REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE OIE FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE AND OTHER EPIZOOTICS COMMISSION Rio de Janeiro (Brazil), November 2002
|
|
|
- Andrew Garrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 71 SG/12/CS3 C Original: English November 2002 REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE OIE FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE AND OTHER EPIZOOTICS COMMISSION Rio de Janeiro (Brazil), November 2002 A meeting of the OIE Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) and Other Epizootics Commission was held at the headquarters of the Centro Panamericano de Fiebre Aftosa (Panaftosa; Pan American Foot and Mouth Disease Centre) in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil from 25 to 29 November The Agenda and List of Participants are given at Appendices I and II, respectively. The Director General of the OIE, Dr Bernard Vallat, welcomed the participants. In his address, Dr Vallat detailed changes to the organisational structure of the OIE, and introduced the invited observers. The President of the Commission, Dr Gavin Thomson, who chaired the meeting, welcomed the Members and Observers. 1. Foot and mouth disease situation in 2002 The global FMD situation between 1 January and 31 October 2002 was outlined by Dr Keith Sumption on behalf of Dr David Paton of the World Reference Laboratory for FMD. Regional reviews were provided for the Europe by Dr Sumption, for the South-East Asia FMD Campaign by Dr John Edwards (OIE Coordinator) and for South American by Dr Eduardo Correa Mello on behalf of Panaftosa. The following is a summary of these reports, which are given at Appendix III. In the western region of Asia, a new group of emerging strains stemming from the Pan Asia lineage have been reported from the Gulf States. Dendograms showing the spread and relationships between the isolates were presented. In South-East Asia, the Philippines recently extended its FMD-free zone; disease in the Philippines is concentrated on the main island and is presently under control. There is considerable involvement of the stakeholders in the development of this project. Indonesia has been free of FMD since Parts of Malaysia are already FMD-free, and the country will soon declare FMD freedom for the southern part of the country. Vietnam and neighbouring countries are endemically infected with FMD, but there is a peninsular campaign to eradicate the disease. The Malaysia Thailand Myanmar Peninsular Campaign for FMD Freedom is based on a strong regionalisation strategy. Countries in this region are still developing and, as in many other developing countries, animal movement is a serious problem. The situation in the Americas is more stable than in previous years. However, a recent occurrence of type O in Paraguay has been reported. The biomolecular classification of this virus was discussed. Office international des épizooties 12, rue de Prony Paris France Tel.: 33 (0) Fax: 33 (0) oie@oie.int
2 2. Evaluation of country submissions for freedom from foot and mouth disease and rinderpest a) Foot and mouth disease Botswana (free-zone without vaccination, recovery of status) The Commission considered an application from Botswana for the recovery of its FMD-free zone without vaccination. After examining the dossier, the Commission concluded that the application met the requirements of Article of the OIE International Animal Health Code and approved the proposal. Rep. of Korea (free country without vaccination, recovery of status) The Commission considered an application from the Republic of Korea for the recovery of its status of an FMD free country without vaccination. After examining the dossier, the Commission concluded that the requirements of Article of the Code have been met and approved the application. Brazil (free-zone with vaccination, recovery of status and application for new zone) b) Rinderpest The Commission considered the data presented by a delegation from Brazil for the recovery of its FMD-free zone with vaccination. After examining the dossier, the Commission concluded that the requirements of Article of the Code have been met and while approving the application made some additional recommendations (the zone covered by the States of Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul). With regard to the application from Brazil for incorporation of the State of Rondonia into the FMD-free zone with vaccination, the Commission concluded that the aforementioned State had met the requirements of Article of the Code, and will recommend its inclusion in the FMD-free zone with vaccination to the International Committee in May Malawi (freedom from rinderpest infection) The Commission considered an application from Malawi for recognition of freedom from rinderpest infection. The Commission will recommend to the International Committee in May 2003 that Malawi be approved as a country free of rinderpest infection under the provisions of Appendix para 3c of the Code. Turkey (freedom from rinderpest disease) The Commission considered an application from Turkey for recognition of freedom from rinderpest disease. The Commission will recommend to the International Committee in May 2003 that Turkey be approved as a country free of rinderpest disease under the provisions of Appendix para 3b of the Code. The Commission was unable to recommend an application from another Member Country for recognition of a rinderpest disease free zone because insufficient information was supplied for the moment. 3. Surveillance guidelines for foot and mouth disease The Commission considered an updated draft of the proposed guidelines on surveillance standards for countries or zones applying for freedom from FMD, either with or without vaccination, and for cases where a country or zone wishes to apply for recovery of its former free status following an outbreak. The draft was again modified to comply with proposed modifications to the Code chapter on FMD to be recommended to the International Committee by the Code Commission in May In addition, a more 2 FMD/November 2002
3 detailed outline was included on the use of serological tests, including those for non-structural proteins, for applications from countries for freedom from FMD as well as reapplications for free countries or zones. The document that was provided to the Code Commission is given at Appendix IV. This will be modified, where necessary, by the Code Commission to ensure harmonisation of style and terminology between the Code chapter on FMD and the surveillance guidelines. 4. Electronic consultation In view of the comments received from various Member Countries at the General Session in May 2002 on the Code chapter on FMD and the proposed guidelines on FMD surveillance (see Item 3 above), the FMD Commission recommended, following its meeting in July 2002, that the Director General create an electronic forum in order to obtain views from the relevant experts on these issues. Comments received through this electronic consultation were considered at the joint meeting with the Code Commission when the revision of the Code chapter on FMD and the proposed surveillance guidelines were discussed. 5. Zoning in response to emergency situations The Commission considered the situation where a Member Country needs to use zoning in an emergency to guarantee its trade from unaffected regions of the country. In discussion with the Code Commission, it was agreed that no change to the Code chapter on FMD would be required to accommodate this approach. However, a new mechanism needs to be developed whereby official approval can be obtained for such free zones without systematic presentation of the case to the International Committee. A Draft Resolution has been prepared for presentation to the International Committee in May 2003 (see Appendix V). 6. Bovine spongiform encephalopathy The report of the Ad hoc Group on evaluation of submissions for recognition of Member Countries complying with the provisions of the Code for freedom from bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) was considered. In this report, the Ad hoc Group indicated that it would need to meet again to finalise the report to be presented to the FMD Commission on the six Member Country submissions received so far. The reason for this is that the Group requires further information from the countries concerned. The document provided by the Ad hoc Group is not yet appended to this report to preserve confidentiality. The Ad hoc Group recommended that, when evaluating the compliance of Member Countries applying for freedom from BSE, other transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) should be considered (the current guidelines indicate that they should not be considered as there is no scientific evidence linking BSE with other TSEs). While the FMD Commission accepts this recommendation, it would ask the Ad hoc Group to indicate on what basis other TSEs should be considered and what importance to accord their presence. In reviewing the excellent work of the Ad hoc Group, the Commission noted potential discrepancies in the application of standards between the FMD Commission itself, when reviewing requests for freedom from other diseases, and the Ad hoc Group, when reviewing requests for freedom from BSE. For this reason it is recommended that a Member of the FMD Commission should participate at meetings of the Ad hoc Group when Member Country applications for recognition of freedom from BSE are being considered. The same should apply when new Ad hoc Group are created to evaluate country s status with respect to other diseases. 7. Report of the Ad hoc Group on Carcass Disposal The Commission reviewed the draft report of the meeting of the Ad hoc Group on Carcass Disposal. While acknowledging its valuable input, the Commission considers that the Ad hoc Group, possibly with additional members, should meet again and develop a document that provides references covering both general considerations as well as details on the various processes available. 8. Joint meeting with the OIE International Animal Health Code Commission The report on this meeting is included in the report of the Code Commission. FMD/November
4 9. Terms of Reference for the Foot and Mouth Disease and Other Epizootics Commission The Commission accepted the proposed new Terms of Reference for the FMD Commission (to be renamed the OIE Scientific Commission if International Committee agrees). The Terms of Reference are given at Appendix VI. 10. Other matters a) Development of guidelines for interpretation and use of genetic, antigenic and biological characterisation of FMD virus isolates The Commission recommends that a, Ad hoc Group in relation with the FMD Commission be formed, including representatives from the OIE Reference Laboratories for FMD and recognised experts, to prepare a basic document on the interpretation and use of genetic, antigenic and biological characterisation of FMD isolates. Furthermore, the subgroup should develop a framework for establishing a system for global information sharing among FMD laboratories. The reason for this proposal is that genetic comparison of FMDV isolates has become a rapid and frequently used means of assisting in the epidemiological understanding of the relationships between FMD outbreaks. There is great potential for the use of this and other methods to facilitate better international control of the disease. Other benefits this approach will provide include: 1. Genetic comparisons that provide supportive evidence in the investigation of putative links between outbreaks and that assist in the development of explanations for persistence and transmission of infection between and within countries. 2. Interpretation of genetic comparisons considering the multiple factors relating to rates of genetic change, the level of change in amino acid sequence, the potential for antigenic change and the availability for comparison of virus sequences from countries or regions of relevance. 3. Selection of appropriate vaccine strains for use in control. 4. Other forms of characterisation that may be necessary to inform a risk assessment of the transmission potential of FMD strain viruses. b) Document on proposed changes to the Code chapter on FMD on behalf of countries of the River Plate Basin Project (Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay) The Commission reviewed a proposal submitted by Dr R. Casas on behalf of the countries of the River Plate Basin Project (Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay). Two points of the proposal were supported by the Commission. c) Letter from Thailand on freedom from rinderpest infection The Commission acknowledged receipt of a letter from the Chief Veterinary Officer of Thailand, requesting consideration of Thailand s freedom from rinderpest infection. As Thailand was declared free from rinderpest disease in May 2002, if all other requirements remain favourable, the country will, in accordance with the provisions of the OIE Pathway, be entitled to apply for recognition of freedom from rinderpest infection after May d) Avian influenza report from Chile The Commission reviewed the OIE expert report on the control of the avian influenza epizootic in Chile. It acknowledges the efforts of the OIE experts and the Chilean authorities for the successful and prompt elimination of the disease. e) Bluetongue meeting (provisional agenda) The Commission was informed of the final arrangements for the III International Symposium on Bluetongue to be held in Italy, in October 2003, under the sponsorship of OIE. 4 FMD/November 2002
5 f) Scientific presentation for the General Session in May 2003 The Commission supported the proposal to seek an expert from an OIE Reference Laboratory to make a presentation on mild and highly pathogenic strains of avian influenza at the OIE General Session in May g) Control of diseases by vaccination: Conference in 2004 The Commission supported the proposal to hold an OIE international conference on the use of vaccination for control of FMD and other transboundary diseases in h) Work programme for the period from July 2002 to May 2003 The Work programme for the FMD Commission for the period from July 2002 to May 2003 is given at Appendix VII. i) Date of the next meeting of the FMD and Other Epizootics Commission The next meeting of the FMD Commission will be held from 12 to 14 February 2003 in Paris. /Appendices FMD/November
6
7 Appendix I MEETING OF THE OIE FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE AND OTHER EPIZOOTICS COMMISSION Rio de Janeiro (Brazil), November 2002 Agenda 1. Foot and mouth disease situation in Evaluation of country submissions for freedom from foot and mouth disease and rinderpest 3. Surveillance guidelines for foot and mouth disease 4. Electronic consultation 5. Zoning in response to emergency situations 6. Bovine spongiform encephalopathy 7. Report of the Ad hoc Group on Carcass Disposal 8. Joint meeting with the OIE International Animal Health Code Commission 9. Terms of Reference of the Foot and Mouth Disease and Other Epizootics Commission 10. Other matters FMD/November
8
9 Appendix II MEETING OF THE OIE FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE AND OTHER EPIZOOTICS COMMISSION Rio de Janeiro (Brazil), November 2002 List of Participants MEMBERS Dr Gavin R. Thomson (President) AU-IBAR African Unity Interafrican Bureau for Animal Resources P.O. Box Nairobi KENYA Tel: (254-2) Fax: (254-2) Prof. Vincenzo Caporale (Vice-President) Director Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale dell Abruzzo e del Molise G. Caporale Via Campo Boario Teramo ITALY Tel: ( ) Fax: ( ) caporale@izs.it Dr Eduardo Correa Melo (Secretary General) Director, Foot and Mouth Disease Coordinator Centro Panamericano de Fiebre Aftosa Caixa Postal Rio de Janeiro BRAZIL Tel: (55-21) Fax: (55-21) ecorrea@panaftosa.ops-oms.org OTHER PARTICIPANTS Dr Richard Paul Kitching Director National Centre for Foreign Animal Disease 1015 Arlington Street Winnipeg, Manitoba R3E 3M4 CANADA Tel: (1-204) Fax: (1-204) kitchingp@inspection.gc.ca Dr Keith Sumption Secretary of the European Commission for the Control of Foot and Mouth Disease FAO Via delle Terme di Caracalla Rome ITALY Tel: (39) Fax: (39) keith.sumption@fao.org Dr John Edwards Regional Coordinator OIE SEAFMD Regional Co-ordination Unit c/o Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Kasetsart University Chatuchak, Bangkok, THAILAND Fax: Tel: oiercu@loxinfo.co.th Dr Raúl Casas Olascoaga Av. del Libertador Gral. Juan Lavalleja 2074 Apto. 804 Montevideo CP URUGUAY Tel: (05982) / 6316 Fax: (05982) raulco@adinet.com.uy Dr Victor E. Saraiva-Vieira Centro Panamericano de Fiebre/OPS-OMS Foot and Mouth Disease Center/PAHO-WHO Av. Presidente Kennedy 7778 Sao Bento Duque de Caxias Rio de Janeiro BRAZIL Tel: (55 21) Fax: (55-21) vsaraiva@panaftosa.ops-oms.org OIE CENTRAL BUREAU Dr Bernard Vallat Director General 12 rue de Prony Paris FRANCE Tel: 33 - (0) Fax: 33 - (0) oie@oie.int Dr Alejandro Schudel Head, Scientific and Technical Department a.schudel@oie.int FMD/November
10
11 Appendix III GLOBAL FMD SITUATION DURING 2002 D.J. Paton, N.P. Ferris and N.J. Knowles FAO/OIE World Reference Laboratory for FMD Institute for Animal Health, Ash Road, Pirbright, Woking, Surrey GU24 ONF, United Kingdom The cumulative data for samples submitted to the OIE/FAO World reference Laboratory for FMD during the first nine months of 2002 is shown in Table 1. FMD remains endemic in many parts of Asia, Africa and South America. A series of maps show the known and presumed distribution of FMD globally in 2001 and The known distribution is an under-representation of the true situation, being based on official reports to OIE (including updates from the monthly reports of the OIE SEAFMD Regional Co-ordination Unit), OIE records, and on the basis of samples received at the FAO/OIE World Reference Laboratory for FMD. Middle East In Turkey, there is a large programme of vaccination, particularly concentrated on Thrace and using vaccines combining serotypes A, O and Asia 1. There have been no FMD outbreaks in Thrace since June 2001, but serotypes O, A and Asia 1 have been isolated in other regions. In 2002, the WRLFMD received type O viruses from Saudi Arabia, Turkey and Iran, type A isolates from Turkey, Iraq and Iran, and an Asia 1 virus from Iran. In 2002 the WRLFMD received serotype O viruses from outbreaks in Lebanon and the Palestinian Autonomous Territories. Asia In May and June 2002, 16 outbreaks of FMD virus serotype O occurred in pigs in South Korea. In July 2002, 21 outbreaks of FMD virus serotype O occurred in Western Mongolia, affecting cattle, sheep and goats. Samples were received at the WRLFMD from S Korea, but not from Mongolia. Additionally, the WRLFMD received samples collected in 2002 from the following countries: Bhutan (types O and Asia 1), Hong Kong (type O), Malaysia (types O and A), Pakistan (types O, A and Asia 1), Thailand (type A) and Vietnam (type O). Africa FMD viruses isolated from samples collected in Botswana in February 2002 were serotyped as SAT 2 and a virus from this group was found to be closely related to one obtained from Zimbabwe in 2001 (see Fig 8). The same virus showed a close antigenic relationship (r 1 value) to the Zimbabwe 11/89 vaccine virus. In May 2002, an outbreak of FMD virus was reported in cattle in Zambia (Mbala district), but the serotype is not known. In June and August 2002, SAT 2 viruses were recovered from cattle in different provinces of Zimbabwe. In September 2002, a serotype O virus was received at the WRLFMD from an outbreak affecting cattle in Burkina Faso. Viruses of serotypes SAT 2, A and O were received from Uganda via Ondestepoort. South America The last outbreak of type A FMD reported from Argentina was in January FMD is believed to remain endemic in the north-westerly Andean region. There is a recent report of FMD type O in Paraguay. Serotype O The PanAsia strain continues to predominate, having been isolated during 2001 and 2002 from many countries throughout Asia. However, a new lineage, related to it has evolved, probably in India, and begun to replace it (Hemadri et al., 2002). This strain has also been found in some of the Gulf States (Oman, United Arab Emirates, Bahrain and Saudi Arabia) in 2001 and Bhutan in 2002 (Fig 1). FMD/November
12 Appendix III (contd) New outbreaks in the Republic of Korea were also due to the PanAsia strain, but the viruses appear to be distinct from previous lineages present in that country in 2000 (Fig. 1). Analyses of two South Korean 2000 isolates suggests that there may have been two slightly different PanAsia lineages introduced in that year (Fig. 1), however, further sequencing of South Korean isolates from that epizootic would be required to determine if this was the case. All of the type O virus isolates that have examined from Iran and Iraq appear to belong to the PanAsia strain, although there is some sequence variation (Fig. 2). Further sequencing of viruses from Iran is in progress. O PanAsia viruses so far analysed seem to be serologically related to existing vaccine strains, such as O Manisa. In south-east Asia four distinct lineages appear to be co-circulating, i) the PanAsia strain (ME-SA topotype); ii) the Cam-94 strain (SEA topotype); iii) the Mya-98 strain (SEA topotype); and iv) the May-94 strain (SEA topotype) (Fig. 3). The PanAsia and Cam-94 strains occur throughout SE Asia, however, the other two appear to have more restricted distributions with the Mya-98 strain occurring in Myanmar, Thailand and Malaysia and the May-94 strain occurring in Malaysia and Thailand. Interestingly, the May-94 strain has not been detected since The Cathay topotype continues to be isolated from pigs in Hong Kong (Fig. 3), which has, so far, remained free of the PanAsia strain (although more isolates remain to be examined). Serotype A The type A viruses which caused extensive outbreaks in Argentina, Uruguay and southern Brazil during 2001 were closely related to each other and part of a larger group of viruses which have been isolated in Argentina and Paraguay since the late 1970 s (Fig. 4). The 2001 outbreak viruses were distinct from the type A virus, which caused a number of cases in Argentina in 2000 (Fig. 4). Recent type A virus isolates from Iran fall into two distinct genetic lineages. Six isolates from 2000 fall within the Middle East-South Asia topotype (which also contains the classical A22 subtype viruses) (Fig. 5). Two isolates form a group which is not closely related to any other type A group so far examined (Fig. 5). Type A virus isolates recently received from Pakistan are currently being sequenced to ascertain their relationship with the Iranian viruses. Recent Iranian and Iraqi field isolates show a poor match with most available vaccine strains apart from A Iran 87, which is locally produced in Iran. Tosh et al. (2002) recently reported the complete VP1 sequences of 83 viruses isolated in India between 1977 and They were able to divide these viruses into four major genotypes, but none were closely related to the new virus from Iran (data not shown). A single type A isolate received from Malaysia in 2002 is related to viruses which have occurred in both Malaysia and Thailand since the mid-1990 s (Fig. 6). Serotype Asia 1 Two type Asia 1 virus isolates received from Iran during 2001 were examined. They were closely related to each other but were completely distinct from all other Asia 1 sequences residing in our database (Fig. 7). Sequencing of a third isolate from Iran and another from Pakistan is in progress. Asia 1 viruses so far analysed seem to be serologically related to existing vaccine strains, such as Asia 1 Shamir. Serotype SAT 1-3 An isolate from the SAT 2 outbreak in Botswana was found to be closely related to one of the Zimbabwe isolates from August 2001 (ZIM/1/2001) isolated from an outbreak near Bulawayo, but it was dissimilar to another virus (ZIM/13/2001) isolated in September 2001 from the Lupane Area, Jotholo North Diptank (near the Hwange National Park) (Fig. 8). OIE Handistatus records isolation of SAT 1 in 2002 from Uganda and Kenya, as well as SAT 3 from Uganda. SAT 3 has not been recorded in domestic species for several years. 12 FMD/November 2002
13 Appendix III (contd) Serotype C There had been no reports of outbreaks due to serotype C since the mid 1990s, but OIE Handistatus records isolation of serotype C from Nigeria in early No such virus has been received by the WRLFMD. Serology carried out at WRLFMD on samples from vaccinated Syrian cattle revealed high titres of antibody to serotype C. However, there were also high titres to other serotypes and it was not possible to come to a conclusion on whether this result indicates infection with serotype C viruses or cross-reactivity following infection or vaccination with other serotypes. Many other virus isolates remain to be sequenced and it is intended that future results will be made more accessible via the WRLFMD website: Acknowledgements We would like to thank Dr. Sinan Aktas (Ankara, Turkey) for providing sequence data on recent type O and type A viruses from Turkey, Dr. Wilna Vosloo (Onderstepoort, South Africa) for the Zimbabwe 2001 sequences and Drs. Jorge Lopez (Panaftosa, Brazil) and Maria Elisa Piccone (INTA, Argentina) for South American sequence data. References Hemadri, D., Tosh, C., Sanyal, A. and Venkataramanan, R. (2002). Emergence of a new strain of type O footand-mouth disease virus: its phylogenetic and evolutionary relationship with the PanAsia pandemic strain. Virus Genes 25: Tosh, C., Sanyal, A., Hemadri, D., and Venkataramanan, R. (2002). Phylogenetic analysis of serotype A footand-mouth disease virus isolated in India between 1977 and Archives of Virology 147: Table 1: OIE/FAO World Reference Laboratory for Foot and Mouth Disease Cumulative Report for January - October, 2002 COUNTRY No. of FMD virus serotypes samples O A C SAT 1 SAT 2 SAT 3 Asia 1 SVDV (a) Bhutan Botswana Burkina Faso Hong Kong (PRC) Iran Iraq Palestinian autonomous territory Kuwait Laos Lebanon Malaysia Pakistan 17* Saudi Arabia Singapore 9 9 South Korea 2 2 Thailand Turkey United Kingdom Vietnam TOTAL NVD (b) * One sample from Pakistan contained a mixture of FMD virus types O and Asia 1 (a) swine vesicular disease virus (b) no foot-and-mouth disease, swine vesicular disease or vesicular stomatitis virus detected FMD/November
14 Appendix III (contd) Cathay SEA ME-SA Euro-SA WA EA 1% TOPOTYPES ME-SA, Middle East-South Asia SEA, South-east Asia EA, East Africa WA, West Africa Euro-SA, Europe-South America Cathay, China O/HKN/4/2001 O/HKN/1/99 O/VIT/3/97 O/PHI/7/96 O/TAW/81/97 O1/Kaufbeuren/FRG/66 O/ARG/3/2000 O/ARG/38779/2000 [INTA-ARGENTINA] O/ARG/38867/2000 [INTA-ARGENTINA] O/URU/1/2000 O/MAU/19/2000 O/ALG/1/99 O/GHA/5/93 O/K83/79 (Kenya) O/UGA/5/96 O/TAI/2/2000 O/TAI/4/99 O/CAM/6/99 O/VIT/2/97 O1/Manisa/TUR/69 O/NEP/12/2000 O/OMN/7/2001 O/BAR/1/2001 O/BHU/7/2002 O/IND/83/2001 [IVRI-MUKTESWAR] O/IND/116/2001 [IVRI-MUKTESWAR] O/IND/96/2001 [IVRI-MUKTESWAR] O/UAE/6/2001 O/OMN/4/2001 O/SAU/3/2001 O/SAU/11/2001 O/KUW/3/97 O/BAR/2/97 O/UAE/7/97 O/SAU/2/97 O/TUR/2/2000 O/TUR/7/2000 O/KUW/1/98 O/BHU/2/2002 O/MAY/1/2001 O/BHU/1/98 O/BHU/2/98 O/SAU/2/99 O/SAU/13/2001 O/QTR/3/99 O/BAR/6/99 O/SAU/38/98 O/IRQ/30/2000 O/IRN/16/2000 O/TUR/5/2000 O/TUR/8/2000 O/TUR/2/2001 O/TUR/15/2001 O/MOG/2000 [ARRIAH-RUSSIA] O/SKR/1/2002 O/SKR/2/2002 O/SKR/2000 [PAIDC-USA] O/Tibet/CHA/3/99 [LANZHOU-PRC] O/BAR/8/98 O/IRN/9/99 O/UAE/4/99 O/UAE/1/2000 O/UAE/2/2000 O/UAE/3/2000 O/Tibet/CHA/1/99 [LANZHOU-PRC] O/JPN/2000 [NIAH-JAPAN] O/SAR/1/2000 Ind2001 strain PanAsia strain O/NET/1/2001 [LELYSTAD] O/IRL/134/2001 O/FRA/1/2001 O/UKG/12/2001 O/1734/Ussuriysk/RUS/2000 [ARRIAH-RUSSIA] O/SKR/1/2000 O/Tibet/CHA/2/99 [LANZHOU-PRC] O/TAW/2/99 O/Hainan/CHA/4/99 [LANZHOU-PRC] O/CAM/2/2000 O/LAO/2/2000 O/MAY/2/2000 [ ] sequence provided by laboratory indicated O/TAI/1/2000 Fig. 1. Genetic relationships between recent FMD type O viruses and reference strains. The tree was based on a comparison of complete VP1-coding sequences. Cathay Euro-SA ME-SA 1% O/IND/R2/75 O1/Manisa/TUR/69 O/IRN/15/97 O/IRQ/26/2000 O/IRQ/27/2000 O/IRQ/30/2000 O/IRQ/29/2000 O/IRQ/31/2000 O/IRN/1/2000 O/IRN/52/2001 O/IRN/16/97 O/IRN/16/2001 O/IRN/41/2001 O/IRN/9/99 O/TAW/2/99 O/SAR/1/2000 O/IRN/24/99 O/UKG/12/2001 O/IRN/2/2000 O/IRN/16/2000 O/IRN/17/2000 O/HKN/6/83 O1/BFS 1860/67 PanAsia strain Fig. 2. Genetic relationships between recent FMD type O viruses from Iran and Iraq and reference viruses. The tree was based on a comparison of complete or nearly complete VP1-coding sequences. 14 FMD/November 2002
15 Appendix III (contd) SEA Euro-SA ME-SA Cathay Cam94 PanAsia NVRQS = National Veterinary Research and Quarantine Service, Rep. of Korea. ARRIAH = All-Russian Research Institute for Animal Health, Russian Federation. PIADC = Plum Island Animal Disease Center, USA. NIAH = National Institute for Animal Health, Japan. LVRI = Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, P.R. China. Mya98 Hkn94 O/CAM/3/98 O/CAM/6/99 O/CAM/1/98 O/CAM/2/98 O/VIT/1/97 O/VIT/2/97 O/VIT/7/97 O/VIT/9/97 O/VIT/6/97 O/VIT/1/99 O/MAY/1/2002 O/TAI/8/99 O/LAO/1/98 O/LAO/4/98 O/TAI/189/87 O/MAY/5/2001 O/MAY/3/2001 O/MAY/2/2001 O/MAY/4/2001 O/MYA/2/2000 O/MYA/4/98 O/MYA/1/98 O/MYA/7/98 O/MYA/5/99 O/TAI/4/99 O1/Kaufbeuren/FRG/66 O/HKN/6/83 O/VIT/3/97 O/HKN/4/2001 O/HKN/9/99 O/HKN/4/99 O/HKN/7/98 O/HKN/10/99 O/HKN/1/99 O/HKN/22/99 O/HKN/7/96 O/HKN/20/96 O/HKN/5/97 O/HKN/6/97 O/HKN/3/98 O/HKN/10/98 O/VIT/2/99 O/VIT/3/99 O/VIT/6/99 O/HKN/16/96 O/PHI/5/95 O/TAW/111/97 O/TAW/13/98 O/TAW/36/97 O/TAW/83/97 O/TAW/81/97 O/TAW/4/99 O/PHI/13/95 O/PHI/7/96 O/PHI/8/98 O/PHI/19/98 O/PHI/25/98 O/PHI/1/99 O/PHI/5/99 O/MYA/13/89 O/BUR/2/89 O/BUR/6/89 O/CAM/11/94 O/CAM/12/94 O/TAI/5/99 O/MAY/6/99 O/MAY/4/99 O/MAY/8/99 O/MAY/17/96 O/TAI/2/2000 O/MAY/1/2001 O/MYA/7/99 O/SKR/2000 [PIADC] O/Tibet/CHA/3/99 [LVRI] TOPOTYPES O/SKR/2/2002 ME-SA, Middle East-South Asia O/CAM/2/2000 SEA, South-east Asia O/CAM/1/2000 Euro-SA, Europe-South America O/CAM/4/2000 O/LAO/1/2000 Cathay, China O/LAO/2/2000 O/VIT/12/99 O/VIT/17/99 O/SKR/1/2000 O/SKR/2000 [NVRQS] O/VIT/23/99 O/Tibet/CHA/2/99 [LVRI] O/TAW/2/99 O/Hainan/CHA/4/99 [LVRI] O/TAI/1/2000 O/MAY/1/2000 O/MAY/2/2000 O/MAY/3/2000 O/JPN/2000 [NIAH] O/TAI/9/99 O/Tibet/CHA/1/99 [LVRI] Fig. 3. Genetic relationships between recent FMD type O viruses and reference strains. The tree was based on a comparison of partial VP1-coding sequences (nt ). 1% A/BRA/1/2001 (W) A/URU/1/2001 (W) A/Chapaleufu/LP/ARG/2001 (I) A/Rivadavia/BA/ARG/2001 (I) A27/Cundinamarca/COL/76 (U) A/ARG/3/2001 (W) A/Union/COR/ARG/2001 (I) A24/Cordoba/ARG/90 (I) A/PAR/82 (I) A/Corrientes/ARG/92 (I) A27/COL/67 (W) A81/URU/79 (I) A/BA/Arg/81 (I) A/Pehuajó/BA/ARG/92 (I) A/96928/COL/97 (P) A/97245/COL/97 (P) A/96929/COL/97 (P) A/Ayacucho/BA/ARG/90 (I) A/San Ignacio/ARG/90 (I) A/25 de Mayo/BA/Arg/87 (I) A/Castellanos/SF/Arg/87 (I) A/Castellanos/SF/Arg/87 (A) A/ARG/1/2000 (W) A/ARG/2000 (I) A32/VEN/70 (P) A24/Cruzeiro/BRA/55 (W) A/Utracan/LP/Arg/87 (I) A/13753/RGdS/BRA/97 (P) A/6562/RGdS/BRA/97 (P) A/105325/BOL/98 (P) A76/ARG/76 (W) 1% A/105330/BOL/98 (P) A/ARG/79 (U) A/105331/BOL/98 (P) A/106455/PER/99 (P) A/106453/PER/99 (P) A/Venceslau/BRA/76 (U) Sequences determined at: W = WRLFMD P = PANAFTOSA I = INTA U = PIADC A = University of Buenos Aires Fig. 4. Genetic relationships between recent FMD type A viruses from South America and reference viruses. The tree was based on a comparison of complete or nearly complete VP1-coding sequences. FMD/November
16 Appendix III (contd) European/South American topotype Indian/Middle Eastern (A22-like) topotype Iran-99 topotype Iran-96 topotype 1% A10/HOL/42 A24/Cruzeiro/BRA/55 A5/Allier/FRA/60 A/IRN/32/2001 A/IRN/34/2001 A/IND/17/77 VS* A/IND/300/94* A/ALB/4/96 A/MCD/1/96 A22/IRQ/24/64 A22/Mahmatli/TUR/65 A/IRN/30/2000 A/IRN/7/2000 A/IRN/8/2000 A/IRN/12/2000 A/IRN/4/2000 A/IRN/10/2000 A/IRN/87 A/IRN/22/99 A/IRQ/24/2002 A/IRQ/33/2002 A/TUR/11/2002* (Aktas) ALB, Albania BRA, Brazil FRA, France HOL, Holland IND, India IRN, Iran IRQ, Iraq MCD, Macedonia SAU, Saudi Arabia TUR, Turkey A/TUR/1/2000 A/IRN/28/99 A/IRQ/17/2000 A/TUR/4/2000 A/TUR/3/2000* (Aktas) A/TUR/1/2000* (Aktas) A/TUR/33/2001* (Aktas) A/TUR/7/2001* (Aktas) A/TUR/17/2001 A/TUR/9/2002* (Aktas) A/TUR/4/2001* (Aktas) A/TUR/5/2001* (Aktas) A/TUR/8/2001* (Aktas) A/TUR/10/2002* (Aktas) A/TUR/6/2001* (Aktas) A/TUR/2/2000* (Aktas) A/TUR/21/2001* (Aktas) A/IRN/4/98 A/IRN/17/96 A/IRN/1/97 A/TUR/38/98 * not WRLFMD reference numbers A/TUR/12/97 A/TUR/14/98 A/TUR/19/98 Fig. 5. Genetic relationships between recent FMD type A viruses from Iran, Iraq and Turkey and reference viruses. The tree was based on a comparison of partial VP1-coding sequences (nt ). ALB = Albania BRA = Brazil CHA = P.R. China FRA = France HOL = Holland IRQ = Iraq MAY = Malaysia MCD = Macedonia PHI = Philippines SAU = Saudi Arabia SPA = Spain TAI = Thailand Euro-SA topotype ME-SA topotype A22/IRQ/24/64 1% A/SKL/TAI/73 A/SAU/16/95 A/ALB/1/96 A/MCD/1/96 A10/HOL/42 A24/Bilbao/SPA/73 A24/Cruzeiro/BRA/55 A5/Allier/FRA/60 A/PHI/10/75 A/PHI/1/76 A/PHI/1/77 A/PHI/2/79 A/XJ/KT/CHA/58 A/GS/LX/CHA/62 A/NM/XZ/CHA/64 A/NM/EL/CHA/60 A15/Bangkok/TAI/60 A/TAI/183/86 A/NPT/TAI/86 A/TAI/179/86 A/TAI/186-2/86 A/TAI/118-1/87 A/TAI/25-1/88 A/MAY/48/95 A/MAY/28/96 A/MAY/69/95 A/MAY/71/95 A/MAY/14/97 A/MAY/10/97 A/MAY/16/97 A/MAY/9/97 A/MAY/12/97 A/MAY/13/97 A/MAY/15/97 A/TAI/1/97 A/TAI/2/97 A/TAI/6/99 A/TAI/7/99 A/MAY/2/2002 A/TAI/2/99 A/TAI/2/98 A/TAI/3/99 A/TAI/1/99 Fig. 6. Genetic relationships between recent FMD type A viruses from Malaysia and Thailand and reference viruses. The tree was based on a comparison of partial VP1-coding sequences (nt ). 16 FMD/November 2002
17 Appendix III (contd) 0.1% IND/63/72 PAK/1/54 Bangkok/TAI/60 IRN/4/2001 IRN/11/2001 TUR/15/73 ISR/1/84 N1214/Armenia/USSR/84 N1181/Azerbaijan/USSR/83 BAR/1/85 LEB/1/84 ISR/3/89 GRE/1/84 LEB/3/83 PAK/3/98 TUR/10/99 TUR/8/99 IRN/58/99 GRE/2/2000 TUR/6/2000 IND/43/95 IND/51/95 IND/40/95 IND/233/95 IND/26/95 SAU/39/94 SAU/40/94 BAN/1/87 IND/9/89 (1988) NEP/8/87 NEP/36/87 NEP/58/88 NEP/28/90 (1989) BHU/1/86 NEP/23/85 WBN/IND/117/85 NEP/19/86 (1985) YEM/2/80 (1979) HKN/20/80 YEM/15/79 IND/10/82 IND/91/79 IND/60/79 SAU/32/92 IND/8/79 Fig. 7. Genetic relationships between recent FMD type Asia 1 viruses from Iran and reference viruses. The tree was based on a comparison of partial VP1-coding sequences (nt ). RWA/2/97 ZIM/13/2001 [Onderstepoort] ZIM/7/83 BOW/1/98 (buffalo 1) BOW/7/98 (buffalo 10) ZIW/4/97 (MUK-48) buffalo ZIM/1/97 ZIM/2/97 ZIM/4/97 ZIM/3/97 KEN/3/57 BOT/13/2002 ZIM/1/2001 [Onderstepoort] RHO/1/48 1% SAU/2/2000 BOT = Botswana BOW = Botswana wildlife KEN = Kenya RHO = Northern Rhodesia (Zambia) RWA = Rwanda SAU = Saudi Arabia ZIM = Zimbabwe ZIW = Zimbabwe wildlife BOW/15/98 (buffalo 29) BOW/4/98 (buffalo 7) Fig. 8. Genetic relationships between recent FMD type SAT 2 viruses from Botswana and Zimbabwe and reference viruses. The tree was based on a comparison of partial VP1-coding sequences. FMD/November
18 Appendix III (contd) 18 FMD/November 2002
19 Appendix III (contd) FMD/November
20 Appendix III (contd) Report from the European Commission for the Control of Foot-and-Mouth Disease on the FMD situation in Europe K.J. Sumption Secretary, EUFMD Commission, FAO At the time of writing, the presence, or possible presence, of FMD in four countries in the east of the European region is of continued concern. Thirty one of the thirty three member states of EUFMD have FMD free status, without vaccination, and the activities of the EUFMD Commission have over many years concentrated on reduction in the risk of entry of FMDV into south-eastern parts of mainland Europe, particularly through maintenance of vaccination and surveillance activities in Turkish Thrace. FMD situation in the Republic of Turkey In Turkey in 2002, up to the end of October, three serotypes were considered to be circulating 1 although outbreaks caused by type Asia-1 had not been recorded since April There had been 39 outbreaks in this period, of which 22 were due to type O, 15 due to type A and 2 due to type Asia-1 (Table 1). Table 1 Outbreaks of FMD Month Type O A Asia-1 Total January February March April May June July August September October TOTAL In relation to 2001, there was an upsurge in Type A outbreaks and a marked reduction in outbreaks caused by Asia-1 (Figures 1 & 2). The seasonality in 2002 was close to the long term trend, with increasing cases through the spring into the summer (Figure 1), and in contrast to situation observed in In September five outbreaks were considered active, in five Provinces. Three of these were in Eastern Anatolia (in Erzurum, Kars, and Siirt provinces), and two in Central Anatolia (Nevşehir and Nigde Provinces). The location of most outbreaks in 2002 is in eastern Anatolia, and far from the land borders with neighbouring countries; a few cases also occurred in provinces bordering the Black Sea, but none were recorded along or close to the meditteranean, and no outbreak has been reported in Thrace region since June All of the FMDV isolates antigenically characterised which originated from outbreaks in 2002 were found to have a good antigenic relationship to vaccine strains used in Turkey. Fourteen virus isolates from 2002 had been characterised at the genetic level; type A viruses were closely related to A/Iran/96 group, and type O viruses were related to O1 Manisa, as previously found. At the time of writing there has been no evidence of entry of FMDV of the most recent type A topotypes circulating Iran or Iraq, including the A-Iran-99 topotype, the as yet unnamed topotype identified among isolates from Iran in 2001, or the A22 like topotype. This suggests recent control measures have been effective in controlling the rate of entry of these viruses into Turkey, probably assisted by a reduced or negative price differential for meat across the Turkey-Iran border in The apparent absence of exotic topotypes among virus isolates studies which had been isolated in 2002 suggests the reservoir of infection is within Turkey. The control of illegal animal movement has been improved in recent years through increase in the penalties for those involved in illegal animal movements, and may have been a contributory factor to the reduction in the number of outbreaks 1 Report of the Tripartite Meeting in Athens, 25th October 2002, EUFMD, FAO, Rome 20 FMD/November 2002
21 Appendix III (contd) reported in These include a 3 month removal of the vehicle license in the case of those found to be carrying animals without the correct licenses. The changes associated with Law 3285 have been reported to have had a high public profile and this has been beneficial for control. A high amount of effort had been required in public relations when the law was introduced and enforced. Strict control measures are performed at the borders working with the co-ordination of the relevant authorities. A national programme with the objective of Identification of all bovine animals in Turkey was started in September 2001, all 81 provincial directorates and most district directorates are reported to have internet connections and addresses to enable connection to the central database. About 7 million cattle out of the 10 million bovines in the country had been tagged and registered. About 4.4 million cattle and approximately 830,000 bovine animal holdings have been recorded into the database. Figure 1 FMD outbreaks in Turkey by month Type Asia-1 Type A Type O January February March April May June July August September October Figure 2 FMD outbreaks in Turkey in Type Asia-1 Type A Type O 5 0 January February March April May June July August September October FMD/November
22 Appendix III (contd) The quality and quantity of FMD vaccine has improved in the last two years through changes in the vaccine production unit of the SAP institute, and in the testing of every batch of vaccine in the field for herd immunity levels. The quantity of vaccine produced was reported as sufficient to cover the needs of the spring and autumn campaign. A total of 21,950,000 monovalent doses of FMD vaccine had been produced so far in The vaccination programme in 2002 aimed at vaccination of at least 80% of all large ruminants, with trivalent FMD vaccine (O1 Manisa, A Aydin 98 (Iran 96), and Asia-1) produced by the SAP Institute Ankara, and mass vaccination twice per year for large ruminants over the country, and once per year for small ruminants in Thrace and Marmara region. Ring vaccination would be used around outbreaks, and strategic vaccination in the Black Sea region. The spring vaccination was carried out in March and April 2002, and 97% of cattle (range 86% to 107% of estimated cattle population) and 73% of small ruminants (range 58% to 82%) were vaccinated in Thrace region, and 70% of cattle in Anatolia. The spring campaign in Thrace used vaccine produced in Turkey. The autumn campaign would draw from the 683,000 doses of trivalent vaccine donated by the EC through EUFMD which were surplus to the requirements in 2001, as reported in the 67th Session of the EUFMD executive committee meeting in April. The autumn campaign in Thrace would require about 394,971 doses of vaccine from the residual 683,000 doses of trivalent vaccine supplied by EC/EUFMD. One reason for the residual amount of vaccine was that the twice yearly vaccination of small ruminants had been discontinued after difficulties with farmer compliance, over the issue of vaccination of pregnant animals. The Tripartite meeting agreed that achieving a vaccination cover of 97% in cattle in Thrace was a major achievement, and that the proposed plan of Turkey to vaccinate small ruminants in the spring campaigns was supported. However the important role of small ruminants in transmission in this region must be kept in mind and the issue of vaccination of small ruminants needs clarification. The meeting considered the major improvements made over the past 7 years to be of great importance in FMD control and that this represented a successful role for the Tripartite group. In relation to the country needs, vaccine supply is reported to be adequate for the country needs in 2003, including in Thrace, but if in future national small ruminant vaccination was required, more vaccine would be required. Although FMD vaccine produced by Bayer was available and could be used, it was more expensive and therefore not the vaccine of choice to the veterinarians; in 2003 supply of vaccine from the SAP Institute should meet all the predicted programme needs. The FMD vaccine produced by Vetal was not currently allowed to be used, and could not be allowed until authorised by the Turkish authorities. The issue of QC of the batch of FMD vaccine intended for use in 2003 was discussed; a batch had been submitted to Pirbright six months before the meeting and the results of QC tests should be available by the end of January The meeting agreed that vaccine QC remained an extremely important issue and that it hoped that an important milestone in FMD control in the region would soon be reached through independent QC at the Bornova facility. The use of serology to determine levels of immunity in cattle and small ruminants in Thrace after vaccination in the spring campaign 2003 will follow a program drawn up by EUFMD and Turkish representatives in Izmir in September. It was also agreed that serology would be used as a routine management tool to determine the level of immunity in the population in Thrace after vaccination. The proposal of Turkey to collect 5,000 sera to determine herd immunity in Thrace, and also to test for antibodies to NSPs would require at least 20,000 tests, and would require strengthening of capacity to ensure timely reporting of results and to undertake other serology, for example in future in other parts of Turkey. The importance of strengthening sero-diagnostic capacity was strongly supported by the meeting. FMD surveillance in EUFMD member countries bordering Turkey The Republics of Greece and Bulgaria are recognised as FMD free without vaccination. The following is taken from information supplied to the recent Tripartite group meeting 2. In late 2000 Greece implemented a new and comprehensive Contingency Plan for combating FMD which, among other things, enhanced disease awareness in the field and provided clear instructions on procedures to be followed for confirming or refuting suspicions of FMD. Between 1 January and 23 October 2002, 12 clinical suspicions were reported in 8 different Prefectures, 2 Report of the Tripartite Meeting in Athens, 25th October 2002, EUFMD, FAO, Rome 22 FMD/November 2002
23 Appendix III (contd) which were widely dispersed in the country; 10 were in cattle and 2 in sheep and goats. The spatial distribution indicated uniformly high awareness across the country. All samples returned negative test results. In 2002 tests for antibodies to type O1 were conducted on 170 cattle, 130 small ruminants and 267 pigs, respectively on animals imported through Border Inspections Posts from third countries, on a random, infrequent and non-discriminatory basis. All returned negative results. Furthermore tests on 257 cattle, 150 small ruminants and 297 pigs which were imported from EU member states returned negative results. In 2002 Greece had had to suspend the active surveillance ( Evros ) programme in areas at risk, and as a substitute, introduced a pre-movement testing regime for animals moving off areas exposed to higher risk. The new regime involves clinical inspection and serological tests for detection of antibodies against types A22, O1, Asia-1 and SAT, on a random sample of all outgoing consignments. A total of 11,941 samples were collected to 23/10/2002, and all tests conducted returned negative results. In Bulgaria in 2002 an FMD surveillance programme was implemented that involved the following; a clinical inspection service for cattle in the 10 km area bordering Turkey; control of movement and slaughter of animals from this 10 km zone; control of grazing and watering of animals in the 10 km strip in regions of Burgas, Yambol, Haskovo alongside the border with Turkey; monthly serologic surveillance of small ruminants bred in and around the border settlements in the border zones previously detailed, and in Kardgali administrative region; control on populations of wild ruminants. Tests for antibodies to NSP (Intervet-Bomelli kit) were conducted collected through the active surveillance programme and none of 660 small ruminant sera returned positive results. Tests for NSP antibodies were used since small ruminants are ear-tagged in this region and therefore illegally imported animals could be identified. As animals were repeatedly sampled the scheme operated as a sentinel scheme rather than a random survey. FMD in the Republics of Georgia, Armenia and Azerbaijan The situation in 2002 was reported and discussed by country representatives on the 5th November at the Tripartite Group meeting at the OIE. The meeting had been organised following the recommendations of the Tripartite Meeting of February 2002, and was attended by representatives of the 3 countries most directly concerned, and also from Russia, from OIE from the Central Bureau and the Regional Commission, from FAO. EUFMD was represented by the Secretary and four members of the Executive Committee of EUFMD. The country representatives from Georgia, Armenia and Azerbaijan reported that FMD had not been reported in 2002 in their countries and that the situation for disease control was extremely difficult because of the very low budget available for epizootic control, and the problem of transboundary animal movement. The representative of Russia suggested that actions of EUFMD or OIE towards FMD control in Iran should be linked in some way to those in the Caucasus. A longer term programme for the three countries was presented by Dr Schudel of the OIE at the meeting, which involved strengthening of the veterinary services over 5 years, mass vaccination of ruminant species with oil-adjuvanted vaccines, and improvement of surveillance. The proposal envisaged funding by the EC and implementation by the EUFMD under management by the Tripartite (EUFMD/OIE/EC) group. Reservations were expressed by FAO and EC representatives that clear progress in the short term activities and in co-operation with international bodies should be a condition of any further support to the region. EUFMD are implementing the short term program in the region as agreed for the first half of Two experts had been identified to go the Caucasus in March-May 2003, Prof. Tekirlikov from Bulgaria, and Dr Celeda, Chairman of the EUFMD; terms of reference had been drafted, the tender for vaccine had been prepared under the guidance of the previous secretary and the Chairman of the Research Group, and a draft letter of agreement with Vladimir prepared. Unconfirmed reports of FMD in Armenia were received in September by EUFMD. FMD in other countries which neighbour the European region Over 1000 outbreaks were reported to the OIE by the Islamic Republic of Iran in for 2001, and the country is seen as a major potential source of risk for entry of FMD into Turkey and into countries in the Caucasus. Types A, O and Asia-1 were associated with outbreaks in 2001 and Of concern is the emergence (and apparent dominance) of topotypes of type A virus which are antigenically distinct, to type A vaccines in use in Turkey and elsewhere in the region, and the frequent appearance of genetically distinct virus topotypes among isolates from Iran. There is no evidence to date of the antigenically distinct type A topotype having entered Turkey but nevertheless the risk remains high, and the impact potentially even more so, since the most appropriate antigen is known to be maintained as a vaccine only in Iran (A-Iran87). A mission to explore the feasibility of a regional FMD/November
GLOBAL FMD SITUATION DURING 2001/2002
 APPENDIX 2 GLOBAL FMD SITUATION DURING 2001/2002 Report of the FAO/OIE World Reference Laboratory for FMD, Institute for Animal Health, Ash Road, Pirbright, Woking, Surrey GU24 ONF, United Kingdom Tables
APPENDIX 2 GLOBAL FMD SITUATION DURING 2001/2002 Report of the FAO/OIE World Reference Laboratory for FMD, Institute for Animal Health, Ash Road, Pirbright, Woking, Surrey GU24 ONF, United Kingdom Tables
1. Report of the President of the Scientific Commission and elaboration of the plan of action of the Commission for the next 3 years
 Original: English August 2003 REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE BUREAU OF THE OIE SCIENTIFIC COMMISSION FOR ANIMAL DISEASES Paris, 11 12 August 2003 A meeting of the Bureau of the OIE Scientific Commission
Original: English August 2003 REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE BUREAU OF THE OIE SCIENTIFIC COMMISSION FOR ANIMAL DISEASES Paris, 11 12 August 2003 A meeting of the Bureau of the OIE Scientific Commission
Overview of WRL FMD. Historical perspective. Principal activities. FMD threats. Needs/prospects. David Paton
 Tracking the emergence and global spread of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) Overview of WRL FMD David Paton Historical perspective Principal activities FMD threats Needs/prospects Historical Perspective FMD
Tracking the emergence and global spread of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) Overview of WRL FMD David Paton Historical perspective Principal activities FMD threats Needs/prospects Historical Perspective FMD
Foot and Mouth Disease Middle East situation Summary of Answers to the Questionnaire Beirut, Lebanon, 7 9 April 2009
 Foot and Mouth Disease Middle East situation Summary of Answers to the Questionnaire Beirut, Lebanon, 7 9 April 2009 Dr Pierre Primot OIE for the Middle East Purpose of the Questionnaire The purpose of
Foot and Mouth Disease Middle East situation Summary of Answers to the Questionnaire Beirut, Lebanon, 7 9 April 2009 Dr Pierre Primot OIE for the Middle East Purpose of the Questionnaire The purpose of
FMD Situation in Europe and other Regions 2000
 27 FMD Situation in Europe and other Regions 2000 Appendix 1 John Ryan, EUFMD Secretariat INTRODUCTION The first outbreaks of Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) in Europe, since type O was reported in Bulgaria
27 FMD Situation in Europe and other Regions 2000 Appendix 1 John Ryan, EUFMD Secretariat INTRODUCTION The first outbreaks of Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) in Europe, since type O was reported in Bulgaria
Report of the FAO-EUFMD/EC/OIE Tripartite Group Meeting on the Balkans held in Athens, Greece on Friday, 25 October 2002
 Report of the FAO-/EC/OIE Tripartite Group Meeting on the Balkans held in Athens, Greece on Friday, 25 October 2002 Keith Sumption, Secretary Animal Health Service, FAO Appendix 4 Introduction The Chairman
Report of the FAO-/EC/OIE Tripartite Group Meeting on the Balkans held in Athens, Greece on Friday, 25 October 2002 Keith Sumption, Secretary Animal Health Service, FAO Appendix 4 Introduction The Chairman
O 38% NVD 42% A 10% Asia 1 9% SAT2 1% SAT1 <1% Institute for Animal Health
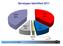 Serotypes Identified 2011 NVD 42% 38% Asia 1 9% A 10% Institute for Animal Health 1% SAT1 600 positive >900 Samples from 23 Countries 23 countries ~900 samples Bulgaria Turkey, A
Serotypes Identified 2011 NVD 42% 38% Asia 1 9% A 10% Institute for Animal Health 1% SAT1 600 positive >900 Samples from 23 Countries 23 countries ~900 samples Bulgaria Turkey, A
Origin of recent outbreaks of foot-and-mouth disease in North Africa, the Middle East and Europe. N.J. Knowles and P.R. Davies
 Origin of recent outbreaks of foot-and-mouth disease in North Africa, the Middle East and Europe N.J. Knowles and P.R. Davies Appendix 3 World Reference Laboratory for Foot-and-Mouth Disease, Institute
Origin of recent outbreaks of foot-and-mouth disease in North Africa, the Middle East and Europe N.J. Knowles and P.R. Davies Appendix 3 World Reference Laboratory for Foot-and-Mouth Disease, Institute
OIE 12, rue de Prony Paris France Tel.: 33 (0) Fax: 33 (0)
 Original: English July 2006 REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE BUREAU OF THE SCIENTIFIC COMMISSION FOR ANIMAL DISEASES Paris, 3-4 July 2006 A meeting of the Bureau of the OIE Scientific Commission for Animal
Original: English July 2006 REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE BUREAU OF THE SCIENTIFIC COMMISSION FOR ANIMAL DISEASES Paris, 3-4 July 2006 A meeting of the Bureau of the OIE Scientific Commission for Animal
Analysis of the Worldwide FMD Situation Trends and Regional Differences
 Analysis of the Worldwide FMD Situation Trends and Regional Differences Dr. Jef M. Hammond, Donald King, Nick Knowles, Valerie Mioulet and Yanmin Li Institute for Animal Health, Pirbright Laboratory, Ash
Analysis of the Worldwide FMD Situation Trends and Regional Differences Dr. Jef M. Hammond, Donald King, Nick Knowles, Valerie Mioulet and Yanmin Li Institute for Animal Health, Pirbright Laboratory, Ash
The Global FMD situation: SEACFMD in the Global Context
 The Global FMD situation: SEACFMD in the Global Context Anna Ludi anna.ludi@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Donald King, Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin,
The Global FMD situation: SEACFMD in the Global Context Anna Ludi anna.ludi@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Donald King, Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin,
WRLFMD: ~1000 samples from 36 countries January- December 2009 (300% up on 2008)
 Appendix 9 IAH Pirbright FMD Reference Laboratory Report: 81st SESSION OF THE EXECUTIVE COMMITTEE OF THE EuFMD COMMISSION 2nd February 2011 Jef M. Hammond, Donald P. King, Nick J. Knowles, Jemma Wadsworth,
Appendix 9 IAH Pirbright FMD Reference Laboratory Report: 81st SESSION OF THE EXECUTIVE COMMITTEE OF THE EuFMD COMMISSION 2nd February 2011 Jef M. Hammond, Donald P. King, Nick J. Knowles, Jemma Wadsworth,
Emma Fishbourne. FMD and SVD Reference Laboratories
 Emma Fishbourne WRLFMD Team: Donald King,David Paton, Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin, Kasia Bachanek-Bankowska, Kelly Adams, Jemma Wadsworth, Begoña
Emma Fishbourne WRLFMD Team: Donald King,David Paton, Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin, Kasia Bachanek-Bankowska, Kelly Adams, Jemma Wadsworth, Begoña
Foot and mouth disease control strategies in North Africa and the Middle East the current
 1. Title, names and addresses of authors Foot and mouth disease control strategies in North Africa and the Middle East the current situation G. Yehia (1), P. Primot (1) (1) OIE Regional Representation
1. Title, names and addresses of authors Foot and mouth disease control strategies in North Africa and the Middle East the current situation G. Yehia (1), P. Primot (1) (1) OIE Regional Representation
Update on current global situation for FMD: New outbreaks and threats
 Update on current global situation for FMD: New outbreaks a threats Donald King (donald.king@pirbright.ac.uk) WRLFMD Team: Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip
Update on current global situation for FMD: New outbreaks a threats Donald King (donald.king@pirbright.ac.uk) WRLFMD Team: Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip
Toward the control of Foot-and-Mouth disease in East Asia
 Symposium on Prevention and Control of Foot and Mouth Disease and Highly Pathogenic Avian influenza in East Asia 20 September, 2017, Tokyo National Agriculture and Food Research Organization Toward the
Symposium on Prevention and Control of Foot and Mouth Disease and Highly Pathogenic Avian influenza in East Asia 20 September, 2017, Tokyo National Agriculture and Food Research Organization Toward the
Development and Current Situation FMD for Asia and the Pacific
 Development and Current Situation FMD for Asia and the Pacific OIE Regional Workshop on Preparation and Submission of Dossiers for the Official Recognition of CFS and for the Endorsement of National Official
Development and Current Situation FMD for Asia and the Pacific OIE Regional Workshop on Preparation and Submission of Dossiers for the Official Recognition of CFS and for the Endorsement of National Official
REPORT ON THE SITUATION OF FMD IN TURKEY
 73 Appendix 7 1. Introduction REPORT ON THE SITUATION OF FMD IN TURKEY Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is one of the most important diseases causing significant economical losses in Turkey. FMD continued
73 Appendix 7 1. Introduction REPORT ON THE SITUATION OF FMD IN TURKEY Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is one of the most important diseases causing significant economical losses in Turkey. FMD continued
Global Update. EuFMD Exec. Committee. Donald King
 Global Update EuFMD Exec. Committee Donald King donald.king@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin, Kasia Bachanek-Bankowska,
Global Update EuFMD Exec. Committee Donald King donald.king@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin, Kasia Bachanek-Bankowska,
FMD Control in South East Asia: science based approach to development of roadmaps and PVS Tools to support capacity building.
 FMD Control in South East Asia: science based approach to development of roadmaps and PVS Tools to support capacity building Ronello Abila Sub-Regional Representative for SE Asia OUTLINE SEACFMD Campaign
FMD Control in South East Asia: science based approach to development of roadmaps and PVS Tools to support capacity building Ronello Abila Sub-Regional Representative for SE Asia OUTLINE SEACFMD Campaign
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report
 Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report October 2013 I N F O R M A T I O N S O U R C E S U S E D: Databases: OIE WAHID World Animal Health
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report October 2013 I N F O R M A T I O N S O U R C E S U S E D: Databases: OIE WAHID World Animal Health
Dr Ghazi Yehia OIE Regional Representative for the Middle East
 Foot and mouth disease control strategies in North Africa and the Middle East The current situation Asuncion, Paraguay, 24-26 June 2009 Dr Ghazi Yehia OIE Regional Representative for the Middle East Acknowledgements
Foot and mouth disease control strategies in North Africa and the Middle East The current situation Asuncion, Paraguay, 24-26 June 2009 Dr Ghazi Yehia OIE Regional Representative for the Middle East Acknowledgements
ANALYSIS OF THE ANIMAL HEALTH SITUATION IN MEMBER COUNTRIES IN THE REGION DURING 2015 AND 2016
 Dr Paula Cáceres Soto Head, World Animal Health Information and Analysis Department ANALYSIS OF THE ANIMAL HEALTH SITUATION IN MEMBER COUNTRIES IN THE REGION DURING 2015 AND 2016 27th Conference of the
Dr Paula Cáceres Soto Head, World Animal Health Information and Analysis Department ANALYSIS OF THE ANIMAL HEALTH SITUATION IN MEMBER COUNTRIES IN THE REGION DURING 2015 AND 2016 27th Conference of the
REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE OIE FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE AND OTHER EPIZOOTICS COMMISSION. Paris, January 2000
 68 SG/12/CS3 B Original: English January 2000 REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE OIE FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE AND OTHER EPIZOOTICS COMMISSION Paris, 24-27 January 2000 A meeting of the OIE Foot and Mouth Disease
68 SG/12/CS3 B Original: English January 2000 REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE OIE FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE AND OTHER EPIZOOTICS COMMISSION Paris, 24-27 January 2000 A meeting of the OIE Foot and Mouth Disease
Progress report on the EUFMD supported actions in FMD Control in the Republic of Azerbaijan. Leos Celeda, Chairman EUFMD
 APPENDIX 8 Progress report on the EUFMD supported actions in FMD Control in the Republic of Azerbaijan I. Introduction Leos Celeda, Chairman EUFMD The mission was undertaken as part of the FAO-EUFMD planned
APPENDIX 8 Progress report on the EUFMD supported actions in FMD Control in the Republic of Azerbaijan I. Introduction Leos Celeda, Chairman EUFMD The mission was undertaken as part of the FAO-EUFMD planned
SECOND FAO/OIE REGIONAL MEETING ON AVIAN INFLUENZA CONTROL IN ASIA Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, February 2005
 SECOND FAO/OIE REGIONAL MEETING ON AVIAN INFLUENZA CONTROL IN ASIA Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 23-25 February 2005 OIE Address for the Opening Session (Dr T. Fujita, OIE Representative, OIE Regional Representation
SECOND FAO/OIE REGIONAL MEETING ON AVIAN INFLUENZA CONTROL IN ASIA Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 23-25 February 2005 OIE Address for the Opening Session (Dr T. Fujita, OIE Representative, OIE Regional Representation
Foot and mouth disease situation and control strategies in the People s Republic of China the current situation
 Foot and mouth disease situation and control strategies in the People s Republic of China the current situation Lu Zengjun (Associate researcher) Shang Youjun (Associate researcher) National Foot-and-Mouth
Foot and mouth disease situation and control strategies in the People s Republic of China the current situation Lu Zengjun (Associate researcher) Shang Youjun (Associate researcher) National Foot-and-Mouth
Southeast Asia and China FMD Campaign
 Southeast Asia and China FMD Campaign Ronello C. Abila SEACFMD Regional Coordinator OIE Sub-Regional Representative for SE Asia OUTLINE SEACFMD Campaign FMD Status Risk factors The new SEACFMD Roadmap
Southeast Asia and China FMD Campaign Ronello C. Abila SEACFMD Regional Coordinator OIE Sub-Regional Representative for SE Asia OUTLINE SEACFMD Campaign FMD Status Risk factors The new SEACFMD Roadmap
PROGRESS REPORT FOR TURKEY ON FMD SITUATION AND CONTROL MEASURES
 Appendix 4 PROGRESS REPORT FOR TURKEY ON FMD SITUATION AND CONTROL MEASURES Dr H Askaroglu Introduction Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) is endemic in the Anatolia Region of Turkey, due to two serotypes. Types
Appendix 4 PROGRESS REPORT FOR TURKEY ON FMD SITUATION AND CONTROL MEASURES Dr H Askaroglu Introduction Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) is endemic in the Anatolia Region of Turkey, due to two serotypes. Types
FMD regional update Gulf States 2017
 FMD regional update Gulf States 2017 Nick Lyons on behalf of Donald King donald.king@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin,
FMD regional update Gulf States 2017 Nick Lyons on behalf of Donald King donald.king@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin,
WRLFMD Quarterly Report July-September 2011
 WRLFMD Quarterly Report July-September 2011 Reference Laboratory Contract Report 26/10/2011 WRLFMD This page deliberately blank 2 OIE/FAO Reference Laboratory Report 1,2 July-September 2011 Foot-and-Mouth
WRLFMD Quarterly Report July-September 2011 Reference Laboratory Contract Report 26/10/2011 WRLFMD This page deliberately blank 2 OIE/FAO Reference Laboratory Report 1,2 July-September 2011 Foot-and-Mouth
Foot and Mouth Disease Status and Control Initiatives in Pakistan. Qurban Ali National Veterinary Laboratories, Islamabad
 Foot and Mouth Disease Status and Control Initiatives in Pakistan Qurban Ali National Veterinary Laboratories, Islamabad Pakistan Total area = 803940 km 2 Total human population =180 Million Ruminant Population
Foot and Mouth Disease Status and Control Initiatives in Pakistan Qurban Ali National Veterinary Laboratories, Islamabad Pakistan Total area = 803940 km 2 Total human population =180 Million Ruminant Population
AND OTHER EPIZOOTICS COMMISSION. Paris, January 2002
 70 SG/12/CS3 B Original: English January 2002 REPORT OF TH E MEETING OF THE OIE FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE AND OTHER EPIZOOTICS COMMISSION Paris, 21 25 January 2002 A meeting of the OIE Foot and Mouth Disease
70 SG/12/CS3 B Original: English January 2002 REPORT OF TH E MEETING OF THE OIE FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE AND OTHER EPIZOOTICS COMMISSION Paris, 21 25 January 2002 A meeting of the OIE Foot and Mouth Disease
Information about activities in the region of possible relevance for the regional strategic plan. GF-TADs for Europe
 First Task-Force meeting Belgrade /Serbia 20-21 December 2016 Information about activities in the region of possible relevance for the regional strategic plan GF-TADs for Europe N. Leboucq Secretariat
First Task-Force meeting Belgrade /Serbia 20-21 December 2016 Information about activities in the region of possible relevance for the regional strategic plan GF-TADs for Europe N. Leboucq Secretariat
Role of the EuFMD/European countries - West EurAsia and other Regional Roadmaps
 Appendix 16 PROGRESSIVE CONTROL PATHWAY (PCP) AND REGIONAL ROADMAPS: TOWARDS A COMMON FRAMEWORK FOR LONG TERM ACTION AGAINST FMD AT NATIONAL AND REGIONAL LEVELS IN EUR-ASIA AND AFRICA Presentation 7 to
Appendix 16 PROGRESSIVE CONTROL PATHWAY (PCP) AND REGIONAL ROADMAPS: TOWARDS A COMMON FRAMEWORK FOR LONG TERM ACTION AGAINST FMD AT NATIONAL AND REGIONAL LEVELS IN EUR-ASIA AND AFRICA Presentation 7 to
David Paton, Yanmin Li and John Bashiruddin on behalf of all the network colleagues
 David Paton, Yanmin Li and John Bashiruddin on behalf of all the network colleagues OIE/WAVLD, Madrid, 19 th June 2009 Presentation overview Background to formation of the Network Network constitution
David Paton, Yanmin Li and John Bashiruddin on behalf of all the network colleagues OIE/WAVLD, Madrid, 19 th June 2009 Presentation overview Background to formation of the Network Network constitution
WRLFMD Global update. Donald King
 WRLFMD Global update Donald King donald.king@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Ginette Wisden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin, Kasia Bachanek-Bankowska, Kelly Adams, Jemma Wadsworth,
WRLFMD Global update Donald King donald.king@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Ginette Wisden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin, Kasia Bachanek-Bankowska, Kelly Adams, Jemma Wadsworth,
FMD Carrier state and role of carrier buffalo as source of transboundary spread in Southeast Asia and Eastern Asia Satya Parida
 FMD Carrier state and role of carrier buffalo as source of transboundary spread in Southeast Asia and Eastern Asia Satya Parida, Pirbright, UK Foot-and-mouth disease Highly contagious disease of all the
FMD Carrier state and role of carrier buffalo as source of transboundary spread in Southeast Asia and Eastern Asia Satya Parida, Pirbright, UK Foot-and-mouth disease Highly contagious disease of all the
Strengthening Veterinary Services in Asia
 Strengthening Veterinary Services in Asia 4 th Steering Committee Highly Pathogenic Emerging and Re-Emerging Diseases (HPED) Programme Session 3 Progress on the OIE component Tokyo (Japan) 16 July 2013
Strengthening Veterinary Services in Asia 4 th Steering Committee Highly Pathogenic Emerging and Re-Emerging Diseases (HPED) Programme Session 3 Progress on the OIE component Tokyo (Japan) 16 July 2013
REGIONAL REFERENCE LABORATORY FOR FMD IN SOUTH EAST ASIA DEPARTMENT OF LIVESTOCK DEVELOPMENT PAKCHONG, NAKHONRATCHASIMA, THAILAND
 University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan, 9-11 June 2015 REGIONAL REFERENCE LABORATORY FOR FMD IN SOUTH EAST ASIA DEPARTMENT OF LIVESTOCK DEVELOPMENT PAKCHONG, NAKHONRATCHASIMA, THAILAND Activities of FMD Laboratory
University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan, 9-11 June 2015 REGIONAL REFERENCE LABORATORY FOR FMD IN SOUTH EAST ASIA DEPARTMENT OF LIVESTOCK DEVELOPMENT PAKCHONG, NAKHONRATCHASIMA, THAILAND Activities of FMD Laboratory
Direct beneficiary Countries: Georgia, Armenia and Azerbaijan Proposed Implementation date: 1/1/06
 Appendix 9 Outline of Project Proposal: Co-ordination of FMD surveillance and control in the Trans-Caucasus countries and strengthening of emergency management capacity Direct beneficiary Countries: Georgia,
Appendix 9 Outline of Project Proposal: Co-ordination of FMD surveillance and control in the Trans-Caucasus countries and strengthening of emergency management capacity Direct beneficiary Countries: Georgia,
The FAO/OIE FMD Global Control Strategy Joseph Domenech, OIE on behalf of the joint FAO/OIE GF TADs PPR Working Group
 The FAO/OIE FMD Global Control Strategy Joseph Domenech, OIE on behalf of the joint FAO/OIE GF TADs PPR Working Group 5 th meeting of the GF TADs Regional Steering Committee for Europe October 8 th -9th
The FAO/OIE FMD Global Control Strategy Joseph Domenech, OIE on behalf of the joint FAO/OIE GF TADs PPR Working Group 5 th meeting of the GF TADs Regional Steering Committee for Europe October 8 th -9th
REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE OIE FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE AND OTHER EPIZOOTICS COMMISSION. Paris, January 2001
 69 SG/12/CS3 B Original: English January 2001 REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE OIE FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE AND OTHER EPIZOOTICS COMMISSION Paris, 23 26 January 2001 A meeting of the OIE Foot and Mouth Disease
69 SG/12/CS3 B Original: English January 2001 REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE OIE FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE AND OTHER EPIZOOTICS COMMISSION Paris, 23 26 January 2001 A meeting of the OIE Foot and Mouth Disease
FMD Current Epidemic Situation in China
 Global and regional status of FMD Reference centre presentations FMD Current Epidemic Situation in China He Jijun Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, CAAS OIE/China national FMD reference laboratory
Global and regional status of FMD Reference centre presentations FMD Current Epidemic Situation in China He Jijun Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, CAAS OIE/China national FMD reference laboratory
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report
 Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report December 2013 Guest editor : Donald King, Head: WRLFMD, The Pirbright Institute, UK I N F O R M A
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report December 2013 Guest editor : Donald King, Head: WRLFMD, The Pirbright Institute, UK I N F O R M A
Keith Sumption Secretary, European FMD Control Commission (EuFMD) FAO, Rome
 Foot and mouth disease situation and control strategies in Europe the current situation Keith Sumption Secretary, European FMD Control Commission (EuFMD) FAO, Rome The European neighborhood wider group
Foot and mouth disease situation and control strategies in Europe the current situation Keith Sumption Secretary, European FMD Control Commission (EuFMD) FAO, Rome The European neighborhood wider group
Unique features of foot and mouth disease in Southern Africa
 Unique features of foot and mouth disease in Southern Africa Gavin Thomson Commodity-based trade and enhanced market access: The vital role of the Department of Veterinary Services Gaborone; 6-7 February
Unique features of foot and mouth disease in Southern Africa Gavin Thomson Commodity-based trade and enhanced market access: The vital role of the Department of Veterinary Services Gaborone; 6-7 February
Contribution of avian influenza data through OFFLU network
 Dr Gounalan Pavade Chargé de Mission, OIE Headquarters Contribution of avian influenza data through OFFLU network Asia-Pacific Workshop on surveillance, prevention and control of zoonotic influenza Paro,
Dr Gounalan Pavade Chargé de Mission, OIE Headquarters Contribution of avian influenza data through OFFLU network Asia-Pacific Workshop on surveillance, prevention and control of zoonotic influenza Paro,
Pillar 2: Reduce Risk to members from the FMD Situation in the European Neighbourhood Accomplishments and Lessons Learned
 41 st General Session of the EuFMD 1 Pillar 2: Reduce Risk to members from the FMD Situation in the European Neighbourhood Accomplishments and Lessons Learned Melissa McLaws and Ibrahim Eldaghayes EuFMD
41 st General Session of the EuFMD 1 Pillar 2: Reduce Risk to members from the FMD Situation in the European Neighbourhood Accomplishments and Lessons Learned Melissa McLaws and Ibrahim Eldaghayes EuFMD
Progress on Implementation of Global FMD Control
 Progress on Implementation of Global FMD Control Part II. Joseph Domenech OIE,Paris 41 th General Session of the European Commission for the control of Foot and Mouth Disease (EuFMD) 23-24 th April 2015,
Progress on Implementation of Global FMD Control Part II. Joseph Domenech OIE,Paris 41 th General Session of the European Commission for the control of Foot and Mouth Disease (EuFMD) 23-24 th April 2015,
Mechanism of FMD spread in East Asia
 Mechanism of FMD spread in East Asia China has the important role of the FMD outbreaks in East Asia 1) Long border with FMD epidemic countries in South East and Central Asia 2) Large numbers of susceptible
Mechanism of FMD spread in East Asia China has the important role of the FMD outbreaks in East Asia 1) Long border with FMD epidemic countries in South East and Central Asia 2) Large numbers of susceptible
Global FMD Surveillance and Regional Risks for West Eurasia
 Global FMD Surveillance and Regional Risks for West Eurasia Anna Ludi anna.ludi@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Donald King, Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin, Kasia
Global FMD Surveillance and Regional Risks for West Eurasia Anna Ludi anna.ludi@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Donald King, Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin, Kasia
The global control of FMD; challenges and opportunities
 EuFMD-Erice 2008 The global control of FMD; challenges and opportunities Keith Sumption, Secretary, European Commission for the Control of Foot-and-Mouth Disease (EuFMD), Food-and-Agriculture Organization
EuFMD-Erice 2008 The global control of FMD; challenges and opportunities Keith Sumption, Secretary, European Commission for the Control of Foot-and-Mouth Disease (EuFMD), Food-and-Agriculture Organization
National Foot and mouth Disease Control and Eradication Plan in Thailand
 National Foot and mouth Disease Control and Eradication Plan in Thailand Bureau of Disease Control and Veterinary Services Department of Livestock Development The FMD control and eradication plan in Thailand
National Foot and mouth Disease Control and Eradication Plan in Thailand Bureau of Disease Control and Veterinary Services Department of Livestock Development The FMD control and eradication plan in Thailand
Elements of the FMD control problem in Southern Africa: 2
 Elements of the FMD control problem in Southern Africa: 2 Gavin Thomson Commodity-based trade of beef and enhanced market access: The vital role of the Department of Veterinary Services Gaborone; 6-7 January
Elements of the FMD control problem in Southern Africa: 2 Gavin Thomson Commodity-based trade of beef and enhanced market access: The vital role of the Department of Veterinary Services Gaborone; 6-7 January
Regional Status and FMD s Control Strategies in North Africa
 Regional Status and FMD s Control Strategies in North Africa Jaouad BERRADA, DVM, Ph.D, Director of Veterinary Services National Office of Sanitary Food Safety Rabat-Morocco SUMMARY - Introduction - Importance
Regional Status and FMD s Control Strategies in North Africa Jaouad BERRADA, DVM, Ph.D, Director of Veterinary Services National Office of Sanitary Food Safety Rabat-Morocco SUMMARY - Introduction - Importance
Report of the Seminar on FMD Progressive Control. Pathway. 18 th December Beirut, Lebanon
 1 Report of the Seminar on FMD Progressive Control. Pathway 18 th December 2012 Beirut, Lebanon 1. Introduction: i. The principal aim of the FMD Seminar was to discuss the preparation of national project
1 Report of the Seminar on FMD Progressive Control. Pathway 18 th December 2012 Beirut, Lebanon 1. Introduction: i. The principal aim of the FMD Seminar was to discuss the preparation of national project
Global FMD Surveillance Report
 Global FMD Surveillance Report Donald King WRLFMD donald.king@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin, Kasia Bachanek-Bankowska,
Global FMD Surveillance Report Donald King WRLFMD donald.king@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin, Kasia Bachanek-Bankowska,
FMD in Tunisia Update situation Critical review Vaccination programme
 FMD in Tunisia Update situation Critical review Vaccination programme Workshop on FMD vaccination strategy in North Africa Tunis, 30 31 March 2016 Direction Générale Des Services Vétérinaires Contents
FMD in Tunisia Update situation Critical review Vaccination programme Workshop on FMD vaccination strategy in North Africa Tunis, 30 31 March 2016 Direction Générale Des Services Vétérinaires Contents
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS AND CONTROL OF FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE IN ASIA
 EPIDEMIOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS AND CONTROL OF FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE IN ASIA Kenichi Sakamoto National Institute of Animal Health, Japan 1 Original: English Summary: In the Asia region, foot and mouth disease
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS AND CONTROL OF FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE IN ASIA Kenichi Sakamoto National Institute of Animal Health, Japan 1 Original: English Summary: In the Asia region, foot and mouth disease
FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE DIAGNOSTICS: REQUIREMENTS FOR DEMONSTRATION OF FREEDOM FROM INFECTION
 70 SG/12/CS3 C Original: English FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE DIAGNOSTICS: REQUIREMENTS FOR DEMONSTRATION OF FREEDOM FROM INFECTION R.P. Kitching Director, Canadian Food Inspection Agency, National Centre for
70 SG/12/CS3 C Original: English FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE DIAGNOSTICS: REQUIREMENTS FOR DEMONSTRATION OF FREEDOM FROM INFECTION R.P. Kitching Director, Canadian Food Inspection Agency, National Centre for
Paper on needs and support to be provided to North African countries, members of REMESA regarding the coordinated control of FMD
 Appendix 4 40 th EuFMD General Session, 22 24 April 2013, Rome Paper on needs and support to be provided to North African countries, members of REMESA regarding the coordinated control of FMD Prepared
Appendix 4 40 th EuFMD General Session, 22 24 April 2013, Rome Paper on needs and support to be provided to North African countries, members of REMESA regarding the coordinated control of FMD Prepared
The New FMD Containment Zone Proposal and Vaccination. April 4, 2017, Pirenopolis, Brazil
 The New FMD Containment Zone Proposal and Vaccination. April 4, 2017, Pirenopolis, Brazil Dr. Tom Smylie Senior Staff Veterinarian Canadian Food Inspection Agency 1 Topics for todays presentation. 1. Current
The New FMD Containment Zone Proposal and Vaccination. April 4, 2017, Pirenopolis, Brazil Dr. Tom Smylie Senior Staff Veterinarian Canadian Food Inspection Agency 1 Topics for todays presentation. 1. Current
THE SOUTH-EAST ASIA AND CHINA FOOT- AND-MOUTH DISEASE 2020 ROADMAP AND CONTEXT
 THE SOUTH-EAST ASIA AND CHINA FOOT- AND-MOUTH DISEASE 2020 ROADMAP AND CONTEXT REGIONAL INFORMATION SEMINAR FOR RECENTLY APPOINTED OIE DELEGATES BEIJING, P.R. CHINA 28-30 APRIL 2014 Karanvir Kukreja OIE
THE SOUTH-EAST ASIA AND CHINA FOOT- AND-MOUTH DISEASE 2020 ROADMAP AND CONTEXT REGIONAL INFORMATION SEMINAR FOR RECENTLY APPOINTED OIE DELEGATES BEIJING, P.R. CHINA 28-30 APRIL 2014 Karanvir Kukreja OIE
Summary Report of Activities/Missions conducted since April 2011, with planned activities into (K.Sumption)
 Appendix Summary Report of Activities/Missions conducted since April, with planned activities into (K.Sumption) FMD Vaccination policy: vaccination against FMD in 8 in West Eurasia-Middle East Ongoing
Appendix Summary Report of Activities/Missions conducted since April, with planned activities into (K.Sumption) FMD Vaccination policy: vaccination against FMD in 8 in West Eurasia-Middle East Ongoing
Update from WRLFMD. Donald King
 Update from WRLFMD Donald King donald.king@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin, Kasia Bachanek-Bankowska, Lissie Henry, Antonello
Update from WRLFMD Donald King donald.king@pirbright.ac.uk WRLFMD Team: Valerie Mioulet, Nick Knowles, Anna Ludi, Ginette Wilsden, Bryony Armson, Pip Hamblin, Kasia Bachanek-Bankowska, Lissie Henry, Antonello
SEACFMD ACTIVITIES FOCUS ON
 SEACFMD ACTIVITIES FOCUS ON 2012-2014 EXPANDED 3RD COORDINATION COMMITTEE MEETING OF OIE/JTF PROJECT ON FMD CONTROL IN ASIA LANZHOU, PR CHINA SEPTEMBER 24, 2014 Dr Karan Kukreja Project Officer OIE Sub-Regional
SEACFMD ACTIVITIES FOCUS ON 2012-2014 EXPANDED 3RD COORDINATION COMMITTEE MEETING OF OIE/JTF PROJECT ON FMD CONTROL IN ASIA LANZHOU, PR CHINA SEPTEMBER 24, 2014 Dr Karan Kukreja Project Officer OIE Sub-Regional
Foot and Mouth Disease in ASEAN countries and related activities
 9 th International Veterinary Immunology Symposium (IVIS) Tokyo, Japan 16-20 August 2010, Foot and Mouth Disease in ASEAN countries and related activities Wilai Linchongsubongkoch, DVM OIE Reference Laboratory
9 th International Veterinary Immunology Symposium (IVIS) Tokyo, Japan 16-20 August 2010, Foot and Mouth Disease in ASEAN countries and related activities Wilai Linchongsubongkoch, DVM OIE Reference Laboratory
Strengthening FMD prevention and emergency response capacity in the Trans-Caucasian countries (MTF/INT/003/EEC)
 Progress towards long term FMD control in the Trans-Caucasus Strengthening FMD prevention and emergency response capacity in the Trans-Caucasian countries (MTF/INT/003/EEC) Carsten Pötzsch, EuFMD/FAO K.Sumption
Progress towards long term FMD control in the Trans-Caucasus Strengthening FMD prevention and emergency response capacity in the Trans-Caucasian countries (MTF/INT/003/EEC) Carsten Pötzsch, EuFMD/FAO K.Sumption
Regulation of FMD vaccines within the European Union
 Introduction Regulation of FMD vaccines within the European Union K De Clercq 1 and D K J Mackay 2 Appendix 36 The EUFMD European Pharmacopoeia Working Group made a proposal for revision of the FMD vaccine
Introduction Regulation of FMD vaccines within the European Union K De Clercq 1 and D K J Mackay 2 Appendix 36 The EUFMD European Pharmacopoeia Working Group made a proposal for revision of the FMD vaccine
FMD Report - Syria 6 th Regional FMD West Eurasia Roadmap Meeting - Almaty, Kazakhstan 28 to 30 April 2015
 FMD Report - Syria 6 th Regional FMD West Eurasia Roadmap Meeting - Almaty, Kazakhstan 28 to 30 April 2015 Dr. Mazen Dib - Directorate Of Animal Health Syria 6th West Eurasia Roadmap Meeting Almaty, Kazakhstan
FMD Report - Syria 6 th Regional FMD West Eurasia Roadmap Meeting - Almaty, Kazakhstan 28 to 30 April 2015 Dr. Mazen Dib - Directorate Of Animal Health Syria 6th West Eurasia Roadmap Meeting Almaty, Kazakhstan
Far-East. Africa. Asia. South America. Somewhere new?
 96 0.005 92 /VIT/4/2005 /VIT/4/05* (TRRL) /VIT/10/05* (TRRL) /HLJC12/03 (China) (DQ119643) 83 /MG/2004 (RRIH) /VIT/6/05* (TRRL) 85 /VIT/9/05* (TRRL) /MY/1/04* (TRRL) /MY/2/04* (TRRL) 100 /MY/10/2009 /MY/11/2009
96 0.005 92 /VIT/4/2005 /VIT/4/05* (TRRL) /VIT/10/05* (TRRL) /HLJC12/03 (China) (DQ119643) 83 /MG/2004 (RRIH) /VIT/6/05* (TRRL) 85 /VIT/9/05* (TRRL) /MY/1/04* (TRRL) /MY/2/04* (TRRL) 100 /MY/10/2009 /MY/11/2009
Lumpy skin disease follow-up project proposal
 1 Lumpy skin disease follow-up project proposal Eeva Tuppurainen, Daniel Beltrán-Alcrudo and Tsviatko Alexandrov FAO Regional Office for Europe and Central Asia, Hungary Beneficiaries and the general aim
1 Lumpy skin disease follow-up project proposal Eeva Tuppurainen, Daniel Beltrán-Alcrudo and Tsviatko Alexandrov FAO Regional Office for Europe and Central Asia, Hungary Beneficiaries and the general aim
OIE Situation Report for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza
 OIE Situation Report for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Latest update: 31/05/2018 The epidemiology of avian influenza (AI) is complex. The AI virus constantly evolves by mutation and re-assortment with
OIE Situation Report for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Latest update: 31/05/2018 The epidemiology of avian influenza (AI) is complex. The AI virus constantly evolves by mutation and re-assortment with
Standing Group of Experts on LSD in South-East Europe
 Standing Group of Experts on LSD in South-East Europe under the GF-TADs umbrella Eleventh meeting (SGE LSD7) Ohrid, the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia, 18-19 October 2018 Summary REPORT The seventh
Standing Group of Experts on LSD in South-East Europe under the GF-TADs umbrella Eleventh meeting (SGE LSD7) Ohrid, the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia, 18-19 October 2018 Summary REPORT The seventh
Main developments in past 24 hours
 ECDC DAILY UPDATE Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Update 02 October 2009, 09:00 hours CEST Main developments in past 24 hours Weekly Influenza Surveillance Overview to be published today; Media highlights and Eurosurveillance
ECDC DAILY UPDATE Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Update 02 October 2009, 09:00 hours CEST Main developments in past 24 hours Weekly Influenza Surveillance Overview to be published today; Media highlights and Eurosurveillance
Recent FMD outbreaks and control strategy in Mongolia
 Recent FMD outbreaks and control strategy in Mongolia GANZORIG Khuukhenbaatar, DVM Director, State Central Veterinary Laboratory, Government Implementation Agency for Veterinary and Animal Breeding, 2011.12.01
Recent FMD outbreaks and control strategy in Mongolia GANZORIG Khuukhenbaatar, DVM Director, State Central Veterinary Laboratory, Government Implementation Agency for Veterinary and Animal Breeding, 2011.12.01
Keith Sumption Secretary, European FMD Control Commission (EuFMD) FAO, Rome
 FMD control in the European neighbourhood priorities/actions of the EuFMD Commission to reduce risk to member states Keith Sumption Secretary, European FMD Control Commission (EuFMD) FAO, Rome The European
FMD control in the European neighbourhood priorities/actions of the EuFMD Commission to reduce risk to member states Keith Sumption Secretary, European FMD Control Commission (EuFMD) FAO, Rome The European
Mission of the Community Veterinary Emergency Team to Bulgaria. (16-21 July 2018)
 Mission of the Community Veterinary Emergency Team to Bulgaria (16-21 July 2018) 1 Terms of Reference Assistance to the scientific, technical, managerial and practical on-thespot assistance on the refinement
Mission of the Community Veterinary Emergency Team to Bulgaria (16-21 July 2018) 1 Terms of Reference Assistance to the scientific, technical, managerial and practical on-thespot assistance on the refinement
OIE/FAO Global Conference on foot and mouth disease. The way towards global control. Paraguay: 24 to 26 June Draft Resolution version 8
 OIE/FAO Global Conference on foot and mouth disease The way towards global control Paraguay: 24 to 26 June 2009 Draft Resolution version 8 Considering that: Foot and mouth disease (FMD) has for centuries
OIE/FAO Global Conference on foot and mouth disease The way towards global control Paraguay: 24 to 26 June 2009 Draft Resolution version 8 Considering that: Foot and mouth disease (FMD) has for centuries
Southeast Asia: Action plans, Future directions and needs
 Scientific Developments and Technical Challenges in the Progressive Control of FMD in South Asia 13 15 February 2012 New Delhi, India Southeast Asia: Action plans, Future directions and needs OIE Reference
Scientific Developments and Technical Challenges in the Progressive Control of FMD in South Asia 13 15 February 2012 New Delhi, India Southeast Asia: Action plans, Future directions and needs OIE Reference
EUROPEAN COMMISSION FOR THE CONTROL OF FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE REPORT
 AGA: EUFMD/X/02/2 EUROPEAN COMMISSION FOR THE CONTROL OF FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE REPORT of the Sixty-eighth Session of the Executive Committee Vilnius, Lithuania 7 and 8 November 2002 FOOD AND AGRICULTURE
AGA: EUFMD/X/02/2 EUROPEAN COMMISSION FOR THE CONTROL OF FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE REPORT of the Sixty-eighth Session of the Executive Committee Vilnius, Lithuania 7 and 8 November 2002 FOOD AND AGRICULTURE
Changing landscape for livestock production and health in China and neighbouring countries; directions and implications for FMD management
 Changing landscape for livestock production and health in China and neighbouring countries; directions and implications for FMD management Professor John Edwards Team Leader, FAO ECTAD China 1 Scope of
Changing landscape for livestock production and health in China and neighbouring countries; directions and implications for FMD management Professor John Edwards Team Leader, FAO ECTAD China 1 Scope of
Number of culled livestock, by species ( )
 Number of culled livestock, by species (2000-2010) Year Camel Cattle Sheep Goat Pig Total 2000 54 552 152 158 0 916 2001 4 1159 16 20 2 1201 2002 0 435 46 4 0 485 2003 0 0 0 0 0 0 2004 0 2072 157 88 0
Number of culled livestock, by species (2000-2010) Year Camel Cattle Sheep Goat Pig Total 2000 54 552 152 158 0 916 2001 4 1159 16 20 2 1201 2002 0 435 46 4 0 485 2003 0 0 0 0 0 0 2004 0 2072 157 88 0
Countries initially targeted: Bangladesh, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Lao People s Demoncratic Republic and Pakistan.
 PUI PROJECT PROPOSAL ON BUILDING AND IMPROVEMENT OF ANIMAL DISEASE DIAGNOSTIC CAPACITIES OF VETERINARY LABORATORIES IN ASIA BY TRANSFER OF NUCLEAR AND NUCLEAR RELATED TECHNIQUES: A REGIONAL APPROACH FOR
PUI PROJECT PROPOSAL ON BUILDING AND IMPROVEMENT OF ANIMAL DISEASE DIAGNOSTIC CAPACITIES OF VETERINARY LABORATORIES IN ASIA BY TRANSFER OF NUCLEAR AND NUCLEAR RELATED TECHNIQUES: A REGIONAL APPROACH FOR
South East Asia and China FMD Campaign
 South East Asia and China FMD Campaign Ronello C. Abila Regional Coordinator OUTLINE The new SEACFMD FMD Status SEACFMD Activities 2009/2010 SEACFMD Plan 2010/2011 The OIE General Assembly has approved
South East Asia and China FMD Campaign Ronello C. Abila Regional Coordinator OUTLINE The new SEACFMD FMD Status SEACFMD Activities 2009/2010 SEACFMD Plan 2010/2011 The OIE General Assembly has approved
Animal health situation of OIE Member Countries in Europe 1 st semester 2012 (and previous)
 Animal health situation of OIE Member Countries in Europe 1 st semester 2012 (and previous) 25 th Conference of the OIE Regional Commission for Europe 17 th to 21 st September 2012, Fleesensee Germany
Animal health situation of OIE Member Countries in Europe 1 st semester 2012 (and previous) 25 th Conference of the OIE Regional Commission for Europe 17 th to 21 st September 2012, Fleesensee Germany
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL SITUATION. for S&GP, PPR andbt
 EPIDEMIOLOGICAL SITUATION A. Naci BULUT for S&GP, PPR andbt On Behalf of Prof. Dr. Irfan EROL General Director General Directorate of Food and Control (GDFC), TURKEY FAO-EuFMD/EC/OIE Tripartite Group Meeting
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL SITUATION A. Naci BULUT for S&GP, PPR andbt On Behalf of Prof. Dr. Irfan EROL General Director General Directorate of Food and Control (GDFC), TURKEY FAO-EuFMD/EC/OIE Tripartite Group Meeting
FMD in Libya. Dr. Abdunaser Dayhum National Center of Animal Health Libya
 FMD in Libya Dr. Abdunaser Dayhum National Center of Animal Health Libya Foot-and-Mouth Disease Cause: Foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV). A total of seven different serologic types are recognized: A,
FMD in Libya Dr. Abdunaser Dayhum National Center of Animal Health Libya Foot-and-Mouth Disease Cause: Foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV). A total of seven different serologic types are recognized: A,
FMD CONTROL IN KYRGYZSTAN State Inspectorate for Veterinary and Phyto- Sanitary Security under the Government of the Kyrgyz Republic
 FMD CONTROL IN KYRGYZSTAN State Inspectorate for Veterinary and Phyto- Sanitary Security under the Government of the Kyrgyz Republic Speaker: Murat Abdraev Head of the Animal Health Control Department
FMD CONTROL IN KYRGYZSTAN State Inspectorate for Veterinary and Phyto- Sanitary Security under the Government of the Kyrgyz Republic Speaker: Murat Abdraev Head of the Animal Health Control Department
Country Report on FMD in Uganda
 Country Report on FMD in Uganda Dr. Ayebazibwe Chrisostom, PhD EARLN FMD Country Focal Person Uganda Ministry of Agriculture Animal Industry and Fisheries, Entebbe EARLN Meeting FMD 29 th August, 2013,
Country Report on FMD in Uganda Dr. Ayebazibwe Chrisostom, PhD EARLN FMD Country Focal Person Uganda Ministry of Agriculture Animal Industry and Fisheries, Entebbe EARLN Meeting FMD 29 th August, 2013,
2004, OIE initiative Ad hoc Group on Antigen & Vaccine Banks for FMD
 2004, OIE initiative Ad hoc Group on Antigen & Vaccine Banks for FMD 2006, progressed by EU Funded project 2009, endorsed at OIE/FAO Global Conference on FMD, Paraguay In May 2010, Dr Jef Hammond presented
2004, OIE initiative Ad hoc Group on Antigen & Vaccine Banks for FMD 2006, progressed by EU Funded project 2009, endorsed at OIE/FAO Global Conference on FMD, Paraguay In May 2010, Dr Jef Hammond presented
Mission of the Community Veterinary Emergency Team to Greece
 Mission of the Community Veterinary Emergency Team to Greece SCOPE of the mission: Sheep pox epidemics on the Lesvos Island (21 24 November 2017) 1 Terms of Reference The experts should provide assistance
Mission of the Community Veterinary Emergency Team to Greece SCOPE of the mission: Sheep pox epidemics on the Lesvos Island (21 24 November 2017) 1 Terms of Reference The experts should provide assistance
OIE s initiative on HPAI control
 Current global situation on HPAI and OIE s initiative on HPAI control The 5 th OIE Regional Meeting on Strengthening e g Animal Health Information Networking for HPAI control and prevention in Asia Hanoi,
Current global situation on HPAI and OIE s initiative on HPAI control The 5 th OIE Regional Meeting on Strengthening e g Animal Health Information Networking for HPAI control and prevention in Asia Hanoi,
Recommendations. FAO/OIE/EC Tripartite meeting on control of Foot-and-Mouth Disease and other exotic diseases in the southern Balkans
 Recommendations FAO/OIE/EC Tripartite meeting on control of Foot-and-Mouth Disease and other exotic diseases in the southern Balkans Introduction Held 17th November 2006 in Ankara, Turkey. A meeting of
Recommendations FAO/OIE/EC Tripartite meeting on control of Foot-and-Mouth Disease and other exotic diseases in the southern Balkans Introduction Held 17th November 2006 in Ankara, Turkey. A meeting of
CURRENT ANIMAL HEALTH SITUATION WORLDWIDE: ANALYSIS OF EVENTS AND TRENDS
 CURRENT ANIMAL HEALTH SITUATION WORLDWIDE: ANALYSIS OF EVENTS AND TRENDS Dr Paula Cáceres Soto Head, World Animal Health Information and Analysis Department 1 Contents 1. Global situation regarding five
CURRENT ANIMAL HEALTH SITUATION WORLDWIDE: ANALYSIS OF EVENTS AND TRENDS Dr Paula Cáceres Soto Head, World Animal Health Information and Analysis Department 1 Contents 1. Global situation regarding five
Vaccination against Bluetongue
 Vaccination against Bluetongue Ivo Claassen Symposium on Bluetongue virus serotype 8, April 19th, Lelystad Vaccination against Bluetongue Introduction Desired characteristics of BT vaccines BT Vaccines
Vaccination against Bluetongue Ivo Claassen Symposium on Bluetongue virus serotype 8, April 19th, Lelystad Vaccination against Bluetongue Introduction Desired characteristics of BT vaccines BT Vaccines
FAOAIDEnews Animal Influenza Disease Emergency
 FAOAIDEnews Animal Influenza Disease Emergency Situation Update 82 17 November 2011 HPAI outbreaks reported in this publication refer to officially confirmed cases only. The information is compiled from
FAOAIDEnews Animal Influenza Disease Emergency Situation Update 82 17 November 2011 HPAI outbreaks reported in this publication refer to officially confirmed cases only. The information is compiled from
Priority diseases in Europe, including transparency aspects
 GF-TADs for Europe Seventh Regional Steering Committee meeting (RSC7) Priority diseases in Europe, including transparency aspects AFSCA - Brussels 16-17 October 2017 Dr Paula Cáceres Soto Head, World Animal
GF-TADs for Europe Seventh Regional Steering Committee meeting (RSC7) Priority diseases in Europe, including transparency aspects AFSCA - Brussels 16-17 October 2017 Dr Paula Cáceres Soto Head, World Animal
General requirements of the Terrestrial Code Chapter on CSF
 Min-Kyung Park Status Department, Chargée de mission, OIE General requirements of the Terrestrial Code Chapter on CSF OIE Regional Workshop on Preparation and Submission of Dossiers for the Official Recognition
Min-Kyung Park Status Department, Chargée de mission, OIE General requirements of the Terrestrial Code Chapter on CSF OIE Regional Workshop on Preparation and Submission of Dossiers for the Official Recognition
