Collapse, Crowding, Consolidation, and Contrast: Imaging Findings of Atelectasis on Computed Tomography
|
|
|
- Barry Clark
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Collapse, Crowding, Consolidation, and Contrast: Imaging Findings of Atelectasis on Computed Tomography Garrana SH 1,2, Desouches SL 1,2, Rosado-de-Christenson ML 1,2, Henry TS 3, Kunin JR 1,2, Walker CM 1,2 1 Saint Luke s Hospital of Kansas City 2 University of Missouri, Kansas City 3 University of California, San Francisco
2 Disclosures Garrana SH No relevant disclosures Desouches SL No relevant disclosures Rosado-de-Christenson ML- Author for American Registry of Pathology, Amirsys, Thieme Medical Publishers, Oxford University Press Henry TS No relevant disclosures Kunin JR No relevant disclosures Walker CM Royalties for Amirsys and Elsevier
3 Goals and Objectives Define atelectasis Describe direct and indirect findings of atelectasis on computed tomography (CT) List different types of atelectasis Illustrate pathology which may be obscured by atelectatic lung Identify common and uncommon mimics of atelectasis on CT
4 Atelectasis and Signs of Volume Loss Atelectasis = Collapse of all or part of the lung Direct Signs Fissure displacement Bronchovascular crowding Indirect Signs Increased lung opacity Ipsilateral mediastinal shift Compensatory hyperinflation Hilar displacement Elevation of the ipsilateral hemidiaphragm
5 Direct Signs of Atelectasis Contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) shows left lower lobe atelectasis due to endobronchial mucus plugging, with fissure displacement (white arrow) and bronchovascular crowding, direct signs of volume loss. 3-month follow-up CT shows re-expansion of previously atelectatic left lower lobe and a normal position of the left major fissure (black arrow).
6 Indirect Signs of Atelectasis * * Axial and coronal CECT show indirect signs of right upper and middle lobe atelectasis, including increased lung opacity (white arrows), ipsilateral mediastinal shift, hemidiaphragm elevation, hyperinflation of adjacent lung (*), and hilar displacement. Note juxtaphrenic peak (black arrow) on the coronal CT from fat being drawn into an inferior accessory fissure.
7 Types of Atelectasis Resorption / Obstructive Relaxation / Compressive or Passive Gravity dependent Adhesive Rounded Cicatricial
8 Resorption / Obstructive Atelectasis Resorption of air distal to airway obstruction Endobronchial lesion (mucus, neoplasm, foreign body, stenosis/fibrosis) Extrinsic compression (neoplasm, lymphadenopathy, infection/inflammation) Alveolar air resorbed by capillary circulation in atelectatic lung, not replaced by inspired air
9 Resorption / Obstructive Atelectasis Acute bronchial obstruction Lobar atelectasis occurs within 24 hours in healthy lungs on room air Lobar atelectasis may occur within an hour in intubated patients on 100% O2 Chronic bronchial obstruction Pneumonitis distal to obstructing lesion, usually lung cancer Drowned Lung Negative intrathoracic pressure causes fluid migration into atelectatic lung with little to no volume loss; may also occur with acute bronchial obstruction Ball-valve obstruction Airway lesions (tumors or polyps) resulting in dynamic airway obstruction Higher pressure gradients required to overcome obstruction Rapid alveolar air resorption and atelectasis
10 Resorption / Obstructive Atelectasis Large airway obstruction Does not always produce atelectasis Collateral ventilation between segments and between lobes that lack a complete fissure may allow an obstructed lobe or segment to remain aerated Small airway obstruction Larger airways remain patent and aerated air bronchograms within atelectatic lung When secretions accumulate, air is replaced by mucus in the bronchi
11 Resorption / Obstructive Atelectasis CECT shows left lower lobe atelectasis due to endobronchial obstruction; note posteriorly displaced major fissure (white arrows) and diffuse lung enhancement. Small tubular and round low attenuation foci within segmental bronchi represent mucus-filled bronchi (black arrow).
12 Relaxation / Compressive Atelectasis Relaxation (passive) atelectasis Lung compression by space occupying process (pleural fluid, pneumothorax) Lung volume reduced to its natural non-aerated state Some authors reserve the term passive atelectasis for when a pneumothorax is the culprit, implying passive loss of alveolar elastic recoil due to loss of negative intrathoracic pressure Compressive atelectasis Often used interchangeably with passive and relaxation atelectasis Reduction in lung volume beyond its natural relaxed state
13 Relaxation Atelectasis * * * CECT shows lower lobe atelectasis (asterisks) due to hemothorax. Hyperattenuation in the dependent pleural space represents blood products (arrows). Note that atelectatic lung always collapses inward toward the hilum. High attenuation in the dependent pleural space is either blood or enhancing tumor, and should not be confused with atelectasis.
14 Compressive Atelectasis * * Axial and coronal CT demonstrate LLL opacities (black asterisks), adjacent to an elevated left hemidiaphragm, consistent with compressive atelectasis. Elevation of the left hemidiaphragm was secondary to phrenic nerve injury with resultant diaphragmatic paralysis.
15 Gravity-Dependent Atelectasis Alveolar collapse in gravity-dependent portions of lung Gravitational forces result in alveolar collapse and subpleural ground-glass opacities or nodularity Changes in patient position (from supine to prone) resolves this abnormality and excludes subpleural fibrosis
16 Gravity-Dependent Atelectasis Dependent atelectasis manifests as linear and ground-glass opacities (arrow) on inspiratory CT (left image). Prone imaging (right image) counters the gravitational effect with resolution of the previously seen posterior opacities, now seen anteriorly in the dependent lung.
17 Adhesive Atelectasis Reduced surface tension results in alveolar collapse Surfactant abnormality (infant respiratory distress syndrome) Acute respiratory distress syndrome Post-operative, especially following CABG Pneumonia, smoke inhalation, thromboembolism, acute radiation pneumonitis
18 Adhesive Atelectasis * * AP chest radiograph and CT show confluent opacities and volume loss of the right lung and left lower lobe consistent with adhesive atelectasis due to infantile respiratory distress syndrome. Left upper lobe lucencies represent pulmonary interstitial emphysema (asterisks).
19 Rounded Atelectasis Folded atelectatic lung with fibrous bands and adhesions to the visceral pleura Most commonly caused by occupational exposure to mineral dusts May follow exudative pleuritis of any etiology Imaging criteria Mass-like or rounded peripheral opacity abutting the pleura Adjacent pleural abnormality including thickening and effusion Comet tail sign vascular convergence into the lesion Volume loss
20 Rounded Atelectasis CECT shows a right lower lobe subpleural nodule (arrow) adjacent to pleural thickening and calcification and bronchovascular structures (curved arrows) producing the comet tail sign. Note posterior displacement of the right major fissure relative to the contralateral side (orange arrow) indicating volume loss. Stability over 10 years and negative PET confirm benign etiology.
21 Cicatricial Atelectasis Reduction in alveolar volume from fibrosis or scarring Localized Typically one or more lobes Reduced lung volumes, scarring and traction bronchiectasis Increased opacity of affected lung, hyperinflation of unaffected lung Common causes: Tuberculosis (typically upper lobes), necrotizing pneumonia, radiation fibrosis (limited to radiation port) Diffuse Reduced lung volumes and reticulation Hyperinflation of unaffected lung Caused by interstitial lung disease
22 Cicatricial Atelectasis Axial and coronal CT demonstrate right upper lobe radiation fibrosis with intrinsic traction bronchiectasis, architectural distortion and fissure displacement (arrow).
23 Mimics and Hidden Pathology Mimics and entities obscured by atelectasis Neoplasm Pneumonia (infectious/aspiration) Inflammation (e.g. vasculitis, granulomatous disease) Infarction Identification of direct and indirect signs of volume loss Most entities are space-occupying lesions Enhancement characteristics on CECT Atelectatic lung enhances more than infectious/inflammatory consolidations, infarctions, and most tumors Intense enhancement of atelectatic lung relates to increased blood flow per unit area of collapsed lung, attributed to bronchovascular crowding
24 Left Upper Lobe Collapse * CECT shows a mass (white arrow) within an atelectatic left upper lobe (asterisk). Proximal extension of the mass into the left mainstem bronchus produces the tip of the iceberg sign (orange arrow), an important clue to the presence of an endobronchial lesion. The atelectatic lung enhances to a greater degree than the tumor. PET demonstrates an FDG-avid mass, proven to represent a primary pulmonary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma on biopsy.
25 Atelectasis + Pneumonia * CECT of a patient with atelectasis and pneumonia shows closely apposed pulmonary vessels in atelectasis that result in homogeneous hyperenhancement (asterisk), in contrast to the hypoenhancing pneumonia (arrows), and the absence of enhancement in necrotizing pneumonia (curved arrows).
26 Atelectasis + Pneumonia CECT (lung window) shows similar appearing lingular and left lower lobe consolidations. Use of soft tissue window settings allows differentiation between the densely enhancing left lower lobe atelectasis and the poorly enhancing lingular pneumonia (curved arrow).
27 Atelectasis + Infarction * * CECT demonstrates a large left lower lobe wedge-shaped infarct (curved arrows) with adjacent combined relaxation and adhesive atelectasis (asterisks). Note the pulmonary embolus within the left lower lobe pulmonary pulmonary artery (arrow).
28 Atelectasis + Infarction * * CECT shows hyperenhancing lower lobe atelectasis (asterisks). Tubular and wedge-shaped low attenuation lesions (arrow) represent mucus filled bronchi and pulmonary infarcts. Left lower lobe cavitary lesion (curved arrow) represents a pulmonary infarct. Necrotizing pneumonia and malignancy would be included in the differential diagnosis for the cavitary lesion.
29 Relaxation Atelectasis + Metastases * * CECT of a patient with renal cell carcinoma shows an enhancing nodule likely along the visceral pleura (arrows) adjacent to an atelectatic right lower lobe (asterisks). Bilateral pleural effusions result in relaxation atelectasis. In contrast to most primary and metastatic pulmonary malignancies, renal cell carcinoma metastases are hypervascular and may enhance more than atelectatic lung.
30 Atelectasis + Endobronchial Neoplasm CECT shows a heterogeneously enhancing partially calcified small cell lung carcinoma (arrow) that completely obliterates the left lower lobe bronchial lumen and produces lobar atelectasis. Although the mass and the atelectatic lung exhibit similar enhancement, the diagnosis of malignancy is made possible by identification of the convex bulge caused by the mass (S sign of Golden).
31 Rounded Atelectasis vs Lung Cancer CECT shows a right lower lobe subpleural mass. Note the absence of the comet tail sign, an important imaging criterion for the diagnosis of rounded atelectasis. In addition, heterogeneous enhancement with central hypoenhancement (arrow) suggests necrosis and favors lung cancer over rounded atelectasis. Biopsy showed non-small cell lung cancer.
32 Rounded Atelectasis vs Lung Cancer CECT shows a left upper lobe rounded opacity that crosses the fissure into the left lower lobe. Left lung volume loss and adjacent pleural thickening might suggest rounded atelectasis, but the lesion does not completely abut the pleural surface, PET was performed showing FDG avidity in the lesion and the adjacent pleura. Biopsy confirmed lung adenocarcinoma.
33 Summary Atelectatic lung produces signs of volume loss including bronchovascular crowding and fissural displacement Assessment of enhancing patterns on CECT is useful for the differentiation of atelectatic lung from other disease processes: Atelectatic lung enhances homogenously, whereas other entities (neoplasm, infection/aspiration, infarct) exhibit heterogeneous or no enhancement Assessment of atelectatic lung on CECT may allow identification of intrinsic abnormalities that may be obscured by surrounding atelectasis. Identification of ancillary findings helps formulate a focused differential diagnosis (e.g., pulmonary artery filling defects, mediastinal lymphadenopathy, traction bronchiectasis, comet tail sign, pleural effusion/thickening, etc.)
34 References Carter BW, Glisson BS, et al. Small cell lung carcinoma: Staging, imaging, and treatment considerations. RadioGraphics. 2014;34(6): Diot Q, Kavanaugh B, et al. Lung deformations and radiation-induced regional lung collapse in patients treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy. Am Assoc Phys Med. 2015;42(11): Edwards RM, Godwin JD, et al. A quantitative approach to distinguish pneumonia from atelectasis using computed tomography attenuation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2016;40(5): Green DB, Raptis CA, et al. Negative computed tomography for acute pulmonary embolism: Important differential considerations for acute dyspnea. Radiol Clin N Am. 2015;53: Hansell DM, Bankier AA, et al. Fleischner society : Glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology. 2008;246(3): Lischalk JW, Malik RM, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for high-risk central pulmonary metasases. Radiation Oncology. 2016:11:28. Minshall CT, Doben AR, et al. Computed tomography pulmonary angiography: More than a screening tool for a pulmonary embolus. Journal of Critical Care. 2015;30: Molina PL, Hiken JN, et al. Imaging evaluation of obstructive atelectasis. J Thorac Imaging. 1996;11(3): Retamal J, Bergamini BC, et al. Non-lobar atelectasis generates inflammation and structural alveolar injury in the surrounding healthy tissue during mechanical ventilation. Critical Care. 2014;18: Shah RM, Friedman AC. CT angiogram sign: Incidence and significance in lobar consolidations evaluation by contrast-enhanced CT. AJR. 1998;170: Walker CM, Abbott GF, et al. Imaging pulmonary infection: Classic signs and patterns. AJR. 2014;202: Yi E, Aubry MC. Pulmonary pseudoneoplasms. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010; 134:
35 Author Contact Information Sherief Garrana, M.D University of Missouri - Kansas City sherief.garrana@gmail.com
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis
 Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
UERMMMC Department of Radiology. Basic Chest Radiology
 UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
An Image Repository for Chest CT
 An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse. Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p
 Title Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse Author(s) Wong, LLS; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p. 513-517 Issued Date 1998 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44672
Title Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse Author(s) Wong, LLS; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p. 513-517 Issued Date 1998 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44672
Signs in Chest Radiology
 Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
Chest X-ray Interpretation
 Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Case of the Day Chest
 Case of the Day Chest Darin White MDCM FRCPC Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic 76 th Annual Scientific Meeting Canadian Association of Radiologists Montreal, QC April 26, 2013 2013 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Case of the Day Chest Darin White MDCM FRCPC Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic 76 th Annual Scientific Meeting Canadian Association of Radiologists Montreal, QC April 26, 2013 2013 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Interesting Cases. Pulmonary
 Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Lung. 10/24/13 Chest X-ray: 2.9 cm mass like density in the inferior lingular segment worrisome for neoplasm. Malignancy cannot be excluded.
 Lung Case Scenario 1 A 54 year white male presents with a recent abnormal CT of the chest. The patient has a history of melanoma, kidney, and prostate cancers. 10/24/13 Chest X-ray: 2.9 cm mass like density
Lung Case Scenario 1 A 54 year white male presents with a recent abnormal CT of the chest. The patient has a history of melanoma, kidney, and prostate cancers. 10/24/13 Chest X-ray: 2.9 cm mass like density
Radiology of the respiratory disease
 Radiology of the respiratory disease [ Color index: Important Notes Extra ] [ Editing file Feedback Share your notes Shared notes ] Resources: - 435 Slides - 434 Team - 435 Notes Done by: - Mai Alageel
Radiology of the respiratory disease [ Color index: Important Notes Extra ] [ Editing file Feedback Share your notes Shared notes ] Resources: - 435 Slides - 434 Team - 435 Notes Done by: - Mai Alageel
A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma
 August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
Chest X rays and Case Studies. No disclosures. Outline 5/31/2018. Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital
 Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chief Complain. For chemotherapy
 Chief Complain For chemotherapy Present Illness 93.12 Progressive weakness of R t arm for 1 year X-ray: peneative lesion over right proximal humorous Bone scan: multiple increased intake Biopsy of distal
Chief Complain For chemotherapy Present Illness 93.12 Progressive weakness of R t arm for 1 year X-ray: peneative lesion over right proximal humorous Bone scan: multiple increased intake Biopsy of distal
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations
 Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays. Objectives. Indications for X-Rays 5/14/2018
 Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Tuberculosis: The Essentials
 Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Bronchial syndrome. Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis
 Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD
 TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
Thoracostomy: An Update on Imaging Features and Current Surgical Practice
 Thoracostomy: An Update on Imaging Features and Current Surgical Practice Robert D. Ambrosini, MD, PhD, Christopher Gange, MD, Katherine Kaproth-Joslin, MD, PhD, Susan Hobbs, MD, PhD Department of Imaging
Thoracostomy: An Update on Imaging Features and Current Surgical Practice Robert D. Ambrosini, MD, PhD, Christopher Gange, MD, Katherine Kaproth-Joslin, MD, PhD, Susan Hobbs, MD, PhD Department of Imaging
4/16/2017. Learning Objectives. Interpretation of the Chest Radiograph. Components. Production of the Radiograph. Density & Appearance
 Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 65-year-old non-smoking woman presented
October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 65-year-old non-smoking woman presented
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus
 Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT
 How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
Diseases of the Lung and Respiratory Tract, Part I. William Bligh-Glover M.D. Department of Anatomy, CWRU
 Diseases of the Lung and Respiratory Tract, Part I William Bligh-Glover M.D. Department of Anatomy, CWRU Educational objectives: Distinguish the types of atelectasis and their etiologies Distinguish the
Diseases of the Lung and Respiratory Tract, Part I William Bligh-Glover M.D. Department of Anatomy, CWRU Educational objectives: Distinguish the types of atelectasis and their etiologies Distinguish the
Imaging of cardio-pulmonary treatment related damage. Radiotheraphy and Lung
 Imaging of cardio-pulmonary treatment related damage Dr. Andrea Borghesi Dr. Emanuele Gavazzi Department of Radiology 2 University of Brescia Radiotheraphy and Lung The goal of radiation therapy (RT) is
Imaging of cardio-pulmonary treatment related damage Dr. Andrea Borghesi Dr. Emanuele Gavazzi Department of Radiology 2 University of Brescia Radiotheraphy and Lung The goal of radiation therapy (RT) is
CT Signs of Solitary Pulmonary Lesions: Revisited
 CT Signs of Solitary Pulmonary Lesions: Revisited Poster No.: C-1764 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Hayashi, K. Ashizawa, Y. Ogihara, A. Nishida, T. Tanaka, 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 2
CT Signs of Solitary Pulmonary Lesions: Revisited Poster No.: C-1764 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Hayashi, K. Ashizawa, Y. Ogihara, A. Nishida, T. Tanaka, 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 2
PULMONARY IMAGING: GETTING THE MOST INFORMATION FROM THORACIC RADIOGRAPHS
 PULMONARY IMAGING: GETTING THE MOST INFORMATION FROM THORACIC RADIOGRAPHS Peter Scrivani, DVM, DACVR Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Ithaca, NY Outline Pulmonary Imaging Pulmonary anatomy
PULMONARY IMAGING: GETTING THE MOST INFORMATION FROM THORACIC RADIOGRAPHS Peter Scrivani, DVM, DACVR Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Ithaca, NY Outline Pulmonary Imaging Pulmonary anatomy
ARDS - a must know. Page 1 of 14
 ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
Acute and Chronic Lung Disease
 KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
Role of CT imaging to evaluate solitary pulmonary nodule with extrapulmonary neoplasms
 Original Research Article Role of CT imaging to evaluate solitary pulmonary nodule with extrapulmonary neoplasms Anand Vachhani 1, Shashvat Modia 1*, Varun Garasia 1, Deepak Bhimani 1, C. Raychaudhuri
Original Research Article Role of CT imaging to evaluate solitary pulmonary nodule with extrapulmonary neoplasms Anand Vachhani 1, Shashvat Modia 1*, Varun Garasia 1, Deepak Bhimani 1, C. Raychaudhuri
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC
 Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
SIR 2008 Annual Meeting Film Panel Case: Radiation-induced Angiosarcoma
 Special Communications SIR 2008 Annual Meeting Film Panel Case: Radiation-induced Angiosarcoma Daniel Y. Sze, MD, PhD, and Judy H. Huang, MD J Vasc Interv Radiol 2008; 19:1133 1137 HISTORY From the Division
Special Communications SIR 2008 Annual Meeting Film Panel Case: Radiation-induced Angiosarcoma Daniel Y. Sze, MD, PhD, and Judy H. Huang, MD J Vasc Interv Radiol 2008; 19:1133 1137 HISTORY From the Division
Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
HRCT in Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease Steps in High Resolution CT Diagnosis. Where are the lymphatics? Anatomic distribution
 Steps in High Resolution CT Diagnosis Pattern of abnormality Distribution of disease Associated findings Clinical history Tomás Franquet MD What is the diagnosis? Hospital de Sant Pau. Barcelona Secondary
Steps in High Resolution CT Diagnosis Pattern of abnormality Distribution of disease Associated findings Clinical history Tomás Franquet MD What is the diagnosis? Hospital de Sant Pau. Barcelona Secondary
Resident Case Review CHEST. Daria Manos CAR 2016
 Resident Case Review CHEST CAR 2016 Daria Manos Disclosure Speakers bureau, Roche CAR 2016 Daria Manos 1. Recognize common and critical chest radiograph and computed tomography signs and use these clues
Resident Case Review CHEST CAR 2016 Daria Manos Disclosure Speakers bureau, Roche CAR 2016 Daria Manos 1. Recognize common and critical chest radiograph and computed tomography signs and use these clues
Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation
 Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Sectional Anatomy Quiz - III
 Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Thoracic CT pattern in lung cancer: correlation of CT and pathologic diagnosis
 19 th Congress of APSR PG of Lung Cancer (ESAP): Update of Lung Cancer Thoracic CT pattern in lung cancer: correlation of CT and pathologic diagnosis Kazuma Kishi, M.D. Department of Respiratory Medicine,
19 th Congress of APSR PG of Lung Cancer (ESAP): Update of Lung Cancer Thoracic CT pattern in lung cancer: correlation of CT and pathologic diagnosis Kazuma Kishi, M.D. Department of Respiratory Medicine,
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping. Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington
 Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Imaging Considerations for the Diagnosis and Management of Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma. Sara Alcorn, HMS-4 Dr. Gillian Lieberman March 2010
 Imaging Considerations for the Diagnosis and Management of Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Sara Alcorn, HMS-4 Dr. Gillian Lieberman March 2010 Overview Presentation of index patient History of present illness
Imaging Considerations for the Diagnosis and Management of Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Sara Alcorn, HMS-4 Dr. Gillian Lieberman March 2010 Overview Presentation of index patient History of present illness
The opaque hemithorax
 The opaque hemithorax Poster No.: C-1480 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Iordache, M. Hanachiuc, C. Moldoveanu, D. Negru; Iasi/RO Keywords: Infection, Atelectasis, elearning, Ultrasound,
The opaque hemithorax Poster No.: C-1480 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Iordache, M. Hanachiuc, C. Moldoveanu, D. Negru; Iasi/RO Keywords: Infection, Atelectasis, elearning, Ultrasound,
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
 A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
When to suspect Wegener Granulomatosis: A radiologic review
 When to suspect Wegener Granulomatosis: A radiologic review Poster No.: P-0038 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Tilve Gómez, R. Díez Bandera, P. Rodríguez Fernández, M. Garcia Vazquez-Noguerol,
When to suspect Wegener Granulomatosis: A radiologic review Poster No.: P-0038 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Tilve Gómez, R. Díez Bandera, P. Rodríguez Fernández, M. Garcia Vazquez-Noguerol,
11/10/2014. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis
 www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN: 2161-2609 Article The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis Xin He, Chuanyu Zhang* Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN: 2161-2609 Article The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis Xin He, Chuanyu Zhang* Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Mimicking DILD:
 Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Mimicking DILD: A Case Report 1 Ju Young Lee, M.D., In Jae Lee, M.D., Dong Gyu Kim, M.D. 2, Soo Kee Min, M.D. 3, Min-Jeong Kim, M.D., Sung Il Hwang, M.D., Yul Lee, M.D., Sang
Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Mimicking DILD: A Case Report 1 Ju Young Lee, M.D., In Jae Lee, M.D., Dong Gyu Kim, M.D. 2, Soo Kee Min, M.D. 3, Min-Jeong Kim, M.D., Sung Il Hwang, M.D., Yul Lee, M.D., Sang
Isolated anthracosis: benign but neglected cause of bronchial stenosis and obstruction
 Isolated anthracosis: benign but neglected cause of bronchial stenosis and obstruction Poster No.: C-0143 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Kahkouee, R. Pourghorban, M. Bitarafan,
Isolated anthracosis: benign but neglected cause of bronchial stenosis and obstruction Poster No.: C-0143 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Kahkouee, R. Pourghorban, M. Bitarafan,
Use of Integrated PET CT in the Clinical Staging of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer
 November 2010 Use of Integrated PET CT in the Clinical Staging of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Laura Myers, Harvard Medical School, Year III Clinical Presentation 79yo woman with cough productive of green
November 2010 Use of Integrated PET CT in the Clinical Staging of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Laura Myers, Harvard Medical School, Year III Clinical Presentation 79yo woman with cough productive of green
Common Blind Spots on Chest CT: Where Are They All Hiding? Part 1 Airways, Lungs, and Pleura
 Residents Section Structured Review Wu et al. Common lind Spots on Chest CT Residents Section Structured Review Carol C. Wu 1 Leila Khorashadi 2 Gerald F. bbott 1 Matthew D. Gilman 1 Wu CC, Khorashadi
Residents Section Structured Review Wu et al. Common lind Spots on Chest CT Residents Section Structured Review Carol C. Wu 1 Leila Khorashadi 2 Gerald F. bbott 1 Matthew D. Gilman 1 Wu CC, Khorashadi
Respiratory Interactive Session. Elaine Borg
 Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA
 Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases. Punnarerk Thongcharoen
 Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH. Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch
 ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch AUTHOR HAS NOTHING TO DECLARE LEARNING OBJETIVES Understand the pathophysiology
ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch AUTHOR HAS NOTHING TO DECLARE LEARNING OBJETIVES Understand the pathophysiology
Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach
 Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach Travis S Henry, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology Cardiac and Pulmonary Imaging Section University of California, San Francisco Large Middle Small 1 Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach Travis S Henry, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology Cardiac and Pulmonary Imaging Section University of California, San Francisco Large Middle Small 1 Bronchiectasis
CT findings of high-attenuation pulmonary abnormalities
 Insights Imaging (2010) 1:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s13244-010-0039-2 PICTORIAL REVIEW CT findings of high-attenuation pulmonary abnormalities Naim Ceylan & Selen Bayraktaroglu & Recep Savaş & Hudaver Alper
Insights Imaging (2010) 1:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s13244-010-0039-2 PICTORIAL REVIEW CT findings of high-attenuation pulmonary abnormalities Naim Ceylan & Selen Bayraktaroglu & Recep Savaş & Hudaver Alper
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP
 Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia. Nitra and the Gangs.
 Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT
 Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Low-dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines for Pulmonary Nodules Management Version 2
 Low-dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines for Pulmonary Nodules Management Version 2 The Committee for Management of CT-screening-detected Pulmonary Nodules 2009-2011 The Japanese Society of CT Screening
Low-dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines for Pulmonary Nodules Management Version 2 The Committee for Management of CT-screening-detected Pulmonary Nodules 2009-2011 The Japanese Society of CT Screening
8/14/2017. Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features
 What is that lung disease? Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Dr. Russell Tucker, DACVR Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features Improved
What is that lung disease? Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Dr. Russell Tucker, DACVR Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features Improved
Lecture 3. Inflammatory Processes
 Lecture 3 Inflammatory Processes Process: Increased vascular permeability Water and cellular infiltrations Results: Abscess, ulceration, cavitation Penetration, perforation and fistula formation Scarring,
Lecture 3 Inflammatory Processes Process: Increased vascular permeability Water and cellular infiltrations Results: Abscess, ulceration, cavitation Penetration, perforation and fistula formation Scarring,
Collaborative Stage. Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG
 Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus
 Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress
 A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order. Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital
 Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY
 (YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
(YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
A pictorial review of thoracic imaging of intensive care patients
 A pictorial review of thoracic imaging of intensive care patients Poster No.: C-1003 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: E. Y. P. Lee, H. C. Mathias; Cardiff/UK Keywords:
A pictorial review of thoracic imaging of intensive care patients Poster No.: C-1003 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: E. Y. P. Lee, H. C. Mathias; Cardiff/UK Keywords:
Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D.
 Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D. Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea
Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D. Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea
Financial disclosure COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT. High Res Chest HRCT. HRCT Pre test. I have no financial relationships to disclose. Anatomy Nomenclature
 Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis?
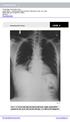 1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University
 objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
Spectrum of Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Proliferation: Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia, Tumorlet, and Carcinoids
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Koo et al. Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Proliferation Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Chi Wan Koo 1 Jeffrey P. Baliff 2 Drew A. Torigian 3 Leslie A. Litzky
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Koo et al. Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Proliferation Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Chi Wan Koo 1 Jeffrey P. Baliff 2 Drew A. Torigian 3 Leslie A. Litzky
Evaluation of the chest Part II.
 Evaluation of the chest Part II. Nagy Endre SZEGEDI TUDOMÁNYEGYETEM ÁOK, RADIOLÓGIAI KLINIKA, SZEGED ANATOMY parenchyma: alveoloacinar system, pulmonary arteries and veins interstitium: connective tissues
Evaluation of the chest Part II. Nagy Endre SZEGEDI TUDOMÁNYEGYETEM ÁOK, RADIOLÓGIAI KLINIKA, SZEGED ANATOMY parenchyma: alveoloacinar system, pulmonary arteries and veins interstitium: connective tissues
Collecting Cancer Data: Lung
 Collecting Cancer Data: Lung NAACCR 2011 2012 Webinar Series 2/2/2012 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this
Collecting Cancer Data: Lung NAACCR 2011 2012 Webinar Series 2/2/2012 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this
Lung Allograft Dysfunction
 Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul. Epidemiology. Risk factors/aetiology
 Slide 1 Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul Department of Thoracic Oncology Papworth Hospital Slide 2 Epidemiology Second most common cancer in the UK (after breast). 38 000 new
Slide 1 Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul Department of Thoracic Oncology Papworth Hospital Slide 2 Epidemiology Second most common cancer in the UK (after breast). 38 000 new
Thoracic sarcoidosis: Pictoral review of typical and atypical findings
 Thoracic sarcoidosis: Pictoral review of typical and atypical findings Poster No.: C-0804 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: A. Ferreira, J. Calha; Lisbon/PT Keywords: Sarcoidosis,
Thoracic sarcoidosis: Pictoral review of typical and atypical findings Poster No.: C-0804 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: A. Ferreira, J. Calha; Lisbon/PT Keywords: Sarcoidosis,
Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP May 4, 2018 Essential Skills for the TB Nurse Case Manager Little Rock, AR May 3 4, 2017 Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP has the following
Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP May 4, 2018 Essential Skills for the TB Nurse Case Manager Little Rock, AR May 3 4, 2017 Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP has the following
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
NONE OVERVIEW FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF (UIP) FOR PATHOLOGISTS. IPF = Idiopathic UIP Radiologic UIP Path UIP
 UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
Elderly Man with Dyspnoea
 Asia Pacific Family Medicine, 2004; 3 (1-2): 46-50 RADIOLOGY SERIES Elderly Man with Dyspnoea Wei-Yang LIM Faculty of Medicine National University of Singapore, Singapore Wilfred CG PEH Singapore Health
Asia Pacific Family Medicine, 2004; 3 (1-2): 46-50 RADIOLOGY SERIES Elderly Man with Dyspnoea Wei-Yang LIM Faculty of Medicine National University of Singapore, Singapore Wilfred CG PEH Singapore Health
I9 COMPLETION INSTRUCTIONS
 The I9 Form is completed for each screening exam at T0, T1, and T2. At T0 (baseline), the I9 documents comparison review of the baseline screen (C2 Form) with any historical images available. At T1 and
The I9 Form is completed for each screening exam at T0, T1, and T2. At T0 (baseline), the I9 documents comparison review of the baseline screen (C2 Form) with any historical images available. At T1 and
CT appearance of radiation injury of the lung after stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for lung cancers: a pictorial review
 CT appearance of radiation injury of the lung after stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for lung cancers: a pictorial review Award: Certificate of Merit Poster No.: C-210 Congress: ECR 2009 Type:
CT appearance of radiation injury of the lung after stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for lung cancers: a pictorial review Award: Certificate of Merit Poster No.: C-210 Congress: ECR 2009 Type:
Introduction to Chest Radiography
 Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
RSV infection and lung ultrasound
 RSV infection and lung ultrasound Neonatology Clinic, University Hospital, Krakow Joanna Hurkała Joanna Pietras Agnieszka Ochoda-Mazur Poznań, 28.09.2018 1 Disclosure In relations to this presentation,
RSV infection and lung ultrasound Neonatology Clinic, University Hospital, Krakow Joanna Hurkała Joanna Pietras Agnieszka Ochoda-Mazur Poznań, 28.09.2018 1 Disclosure In relations to this presentation,
Signs in Thoracic Radiology : Role of radiographic signs in the present era
 Signs in Thoracic Radiology : Role of radiographic signs in the present era Poster No.: C-3278 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: A. Mahajan; Mumbai/IN Keywords: CHEST XRAY,
Signs in Thoracic Radiology : Role of radiographic signs in the present era Poster No.: C-3278 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: A. Mahajan; Mumbai/IN Keywords: CHEST XRAY,
Radiology Pathology Conference
 Radiology Pathology Conference Sharlin Johnykutty,, MD, Cytopathology Fellow Sara Majewski, MD, Radiology Resident Friday, August 28, 2009 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights
Radiology Pathology Conference Sharlin Johnykutty,, MD, Cytopathology Fellow Sara Majewski, MD, Radiology Resident Friday, August 28, 2009 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights
Web Chapter 3. Image Gallery: Lesion detection on low dose chest CT
 Web Chapter 3 Image Gallery: Lesion detection on low dose chest CT Sarabjeet Singh, MD Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD *Eugene J. Mark, MD *James Stone, MD James H. Thrall, MD Department of Radiology and *Department
Web Chapter 3 Image Gallery: Lesion detection on low dose chest CT Sarabjeet Singh, MD Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD *Eugene J. Mark, MD *James Stone, MD James H. Thrall, MD Department of Radiology and *Department
Bronchial carcinosarcoma
 Bronchial carcinosarcoma Carolina Carcano 1*, Edward Savage 2, Maria Julia Diacovo 3, Jacobo Kirsch 1 1. Division of Radiology, Cleveland Clinic Florida, Weston, Fl, USA 2. Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular
Bronchial carcinosarcoma Carolina Carcano 1*, Edward Savage 2, Maria Julia Diacovo 3, Jacobo Kirsch 1 1. Division of Radiology, Cleveland Clinic Florida, Weston, Fl, USA 2. Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular
Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia.
 Supplementary 1 Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia. Imaging finding Definition Implication CR Consolidation Interstitial
Supplementary 1 Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia. Imaging finding Definition Implication CR Consolidation Interstitial
Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes
 CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
