A CASE OF MULTIPLE MYELOMA AND CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF AN EARLY ISLAMIC SKELETON FROM TELL ABU AL-KHARAZ, JORDAN
|
|
|
- Elijah Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
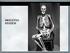
1 ANTHROPOLOGIE LIV/3 pp ALI M. KHWAILEH A CASE OF MULTIPLE MYELOMA AND CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF AN EARLY ISLAMIC SKELETON FROM TELL ABU AL-KHARAZ, JORDAN ABSTRACT: The female skeletal remains that were recovered at the site of Tell Abu al-kharaz in 2014 in Jordan Valley suffered the diseases of multiple myeloma, congenital anomalies and osteoarthritis. She died at an age of about years old. Although the remains were found next to an Iron Age structure, the burial type and body position probably suggest an Islamic date. Palaeopathologically, multiple myeloma and secondary cancer (metastatic), such as breast cancer in the case of women, are often difficult to distinguish. However, the female skeleton of this study shows no new bone formation surrounding the perforations, which means that secondary cancer is unlikely to be the cause. This also excludes syphilis as a possible diagnosis. KEY WORDS: Multiple myeloma Tell Abu al-kharaz Jordan Valley INTRODUCTION During the field season of 2014, the Swedish archaeological team at the site of Tell Abu al-kharaz in the Jordan Valley directed by Peter Fischer accidently recovered a human skeleton beside an Iron Age wall, where the legs were positioned during the internment under a recent wall. The area where the skeleton was recovered is an Iron Age area with some walls from recent periods on top. This actually indicates an age younger than the Iron Age and suggested by the director of the excavation to be from the Islamic period (Fischer 2014: personal communication). The body was laid on the right side with the head facing Qibla (south in Jordan), a typical Islamic burial (Figure 2). Excavations around the burial revealed no further burials, which is unusual and probably signifies the lower social status of the individual (Al-Shorman 2007). The site was first occupied during the Early Bronze Age and continued throughout the Middle/Late Bronze Ages and the Iron Age (Fischer 2013). Further excavations at the site have not revealed burials but dwelling structures. As Received 16 February 2015; accepted 19 August Moravian Museum, Anthropos Institute, Brno. All rights reserved. 317
2 Ali M. Khwaileh the site was densely occupied during the various phases of the Iron Age (Fischer 2013), the cemetery might have been located outside the settlement area. The 2014 season aimed to investigate the area around the geographical center of the city. MATERIALS AND METHODS The study comprised one skeleton that was recovered from the archaeological site of Tell Abu al- Kharaz in Jordan Valley (Figure 1). According to the director of the excavation, the skeleton is dated to the Islamic period and most probably Abbasid (Fischer 2014: Personal communication). The skeleton was found buried under an Iron Age structure on its right side (east-west) and facing south signifying an Islamic burial practice (Figure 2). Upon recovery, the bones were in a very poor preservation condition, fragile with longitudinal cracks and bleached. The preservation condition indicates a shallow burial and prolonged exposure to the sun. The skeleton was transferred to the physical anthropology labs at Yarmouk University for bioarchaeological analysis. Visual examination and radiography were used to extract the data concerning demographic variables and paleopathological lesions. These methods were carried out according to the standards by Buikstra and Ubelaker (1994). FIGURE 1. The map of Jordan showing the site of Tell Abu al-kharaz in the Jordan Valley. Mapped by Muwafaq Al-Bataineh. 318
3 A Case of Multiple Myeloma and Congenital Anomalies of an Early Islamic Skeleton from Tell Abu Al-Kharaz, Jordan FIGURE 2. The burial showing internment. Photographed by P. Fischer. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The examination of the os coxae, skull and mandible indicates female sex. The age at death was estimated using the auricular surface, long bones epiphyseal union, and dental attrition. Based on the previous criteria, age is estimated to be in the late twenties (Table 1). The visual examination of the skeleton revealed many pathological lesions. These lesions are listed with their location and possible diagnosis (Table 2). The results show that the individual endured the severity of congenital anomalies in the skull, sternum and pelvis. Beside sternal asymmetry, osteoarthritis of the costal notches was prominent and manifested by new bone formation and pitting (Figure 3). The exostosis anterior to the foramen magnum was probably congenital as being regular in shape and smooth (not an inflammatory reaction) (Figure 4). This lesion would have restricted right rotation of the head. The osteophytosis and vertebral body degeneration triggered the formation of Schmorl s nodes (Figure 5). The asymmetry of the sacrum also must have altered the body posture and gate, which usually impairs daily activity pattern. The skull shows multiple perforations in the frontal, parietals, temporals and maxillas typical of multiple myeloma (Figure 6). Multiple myeloma is a cancer of plasma cells which accumulates in bone marrow. It is difficult in palaeopathological diagnosis to differentiate between myelomatous perforations in the skull and perforations of secondary cancer (Cattaneo et al. 1994). For example, the Egyptian skull ( BC) that was diagnosed as cancer of the TABLE 1. Age estimation of the skeleton. Bone Feature Age in years Os coxa (auricular No porosity and no apical activity (Buikstra, Ubelaker, 1994) surface) Clavicle The surface of the facet is smooth without a rim (Steele, Bramblett, 1988) Third molar Fully erupted (Steele, Bramblett, 1988) >18 319
4 Ali M. Khwaileh TABLE 2. The pathological lesions of the skeleton and their probable diagnosis. Pathological lesion Location Probable diagnosis Mild osteophytosis Lumbar vertebra (L 6) Osteoarthritis Mild osteophytosis Thoracic vertebrae (T 10) Osteoarthritis Mild osteophytosis Cervical vertebrae (C6) Osteoarthritis Schmorl s node Lumbar vertebra(l 6) Osteoarthritis Left lower first molar Premortem loss Caries Cartilage ossification Trachea Hypercalcemia Bone resorption Ossified trachea Multiple Myeloma Asymmetry Sternum Congenital Asymmetry Sacrum Congenital Exostosis and pitting Rt. and Lt. clavicular notch Osteoarthritis Exostosis Anterior to foramen magnum Congenital New bone formation and pitting 5 th Lt costal notch Osteoarthritis New bone formation and pitting 4 th Lt costal notch Osteoarthritis New bone formation and pitting 3 rd Rt. Costal notch Osteoarthritis New bone formation and pitting 5 th Rt. Costal notch Osteoarthritis Cracks Vault Postmortem sun exposure Holes Frontal (1 Lt.), parietal (2 Rt. and 2 Lt.), temporal (2 Rt.) and maxilla (2 Rt.) Multiple myeloma Abnormal bone fusion Sagittal suture Congenital craniostenosis Wear Anterior and posterior teeth Dental wear Cut marks Left parietal Anthropogenic (during excavation) nasopharynx has a number of secondary vault perforations (Wells 1963). However, in multiple myeloma, the lesions are sharply defined holes typically 5 to 20 mm in diameter and often penetrate both tables in the skull (Aufderheide, Rodiguez- Martin 1998). The malignant plasma cells inhibit local osteoblastic activity at the site of the lytic focus, so sclerotic margins do not occur in most cases (Mulligan 2000). Myelomatous perforations are round and small, but individual large lesions, particularly the primary lesion, do occur and small lesions can become confluent, often showing scalloped margins as in the case of the right parietal perforation (Figure 7). In metastatic carcinoma, even if it is predominately lytic, some of the lesions usually show osteoblastic response in association with at least some of the lesions (Marcsik et al. 2002, Ortner 2003). Multiple myeloma frequently involves the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the lateral portion of the clavicle, and disseminates into the radius and the ulna (Schinz et al ). In multiple myeloma, the multiple and clearly destructive nature of skull perforations distinguishes them from the perforations of chronic infections such as venereal syphilis and from the perforations of trauma (Robert and Manchester 2007); the lesions often have scalloped margins (Mulligan 2000: 127) with localized lytic loci in the diploë that can be seen using radiographs (Figure 8) (Molnar et al. 2009). Based on the scalloped margins of the perforations, 320
5 A Case of Multiple Myeloma and Congenital Anomalies of an Early Islamic Skeleton from Tell Abu Al-Kharaz, Jordan FIGURE 4. Exostosis anterior to the foramen magnum. Photographed by H. Deebajeh. FIGURE 3. Asymmetric corpus sterni and osteoarthritic evidence. Photographed by H. Deebajeh. FIGURE 5. Lumbar osteophytosis and vertebral body degeneration. Photographed by H. Deebajeh. FIGURE 6. Lateral view of the skull showing the multiple perforations in the right parietal and mastoid process. Photographed by P. Fischer. 321
6 Ali M. Khwaileh FIGURE 7. The myelomatous perforations of the ossified trachea. Photographed by H. Deebajeh. FIGURE 8. The porotic cervical vertebrae. Photographed by H. Deebajeh. osteoblastic response, penetration and shape, the skull is diagnosed as having multiple myeloma. The vertebrae also shows lesions typical of multiple myeloma and the most evident lesions throughout the skeleton were ossified trachea as shown in figure 9 below. Hypercalcemia is usually encountered in multiple myeloma, which explains the ossification of the trachea (Raab et al. 2009). The teeth exhibited gross dental wear and dental caries, which were attributed to the consumption of hard food items, rich carbohydrate diet, and poor oral hygiene. The lower canines show clear linear enamel hypoplasia reflecting childhood stress. possible by loaning the skeletal material. Special thanks goes to Muwafaq Al-Bataineh for his advice and loaning the map and Hussein Deebajeh for the photography. CONCLUSION The woman of this study was born with bone anomalies in the head, pelvis, and chest that certainly created improper posture and gate. She lived suffering from the diseases of cancer and congenital anomaly. Trodden sharp knife put an end to her misery. Even after death, she did not receive a decent burial but a humble place in an abandoned area of a vanished society. This probably questions either her social status or the people's fear of her diseases. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The Author would like to express the thanks to Professor Abdulla Al-Shorman for his valuable advice and assistance in palaeopathological diagnosis. Professor Peter Fischer made this publication FIGURE 9. Radiograph additional lytic loci localized in the diploe. 322
7 A Case of Multiple Myeloma and Congenital Anomalies of an Early Islamic Skeleton from Tell Abu Al-Kharaz, Jordan REFERENCES AL-SHORMAN A., 2007: Archaeothanatology of Jordan. Yarmouk University, Irbid. AUFDERHEIDE A., RODIGUEZ-MARTIN C., 1998: The Cambridge Encyclopedia of Human Paleopathology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. BUIKSTRA J., UBELAKER D., 1994: Standards for Data Collection from Human Skeletal Remains. Arkansas Archaeological Survey, Fayettevilla. CATTANEO C., GELSTHORPE K., PHILLIPS P., WALDRON T., BOOTH J., SOKOL R., 1994: Immunological diagnosis of multiple myeloma in a medieval bone. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology 4: 1 2. FISCHER P., 2013: Tell Abu al-kharaz in the Jordan Valley. Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, Wien. MARCSIK A., SZANTHMARY L., FINNEGAN M., 2002: Multiple myeloma and metastatic skeletal lesions in osteoarchaeology samples. Journal of Paleopathology 14, 2: MOLNAR E., MARCSIK A., BERECZKI Z., SCHMIDT- SCHULTZ T., SCHULTZ M., PÁLFI G., 2009: Malignant tumors in osteoarchaeological samples from Hungary. Acta Biologica Szegediensis 53, 2: MULLIGAN M., 2000: Myeloma and lymphoma. Seminars in Musculoskeletal Radiology 4: ORTNER D., 2003: Identification of Pathological Conditions from Human Skeletal Remains. Academic Press, New York. RAAB M., PODAR K., BREITKREUTZ I., RICHARDSON P., ANDERSON, K., 2009: Multiple myeloma. Lancet 374: ROBERT C., MANCHESTER K., 2007: The Archaeology of Disease. Cornell University Press, Ithaca. SCHINZ H., BAENSCH W., FRIEDL E., UEHLINGER E., : Roentgen Diagnostics: Skeleton (Vols. 1 2). Grune and Stratton, New York. STEELE D., BRAMBLETT C., 1988: The Anatomy and Biology of the Human Skeleton. Texas A&M University Press, College Station, Texas. WELLS C., 1963: Ancient Egyptian pathology. The Journal of Laryngology and Otololgy 77, 3: Ali M. Khwaileh Department of Anthropology Faculty of Archaeology and Anthropology Yarmouk University Irbid Jordan khwaileh@yu.edu.jo 323
HUMAN SKELETAL REMAINS FROM CHOTUNA
 APPENDIX 3 HUMAN SKELETAL REMAINS FROM CHOTUNA JOHN W. VERANO Nineteen human burials were excavated at Chotuna during the 1980 82 field seasons. All can be assigned to the Late Phase (AD 1370 1600). Skeletal
APPENDIX 3 HUMAN SKELETAL REMAINS FROM CHOTUNA JOHN W. VERANO Nineteen human burials were excavated at Chotuna during the 1980 82 field seasons. All can be assigned to the Late Phase (AD 1370 1600). Skeletal
Osteological Analysis Scarborough Road Rillington North Yorkshire
 Osteological Analysis 30-32 Scarborough Road Rillington North Yorkshire Site Code: 01.11.04 NGR: SE 8551 7441 Report No 0606 May 2006 Prepared for MAP Archaeological Consultancy Ltd Showfield Lane Malton
Osteological Analysis 30-32 Scarborough Road Rillington North Yorkshire Site Code: 01.11.04 NGR: SE 8551 7441 Report No 0606 May 2006 Prepared for MAP Archaeological Consultancy Ltd Showfield Lane Malton
Report on the human inhumation from Campanaio, Province of Agrigento, Sicily (Site code MO97)
 Reports from the Environmental Archaeology Unit, York 97/43, 7 pp. Report on the human inhumation from Campanaio, Province of Agrigento, Sicily (Site code MO97) by Cluny Johnstone Summary A single human
Reports from the Environmental Archaeology Unit, York 97/43, 7 pp. Report on the human inhumation from Campanaio, Province of Agrigento, Sicily (Site code MO97) by Cluny Johnstone Summary A single human
Osteological Evaluation. Prepared by Tori D. Randall, Ph.D. Biological Anthropologist
 Osteological Evaluation Prepared by Tori D. Randall, Ph.D. Biological Anthropologist Adult Female Asian Skull Product Number: BC-299 Specimen Evaluated: Bone Clones replica Skeletal Inventory: Cranium
Osteological Evaluation Prepared by Tori D. Randall, Ph.D. Biological Anthropologist Adult Female Asian Skull Product Number: BC-299 Specimen Evaluated: Bone Clones replica Skeletal Inventory: Cranium
Malignant tumors in osteoarchaeological samples from Hungary
 Volume 53(2):117-124, 2009 Acta Biologica Szegediensis http://www.sci.u-szeged.hu/abs ARTICLE Malignant tumors in osteoarchaeological samples from Hungary Erika Molnár 1 *, Antónia 1, Zsolt Bereczki 1,
Volume 53(2):117-124, 2009 Acta Biologica Szegediensis http://www.sci.u-szeged.hu/abs ARTICLE Malignant tumors in osteoarchaeological samples from Hungary Erika Molnár 1 *, Antónia 1, Zsolt Bereczki 1,
Skeleton Tedeschi Register (1911) Sex:: M- S. A. Age: 31 years Job:
 Skeleton 1438 Tedeschi Register (1911) Sex:: M- S. A. Age: 31 years Job: Blacksmith Date of death: 9 th of February, 1911 Cause of death: Lung tuberculosis Origin: General Hospital (Padova) Bone Remains
Skeleton 1438 Tedeschi Register (1911) Sex:: M- S. A. Age: 31 years Job: Blacksmith Date of death: 9 th of February, 1911 Cause of death: Lung tuberculosis Origin: General Hospital (Padova) Bone Remains
The Skeletal System. Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments
 The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
Spring Written By: J. E. Sutton. Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV.
 Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Report on the Human Remains Recovered from Block 23CB on Colonial Williamsburg Property
 Report on the Human Remains Recovered from Block 23CB on Colonial Williamsburg Property By: Michael L. Blakey, Director Shannon Mahoney, Graduate Research Associate Institute for Historical Biology Department
Report on the Human Remains Recovered from Block 23CB on Colonial Williamsburg Property By: Michael L. Blakey, Director Shannon Mahoney, Graduate Research Associate Institute for Historical Biology Department
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives
 Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Human Skeletal Remains from Brimstone Hill Fortress National Park, St. Kitts, West Indies, 2006
 Human Skeletal Remains from Brimstone Hill Fortress National Park, St. Kitts, West Indies, 2006 Brimstone Hill Fortress Archaeological Project Report No. 30 By Elizabeth A. DiGangi Submitted to The Brimstone
Human Skeletal Remains from Brimstone Hill Fortress National Park, St. Kitts, West Indies, 2006 Brimstone Hill Fortress Archaeological Project Report No. 30 By Elizabeth A. DiGangi Submitted to The Brimstone
Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology. ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations
 Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations Anthropology & Archaeology Anthropology is the study of the biological and cultural aspects of all humans in all places
Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations Anthropology & Archaeology Anthropology is the study of the biological and cultural aspects of all humans in all places
Osteological Analysis of Human Remains from The Chapter House, Worcester Cathedral
 Osteological Analysis of Human Remains from The Chapter House, Worcester Cathedral A report for Worcester Cathedral December 2003 Mercian Archaeology Project: PJ 112 1. Introduction This report contains
Osteological Analysis of Human Remains from The Chapter House, Worcester Cathedral A report for Worcester Cathedral December 2003 Mercian Archaeology Project: PJ 112 1. Introduction This report contains
Paleopathological conditions in an Eneolithic Community from Sultana - Malu Roşu
 Paleopathological conditions in an Eneolithic Community from Sultana - Malu Roşu Alexandra ION * Andrei D. SOFICARU * Abstract: The present article provides an anthropological research regarding 12 graves
Paleopathological conditions in an Eneolithic Community from Sultana - Malu Roşu Alexandra ION * Andrei D. SOFICARU * Abstract: The present article provides an anthropological research regarding 12 graves
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
2004 ANGLO-GEORGIAN NOKALAKEVI EXPEDITION. Osteological Assessment for Trench B Benjamin Neil
 2004 ANGLO-GEORGIAN NOKALAKEVI EXPEDITION. Osteological Assessment for Trench B Benjamin Neil SUMMARY The Excavation of 10 burials in trench 'B' is reported. In total, 14 individuals were found plus an
2004 ANGLO-GEORGIAN NOKALAKEVI EXPEDITION. Osteological Assessment for Trench B Benjamin Neil SUMMARY The Excavation of 10 burials in trench 'B' is reported. In total, 14 individuals were found plus an
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Nervous & Skeletal Systems. Virtual Science University
 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
Human remains from Bakr Awa, Iraqi Kurdistan, 2017
 Bioarchaeology of the Near East, 11:63 69 (2017) Short fieldwork report Human remains from Bakr Awa, Iraqi Kurdistan, 2017 Rafał A. Fetner *1, Joanna Szymczak 2 1 Department of Bioarchaeology, University
Bioarchaeology of the Near East, 11:63 69 (2017) Short fieldwork report Human remains from Bakr Awa, Iraqi Kurdistan, 2017 Rafał A. Fetner *1, Joanna Szymczak 2 1 Department of Bioarchaeology, University
TWO CASES OF JOINT DISEASE FROM THE AVAR AGE, HUNGARY
 XLI/1 2 pp. 79 85 2003 SÁNDOR ÉVINGER, ZSOLT BERNERT, LÁSZLÓ JÓZSA, LILLA ALIDA KRISTÓF TWO CASES OF JOINT DISEASE FROM THE AVAR AGE, HUNGARY ABSTRACT: The authors describe two cases of joint disease from
XLI/1 2 pp. 79 85 2003 SÁNDOR ÉVINGER, ZSOLT BERNERT, LÁSZLÓ JÓZSA, LILLA ALIDA KRISTÓF TWO CASES OF JOINT DISEASE FROM THE AVAR AGE, HUNGARY ABSTRACT: The authors describe two cases of joint disease from
Lab-1. Miss. Lina Al-Onazy & samar Al-Wgeet =)
 Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Bone Flashcards for 10a
 Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
HUMAN REMAINS ANALYSIS FOR EL DORNAJO SITE
 HUMAN REMAINS ANALYSIS FOR EL DORNAJO SITE By: María Patricia Ordoñez, (Department of Anthropology, Universidad Católica del Ecuador), September 2008. The following report consists of the analysis of human
HUMAN REMAINS ANALYSIS FOR EL DORNAJO SITE By: María Patricia Ordoñez, (Department of Anthropology, Universidad Católica del Ecuador), September 2008. The following report consists of the analysis of human
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Forensic Anthropology Open Notes Practice Test
 Name: Date: 1/2/18 Section Broughton High School 1 Section 1: - True or False Forensic Anthropology Open Notes Practice Test 1. The number of bones in the body increases from the time of birth to adulthood.
Name: Date: 1/2/18 Section Broughton High School 1 Section 1: - True or False Forensic Anthropology Open Notes Practice Test 1. The number of bones in the body increases from the time of birth to adulthood.
Human Male European Skull
 Human Male European Skull Product Number: BCM-892 Known Information: This skull is associated with a skeleton of a 34-year-old European male, who stood 5' 8" and weighed 185 pounds at time of death. Cause
Human Male European Skull Product Number: BCM-892 Known Information: This skull is associated with a skeleton of a 34-year-old European male, who stood 5' 8" and weighed 185 pounds at time of death. Cause
Exercise 10. The Axial Skeleton
 Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet
 1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
SAMPLE. Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS ICD-10. Cross Coder
 Cross Coder www.optumcoding.com Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS 2017 a ICD-10 A full suite of resources including the latest code set, mapping products, and expert training
Cross Coder www.optumcoding.com Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS 2017 a ICD-10 A full suite of resources including the latest code set, mapping products, and expert training
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System
 Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Classification of bones
 Classification of bones compact intramembranous axial histology development regional spongy Intra cartilaginous appendicular flat Irregular shape Sesamoid Long Short Wormian pneumatic Classification
Classification of bones compact intramembranous axial histology development regional spongy Intra cartilaginous appendicular flat Irregular shape Sesamoid Long Short Wormian pneumatic Classification
Skeletal system overview. Classification of Bones
 Skeletal system overview BIOL241 Lab #9 Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Skeletal system overview BIOL241 Lab #9 Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Human Female European Skull
 Human Female European Skull Product Number: BCM-891 Known Information: This skull is associated with a skeleton of a 41-year-old European female, who stood 5' 6 and weighed 133 pounds at time of death.
Human Female European Skull Product Number: BCM-891 Known Information: This skull is associated with a skeleton of a 41-year-old European female, who stood 5' 6 and weighed 133 pounds at time of death.
Important Parts of Bones
 Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
IDENTIFICATION OF SKELETAL REMAINS FROM A MYCENAEAN BURIAL IN KASTROULI-DESFINA, GREECE
 Copyright 2017 MAA Open Access. Printed in Greece. All rights reserved. 10.5281/zenodo.556353 IDENTIFICATION OF SKELETAL REMAINS FROM A MYCENAEAN BURIAL IN KASTROULI-DESFINA, GREECE Maria-Eleni Chovalopoulou,
Copyright 2017 MAA Open Access. Printed in Greece. All rights reserved. 10.5281/zenodo.556353 IDENTIFICATION OF SKELETAL REMAINS FROM A MYCENAEAN BURIAL IN KASTROULI-DESFINA, GREECE Maria-Eleni Chovalopoulou,
Human, European American, Male 13-Year- Old Partial Skeleton
 Human, European American, Male 13-Year- Old Partial Skeleton Product Number: FM-509-SET Known Information: These bones are from a 13-year-old, 5'3" and 120 lbs, European American male. This information
Human, European American, Male 13-Year- Old Partial Skeleton Product Number: FM-509-SET Known Information: These bones are from a 13-year-old, 5'3" and 120 lbs, European American male. This information
What is the primary job of a forensic anthropologist? What are the three main things that can determined from a skeleton?
 What is the primary job of a forensic anthropologist? What are the three main things that can determined from a skeleton? What three areas of a skeleton can be used to determine sex? Physical anthropologists
What is the primary job of a forensic anthropologist? What are the three main things that can determined from a skeleton? What three areas of a skeleton can be used to determine sex? Physical anthropologists
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System
 Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Human Male European Disarticulated Skeleton
 Human Male European Disarticulated Skeleton Product Number: SCM-192-D Known Information: All bones are associated in this skeleton of a 34-year-old European male, who stood 5' 8" and weighed 185 pounds
Human Male European Disarticulated Skeleton Product Number: SCM-192-D Known Information: All bones are associated in this skeleton of a 34-year-old European male, who stood 5' 8" and weighed 185 pounds
Health profiles of a Bronze Age population from northeastern Hungary
 ANNALES HISTORICO-NATURALES MUSEI NATIONALIS HUNGARICI Volume 88. Budapest. 1996 pp. 271-296. Health profiles of a Bronze Age population from northeastern Hungary D. H. UBELAKER 1 & I. PAP 2 Department
ANNALES HISTORICO-NATURALES MUSEI NATIONALIS HUNGARICI Volume 88. Budapest. 1996 pp. 271-296. Health profiles of a Bronze Age population from northeastern Hungary D. H. UBELAKER 1 & I. PAP 2 Department
Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium,
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium,
o Diaphysis o Area where red marrow is found o Area where yellow marrow is found o Epiphyseal plate AXIAL SKELETON Skull
 64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
Human, Adolescent (15-18 years)
 Human, Adolescent (15-18 years) PRODUCT NUMBER: SPECIMEN EVALUATED: SKELETAL INVENTORY: SC-301 Original specimen 1 Cranium with 11 maxillary teeth 1 Mandible with 13 teeth 1 Complete postcranial skeleton
Human, Adolescent (15-18 years) PRODUCT NUMBER: SPECIMEN EVALUATED: SKELETAL INVENTORY: SC-301 Original specimen 1 Cranium with 11 maxillary teeth 1 Mandible with 13 teeth 1 Complete postcranial skeleton
Labs 9 and 10. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes 1/05/13. Skeletal system overview. Bone are identified by:
 Labs 9 and 10 Skeletal system overview Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Labs 9 and 10 Skeletal system overview Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Human Male Asian Skeleton, Robust
 Human Male Asian Skeleton, Robust Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: SC-287 Original Specimen Near-complete human skeleton with 28 teeth. Osteological Observations: This is a clean,
Human Male Asian Skeleton, Robust Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: SC-287 Original Specimen Near-complete human skeleton with 28 teeth. Osteological Observations: This is a clean,
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME
 TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
Avulsion Fractures of the Transverse Processes of the First Thoracic Vertebra: An Archaeological Case Study from Raunds
 International Journal of Osteoarchaeology Int. J. Osteoarchaeol. 19: 116 122 (2009) Published online 23 July 2008 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).977 SHORT REPORT Avulsion Fractures
International Journal of Osteoarchaeology Int. J. Osteoarchaeol. 19: 116 122 (2009) Published online 23 July 2008 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).977 SHORT REPORT Avulsion Fractures
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Spine and Neck
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
P C A 300 HIGH STREET, BERKHAMSTED, HERTFORDSHIRE EXCAVATION SUMMARY LOCAL PLANNING AUTHORITY: DACORUM BOROUGH COUNCIL
 00 HIGH STREET, BERKHAMSTED, HERTFORDSHIRE EXCAVATION SUMMARY LOCAL PLANNING AUTHORITY: DACORUM BOROUGH COUNCIL PLANNING APPLICATION NUMBER: 4/01211/12/MFA PCA REPORT NO: 11614 SITE CODE: HHST12 P C A
00 HIGH STREET, BERKHAMSTED, HERTFORDSHIRE EXCAVATION SUMMARY LOCAL PLANNING AUTHORITY: DACORUM BOROUGH COUNCIL PLANNING APPLICATION NUMBER: 4/01211/12/MFA PCA REPORT NO: 11614 SITE CODE: HHST12 P C A
bio4165 lab quiz 1 Posterior View Anterior View Lateral View Anterior View bio fall.quarter lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6
 B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
070:358 and 070:359 Spring 2008 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN OSTEOLOGY WITH LABORATORY Department of Anthropology, Rutgers University
 070:358 and 070:359 Spring 2008 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN OSTEOLOGY WITH LABORATORY Department of Anthropology, Rutgers University INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Rob Scott Office: Biosciences Building 210, Douglass Campus
070:358 and 070:359 Spring 2008 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN OSTEOLOGY WITH LABORATORY Department of Anthropology, Rutgers University INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Rob Scott Office: Biosciences Building 210, Douglass Campus
BIO 137 AXIAL SKELETON BONE STUDY THE HUMAN SKELETON
 BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton
 Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones upper & lower limbs
Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones upper & lower limbs
External Acoustic Meatus. Mastoid Process. Zygomatic Process. Temporal Bone
 Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings
 Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Bone Composition. Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are:
 Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
ANTHROPOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF MUMMIFIED BURIALS FROM SAQQARA
 ANTHROPOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF MUMMIFIED BURIALS FROM SAQQARA Maria Kaczmarek The main aim of the study was to describe the range of biological variation in craniofacial and dental morphological traits of
ANTHROPOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF MUMMIFIED BURIALS FROM SAQQARA Maria Kaczmarek The main aim of the study was to describe the range of biological variation in craniofacial and dental morphological traits of
Report on a human inhumation and other vertebrate remains from Staxton Motel, North Yorkshire (site code OSA98EV12) Summary
 Reports from the Environmental Archaeology Unit, York 99/14, 6 pp. Report on a human inhumation and other vertebrate remains from Staxton Motel, North Yorkshire (site code OSA98EV12) by Cluny Johnstone,
Reports from the Environmental Archaeology Unit, York 99/14, 6 pp. Report on a human inhumation and other vertebrate remains from Staxton Motel, North Yorkshire (site code OSA98EV12) by Cluny Johnstone,
Bone List Anatomy
 1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Forensic Anthropology Notes
 Forensic Anthropology Notes 1 Chapter 13 Forensic Anthropology: What We Learn from Bones describe how bone is formed distinguish between male and female skeletal remains explain how bones contain a record
Forensic Anthropology Notes 1 Chapter 13 Forensic Anthropology: What We Learn from Bones describe how bone is formed distinguish between male and female skeletal remains explain how bones contain a record
Name Period Unit 17 Forensic Anthropology Test Review
 Name Period Unit 17 Forensic Anthropology Test Review 1. Define Forensic Anthropology - The study of skeletonized human remains. 2. List 4 ways Forensic Anthropology can be used to possibly identify remains
Name Period Unit 17 Forensic Anthropology Test Review 1. Define Forensic Anthropology - The study of skeletonized human remains. 2. List 4 ways Forensic Anthropology can be used to possibly identify remains
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) - hemopoiesis Storage of inorganic materials (salt,
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) - hemopoiesis Storage of inorganic materials (salt,
Chapter 7: Skeletal System
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Support and protection. Body movement. Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
Osteological Analysis Queen s Hotel York North Yorkshire
 Osteological Analysis Queen s Hotel York North Yorkshire Site Code: 1989.17 NGR: SE 601 515 Report No 0316 February 2016 Prepared for York Archaeological Trust for Excavation & Research Ltd 47 Aldwark
Osteological Analysis Queen s Hotel York North Yorkshire Site Code: 1989.17 NGR: SE 601 515 Report No 0316 February 2016 Prepared for York Archaeological Trust for Excavation & Research Ltd 47 Aldwark
NOTES SKELETAL SYSTEM
 NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1
 Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
JACEK TOMCZYK Instytut Ekologii i Bioetyki, UKSW, Warszawa
 Studia Ecologiae et Bioethicae UKSW 11(2013)1 JACEK TOMCZYK Instytut Ekologii i Bioetyki, UKSW, Warszawa 1 Key words: Middle Euphrates Valley, human bones, pathology SUMMARY The middle Euphrates valley
Studia Ecologiae et Bioethicae UKSW 11(2013)1 JACEK TOMCZYK Instytut Ekologii i Bioetyki, UKSW, Warszawa 1 Key words: Middle Euphrates Valley, human bones, pathology SUMMARY The middle Euphrates valley
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Osteological Analysis Tadcaster Castle Castle Hill House North Yorkshire
 Osteological Analysis Tadcaster Castle Castle Hill House North Yorkshire Site Code: TADCH09 NGR: SE 485 436 Report No 0911 May 2011 Prepared for Towton Battlefield Society Prepared by Katie Keefe and Malin
Osteological Analysis Tadcaster Castle Castle Hill House North Yorkshire Site Code: TADCH09 NGR: SE 485 436 Report No 0911 May 2011 Prepared for Towton Battlefield Society Prepared by Katie Keefe and Malin
TWO CASES OF ARTHRITIC DISEASE FROM THE MEDIEVAL AGE, HUNGARY
 Two Cases of Arthritic Disease from the Medieval Age, Hungary XLI/1 2 pp. 71 78 2003 ZSOLT BERNERT, SÁNDOR ÉVINGER, TAMÁS HAJDU, ILDIKÓ PAP, PÉTER ZSOLT VARGA, ERZSÉBET FÓTHI TWO CASES OF ARTHRITIC DISEASE
Two Cases of Arthritic Disease from the Medieval Age, Hungary XLI/1 2 pp. 71 78 2003 ZSOLT BERNERT, SÁNDOR ÉVINGER, TAMÁS HAJDU, ILDIKÓ PAP, PÉTER ZSOLT VARGA, ERZSÉBET FÓTHI TWO CASES OF ARTHRITIC DISEASE
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7
 TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
Dr.Israa H. Mohsen. Lecture 5. The vertebral column
 Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Bone. Mental Foramen Mandible
 Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
CATALOGUE OF BURIALS Katherine Gruspier
 CATALOGUE OF BURIALS Katherine Gruspier Forum II Burials JUVENILES Burial 1B Burial: Extended on its back, right upper body turned over onto the left side, head SW. Age: 13 to 16 years (epiphyseal union).
CATALOGUE OF BURIALS Katherine Gruspier Forum II Burials JUVENILES Burial 1B Burial: Extended on its back, right upper body turned over onto the left side, head SW. Age: 13 to 16 years (epiphyseal union).
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
The Thoracic Cage ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process
ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process
Osteological Analysis of the Human Remains Skriðuklaustur 2011
 Elin Ahlin Sundman Osteological Analysis of the Human Remains Skriðuklaustur 2011 Skýrslur Skriðuklaustursrannsókna XXXI Elin Ahlin Sundman 2011 Osteological Analysis of the Human Remains Skriðuklaustur
Elin Ahlin Sundman Osteological Analysis of the Human Remains Skriðuklaustur 2011 Skýrslur Skriðuklaustursrannsókna XXXI Elin Ahlin Sundman 2011 Osteological Analysis of the Human Remains Skriðuklaustur
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5. Subject: The Skeletal System
 Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Report on two further human inhumations from Campanaio, Province of Agrigento, Sicily (site code MO98)
 Reports from the Environmental Archaeology Unit, York 98/39, 8 pp. Report on two further human inhumations from Campanaio, Province of Agrigento, Sicily (site code MO98) by Cluny Johnstone Summary Two
Reports from the Environmental Archaeology Unit, York 98/39, 8 pp. Report on two further human inhumations from Campanaio, Province of Agrigento, Sicily (site code MO98) by Cluny Johnstone Summary Two
Osteological Report on the Human Skeletons from Eden Roc, Bay Hill, St. Margarets. Amanda Bailey (MSc Osteoarchaeology) July, 2009.
 Osteological Report on the Human Skeletons from Eden Roc, Bay Hill, St. Margarets Amanda Bailey (MSc Osteoarchaeology) July, 2009. 1 Non-Technical Summary Six crouched Bronze Age inhumations excavated
Osteological Report on the Human Skeletons from Eden Roc, Bay Hill, St. Margarets Amanda Bailey (MSc Osteoarchaeology) July, 2009. 1 Non-Technical Summary Six crouched Bronze Age inhumations excavated
Skeletal System. Supplementary Information
 Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
THE PROFESSIONS WHEN ANALYZING PREHISTORIC SKELETONS
 ANTHROPOLOGIE x x x 11/1 1994 Research Reports and News J. J. Gladykowska-Rzeczycka PROBLEMS OF ESTIMATING AGE AND DETERMINING THE PROFESSIONS WHEN ANALYZING PREHISTORIC SKELETONS A BSTRA CT: The problems
ANTHROPOLOGIE x x x 11/1 1994 Research Reports and News J. J. Gladykowska-Rzeczycka PROBLEMS OF ESTIMATING AGE AND DETERMINING THE PROFESSIONS WHEN ANALYZING PREHISTORIC SKELETONS A BSTRA CT: The problems
