MIT 9.14 Class 15 Motor systems 2: Descending pathways and evolution; Temporal patterns
|
|
|
- Adrian Ryan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brain Structure and its Origins Spring 2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins G. E. Schneider 2005 Part 6: A brief look at motor systems MIT 9.14 Class 15 Motor systems 2: Descending pathways and evolution; Temporal patterns
2 Motoneuron Pools Central Pattern Generator Networks Magnocellular neuroendocrine Parvicellular neuroendocrine Parasympathetic autonomic Sympathetic autonomic The three motor systems (Where are the central pattern generator networks that coordinate the three systems?)* Somatomotor Figure by MIT OCW.
3 Distribution of somatic motor neurons III V VII X XI ce VH le =: : IV VI XII Where are these neurons located in frontal sections of CNS? Figure by MIT OCW.
4 The spatial arrangements of motor neurons in the spinal cord Spinal cord at one of the enlargements Illustrated for human and for monkey Radial projections of interneurons Descending connections in the cord (see figures)
5 Topographic distribution of somatic motor neurons, human spinal cord Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Please see Figure 6.3 in Swanson, Larry W. Brain Architecture, Understanding the Basic Plan. Oxford, New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 2003, p ISBN:
6 Topographic distribution of somatic motor neurons, human spinal cord Figure removed due to copyright reasons. From Lawrence & Kuypers, 1968
7 is Terminal distribution pattern of descending cortical and subcortical pathways, spinal cord, rhesus monkey (Lawrence & Kuypers, 1968) Figure removed due to copyright reasons.
8 Three Descending Motor Pathways: Distinguishing the course of axons influencing axial and distal muscle control [Enlarged on next slides]
9 Distinguishing the axons influencing axial vs distal muscles: Corticospinal pathway
10 Distinguishing the axons influencing axial vs distal muscles: Lateral and ventromedial brainstem pathways
11 Effects of lesions: The logic of Lawrence & Kuypers, 1968 paper in the journal Brain Begin with elimination of the corticospinal projections; wait for recovery from diaschisis effects Then, ablate either the medial or the lateral pathways descending from the hindbrain and midbrain
12 Lesion 1 Selective lesions of the descending motor pathways Lesion 3 added Lesion 2 added
13 Lawrence & Kuypers, 1968: Lesion #1: pyramidotomy Loss of speed and strength Loss of control of digits used one at a time
14 Lawrence & Kuypers, 1968: Lesion #2: destruction of medial brainstem pathways (added to pyramidotomy) Defective axial control: Righting: only after days Falling: failure to elicit the usual corrective movements Walking: only one monkey could take many steps because of disorientation; he veered from course, bumped into obstacles Better distal control: If monkey was strapped into a chair, it could grasp food objects with the whole hand
15 Lawrence & Kuypers, 1968: Lesion #3: destruction of lateral brainstem pathways (added to pyramidotomy) Defective limb control: Hand flexion done only with total arm movements Good axial control Hand used dramatically better in running & climbing (total body movements)
16 Brief digression: The brain disconnected from the motor output: Motor cortical activity in human tetraplegics Thought without the ability to act: Activation of specific parts of the motor cortex Question: Can the long pathways be reconnected in people or animals with such injuries?
17 Motor-cortical activity in tetraplegics Figures removed due to copyright reasons. Please see Figure 1 in Shoham, S., E. Halgren, E. M. Maynard, and R. A. Normann. "Motor-cortical activity in tetraplegics." Nature 413, no (October 25, 2001): 793.
18 Motor cortex and corticospinal projections in phylogeny (from Striedter, 2005) 1) The sensorimotor amalgam hypothesis VL and VP projections (projections to motor and somatosensory cortex): Opossum and rat compared 2) Corticospinal invasion and dexterity Correlated 3) Comparative analysis of corticospinal neurons More of them when total size of neocortex is greater
19 The sensorimotor amalgam hypothesis Figure removed due to copyright reasons.
20 Penetration of corticospinal axons into ventral horn vs. neocortical volume Figure removed due to copyright reasons.
21 Penetration of corticospinal axons down the spinal cord vs. neocortical volume Figure removed due to copyright reasons.
22 Correlations with dexterity Figure removed due to copyright reasons.
23 Neocortex : Spinal Cord Ratio vs. Neocortical Volume Figure removed due to copyright reasons. The greater invasion of spinal cord with increasing neocortical size fits Deacon s rule which is summarized as large equals well-connected.
24 Figure removed due to copyright reasons. (Upper) Corticospinal neuron locations and densities A) rhesus monkey B) squirrel monkey C) galago (bush baby) D) tree shrew E) squirrel F) rat G) domestic cat H) mole I) hedgehog J) opossum, short-tailed K) opossum, Virginia (Lower) Corticospinal neuron number vs. neocortical surface area
25 Rhythmic output and timing Topics Temporal patterns in animal movements: Explanations These have led to basic theoretical ideas of how the brain functions at the level of circuits Activity rhythms and behavioral state control: Underlying structures and pathways
26 Temporal patterns in movements: types of explanations Straight-through processing concepts (S-R models) Feedback circuitry Spontaneous CNS activity
27 Straight-through processing concepts (S-R models) Topics Timing of movements in reflexes Conduction time: temporal pattern in startle reflex Chaining of reflexes or fixed action patterns Lashley s 1917 paper: The problem of serial order in behavior :
28 Timing of movements in reflexes : Conduction time Temporal pattern in startle reflex: 1. eye blink, 2. then contraction of other facial muscles, 3. then neck flexion, 4. then arm flexion, 5. then leg flexion (with very intense sound). Timing due to: fiber size, synaptic delays; temporal summation times
29 Chaining of reflexes or fixed action patterns Tinbergen (1951): the stickleback s courtship pattern as an S-R series Reflex deglutition (swallowing reflex): Same or different type of explanation?
30 Tinbergen (1951): The courtship behavior of the three-spined stickleback fish Movements by a pair of animals rather than just one animal If a step is interrupted: The sequence cannot proceed Each step gives a necessary stimulus for triggering the next step. This is presented just to illustrate the chaining of S-R events, often called reflex chaining
31 Tinbergen (1951): The courtship behavior of the three-spine stickleback fish Female Appears, swollen belly Courts (approaches) Follows Enters nest Spawns Male Zig-zag dance Leads to nest Special posture at entrance Trembles, snout to her tail Fertilizes
32 Reflex deglutition (swallowing) Involves about 20 muscles controlled by neurons from midbrain to cervical spinal cord levels. In this case the pattern of contraction is centrally programmed: It is a fixed action pattern (FAP), inborn, and is executed rhythmically with a steady or varied stimulus via the superior laryngeal nerve. Pattern is not changed by elimination of proprioceptive feedback during any stage of the movement once it is triggered. It is normally triggered by stimulation of the tongue deep in the throat, but there is also an endogenous input that builds up over time and lowers the threshold for eliciting the response. [Study by Doty & Bosma, 1956]
33 Karl Lashley s 1917 paper: The problem of serial order in behavior He argued against the adequacy of the reflex chaining hypothesis. Example: The finger strokes of a musician may reach 16/sec in passages which call for a definite and changing order of successive finger movements. The succession of movements is too quick even for visual reaction time. Therefore, there must be central generation of patterns of movement.
34 Similarly, many fixed action patterns are centrally generated. They are inherited movement abilities. Grooming by mice (Fentriss experiments): Movement patterns continue even without the usual feedback stimulation. Egg rolling in gulls (Tinbergen): Movements can occur in absence of stimulus Other examples of in vacuo movement patterns Locomotor movements in fish: Central generation Locomotor movements in mammals are similarly generated in the spinal cord, but they require activation from the periphery or from descending fiber systems (from the brain) How are these action patterns generated, if not by reflex circuitry?
35 Temporal patterns in movements: types of explanations Straight-through processing concepts (S-R models) Feedback circuitry Spontaneous CNS activity
36 Feedback circuitry: the reverberating circuits idea Self re-exciting loops Æ regular bursts of action potentials (a kind of central oscillator) Negative feedback in homeostatic mechanisms: The response oscillates around a certain level of some input (the set point).
37 Feedback circuit: patterned output from unpatterned input
38 Complexity and control To get more complex patterns, combine more than one such circuit. How stop the rhythm? Example: Breathing rhythms can be at least partially explained by such circuits.
39 Temporal patterns in movements: types of explanations Straight-through processing concepts (S-R models) Feedback circuitry Spontaneous CNS activity
40 Spontaneous CNS activity Endogenously generated rhythmic potentials can also cause bursting patterns of action potentials Felix Strumwasser s Aplysia (sea slug) recordings Circadian rhythms in vertebrates
41 Felix Strumwasser s Aplysia (sea slug) experiments Recordings form an identifiable large secretory neuron of the abdominal ganglion: T=40 sec (rhythm persists if action potentials are blocked with TTX), but not if sodium pump is blocked with Ouabain. This cell also showed a circadian rhythm that could be entrained by light.
42 Endogenous oscillator The potential for complex temporal pattern generation: Multiple oscillators added together could give any pattern! This is known from the mathematics of Fourier Analysis.
43 Circadian rhythms in vertebrates Dependence of animals on such biological clocks with a period of approximately 24 hr. Temporal schedules are crucial to animal survival An intriguing experiment: Give mice heavy water (D 2 O,) and their free-running circadian activity rhythm slows down to a degree proportional to the % D 2 O in their drinking water. What is the anatomy of brain-state changes that underlie changes in behavioral state, such as going to sleep or becoming aroused?
44 Contributions to theory Study of how organized sequences of movement are produced, and how they can change, has led to the development of basic ideas about how the brain works. These ideas are basic organizing concepts in theories of CNS functions when we think of them at the level of connections and circuits.
45 Basic organizing concepts in theories of CNS functions: The circuit level Straight-through processing concepts Reflexes, S-R models Input analysis Feedback control Reverberating circuits (positive feedback) Reciprocal inhibition Homeostats Spontaneous CNS activity (of endogenous origin) Rhythmic activity; periodic bursts of activity Maintained excitatory states Plasticity (usually meaning a change in connections) Molecular (synaptic change, etc.) Anatomical (sprouting of various kinds)
46 Behavioral state control: Brain states influenced by widely projecting axon systems, and by chemical secretions State changes involve pathways fundamentally different from the type considered above. Examples: The reticular activating system Monoamine systems Widely projecting neurons of lateral hypothalamus Secretions into the cerebrospinal fluid should be added to this list, e.g., during sleep onset.
47 Reticular activating system: Example of widely distributed axon from hindbrain cell Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Many such cells use acetylcholine as their transmitter. Cholinergic cells with widely distributed axons are also found in the basal forebrain; the axons project to neocortex.
48 Monoamine systems Serotonin (5 hydroxy tryptamine, 5-HT) Neurons of the raphe nuclei with widely distributed axons Role in sleep and waking/arousal Reading: Allman pp Catecholamines Norepinephrine-containing axon systems, e.g., from the locus coeruleus of the rostral hindbrain Role in sleep and waking/arousal Dopamine-containing axon systems, e.g., from the ventral tegmental area of the limbic portions of the midbrain Role in reward/ reinforcement in learning processes
49 Other widely projecting axon systems which influence behavioral state Cell groups in the paleothalamus (midline and intralaminar nuclei) Projections to large territories in the neocortex One with projections to layer 1 of nearly the entire neocortex Cell groups in the lateral hypothalamus and adjoining subthalamus One containing Melanin Concentrating Hormone One using peptides Hypocretin/Oxerin and Dynorphin as transmitters Mutations in the gene for H/O or its receptor cause narcolepsy One using Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) in anorexia states See Swanson (2003), ch 7
50 This is a bare-bones introduction to brain mechanisms that can change the state of much of the brain, if not all. They were not all present in the earliest chordates E.g., Amphioxus has only one monoamine system/receptor dopamine Hagfish and lampreys have at least two: DA and NE However, the primitive state of many axons was that of widely branched and extensive distribution. In evolution, specific axon systems have become specialized for this kind of connection
51 Selected References Slide 2: Swanson, Larry W. Brain Architecture, Understanding the Basic Plan. Oxford, New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 2003, p ISBN: Slide 3: Swanson, Larry W. Brain Architecture, Understanding the Basic Plan. Oxford, New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 2003, p ISBN:
Lawrence & Kuypers, 1968:
 Lawrence & Kuypers, 1968: Lesion #2: destruction of medial brainstem pathways (added to pyramidotomy) Defective axial control: Righting: only after 10-40 days Falling: failure to elicit the usual corrective
Lawrence & Kuypers, 1968: Lesion #2: destruction of medial brainstem pathways (added to pyramidotomy) Defective axial control: Righting: only after 10-40 days Falling: failure to elicit the usual corrective
MITOCW MIT9_14S14_lec17.mp3
 MITOCW MIT9_14S14_lec17.mp3 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW MIT9_14S14_lec17.mp3 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
9.01 Midterm Examination NAME October 27, 2003
 9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior, Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider 9.01 Midterm Examination NAME 1) Karl Wernicke, in the 1870s, formulated a model of
9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior, Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider 9.01 Midterm Examination NAME 1) Karl Wernicke, in the 1870s, formulated a model of
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Cortical Control of Movement
 Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Page 1 L 58. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems /2013 RETICULAR FORMATION
 Page 1 L 58 Douglas L. Oliver, Ph.D. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems 1 2012/2013 RETICULAR FORMATION Lecture Lecture: Douglas Oliver
Page 1 L 58 Douglas L. Oliver, Ph.D. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems 1 2012/2013 RETICULAR FORMATION Lecture Lecture: Douglas Oliver
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Motor systems.... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington
 Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Nervous Systems. Brain Development
 Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
9.14 Classes #21-23: Visual systems
 9.14 Classes #21-23: Visual systems Questions based on Schneider chapter 20 and classes: 1) What was in all likelihood the first functional role of the visual sense? Describe the nature of the most primitive
9.14 Classes #21-23: Visual systems Questions based on Schneider chapter 20 and classes: 1) What was in all likelihood the first functional role of the visual sense? Describe the nature of the most primitive
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Cephalization. Nervous Systems Chapter 49 11/10/2013. Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells
 Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX:
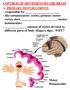 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to
 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9
 Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29:
 The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29: 7) What is the "basal forebrain", and what is its involvement in Alzheimer' s Disease? The acetylcholine-containing neurons of the nucleus basalis of Meynart
The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29: 7) What is the "basal forebrain", and what is its involvement in Alzheimer' s Disease? The acetylcholine-containing neurons of the nucleus basalis of Meynart
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
PSYCH 260 Exam 2. March 2, Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name:
 PSYCH 260 Exam 2 March 2, 2017 Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name: 1 1 Main Please put in their proper order the steps that lead to synaptic communication between neurons. Begin with the
PSYCH 260 Exam 2 March 2, 2017 Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name: 1 1 Main Please put in their proper order the steps that lead to synaptic communication between neurons. Begin with the
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Nervous and Endocrine System Exam Review
 Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Thus, there evolved the major types of functions of the neocortical mantle:
 Thus, there evolved the major types of functions of the neocortical mantle: Location sense This set the stage for more and more anticipation of inputs Object sense This also set the stage for more and
Thus, there evolved the major types of functions of the neocortical mantle: Location sense This set the stage for more and more anticipation of inputs Object sense This also set the stage for more and
Questions Addressed Through Study of Behavioral Mechanisms (Proximate Causes)
 Jan 28: Neural Mechanisms--intro Questions Addressed Through Study of Behavioral Mechanisms (Proximate Causes) Control of behavior in response to stimuli in environment Diversity of behavior: explain the
Jan 28: Neural Mechanisms--intro Questions Addressed Through Study of Behavioral Mechanisms (Proximate Causes) Control of behavior in response to stimuli in environment Diversity of behavior: explain the
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Applied Neuroscience. Conclusion of Science Honors Program Spring 2017
 Applied Neuroscience Conclusion of Science Honors Program Spring 2017 Review Circle whichever is greater, A or B. If A = B, circle both: I. A. permeability of a neuronal membrane to Na + during the rise
Applied Neuroscience Conclusion of Science Honors Program Spring 2017 Review Circle whichever is greater, A or B. If A = B, circle both: I. A. permeability of a neuronal membrane to Na + during the rise
E) A, B, and C Answer: D Topic: Concept 49.1 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension
 Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) characteristic of a simple nervous system? A) a nerve net such as is found in cnidarians B) nerve cell ganglia C)
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) characteristic of a simple nervous system? A) a nerve net such as is found in cnidarians B) nerve cell ganglia C)
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization
 Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal:
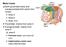 Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Spinal Interneurons. Control of Movement
 Control of Movement Spinal Interneurons Proprioceptive afferents have a variety of termination patterns in the spinal cord. This can be seen by filling physiologically-identified fibers with HRP, so their
Control of Movement Spinal Interneurons Proprioceptive afferents have a variety of termination patterns in the spinal cord. This can be seen by filling physiologically-identified fibers with HRP, so their
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
Degree of freedom problem
 KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Circadian rhythm and Sleep. Radwan Banimustafa MD
 Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement. Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement. Neural control of movement
 KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor of the Chair of Human Anatomy, Candidate of Medicine
 Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Biological Psychology. Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!!
 Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Biological Psychology
 Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Classes #5-6: Specializations in CNS evolution
 Classes #5-6: Specializations in CNS evolution Questions based on Schneider chapter 5: 1. Does ontogeny really recapitulate phylogeny? What is a phylotypic stage? Explain the terms and discuss the concepts
Classes #5-6: Specializations in CNS evolution Questions based on Schneider chapter 5: 1. Does ontogeny really recapitulate phylogeny? What is a phylotypic stage? Explain the terms and discuss the concepts
Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]
![Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1] Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]](/thumbs/90/103926552.jpg) Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Rhythmic Movements. Questions: How do they happen? What do they mean? Where do they come from?
 Rhythmic Movements Questions: How do they happen? What do they mean? Where do they come from? Reflex chain? Sequential pattern of activation? Reverberatory circuits? Lamprey swimming one wavelength, approx.
Rhythmic Movements Questions: How do they happen? What do they mean? Where do they come from? Reflex chain? Sequential pattern of activation? Reverberatory circuits? Lamprey swimming one wavelength, approx.
All questions below pertain to mandatory material: all slides, and mandatory homework (if any).
 ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Primary Functions. Monitor changes. Integrate input. Initiate a response. External / internal. Process, interpret, make decisions, store information
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Week 2 Psychology. The Brain and Behavior
 Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of
 Cornell Notes Textbook Diagrams Video notes Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of the human nervous system. Name: Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: How does the nervous system
Cornell Notes Textbook Diagrams Video notes Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of the human nervous system. Name: Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: How does the nervous system
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function. Dr Z Akbari
 Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System. Anatomy of the CNS
 CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8
 NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8 CAN AN INJURED SPINAL CORD BE FIXED? Injuries to the spinal cord disrupt communication between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body
NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8 CAN AN INJURED SPINAL CORD BE FIXED? Injuries to the spinal cord disrupt communication between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5
 NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
The Human Brain. I Think Therefore I am
 The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
skilled pathways: distal somatic muscles (fingers, hands) (brainstem, cortex) are giving excitatory signals to the descending pathway
 L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Visual system invades the endbrain: pathways to striatum and cortex (continued) Why this happened in evolution
 Visual system invades the endbrain: pathways to striatum and cortex (continued) Why this happened in evolution What were the adaptive advantages? Visual information reaching the striatum directly: Advantages
Visual system invades the endbrain: pathways to striatum and cortex (continued) Why this happened in evolution What were the adaptive advantages? Visual information reaching the striatum directly: Advantages
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07)
 NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue
 9/12/11 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Overview of the nervous system Cells of the nervous system Electrophysiology of neurons Synapses Neural integration Subdivisions of the Nervous System 1 Subdivisions of
9/12/11 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Overview of the nervous system Cells of the nervous system Electrophysiology of neurons Synapses Neural integration Subdivisions of the Nervous System 1 Subdivisions of
Voluntary Movement. Ch. 14: Supplemental Images
 Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM Topic from General functions of the nervous system Organization of the nervous system from both anatomical & functional perspectives Gross & microscopic anatomy of nervous tissue
Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM Topic from General functions of the nervous system Organization of the nervous system from both anatomical & functional perspectives Gross & microscopic anatomy of nervous tissue
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins
 A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins G. E. Schneider 2014 Part 3: Specializations in the evolving CNS; introduction to connection patterns MIT 9.14 Class 6 Interlude: Some specializations
A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins G. E. Schneider 2014 Part 3: Specializations in the evolving CNS; introduction to connection patterns MIT 9.14 Class 6 Interlude: Some specializations
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System. Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output
 The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System
 The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Neurophysiology of systems
 Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
The Nervous System. B. The Components: 1) Nerve Cells Neurons are the cells of the body and are specialized to carry messages through an process.
 The Nervous System A. The Divisions: 1) The Central Nervous System includes the and. The brain contains billions of nerve cells called, and trillions of support cells called. 2) The Peripheral Nervous
The Nervous System A. The Divisions: 1) The Central Nervous System includes the and. The brain contains billions of nerve cells called, and trillions of support cells called. 2) The Peripheral Nervous
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
Vocabulary. Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold
 Unit 2: Biopsychology The Nervous System Vocabulary Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold Synapse Neurotransmitters Somatic
Unit 2: Biopsychology The Nervous System Vocabulary Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold Synapse Neurotransmitters Somatic
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. FUNCTION The major function of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1).
 1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION The major function of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1). Sensory input. Multiple signals from both, internal and external environment are detected
1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION The major function of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1). Sensory input. Multiple signals from both, internal and external environment are detected
