d). Draw the following neural circuits (using the notation taught in class) and then say what would happen if they were stimulated as specified.
|
|
|
- Rolf Jennings
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. The neuropsychology of perception. a). Describe the process in which a neural impulse travel down one axon, making sure to specify chemical substances involved and how that affects the charge within the cell at each stage. Use a graph to show how the membrane potential changes as a function during the different stages of the process. Answer: neural impulses, or action potentials travel down an axon when stimulated enough and there is a transfer of ions; the neuron goes up to 40 positive millivolts and let in sodium ions and boots out potassium ions, it will then go down to below 70 negative millivolts which is the recovery phase during which the sodium ions are booted out and the potassium ions are taken back in; it will then return to its resting potential of -70 millivolts b). What are neurotransmitters? Describe the difference between neurotransmitters that have excitatory and inhibitory effects, using examples of neurotransmitters of each type to clarify your description. Answer: neurotransmitters are different types of chemicals that travel through neurons to send information; excitatory neurotransmitters increase the probability that the receiver will have an action potential (they increase the positivity, or in other words depolarize), acetylcholine, curare and glutamate are exctitatory. Inhibitory neurotransmitters reduce the probability that a neuron will have an action potential; gaba and serotonin are examples c). What does it mean to say that cells have a rate of spontaneous activity? Why is this important to understanding the way that neurons send messages and communicate? Answer: spontaneous activity means that neurotransmitters are released through the synaptic gap to other neurons (action potential) without any stimulation; this is important to know because a neuron that is stimulated is already firing off action potentials from its spontaneous activity and neurons will be affected differently depending on whether it is being stimulated by an excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitter d). Draw the following neural circuits (using the notation taught in class) and then say what would happen if they were stimulated as specified. i). A simple excitatory linear circuit between neurons A and B and C. What would happen to the activity of B if A were stimulated? A B C Answer: A would receive an action potential and since it is an excitatory neuron, B would therefore be stimulated ii). A circuit that shows convergence between neurons that send excitatory neurotransmitters. eurons A, B, and C each lead into neuron D (and no other neuron).
2 What would happen to the activity of neuron C if A and B were stimulated? Answer: othing would happen to C because they are attached to neuron D and therefore wouldn t stimulate eachother, only neuron D iii). A circuit that shows convergence between neurons that have excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters. eurons A and B each lead into neuron C (and no other neuron). What would happen to the activity of neuron C if neurons A and B were stimulated at the same time (and to an equal extent). Assume that all axons are the same length and there is no difference in the effectiveness of neurotransmitters. Answer: Since neurons A and B are an excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitter, if both were stimulating neuron C to an equal extent, they would cancel each other out and neuron C would receive no stimulation. 2. Psychophysics I. a). Describe the *3* major psychological methods for measuring the absolute threshold, making use of the example of your own creation to illustrate how each would work. Answer: method of limits involves the experimenter presenting the stimulus in ascending order and then descending order, after which the two results are averaged out to give you the participants absolute threshold; the method of adjustments involves the participant manually adjusting the stimulus intensity until they cant just barely detect it and then that is their absolute threshold; the constant stimuli method involves the experimenter presenting 5-9 stimuli with different intensities in random order many times and the absolute threshold is determined by which intensity is detected 50% of the time b). What is a difference threshold and how is it measured? What is a JD? (Use an example of your own creation to clarify these ideas.) Answer: the difference limens is the smallest difference detectable between two stimuli, it is measured by the method of limits, method of adjustment or method of constants; the JD is just noticeable difference c). Describe Weber's Law using an example of your own creation to clarify your ideas. Answer: Webers Law: K = JD/S; K is a constant called the Weber fraction, S is the value of the standard stimulus and JD is the just noticeable difference or difference threshold (or differenze limenz) d) A researcher was interested in measuring the faintest sound that people could detect. Sound intensities range from 1 to 10 in this study (with 10 being the most intense or loudest sound). What is the absolute threshold in this study? Y= subject says that they sense it. = subject says no they do not sense it.
3 Intensity Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Trial 4 23 Y Y Y Y 22 Y Y Y Y 21 Y Y Y Y 20 Y Y Y 19 Y Answer: Trial 1 is 18.5, Trial 2 is 20.5, Trial 3 is 19.5 and Trial 4 is 19.5; ( )/4=19.5 THEREFORE the absolute threshold for the participant is 19.5 i. What type of study is this? Answer: This is a method of limits study ii. ii. Calculate the absolute threshold in this study. (I'm looking for a numerical answer.) Answer: 19.5 iii. What is the difference between how absolute and difference thresholds are calculated in method of constants studies? Illustrate the difference using an example of your own creation involving absolute and difference taste thresholds for substance X. [The physical intensity of a tasted substance can be measured in terms of the number of mg of the substance (substance X in this case) per 1000 liters of water.] You should be getting numerical answers here, reflecting the values you have calculated from your hypothetical study
4 3. Psychophysics II. based on your graphs. You will need to be able to do this type of calculation for the exam. a. What is the difference between a signal detection study and other types of study? Answer: signal detection studies distinguishes between true sensitivity and the tendency to say yes or no; they involve a tone, or intensity, being presented half the time with nothing being presented the other half of the time b. A researcher was interested in finding out who had the most acute sense of sight. > Who has most sensitivity? How do you know? Answer: Trudy has the most sensitivity because she had 20 hits and zero misses (+20) whereas Biff had 80 hits and 70 misses (+10) A criterion is a rule for deciding when to say yes or no. Some people need more sensory evidence before they say "yes" I sense it (which means that they don't say "yes" very often). These people have a conservative criterion. Others don t take as much evidence before they say Yes, I sense it.. These people are said to have a liberal criterion. How would you know what type of criterion they had? (Hint: It's simpler than you would think...) Answer: Someone who has a lot of yes answers (and therefore a lot of hits and a lot of false alarms) would be considered liberal and someone who has a lot of no answers (and therefore a lot of misses and correct rejections) would be considered conservative c. What is the ROC curve? What does it measure (describe each axis)? How could a person be induced to develop a COSERVATIVE criterion? How could a person be induced to develop a LIBERAL criterion? Answer: a ROC curve is a receiving operating characteristics curve; it considers variables that could affect someones response other than their sensitivity: we can manipulate a persons motivation by means of payoffs, for example, by giving 100$ for hits we can encourage liberal answering but for 100$ for correct rejections we can encourage conservative answering 4. Psychophysics III. a). Your task is to measure how the perceived sweetness of a glass of lemonade varies with the amount of sugar in it. How would you go about measuring this? (Hint: You will need to be able to plot a power function from the resulting data.) b). What does the power function tell us? What is the functional significance of exponents of less than 1.0 and of more than 1.0? Use examples to clarify and illustrate your answer (i.e., if you had an exponent of less than 1.0 what would this tell you about
5 how perceived sweetness increases with sugar? What if it was more than 1.0?) Power functions: P=KSn; P is perceived magnitude, K is a constant times the stimulus intensity (S) raised to a power (n) The relationship between the intensity of a stimulus and our perception of its magnitude follow that equation; as intensity increases, perceptual magnitude increases more than intensity 5. Anomalies in vision. a). In lecture we discussed a number of things that change in your visual system as you get older. Describe *3* changes that occur with normal aging. (Hint: These are not associated with specific diseases or conditions affecting only a certain proportion of the population. Instead, these conditions will affect everyone or almost everyone as they age.) For each anomaly describe the following: i) the part of the visual system affected; ii) how vision is affected and what causes it to be affected in that way; iii) the practical consequences of this condition in terms of dayto-day life. Answer: presbyopia is when your lens grows like an onion and the tissue gets more packed and hardened and therefore doesn t bend well and you cant see things that are near as well, a convex glasses lens can help eyesight; cataracts is a lens disorder where the lens gets milky and there are problems in seeing the just noticeable differences in light perception and can be fixed through phacoemulsification; senile myosis is when your iris cant go as wide as you get older and you cant see as well in the dark b). Everyone knows someone who has some sort of visual anomaly. (It may be you!) Describe the visual problem of the person you know, how it affects their life, and then explain why it occurs in terms of what is going on with the structures of the eye. (Hint: It should not be one of the deficits discussed in parts a of this question.) Answer: accommodation is when you have to bend light rays by rounding out or flattening your lens to see things that are close or far: myopia is nearsightedness; you can have axial myopia which is when someone is born with an elongated eyeball and therefore things that are far away are out of focus but things that are close are very focused, or refractive myopia is when your lens and cornea together are too powerful; you must wear concaved glasses lens that curve inward and therefore the light rays in your vision are artificially widened or you can have excimer laser surgery which shaves off park of the cornea 6. Rod and cone vision. a). What is the difference between rods and cones in terms of their physiology (i.e., their physical makeup, location)?
6 Answer: there are more rods in our eyes than cones, rods are located in our peripheral vision and cones are in the fovea and perceive fine detail; rods contain rhodopsin and are responsible for night vision and cones have 3 kinds of photopigments that absorb red, green and blue light really well b). Describe *2* reasons that rod vision is more sensitive than cone vision. Answer: rod vision is more sensitive because they don t require much light to work and a rod receptor can be activated by the isomerization of just 1 visual pigment molecule c). What is the Purkinje effect? How does that relate to rod and cone vision? (Use a practical example of your own construction to clarify your points.) Answer: at low light levels, the tendency for the peak luminance sensitivity of the human eye to shift toward the blue end of the illumination levels; there is an initial rapid stage due to adaptation of the cone receptors and later a slower stage due to adaptation of the rod receptors; as soon as the light is extinguished, the sensitivity of both the cones and the rods begins increasing, but because our vision is controlled by the receptor system that is most sensitive, the cones determine the early part of the dark adaptation curve; the rods are increasing in their sensitivity in the dark during the cone part of the dark adaptation curve, after the cones finish off, the rods sensitivity continues to increase, then catch up to the cones and then become more sensitive and control the persons vision and the course of rod dark adaptation becomes visible in the place where the rods begin to determine the dark adaptation curve is called the rod-cone break
What do we perceive?
 THE VISUAL SYSTEM Aditi Majumder What do we perceive? Example: Switch off the light in room What we perceive Not only the property of the scene But also that of the visual system Our perception is filtered
THE VISUAL SYSTEM Aditi Majumder What do we perceive? Example: Switch off the light in room What we perceive Not only the property of the scene But also that of the visual system Our perception is filtered
Myers PSYCHOLOGY. (6th Ed) Chapter 5. Sensation
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (6th Ed) Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energy Perception a process of organizing and
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (6th Ed) Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energy Perception a process of organizing and
Introduction. Chapter The Perceptual Process
 Chapter 1 Introduction Most of us take for granted our ability to perceive the external world. However, this is no simple deed at all. Imagine being given a task of designing a machine that can perceive,
Chapter 1 Introduction Most of us take for granted our ability to perceive the external world. However, this is no simple deed at all. Imagine being given a task of designing a machine that can perceive,
Test Bank Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception
 Test Bank Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Our perception of the environment depends on a. the properties of the objects in the environment. b. the properties of the electrical
Test Bank Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Our perception of the environment depends on a. the properties of the objects in the environment. b. the properties of the electrical
SENSES: VISION. Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014
 SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II
 Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South AP Psychology Name: Date: Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II Psychophysics study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological
Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South AP Psychology Name: Date: Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II Psychophysics study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological
Schwartz and Krantz, Sensation and Perception
 Test Bank Chapter 2 1. The Scoville scale measures: a. Any psychophysical measure of sensitivity *b. The amount of capsaicin in food c. The strength of auditory amplitude d. The number of caffeine molecules
Test Bank Chapter 2 1. The Scoville scale measures: a. Any psychophysical measure of sensitivity *b. The amount of capsaicin in food c. The strength of auditory amplitude d. The number of caffeine molecules
Sensation, Part 1 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4
 Sensation, Part 1 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A February 11, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 Origins of Knowledge Empiricism knowledge
Sensation, Part 1 Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 4 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A February 11, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 Origins of Knowledge Empiricism knowledge
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AD Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AD Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Sensory and Perception Though each sense works a little differently to do this, psychologists have developed principles to describe
Biological Psychology Unit Two AD Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Sensory and Perception Though each sense works a little differently to do this, psychologists have developed principles to describe
The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect. absolute threshold. Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information.
 absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
Fundamentals of Psychophysics
 Fundamentals of Psychophysics John Greenwood Department of Experimental Psychology!! NEUR3045! Contact: john.greenwood@ucl.ac.uk 1 Visual neuroscience physiology stimulus How do we see the world? neuroimaging
Fundamentals of Psychophysics John Greenwood Department of Experimental Psychology!! NEUR3045! Contact: john.greenwood@ucl.ac.uk 1 Visual neuroscience physiology stimulus How do we see the world? neuroimaging
7. Sharp perception or vision 8. The process of transferring genetic material from one cell to another by a plasmid or bacteriophage
 1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
PSY 214 Lecture 5 (09/19/2010) (Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 5 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 55-71
 Corrections: No corrections needed Announcements: After the completion of chapter 4 a movie will be shown First test is October 3, 2011 Dr. Achtman is available during her office hours The test will include
Corrections: No corrections needed Announcements: After the completion of chapter 4 a movie will be shown First test is October 3, 2011 Dr. Achtman is available during her office hours The test will include
2Lesson. Outline 3.3. Lesson Plan. The OVERVIEW. Lesson 3.3 Why does applying pressure relieve pain? LESSON. Unit1.2
 Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson introduces students to inhibitory synapses. To review synaptic transmission, the class involves a student model pathway to act out synaptic transmission.
Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson introduces students to inhibitory synapses. To review synaptic transmission, the class involves a student model pathway to act out synaptic transmission.
2 Sensing the Environment
 CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
Categorical Perception
 Categorical Perception Discrimination for some speech contrasts is poor within phonetic categories and good between categories. Unusual, not found for most perceptual contrasts. Influenced by task, expectations,
Categorical Perception Discrimination for some speech contrasts is poor within phonetic categories and good between categories. Unusual, not found for most perceptual contrasts. Influenced by task, expectations,
Practice Test Questions
 Practice Test Questions Multiple Choice 1. Which term is most descriptive of the process of sensation? a. transportation c. selection b. interpretation d. transduction 2. Which terms are most descriptive
Practice Test Questions Multiple Choice 1. Which term is most descriptive of the process of sensation? a. transportation c. selection b. interpretation d. transduction 2. Which terms are most descriptive
Sensory Thresholds and Signal Detection. Lecture 13
 Sensory Thresholds and Signal Detection Lecture 13 1 Qualities of Sensation Boring (1953) Modality-Specific Vision: Hue, Saturation Audition: Pitch, Timbre Olfaction: Odor Gustation: Flavor Touch: Roughness,
Sensory Thresholds and Signal Detection Lecture 13 1 Qualities of Sensation Boring (1953) Modality-Specific Vision: Hue, Saturation Audition: Pitch, Timbre Olfaction: Odor Gustation: Flavor Touch: Roughness,
Research methods in sensation and perception. (and the princess and the pea)
 Research methods in sensation and perception (and the princess and the pea) Sensory Thresholds We can measure stuff in the world like pressure, sound, light, etc. We can't easily measure your psychological
Research methods in sensation and perception (and the princess and the pea) Sensory Thresholds We can measure stuff in the world like pressure, sound, light, etc. We can't easily measure your psychological
Three methods for measuring perception. Magnitude estimation. Steven s power law. P = k S n
 Three methods for measuring perception 1. Magnitude estimation 2. Matching 3. Detection/discrimination Magnitude estimation Have subject rate (e.g., 1-10) some aspect of a stimulus (e.g., how bright it
Three methods for measuring perception 1. Magnitude estimation 2. Matching 3. Detection/discrimination Magnitude estimation Have subject rate (e.g., 1-10) some aspect of a stimulus (e.g., how bright it
Introduction. Visual Perception Aditi Majumder, UCI. Perception is taken for granted!
 Introduction Visual Perception Perception is taken for granted! Slide 2 1 Perception is very complex Perceive Locate Identify/Recognize Different objects Their relationship with each other Qualitative
Introduction Visual Perception Perception is taken for granted! Slide 2 1 Perception is very complex Perceive Locate Identify/Recognize Different objects Their relationship with each other Qualitative
Psychophysics & a brief intro to the nervous system
 Psychophysics & a brief intro to the nervous system Jonathan Pillow Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Lec. 3 Outline for today: psychophysics Weber-Fechner Law Signal Detection
Psychophysics & a brief intro to the nervous system Jonathan Pillow Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Lec. 3 Outline for today: psychophysics Weber-Fechner Law Signal Detection
Definition Slides. Sensation. Perception. Bottom-up processing. Selective attention. Top-down processing 11/3/2013
 Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
= add definition here. Definition Slide
 = add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
= add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003
 ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
 Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Neural circuits PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 05. Rods and cones
 Neural circuits PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 05 Why do you need bright light to read? Rods and cones Photoreceptors are not evenly distributed across the retina 1 Rods and cones Cones are most dense in
Neural circuits PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 05 Why do you need bright light to read? Rods and cones Photoreceptors are not evenly distributed across the retina 1 Rods and cones Cones are most dense in
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception
 Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
Perception Lecture 1
 Page 1 Perception Lecture 1 Sensation vs Perception Sensation is detection Perception is interpretation The distal and proximal stimulus Distal stimulus: the object out there in the world (distal=distant).
Page 1 Perception Lecture 1 Sensation vs Perception Sensation is detection Perception is interpretation The distal and proximal stimulus Distal stimulus: the object out there in the world (distal=distant).
Senses are transducers. Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What?
 1 Vision 2 TRANSDUCTION Senses are transducers Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What? Action potentials! Sensory codes Frequency code encodes information about intensity
1 Vision 2 TRANSDUCTION Senses are transducers Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What? Action potentials! Sensory codes Frequency code encodes information about intensity
Introduction to Sensation and Perception
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Introduction to Sensation and Perception Module 12 2 Sensation Sensing the World: Some Basic Principles Threshold
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Introduction to Sensation and Perception Module 12 2 Sensation Sensing the World: Some Basic Principles Threshold
PSYC& Lilienfeld et al. - Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception: How We Sense and Conceptualize the World Study Guide
 Many first time college students struggle adjusting to expectations of college-level courses. One reason for this is that college-level courses require students to learn new content and apply that content
Many first time college students struggle adjusting to expectations of college-level courses. One reason for this is that college-level courses require students to learn new content and apply that content
Shaw - PSYC& 100 Lilienfeld et al (2014) - Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception: How we sense and conceptualize the world
 Name: 1 Shaw - PSYC& 100 Lilienfeld et al (2014) - Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception: How we sense and conceptualize the world 1 Distinguish between sensation and perception. Include as part of your answer
Name: 1 Shaw - PSYC& 100 Lilienfeld et al (2014) - Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception: How we sense and conceptualize the world 1 Distinguish between sensation and perception. Include as part of your answer
Topics Review Questions. 1) It is a process that is used to find answers to questions about the world around us.
 Topics Review Questions Scientific Method Notes & Lab: 1) It is a process that is used to find answers to questions about the world around us. scientific method 2) It is an educated guess based on observations
Topics Review Questions Scientific Method Notes & Lab: 1) It is a process that is used to find answers to questions about the world around us. scientific method 2) It is an educated guess based on observations
PSY 215 Lecture 3 (1/19/2011) (Synapses & Neurotransmitters) Dr. Achtman PSY 215
 Corrections: None needed. PSY 215 Lecture 3 Topic: Synapses & Neurotransmitters Chapters 2 & 3, pages 40-57 Lecture Notes: SYNAPSES & NEUROTRANSMITTERS, CHAPTER 3 Action Potential (above diagram found
Corrections: None needed. PSY 215 Lecture 3 Topic: Synapses & Neurotransmitters Chapters 2 & 3, pages 40-57 Lecture Notes: SYNAPSES & NEUROTRANSMITTERS, CHAPTER 3 Action Potential (above diagram found
Omar Sami. Muhammad Abid. Muhammad khatatbeh
 10 Omar Sami Muhammad Abid Muhammad khatatbeh Let s shock the world In this lecture we are going to cover topics said in previous lectures and then start with the nerve cells (neurons) and the synapses
10 Omar Sami Muhammad Abid Muhammad khatatbeh Let s shock the world In this lecture we are going to cover topics said in previous lectures and then start with the nerve cells (neurons) and the synapses
QUIZ YOURSELF COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
 QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
DO NOW: ANSWER ON PG 73
 DO NOW: ANSWER ON PG 73 1. Name 1 neurotransmitter that we have learned about. 2. Draw a basic graph of a neuron action potential. Label resting potential, threshold, depolarization, and repolarization
DO NOW: ANSWER ON PG 73 1. Name 1 neurotransmitter that we have learned about. 2. Draw a basic graph of a neuron action potential. Label resting potential, threshold, depolarization, and repolarization
4. Which letter in figure 9.1 points to the fovea centralis? Ans: b
 Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION KEY TERMS
 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION KEY TERMS BOTTOM-UP PROCESSING BOTTOM-UP PROCESSING refers to processing sensory information as it is coming in. In other words, if I flash a random picture on the screen, your
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION KEY TERMS BOTTOM-UP PROCESSING BOTTOM-UP PROCESSING refers to processing sensory information as it is coming in. In other words, if I flash a random picture on the screen, your
Function of the Nervous System
 Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
[CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY]
![[CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY] [CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY]](/thumbs/71/65616244.jpg) WORDBANK: Cholinesterase Dopamine Axon Choroid layer Cochlea Incus Action Potential Cataract Cornea Astigmatism Dendrite Malleus Alzheimer s Disease Central Excitatory Response Fovea Centralis Acetylcholine
WORDBANK: Cholinesterase Dopamine Axon Choroid layer Cochlea Incus Action Potential Cataract Cornea Astigmatism Dendrite Malleus Alzheimer s Disease Central Excitatory Response Fovea Centralis Acetylcholine
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
Chapter 6 subtitles postsynaptic integration
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 6 subtitles postsynaptic integration INTRODUCTION (1:56) This sixth and final chapter deals with the summation of presynaptic currents. Glutamate and
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 6 subtitles postsynaptic integration INTRODUCTION (1:56) This sixth and final chapter deals with the summation of presynaptic currents. Glutamate and
Sensation and Perception. Chapter 6
 Sensation and Perception Chapter 6 1 Sensation & Perception How do we construct our representations of the external world? Text To represent the world, we must detect physical energy (a stimulus) from
Sensation and Perception Chapter 6 1 Sensation & Perception How do we construct our representations of the external world? Text To represent the world, we must detect physical energy (a stimulus) from
A. Acuity B. Adaptation C. Awareness D. Reception E. Overload
 Unit 4 Review #1 The longer an individual is exposed to a strong odor, the less aware of the odor the individual becomes. This phenomenon is known as sensory A. Acuity B. Adaptation C. Awareness D. Reception
Unit 4 Review #1 The longer an individual is exposed to a strong odor, the less aware of the odor the individual becomes. This phenomenon is known as sensory A. Acuity B. Adaptation C. Awareness D. Reception
Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds. Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor
 Chapter 8 Sensation and Perception Sec 1: Sensation Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor Perception
Chapter 8 Sensation and Perception Sec 1: Sensation Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor Perception
Vision Seeing is in the mind
 1 Vision Seeing is in the mind Stimulus: Light 2 Light Characteristics 1. Wavelength (hue) 2. Intensity (brightness) 3. Saturation (purity) 3 4 Hue (color): dimension of color determined by wavelength
1 Vision Seeing is in the mind Stimulus: Light 2 Light Characteristics 1. Wavelength (hue) 2. Intensity (brightness) 3. Saturation (purity) 3 4 Hue (color): dimension of color determined by wavelength
Sight, more than any of our senses, helps us navigate the world around us. In a single glance, lasting a fraction of a second, our eyes work with our
 The Eye Sight, more than any of our senses, helps us navigate the world around us. In a single glance, lasting a fraction of a second, our eyes work with our brains to tell us the size, shape, colour,
The Eye Sight, more than any of our senses, helps us navigate the world around us. In a single glance, lasting a fraction of a second, our eyes work with our brains to tell us the size, shape, colour,
Laboratory Exercise in Sensory Physiology Student Lab Manual
 Laboratory Exercise in Sensory Physiology Student Lab Manual Introduction Sensory organs allow us to perceive our environment by converting energy sources in the environment, like light or sound, to nerve
Laboratory Exercise in Sensory Physiology Student Lab Manual Introduction Sensory organs allow us to perceive our environment by converting energy sources in the environment, like light or sound, to nerve
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Scrub In. What is the function of vitreous humor? What does the pupil do when exposed to bright light? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision
 Scrub In What is the function of vitreous humor? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision b. Maintain eye shape and refract light rays c. Provide night vision and color vision d. Provide night vision
Scrub In What is the function of vitreous humor? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision b. Maintain eye shape and refract light rays c. Provide night vision and color vision d. Provide night vision
Chapter 1 Introduction. Welcome to Our World Thresholds and the Dawn of Psychophysics Sensory Neuroscience and the Biology of Perception
 1 Introduction Chapter 1 Introduction Welcome to Our World Thresholds and the Dawn of Psychophysics Sensory Neuroscience and the Biology of Perception Introduction What do we mean by Sensation & Perception?
1 Introduction Chapter 1 Introduction Welcome to Our World Thresholds and the Dawn of Psychophysics Sensory Neuroscience and the Biology of Perception Introduction What do we mean by Sensation & Perception?
Ameen Alsaras. Ameen Alsaras. Mohd.Khatatbeh
 9 Ameen Alsaras Ameen Alsaras Mohd.Khatatbeh Nerve Cells (Neurons) *Remember: The neural cell consists of: 1-Cell body 2-Dendrites 3-Axon which ends as axon terminals. The conduction of impulse through
9 Ameen Alsaras Ameen Alsaras Mohd.Khatatbeh Nerve Cells (Neurons) *Remember: The neural cell consists of: 1-Cell body 2-Dendrites 3-Axon which ends as axon terminals. The conduction of impulse through
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY
 NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
Psy393: Cognitive Neuroscience. Prof. Anderson Department of Psychology Week 3
 Psy393: Cognitive Neuroscience Prof. Anderson Department of Psychology Week 3 The Eye: Proof for the existence of God? And then there was light Optics Perception Absorption Eye is receiver not sender Plato
Psy393: Cognitive Neuroscience Prof. Anderson Department of Psychology Week 3 The Eye: Proof for the existence of God? And then there was light Optics Perception Absorption Eye is receiver not sender Plato
Dikran J. Martin. Psychology 110. Name: Date: Making Contact with the World around Us. Principal Features
 Dikran J. Martin Psychology 110 Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 3 Sensation and Perception: Pages: 31 Making Contact with the World around Us TEXT: Baron, Robert A. (2001). Psychology (Fifth Edition).
Dikran J. Martin Psychology 110 Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 3 Sensation and Perception: Pages: 31 Making Contact with the World around Us TEXT: Baron, Robert A. (2001). Psychology (Fifth Edition).
Biology 3201 The Nervous System Test
 Biology 3201 The Nervous System Test 1. The central nervous system consists of: a. Nerves and neurons c. spinal chord and nerves b. brain and neurons d. brain and spinal chord 2. This part of the brain
Biology 3201 The Nervous System Test 1. The central nervous system consists of: a. Nerves and neurons c. spinal chord and nerves b. brain and neurons d. brain and spinal chord 2. This part of the brain
Psychology Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception. Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed!
 Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Structure of the eye and retina
 1 of 10 3/6/2012 1:06 PM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina 2 of 10 3/6/2012 1:06 PM In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) Focusing, changes
1 of 10 3/6/2012 1:06 PM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina 2 of 10 3/6/2012 1:06 PM In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) Focusing, changes
Vision. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Vision Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vision is the ability to detect light patterns from the outside environment and interpret them into images. Animals are bombarded with sensory information, and the sheer volume
Vision Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vision is the ability to detect light patterns from the outside environment and interpret them into images. Animals are bombarded with sensory information, and the sheer volume
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus
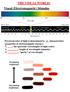 THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. : the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color) 2.
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. : the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color) 2.
Introduction to Physiological Psychology
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html This class n Sensation vs. Perception n How light is translated into what we see n Structure
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html This class n Sensation vs. Perception n How light is translated into what we see n Structure
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001
 ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, so keep your eyes foveated on your own exam. I tend to think of a point as a minute, so be sure to spend the appropriate amount
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, so keep your eyes foveated on your own exam. I tend to think of a point as a minute, so be sure to spend the appropriate amount
PSY 214 Lecture # 3 (09/07/2011) - Physiology of Perception Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 3 Topic: Physiology of Perception Chapter 2, pages 23-31
 PSY 214 Corrections: Lecture 3 Topic: Physiology of Perception Chapter 2, pages 23-31 None needed Lecture Notes: I. Review The Perceptual Process Dillon Foley, Dfoley7@mail.naz.edu Page 1 of 8 A: Psychophysics-
PSY 214 Corrections: Lecture 3 Topic: Physiology of Perception Chapter 2, pages 23-31 None needed Lecture Notes: I. Review The Perceptual Process Dillon Foley, Dfoley7@mail.naz.edu Page 1 of 8 A: Psychophysics-
Sensation and Perception. A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations
 I. Overview Sensation and Perception A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations C. Top-Down vs Bottom-up Processing D. Psychophysics -- thresholds 1.
I. Overview Sensation and Perception A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations C. Top-Down vs Bottom-up Processing D. Psychophysics -- thresholds 1.
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
 Synapses and Neurotransmitters Action Potentials We have been talking about action potentials and how they allow an electrical impulse to travel from the dendrites to the end plates of a neuron. These
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Action Potentials We have been talking about action potentials and how they allow an electrical impulse to travel from the dendrites to the end plates of a neuron. These
Name Psychophysical Methods Laboratory
 Name Psychophysical Methods Laboratory 1. Classical Methods of Psychophysics These exercises make use of a HyperCard stack developed by Hiroshi Ono. Open the PS 325 folder and then the Precision and Accuracy
Name Psychophysical Methods Laboratory 1. Classical Methods of Psychophysics These exercises make use of a HyperCard stack developed by Hiroshi Ono. Open the PS 325 folder and then the Precision and Accuracy
Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System
 Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System Looking for answers? Visit http://msjadah.weebly.com 1. The Nervous System a) What is the function of nervous system? The nervous system receives,
Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System Looking for answers? Visit http://msjadah.weebly.com 1. The Nervous System a) What is the function of nervous system? The nervous system receives,
1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells
 Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION
 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION CHAPTER 5 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe transduction, sensation, and perception for the following sensory systems: Vision Audition (hearing) Skin and body Touch Pain Chemical
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION CHAPTER 5 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe transduction, sensation, and perception for the following sensory systems: Vision Audition (hearing) Skin and body Touch Pain Chemical
Prof. Greg Francis 7/31/15
 s PSY 200 Greg Francis Lecture 06 How do you recognize your grandmother? Action potential With enough excitatory input, a cell produces an action potential that sends a signal down its axon to other cells
s PSY 200 Greg Francis Lecture 06 How do you recognize your grandmother? Action potential With enough excitatory input, a cell produces an action potential that sends a signal down its axon to other cells
Bio11 schedule. Chapter 13 and 14. The Nervous System. The Nervous System. Organization of Nervous Systems. Nerves. Nervous and Sensory Systems
 Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Sensing and Perceiving Our World
 PSYCHOLOGY: Perspectives & Connections 2 nd Edition GREGORY J. FEIST ERIKA L. ROSENBERG Sensing and Perceiving Our World Chapter Four Chapter Preview The Long Strange Trip From Sensation to Perception
PSYCHOLOGY: Perspectives & Connections 2 nd Edition GREGORY J. FEIST ERIKA L. ROSENBERG Sensing and Perceiving Our World Chapter Four Chapter Preview The Long Strange Trip From Sensation to Perception
Neuroscience - Problem Drill 13: The Eye and Visual Processing
 Neuroscience - Problem Drill 13: The Eye and Visual Processing Question No. 1 of 10 needed, (3) Pick the answer, and (4) Review the core concept tutorial as needed. 1. Which of the following statements
Neuroscience - Problem Drill 13: The Eye and Visual Processing Question No. 1 of 10 needed, (3) Pick the answer, and (4) Review the core concept tutorial as needed. 1. Which of the following statements
Welcome it is a great day to learn about the Brain
 Welcome it is a great day to learn about the Brain What does the Brain do? Stand up Walk around every person you pass tell them a different function the brain performs Do this until you are told to stop
Welcome it is a great day to learn about the Brain What does the Brain do? Stand up Walk around every person you pass tell them a different function the brain performs Do this until you are told to stop
Part 1 Making the initial neuron connection
 To begin, follow your teacher's directions to open the Virtual Neurons software. On the left side of the screen is a group of skin cells. On the right side of the screen is a group of muscle fibers. In
To begin, follow your teacher's directions to open the Virtual Neurons software. On the left side of the screen is a group of skin cells. On the right side of the screen is a group of muscle fibers. In
Biological Process 9/7/10. (a) Anatomy: Neurons have three basic parts. 1. The Nervous System: The communication system of your body and brain
 Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System nervous system stimulus response Neuron structure and function neurons nerve impulses dendrite
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system is a network of communication used by body parts to maintain homeostasis and bodily functions. The nervous system gathers information
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system is a network of communication used by body parts to maintain homeostasis and bodily functions. The nervous system gathers information
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition
 Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Chapter 5 Test Review. Try the practice questions in the Study Guide and on line
 Chapter 5 Test Review Try the practice questions in the Study Guide and on line Printing game plan Put six slides on a page Select pure black and white as the printing option Okay, now wade into the answers>>>>
Chapter 5 Test Review Try the practice questions in the Study Guide and on line Printing game plan Put six slides on a page Select pure black and white as the printing option Okay, now wade into the answers>>>>
9/28/2016. Neuron. Multipolar Neuron. Astrocytes Exchange Materials With Neurons. Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system)
 Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Chapter 29 The Senses
 Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
1) The nucleus of a neuron, the area which houses all the genetic material, is found is which part of the nerve cell? cell body
 PSYA01 Mtuner 2 1) The nucleus of a neuron, the area which houses all the genetic material, is found is which part of the nerve cell? cell body 2) According to evolutionary theory by natural selection,
PSYA01 Mtuner 2 1) The nucleus of a neuron, the area which houses all the genetic material, is found is which part of the nerve cell? cell body 2) According to evolutionary theory by natural selection,
35-2 The Nervous System Slide 1 of 38
 1 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. 2 of 38 Neurons Neurons The messages carried by
1 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. 2 of 38 Neurons Neurons The messages carried by
Neurons Chapter 7 2/19/2016. Learning Objectives. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System
 Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
(2) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. the two different types of effector
 NERVOUS SYSTEM. NAME.. Q.This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin. A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector.
NERVOUS SYSTEM. NAME.. Q.This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin. A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector.
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology
 Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy. (the part that s visible to us!)
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy (the part that s visible to us!)
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy (the part that s visible to us!)
l3;~~?~~~,'0~'~~t~t:~:~~~~~~~~~~!,1
 112 Sensation and Perception Line A should look longer, even though both lines are actually the same length. People who come from noncarpentered cultures that do not use right angles and corners often
112 Sensation and Perception Line A should look longer, even though both lines are actually the same length. People who come from noncarpentered cultures that do not use right angles and corners often
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus
 THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. Hue: the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color)
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. Hue: the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color)
SAMPLE WHAT LASIK CAN DO
 DECIDING ON LASIK Imagine being able to work, drive, and play sports without having to depend on glasses or contact lenses. LASIK (laser in-situ keratomileusis) may make this a reality for you. This laser
DECIDING ON LASIK Imagine being able to work, drive, and play sports without having to depend on glasses or contact lenses. LASIK (laser in-situ keratomileusis) may make this a reality for you. This laser
Nervous System. Chapter Structure of the Nervous System. Neurons
 33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
MITOCW watch?v=nx76xs_4fre
 MITOCW watch?v=nx76xs_4fre The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=nx76xs_4fre The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AA Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AA Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What are the biological factors that affect our behavior? In this unit we are going to take a look at biological psychology,
Biological Psychology Unit Two AA Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What are the biological factors that affect our behavior? In this unit we are going to take a look at biological psychology,
let's continue talking about the eye,
 Eye is mainly composed of 3 layers: External layer, which called The Sclera which is a hard connective tissue that gives the eye its round shape. Extension of the sclera into the front is the cornea, which
Eye is mainly composed of 3 layers: External layer, which called The Sclera which is a hard connective tissue that gives the eye its round shape. Extension of the sclera into the front is the cornea, which
Axon Nerve impulse. Axoplasm Receptor. Axomembrane Stimuli. Schwann cell Effector. Myelin Cell body
 Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Chapter 7, Section 1 Review Questions. Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. Name PER Date
 Name PER Date Chapter 7, Section 1 Review Questions Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. A. the middle layer of the wall of the eye B. the structure between the choroid
Name PER Date Chapter 7, Section 1 Review Questions Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. A. the middle layer of the wall of the eye B. the structure between the choroid
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
