AP Biology. Overview. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Types of ER. Smooth ER function. Rough ER function
|
|
|
- Osborne Carroll
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Cell: Endomembrane System Endoplasmic Reticulum,, Lysosomes, Peroxisomes, Vacuoles, Vesicles Overview Play key role in synthesis (& hydrolysis) of macromolecules in cell Various players modify macromolecules for various functions 2 Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) manufactures membranes & performs many bio-synthesis functions membrane connected to nuclear envelope & extends throughout cell accounts for 50% membranes in eukaryotic cell rough ER = bound ribosomes smooth ER = no ribosomes Types of ER 3 4 Smooth ER function Factory processing operations many metabolic processes synthesis & hydrolysis enzymes of smooth ER synthesize lipids, oils, phospholipids, steroids & sex hormones hydrolysis (breakdown) of glycogen (in liver) into glucose detoxify drugs & poisons (in liver) ex. alcohol & barbiturates Rough ER function Produce proteins for export out of cell protein secreting cells packaged into transport vesicles for export which cells have a lot of rough ER? 5 6 1
2 Membrane Factory Synthesize membrane phospholipids build new membrane as ER membrane expands, bud off & transfer to other parts of cell that need membranes Synthesize membrane proteins membrane bound proteins synthesized directly into membrane processing to make glycoproteins finishes, sorts, & ships cell products shipping & receiving department center of manufacturing, warehousing, sorting & shipping extensive in cells specialized for secretion which cells have a lot of Golgi? 7 8 flattened membranous sacs = cisternae look like stack of pita bread 2 sides = 2 functions cis = receives material by fusing with vesicles = receiving trans buds off vesicles that travel to other sites = shipping (transport) cis trans 9 10 Golgi processing During path from cis to trans, products from ER are modified into final form tags, sorts, & packages materials into transport vesicles Golgi = UPS headquarters Transport vesicles = UPS trucks delivering packages that have been tagged with their own barcodes Putting it together
3 13 14 Lysosomes membrane-bounded sac of hydrolytic enzymes that digests macromolecules enzymes & membrane of lysosomes are synthesized by rough ER & transferred to the Golgi Lysosomes a little stomach for the cell lyso = breaking things apart some = body also the clean up crew of the cell only in animal cells 15 Why was this discovery so important? 1974 Nobel prize: Christian de Duve Lysosomes discovery in 1960s 16 Cellular digestion Lysosomes fuse with food vacuoles Polymers are digested into monomers pass to cytosol to become nutrients of cell The Recycler Fuse with organelles or macromolecules in cytosol to recycle materials Where old proteins go to die!
4 Lysosomal enzymes Lysosomal enzymes work best at ph 5 organelle creates custom ph how? proteins in lysosomal membrane pump H + ions from the cytosol into lysosome why? enzymes are very sensitive to ph why? enzymes are proteins ph affects structure why evolve digestive enzymes which function at ph different from cytosol? digestive enzymes won t function well if leak into cytosol = don t want to digest yourself! 19 When things go wrong What if a lysomome digestive enzyme doesn t function? don t digest a biomolecule instead biomolecule collects in lysosomes lysosomes fill up with undigested material lysosomes grow larger & larger eventually disrupt cell & organ function Lysosomal storage diseases are usually fatal Tay-Sachs disease lipids build up in brain cells child dies before age 5 Tay-Sachs 20 Sometimes its supposed to work that way Fetal development syndactyly Apoptosis = cell death critical role in programmed destruction of cells in multicellular organisms auto-destruct mechanism cell suicide some cells have to die in an organized fashion, especially during development ex: development of space between your fingers during embryonic development ex: if cell grows improperly this self-destruct mechanism is triggered to remove damaged cell» cancer over-rides this to enable tumor growth 21 6 weeks 15 weeks 22 Peroxisomes Other digestive enzyme sacs in both animals & plants breakdown fatty acids to sugars easier to transport & use as energy source detoxify cell detoxifies alcohol & other poisons produce peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) must breakdown H 2 O 2 H 2 O
5 Vacuoles & vesicles little transfer ships Food vacuoles phagocytosis, fuse with lysosomes Contractile vacuoles in freshwater protists, pump excess H 2 O out of cell Central vacuoles in many mature plant cells video Vacuoles in plants s storage stockpiling proteins or inorganic ions depositing metabolic byproducts storing pigments storing defensive compounds against herbivores selective membrane control what comes in or goes out Vacuole Vesicles 27 Vesicles 28 Putting it all together Video 29 5
Types of ER. Chapter 6 The Cell: Endomembrane System Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, Lysosomes, Peroxisomes, Vacuoles, Vesicles.
 WH Chapter 6 The Cell: Endomembrane System Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, Lysosomes, Peroxisomes, Vacuoles, Vesicles Types of ER Overview Play key role in synthesis (& hydrolysis) of macromolecules
WH Chapter 6 The Cell: Endomembrane System Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, Lysosomes, Peroxisomes, Vacuoles, Vesicles Types of ER Overview Play key role in synthesis (& hydrolysis) of macromolecules
AP Biology. Tour of the Cell 1
 Tour of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized structures specialized functions cilia
Tour of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized structures specialized functions cilia
/searchlist/6850.html Tour of the Cell 1
 http://www.studiodaily.com/main /searchlist/6850.html Tour of the Cell 1 2011-2012 Cytology: science/study of cells To view cells: Light microscopy resolving power: measure of clarity Electron microscopy
http://www.studiodaily.com/main /searchlist/6850.html Tour of the Cell 1 2011-2012 Cytology: science/study of cells To view cells: Light microscopy resolving power: measure of clarity Electron microscopy
Ch. 4 Cells: The Working Units of Life
 Ch. 4 Cells: The Working Units of Life Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Types of cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized functions
Ch. 4 Cells: The Working Units of Life Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Types of cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized functions
The Jobs of Cells. Food & water storage. Vacuoles & vesicles. Vacuoles in plants 10/5/2015. plant cells
 Cells have 3 main jobs make energy need energy for all activities need to clean up waste produced while making energy make proteins proteins do all the work in a cell, so we need lots of them make more
Cells have 3 main jobs make energy need energy for all activities need to clean up waste produced while making energy make proteins proteins do all the work in a cell, so we need lots of them make more
AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Cell Lecture Part 1 COMPARISONS OF SCOPES CELL THEORY
 CELL THEORY All organisms are made of one or more cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things Cells arise by division of pre- existing cells. Cell Lecture Part 1 1 2 How
CELL THEORY All organisms are made of one or more cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things Cells arise by division of pre- existing cells. Cell Lecture Part 1 1 2 How
Types of cells. Cell size comparison. The Jobs of Cells 10/5/2015. Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Biological diversity & Unity. Chapter 7. Activities of life. How do we study cells? Light Microscope. Electron Microscope 9/7/2012
 Biological diversity & Unity Chapter 7 The cell: Basic unit of Life Underlying the diversity of life is a striking unity DNA is universal genetic language Cells are the basic unit of structure & function
Biological diversity & Unity Chapter 7 The cell: Basic unit of Life Underlying the diversity of life is a striking unity DNA is universal genetic language Cells are the basic unit of structure & function
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Don t Freak Out. Test on cell organelle on Friday!
 Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Compare the 2 Types of Cells PROKARYOTES BOTH EUKARYOTES Domain: Domain: Relative Size & Complexity: Relative Size & Complexity: No DNA in No Examples: Has Has Examples: 2.
Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Compare the 2 Types of Cells PROKARYOTES BOTH EUKARYOTES Domain: Domain: Relative Size & Complexity: Relative Size & Complexity: No DNA in No Examples: Has Has Examples: 2.
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae.
 Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae. Cisternae serve as channels for the transport of
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae. Cisternae serve as channels for the transport of
Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts, *Mitochondria. *Learn these from text/connect1. Fertilization of a human cell
 Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
Cell Theory All living matter is composed of one or more The cell is the structural and functional unit of life All cells come from pre-existing cell
 Cell Theory All living matter is composed of one or more The cell is the structural and functional unit of life All cells come from pre-existing cell Prokeryotic Bacteria or archaea Cell wall, small circular
Cell Theory All living matter is composed of one or more The cell is the structural and functional unit of life All cells come from pre-existing cell Prokeryotic Bacteria or archaea Cell wall, small circular
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane, includes the organelles, cytosol, and
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
LECTURE 3 CELL STRUCTURE
 LECTURE 3 CELL STRUCTURE HISTORY The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 examining very thin slices of cork and saw a multitude of tiny pores that remarked looked like the walled compartments
LECTURE 3 CELL STRUCTURE HISTORY The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 examining very thin slices of cork and saw a multitude of tiny pores that remarked looked like the walled compartments
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles. Hüseyin Çağsın
 Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
Ch 3 Cell Structure 10/1/2008. Cells Under the Microscope. Natural laws limit cell size. Biology Periods 2, 3, 4, & 6 Mrs.
 Ch 3 Cell Structure Cells Under the Microscope Electron microscopes have much higher magnifying and resolving powers than light microscopes. Biology Periods 2, 3, 4, & 6 Mrs. Stolipher Cell size and shape
Ch 3 Cell Structure Cells Under the Microscope Electron microscopes have much higher magnifying and resolving powers than light microscopes. Biology Periods 2, 3, 4, & 6 Mrs. Stolipher Cell size and shape
Cell Structure and Organelles SBI4U 2016/10/14
 Cell Structure and Organelles SBI4U 2016/10/14 Inside the cell These are generalizations, not rules! Everything inside the cell membrane besides the nucleus is called the cytoplasm; The liquid is known
Cell Structure and Organelles SBI4U 2016/10/14 Inside the cell These are generalizations, not rules! Everything inside the cell membrane besides the nucleus is called the cytoplasm; The liquid is known
The most valuable lipid ever?
 The most valuable lipid ever? Spermaceti whale oil Used by sperm whales in a special organ in the huge head cavity Largely comprised of cetyl palmitate ww.thisrecording.com www.greenpeace.org Peer Instruction
The most valuable lipid ever? Spermaceti whale oil Used by sperm whales in a special organ in the huge head cavity Largely comprised of cetyl palmitate ww.thisrecording.com www.greenpeace.org Peer Instruction
THE CELL Cells: Part 1
 THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
A Tour of the cell. 2- Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions
 A Tour of the cell 1- To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 2- Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions 3- The eukaryotic cell s
A Tour of the cell 1- To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 2- Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions 3- The eukaryotic cell s
A Tour of the Cell Period
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Name Date Period California State standard covered within this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Name Date Period California State standard covered within this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical
3- The Endomembrane System
 B- Eukaryotic Cell 3- The Endomembrane System a) The endoplasmic reticulum الشبكة الندوبلزمية manufacturers membranes and performs many other biosynthetic functions b) The Golgi apparatus جولچى, finishesجهاز
B- Eukaryotic Cell 3- The Endomembrane System a) The endoplasmic reticulum الشبكة الندوبلزمية manufacturers membranes and performs many other biosynthetic functions b) The Golgi apparatus جولچى, finishesجهاز
Chapter 3 Review Assignment
 Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Endomembrane system 11/1/2018. Endomembrane System. Direct physical continuity. Transfer of membrane segments as vesicles. Outer Nuclear envelope
 Endomembrane system Endomembrane System Outer Nuclear envelope Direct physical continuity Transfer of membrane segments as vesicles Endoplasmic reticulum BUT membranes are not identical in structure and
Endomembrane system Endomembrane System Outer Nuclear envelope Direct physical continuity Transfer of membrane segments as vesicles Endoplasmic reticulum BUT membranes are not identical in structure and
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Theory Cell Structure and Function Chapter 6 Pg. 94-124 What is a cell? The basic functional unit of all living things. The Cell Theory states All organisms are made of one or more cells. Cells are
Cell Theory Cell Structure and Function Chapter 6 Pg. 94-124 What is a cell? The basic functional unit of all living things. The Cell Theory states All organisms are made of one or more cells. Cells are
Cytology. Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges
 Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell. The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes.
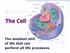 The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function
 Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Chapter 6 Review Page 1
 hapter 6 Review Page 1 1 Which of the following statements about prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells is FLS? They both contain ribosomes. They both contain mitochondria. They are both bounded by a plasma
hapter 6 Review Page 1 1 Which of the following statements about prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells is FLS? They both contain ribosomes. They both contain mitochondria. They are both bounded by a plasma
3. Which cell has the greater ratio of surface area to volume?
 Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
EK 2.B.c.3 LO 2.14 EK 2.B.c.3 LO 2.14
 EK 2.B.c.3 LO 2.14 EK 2.B.c.3 LO 2.14 Cell Theory Cell Theory 1. The cell is the basic unit of life. 2. All living things are composed of cells 3. Cells only come from preexisting cells. Types of Cell
EK 2.B.c.3 LO 2.14 EK 2.B.c.3 LO 2.14 Cell Theory Cell Theory 1. The cell is the basic unit of life. 2. All living things are composed of cells 3. Cells only come from preexisting cells. Types of Cell
SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells
 SACE Biology Year 2016 Mark 20.00 Pages 26 Published Jan 4, 2017 SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells By Elizabeth (99.75 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Elizabeth. Elizabeth achieved
SACE Biology Year 2016 Mark 20.00 Pages 26 Published Jan 4, 2017 SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells By Elizabeth (99.75 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Elizabeth. Elizabeth achieved
CHAPTER 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL
 CHAPTER 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL Microscopes Con. 4.1 magnification: size resolution: clarity contrast: differences in parts Light Microscopy Techniques (p.68) a. Brightfield unstained b. Brightfield stained
CHAPTER 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL Microscopes Con. 4.1 magnification: size resolution: clarity contrast: differences in parts Light Microscopy Techniques (p.68) a. Brightfield unstained b. Brightfield stained
lysosomes Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types:
 lysosomes Digests Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types: Proteins Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Lipids Single membrane bound vesicle, contains up to 50 digestive
lysosomes Digests Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types: Proteins Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Lipids Single membrane bound vesicle, contains up to 50 digestive
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
Name 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of
 Name _ 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. The
Name _ 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. The
A TOUR OF THE CELL 10/1/2012
 A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81
 Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81 The Cellular Basis of Life Before people had a scientific explanation for where life came from, they believed in the theory of spontaneous generation, where organisms
Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81 The Cellular Basis of Life Before people had a scientific explanation for where life came from, they believed in the theory of spontaneous generation, where organisms
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
Cytology II Study of Cells
 Cytology II Study of Cells Biology 20 Cellular Basis of Life 1. Basic unit of Life 2. Composed of one or more cells 3. Arises from pre-existing cells Asexual (Mitosis)/Sexual (Meiosis) 4. Surrounded by
Cytology II Study of Cells Biology 20 Cellular Basis of Life 1. Basic unit of Life 2. Composed of one or more cells 3. Arises from pre-existing cells Asexual (Mitosis)/Sexual (Meiosis) 4. Surrounded by
Plasma Membrane. comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
11/1/2014. accumulate in brain.
 EU 4.A: Interactions within biological systems lead to complex properties. EU 4.B: Competition and cooperation are important aspects of biological systems. EU 4.C: Naturally occurring diversity among and
EU 4.A: Interactions within biological systems lead to complex properties. EU 4.B: Competition and cooperation are important aspects of biological systems. EU 4.C: Naturally occurring diversity among and
By Calypso Harmon Fall 2002
 By Calypso Harmon Fall 2002 This is an extremely thin slice through a plant cell. Are there any structures you recognize? Chloroplasts collect the energy from the sun and change it into chemical energy
By Calypso Harmon Fall 2002 This is an extremely thin slice through a plant cell. Are there any structures you recognize? Chloroplasts collect the energy from the sun and change it into chemical energy
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #7
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes
 Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Organelles Defined. Class Copy CELL STUDY NOTES Class Copy
 Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Unit A: Cells. Ch. 4 A Tour of the Cell
 Unit A: Cells Ch. 4 A Tour of the Cell Standards By the end of this unit you should be able to: Recognize and explain the function of each organelle Look at micrographs/diagrams/pictures and correctly
Unit A: Cells Ch. 4 A Tour of the Cell Standards By the end of this unit you should be able to: Recognize and explain the function of each organelle Look at micrographs/diagrams/pictures and correctly
(Please activate your clickers)
 Organelles in prokaryotes and eukaryotes! Plasma membrane! Cell wall (in prokaryotes, plants, fungi, some protists)! Ribosomes! Nucleoid/nucleus! Mitochondria! Plastids (Please activate your clickers)
Organelles in prokaryotes and eukaryotes! Plasma membrane! Cell wall (in prokaryotes, plants, fungi, some protists)! Ribosomes! Nucleoid/nucleus! Mitochondria! Plastids (Please activate your clickers)
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
(A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids. A. Incorrect! Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have cell membranes.
 High School Biology - Problem Drill 03: The Cell No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is NOT found in prokaryotic cells? #01 (A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids Both prokaryotic
High School Biology - Problem Drill 03: The Cell No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is NOT found in prokaryotic cells? #01 (A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids Both prokaryotic
10/5/2015. Cell Size. Relative Rate of Reaction
 The Cell Biology 102 Fundamental unit of life Smallest unit that displays all the basic elements of life Lecture 5: Cells Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells Cell Theory 2. The
The Cell Biology 102 Fundamental unit of life Smallest unit that displays all the basic elements of life Lecture 5: Cells Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells Cell Theory 2. The
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Objectives. By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles
 Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
The Cell. The building blocks of life
 The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head
 CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Hydrophobic regions of protein Hydrophilic regions of protein
CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Hydrophobic regions of protein Hydrophilic regions of protein
1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment
 Science 10 Dec. 3 1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment Chapter Two Structure and Cell Function 2.1 The Cell as an Efficient System Thought
Science 10 Dec. 3 1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment Chapter Two Structure and Cell Function 2.1 The Cell as an Efficient System Thought
Lecture 5- A Tour of the Cell
 Lecture 5- A Tour of the Cell 1 In this lecture Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes The organelles of the eukaryotic cell The cytoskeleton Extracellular components 2 What are cells? Cells are the fundamental unit
Lecture 5- A Tour of the Cell 1 In this lecture Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes The organelles of the eukaryotic cell The cytoskeleton Extracellular components 2 What are cells? Cells are the fundamental unit
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell
 Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Nuclear Membrane 5. Nucleoplasm 6. Nucleolus 7. Chromosomes 8. Vacuole 9. Ribosomes 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Nuclear Membrane 5. Nucleoplasm 6. Nucleolus 7. Chromosomes 8. Vacuole 9. Ribosomes 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department
 Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
Unit 2:The Cell. Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology
 Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Cytoskeleton. Provide shape and support for the cell. Other functions of the cytoskeleton. Nucleolus. Nucleus
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Tour of the Cell 1. Types of cells. Why organelles? Eukaryote animal cells. Eukaryote plant cells. Prokaryote bacteria cells.
 Tor of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Ekaryote animal cells Ekaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized strctres specialized fnctions mitochondria
Tor of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Ekaryote animal cells Ekaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized strctres specialized fnctions mitochondria
2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope. nucleus, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, ribosomes
 Honors Biology Unit 2 Chapter 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL 1. light microscope 2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope 3. surface area to volume ratio 4. prokaryotic cell vs. animal
Honors Biology Unit 2 Chapter 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL 1. light microscope 2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope 3. surface area to volume ratio 4. prokaryotic cell vs. animal
Lesson Overview. 7.2 Cell Structure
 7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function.
 Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Cells. 1. Smallest living structures. 2. Basic structural and functional units of the body. 3. Derived from pre-existing cells. 4. Homeostasis.
 Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS. All living things are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all of the processes of life.
 CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
The Cell. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Cell Cell Theory The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life The organism activity depends on individual and collective activity of cells Biochemical activities of cells are dictated
The Cell Cell Theory The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life The organism activity depends on individual and collective activity of cells Biochemical activities of cells are dictated
Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang
 Today s Agenda: I. Review of organelles II. More important organelles III. Plasma membrane structure IV. Diffusion and transport Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang I. Review
Today s Agenda: I. Review of organelles II. More important organelles III. Plasma membrane structure IV. Diffusion and transport Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang I. Review
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Chapter Seven. A View of the Cell
 Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Chapter 6. A Tour of the Cell. Concept 6.1 Biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry to study cells
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Chapter Outline Concept 6.1 Biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry to study cells In a light microscope (LM), visible light passes through the specimen and
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Chapter Outline Concept 6.1 Biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry to study cells In a light microscope (LM), visible light passes through the specimen and
BIOLOGY. A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL. Robert Hooke (1665) Antoni van Leeuwenhoek (1674) Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 6 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Robert Hooke (1665) Figure 1.1 The structure
6 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Robert Hooke (1665) Figure 1.1 The structure
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
