancer Marc Streit 1,6, Alexander Lex 2,6, Samuel Gratzl¹, Christian Partl³, Dieter Schmalstieg³, Hanspeter Pfister², Peter
Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks
 Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks Analyzing 24 Proteomes Per Day by Microflow SWATH Acquisition and Spectronaut Pulsar Analysis Jan Muntel 1, Nick Morrice 2, Roland M. Bruderer 1, Lukas
Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks Analyzing 24 Proteomes Per Day by Microflow SWATH Acquisition and Spectronaut Pulsar Analysis Jan Muntel 1, Nick Morrice 2, Roland M. Bruderer 1, Lukas
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/7/283/283ra54/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Clonal status of actionable driver events and the timing of mutational processes in cancer evolution
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/7/283/283ra54/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Clonal status of actionable driver events and the timing of mutational processes in cancer evolution
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from
 Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical Informatics (CoSBBI) Outline. Molecular Biology of Cancer AND. Goals/Expectations. David Boone 7/1/2015
 Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/7/303/303ra139/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Magnetic resonance image features identify glioblastoma phenotypic subtypes with distinct molecular
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/7/303/303ra139/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Magnetic resonance image features identify glioblastoma phenotypic subtypes with distinct molecular
Gender-related prognostic value and genomic pattern of intra-tumor heterogeneity in colorectal cancer
 Carcinogenesis, 2017, Vol. 38, No. 8, 837 846 doi:10.1093/carcin/bgx046 Advance Access publication May 20, 2017 Original Manuscript original manuscript Gender-related prognostic value and genomic pattern
Carcinogenesis, 2017, Vol. 38, No. 8, 837 846 doi:10.1093/carcin/bgx046 Advance Access publication May 20, 2017 Original Manuscript original manuscript Gender-related prognostic value and genomic pattern
Statistics 202: Data Mining. c Jonathan Taylor. Final review Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes.
 Final review Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 5, 2012 1 / 1 Final review Overview Before Midterm General goals of data mining. Datatypes. Preprocessing & dimension
Final review Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 5, 2012 1 / 1 Final review Overview Before Midterm General goals of data mining. Datatypes. Preprocessing & dimension
Integration of Cancer Genome into GECCO- Genetics and Epidemiology of Colorectal Cancer Consortium
 Integration of Cancer Genome into GECCO- Genetics and Epidemiology of Colorectal Cancer Consortium Ulrike Peters Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center University of Washington U01-CA137088-05, PI: Peters
Integration of Cancer Genome into GECCO- Genetics and Epidemiology of Colorectal Cancer Consortium Ulrike Peters Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center University of Washington U01-CA137088-05, PI: Peters
Supplemental Information. Integrated Genomic Analysis of the Ubiquitin. Pathway across Cancer Types
 Cell Reports, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Integrated Genomic Analysis of the Ubiquitin Pathway across Zhongqi Ge, Jake S. Leighton, Yumeng Wang, Xinxin Peng, Zhongyuan Chen, Hu Chen, Yutong Sun,
Cell Reports, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Integrated Genomic Analysis of the Ubiquitin Pathway across Zhongqi Ge, Jake S. Leighton, Yumeng Wang, Xinxin Peng, Zhongyuan Chen, Hu Chen, Yutong Sun,
ncounter Assay Automated Process Capture & Reporter Probes Bind reporter to surface Remove excess reporters Hybridize CodeSet to RNA
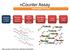 ncounter Assay Automated Process Hybridize CodeSet to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes mrna Capture & Reporter Probes slides
ncounter Assay Automated Process Hybridize CodeSet to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes mrna Capture & Reporter Probes slides
APPLICATION NOTE. Highly reproducible and Comprehensive Proteome Profiling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissues Slices
 APPLICATION NOTE Highly reproducible and Comprehensive Proteome Profiling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissues Slices INTRODUCTION Preservation of tissue biopsies is a critical step to This
APPLICATION NOTE Highly reproducible and Comprehensive Proteome Profiling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissues Slices INTRODUCTION Preservation of tissue biopsies is a critical step to This
Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma. Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
 Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Outline Anaplastic meningioma compared to other cancers Whole genomes
Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Outline Anaplastic meningioma compared to other cancers Whole genomes
DNA methylation signatures for 2016 WHO classification subtypes of diffuse gliomas
 Paul et al. Clinical Epigenetics (2017) 9:32 DOI 10.1186/s13148-017-0331-9 RESEARCH Open Access DNA methylation signatures for 2016 WHO classification subtypes of diffuse gliomas Yashna Paul, Baisakhi
Paul et al. Clinical Epigenetics (2017) 9:32 DOI 10.1186/s13148-017-0331-9 RESEARCH Open Access DNA methylation signatures for 2016 WHO classification subtypes of diffuse gliomas Yashna Paul, Baisakhi
Supplementary Figure 1. Estimation of tumour content
 Supplementary Figure 1. Estimation of tumour content a, Approach used to estimate the tumour content in S13T1/T2, S6T1/T2, S3T1/T2 and S12T1/T2. Tissue and tumour areas were evaluated by two independent
Supplementary Figure 1. Estimation of tumour content a, Approach used to estimate the tumour content in S13T1/T2, S6T1/T2, S3T1/T2 and S12T1/T2. Tissue and tumour areas were evaluated by two independent
Supplementary Figure 1. IDH1 and IDH2 mutation site sequences on WHO grade III
 Supplementary Materials: Supplementary Figure 1. IDH1 and IDH2 mutation site sequences on WHO grade III patient samples. Genomic DNA samples extracted from punch biopsies from either FFPE or frozen tumor
Supplementary Materials: Supplementary Figure 1. IDH1 and IDH2 mutation site sequences on WHO grade III patient samples. Genomic DNA samples extracted from punch biopsies from either FFPE or frozen tumor
MSI and other molecular markers: how useful are they? Daniela E. Aust, Institute for Pathology, University Hospital Dresden, Germany
 MSI and other molecular markers: how useful are they? Daniela E. Aust, Institute for Pathology, University Hospital Dresden, Germany Disclosure slide I Member of advisory boards for AMGEN, ROCHE I Speaker
MSI and other molecular markers: how useful are they? Daniela E. Aust, Institute for Pathology, University Hospital Dresden, Germany Disclosure slide I Member of advisory boards for AMGEN, ROCHE I Speaker
The Cancer Genome Atlas
 The Cancer Genome Atlas July 14, 2011 Kenna M. Shaw, Ph.D. Deputy Director The Cancer Genome Atlas Program TCGA: Core Objectives Launched in 2006 as a pilot and expanded in 2009, the goals of TCGA are
The Cancer Genome Atlas July 14, 2011 Kenna M. Shaw, Ph.D. Deputy Director The Cancer Genome Atlas Program TCGA: Core Objectives Launched in 2006 as a pilot and expanded in 2009, the goals of TCGA are
La genetica del carcinoma colo-rettale
 La genetica del carcinoma colo-rettale Ivana Cataldo Ospedale Ca Foncello, Treviso ARC-NET Centro di Ricerca Applicata sul Cancro AOUI, Verona OUTLINE What s new in colorectal cancer? Pathological Markers
La genetica del carcinoma colo-rettale Ivana Cataldo Ospedale Ca Foncello, Treviso ARC-NET Centro di Ricerca Applicata sul Cancro AOUI, Verona OUTLINE What s new in colorectal cancer? Pathological Markers
Broad GDAC. Lung Adenocarcinoma AWG Run 2013_02_07. Dan DiCara Hailei Zhang Michael Noble
 Broad GDAC Lung Adenocarcinoma AWG Run 2013_02_07 Dan DiCara Hailei Zhang Michael Noble Copyright 2013 Broad Institute. All rights reserved. gdac@broadinstitute.org http://gdac.broadinstitute.org GDAC
Broad GDAC Lung Adenocarcinoma AWG Run 2013_02_07 Dan DiCara Hailei Zhang Michael Noble Copyright 2013 Broad Institute. All rights reserved. gdac@broadinstitute.org http://gdac.broadinstitute.org GDAC
From Biostatistics Using JMP: A Practical Guide. Full book available for purchase here. Chapter 1: Introduction... 1
 From Biostatistics Using JMP: A Practical Guide. Full book available for purchase here. Contents Dedication... iii Acknowledgments... xi About This Book... xiii About the Author... xvii Chapter 1: Introduction...
From Biostatistics Using JMP: A Practical Guide. Full book available for purchase here. Contents Dedication... iii Acknowledgments... xi About This Book... xiii About the Author... xvii Chapter 1: Introduction...
Predicting clinical outcomes in neuroblastoma with genomic data integration
 Predicting clinical outcomes in neuroblastoma with genomic data integration Ilyes Baali, 1 Alp Emre Acar 1, Tunde Aderinwale 2, Saber HafezQorani 3, Hilal Kazan 4 1 Department of Electric-Electronics Engineering,
Predicting clinical outcomes in neuroblastoma with genomic data integration Ilyes Baali, 1 Alp Emre Acar 1, Tunde Aderinwale 2, Saber HafezQorani 3, Hilal Kazan 4 1 Department of Electric-Electronics Engineering,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
PBZ FT01_PBZ FT01_TZ FT01_NZ. interface zone (I) tumor zone (TZ) necrotic zone (NZ)
 Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ SUPPLEMENTRY FLES ndividuals factor map (P) FT_ FT_ FT_ Dim (.%) Dim (.%) >% peripheral brain zone () around % interface zone () FT
Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ SUPPLEMENTRY FLES ndividuals factor map (P) FT_ FT_ FT_ Dim (.%) Dim (.%) >% peripheral brain zone () around % interface zone () FT
Supplementary. properties of. network types. randomly sampled. subsets (75%
 Supplementary Information Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common system-level prognostic genes across cancer types properties of Supplementary Figure 1 The robustness and overlap of prognostic
Supplementary Information Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common system-level prognostic genes across cancer types properties of Supplementary Figure 1 The robustness and overlap of prognostic
Supplementary Figure 1: Attenuation of association signals after conditioning for the lead SNP. a) attenuation of association signal at the 9p22.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Attenuation of association signals after conditioning for the lead SNP. a) attenuation of association signal at the 9p22.32 PCOS locus after conditioning for the lead SNP rs10993397;
Supplementary Figure 1: Attenuation of association signals after conditioning for the lead SNP. a) attenuation of association signal at the 9p22.32 PCOS locus after conditioning for the lead SNP rs10993397;
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Supplemental Figure legends
 Supplemental Figure legends Supplemental Figure S1 Frequently mutated genes. Frequently mutated genes (mutated in at least four patients) with information about mutation frequency, RNA-expression and copy-number.
Supplemental Figure legends Supplemental Figure S1 Frequently mutated genes. Frequently mutated genes (mutated in at least four patients) with information about mutation frequency, RNA-expression and copy-number.
Abstract. Optimization strategy of Copy Number Variant calling using Multiplicom solutions APPLICATION NOTE. Introduction
 Optimization strategy of Copy Number Variant calling using Multiplicom solutions Michael Vyverman, PhD; Laura Standaert, PhD and Wouter Bossuyt, PhD Abstract Copy number variations (CNVs) represent a significant
Optimization strategy of Copy Number Variant calling using Multiplicom solutions Michael Vyverman, PhD; Laura Standaert, PhD and Wouter Bossuyt, PhD Abstract Copy number variations (CNVs) represent a significant
Nature Getetics: doi: /ng.3471
 Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of exome sequencing data. ( a ) Exome tumor normal sample sizes for bladder cancer (BLCA), breast cancer (BRCA), carcinoid (CARC), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLLX), colorectal
Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of exome sequencing data. ( a ) Exome tumor normal sample sizes for bladder cancer (BLCA), breast cancer (BRCA), carcinoid (CARC), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLLX), colorectal
Supporting Information. Lysine Propionylation to Boost Proteome Sequence. Coverage and Enable a Silent SILAC Strategy for
 Supporting Information Lysine Propionylation to Boost Proteome Sequence Coverage and Enable a Silent SILAC Strategy for Relative Protein Quantification Christoph U. Schräder 1, Shaun Moore 1,2, Aaron A.
Supporting Information Lysine Propionylation to Boost Proteome Sequence Coverage and Enable a Silent SILAC Strategy for Relative Protein Quantification Christoph U. Schräder 1, Shaun Moore 1,2, Aaron A.
Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation
 Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation Hang Yu, 1, 2, a) Wei Han, 1, 3, b) Wen Ma, 1, 2 1, 2, 3, c) and Klaus Schulten 1) Beckman
Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation Hang Yu, 1, 2, a) Wei Han, 1, 3, b) Wen Ma, 1, 2 1, 2, 3, c) and Klaus Schulten 1) Beckman
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/content/355/6332/eaai8478/suppl/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Decoupling genetics, lineages, and microenvironment in IDH-mutant gliomas by single-cell RNA-seq Andrew S. Venteicher,
www.sciencemag.org/content/355/6332/eaai8478/suppl/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Decoupling genetics, lineages, and microenvironment in IDH-mutant gliomas by single-cell RNA-seq Andrew S. Venteicher,
TITLE: Total RNA Sequencing Analysis of DCIS Progressing to Invasive Breast Cancer.
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0080 TITLE: Total RNA Sequencing Analysis of DCIS Progressing to Invasive Breast Cancer. PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Christopher B. Umbricht, MD, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0080 TITLE: Total RNA Sequencing Analysis of DCIS Progressing to Invasive Breast Cancer. PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Christopher B. Umbricht, MD, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns
Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser
 Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser Melissa S. Cline 1*, Brian Craft 1, Teresa Swatloski 1, Mary Goldman 1, Singer Ma 1, David Haussler 1, Jingchun Zhu 1 1 Center for Biomolecular
Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser Melissa S. Cline 1*, Brian Craft 1, Teresa Swatloski 1, Mary Goldman 1, Singer Ma 1, David Haussler 1, Jingchun Zhu 1 1 Center for Biomolecular
Colorectal Cancer in 2017: From Biology to the Clinics. Rodrigo Dienstmann
 Colorectal Cancer in 2017: From Biology to the Clinics Rodrigo Dienstmann MOLECULAR CLASSIFICATION Tumor cell Immune cell Tumor microenvironment Stromal cell MOLECULAR CLASSIFICATION Biomarker Tumor cell
Colorectal Cancer in 2017: From Biology to the Clinics Rodrigo Dienstmann MOLECULAR CLASSIFICATION Tumor cell Immune cell Tumor microenvironment Stromal cell MOLECULAR CLASSIFICATION Biomarker Tumor cell
Expanded View Figures
 EMO Molecular Medicine Proteomic map of squamous cell carcinomas Hanibal ohnenberger et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. Technical reproducibility. Pearson s correlation analysis of normalised SILC
EMO Molecular Medicine Proteomic map of squamous cell carcinomas Hanibal ohnenberger et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. Technical reproducibility. Pearson s correlation analysis of normalised SILC
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs.
 Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity
 Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity A Consistently unmethylated sites (30%) in 21 cancer types 174,696
Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity A Consistently unmethylated sites (30%) in 21 cancer types 174,696
HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA LEO TUNKLE *
 CERNA SEARCH METHOD IDENTIFIED A MET-ACTIVATED SUBGROUP AMONG EGFR DNA AMPLIFIED LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA PATIENTS HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA Email:
CERNA SEARCH METHOD IDENTIFIED A MET-ACTIVATED SUBGROUP AMONG EGFR DNA AMPLIFIED LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA PATIENTS HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA Email:
Mosaic loss of chromosome Y in peripheral blood is associated with shorter survival and higher risk of cancer
 Supplementary Information Mosaic loss of chromosome Y in peripheral blood is associated with shorter survival and higher risk of cancer Lars A. Forsberg, Chiara Rasi, Niklas Malmqvist, Hanna Davies, Saichand
Supplementary Information Mosaic loss of chromosome Y in peripheral blood is associated with shorter survival and higher risk of cancer Lars A. Forsberg, Chiara Rasi, Niklas Malmqvist, Hanna Davies, Saichand
Machine Learning! Robert Stengel! Robotics and Intelligent Systems MAE 345,! Princeton University, 2017
 Machine Learning! Robert Stengel! Robotics and Intelligent Systems MAE 345,! Princeton University, 2017 A.K.A. Artificial Intelligence Unsupervised learning! Cluster analysis Patterns, Clumps, and Joining
Machine Learning! Robert Stengel! Robotics and Intelligent Systems MAE 345,! Princeton University, 2017 A.K.A. Artificial Intelligence Unsupervised learning! Cluster analysis Patterns, Clumps, and Joining
Introduction. Introduction
 Introduction We are leveraging genome sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to more accurately define mutated and stable genes and dysregulated metabolic pathways in solid tumors. These efforts
Introduction We are leveraging genome sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to more accurately define mutated and stable genes and dysregulated metabolic pathways in solid tumors. These efforts
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Statistical Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Microarrays in Cancer Studies
 Statistical Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Microarrays in Cancer Studies Stanford Biostatistics Workshop Pierre Neuvial with Henrik Bengtsson and Terry Speed Department of Statistics, UC Berkeley
Statistical Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Microarrays in Cancer Studies Stanford Biostatistics Workshop Pierre Neuvial with Henrik Bengtsson and Terry Speed Department of Statistics, UC Berkeley
Next Generation Cancer Diagnostics For First Time Right Therapy Choice. Anja van de Stolpe
 Next Generation Cancer Diagnostics For First Time Right Therapy Choice Anja van de Stolpe Paradigm shift in cancer treatment towards personalized treatment Chemotherapy for all therapy targeting cancer
Next Generation Cancer Diagnostics For First Time Right Therapy Choice Anja van de Stolpe Paradigm shift in cancer treatment towards personalized treatment Chemotherapy for all therapy targeting cancer
Supplementary Table 1. PIK3CA mutation in colorectal cancer
 Liao X et al. PIK3CA Mutation in Colorectal Cancer. Page 1 Supplementary Table 1. PIK3CA mutation in colorectal cancer Exon Domain Nucleotide change* Amino acid change* cases 9 Helical c.1621t>a p.e541t
Liao X et al. PIK3CA Mutation in Colorectal Cancer. Page 1 Supplementary Table 1. PIK3CA mutation in colorectal cancer Exon Domain Nucleotide change* Amino acid change* cases 9 Helical c.1621t>a p.e541t
Genetic alterations of histone lysine methyltransferases and their significance in breast cancer
 Genetic alterations of histone lysine methyltransferases and their significance in breast cancer Supplementary Materials and Methods Phylogenetic tree of the HMT superfamily The phylogeny outlined in the
Genetic alterations of histone lysine methyltransferases and their significance in breast cancer Supplementary Materials and Methods Phylogenetic tree of the HMT superfamily The phylogeny outlined in the
Putative effectors for prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma are ethnic and gender specific
 /, Advance Publications 2015 Putative effectors for prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma are ethnic and gender specific Andrew Woolston 1, Nardnisa Sintupisut 1, Tzu-Pin Lu 2, Liang-Chuan Lai 3, Mong-Hsun
/, Advance Publications 2015 Putative effectors for prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma are ethnic and gender specific Andrew Woolston 1, Nardnisa Sintupisut 1, Tzu-Pin Lu 2, Liang-Chuan Lai 3, Mong-Hsun
Supplementary Figure 1. Experimental paradigm. A combination of genome and exome sequencing coupled with array-comparative genome hybridization was
 Supplementary Figure 1. Experimental paradigm. A combination of genome and exome sequencing coupled with array-comparative genome hybridization was performed on a total of 85 SS patients. Data filtration
Supplementary Figure 1. Experimental paradigm. A combination of genome and exome sequencing coupled with array-comparative genome hybridization was performed on a total of 85 SS patients. Data filtration
Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis
 5/17/13 Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis Johannes Kratz, MD Post-doctoral Fellow, Thoracic Oncology Laboratory
5/17/13 Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis Johannes Kratz, MD Post-doctoral Fellow, Thoracic Oncology Laboratory
Risk-prediction modelling in cancer with multiple genomic data sets: a Bayesian variable selection approach
 Risk-prediction modelling in cancer with multiple genomic data sets: a Bayesian variable selection approach Manuela Zucknick Division of Biostatistics, German Cancer Research Center Biometry Workshop,
Risk-prediction modelling in cancer with multiple genomic data sets: a Bayesian variable selection approach Manuela Zucknick Division of Biostatistics, German Cancer Research Center Biometry Workshop,
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Rates of different mutation types in CRC.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Rates of different mutation types in CRC. (a) Stratification by mutation type indicates that C>T mutations occur at a significantly greater rate than other types. (b) As for the
Supplementary Figure 1 Rates of different mutation types in CRC. (a) Stratification by mutation type indicates that C>T mutations occur at a significantly greater rate than other types. (b) As for the
TITLE: Unique Genomic Alterations in Prostate Cancers in African American Men
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0046 TITLE: Unique Genomic Alterations in Prostate Cancers in African American Men PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Ittmann, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Baylor College
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0046 TITLE: Unique Genomic Alterations in Prostate Cancers in African American Men PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Ittmann, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Baylor College
Supplementary Figure 1. Copy Number Alterations TP53 Mutation Type. C-class TP53 WT. TP53 mut. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.
 Supplementary Figure a Copy Number Alterations in M-class b TP53 Mutation Type Recurrent Copy Number Alterations 8 6 4 2 TP53 WT TP53 mut TP53-mutated samples (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 Missense Truncating M-class
Supplementary Figure a Copy Number Alterations in M-class b TP53 Mutation Type Recurrent Copy Number Alterations 8 6 4 2 TP53 WT TP53 mut TP53-mutated samples (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 Missense Truncating M-class
Nationwide Children s Hospital Biospecimen Core Resource Training
 Nationwide Children s Hospital Biospecimen Core Resource Training Team Science: A Collaboration in Medical Genomics Sponsored by the National Cancer Institute, the National Institutes of Health Nationwide
Nationwide Children s Hospital Biospecimen Core Resource Training Team Science: A Collaboration in Medical Genomics Sponsored by the National Cancer Institute, the National Institutes of Health Nationwide
CoINcIDE: A framework for discovery of patient subtypes across multiple datasets
 Planey and Gevaert Genome Medicine (2016) 8:27 DOI 10.1186/s13073-016-0281-4 METHOD CoINcIDE: A framework for discovery of patient subtypes across multiple datasets Catherine R. Planey and Olivier Gevaert
Planey and Gevaert Genome Medicine (2016) 8:27 DOI 10.1186/s13073-016-0281-4 METHOD CoINcIDE: A framework for discovery of patient subtypes across multiple datasets Catherine R. Planey and Olivier Gevaert
Supplemental Digital Content 1: Supplemental Results
 Supplemental Digital Content 1: Supplemental Results Fig. 1 presents the normalized symbolic transfer entropy (NSTE) matrix of eight electroencephalographic channels and significant changes of connectivity
Supplemental Digital Content 1: Supplemental Results Fig. 1 presents the normalized symbolic transfer entropy (NSTE) matrix of eight electroencephalographic channels and significant changes of connectivity
Colon Cancer and Hereditary Cancer Syndromes
 Colon Cancer and Hereditary Cancer Syndromes Gisela Keller Institute of Pathology Technische Universität München gisela.keller@lrz.tum.de Colon Cancer and Hereditary Cancer Syndromes epidemiology models
Colon Cancer and Hereditary Cancer Syndromes Gisela Keller Institute of Pathology Technische Universität München gisela.keller@lrz.tum.de Colon Cancer and Hereditary Cancer Syndromes epidemiology models
Supplementary Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs
 Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Applications. DSC 410/510 Multivariate Statistical Methods. Discriminating Two Groups. What is Discriminant Analysis
 DSC 4/5 Multivariate Statistical Methods Applications DSC 4/5 Multivariate Statistical Methods Discriminant Analysis Identify the group to which an object or case (e.g. person, firm, product) belongs:
DSC 4/5 Multivariate Statistical Methods Applications DSC 4/5 Multivariate Statistical Methods Discriminant Analysis Identify the group to which an object or case (e.g. person, firm, product) belongs:
Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood
 Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood tree illustrating CRF01_AE gp120 protein sequence relationships between 107 Envs sampled in the RV144 trial
Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood tree illustrating CRF01_AE gp120 protein sequence relationships between 107 Envs sampled in the RV144 trial
Multiplexed Cancer Pathway Analysis
 NanoString Technologies, Inc. Multiplexed Cancer Pathway Analysis for Gene Expression Lucas Dennis, Patrick Danaher, Rich Boykin, Joseph Beechem NanoString Technologies, Inc., Seattle WA 98109 v1.0 MARCH
NanoString Technologies, Inc. Multiplexed Cancer Pathway Analysis for Gene Expression Lucas Dennis, Patrick Danaher, Rich Boykin, Joseph Beechem NanoString Technologies, Inc., Seattle WA 98109 v1.0 MARCH
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant
 National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
Development of Carcinoma Pathways
 The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
Interactive analysis and quality assessment of single-cell copy-number variations
 Interactive analysis and quality assessment of single-cell copy-number variations Tyler Garvin, Robert Aboukhalil, Jude Kendall, Timour Baslan, Gurinder S. Atwal, James Hicks, Michael Wigler, Michael C.
Interactive analysis and quality assessment of single-cell copy-number variations Tyler Garvin, Robert Aboukhalil, Jude Kendall, Timour Baslan, Gurinder S. Atwal, James Hicks, Michael Wigler, Michael C.
Research Strategy: 1. Background and Significance
 Research Strategy: 1. Background and Significance 1.1. Heterogeneity is a common feature of cancer. A better understanding of this heterogeneity may present therapeutic opportunities: Intratumor heterogeneity
Research Strategy: 1. Background and Significance 1.1. Heterogeneity is a common feature of cancer. A better understanding of this heterogeneity may present therapeutic opportunities: Intratumor heterogeneity
Enterprise Interest Thermo Fisher Scientific / Employee
 Enterprise Interest Thermo Fisher Scientific / Employee A next-generation sequencing assay to estimate tumor mutation load from FFPE research samples Fiona Hyland. Director of R&D, Bioinformatics Clinical
Enterprise Interest Thermo Fisher Scientific / Employee A next-generation sequencing assay to estimate tumor mutation load from FFPE research samples Fiona Hyland. Director of R&D, Bioinformatics Clinical
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
