Background Information
|
|
|
- Milton Carson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 art of Exercise 4 of Human Anatomy & hysiology Laboratory Manual, 8th Edition, by Elaine Marieb lease wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click to advance. Arrow keys etc.also work. Hit ESCAE Key to exit. Dr.Susan Maskel BIO 105 Western Connecticut State University A& I BIO 211 Naugatuck Valley Community College A& I Some graphics and all definitions courtesy of Benjamin Cummings Background Information CHROMOSOMES DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) stores genetic information rotein controls processes DNA 2 strands double helix each strand contains: sugars (deoxyribose) phosphates (O 4 ) nitrogenous bases adenine thymine guanine cytosine - O - = O O phosphate Structure of Components of DNA O -
2 DNA S S B B B B S S S B B S S B B S S B B S Key: S = sugar = phosphate B = base sugarphosphate backbone nitrogenous bases form rungs of ladder Bases in DNA Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) Specificity of base pairing A - T C - G Types of Chromosomes DNA (1 double stranded (ds) DNA + protein) duplicated (2 ds DNAs + protein)
3 Duplicated Chromosomes centromere DNA Humans have 46 in their somatic (i.e., not sperm or egg) cells. Diploid number = 2 N = 46 Humans have 23 in their sex cells (sperm & egg). Haploid number = 1 N = 23 sister chromatids THE CELL CYCLE At any given time, a cell is either: not dividing dividing When Cells are Not Dividing: Interphase G1 Normal cell metabolism Synthesis of proteins not used for mitosis Chromosomes Centrioles replicate S Normal cell metabolism DNA synthesis (DNA replication): duplicated G2 Normal cell metabolism Synthesis of proteins used for mitosis Chromosomes duplicated DNA Replication DNA unzips New nucleotides (sugar-phosphatebase combinations) add according to specificity of base pairing
4 NOTE: forming sister chromatid of duplicated chromosome old strand new strand The 2 forming sister chromatids have an identical base sequence to each other. Semiconservative Replication: each sister chromatid has 1 new & 1 old strand ds DNA of chromosome sister chromatids of duplicated chromosome When Cells Are Dividing: Nuclear Division Mitosis occurs in somatic cells maintains the # of Meiosis occurs in sex cells halves the # of Cytokinesis division of cytoplasm occurs during mitosis & meiosis G1 S duplicate G2 duplicated M start with duplicated ; end with
5 Before mitosis begins, the cell is in INTERHASE. INTERHASE cell is not dividing includes G1, S & G2 nuclear membrane visible nucleoli visible chromatin in nucleus NOT ART OF MITOSIS Interphase NOTE: Interphase Nuclear membrane present Chromatin not visible -nuclear membrane intact nucleolus visible chromatin not visible Interphase Nuclear division in somatic cells takes place via MITOSIS.
6 prophase metaphase anaphase telophase ROHASE (1 - several hours) nuclear membrane disappears nucleoli disappear chromatin centrioles move to opposite poles of cell spindle & asters form Centrioles Spindle & Asters at end of G1, centrioles replicated (to form 2 pairs) made of microtubules aster probably anchors apparatus to cell membrane spindle helps organize during mitosis rophase rophase NOTE: nuclear membrane disappears nucleolus disappears chromatin spindle & asters form In this hypothetical cell, 2 N = 4. In humans, 2 N = 46. Nuclear membrane still present but is disappearing
7 rophase METAHASE (5-15 minutes) line up on center of spindle are attached to spindle fibers in area of centromere Metaphase Metaphase NOTE: lined up in single file in center of spindle aster Chromosomes lined up on center of spindle aster In this hypothetical cell, 2 N = 4. In humans, 2 N = 46. Metaphase ANAHASE (2-10 minutes) spindle fibers pulled toward opposite poles of cell centromeres splits sister chromatids pulled toward opposite poles of cell as microtubules of spindle shorten
8 Anaphase Anaphase aster NOTE: sister chromatids being pulled toward opposite poles of cell chromatids separated & being pulled toward opposite poles of cell aster In this hypothetical cell, 2 N = 4. In humans, 2 N = 46. Anaphase TELOHASE (10-30 minutes) cleavage furrow formed cell invaginates at cleavage furrow until 2 daughter cells formed (= cytokinesis) opposite of prophase nuclear membrane reappears nucleoli reappear uncoil to chromatin spindle & asters disappear Telophase NOTE: cleavage furrow forms; 2 daughter cells will form; the opposite of prophase will occur In this hypothetical cell, 2 N = 4. In humans, 2 N = 46. Telophase cleavage furrow unwinding unwinding
9 INTERHASE ROHASE METAHASE Telophase spindle ANAHASE TELOHASE TELOHASE art of Exercise 4 of Human Anatomy & hysiology Laboratory Manual, 8th Edition, by Elaine Marieb Dr.Susan Maskel BIO 105 Western Connecticut State University A& I BIO 211 Naugatuck Valley Community College A& I Name the phase of mitosis indicated. Some graphics and all definitions courtesy of Benjamin Cummings Name the phase of mitosis indicated. Answer: metaphase
10 Name the phase of mitosis seen. Answer Anaphase ANSWER: prophase Name the phases of mitosis indicated ANSWERS 2 Name the phases of mitosis indicated. 1 = metaphase 2 = telophase 3 = anaphase 4 = prophase
11 1 = anaphase 2 = metaphase ANSWERS 3 = anaphase Now it s YOUR turn to identify stages of mitosis with a microscope!
MITOSIS PRESENTATION DR. SUSAN MASKEL (WCSU)
 MITOI REENTATION 1 2 MITOI ackground Information CHROMOOME proteins deoxyribonucleic acid interspersed with stores genetic info controls processes Dr. usan Maskel Western CT tate University 2 strands double
MITOI REENTATION 1 2 MITOI ackground Information CHROMOOME proteins deoxyribonucleic acid interspersed with stores genetic info controls processes Dr. usan Maskel Western CT tate University 2 strands double
Cell Division. The Process of Cell Division Section Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division 12/8/2010
 The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
Chromosomes & Cell Division
 Chromosomes & Cell Division Cell Division The growth and splitting of cells into two new, identical cells called daughter cells. Mitosis Meiosis DNA replicates Parent cell Chromosomes separate Cell division
Chromosomes & Cell Division Cell Division The growth and splitting of cells into two new, identical cells called daughter cells. Mitosis Meiosis DNA replicates Parent cell Chromosomes separate Cell division
An Introduction to Genetics. 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid
 An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
Overview of the CELL CYCLE
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. CHAPTER 03 and Lab Overview of the CELL CYCLE Dr. Lawrence
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. CHAPTER 03 and Lab Overview of the CELL CYCLE Dr. Lawrence
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide)
 Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide) Meiosis: cell division that forms daughter cells with half the number
Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide) Meiosis: cell division that forms daughter cells with half the number
Mitosis: Cell Division
 Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
 B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Cell Cycle. Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer
 Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Genetics and Cellular Function
 Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE Structures in the nucleus that carry genetic information Composed of DNA coiled around proteins called histones Consists of 2 identical parts called sister
CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE Structures in the nucleus that carry genetic information Composed of DNA coiled around proteins called histones Consists of 2 identical parts called sister
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Mitosis and Cellular Division. EQ: How do the cells in our body divide?
 Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Name Date Class. Interphase. (1) The. grows. DNA is duplicated.
 Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
Chromosomes and Cell Cycle
 Chromosomes and Cell Cycle Cell Basics There are trillions of cells in your body Cells are microscopic Cells have DNA inside a structure called the nucleus The nucleus is enclosed by a structure called
Chromosomes and Cell Cycle Cell Basics There are trillions of cells in your body Cells are microscopic Cells have DNA inside a structure called the nucleus The nucleus is enclosed by a structure called
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
Organisms that reproduce Sexually are made up of two different types of cells.
 MEIOSIS Organisms that reproduce Sexually are made up of two different types of cells. 1. Somatic Cells are body cells and contain the normal number of chromosomes.called the Diploid number (the symbol
MEIOSIS Organisms that reproduce Sexually are made up of two different types of cells. 1. Somatic Cells are body cells and contain the normal number of chromosomes.called the Diploid number (the symbol
The Cell Cycle. Packet #9. Thursday, August 20, 2015
 1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division. diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
 Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
Unit 6: Study Guide Cell Division 1. Define: chromatin chromosome chromatid pair (sister chromatid) centromere spindle fibers haploid diploid gene allele interphase (G1, S, G2) prophase metaphase anaphase
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Science 9- Mr. Klasz
 Science 9- Mr. Klasz Asexual reproduction requires only one parent. The offspring produced are identical to the parent. Asexual reproduction occurs in our somatic cells. This means all of our cells except
Science 9- Mr. Klasz Asexual reproduction requires only one parent. The offspring produced are identical to the parent. Asexual reproduction occurs in our somatic cells. This means all of our cells except
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
Cell Division (Mitosis)
 Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell plate Carcinogen Oncogenes. Haploid cell Diploid cell Chromosome. Telophase Keywords Mitosis
 Cell Division Cell plate Carcinogen Oncogenes Haploid cell Diploid cell Chromosome Gene Interphase Anaphase Metaphase Telophase Keywords Mitosis Meiosis Centromere Cleavage furrow Middle lamella What is
Cell Division Cell plate Carcinogen Oncogenes Haploid cell Diploid cell Chromosome Gene Interphase Anaphase Metaphase Telophase Keywords Mitosis Meiosis Centromere Cleavage furrow Middle lamella What is
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities
 Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities In this simulation, you will demonstrate an understanding of mitosis, meiosis, segregation, independent assortment, and crossing over, all processes involved with
Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities In this simulation, you will demonstrate an understanding of mitosis, meiosis, segregation, independent assortment, and crossing over, all processes involved with
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide
 The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 10
 The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
3/19/17. Chromosomes. Chromosome Structure. Chromosome Structure. Chromosome Structure. Chapter 10: Cell Growth & Division
 Chapter 10: Cell Growth & Division Section 2: The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) a molecule that stores genetic information, which controls the development and functioning
Chapter 10: Cell Growth & Division Section 2: The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) a molecule that stores genetic information, which controls the development and functioning
Essential Questions. Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase?
 Essential Questions Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase? Cellular Growth Vocabulary Review selective permeability New cell cycle
Essential Questions Why are cells relatively small? What are the primary stages of the cell cycle? What are the stages of interphase? Cellular Growth Vocabulary Review selective permeability New cell cycle
Mitosis & Meiosis. Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair
 Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
2.1 The Importance of Cell Division
 2.1 The Importance of Cell Division Functions of cell division Growth Repair Reproduction Growth All organisms begin as a single cell. Cell divisions will increase as an organism s size increases. There
2.1 The Importance of Cell Division Functions of cell division Growth Repair Reproduction Growth All organisms begin as a single cell. Cell divisions will increase as an organism s size increases. There
5.2. Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis.
 5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis VOCABULARY chromosome histone chromatin chromatid centromere prophase metaphase anaphase telophase Biochemistry As you will learn in the chapter From DNA to Proteins, a nucleotide
5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis VOCABULARY chromosome histone chromatin chromatid centromere prophase metaphase anaphase telophase Biochemistry As you will learn in the chapter From DNA to Proteins, a nucleotide
Vocabulary: cell division, centriole, centromere, chromatid, chromatin, chromosome, cytokinesis, DNA, interphase, mitosis
 Cell Division Answer Key Vocabulary: cell division, centriole, centromere, chromatid, chromatin, chromosome, cytokinesis, DNA, interphase, mitosis Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
Cell Division Answer Key Vocabulary: cell division, centriole, centromere, chromatid, chromatin, chromosome, cytokinesis, DNA, interphase, mitosis Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
Cell Division. Learning Objectives: Introduction. Revised Fall 2018
 Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
Chapter 10. Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
Cell Division. Introduction. Chromatin, Chromosomes, and Chromatids, Oh My! The Cell Cycle
 Introduction Cell Division Just like a butterfly passes through different phases (such as caterpillar, chrysalis, and adult butterfly) there are a series of phases in a cell's life as it gets ready to
Introduction Cell Division Just like a butterfly passes through different phases (such as caterpillar, chrysalis, and adult butterfly) there are a series of phases in a cell's life as it gets ready to
Pre-Test. 4. Inside of cells, nearly all the genes are located on special structures known as microtubules.
 1 Pre-Test Directions: Answer each question TRUE OR FALSE. 1. Cells in the bodies of multicelled creatures, such as humans, are reproduced in a way that is very similar to the method used by most protozoa.
1 Pre-Test Directions: Answer each question TRUE OR FALSE. 1. Cells in the bodies of multicelled creatures, such as humans, are reproduced in a way that is very similar to the method used by most protozoa.
The Cell Cycle Guided Reading
 Name Date Period 1. List three things that multi-celled organisms need cell division for. a. b. c. 2. Why do single-celled organisms need to go through cell division? 3. What is the cell cycle? 4. True
Name Date Period 1. List three things that multi-celled organisms need cell division for. a. b. c. 2. Why do single-celled organisms need to go through cell division? 3. What is the cell cycle? 4. True
The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Chromosomes
 & Karyotypes The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Homologous Chromosomes Pair of chromosomes (maternal and paternal) that are similar in shape,
& Karyotypes The form of cell division by which gametes, with half the number of chromosomes, are produced. Homologous Chromosomes Pair of chromosomes (maternal and paternal) that are similar in shape,
10-2 Cell Division. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction
 Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Chromosomes Organisms grow by dividing of cells Binary Fission form of asexual reproduction that produces identical offspring (Bacteria) Eukaryotes have two
Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Chromosomes Organisms grow by dividing of cells Binary Fission form of asexual reproduction that produces identical offspring (Bacteria) Eukaryotes have two
Name: Cell division and cancer review
 Name: Cell division and cancer review 1. What type of cell undergoes meiosis? Gamete cells or Somatic cells 2. Define homologous chromosomes. 2 chromosomes with similar structure 3. For each of the following
Name: Cell division and cancer review 1. What type of cell undergoes meiosis? Gamete cells or Somatic cells 2. Define homologous chromosomes. 2 chromosomes with similar structure 3. For each of the following
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Ploidy and Human Cell Types. Cell Cycle and Mitosis. DNA and Chromosomes. Where It All Began 11/19/2014. Chapter 12 Pg
 Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase
 Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase TEACHER S INSTRUCTIONS 1) Choose one of the foldables from the choices below. Three Color Choices Black & White Cells without Chromosomes Choose this option if you
Mitosis Flap Book Excludes Prometaphase TEACHER S INSTRUCTIONS 1) Choose one of the foldables from the choices below. Three Color Choices Black & White Cells without Chromosomes Choose this option if you
BIOLOGY. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes
 1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
Cellular Reproduction
 Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
Section 1: Cellular Growth Section 2: Mitosis and Cytokinesis Section 3: Cell Cycle Regulation Click on a lesson name to select. Section 1 Cellular Growth Ratio of Surface Area to Volume Section 1 Cellular
CELL GROWTH & DIVISION
 CELL GROWTH & DIVISION 2 Reasons why cells divide 1. DNA OVERLOAD As cell grows bigger demand on DNA genetic library becomes too great Ex: Small town library has 1000 books. As town grows and more people
CELL GROWTH & DIVISION 2 Reasons why cells divide 1. DNA OVERLOAD As cell grows bigger demand on DNA genetic library becomes too great Ex: Small town library has 1000 books. As town grows and more people
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
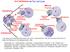 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
BIOLOGY 4/6/2015. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
5.2. Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Connecting
 5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis KEY CONCEPT Cells divide during mitosis and cytokinesis. MAIN IDEAS Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Mitosis and cytokinesis produce two genetically identical daughter
5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis KEY CONCEPT Cells divide during mitosis and cytokinesis. MAIN IDEAS Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Mitosis and cytokinesis produce two genetically identical daughter
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular
 Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
The Cell Life Cycle. S DNA replication, INTERPHASE. G 2 Protein. G 1 Normal THE CELL CYCLE. Indefinite period. synthesis. of histones.
 Mitosis & Meiosis The Cell Life Cycle INTERPHASE G 1 Normal cell functions plus cell growth, duplication of organelles, protein synthesis S DNA replication, synthesis of histones THE CELL CYCLE M G 2 Protein
Mitosis & Meiosis The Cell Life Cycle INTERPHASE G 1 Normal cell functions plus cell growth, duplication of organelles, protein synthesis S DNA replication, synthesis of histones THE CELL CYCLE M G 2 Protein
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes
 Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS
 Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
Cell Division and Mitosis
 Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
NOTES: Cell Growth and Division. centriole spindle prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis
 NOTES: 10.1 10.2 Cell Growth and Division centriole spindle prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis How big do you think the largest cell is? Yolk of ostrich egg ~8 cm in diameter Average cell
NOTES: 10.1 10.2 Cell Growth and Division centriole spindle prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis How big do you think the largest cell is? Yolk of ostrich egg ~8 cm in diameter Average cell
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells. 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells
 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT. Activity #3
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION
 NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION Section I Chromosomes Formation of New Cells by Cell Division New cells are formed when old cells divide. 1. Cell division is the same as cell reproduction.
NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION Section I Chromosomes Formation of New Cells by Cell Division New cells are formed when old cells divide. 1. Cell division is the same as cell reproduction.
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes
 Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
5/25/2015. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork
 Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Nucleus. centriole spindle prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis
 Nucleus VOCABULARY: chromatid centromere interphase cell cycle mitosis centriole spindle prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis How big do you think the largest cell is? Yolk of ostrich egg
Nucleus VOCABULARY: chromatid centromere interphase cell cycle mitosis centriole spindle prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis How big do you think the largest cell is? Yolk of ostrich egg
The Cell Cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
DR. RAMESH U2 L3. MITOSIS and Cell Cycle
 DR. RAMESH U2 L3 MITOSIS and Cell Cycle Do Now! Directions: Answer the following questions in complete sentences. 1. Describe how bacteria reproduce. Describe how cats reproduce.are there any similarities
DR. RAMESH U2 L3 MITOSIS and Cell Cycle Do Now! Directions: Answer the following questions in complete sentences. 1. Describe how bacteria reproduce. Describe how cats reproduce.are there any similarities
The Cell Cycle and Cell Division
 Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
T R L J. Version 2, 2018 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle
 Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes-
 Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles Sexual reproduction mitosis
 meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
Almost every cell in the human body has an identical set of 46 chromosomes, produced through the process of mitosis.
 M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.12 - CELL DIVISION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
Name: Date: Block: 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet
 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
Cell Division. Chromosome structure. Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division
 Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
CHAPTER 8: CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION 8-1: CELL GROWTH 8-2: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS
 CHAPTER 8: CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION 8-1: CELL GROWTH 8-2: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Give two physical reasons why mitosis must occur. Draw a chromosome
CHAPTER 8: CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION 8-1: CELL GROWTH 8-2: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Give two physical reasons why mitosis must occur. Draw a chromosome
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Omnis cellula e cellula
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Major concepts: Notes: Cell Reproduction: From One Cell to Two. Why do Cells Reproduce?
 Grade 7 Standard: Life Science 1e Students know cells divide to increase their numbers through a process of mitosis, which results in two daughter cells with identical sets of chromosomes. Major concepts:
Grade 7 Standard: Life Science 1e Students know cells divide to increase their numbers through a process of mitosis, which results in two daughter cells with identical sets of chromosomes. Major concepts:
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS
 The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category:
 Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
