The management and control of pain sensation is a matter of intense study and of great clinical interest. Drugs like aspirin
|
|
|
- Kerry Bailey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Melatonin in Antinociception: Its Therapeutic Applications Venkatramanujam Srinivasan, Edward C. Lauterbach, Khek Yu Ho, Dario Acuña-Castroviejo, Rahimah Zakar rencia : Curr Neuropharmacol Jun;10(2): doi: / Tipográfia Reducir tamaño (-a) Aumentar tamaño (+A) Servicios Versión de impresión Recomendar este artículo Texto completo No se dispone del texto completo Abstract: The intensity of pain sensation exhibits marked day and night variations. Since the intensity of pain perception is low during dark hours of the night when melatonin levels are high, this hormone has been implicated as one of the prime antinociceptive substances. A number of studies have examined the antinociceptive role of melatonin in acute, inflammatory and neuropathic pain animal models. It has been demonstrated that melatonin exerts antinociceptive actions by acting at both spinal cord and supraspinal levels. The mechanism of antinociceptive actions of melatonin involves opioid, benzodiazepine,?1- and?2-adrenergic, serotonergic and cholinergic receptors. Most importantly however, the involvement of MT1/MT2 melatonergic receptors in the spinal cord has been well documented as an antinociceptive mechanism in a number of animal models of pain perception. Exogenous melatonin has been used effectively in the management of pain in medical conditions such as fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome and migraine and cluster headache. Melatonin has been tried during surgical operating conditions and has been shown to enhance both preoperative and post-operative analgesia. The present review discusses the available evidence indicating that melatonin, acting through MT1/MT2 melatonin receptors, plays an important role in the pathophysiological mechanism of pain. Keywords: Pain, nociception, analgesia, melatonin, inflammatory, neuropathic, fibromyalgia, cluster headache, migraine. 1. INTRODUCTION Pain is classically described as an unpleasant sensation. By definition pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage [1]. Clinical pain has been divided into two conditions, including inflammatory pain caused by inflammation and neuropathic pain caused by actual injury to the nervous system [2]. These types of pain are characterized by persistent pain hypersensitivity [2]. In addition to hyperalgesia, neuropathic pain also manifests as allodynia (pain occurring in response to normally innocuous stimuli). Multiple nociceptive mechanisms have been suggested to underlie neuropathic pain [3]. As this type of pain can persist for years, it is also associated with symptoms like anxiety, depression, and sleep-disturbances [4, 5]. On the other hand symptoms of pain can also constitute a presenting feature of major depressive disorder, suggesting pathophysiological similarities between clinical pain and certain psychiatric disorders, particularly major depression [6, 7]. The mechanism of pain perception is considered to be multifactorial involving many biochemical, humoral, neurophysiological and psychological factors [8]. Damage or inflammation of tissue releases a variety of inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins (PGE2), leukotrienes, bradykinin, substance P and inflammatory cytokines like tumor-necrosis factor (TNF-?), ATP and adenosine. Each of these substances either directly activates nociceptors or releases local allogenic agents which sensitize nociceptors and enhance the neuronal excitability of pain transmission pathways [9]. The transmission of pain sensation involves nociceptors (the primary sensory nerve endings of A? and C fibers) that have their central processes in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. The dorsal horn of the spinal cord is the first site of synaptic transfer in the nociceptive pathway and it is the primary region where peripheral afferent signals are integrated and modulated. A number of neurotransmitterreceptor sites such as NMDA, AMPA, opioid (? and?),?2- adrenoceptors, and adenosine are located in the dorsal horn projection neurons. The dorsal horn region of the spinal cord is the region of central sensitization and this is mediated by neurotransmitters like glutamate, substance P and neurokinin which interact with the NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartic acid) receptor system [10, 11]. In addition to this, the dorsal horn neuron is also subjected to the influences of interneurons of the dorsal horn itself and descending pathways that modulate pain perception [7, 12]. These spinal interneurons and descending neural tracts from the brain constitute endogenous pain modulatory systems that inhibit pain transmission signals. These pain modulatory systems are activated by opioid and GABAergic mechanisms located in and around the periaqueductal gray region (PAG). From the PAG, descending fibers project to the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVM) and dorsolateral pontine structures that in turn send inhibitory projections to the spinal cord to induce antinociceptive effects. Inhibitory?2-adrenergic,?,?, and? opioid and 5-HT1A receptors are present in the post-synaptic dorsal horn neurons along with GABA-A/B receptors [7, 13]. Descending fibres synapse with primary afferent neurons, and secondary neurons or interneurons to stimulate them to release opioid peptides. The management and control of pain sensation is a matter of intense study and of great clinical interest. Drugs like aspirin
2 and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) exert their antinociceptive effects by inhibiting cyclooxygenases (COX) [14]. But the side effects of aspirin and NSAIDS including gastrointestinal bleeding and ulceration make them unsafe for long-term clinical use. Other classes of drugs like morphine or the anti-inflammatory drugs that act through the NO-cyclic GMP pathway exert their antinociceptive actions by blocking the ascending transmission of pain sensation [15]. The side effects associated with morphine including sedation, respiratory depression and dependence complicate its use in controlling nociceptive mechanisms [16, 17]. In addition there are many other painful conditions like neurodegenerative pain and varieties of neuropathic pain that are not responsive to potent analgesics including opioids. Neuropathic pain is also a frequent manifestation of neurodegenerative diseases. Although it is less appreciated in Parkinson s disease (PD), the prevalence of pain is nearly 40% in PD. Pain presentations in PD include several categories such as musculoskeletal pain, radicular or neuropathic pain, and primary central parkinsonian pain [18]. Neurodegenerative mitochondrial and cytoskeletal cellular mechanisms producing painful hyperactivity in primary afferent nociceptors have been suggested as possible causative factors contributing to hyperalgesia [19]. Tricyclic antidepressants and gabapentin are often prescribed for the treatment of neuropathic pain with variable results of response [20-22], suggesting thereby the need for the development of novel analgesic drugs that can be used for effective treatment and management of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. 2. MELATONIN AND NOCICEPTION Diurnal variations in the perception of pain have been described both in rodents and humans [23-26]. It has been reported that patients suffer less pain during the dark phase of the photoperiod and prolonged latencies in pain thresholds have been detected in healthy human subjects during night time. These observations were recorded by Laikin and his co-workers [26] and they attributed this phenomenon to high melatonin levels occurring at night and their possible analgesic effects. Based upon this initial observation a number of investigators have evaluated the antinociceptive effects of melatonin in animals by using a variety of experimental models and designs. 3. MELATONIN BIOSYNTHESIS Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) is a neurohormone produced mainly in the pineal gland of all vertebrates in a circadian fashion [27]. Tryptophan serves as the precursor for its biosynthesis and is converted into 5- hydroxytrptophan. Serotonin is then acetylated to form Nacetylserotonin by the enzyme arylalkylamine Nacetyltransferase (NAT) and then O- methylated by hydroxyindole- O-methyltransferase (HIOMT) to form melatonin (Fig. 1). Biosynthesis of melatonin in the pineal gland is regulated by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus and is synchronized to the environmental light-dark cycle [28, 29]. Special melanopsin containing ganglion cells [30] transmit this photoperiodic information to the SCN through the retino-hypothalamic tract [31]. Fibers from the SCN project to the superior cervical ganglion (SCG) through a circuitous route. Post-ganglionic fibers from SCG regulate pineal melatonin synthesis by releasing norepinephrine (NE) at pinealocyte receptor sites. NE released from the postganglionic sympathetic fibers interacts with?- adrenergic receptors as well as?1-adrenergic receptors of the pinealocyte membrane, activating the adenyl cyclase cyclic AMP pathway that in turn regulates the expression of NAT and other enzymes involved in melatonin biosynthesis [32]. Exposure to bright light during dark hours of the night suppresses melatonin production by degradation of NAT enzyme [33]. Once formed, melatonin is not stored in the pineal gland but diffuses into the blood [34]. But most of the melatonin from the pineal gland is also released simultaneously into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in primates [35]. The concentration of melatonin in the CSF of the third ventricle is 20 to 30 times higher than that found in the blood [36]. Circulating melatonin is metabolized mainly in the liver where it is first hydroxylated in the C6 position by cytochrome P450 mono-oxygenases (isoenzymes CYP1A2, CYP1A1, and to a lesser extent CYP1B1) and thereafter conjugated with sulphate to be excreted as 6-sufatoxymelatonin (amt6s). In the brain a substantial amount of melatonin is metabolized to kynuramine derivatives [37]. This is of interest as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of melatonin are shared by some of these metabolites, N1 acetyl-n2 formyl-5-methoxy kynuramine (AFMK) and also by N2-acetyl-5-methoxykynuramine (AMK) [38].
3 Melatonin is also synthesized in many other regions of the body like skin [39], gastrointestinal tract, lymphocytes [40] and thymus [41]. In these regions melatonin has either a paracrine or autocrine role. Among other functions, extrapineal melatonin has a modulatory role on inflammation, reducing hyperalgesia, thus contributing to pain control [42]. Melatonin is synthesized by a number of plants. Of these, St John s Wort (Hypericum perforatum) is of medical importance and it has very high concentrations of melatonin [43, 44]. In a recent study it is reported that extracts of Hypericum perforatum (St John s Wort or SJW), Harpagophytum procumbens (HPE) and grape seed proanthocyanidins (GSPE) exerted significant antinociceptive effects in mice [45]. Nearly 60 commonly used Chinese medicinal herbs contain melatonin in concentrations ranging from 12 to 3771 ng/g [46]. It is an interesting fact that many of these melatonin containing herbs used in Chinese traditional medicine have age retarding effects and have been in use for treating diseases associated with increased generation of free radicals. Indeed the presence of melatonin in plants helps to protect them from oxidative damage and also from many environmental insults to which they have been subjected [47, 48]. Melatonin was observed to be elevated in alpine and Mediterranean plants exposed to strong UV radiation, a finding amenable to the interpretation that melatonin s antioxidant properties can antagonize damage caused by light-induced oxidants [49]. Melatonin in plants serves as a good antioxidant nutrient. The high concentration of melatonin detected in seeds also provide anti-oxidative defence even in a dormant and more or less dry system when most of the other substances and enzymes are not able to provide their full capacity as antioxidants [50]. 4. MELATONIN RECEPTORS Most of the physiological and pharmacological actions of melatonin are mediated through the activation of high affinity G-
4 protein coupled receptors, namely MT1 and MT2 and belong to the seven-transmembrane receptor family [51-53]. Melatonin binding to nuclear receptors has been demonstrated [54]. Some of these binding sites were identified as belonging to retinoid orphan related receptors like RZR? and RZR?, and they are present in the central and peripheral nervous systems [55]. Both MT1 and MT2 receptors have been identified in the ventral and dorsal horn of thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord, specifically in lamina I-V and X of the spinal cord which are involved in the pain regulatory mechanisms [56]. Earlier studies have localized melatonin receptors in different areas of the brain like the thalamus, hypothalamus, spinal trigeminal tract and trigeminal nucleus [57, 58]. 5. MELATONIN S ANTINOCICEPTIVE ACTION: EVIDENCES FROM ANIMAL MODELS Melatonin s antinociceptive effects have been demonstrated in animals like mice and rats by using a number of experimental models of nociception and this has been brought out extensively in an earlier review [59]. A brief analysis of this is presented in this paper with the aim of understanding the clinical significance of the antinociceptive and beneficial effects of melatonin. Using the hotplate procedure, it was shown that a melatonin injection (20-40 mg/kg, i.p) exerted its maximal analgesic effect when given in the late afternoon. This analgesic effect was blunted by the administration of either the opiate antagonist naloxone or the central benzodiazepine antagonist flumazenil, showing thereby the involvement of central opioid or benzodiazepine (BZD) receptors [60]. Soon after, it was showed that?- endorphin, through?-opioid receptors, is involved in melatonin-induced modulation of brain BZD receptors [61]. Dose-dependent antinociceptive effects of melatonin were evaluated by means of the hot-water tail flick test in a group of rats in which melatonin, injected (i.p) at three different doses (30, 60, 120 mg/kg), produced dosedependent antinociception [62]. The antinociceptive effect began within 15 minutes after injection and reached a peak in 30 minutes, and with mg/day doses, lasted for 100 minutes. Melatonin s antinociceptive effect with 60 to 120 mg/kg (i.p) was antagonized by an i.c.v injection of naloxone within 10 minutes after injection and lasted for 45 minutes. As the i.c.v injection of naloxone blocked melatonin s antinociceptive effect it was concluded that the CNS is the primary site for melatonin s antinociceptive effect. In another study, it was found that melatonin potentiated the antinociceptive effects of deltorphin-1 a,?-opioid agonist but not of the?-opioid agonist endomorphin-1. In this study melatonin was injected either i.p (1, 5, 25 mg/kg) or i.c.v (0.25, 0.5, 1 mg/kg), which produced significant tail withdrawal latencies, thereby confirming antinociceptive effects of melatonin [63]. A summary of the antinociceptive effects of melatonin in a variety of animal models is presented in Table 1.
5
6
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation
 Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Pain Pathways. Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH
 Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus. MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive
 PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
PAIN & ANALGESIA. often accompanied by clinical depression. fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue, etc. COX 1, COX 2, and COX 3 (a variant of COX 1)
 Pain - subjective experience associated with detection of tissue damage ( nociception ) acute - serves as a warning chronic - nociception gone bad often accompanied by clinical depression fibromyalgia,
Pain - subjective experience associated with detection of tissue damage ( nociception ) acute - serves as a warning chronic - nociception gone bad often accompanied by clinical depression fibromyalgia,
San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001
 PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
PAIN. Physiology of pain relating to pain management
 PAIN Physiology of pain relating to pain management What is pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. (Melzac and Wall) The generation of pain
PAIN Physiology of pain relating to pain management What is pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. (Melzac and Wall) The generation of pain
Melatonin in Antinociception: Its Therapeutic Applications
 Current Neuropharmacology, 2012, 10, 167-178 167 Melatonin in Antinociception: Its Therapeutic Applications Venkatramanujam Srinivasan 1,*, Edward C. Lauterbach 2, Khek Yu Ho 3, Dario Acuña-Castroviejo
Current Neuropharmacology, 2012, 10, 167-178 167 Melatonin in Antinociception: Its Therapeutic Applications Venkatramanujam Srinivasan 1,*, Edward C. Lauterbach 2, Khek Yu Ho 3, Dario Acuña-Castroviejo
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT
 CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
Pediatrics Grand Rounds 16 July University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio
 Light Pollution and Melatonin Suppression: Implications for Pediatrics Russel J. Reiter University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio, Texas reiter@uthscsa.edu Evolution has dictated biological
Light Pollution and Melatonin Suppression: Implications for Pediatrics Russel J. Reiter University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio, Texas reiter@uthscsa.edu Evolution has dictated biological
Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture the student should be familiar with: 1. The relationship between nociception
Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture the student should be familiar with: 1. The relationship between nociception
Chapter 16. Sense of Pain
 Chapter 16 Sense of Pain Pain Discomfort caused by tissue injury or noxious stimulation, and typically leading to evasive action important /// helps to protect us lost of pain in diabetes mellitus = diabetic
Chapter 16 Sense of Pain Pain Discomfort caused by tissue injury or noxious stimulation, and typically leading to evasive action important /// helps to protect us lost of pain in diabetes mellitus = diabetic
Spinal Cord Injury Pain. Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018
 Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Pathophysiology of Pain
 Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Seizure: the clinical manifestation of an abnormal and excessive excitation and synchronization of a population of cortical
 Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Pain. Pain. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Psyc 2906: Sensation--Introduction 9/27/2006
 Pain Pain Pain: One Definition Classic Paths A new Theory Pain and Drugs According to the international Association for the Study (Merskey & Bogduk, 1994), Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience
Pain Pain Pain: One Definition Classic Paths A new Theory Pain and Drugs According to the international Association for the Study (Merskey & Bogduk, 1994), Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT
 CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress REDUCING THE PAIN FACTOR AN UPDATE ON PERI-OPERATIVE ANALGESIA Sandra Forysth, BVSc DipACVA Institute of Veterinary,
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress REDUCING THE PAIN FACTOR AN UPDATE ON PERI-OPERATIVE ANALGESIA Sandra Forysth, BVSc DipACVA Institute of Veterinary,
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor
 Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
The Nervous System Mark Stanford, Ph.D.
 The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
Complex Acute Surgical Pain Management. Thomas Baribeault MSN, CRNA
 Complex Acute Surgical Pain Management Thomas Baribeault MSN, CRNA Introduction Anatomy and pathophysiology of acute surgical pain Pharmacology Chronic pain patient Opioid tolerant patient Introduction
Complex Acute Surgical Pain Management Thomas Baribeault MSN, CRNA Introduction Anatomy and pathophysiology of acute surgical pain Pharmacology Chronic pain patient Opioid tolerant patient Introduction
The anatomy and physiology of pain
 The anatomy and physiology of pain Charlotte E Steeds Abstract Pain is an unpleasant experience that results from both physical and psychological responses to injury. A complex set of pathways transmits
The anatomy and physiology of pain Charlotte E Steeds Abstract Pain is an unpleasant experience that results from both physical and psychological responses to injury. A complex set of pathways transmits
Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis
 Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis About This Chapter Cell-to-cell communication Signal pathways Novel signal molecules Modulation of signal pathways Homeostatic reflex pathways Cell-to-Cell
Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis About This Chapter Cell-to-cell communication Signal pathways Novel signal molecules Modulation of signal pathways Homeostatic reflex pathways Cell-to-Cell
Pain Mechanisms. Prof Michael G Irwin MD, FRCA, FANZCA FHKAM Head Department of Anaesthesiology University of Hong Kong. The Somatosensory System
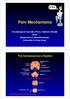 ain Mechanisms rof Michael G Irwin MD, FRCA, FANZCA FHKAM Head Department of Anaesthesiology University of Hong Kong The Somatosensory System Frontal cortex Descending pathway eriaqueductal gray matter
ain Mechanisms rof Michael G Irwin MD, FRCA, FANZCA FHKAM Head Department of Anaesthesiology University of Hong Kong The Somatosensory System Frontal cortex Descending pathway eriaqueductal gray matter
A. Correct! Nociceptors are pain receptors stimulated by harmful stimuli, resulting in the sensation of pain.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 19: Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Drugs No. 1 of 10 1. are pain receptors stimulated by harmful stimuli, resulting in the sensation of pain. #01 (A) Nociceptors (B) Histamines
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 19: Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Drugs No. 1 of 10 1. are pain receptors stimulated by harmful stimuli, resulting in the sensation of pain. #01 (A) Nociceptors (B) Histamines
Analgesic Drugs PHL-358-PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS-I. Mr.D.Raju,M.pharm, Lecturer
 Analgesic Drugs PHL-358-PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS-I Mr.D.Raju,M.pharm, Lecturer Mechanisms of Pain and Nociception Nociception is the mechanism whereby noxious peripheral stimuli are transmitted to
Analgesic Drugs PHL-358-PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS-I Mr.D.Raju,M.pharm, Lecturer Mechanisms of Pain and Nociception Nociception is the mechanism whereby noxious peripheral stimuli are transmitted to
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS AND PAIN
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS AND PAIN A 21 year old man presented with a stab wound of the right side of the neck (Panel A). Neurological examination revealed right hemiplegia and complete right-sided loss of
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS AND PAIN A 21 year old man presented with a stab wound of the right side of the neck (Panel A). Neurological examination revealed right hemiplegia and complete right-sided loss of
Basics of Pharmacology
 Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
211MDS Pain theories
 211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
By the end of this lecture the students will be able to:
 UNIT VII: PAIN Objectives: By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Review the concept of somatosensory pathway. Describe the function of Nociceptors in response to pain information. Describe
UNIT VII: PAIN Objectives: By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Review the concept of somatosensory pathway. Describe the function of Nociceptors in response to pain information. Describe
DRUGS THAT ACT IN THE CNS
 DRUGS THAT ACT IN THE CNS Anxiolytic and Hypnotic Drugs Dr Karamallah S. Mahmood PhD Clinical Pharmacology 1 OTHER ANXIOLYTIC AGENTS/ A. Antidepressants Many antidepressants are effective in the treatment
DRUGS THAT ACT IN THE CNS Anxiolytic and Hypnotic Drugs Dr Karamallah S. Mahmood PhD Clinical Pharmacology 1 OTHER ANXIOLYTIC AGENTS/ A. Antidepressants Many antidepressants are effective in the treatment
Chronic pain: We should not underestimate the contribution of neural plasticity. *Gwyn N Lewis 1, David A Rice 1,2
 Chronic pain: We should not underestimate the contribution of neural plasticity *Gwyn N Lewis 1, David A Rice 1,2 1 Health and Rehabilitation Research Institute, AUT University, Auckland, New Zealand 2
Chronic pain: We should not underestimate the contribution of neural plasticity *Gwyn N Lewis 1, David A Rice 1,2 1 Health and Rehabilitation Research Institute, AUT University, Auckland, New Zealand 2
Virtually everyone has experienced pain in one
 Transfer of Advances in Sciences into Dental Education Recent Insights into Brainstem Mechanisms Underlying Craniofacial Pain Barry J. Sessle, B.D.S., M.D.S., B.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.S.C., D.Sc. (honorary) Abstract:
Transfer of Advances in Sciences into Dental Education Recent Insights into Brainstem Mechanisms Underlying Craniofacial Pain Barry J. Sessle, B.D.S., M.D.S., B.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.S.C., D.Sc. (honorary) Abstract:
PAIN MODULATION. numerical value. adjectives. DR SYED SHAHID HABIB Professor & Consultant Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH
 PAIN MODULATION numerical value adjectives DR SYED SHAHID HABIB Professor & Consultant Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe:
PAIN MODULATION numerical value adjectives DR SYED SHAHID HABIB Professor & Consultant Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe:
INTRODUCTION TO THE BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONES AND THEIR RECPTORS
 INTRODUCTION TO THE BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONES AND THEIR RECPTORS 1 Introduction to the Biochemistry of Hormones and their Receptors Lectuctre1 Sunday 17/2/ Objectives: 1. To understand the biochemical nature
INTRODUCTION TO THE BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONES AND THEIR RECPTORS 1 Introduction to the Biochemistry of Hormones and their Receptors Lectuctre1 Sunday 17/2/ Objectives: 1. To understand the biochemical nature
AKA a painful lecture by Colleen Blanchfield, MD Full Circle Neuropsychiatric Wellness Center
 A lecture on PAIN AKA a painful lecture by Colleen Blanchfield, MD Full Circle Neuropsychiatric Wellness Center 1 Overview of the lecture Anatomy of the Pain Tract How a painful stimulus travels from the
A lecture on PAIN AKA a painful lecture by Colleen Blanchfield, MD Full Circle Neuropsychiatric Wellness Center 1 Overview of the lecture Anatomy of the Pain Tract How a painful stimulus travels from the
BEYOND OPIOIDS: ADJUNCTS FOR TREATING PAIN
 BEYOND OPIOIDS: ADJUNCTS FOR TREATING PAIN Ronald Januchowski, D.O. 2017 Objectives By the end of the presentation, the learner should be able to: Summarize the risks of opiates when used for non-cancer
BEYOND OPIOIDS: ADJUNCTS FOR TREATING PAIN Ronald Januchowski, D.O. 2017 Objectives By the end of the presentation, the learner should be able to: Summarize the risks of opiates when used for non-cancer
What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. Pain is always subjective
 Pain & Acupuncture What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. NOCICEPTION( the neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli.)
Pain & Acupuncture What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. NOCICEPTION( the neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli.)
Pathophysiology of Pain. Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC
 Pathophysiology of Pain Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC Learning Objectives Anatomic pathway of nociception Discuss the multiple target sites of pharmacological
Pathophysiology of Pain Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC Learning Objectives Anatomic pathway of nociception Discuss the multiple target sites of pharmacological
Neurophysiology and Neurochemistry in PsychoGeriatrics
 Tel Aviv University Sackler Faculty of Medicine CME in Psychiatry Neurophysiology and Neurochemistry in PsychoGeriatrics Nicola Maggio, MD, PhD Sackler Faculty of Medicine Tel Aviv University Department
Tel Aviv University Sackler Faculty of Medicine CME in Psychiatry Neurophysiology and Neurochemistry in PsychoGeriatrics Nicola Maggio, MD, PhD Sackler Faculty of Medicine Tel Aviv University Department
Cephalization. Nervous Systems Chapter 49 11/10/2013. Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells
 Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
SYLLABUS SPRING 2011 COURSE: NSC NEUROBIOLOGY OF PAIN
 SYLLABUS NSC 4358 NEUROBIOLOGY OF PAIN SPRING 2011 1 SYLLABUS SPRING 2011 COURSE: NSC 4358 001 NEUROBIOLOGY OF PAIN Instructor: Aage R. Møller PhD E-mail: AMOLLER@UTDALLAS.EDU Class schedule: Main Campus:
SYLLABUS NSC 4358 NEUROBIOLOGY OF PAIN SPRING 2011 1 SYLLABUS SPRING 2011 COURSE: NSC 4358 001 NEUROBIOLOGY OF PAIN Instructor: Aage R. Møller PhD E-mail: AMOLLER@UTDALLAS.EDU Class schedule: Main Campus:
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1
 Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Pain classifications slow and fast
 Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT
 PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07)
 NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work!
 PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
A New Era of Migraine Management: The Challenging Landscape in Prevention
 Provided by MediCom Worldwide, Inc. Supported by an educational grant from Teva Pharmaceuticals What is a Neuropeptide? Small chains of amino acids released by neural cells (neurons or glial cells) to
Provided by MediCom Worldwide, Inc. Supported by an educational grant from Teva Pharmaceuticals What is a Neuropeptide? Small chains of amino acids released by neural cells (neurons or glial cells) to
Classes of Neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters
 1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
Nervous system. The main regulation mechanism of organism's functions
 Nervous system The main regulation mechanism of organism's functions Questions Neuron The reflex arc The nervous centers Properties of the nervous centers The general principles of coordination Inhibition
Nervous system The main regulation mechanism of organism's functions Questions Neuron The reflex arc The nervous centers Properties of the nervous centers The general principles of coordination Inhibition
1 The Physiology of Pain
 1 The Physiology of Pain Rohit Juneja and Siân Jaggar Introduction Definitions Key Messages Pain is still underdiagnosed and undertreated. Pain is a subjective experience and may even be present in the
1 The Physiology of Pain Rohit Juneja and Siân Jaggar Introduction Definitions Key Messages Pain is still underdiagnosed and undertreated. Pain is a subjective experience and may even be present in the
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
Prescription Pain Management. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita 1 Narciso Pharm D
 Prescription Pain Management University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita 1 Narciso Pharm D 2 Objectives Understand how to preform a pain assessment Know which medications
Prescription Pain Management University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita 1 Narciso Pharm D 2 Objectives Understand how to preform a pain assessment Know which medications
NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8
 NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8 CAN AN INJURED SPINAL CORD BE FIXED? Injuries to the spinal cord disrupt communication between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body
NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8 CAN AN INJURED SPINAL CORD BE FIXED? Injuries to the spinal cord disrupt communication between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body
Autonomic nervous system
 Autonomic nervous system Key notes Autonomic: an independent system that runs on its own The ANS is a visceral and involuntary sensory and motor system The visceral motor fibers in the autonomic nerves
Autonomic nervous system Key notes Autonomic: an independent system that runs on its own The ANS is a visceral and involuntary sensory and motor system The visceral motor fibers in the autonomic nerves
Overview of Neuropathic pain
 Overview of Neuropathic pain Kongkiat Kulkantrakorn,M.D. Neurology division Thammasat University 1 Contents Overview of pain New concepts and mechanism Treatment options New data in management 2 3 Breaking
Overview of Neuropathic pain Kongkiat Kulkantrakorn,M.D. Neurology division Thammasat University 1 Contents Overview of pain New concepts and mechanism Treatment options New data in management 2 3 Breaking
EEK 16. MPharm Programme PAIN & ANALGESIA. Dr Abdel Ennaceur. Slide 1 of 78 M14 Pain Lecture notes
 MPharm Programme PAIN & ANALGESIA Dr Abdel Ennaceur Slide 1 of 78 M14 Pain Lecture notes WEEK Terminology Tract: collection of axons in the CNS Nucleus:(nuclei, plural) collection of neuron cell bodies
MPharm Programme PAIN & ANALGESIA Dr Abdel Ennaceur Slide 1 of 78 M14 Pain Lecture notes WEEK Terminology Tract: collection of axons in the CNS Nucleus:(nuclei, plural) collection of neuron cell bodies
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization
 Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT
 Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT Pain & Suffering an unpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage International
Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT Pain & Suffering an unpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage International
Cell Signaling (part 1)
 15 Cell Signaling (part 1) Introduction Bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes respond to environmental signals and to signaling molecules secreted by other cells for mating and other communication. In multicellular
15 Cell Signaling (part 1) Introduction Bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes respond to environmental signals and to signaling molecules secreted by other cells for mating and other communication. In multicellular
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Autonomic Nervous System. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitters. Chemical transmission of a nerve signal by neurotransmitters at a synapse
 Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
Neuropathic Pain in Palliative Care
 Neuropathic Pain in Palliative Care Neuropathic Pain in Advanced Cancer Affects 40% of patients Multiple concurrent pains are common Often complex pathophysiology with mixed components Nocioceptive Neuropathic
Neuropathic Pain in Palliative Care Neuropathic Pain in Advanced Cancer Affects 40% of patients Multiple concurrent pains are common Often complex pathophysiology with mixed components Nocioceptive Neuropathic
SLEEP DISORDERS IN HUNTINGTON S DISEASE. Gary L. Dunbar, Ph.D.
 SLEEP DISORDERS IN HUNTINGTON S DISEASE Gary L. Dunbar, Ph.D. Executive Director, Field Neurosciences Institute Co-Director, Program in Neuroscience Central Michigan University Pre-Talk Test 1. Which type
SLEEP DISORDERS IN HUNTINGTON S DISEASE Gary L. Dunbar, Ph.D. Executive Director, Field Neurosciences Institute Co-Director, Program in Neuroscience Central Michigan University Pre-Talk Test 1. Which type
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?!
 Warm Up! Take out your 11C Notes What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?! Astrocytes Microglia Ependymal Cells Satellite Cells Schwann Cells Oligodendrocytes Support, brace, & nutrient transfer
Warm Up! Take out your 11C Notes What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?! Astrocytes Microglia Ependymal Cells Satellite Cells Schwann Cells Oligodendrocytes Support, brace, & nutrient transfer
The Nervous System. Anatomy of a Neuron
 The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
1. At the venous end of a capillary, is the dominant force determining water movement. a. Pcap b. cap c. PIF d. IF e. [Na+]
![1. At the venous end of a capillary, is the dominant force determining water movement. a. Pcap b. cap c. PIF d. IF e. [Na+] 1. At the venous end of a capillary, is the dominant force determining water movement. a. Pcap b. cap c. PIF d. IF e. [Na+]](/thumbs/95/122587355.jpg) P531: Exam 1 Sample Question Set #3 The first 9 questions are the relevant questions from the beginning of lecture each day. The remaining 16 questions cover material from the last week of lectures. 1.
P531: Exam 1 Sample Question Set #3 The first 9 questions are the relevant questions from the beginning of lecture each day. The remaining 16 questions cover material from the last week of lectures. 1.
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
E) A, B, and C Answer: D Topic: Concept 49.1 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension
 Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) characteristic of a simple nervous system? A) a nerve net such as is found in cnidarians B) nerve cell ganglia C)
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) characteristic of a simple nervous system? A) a nerve net such as is found in cnidarians B) nerve cell ganglia C)
Neurobiology of Pain Adjuvant analgesia
 Neurobiology of Pain Adjuvant analgesia Jason Brooks Consultant Anaesthesia and Pain Management BCH March 2017 The Brief A broad overview of the abnormal and normal anatomy and physiology of pain pathways
Neurobiology of Pain Adjuvant analgesia Jason Brooks Consultant Anaesthesia and Pain Management BCH March 2017 The Brief A broad overview of the abnormal and normal anatomy and physiology of pain pathways
NEUROSCIENCE and BEHAVIOR EXAM CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR EACH OF THE STATEMENTS BELOW:
 NEUROSCIENCE and BEHAVIOR EXAM 1-2002 CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR EACH OF THE STATEMENTS BELOW: 1. Which of the following statements about CNS development is TRUE: A. the most likely time for a neural
NEUROSCIENCE and BEHAVIOR EXAM 1-2002 CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR EACH OF THE STATEMENTS BELOW: 1. Which of the following statements about CNS development is TRUE: A. the most likely time for a neural
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Narcotic Analgesics. Jacqueline Morgan March 22, 2017
 Narcotic Analgesics Jacqueline Morgan March 22, 2017 Pain Unpleasant sensory and emotional experience with actual or potential tissue damage Universal, complex, subjective experience Number one reason
Narcotic Analgesics Jacqueline Morgan March 22, 2017 Pain Unpleasant sensory and emotional experience with actual or potential tissue damage Universal, complex, subjective experience Number one reason
PAIN MANAGEMENT. It is important to know as much about the man who has pain as it is to know about pain the man has Quote by Macnab et al
 PAIN MANAGEMENT It is important to know as much about the man who has pain as it is to know about pain the man has Quote by Macnab et al DEFINATION OF PAIN International Association for the study of pain
PAIN MANAGEMENT It is important to know as much about the man who has pain as it is to know about pain the man has Quote by Macnab et al DEFINATION OF PAIN International Association for the study of pain
Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways.
 Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways. Each higher level will control the level under It. In controlling
Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways. Each higher level will control the level under It. In controlling
NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions as Related to Analgesia and Tolerance
 Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells.
 BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior
 Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior John Nyby Department of Biological Sciences Lehigh University What is a drug? Difficult to define Know it when you see it Neuroactive vs Non-Neuroactive drugs Two major types
Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior John Nyby Department of Biological Sciences Lehigh University What is a drug? Difficult to define Know it when you see it Neuroactive vs Non-Neuroactive drugs Two major types
Transition from acute to chronic pain
 A Feizerfan FRCA G Sheh BHB MBChB FAFRM(RACP) FFPMANZCA Matrix reference 3E00 Key points Physiology of pain involves activation and complex interactions of autonomic, peripheral and central nervous systems,
A Feizerfan FRCA G Sheh BHB MBChB FAFRM(RACP) FFPMANZCA Matrix reference 3E00 Key points Physiology of pain involves activation and complex interactions of autonomic, peripheral and central nervous systems,
Nervous system. Made up of. Peripheral nervous system. Central nervous system. The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system.
 Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Mechanism of Pain Production
 Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
NEUROBIOLOGY ALCOHOLISM
 NEUROBIOLOGY ALCOHOLISM THERE HAS BEEN A MAJOR THEORETICAL SHIFT IN MEDICATION DEVELOPMENT IN ALCOHOLISM Driven by animal models of intermittent ethanol administration followed by termination, then access
NEUROBIOLOGY ALCOHOLISM THERE HAS BEEN A MAJOR THEORETICAL SHIFT IN MEDICATION DEVELOPMENT IN ALCOHOLISM Driven by animal models of intermittent ethanol administration followed by termination, then access
Derived copy of Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56161 1 Derived copy of Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System * Stephanie Fretham Based on Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX
OpenStax-CNX module: m56161 1 Derived copy of Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System * Stephanie Fretham Based on Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX
Unit 2 Multiple Choice test
 Name: Date: 1. Resting potential is to action potential as is to. A) adrenal gland; pituitary gland B) sensory neuron; motor neuron C) temporal lobe; occipital lobe D) polarization; depolarization E) dendrite;
Name: Date: 1. Resting potential is to action potential as is to. A) adrenal gland; pituitary gland B) sensory neuron; motor neuron C) temporal lobe; occipital lobe D) polarization; depolarization E) dendrite;
The Nervous System PART A
 7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
Pathophysiological Classification of Pain
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Overview Pathophysiological Classification of Pain Central sensitization/ dysfunctional pain Nociceptive pain - Somatic - Visceral Multiple pain mechanisms may coexist (mixed pain) Neuropathic
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Overview Pathophysiological Classification of Pain Central sensitization/ dysfunctional pain Nociceptive pain - Somatic - Visceral Multiple pain mechanisms may coexist (mixed pain) Neuropathic
University of Groningen. Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan
 University of Groningen Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
ANAT2010. Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018
 ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
Pain and impulse conduction
 1 Pain and impulse conduction L.H.D.J. Booij According to the World Health Organisation pain is defined as an unpleasant sensation that occurs from imminent tissue damage. From a physiological perspective,
1 Pain and impulse conduction L.H.D.J. Booij According to the World Health Organisation pain is defined as an unpleasant sensation that occurs from imminent tissue damage. From a physiological perspective,
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Karam Darwish. Dr. Munir. Munir Gharaibeh
 7 Karam Darwish Dr. Munir Munir Gharaibeh Opioid Analgesics Pain is an important symptom as it is usually the symptom that brings the patient to the hospital, and an Analgesic is a drug used to relieve
7 Karam Darwish Dr. Munir Munir Gharaibeh Opioid Analgesics Pain is an important symptom as it is usually the symptom that brings the patient to the hospital, and an Analgesic is a drug used to relieve
CNS part 2 & Intro to Sensory Systems
 CNS part 2 & Intro to Sensory Systems Brain Function Important Concepts Functional areas of the cerebral cortex Sensory, Motor, Association Cerebral lateralization each hemisphere has functions not shared
CNS part 2 & Intro to Sensory Systems Brain Function Important Concepts Functional areas of the cerebral cortex Sensory, Motor, Association Cerebral lateralization each hemisphere has functions not shared
