New Mandible Microsystem in Pain Therapy -
|
|
|
- Arthur Campbell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Pain & Relief Research Article New Mandible Microsystem in Pain Therapy - Yasser M. Elnaggar*, Dina Y Alnaggar, Fatimah M Altaweel and Mohamed Y Elnaggar Acupuncture unit, Anesthesia department, Faculty of medicine, Zagazig university, Egypt *Address for Correspondence: Yasser M. Elnaggar,143 Altahrir street, Dokki, Giza, Egypt, Tel: , ; elnaggarym@gmail.com Submitted: 05 October 2017; Approved: 28 November 2017; Published: 01 December 2017 Cite this article: Elnaggar YM, Alnaggar DY, Altaweel FM, Elnaggar MY. New Mandible Microsystem in Pain Therapy. Int J Pain Relief. 2017;1(1): Copyright: 2017 Elnaggar YM, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 ABSTRACT This study presenting the new acupuncture mandible microsystem, its anatomical representation on the face and its role in treating different acute painful disorders in the body. It is the latest microsystem discovered after about eighteen known microsystems throughout the history of acupuncture. It is a mini anatomical copy of the human body with unique distribution of body parts, the brain, the Spinal cord and the autonomic nervous system on the bilateral sides of the face. It differs from other microsystems on which body parts are not arranged in a systematic way like the human body anatomy. All the patients received acupuncture treatment. The main group of 234 patients received treatment in points on the mandible microsystem and the control group of 35 patients received treatment in a nonacupuncture point near the mandible microsystem. All The main group patients showed signifi cant pain relief after the fi rst treatment sessions, with varying degrees between 50 to 100 %, Compared with the sham effect which was 44% of the analgesic response. Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) for pain improved between 0 (no pain) and 3 (mild pain), which was not irritating to the patients and hence they returned to work and their normal daily life. Of the main group 137 patients showed 100% pain relief. 15 showed 90%, 46 showed 80%, 32 showed 70% and 4 showed 60% improvement. Follow-up showed improvement of functional and quality of life with no adverse effects or relapse. For the fi rst time, we can use a technique for relieving pain in most parts of the body, with reproducible effects. Mandible microsystem is a unique in its anatomy and a new method of treating pain. Keywords: Acupuncture; Mandible microsystem; Pain therapy INTRODUCTION Acupuncture Microsystems are regions of the body that contain maps of the entire organism with specific points or areas that correspond to each part. Ear acupuncture is the best-known system. Stimulating these points and areas has a rapid and powerful regulatory effect on energy and blood, they improve the function of the corresponding part of the body and they can be successfully used to relief any acute pain [1]. Microsystems are considered holographic images of the entire individual projected onto a particular part of the body. The ear, hand, scalp, foot, face, tongue, and the iris are some of the commonly recognized acupuncture microsystems [2]. Before the discovery of the holographic theory, man had already found that in specific areas of the body, diseases in any part of the body could be diagnosed and treated, such as ear, face, iris, nose and foot. Each part contains all the patho-physiological information of various regions of the whole body [3]. According to holographic theory, any abnormal changes have an effect both on a specific organ and on the holographic units in the other parts of the body. These holographic units can be used to diagnose and treat diseases [4]. The number of newly discovered microsystems is unlimited [5]. In 1973, Zhang developed the bio holographic theory. Dale was the first who suggested that, not only the ear, but every part of the body can function as a complete system for diagnosis and therapy [6]. In 1976, he introduced fourteen microsystems in the ear, hand, foot, abdomen, back, neck, scalp, face, nose, wrist, ankle, arm, leg and eye [7]. Since Dale the scientists developed these microsystems and discovered new ones. Up till recent time there are about eighteen acupuncture microsystems have been discovered in the world [4]. This study present the anatomy of the mandible microsystem and its relations to the mandible and the structures of the face. It also proved its role in relief of different acute painful conditions. Anatomy of the mandible The mandible is the lower jaw and contain the lower teeth. It consists of two symmetrical halves. The mandible halves were separated at birth and their fusion completed by the end of first year. Each half is composed of horizontal part called the body and a vertical part called the ramus. The anterior triangular part of the body of the mandible is the mental process which forms the bony chin. The connection of the body and the ramus is the angle of the mandible. The upper end of the ramus extends to form the coronoid process anteriorly and the condyloid process posteriorly. The notch of the mandible separates the condyloid process from the coronoid process. Each half of the mandible is extending from the symphysis up to the condyloid and coronoid processes. The symphysis is the fusion line of the two halves of the mandible. Each half is called a hemi mandible and is separated from the other half at birth, so it can be considered as a micro system that carries all the information of the body like ear, hand and foot (Figure 1) [16,17]. MATERIALS AND METHODS This study included 234 patients, 119 males and 115 females. Their ages were between years with mean age of 47 years. After committee acceptance, we started this prospective study on 2 groups: a main group of 234 patients and a control group of 30 patients. Each patient had acute pain in an area of body and received acupuncture treatment in points or areas on the mandible corresponding to anatomical pain regions in the main group and in the control group in a non-acupuncture point, one finger breadth below the small intestine 18 point (Quanliao) which lie directly below the outer canthus of the eye on the lower border of the zygomatic bone. All patients had acute pain (less than 3 months): In the main group 45 patients had pain in the neck, 38 in shoulders (14 bilateral, Why we need the mandible microsystem Ear microsystem had about 8 classifications for distribution of body parts. For example liver point had 8 different sites on the ear, one for liver and the other 7 sites on the sites of other organs and also every other organ had 8 different sites [8-15]. This disturbed practitioners and practice itself. That is why since about 20 years I am thinking in a microsystem that contain all body parts in one fixed place not liable to change by any scientist. Figure 1: Body representation on right side of female face. SCIRES Literature - Volume 1 Issue Page -021
3 12 right, 12 left), 22 in upper limbs (5 arm, 9 elbow, 3 wrist, 3 hand, 2 fingers), 44 in trunk and 85 in lower limbs (31 sciatica, 29 knee, 8 leg, 6 ankle, 5 heel 2 foot, 2 sole, 2 toes). Numeric Rating scale (NRS) for pain [18] was evaluated before and after the first session. Successful treatment was evaluated by no recurrence of pain, functional improvement and quality of life. Monthly follow up visits were made for 3 months and the condition of each patient was reevaluated to document any relapse or adverse effects. Mandible is a newly discovered microsystem The mandible, used as a micro acupuncture system which has the same physiological functions that can regulate the human body functions through stimulation of their micro organs and structures (Figure 2). The treatment through mandible microsystem can be proved easily in pain therapy by any trained practitioner. It was successful with me for nine years of daily clinical practice. Because of absence of any facilities I had no choice to prove the anatomical representation of this system except by the clinical testing of the sites of the organs and areas of the body. It was the most suitable method to prove the effectiveness of this new system and its high accuracy rate. So, if the patient suffered of pain, an acupuncture needle is inserted in the skin of the corresponding part on either half of the mandible, Pain improved directly with varying degrees. This means that the site of the corresponding point or area is correct. I tested nearly every part of the body during these nine years mainly for pain and also for other diseases and symptoms. Mandible is a remote-control system This microsystem is similar to original human body but in mini parts which control the functions of the original macro parts Figure 2: Body representation on face and mandible. (A) Human body is represented on two sides of face. (B) Human body is represented on two sides of mandible. Figure 3: Anatomical land marks of mandible microsystem (A) Landmark lines localize body areas on left side of male face (B) Vertical landmark lines localize body areas on female face. and repair them, if disturbed, by four systems; (i) two separate complete control systems on either halves of the mandible, (ii) two central nervous systems including brain and spinal cord, (iii) two microsystems of mini parts that regulate the functions of the macro original parts of the body and (iv) two autonomic nervous systems which control the functions of most organs of the body. No other microsystem discovered up till now, can explain all the anatomical and physiological functions of the body like this system because it is a mini copy of the human body. Therapy technique The needle is inserted in the skin, connective tissue and muscles over the mandible. The skin of the face varies in thickness. It is thin around the eyes, thick over the forehead, temples and around the mouth and thickest over the chin. The muscles of the face are embedded within the connective tissue under the skin [19]. The needle is stimulated for one minute or more by even method that means moving the acupuncture needle to and fro and up and down movements at the same time. A 32 or 34-gauge filiform needle, 2.5 or 4 cm in length is used. The skin of the mandible is thin in comparison to other areas like the abdomen or thigh, so only the horizontal and oblique techniques are used. Needles are retained for 10 to 30 minutes after the energy arrival to the point. Anatomical landmarks of mandible microsystem There are six vertical lines that determine the main anatomical areas of the body (Figure 3). 1. Vertical line in the anterior midline of the body from midpoint of lower lip to the lower border of the mandible, 2. Vertical line from medial angle of the eye to the lower border of the mandible, 3. Vertical line from lateral angle of mouth to the lower border of the mandible, 4. Vertical line from the center of the pupil of the eye to the lower border of mandible. 5. Vertical line from the lateral angle of the eye to the lower border of mandible and 6. Vertical line from the lateral end of the eye brow to lower border of mandible. Body representation on the mandible Head and Face: The head with the face are represented on the mental process. Its medial border is the midline of the body. Its lateral border is the vertical line that extend from the medial angle of the eye to the lower border of the mandible. Its upper border is the transverse crease of the chin and its lower border is the lower border of the mandible (Figure 4). Nervous System: Firstly, the Brain - The brain and brain stem occupies the area of the head. It is represented on the right and left halves of the mandible, with its right and left halves (Figure 5). Its upper border is the midline of the body. Its lower border is the vertical line that extend from the medial angle of the eye to the lower border of the mandible. Its frontal border is the transverse crease of the chin and its occipital border is the lower border of the mandible. The brain motor and sensory areas occupy an area about three millimeters in breath on both sides of the line extend from the midpoint of upper border of the brain to the transverse line midway between the upper and lower borders of the brain (Figure 5). Secondly, the Spinal Cord - The spinal column and spinal cord inside lie on the lower border of the mandible. It extends from the level of the lateral angle of the mouth to the lateral angle of the mandible. It is divided into anterior half which includes the cervical and thoracic vertebrae and segments and posterior half which includes the lumbar, SCIRES Literature - Volume 1 Issue Page -022
4 level of the lateral angle of the eye. The hand is between the lower end of the abdomen and the lateral angle of the mandible. Seventhly, the Lower Limb - The two legs lie along the right and left halves of the ramus of the mandible. Each along its whole length from the angle of the mandible to the level of the helix crus of ear (Figure 7). The hip joint is at the level of the lateral angle of the mandible. The knee joint is at the midpoint between the hip and ankle joints. The ankle joint is at level of the lower border of the inter-tragic notch of the ear. The feet lie anterior to the ear. Each foot occupies an area of one index finger breadth from the level of the lower border of the cartilage of the inter-tragic notch to the level of the transverse helix crus. Figure 4: Head and face representation on half face and half mandible. (A) Head and face are represented on left half of female face. (B) Head and face are represented on right half of mandible. Techniques of relieving pain in the mandible microsystem: For the first time in the history of acupuncture we can use a method for relieving pain, in most parts of the body, through three centers) local, spinal and brain centers) on each half of the mandible which are not known in any microsystem. The following is an example of treating left shoulder pain using these 6 centers (Figures 8-10). RESULTS This study included 234 patients, 119 males and 115 females. Their ages were between years with mean age of 47 years. In the main group the mean NRS before and after the first session was Figure 5: Brain represented on both halves of chin. (A) Brain is represented on left half of face (B) Brain is represented on both sides of face. (C) Left and right halves of brain are represented on front and underside of left half of chin. (D) Bilateral brains with their halves are represented on front and underside of bilateral halves of chin. Figure 6: Motor and sensory areas and spinal column representation. (A) Motor and sensory areas, spinal column and spinal cord inside are represented on left side of face. (B) Motor and sensory areas, spinal column and spinal cord inside are represented on left border of mandible. sacral and coccygeal vertebrae and segments. The spinal cord fills the spinal canal as in the three months old fetus in which the spinal cord occupies the whole length of the spinal canal [20-22], (Figure 6). Thirdly, the Autonomic nervous system - The autonomic nervous system is represented in the brain stem and on both sides of spinal cord area on the lower border of the mandible similar to the anatomy of the human spinal cord and brain stem. Fourthly, the Neck - The neck occupies an area of half an index finger breadth on both sides of the cervical Vertebrae on the lower border of the mandible from the level of the medial angle of the eye to the level of the angle of the mouth. Figure 7: Neck, trunk and limbs representation. (A) Neck, trunk and limbs are represented on left side of face. (B) Trunk and limbs are represented on left side of mandible. Fifthly, the Trunk - The trunk is divided into the chest, abdomen and pelvis. It is represented on both sides of the border of the mandible for an index finger breadth. From the level from lateral angle of mouth to the angle of the mandible. Sixthly, the Upper Limb - The arms extend for half an index finger breadth on both sides of the chest, abdomen and pelvis areas. The shoulder lies at the level of the lateral angle of the mouth. The elbow lie at the level of the lower border of the chest midway between wrist and shoulder. The wrist is at the lower end of abdomen at the Figure 8: Peripheral site of pain (Left shoulder centers on the side of face): (A) Left shoulder center on left half of mandible, (B) Left shoulder center on right half of mandible, and (C) Left shoulder centers on both of mandible halves. SCIRES Literature - Volume 1 Issue Page -023
5 7.90 and 1.00 with pain relief percent of The minimum and maximum NRS was 7 and 10 before the first session and 0 and 4 after it with pain relief percent between 50 and 100. In The control group the mean NRS before and after the first session was 8.90 and 7.33 with pain relief percent of The minimum and maximum NRS was 8 and 10 before the first session and 5 and 8 after it with pain relief percent between 0 and 44. In the main group the significant improvement in function and in pain relief was between 50 to 100 %, compared with sham effect which was 44% Relation between session numbers and pain duration There was a significant increase in session numbers with increase of pain duration (Figure 11). Relation between patient s groups improved after the first session and their numbers with their improvement percentage All the 234 patients showed pain relief after the first session with varying degrees. 137 patients showed complete relief of pain (100%), 15 showed 90% improvement, 46 showed 80% improvement, 32 showed 70% improvement and 4 showed 60% improvement (Figure 12). Relation between number of sessions and number of patients with their percent 123 patients improved after one session, 33 improved after two sessions, 24 improved after three sessions, 21 improved after four sessions, 16 improved after 5 sessions and17 after 6 sessions (Figure13). Number of patients treated through local area, spinal cord area, brain areas or combinations of them Pain relieved in 35 patients using local areas only, in 77 patients using spinal cord centers, in 44 patients using brain motor and sensory areas and in 78 patients using either 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 combinations of local, spinal cord or brain centers or areas (Table 1). DISCUSSION Mandible microsystem is a micro human anatomy system on which the structures of the body are represented in the same positions as in the human body anatomy. The mandible, as a micro anatomy system, can be used as a micro acupuncture system which has the same physiological functions that can regulate the human body functions through stimulation of their micro organs and structures. This system is unique and new because it treats pain along its pathway by three ways: 1. Stimulating the primary site of pain in the body. 2. Stimulating its representing area on the spinal cord. 3. Stimulating its controlling motor and sensory areas in the brain. Stimulation of any area of the body can affect the superficial and deep structures in this area from the skin on the front of the body to the skin on the back of the same area and correct any functional disorders in them. This system differs from all other microsystems in that the brain and spinal cord are represented anatomically in the same way as in modern medicine. Also, the right and left halves of the brain are represented on both halves of the mandible, so double stimulation of the brain can improve the results of therapy. Also, Figure 9: Spinal cord segments level (Left shoulder centers on spinal cord): (A) Right anterior half of border of mandible, (B) Left anterior half of border of mandible, and (C) Bilateral anterior halves of mandible. Figure 10: Brain motor and sensory centers level (Left shoulder motor and sensory brain centers): (A) Right half of the brain motor and sensory areas on left side of chin, (B) Right half of the brain motor and sensory areas on right side of chin, and (C) Bilateral right halves of brain motor and sensory centers on chin. Figure 11: Graph shows relation between number of sessions and duration of pain. Figure 12: Graph shows relation between patients' groups improved after the first session and their numbers with their improvement percentage. Figure 13: Graph shows relation between number of sessions and number of patients with their percent. SCIRES Literature - Volume 1 Issue Page -024
6 Table 1: Number of patients treated through local areas, spinal cord areas, brain areas or combinations of them. Needle insertion Site One area Local areas Both areas Spinal cord areas one area Both areas Cortical areas (motor & sensory) one area Both areas Different areas No. patients double representation of the body on bilateral halves of the mandible means that we can use two methods of treatment at the same time which increases the chances of cure of most pains and diseases. Throughout the nine years of practice, using this method the results were clear cut immediate or within minutes which make this system of value to be added to other microsystems. CONCLUSION Mandible microsystem is a functional image of the whole body in well-defined localized areas. Representation of the body parts on the mandible is correct and obeys the rules of the normal anatomy of the body. Furthermore, treatment of acute pain in any body area had reproducible effects. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors wish to thank all patients for giving us their written consent for inserting the acupuncture needles in their skin and took photos for needles positions. REFERENCES 1. Starwynn D. Rapid Cancer Pain Relief with Auricular Micro-Macro technique. Acupuncture Today. 2008; Soliman NE, Frank, BL Soliman Frank 3 Phase hand acupuncture. A Journal for Physicians by Physicians. 2005; 17: Zhang Y. ECIWO Biology and Medicine: A New Theory of Conquering Cancer and a Completely New Acupuncture Therapy. China: Neimenggu People s Press; 1987; Wang Y. Micro- Acupuncture in practice. Churchill Livingstone. Elsevier. 2009; Bouevitch, V. Microacupuncture Systems as Fractals of the Human Body. Medical Acupuncture. A Journal for Physicians by Physicians. 2003; 14: Oleson, T. Auriculotherapy Manual Chinese and Western Systems of Ear Acupuncture. 3rd Ed Reprent Dale R. The Micro Acupuncture Systems, Part I & II. Am J Acupuncture. 1976: 4: Oleson, T. Auriculotherapy Manual, Chinese and Western Systems of Ear Acupuncture. 3rd Ed Akerele D. WHO and the Development of Acupuncture Nomenclature, Overcoming a Tower of Babel. Am J Chinese Med. 1991; 1: goo.gl/72ilor 10. WHO: A Standard International Acupuncture Nomenclature: Memorandum from a WHO meeting. WHO Bulletin. 1990; 68: CZHpd3 11. Wexo M. The Ear Gateway to Balancing the Body: A Modern Guide to Ear Acupuncture. New York: ASI Publishers; Essentials of Chinese Acupuncture: Ear Acupuncture Therapy. 1st Ed Chen K, Cui Y. Handbook to Chinese Auricular Therapy. 1st Ed. Beijing, China: Foreign Languages Press; Acupuncture, A comprehensive Text: Ear Acupuncture. 5th Ed. pp , Rubach A. Principles of Ear Acupuncture. Microsystem of the Auricle Hugo L O, Hans U. Mandibular Growth Anomalies gl/jrrka6 17. Lewis A. Gray's Anatomy of the Human Body: The Mandible (Lower Jaw). 20th Ed. II. Osteology. 5b. 8. The Mandible (Lower Jaw) gl/ko4tsb 18. Childs J D, Piva S R, Fritz J M. Responsiveness of the Numeric Pain Rating Scale in Patients with Low Back Pain. Spine. 2005; 30: goo.gl/t1j7rd 19. Clemente, D. Clemente s Anatomy Dissector. 2nd Ed. Carmine. 2007; Charles R, et al. The Human Nervous System: Structure and Function. 6th Ed. Springer. 2007; Cochard R. Netter's Atlas of Human Embryology. The Nervous System. Elsevier Health Science Vernon L. Spinal Cord Medicine: Principles & Practice. Demos Medical Publishing, 2nd Ed SCIRES Literature - Volume 1 Issue Page -025
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele
 OpenStax-CNX module: m47807 1 Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m47807 1 Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract By the end of this section,
Anatomy The study of the body's structure.
 Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
CLASSIC AURICULAR POINTS
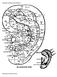 CLASSIC AURICULAR POINTS New Style Auricular Points (1) Anaesthesia forextraction of Teeth 1 At the postero-inferior of the 1st area. (2) Upper Jaw At the postero-inferior part of the 2nd area. (3) Lower
CLASSIC AURICULAR POINTS New Style Auricular Points (1) Anaesthesia forextraction of Teeth 1 At the postero-inferior of the 1st area. (2) Upper Jaw At the postero-inferior part of the 2nd area. (3) Lower
ENCR RECOMMENDATIONS
 E N C R EUROPEAN NETWORK OF CANCER REGISTRIES (ENCR) ENCR RECOMMENDATIONS Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers Members of the Working Group: Dr T. Davies, East Anglian Cancer Registry, Cambridge, UK Mrs M. Page,
E N C R EUROPEAN NETWORK OF CANCER REGISTRIES (ENCR) ENCR RECOMMENDATIONS Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers Members of the Working Group: Dr T. Davies, East Anglian Cancer Registry, Cambridge, UK Mrs M. Page,
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS
 BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology. ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations
 Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations Anthropology & Archaeology Anthropology is the study of the biological and cultural aspects of all humans in all places
Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations Anthropology & Archaeology Anthropology is the study of the biological and cultural aspects of all humans in all places
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives
 Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
 CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
Body Organizations Flashcards
 1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts Most of the terms used in anatomy and physiology are of either Greek or Latin origin. (In fact, the term anatomy is derived from
Chapter 1 Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts Most of the terms used in anatomy and physiology are of either Greek or Latin origin. (In fact, the term anatomy is derived from
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001)
 Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
SD School Anatomy Program 1: Bones QuikNotes. Student Notes
 QuikNotes The transverse plane runs from right to left and divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) sections. Student Notes The frontal plane lies vertically along the body from head
QuikNotes The transverse plane runs from right to left and divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) sections. Student Notes The frontal plane lies vertically along the body from head
If time is limited, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment.
 EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
NFP Process Centers 95 SWG DCR
 NFP NFP Process Centers 8. ungs, Posterior Back 17. Emotional (R) 18. Mental Body () 6. Heart / Center & eft 7. ungs, Anterior Chest 12. Kidneys / Back 14. Upper Arms 15. Forearms 9. Spleen / eft Side
NFP NFP Process Centers 8. ungs, Posterior Back 17. Emotional (R) 18. Mental Body () 6. Heart / Center & eft 7. ungs, Anterior Chest 12. Kidneys / Back 14. Upper Arms 15. Forearms 9. Spleen / eft Side
The Second Metacarpal Bone Therapy
 The Second Metacarpal Bone Therapy Yuxing Liu Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin Introduction and anatomy History: discovered by Prof. Zhang, Yingqing firstly in 1973. Shandong University, China. ECIWO
The Second Metacarpal Bone Therapy Yuxing Liu Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin Introduction and anatomy History: discovered by Prof. Zhang, Yingqing firstly in 1973. Shandong University, China. ECIWO
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Anatomical Language. Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors Ms. Chase
 Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
Functional Movement Test. Deep Squat
 Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank
 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
TERMINOLOGY AS IT APPLIES TO TICA BREED STANDARDS. Interpretation by Marge Hanna
 TERMINOLOGY AS IT APPLIES TO TICA BREED STANDARDS Interpretation by Marge Hanna 1. Nose: The area, with its underlying cartilage, from the top edge of the nose leather up to the bottom of the bridge of
TERMINOLOGY AS IT APPLIES TO TICA BREED STANDARDS Interpretation by Marge Hanna 1. Nose: The area, with its underlying cartilage, from the top edge of the nose leather up to the bottom of the bridge of
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
POSTERIOR 1. situated behind: situated at or toward the hind part of the body :
 ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1
 1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
Medical Terminology. Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements
 Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
2. Draw or define ANTERIOR/VENTRAL and POSTERIOR/DORSAL. Give an example.
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Anatomical Terminology: Relative Position Go to the following site: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=ap15305 1. Draw or define
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Anatomical Terminology: Relative Position Go to the following site: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=ap15305 1. Draw or define
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Chapter 1: The Human Organism
 Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
3. The Jaw and Related Structures
 Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy. General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position
 #1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
Injuries to the Head and Spine From Bradys Emergency Care 10 th Edition
 Injuries to the Head and Spine From Bradys Emergency Care 10 th Edition 1. When performing the four-rescuer log roll, which responder pulls the board into position? A.) Head B.) Waist C.) Knee D.) Shoulder
Injuries to the Head and Spine From Bradys Emergency Care 10 th Edition 1. When performing the four-rescuer log roll, which responder pulls the board into position? A.) Head B.) Waist C.) Knee D.) Shoulder
https://testbanksolution.net/
 Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME
 TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
Country Health SA Medical Imaging
 Country Health SA Medical Imaging REMOTE OPERATORS POSITIONING GUIDE Contents Image Evaluation Page 4 Positioning Guides Section 1 - THORAX 1.1 Chest Page 5 1.2 Bedside Chest Page 7 1.3 Ribs Page 8 Section
Country Health SA Medical Imaging REMOTE OPERATORS POSITIONING GUIDE Contents Image Evaluation Page 4 Positioning Guides Section 1 - THORAX 1.1 Chest Page 5 1.2 Bedside Chest Page 7 1.3 Ribs Page 8 Section
Important Parts of Bones
 Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
Spinal Column. Anatomy Of The Spine
 Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2. Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University
 1 LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ACROMIAL pertaining to the point of the shoulder Note: this term was also used in Language of Anatomy Part
1 LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ACROMIAL pertaining to the point of the shoulder Note: this term was also used in Language of Anatomy Part
Radiographic Procedures 1
 Western Technical College 10526149 Radiographic Procedures 1 Course Outcome Summary Course Information Textbooks Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 5 Prepares radiography students
Western Technical College 10526149 Radiographic Procedures 1 Course Outcome Summary Course Information Textbooks Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 5 Prepares radiography students
Assignment 2: Human Anatomy
 Assignment 2: Human Anatomy Chapter 2 Quiz: How Much Do You Know About Anatomy? 1. Which of the following is not a feature of the anatomical position: A) The body stands erect. B) The body is facing forward.
Assignment 2: Human Anatomy Chapter 2 Quiz: How Much Do You Know About Anatomy? 1. Which of the following is not a feature of the anatomical position: A) The body stands erect. B) The body is facing forward.
Anatomy and Physiology 2016
 Anatomy and Physiology 2016 O = Temporal line I = coronoid process (Mandible) A = elevates mandible (chewing) O = galea aponeurotica (layer of dense fibrous tissue which covers the upper part of the cranium)
Anatomy and Physiology 2016 O = Temporal line I = coronoid process (Mandible) A = elevates mandible (chewing) O = galea aponeurotica (layer of dense fibrous tissue which covers the upper part of the cranium)
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
human anatomy 2015 lecture four Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
Station 2: Torso Model Practical
 Station 2: Torso Model Practical Label # Organ System Cavity 1 Spinal cord Nervous Spinal or vertebral 2 Liver Digestive Abdominal 3 Large Intestine Digestive Abdominal 4 Small Intestine Digestive Abdominal
Station 2: Torso Model Practical Label # Organ System Cavity 1 Spinal cord Nervous Spinal or vertebral 2 Liver Digestive Abdominal 3 Large Intestine Digestive Abdominal 4 Small Intestine Digestive Abdominal
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions
 Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation
 1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers. Workbook 11 The articular system
 NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 11 The articular system Contents Workbook 11 The articular system 1 11.1 Aim 3 11.2 Learning outcomes 3 11.3 The articular system 4 11.4 Individual
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 11 The articular system Contents Workbook 11 The articular system 1 11.1 Aim 3 11.2 Learning outcomes 3 11.3 The articular system 4 11.4 Individual
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1
 Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual
 Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory
 CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 10 Channel Diagnosis - 8 Principles Channels & Collaterals of the Bladder Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P.,
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 10 Channel Diagnosis - 8 Principles Channels & Collaterals of the Bladder Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P.,
Clinical Anatomy, Embryology and Imaging BMS 6115C. Summer Semester 2009 Lynn J. Romrell, Ph.D. Course Director. Course Schedule
 Anatomy, Embryology and Imaging BMS 6115C Summer Semester 2009 Lynn J. Romrell, Ph.D. Course Director Course Schedule Color codes for course activities: Anatomy Sessions Anatomic Radiology Sessions Embryology
Anatomy, Embryology and Imaging BMS 6115C Summer Semester 2009 Lynn J. Romrell, Ph.D. Course Director Course Schedule Color codes for course activities: Anatomy Sessions Anatomic Radiology Sessions Embryology
1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body
 1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body Midclavicular line: Imaginary line at center of clavicle (collar
1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body Midclavicular line: Imaginary line at center of clavicle (collar
PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY
 PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy Lecture #19 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE THORAX April 3, 2012
 Page 1 بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم The Thoracic Wall Firstly, when we talk about thorax, we should begin with the thorax wall which means not only bones that construct the thorax but also the muscles which
Page 1 بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم The Thoracic Wall Firstly, when we talk about thorax, we should begin with the thorax wall which means not only bones that construct the thorax but also the muscles which
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomy 25 KEY ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Guthrie
 THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
LAB Notes#1. Ahmad Ar'ar. Eslam
 LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
Lab Activity 11: Group I
 Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory
 CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 12 Channels & Collaterals of the Gallbladder Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P., Al-Khafaji, M., & Baker, K. (2007).
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 12 Channels & Collaterals of the Gallbladder Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P., Al-Khafaji, M., & Baker, K. (2007).
Bones of Thorax (Rib Cage)
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW
 INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park):
 Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park): (Lower Extremity): patient is fully gowned / no artifacts / properly shielded (exposure for femur and below : hold still, don t move ) (exposure
Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park): (Lower Extremity): patient is fully gowned / no artifacts / properly shielded (exposure for femur and below : hold still, don t move ) (exposure
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018
 Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
Introduction to Human Anatomy. Prepared by:- Mohammad Zmaili
 Introduction to Human Anatomy 1 Prepared by:- Mohammad Zmaili Definitions Anatomy: the science of the structure and shape of living organisms and their parts. Physiology: the science that deals with the
Introduction to Human Anatomy 1 Prepared by:- Mohammad Zmaili Definitions Anatomy: the science of the structure and shape of living organisms and their parts. Physiology: the science that deals with the
Skeletal System. It s all about the bones!!!
 Skeletal System It s all about the bones!!! The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkv cg&list=plzile25upgebvru0jneppcabh0fhktgt Q 1. FYI 5
Skeletal System It s all about the bones!!! The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkv cg&list=plzile25upgebvru0jneppcabh0fhktgt Q 1. FYI 5
GLOSSARY OF COMMON MEDICAL TERMS
 GLOSSARY OF COMMON MEDICAL TERMS PROCEDURES craniotomy: making a surgical incision through the cranium (the part of the skull that encloses the brain); usually done to relieve pressure around the brain.
GLOSSARY OF COMMON MEDICAL TERMS PROCEDURES craniotomy: making a surgical incision through the cranium (the part of the skull that encloses the brain); usually done to relieve pressure around the brain.
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Chapter 7 /8 pgs SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
The Muscular System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet
 1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
The Muscular System Part A
 10 The Muscular System Part A Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Organization of the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 10.1 Describe the general function of the body s axial and
10 The Muscular System Part A Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Organization of the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 10.1 Describe the general function of the body s axial and
