Biology 3201 Midterm Examination January 27 th, 2012
|
|
|
- Jack Richards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology 3201 Midterm Examination January 27 th, 2012 Instructions for Students: 1 This test is composed of two parts. Part 1 consists of 60 multiple choice items. Part 2 consists of constructed response items. 2 The total value of the test is 70 marks. 3 Students are to use the Multiple Choice Answer sheet to complete Part 1. 4 Part 2 questions are to be completed directly on the paper provided. If extra paper is required, students must ensure they have their name and site included at the top of the page. 5 Students MUST complete ALL questions from part 2. Instructions to M-team Members 1 When students have finished the examination, please collect all materials. 2 Collate the multiple choice answer sheets and constructed response portion for each student. Place them in order by student 3 Scan ALL tests together (except the multiple choice questions not needed) and save as one complete file. Give the file the following name B3Midterm_yourschool where yourschool = your school name. Load the test into the Exam drop box found in the CDLI portal.
2 Section A Selected Response. Biology 3201 Midterm 2012 Indicate the answers to each of the following questions in the provided answer sheet. 1. Damage to which structure below would result in the heart stopping? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 2. Which nervous system division is directly responsible for relaying information to and from the skeletal muscles? (A) autonomic (B) parasympathetic (C) somatic (D) sympathetic 3. In which order does an impulse pass through a reflex arc? (A) receptor motor neuron interneuron sensory neuron effector (B) receptor motor neuron sensory neuron interneuron effector (C) receptor sensory neuron motor neuron interneuron effector (D) receptor sensory neuron interneuron motor neuron effector
3 4. Which structure below is responsible for receiving information from another neuron? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 5. Which shows the ion distribution inside the neuron membrane during an action potential? 6. Which best describes the role of cholinesterase? (A) breaking down a neurotransmitter (B) inhibiting a post-synaptic neuron (C) stimulating a post-synaptic neuron (D) synthesizing a neurotransmitter 7. Which nervous system disorder is caused by low dopamine production? (A) Alzheimer s (B) Meningitis (C) Multiple Sclerosis (D) Parkinson s 8. Which technology would produce a 3-D image of the brain? (A) CAT Scan (B) EEG (C) PET Scan (D) X-ray 9. Which structure of the eye enables a person to see in low light situations? (A) cones (B) cornea (C) rods (D) sclera
4 10. Which structure below allows air pressure to equalize? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 11. Which structure is part of the central nervous system? (A) heart (B) skin (C) spinal cord (D) thyroid gland 12. Which part of the brain controls hunger, body temperature, and aggression? (A) cerebellum (B) cerebrum (C) hypothalamus (D) thalamus 13. Which division of the nervous system is directly responsible for physiological responses to fear? (A) parasympathetic (B) sensory (C) somatic (D) sympathetic
5 14. Which region of the neuron below enhances the rate of impulse transmission? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 15. What is the normal ion distribution outside the neural membrane when a neuron is at rest? 16. Which neurotransmitter stimulates skeletal muscles but inhibits cardiac muscles? (A) acetylcholine (B) dopamine (C) glutamate (D) serotonin 17. Which part of the nerve cell is affected most by multiple sclerosis? (A) axon (B) cell body (C) dendrites (D) myelin sheath
6 18. Which part of the human eye is considered to be an adaptation for living in a low light environment? (A) cones (B) iris (C) retina (D) rods 19. Which structure of the human ear allows air pressure to equalize? (A) cochlea (B) eustachian tube (C) hammer (D) semi-circular canal 20. In which part of the brain is all the information from our senses sorted and interpreted? (A) cerebellum (B) cerebrum (C) medulla oblongata (D) midbrain 21. Which would receive information from a sensory neuron? (A) brain (B) gland (C) muscle (D) receptor 22. Which structure has been damaged if a needle being put into the arm of a stroke patient cannot be felt by the patient? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 23. Which neurotransmitter elevates mood and controls skeletal muscles? (A) dopamine (B) glutamate (C) noradrenaline (D) oxytocin 24. Which is caused by the gradual death of the neurons that produce dopamine? (A) Alzheimer s disease (B) meningitis (C) multiple sclerosis (D) Parkinson s disease
7 25. The data below were collected by a micro-electrode implanted in the membrane of a neuron. Which represents the point at which the potassium ion concentration inside the cell membrane is lowest? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 26. Which disease of the human eye is caused by a buildup of aqueous humour between the lens and the cornea? (A) astigmatism (B) cataract (C) glaucoma (D) myopia 27. Which medical procedure would most likely be used if a patient were diagnosed with cataracts? (A) contact lenses (B) corneal transplant (C) laser surgery (D) lens replacement 28. Which is most typical of nerve deafness? (A) It is caused by damage to the eardrum or ossicles. (B) It is caused by damage to the hair cells in the cochlea. (C) It is more common in younger people. (D) It results in loss of balance and coordination. 29. Which endocrine gland releases thyroxin? (A) adrenal (B) hypothalamus (C) pineal (D) thyroid 30. Which hormone triggers the cellular release of glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids into the bloodstream? (A) glucagon (B) insulin (C) melatonin (D) thyroxine 31. Why might a doctor prescribe exposure to sunlight for a person experiencing symptoms of depression and an overwhelming desire for sleep? (A) decrease melatonin levels (B) decrease somatotropin levels (C) increase acetylcholine levels (D) increase thyroxine levels
8 32. Which gland secretes melatonin? Biology 3201 Midterm 2012 (A) lacrimal (B) pineal (C) pituitary (D) sweat 33. Which gland functions improperly when there is a lack of iodine in the diet? (A) adrenal (B) salivary (C) tear (D) thyroid 34. Why do protein hormones need to trigger a second messenger to activate a target cell? (A) They are not water soluble. (B) They bind to multiple types of cells. (C) They cannot cross cell membranes. (D) They require activation by ATP. 35. Which disorder is caused by an over-secretion of the human growth hormone (HGH)? (A) diabetes mellitus (B) dwarfism (C) giantism (D) hyperthyroidism 36. Which would result if the target gland were not stimulated during a negative feedback loop? (A) The hypothalamus would be inhibited. (B) The hypothalamus would be stimulated. (C) The target gland would not secrete its hormone. (D) The target gland would secrete its hormone. 37. The graph below shows the blood glucose levels of a healthy person over a short period of time. Which hormone is most likely secreted by the pancreas at point A? (A) glucagon (B) insulin (C) melatonin (D) somatotropin
9 38. Which hormone best fits the graph below? (A) adrenaline (B) estrogen (C) melatonin (D) thyroxine 39. Which would result if the target gland were not stimulated during a negative feedback loop? (A) The hypothalamus would be inhibited. (B) The hypothalamus would be stimulated. (C) The target gland would not secrete its hormone. (D) The target gland would secrete its hormone. 40. Which hormone acts on a positive feedback control mechanism? (A) calcitonin (B) oxytocin (C) parathyroid (D) thyroxine 41. Which phase is indicated in the diagram below? (A) anaphase (B) metaphase (C) prophase (D) telophase
10 42. An error in which stage of meiosis would produce a human egg cell with 24 chromosomes? (A) anaphase (I) (B) prophase (I) (C) metaphase (II) (D) telophase (II) 43. Which best describes a sperm cell? (A) contains large amounts of cytoplasm (C) larger size than egg cells (B) diploid (D) motile 44. Which involves culturing human cells for treating medical disorders? (A) amniocentesis (B) fetoscopy (C) in vitro maturation (D) therapeutic cloning 45. Which type of asexual reproduction is used by bacteria? (A) binary fission (B) budding (C) fragmentation (D) parthenogenesis 46. Which best describes why human sperm may lack energy to swim to the egg? (A) The acrosome s contents have been emptied. (B) The middle piece of the sperm cell is damaged. (C) The prostate gland secretes an acid fluid. (D) The scrotum holds the testis too close to the body. 47. What is structure A in the diagram below? (A) anther (B) pistil (C) pollen (D) stigma
11 48. What is structure A in the diagram below? Biology 3201 Midterm 2012 (A) epididymis (B) prostate (C) urethra (D) van deferens 49. In which structure below does fertilization occur? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 50. Which structure is shed during normal menstrual flow? (A) cervix (B) endometrium (C) fimbriae (D) oviduct 51. Which sexually transmitted infection most commonly affects the liver? (A) chlamydia (B) gonorrhea (C) hepatitis (D) syphilis
12 52. Which requires superovulation? (A) artifical insemination (C) tubal ligation (B) in vitro fertilization (D) vasectomy 53. What is the most probable explanation for the hormone levels at day 17 below? (A) Corpus luteum prohibits FSH production. (B) Menstruation is occurring. (C) The egg is being released. (D) The female is using oral contraceptives. 54. Which is best for regulating menstrual cycles? (A) birth control pill (B) rhythm method (C) spermicidal jelly (D) tubal ligation 55. Which is the correct pathway of sperm to the egg? (A) vagina- cervix oviduct - uterus (B) vagina cervix uterus - oviduct (C) vagina oviduct - cervix - uterus (D) vagina oviduct - uterus - cervix 56. Which hormone maintains the corpus luteum for the first three months of pregnancy and can also be detected in the urine of a pregnant woman? (A) follicle stimulating hormone (B) human chorionic gonadotropin (C) human growth hormone (D) thyroid stimulating hormone
13 57. Which method of birth control is most effective at preventing sperm from entering the cervix? (A) condom (B) IUD (C) rhythm method (D) tubal ligation 58. What is true when progesterone levels are high during the menstrual cycle? (A) Estrogen production is inhibited. (B) Estrogen production is stimulated. (C) Luteinizing hormone production is inhibited. (D) Luteinizing hormone production is stimulated. 59. The diagram below shows the growth pattern of some human skin cells after they have been exposed to ultraviolet radiation. What type of cells are most likely found in area X? (A) cancer (B) red blood (C) sex (D) white blood 60. Double fertilization leads to the production of which two structures in flowering plants? (A) endosperm and pollen (B) endosperm and zygote (C) ovule and seed (D) ovule and zygote
14 Section A Answer Sheet Place your answers to the questions from section A in the table below. Section A Answer Sheet Section B Constructed Reponse Answer all Questions in the provided Space 1.. If a person experienced memory loss after a concussion, which part of the brain was most likely injured? Explain how you know this. (2 Marks) 2. Using a diagram to illustrate explain how the body maintains Glucose balance in the body. (4 Marks)
15 3. Due to a mutation, the sodium binding site on a sodium potassium pump has changed such that it now binds with chloride ions (Cl-). Sodium ions (Na+) remain inside the membrane. What happens to nerve transmission? Give two reasons to justify your answer. (3 Marks) 4. The rhythm method is a method of birth control in which a couple does not have sexual intercourse while they believe ovulation is occurring. Give three biological reasons why this is an ineffective method of birth control. (3 Marks)
16 5. Describe in detail the process of Spermatogenesis. Use a diagram to assist. (4 Marks) 6. PID (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease) can reduce fertility in both males and Females. Explain how a person may develop PID and how it can cause infertility to develop. (4 Marks)
Biology 3201 Unit 1 Timeline. Page(s) in Text. Learning Objective # 4
 Biology 3201 Unit 1 Timeline 1 Learning Objective # 1 Analyze the nervous system and explain its structure and dynamics 1. Explain the basic structure and function of the central nervous system. Include:
Biology 3201 Unit 1 Timeline 1 Learning Objective # 1 Analyze the nervous system and explain its structure and dynamics 1. Explain the basic structure and function of the central nervous system. Include:
Bio 3201 Unit 2 REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT. Cell Division MITOSIS (P )
 Bio 3201 Unit 2 REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT 31 Hours Cell Division MITOSIS (P. 460-469) 1. Describe mitosis in detail; Specifically describe, in detail, the events of interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis
Bio 3201 Unit 2 REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT 31 Hours Cell Division MITOSIS (P. 460-469) 1. Describe mitosis in detail; Specifically describe, in detail, the events of interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis
Biology 3201 The Nervous System Test
 Biology 3201 The Nervous System Test 1. The central nervous system consists of: a. Nerves and neurons c. spinal chord and nerves b. brain and neurons d. brain and spinal chord 2. This part of the brain
Biology 3201 The Nervous System Test 1. The central nervous system consists of: a. Nerves and neurons c. spinal chord and nerves b. brain and neurons d. brain and spinal chord 2. This part of the brain
1. The diagram below represents the homeostatic control of body temperature. What does the part labelled X represent? D. Hypothalamus (Total 1 mark)
 1. The diagram below represents the homeostatic control of body temperature. What does the part labelled X represent? A. Heart B. Kidney C. Pituitary D. Hypothalamus 2. What is the sequence of operations
1. The diagram below represents the homeostatic control of body temperature. What does the part labelled X represent? A. Heart B. Kidney C. Pituitary D. Hypothalamus 2. What is the sequence of operations
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis. Regents Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
Endocrine System Hormones & Homeostasis 2009-2010 Homeostasis Homeostasis maintaining internal balance in the body organism must keep internal conditions stable even if environment changes also called
[CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY]
![[CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY] [CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY]](/thumbs/71/65616244.jpg) WORDBANK: Cholinesterase Dopamine Axon Choroid layer Cochlea Incus Action Potential Cataract Cornea Astigmatism Dendrite Malleus Alzheimer s Disease Central Excitatory Response Fovea Centralis Acetylcholine
WORDBANK: Cholinesterase Dopamine Axon Choroid layer Cochlea Incus Action Potential Cataract Cornea Astigmatism Dendrite Malleus Alzheimer s Disease Central Excitatory Response Fovea Centralis Acetylcholine
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: ( Division B) Boyceville Invite Dec. 3, 2016 (50pts.)
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: ( Division B) Boyceville Invite Dec. 3, 2016 (50pts.) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following statements
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: ( Division B) Boyceville Invite Dec. 3, 2016 (50pts.) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following statements
Study Guide. Biology 3101B. Science. Reproduction and Development. Adult Basic Education. Biology 2101A Biology 2101C Biology 3101A.
 Adult Basic Education Science Reproduction and Development Prerequisites: Biology 2101A Biology 2101C Biology 3101A Credit Value: 1 Text: Biology. Bullard, Chetty, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2003 Biology
Adult Basic Education Science Reproduction and Development Prerequisites: Biology 2101A Biology 2101C Biology 3101A Credit Value: 1 Text: Biology. Bullard, Chetty, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2003 Biology
Homeostasis AnswerIT The regulation of the internal conditions of a cell or organism to maintain optimum conditions.
 Homeostasis AnswerIT 1. Define homeostasis. The regulation of the internal conditions of a cell or organism to maintain optimum conditions. 2. Why does homeostasis need to maintain optimal conditions?
Homeostasis AnswerIT 1. Define homeostasis. The regulation of the internal conditions of a cell or organism to maintain optimum conditions. 2. Why does homeostasis need to maintain optimal conditions?
Homeostasis. Endocrine System Nervous System
 Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
This presentation will be posted to the website.
 This presentation will be posted to the website. 1. Steroid hormones operate by: A. crossing the cell membrane and triggering transcription for the appropriate protein B. attaching to the cell membrane
This presentation will be posted to the website. 1. Steroid hormones operate by: A. crossing the cell membrane and triggering transcription for the appropriate protein B. attaching to the cell membrane
Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism
 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
BIOLOGY Schwaan cell - cells that help to make up the myelin sheath.
 BIOLOGY 3201 TERMINOLOGY NERVOUS/ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS 1. Dendrite - hairlike receptors on the ends of neurons. 2. Neuron - Basic unit of the nervous system. 3. Soma - Cell body. 4. Axon - long extension leading
BIOLOGY 3201 TERMINOLOGY NERVOUS/ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS 1. Dendrite - hairlike receptors on the ends of neurons. 2. Neuron - Basic unit of the nervous system. 3. Soma - Cell body. 4. Axon - long extension leading
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Chapter 12 Nervous System Review Assignment
 Name: Class: Date: Chapter 12 Nervous System Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which part of a neuron receives an impulse
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 12 Nervous System Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which part of a neuron receives an impulse
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems. Chapter 39: Biology II
 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Grade 10 IGCSE_ Biology Term 1 Final Exam _ Study Guide. The exam lasts 120 minutes and will include:
 The exam lasts 120 minutes and will include: multiple Choice questions short-answers questions Alternative to practical Chapter 14 Coordination and response, P: 161-174 14.1 Nervous control in humans Describe
The exam lasts 120 minutes and will include: multiple Choice questions short-answers questions Alternative to practical Chapter 14 Coordination and response, P: 161-174 14.1 Nervous control in humans Describe
These questions are meant for your review but it doesn t cover every part of what we learned in this unit.
 These questions are meant for your review but it doesn t cover every part of what we learned in this unit. Nervous System Review 1. What is a neuron? 2. Identify the three types of neurons. 3. What is
These questions are meant for your review but it doesn t cover every part of what we learned in this unit. Nervous System Review 1. What is a neuron? 2. Identify the three types of neurons. 3. What is
SBI4U PRACTICE QUIZ Endocrine and Nervous Systems
 SBI4U PRACTICE QUIZ Endocrine and Nervous Systems Part I: Multiple Choice 1. Steroid hormones operate by: A. crossing the cell membrane and starting transcription for the appropriate protein B. attaching
SBI4U PRACTICE QUIZ Endocrine and Nervous Systems Part I: Multiple Choice 1. Steroid hormones operate by: A. crossing the cell membrane and starting transcription for the appropriate protein B. attaching
Part 1- Biology Paper 2 Homeostasis and Response Knowledge Questions
 Part 1- Biology Paper 2 Homeostasis and Response Knowledge Questions AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.5 Homeostasis and response Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe what homeostasis is
Part 1- Biology Paper 2 Homeostasis and Response Knowledge Questions AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.5 Homeostasis and response Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe what homeostasis is
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY
 Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY 1. Describe, in correct order, the events that occur during the transmission of a nerve impulse (action potential) as it travels from point X to point Y.
Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY 1. Describe, in correct order, the events that occur during the transmission of a nerve impulse (action potential) as it travels from point X to point Y.
Summary The Endocrine System The Reproductive System Human Endocrine Glands. Endocrine and Reproductive Systems.
 Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Y11 Homeostasis & Response
 Key words: 1. Homeostasis: Maintaining a constant internal environment 2. Receptor: Detect a change in the environment 3. Effector: Muscle or gland that carries out a response 4. Stimulus: A change in
Key words: 1. Homeostasis: Maintaining a constant internal environment 2. Receptor: Detect a change in the environment 3. Effector: Muscle or gland that carries out a response 4. Stimulus: A change in
Y11 Homeostasis & Response
 Key words: 1. Homeostasis: Maintaining a constant internal environment 2. Receptor: Detects a change in the environment 3. Effector: Muscle or gland that carries out a response 4. Stimulus: A change in
Key words: 1. Homeostasis: Maintaining a constant internal environment 2. Receptor: Detects a change in the environment 3. Effector: Muscle or gland that carries out a response 4. Stimulus: A change in
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
1. When substances move from the nephron to the peritubular capillaries. This is known as:
 3 rd Test Sp 09 3:30 1. When substances move from the nephron to the peritubular capillaries. This is known as: a. secretion b. excretion c. reabsorption d. filtration 2. The nephron is located in the:
3 rd Test Sp 09 3:30 1. When substances move from the nephron to the peritubular capillaries. This is known as: a. secretion b. excretion c. reabsorption d. filtration 2. The nephron is located in the:
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
Biology 3201 Quiz on Nervous System. Total 33 points
 Biology 3201 Quiz on Nervous System Total 33 points Name: Circle the best response to the following: (33 points) 1. What do we call the long fibre that carries impulses away from the nerve cell body? A.
Biology 3201 Quiz on Nervous System Total 33 points Name: Circle the best response to the following: (33 points) 1. What do we call the long fibre that carries impulses away from the nerve cell body? A.
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
BIOLOGY 30 Review Assignment Part I
 BIOLOGY 30 Review Assignment Part I Nervous System Answer Sheet Question #1 Numeric Response #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 Question #5 Numeric Response #2 Numeric Response #3 Numeric Response
BIOLOGY 30 Review Assignment Part I Nervous System Answer Sheet Question #1 Numeric Response #1 Question #2 Question #3 Question #4 Question #5 Numeric Response #2 Numeric Response #3 Numeric Response
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Nervous System. Chapter Structure of the Nervous System. Neurons
 33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
YR 2 NERVOUS, SENSE ORGANS, ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS
 YR 2 NERVOUS, SENSE ORGANS, ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS Station A: Neurons and Reflex Arc Diagram 1 Diagram 2 Use the Diagram 1 in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled
YR 2 NERVOUS, SENSE ORGANS, ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS Station A: Neurons and Reflex Arc Diagram 1 Diagram 2 Use the Diagram 1 in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled
Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous System 2 C 1 2 : A N A L Y Z E T H E F U N C T I O N A L I N T E R R E L A T I O N S H I P S O F T H E D I V I S I O N S O F T H E N E R V O U S S Y S T E M Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
Nervous System 2 C 1 2 : A N A L Y Z E T H E F U N C T I O N A L I N T E R R E L A T I O N S H I P S O F T H E D I V I S I O N S O F T H E N E R V O U S S Y S T E M Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
School Islip Invy 16' Anatomy Team #
 School Islip Invy 16' Anatomy Team # Student #1 Student #2 1. If the smell of food cooking causes activation of the salivary glands, which system will cause inhibition of the secretion? A) Sympathetic
School Islip Invy 16' Anatomy Team # Student #1 Student #2 1. If the smell of food cooking causes activation of the salivary glands, which system will cause inhibition of the secretion? A) Sympathetic
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Endocrine System. A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body.
 Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System
 9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
Main Function: signal other cells to behave in certain. of communication.
 Main Function: It releases hormones into the blood to signal other cells to behave in certain ways. It is a slow but widespread form of communication. Consists of: Endocrine glands Release hormones into
Main Function: It releases hormones into the blood to signal other cells to behave in certain ways. It is a slow but widespread form of communication. Consists of: Endocrine glands Release hormones into
Web Activity: Simulation Structures of the Female Reproductive System
 differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Human Reproduction. Human Reproductive System. Scrotum. Male Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
BIO 115 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 4: The Nervous System & The Senses This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 115 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 4: The Nervous System & The Senses This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. This figure depicts a typical neuron. What structures
BIO 115 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 4: The Nervous System & The Senses This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. This figure depicts a typical neuron. What structures
Lesson 1. Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms
 Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Nervous and Endocrine System Exam Review
 Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Sex Chromosomes Polygenic Trait
 Semester 2 Final Study Guide Part 2 Name Inheritance Key Term Definition Example Gene Allele Trait Dominant Allele Dominant Trait Recessive Allele Recessive Trait Genotype Phenotype Homozygous Heterozygous
Semester 2 Final Study Guide Part 2 Name Inheritance Key Term Definition Example Gene Allele Trait Dominant Allele Dominant Trait Recessive Allele Recessive Trait Genotype Phenotype Homozygous Heterozygous
6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction
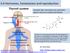 6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Thyroxin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It's key role is in controlling
6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Thyroxin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It's key role is in controlling
DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 14 Test
 Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
LIFE SCIENCES Grade 12 REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014
 REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014 Checklist Make sure you Can describe different reproductive strategies of vertebrates Are able to identify the structure and function of the male and female reproductive organs
REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014 Checklist Make sure you Can describe different reproductive strategies of vertebrates Are able to identify the structure and function of the male and female reproductive organs
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction
 Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
The beginning of puberty is marked by the progressive increase in the production of sex hormones.
 Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Introduction to Health Care & Careers. Chapter 27. Answers to Checkpoint and Review Questions
 Introduction to Health Care & Careers Chapter 27 Answers to Checkpoint and Review Questions Checkpoints 1. The nervous system can be divided functionally into two divisions. Which division is under a person
Introduction to Health Care & Careers Chapter 27 Answers to Checkpoint and Review Questions Checkpoints 1. The nervous system can be divided functionally into two divisions. Which division is under a person
Endocrine System Worksheet
 Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
MC 17 B SECTION I (40 Marks) Attempt all questions from this section.
 MC 17 B - 11 SECTION I (40 Marks) Attempt all questions from this section. Question 1 (a) Name the following. (i) The part of the female reproductive system where development of foetus is completed. (ii)
MC 17 B - 11 SECTION I (40 Marks) Attempt all questions from this section. Question 1 (a) Name the following. (i) The part of the female reproductive system where development of foetus is completed. (ii)
Fact Sheet B2.1 Homeostasis
 Fact Sheet B2.1 Homeostasis Homeostasis What is homeostasis? Why is homeostasis important? State the components that all control systems have. Describe the roles of the above components. Define negative
Fact Sheet B2.1 Homeostasis Homeostasis What is homeostasis? Why is homeostasis important? State the components that all control systems have. Describe the roles of the above components. Define negative
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Nervous System Integumentary System Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System
 Nervous System Integumentary System Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Excretory System Endocrine System Reproductive System Lymphatic/Immune Systems
Nervous System Integumentary System Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Excretory System Endocrine System Reproductive System Lymphatic/Immune Systems
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM 1) State the 3 functions of the nervous system. 1) 2) 3)
 UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
4-5 Homeostasis and response Trilogy
 4-5 Homeostasis and response Trilogy.0 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose (sugar) concentration may rise more than normal.. Which organ in the body monitors this rise in blood sugar? Tick one
4-5 Homeostasis and response Trilogy.0 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose (sugar) concentration may rise more than normal.. Which organ in the body monitors this rise in blood sugar? Tick one
B5 Quick Revision Questions
 B5 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 Why does body temperature need to be kept constant? Answer 1... of 50 Enzyme action Cellular functions Question
B5 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 Why does body temperature need to be kept constant? Answer 1... of 50 Enzyme action Cellular functions Question
Unit 2 Multiple Choice test
 Name: Date: 1. Resting potential is to action potential as is to. A) adrenal gland; pituitary gland B) sensory neuron; motor neuron C) temporal lobe; occipital lobe D) polarization; depolarization E) dendrite;
Name: Date: 1. Resting potential is to action potential as is to. A) adrenal gland; pituitary gland B) sensory neuron; motor neuron C) temporal lobe; occipital lobe D) polarization; depolarization E) dendrite;
Female Reproductive System. Lesson 10
 Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Part 1- Biology Paper 2 Homeostasis and Response Application Questions Triple Science
 Part 1- Biology Paper 2 Homeostasis and Response Application Questions Triple Science AQA Biology (8461) from 2016 Topic B4.5 Homeostasis and response Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe what homeostasis
Part 1- Biology Paper 2 Homeostasis and Response Application Questions Triple Science AQA Biology (8461) from 2016 Topic B4.5 Homeostasis and response Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe what homeostasis
Refer to the figure below, a diagram of a renal tubule, to answer the following questions.
 1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
Unit 5: Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis & Drug Influence Influence on Nervous System
 Unit 5: Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis & Drug Influence Influence on Nervous System 1. Which of the following is NOT related to a cell s surface area to volume ratio? a. Cell size b. Number of nuclei c.
Unit 5: Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis & Drug Influence Influence on Nervous System 1. Which of the following is NOT related to a cell s surface area to volume ratio? a. Cell size b. Number of nuclei c.
Human Reproductive Anatomy The female anatomy first just the reproductive parts:
 Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Class X: Biology. Chapter 2: Control and coordination.
 Class X: Biology Chapter 2: Control and coordination. Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) A system of control and coordination is essential in living organisms so that the different body parts can function
Class X: Biology Chapter 2: Control and coordination. Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) A system of control and coordination is essential in living organisms so that the different body parts can function
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Homeostasis and Response. AQA Biology topic 5
 Homeostasis and Response AQA Biology topic 5 5.1 Homeostasis Homeostasis: An introduction Wow it s hot here! What would happen if I stand here for too long? What would happen if I drank too much water?
Homeostasis and Response AQA Biology topic 5 5.1 Homeostasis Homeostasis: An introduction Wow it s hot here! What would happen if I stand here for too long? What would happen if I drank too much water?
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System
 Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Reproduction and Development. Female Reproductive System
 Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Biology 12 Human Biology - The Nervous System Name. Main reference: Biology Concepts and Connects Sixth edition Chapter 28
 Biology 12 Human Biology - The Nervous System Name Main reference: Biology Concepts and Connects Sixth edition Chapter 28 Vocabulary acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholinesterase (AChE), action potential,
Biology 12 Human Biology - The Nervous System Name Main reference: Biology Concepts and Connects Sixth edition Chapter 28 Vocabulary acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholinesterase (AChE), action potential,
Human Physiology 6.6- Hormones, Homeostasis, and Reproduction
 Human Physiology 6.6- Hormones, Homeostasis, and Reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Application: William Harvey s investigation of sexual reproduction
Human Physiology 6.6- Hormones, Homeostasis, and Reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Application: William Harvey s investigation of sexual reproduction
Biology of fertility control. Higher Human Biology
 Biology of fertility control Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Compare fertile periods in females and males What is infertility? Infertility is the inability of a sexually active, non-contracepting
Biology of fertility control Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Compare fertile periods in females and males What is infertility? Infertility is the inability of a sexually active, non-contracepting
Biology Chapter 12 The Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Chapter 12 The Nervous System The Nervous System The evolution of the human nervous system is the most complex of all organisms on Earth. How the human brain works is still one of the least
Biology 3201 Chapter 12 The Nervous System The Nervous System The evolution of the human nervous system is the most complex of all organisms on Earth. How the human brain works is still one of the least
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
I. Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission
 I. Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Objectives: Explain why psychologists are concerned with human biology. Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. Describe
I. Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Objectives: Explain why psychologists are concerned with human biology. Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. Describe
Endocrine Glands System. Agha Zohaib Khan
 Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling. Chapter 48
 Neurons, Synapses and Signaling Chapter 48 Warm Up Exercise What types of cells can receive a nerve signal? Nervous Organization Neurons- nerve cells. Brain- organized into clusters of neurons, called
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling Chapter 48 Warm Up Exercise What types of cells can receive a nerve signal? Nervous Organization Neurons- nerve cells. Brain- organized into clusters of neurons, called
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
