7.1 Life is Cellular. Mrs. Baldessari Biology
|
|
|
- Darrell McLaughlin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 7.1 Life is Cellular Mrs. Baldessari Biology The key to every biological problem must finally be sought in the cell, for every living organism is, or at some time has been, a cell. E.B. Wilson,
2 Cells are Us 2
3 Cells are Us Cilia on a protozoan Sperm meets egg 3
4 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular THINK ABOUT IT What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or is there a point at which what s left is no longer alive? As you will see, there is such a limit. The smallest living unit of any organism is the cell. 4
5 Cells are Us A person contains about 100 trillion cells. That s 100,000,000,000,000 or 1 x cells. There are about 200 different cell types in mammals (one of us). Red and white blood cells above vesselforming cells. nerve cell 5
6 CELL SIZE Smallest cell in the human body is the sperm cell Largest cell in the human body is the egg cell 6
7 Most cells are small 1. Surface to volume ratio: cell has to be small enough to get Waste out Nutrients in 2. The nucleus can only control a certain size cell 7
8 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell What is the cell theory? The cell theory states: - All living things are made up of cells. - Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. - New cells are produced from existing cells. 8
9 Early Microscopes Prototypes were developed in the late 1500 s by European eyeglass makers It was not until the mid-1600s that scientists began to use microscopes to observe living things. Early compound microscope 17 th century 9
10 In 1665, Robert Hooke used an early compound microscope to look at cork Observed that cork was made up of thousands of hollow chambers Dubbed them cells since they looked like the monatsery s tiny rooms called cellula. Today we know that living cells are not empty chambers, but contain a huge array of working parts, each with its own function. 10
11 Anton von Leewenhoek FIRST person to OBSERVE and DESCRIBE MICROSCOPIC ORGANISMS and LIVING CELLS Late 1600 s- Dutch textile salesman Created different types of microscopes Discovered over 5,000 types of microscopic life Lenses were able to magnify up to 300X. 11
12 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Early Microscopes Anton van Leeuwenhoek examined pond water and other things, including a sample taken from a human mouth. He drew the organisms he saw in the mouth which today we call bacteria. 12
13 The Cell Theory In 1838, German botanist Matthias Schleiden concluded: plants are made of cells The next year, German biologist Theodor Schwann stated that all: Animals are made of cells Schleiden Schwann 13
14 Cell Theory In 1855, German physician Rudolf Virchow concluded that new cells could be produced only from the division of existing cells. 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function 3. New cells come from preexisting cells. *cells are different shapes and sizes based on their function 14
15 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Exploring the Cell How do microscopes work? Most microscopes use lenses to magnify the image of an object by focusing light or electrons. 15
16 A Sense of Scale and Abundance Bacteria on the Head of a Pin 16
17 Exploring the Cell- 3 major types of microscopes 1. There are 1) Light Microscope Allows light to pass through a specimen and uses two lenses to form an image. The first set of lenses, located just above the specimen, produces an enlarged image of the specimen. The second set of lenses magnifies this image still further. Because light waves are diffracted, or scattered, as they pass through matter, light microscopes can produce clear images of objects only to a magnification from 40 1,000 times depending on objective being used 17
18 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular 1) Light Microscopes magnification from 40 1,000 Eyepiece magnifies 10X Total magnification calculation: multiply the eyepiece by the objective being used. Example- eyepiece (10X) times low power objective (4X) = 40X Used to magnify objects that light can pass through. Uses slides 18
19 Dissecting Microscope Magnifies 10 to 30 times Eyepiece magnifies 10X Objectives: 1X and 2X (3X) Used to magnify objects that light cannot pass through Used mostly by research scientists and jewelers Advantage: objects are 3-D Disadvantage: can t view small objects 19
20 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Light Microscopes and Cell Stains A problem with light microscopy is that most living cells are nearly transparent, making it difficult to see the structures within them. Using chemical stains or dyes can usually solve this problem. Some of these stains are so specific that they reveal only compounds or structures within the cell. 20
21 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Light Microscopes and Cell Stains Some dyes give off light of a particular color when viewed under specific wavelengths of light, a property called fluorescence. Fluorescent dyes can be attached to specific molecules and can then be made visible using a special fluorescence microscope. Fluorescence microscopy makes it possible to see and identify the locations of these molecules, and even to watch them move about in a living cell. 21
22 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular 2) Electron Microscopes Light microscopes can be used to see cells and cell structures as small as 1 millionth of a meter. To study something smaller than that, scientists need to use electron microscopes. Electron microscopes use beams of electrons, not light, that are focused by magnetic fields. Electron microscopes offer much higher resolution than light microscopes. There are two major types of electron microscopes: transmission and scanning. 22
23 Electron Microscope -Two types: Transmission and Scanning Uses electrons to illuminate objects Can magnify from 30,000 to 9 million times Mostly large institutions have them Costly to own and maintain Can only be used to look at dead specimens Used for cytology, forensics, and virology 23
24 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Transmission Electron Microscopes Transmission electron microscopes make it possible to explore cell structures and large protein molecules. Because beams of electrons can only pass through thin samples, cells and tissues must be cut first into ultra thin slices before they can be examined under a transmission electron microscope. Transmission electron microscopes produce flat, twodimensional images. 24
25 Transmission Electron Microscope TEM- thin slices need to be made to have clear images, images are 2-D Useful for studying internal structures 25
26 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Scanning Electron Microscopes In scanning electron microscopes, a pencil-like beam of electrons is scanned over the surface of a specimen. Because the image is of the surface, specimens viewed under a scanning electron microscope do not have to be cut into thin slices to be seen. Scanning electron microscopes produce threedimensional images of the specimen s surface. 26
27 SEM- samples do not need to be cut, are in 3-D Useful for studying external structure 27
28 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Electron Microscopes Because electrons are easily scattered by molecules in the air, samples examined in both types of electron microscopes must be placed in a vacuum in order to be studied. Researchers chemically preserve their samples first and then carefully remove all of the water before placing them in the microscope. This means that electron microscopy can be used to examine only nonliving cells and tissues. 28
29 General info about cells Cells come in a variety of shapes Range in size from microscopic bacteria to giant amoeba Mycoplasma pneumoniae Chaos carolinensis Giant amoeba, approximately 1mm in length 29
30 General info about cells c. All contain DNA d. All have a cell membrane- an outer, flexible barrier Cell membrane Nucleuscontaining DNA 30
31 Two Main Categories of Cells a. Eukaryotes- have cells that enclose their DNA in a nucleus b. Prokaryotes- cells that do not enclose their DNA in a nucleus 31
32 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells different? Prokaryotic cells do not separate their genetic material within a nucleus. In eukaryotic cells, the nucleus separates the genetic material from the rest of the cell. 32
33 Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Organisms whose cell contain a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles are called EUKARYOTES Organisms whose cells never contain (or lack) a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles are called PROKARYOTES 33
34 A rat liver cell (with color enhancement to show organelles) 34
35 It s Crowded In There An artist s conception of the cytoplasm - the region of a cell that s not in the nucleus or within an organelle. 35
36 It s Crowded In There A micrograph showing cytoskeleton (red), ribosomes (green), and membrane (blue) 36
37 Two Fundamentally Different Types of Cells 37
38 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Cells fall into two broad categories, depending on whether they contain a nucleus. The nucleus is a large membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cell s genetic material in the form of DNA. The nucleus controls many of the cell s activities. 38
39 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Eukaryotes are cells that enclose their DNA in nuclei. Prokaryotes are cells that do not enclose DNA in nuclei. 39
40 Prokaryotes Are generally smaller than eukaryotic cells Have no nucleus Carry out all of life s processes Ex: bacteria Bacillus anthracis 40
41 Eukaryotes a. Are generally larger and more complex than prokaryotes b. Contain dozens of membrane bound structures that are specialized c. Nucleus separates DNA from rest of cell 41
42 Eukaryotes Come in a variety of shapes and size Ex: protists, fungi, plant, and animal cells 42
43 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Eukaryotes Eukaryotic cells are generally larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells. Most eukaryotic cells contain dozens of structures and internal membranes. Many eukaryotes are highly specialized. There are many types of eukaryotes: plants, animals, fungi, and organisms commonly called protists. 43
44 Us vs. Them - Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes 44
45 7.2 Cell Structure Cell organization Organelles- tiny organs ; the specialized structures within the cell that perform a function 45
46 Animal vs Plant cells 46
47 Animal and Plant Cells Have More Similarities Than Differences 47
48 The cell as a factory The different organelles of a cell can be compared to a living version of a modern factory Cells, like factories follow instructions to produce products 48
49 Cytoplasm Cytoplasm- the portion of the cell outside of the nucleus; the fluid that fills the entire cell Makes up about 70% of the cells volume. Most of the cells chemical reactions occur here 49
50 The Nucleus Control center of the cell Surrounded by a nuclear envelope with pores DNA is in the form of chromatin which condenses down into chromosomes Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus, but they do have DNA 50
51 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular The Nucleus Most nuclei also contain a small, dense region known as the nucleolus. The nucleolus is where the assembly of ribosomes begins. 51
52 Organelles that Store, Clean-up, and Support 1. Vacuoles- large sac-like, membrane enclosed structures - store water, salts, proteins, carbohydrates 2. Lysosomes- the clean-up crew ; small organelles filled with enzymes 3. Cytoskeleton-The framework of the cell ; a network of protein filaments; made up of microfilaments and microtubules; some parts help in transport of materials a. Centrioles - Are located near the nucleus; help organize cell division; not found in plant cells 52
53 Vacuoles large sac-like, membrane enclosed structures Function- store water, salts, proteins, carbohydrates Larger in plant cells Found in some unicellular organisms and animal cells Ex: Paramecium Contractile vacuole in paramecium cell 53
54 Vacuoles Typically called vesicles in animal cells- store and move materials between cell organelles and to the cell surface 54
55 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Vacuoles and Vesicles saclike, membrane-enclosed structures that store materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates Larger in plant cells 55
56 Lysosomes- the clean-up crew ; small organelles filled with enzymes Break down many types of materials Lipids Carbohydrates Proteins Cellular debri Found mostly in animal cells 56
57 The Lysosome Functions: Digesting food or cellular invaders Recycling cellular components 57
58 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Lysosomes Lysosomes are small organelles filled with enzymes that function as the cell s cleanup crew. Lysosomes perform the vital function of removing junk that might otherwise accumulate and clutter up the cell. Found mostly in white blood cells Have been linked to diseases, such as Tay Sach s Tay Sach s is a disorder that is caused by a genetic defect that prevents the formation of an essential enzyme that breaks down lipids These lipids build up in the body and can cause nerve damage; prognosis is not good 58
59 The Lysosome This bacterium about to be eaten by an immune system cell will spend the last minutes of its existence within a lysosome. 59
60 Many Diseases are Caused by Lysosome Malfunction 60
61 Cytoskeleton The framework of the cell ; a network of protein filaments Some parts help in transport of materials Aids the cell in movement Made up of microfilaments and microtubules 61
62 The Cytoskeleton The name is misleading. The cytoskeleton is the skeleton of the cell, but it s also like the muscular system, able to change the shape of cells in a flash. Maintains the shape of the cell Aids in movement An animal cell cytoskeleton 62
63 A Cytoskeleton Gallery 63
64 The Cytoskeleton in Action Cilia on a protozoan Beating sperm tail at fertilization Smoker s cough is due to destruction of cilia linking the airways. 64
65 Cytoskeleton Microfilaments- threadlike structures made up of a protein called actin Help cell maintain shape and allow it to move Assembly and dissasembly are responsible for amoeboid movement 65
66 Cytoskeleton Microtubules- are hollow structures made up of proteins known as tubulins Important for cells in maintaining shape, as well as for cell division Help build projections from the cell surface 66
67 Centrioles Are located near the nucleus Function- help organize cell division Not found in plant cells 67
68 Organelles That Build Proteins 1. Ribosomes- are small pieces of RNA and protein; the worktable for making proteins 2. Endoplasmic Reticulum- Protein synthesis (about half the cell s proteins are made here); Protein movement (transport) 3. Golgi Apparatus-Proteins produced in the rough ER move here for packaging 68
69 Organelles That Build Proteins Ribosomes- are small pieces of RNA and protein Function- the worktable for making proteins Build proteins based on DNA s coded instructions Located throughout the cell 69
70 Ribosomes and the Endoplasmic Reticulum 70
71 Ribosome Ribosomes Are Not Surrounded by a membrane. They are the site of PROTEIN SYNTHESIS (Production or Construction) in a cell. 71
72 Cystic Fibrosis Click here to see the article. 72
73 Endoplasmic reticulum- ER Found in eukaryotic cells only Internal membrane system responsible for assembling lipids for the cell membrane Also assembles proteins for and other materials that are exported from the cell Two types- rough and smooth 73
74 The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Studded with ribosomes Protein synthesis (about half the cell s proteins are made here). Protein movement (transport) 74
75 The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough ER- builds proteins; contains ribosomes on its surface Rough ER chemically modifies the proteins made by the ribosomes Produces proteins that will eventually be secreted out of the cell 75
76 Smooth ER IS NOT Covered with RIBOSOMES and processes LIPIDS and CARBOHYDRATES. The Smooth ER is involved in the synthesis of steroids in gland cells, the regulation of calcium levels in muscle cells, and the breakdown of toxic substances by liver cells. 76
77 Smooth ER- known as smooth because there are no ribosomes on its surface Contains enzymes that allow it to synthesize membrane and detoxify drugs Highly concentrated in liver cells Right: rough er; Left: smooth er Human liver cell 77
78 Golgi Apparatus Found in eukaryotic cells Proteins produced in the rough ER move here Appears as a stack of flat discs Function- modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials from the ER for storage in the cell or release outside the cell 78
79 Golgi Apparatus Processing, Packaging and Secreting Organelle of the Cell that is made of flattened SAC 79
80 Animal vs. Plant Cells Chloroplasts Are a Big Part of the Difference 80
81 Cells In a Leaf 81
82 Two Other Unique Features of Plant Cells The central vacuole may occupy 90% of a plant cell. 82
83 Organelles that Capture and Release Energy 1. Chloroplasts - Found in plant cells, algae, and some bacteria; Capture light energy and convert it into food that contains chemical energy ; Where photosynthesis occurs 2. Mitochondria-Found in all eukaryotic cell; powerplant of the cell; Converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use (ATP) 83
84 Chloroplasts Found in plant cells, algae, and some bacteria Capture light energy and convert it into food that contains chemical energy Where photosynthesis occurs 84
85 The Chloroplast Think of the chloroplast as the solar panel of the plant cell. Only plants have chloroplasts; they perform photosynthesis 85
86 Chloroplast Structure 2 membranes surround the organelle Stacks of membranes called grana are where chlorophyll occurs Chlorophyll- green pigment 86
87 Mitochondria Found in all eukaryotic cells Function- powerplant of the cell Converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use (ATP) 87
88 The Mitochondrion Think of the mitochondrion as the powerhouse of the cell. Both plant and animal cells contain many mitochondria. 88
89 Mitochondrial Diseases 89
90 Mitochondria and Health 90
91 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Cellular Boundaries Cells are surrounded by a barrier known as the cell membrane. Many cells, including most prokaryotes, also produce a strong supporting layer around the membrane known as a cell wall. 91
92 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Cell Membranes All cells contain a cell membrane that regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also protects and supports the cell. 92
93 Cell membrane The Cell Membrane is a complex barrier separating the cell from it's external environment. The "Selectively Permeable" Membrane regulates what passes into and out of the cell. 93
94 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular Cell Membranes The composition of nearly all cell membranes is a double-layered sheet called a lipid bilayer, which gives cell membranes a flexible structure and forms a strong barrier between the cell and its surroundings. 94
95 Cell membrane- outermost boundary of the cell Is made up of a flexible double layer called a lipid bilayer Gives cell shape and holds cytoplasm in Receptor Proteins Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tails 95 Lipid Bilayer
96 Cell membrane- Selective Permeability- some substances can cross over the cell membrane, some cannot Gets in: Oxygen, water, and Carbon Dioxide Does Not Get in: Sodium, Potassium, Calcium, Chlorine, proteins (need active support), most large molecules 96
97 You will not be tested on the material presented on the next 7 slides covering lipids and fluid mosaic model these slides do not appear in you powerpoint this material is covered in Honors Bio ad AP bio I am presenting it for those who like to understand how things work. 97
98 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular The Properties of Lipids that control how a cell membrane works Many lipids have oily fatty acid chains attached to chemical groups that interact strongly with water. The fatty acid portions of such a lipid are hydrophobic, or water-hating, while the opposite end of the molecule is hydrophilic, or water-loving. 98
99 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular The Properties of Lipids When such lipids are mixed with water, their hydrophobic fatty acid tails cluster together while their hydrophilic heads are attracted to water. A lipid bilayer is the result. 99
100 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular The Properties of Lipids The head groups of lipids in a bilayer are exposed to water, while the fatty acid tails form an oily layer inside the membrane from which water is excluded. 100
101 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular The Fluid Mosaic Model Most cell membranes contain protein molecules that are embedded in the lipid bilayer. Carbohydrate molecules are attached to many of these proteins. 101
102 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular The Fluid Mosaic Model Because the proteins embedded in the lipid bilayer can move around and float among the lipids, and because so many different kinds of molecules make up the cell membrane, scientists describe the cell membrane as a fluid mosaic. 102
103 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular The Fluid Mosaic Model Some of the proteins form channels and pumps that help to move material across the cell membrane. Many of the carbohydrate molecules act like chemical identification cards, allowing individual cells to identify one another. 103
104 Lesson Overview Life Is Cellular The Fluid Mosaic Model Although many substances can cross biological membranes, some are too large or too strongly charged to cross the lipid bilayer. If a substance is able to cross a membrane, the membrane is said to be permeable to it. A membrane is impermeable to substances that cannot pass across it. Most biological membranes are selectively permeable, meaning that some substances can pass across them and others cannot. Selectively permeable membranes are also called semipermeable membranes. 104
105 Cell Wall Plant cells have a cell wall. A Cell Wall DOES NOT REPLACE the Cell Membrane Cells with WALLS also have a CELL MEMBRANE. Plant Cells are covered by a Rigid Cell Wall that lies Outside the Cell Membrane. 105
106 Cellular Walls Cell Wall- a strong, supporting layer around the cell membrane Found in prokaryotes, plants, and fungi Not found in animal cells 106
107 Cellular Walls Function- supports, shapes, and protects the cell Porous enough to allow water, O2, and CO2 to pass through In plants, it s made up of cellulose Right: products made from cellulose 107
108 The Central Vacuole Controls Turgor Pressure Flaccid no water Turgid full of water 108
109 Cellular Anatomy 109
110 Plants vs Animals Chloroplasts Cell Wall Centrioles Both Nucleus Cytoskeleton Nucleolus Vacuoles Mitochondria Ribosomes Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes ER Cytoplasm 110
111 Cell Structure Review You must know the similarities and differences between plant and animal cells You must be able to locate the various organelles in a cell diagram You must know the function of each organelle 111
112 The Nucleus - review The largest membranebound organelle in the eukaryotic cell Enclosed by the nuclear envelope contains pores Contains a dark spot - the nucleolus builds ribosomes Contains chromatin (DNA and proteins) when coiled forms chromosomes
113 Plasma Membrane - review Composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins Provides a barrier that controls what enters and leaves the cell. All cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, contain plasma membranes. 113
114 Cell Wall - review Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells can have a cell wall. Composed of cellulose in plant cells. A rigid, protective covering that provides structural support
115 Cell fluid which surrounds the organelles and contains many dissolved solutes. Site of many cellular chemical reactions. Cytoplasm - review 115
116 Bag-like storage structure Can take up to 90% of the volume of a plant cell Stores food, water, wastes, or other substances Animal cell vacuoles are much smaller Vacuole - review 116
117 The site of cellular respiration. Mitochondria - review Provides energy for the cell by producing a molecule called ATP. Has a highly folded inner membrane that provides increased surface area for chemical reactions
118 Site of photosynthesis. Chloroplast - review Contains the green pigment chlorophyll. Has a highly folded inner membrane that provides increased surface area for chemical reactions
119 Ribosomes - review Composed of RNA and protein Made up of two subunits Responsible for protein synthesis Found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 119
120 Other Organelles - review Other organelles help to carry out cell functions. ER makes lipids and helps build new membrane. Golgi receives and modifies proteins and then ships them to new locations in the cell. Lysosomes digest worn out cell parts and food. Golgi Apparatus Endoplasmic Reticulum Lysosome Transport Vesicle 120
Chapter 7 Notes. Section 1
 Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Lesson Overview. 7.2 Cell Structure
 7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
7.2 Cell Structure. Sunday, December 16, :13 PM. Chapter 7 Cell Strucutre and Function Page 1
 7.2 Cell Structure Sunday, December 16, 2012 5:13 PM Vocabulary: Cytoplasm: in eukaryotic cells, all cellular contents outside the nucleus; in prokaryotic cells, all of the cells' contents Organelle: specialized
7.2 Cell Structure Sunday, December 16, 2012 5:13 PM Vocabulary: Cytoplasm: in eukaryotic cells, all cellular contents outside the nucleus; in prokaryotic cells, all of the cells' contents Organelle: specialized
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function The Discovery of the Cell - microscopes invented in 1600 s - Robert Hooke observed cork in 1665 and described them as little boxes he called cells - Hooke did not
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function The Discovery of the Cell - microscopes invented in 1600 s - Robert Hooke observed cork in 1665 and described them as little boxes he called cells - Hooke did not
UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function
 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
6. What surrounds the nucleus? How many membranes does it have?
 Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Think About it. Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells. The Discovery of the Cell. The cell theory states: Exploring the Cell 10/10/2016
 Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
Cell Structure and and Function Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Chapter 7
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic
 Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s)
 Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
THE CELL Cells: Part 1
 THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
Interest Grabber. All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells.
 Interest Grabber Section 7-1 Are All Cells Alike? All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells. 1. What are the advantages
Interest Grabber Section 7-1 Are All Cells Alike? All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells. 1. What are the advantages
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
8/7/18. UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function. I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory
 8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
The Cell. The building blocks of life
 The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS. All living things are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all of the processes of life.
 CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
Unit 2:The Cell. Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology
 Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Chapter Seven. A View of the Cell
 Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7
 Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cell Theory. Cells are the basic unit of life.
 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Image Guide. Do NOT Write on this page. It is an Image guide for test questions.
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells
 What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes
 Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81
 Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81 The Cellular Basis of Life Before people had a scientific explanation for where life came from, they believed in the theory of spontaneous generation, where organisms
Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81 The Cellular Basis of Life Before people had a scientific explanation for where life came from, they believed in the theory of spontaneous generation, where organisms
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE
 CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
Chapter Seven. A View of the Cell
 Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function. Section Objectives: Relate advances in microscope technology to discoveries about cells and cell structure.
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Section Objectives: Relate advances in microscope technology to discoveries about cells and cell structure. Compare the operation of a microscope with that of an electron
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Section Objectives: Relate advances in microscope technology to discoveries about cells and cell structure. Compare the operation of a microscope with that of an electron
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A View of the Cell CHAPTER 7
 A View of the Cell CHAPTER 7 CELL THEORY Before microscopes, people thought diseases were caused by curses and supernatural spirits They had no idea microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses existed
A View of the Cell CHAPTER 7 CELL THEORY Before microscopes, people thought diseases were caused by curses and supernatural spirits They had no idea microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses existed
Household pin w/ bactera. Cell Structure and Function
 Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Objectives. To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles.
 Cell Organelles 3.2 Objectives To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles. Basic Cellular Structures Cell membrane (cytoplasmic
Cell Organelles 3.2 Objectives To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles. Basic Cellular Structures Cell membrane (cytoplasmic
CH 7 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 1 Review What is a cell Explain What three statements make up the cell theory Infer How did the invention of the microscope help the development of the cell theory 2 Review How do microscopes work Apply
1 Review What is a cell Explain What three statements make up the cell theory Infer How did the invention of the microscope help the development of the cell theory 2 Review How do microscopes work Apply
Cellular Boundaries. Cell Organelles. The Nucleus and Cell Control. Cell Membrane. Cell Wall. Nucleus 10/11/2012. Cell Membrane Cell Wall
 Cell Organelles Cellular Boundaries Protects cell Support and shape Controls what comes in and out of the cell Selectively permeable the process in which a membrane allows some molecules to pass through
Cell Organelles Cellular Boundaries Protects cell Support and shape Controls what comes in and out of the cell Selectively permeable the process in which a membrane allows some molecules to pass through
Cell Structure and Function. The Basic Unit of Life
 Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke The word " cell was first used in late 1665 by Robert Hooke. He looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under
Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke The word " cell was first used in late 1665 by Robert Hooke. He looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam
 Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Cell Structure and Function
 Freshwater diatoms unicellular algae with hard silica cell wall come in many shapes and sizes. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Chapter Mystery Death by Water? Michelle was a healthy 25-year-old running
Freshwater diatoms unicellular algae with hard silica cell wall come in many shapes and sizes. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Chapter Mystery Death by Water? Michelle was a healthy 25-year-old running
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function.
 Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Cell Structure and Function
 Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Same bacteria on pinhead Fig. 4-1c, p.50 Review: Ionic Bonds Na has 11p and 10e making it (+) Cl has 18e and 17 p making it (-) The attraction
Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Same bacteria on pinhead Fig. 4-1c, p.50 Review: Ionic Bonds Na has 11p and 10e making it (+) Cl has 18e and 17 p making it (-) The attraction
Plant Cells. Chapter 3
 Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. RPTSE Biology Fall 2015, Dr. Jong B. Lee 1. Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells Antibiotics were first isolated from mold in 1928. The widespread use of antibiotics drastically decreased
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells Antibiotics were first isolated from mold in 1928. The widespread use of antibiotics drastically decreased
The Cell. The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes.
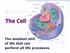 The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
History of the Cell. History of the Cell 10/24/2013. Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function. Robert Hooke (1665) Robert Hooke (1665)
 Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Journey to the World of Cells
 Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Theory Cell Structure and Function Chapter 6 Pg. 94-124 What is a cell? The basic functional unit of all living things. The Cell Theory states All organisms are made of one or more cells. Cells are
Cell Theory Cell Structure and Function Chapter 6 Pg. 94-124 What is a cell? The basic functional unit of all living things. The Cell Theory states All organisms are made of one or more cells. Cells are
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell.
 Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4. Outline. Early contributors to Understanding Cells. Cell Theory. Cell Size s Matt Schleiden & Ted Schann
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Inner Life of Cell. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
A Tour of the Cell. reference: Chapter 6. Reference: Chapter 2
 A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
Don t Freak Out. Test on cell organelle on Friday!
 Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
CELLS.
 CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
A Tour of the Cell Period
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Name Date Period California State standard covered within this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Name Date Period California State standard covered within this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical
Unit 2 Notes: Cells. What you need to know:
 1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Cell Structure and Function
 Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
Chapter 3. Cell Structure
 Chapter 3 Cell Structure Looking at Cells l The invention of microscopes allowed scientists to view cells for the first time l Scientists use the metric system to measure the size of cells l Metric Units
Chapter 3 Cell Structure Looking at Cells l The invention of microscopes allowed scientists to view cells for the first time l Scientists use the metric system to measure the size of cells l Metric Units
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and function
 Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
Cell Biology. a review! Cell Theory & Cell Structures
 Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cells. Cells are the best!
 Cells Cells are the best! All living things are made of cells Some life forms are just one teeny, tiny cell We are made of trillions of cells! (1,000,000,000,000 = 1 trillion) Cells are really, really
Cells Cells are the best! All living things are made of cells Some life forms are just one teeny, tiny cell We are made of trillions of cells! (1,000,000,000,000 = 1 trillion) Cells are really, really
CELL THEORY- EQ: What are the 3 facts of the cell theory? - pp191. EQ- Which Scientists are connected to cell discovery?
 UNIT 3 - CELLS Cell theory Types of cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic,plant and animal) Homeostasis in cells Enzymes Biomolecules Cell structure and function and processes Transport across cellular membranes
UNIT 3 - CELLS Cell theory Types of cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic,plant and animal) Homeostasis in cells Enzymes Biomolecules Cell structure and function and processes Transport across cellular membranes
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 62-107 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 527) 1. 2. 3. 4. 9. What
Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 62-107 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 527) 1. 2. 3. 4. 9. What
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism
 Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Organelles Defined. Class Copy CELL STUDY NOTES Class Copy
 Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
