1. Developmental disturbances of teeth, jaws and soft tissues of oral & paraoral region :
|
|
|
- Egbert Page
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SYLLABUS (ACCORDING TO DENTAL COUNCIL OF INDIA) ORAL PATHOLOGY & ORAL MICROBIOLOGY 1. Developmental disturbances of teeth, jaws and soft tissues of oral & paraoral region : Introduction to developmental disturbances - Hereditary, Familial mutation, Hormonal etc. causes to be highlighted. 20 Developmental disturbances of teeth - Etiopathogenesis, clinical features, radiological features & histopathological features as appropriate :- The size, shape, number, structure & eruption of teeth & clinical significance of the anomalies to be emphasized. Forensic Odontology. Developmental disturbances of jaws - size & shape of the jaws. Developmental disturbances of oral & paraoral soft tissues - lip & palate - clefts, tongue, gingiva, mouth, salivary glands & face. 2. Dental Caries : Etiopathogenesis, microbiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, immunology, prevention of dental caries & its sequelae. 3. Pulp & Periapical Pathology & Osteomyelitis. Etiopathogenesis & interrelationship, clinical features, microbiology, histopathology & radiological features (as appropriate) of pulp & periapical lesions & osteomyelitis.
2 Sequelae of periapical abscess - summary of space infections, systemic complications & significance. 4. Periodontal Diseases : Etiopathogenesis, microbiology, clinical features, histopathology & radiological features (as appropriate) of gingivitis, gingival enlargements & periodontitis. Basic immunological mechanisms of periodontal disease to be highlighted. 5. Microbial infections of oral soft tissues : Microbiology, defence mechanisms including immunological aspects, oral manifestations, histopathogy and laboratory diagnosis of common bacterial, viral & fungal infections namely :- Bacterial : Tuberculosis, Syphilis, ANUG & its complications - Cancrum Oris. Viral : Herpes Simplex, Varicella zoster, Measles, Mumps & HIV infection. Fungal : Candidal infection. Apthous Ulcers. 6. Common non- inflammatory diseases involving the jaws : Etiopathogenesis, clinical features, radiological & laboratory values in diagnosis of : Fibrous dysplasia, Cherubism, Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Paget's disease, Cleidocranial dysplasia, Rickets, Achondroplasia, Marfan's syndrome & Down's syndrome. 7. Diseases of TM Joint : Ankylosis, summary of different types of arthritis & other developmental malformations, traumatic injuries & myofascial pain dysfunction syndrome. 8. Cysts of the Oral & Paraoral region : Classification, etiopathogenesis, clinical features, histopathology, laboratory & radiological features
3 (as appropriate) of Odontogenic cysts, Non-Odontogenic cysts, Pseudocysts of jaws & soft tissue cysts of oral & paraoral region. 9. Tumours of the Oral Cavity : Classification of Odontogenic, Non-Odontogenic & Salivary Gland Tumours. Etiopathogenesis, clinical features, histopathology, radiological features & laboratory diagnosis (as appropriate) of the following common tumours :- a) Odontogenic - all lesions. b) Non-odontogenic - Benign Epithelial - Papilloma, Keratoacanthoma & Naevi. - Benign Mesenchymal - Fibroma, Aggressive fibrous lesions, Lipoma, Haemangioma,Lymphangioma, Neurofibroma, Schwannoma, Chondroma, Osteoma & Tori. - Malignant Epithelial - Basal Cell Carcinoma, Verrucous Carcinoma, Squamous Cell carcinoma & Malignant Melanoma. - Malignant Mesenchymal - Fibrosarcoma, Osteosarcoma, Giant cell tumour, Chondrosarcoma, Angiosarcoma, Kaposi's sarcoma, Lymphomas, Ewing s sarcoma & 21 Other Reticuloendothelial tumours. c) Salivary Gland - Benign Epithelial neoplasms - Pleomorphic Adenoma, Warthin's tumour, & Oncocytoma. - Malignant Epithelial neoplasms - Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma,
4 Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma, Acinic Cell Carcinoma & Adenocarcinomas. d) Tumours of Disputed Origin - Congenital Epulis & Granular Cell Myoblastoma. e) Metastatic tumours - Tumors metastasizing to & from oral cavity & the routes of metastasis. 10. Traumatic, Reactive & Regressive lesions of Oral Cavity : Pyogenic & Giant cell granuloma, exostoses Fibrous Hyperplasia, Traumatic Ulcer & Traumatic Neuroma. Attrition, Abrasion, Erosion, Bruxism, Hypercementosis, Dentinal changes, Pulp calcifications & Resorption of teeth. Radiation effects of oral cavity, summary of Physical & Chemical injuries including allergic reactions of the oral cavity. Healing of Oral wounds & complications - Dry socket. 11. Non neoplastic Salivary Gland Diseases : Sialolithiasis, Sialosis, Sialadenitis, Xerostomia & Ptyalism. 12. Systemic Diseases involving Oral cavity : Brief review & oral manifestations, diagnosis & significance of common Blood, Nutritional, Hormonal & Metabolic diseases of Oral cavity. 13. Mucocutaneous Lesions : Etiopathogenesis, clinical features & histopathology of the following common lesions. Lichen Planus, Lupus Erythematosus, Pemphigus & Pemphigoid lesions, Erythema Multiforme,
5 Psoriasis, Scleroderma, Ectodermal Dysplasia, Epidermolysis bullosa & White sponge nevus Diseases of the Nerves : Facial neuralgias - Trigeminal & Glossopharyngeal. VII nerve paralysis, Causalgia. Psychogenic facial pain & Burning mouth syndrome. 15. Pigmentation of Oral & Paraoral region & Discolouration of teeth : causes & clinical manifestations. 16. Diseases of Maxillary Sinus : Traumatic injuries to sinus, Sinusitis, Cysts & Tumours involving antrum. 17. a) ORAL PRECANCER CANCER; Epidemiology, aetiology, clinical and histopatholotgical features, TNM classification. Recent advances in diagnosis, management and prevention. b) Biopsy : Types of biopsy, value of biopsy, cytology, histo chemistry & frozen sections in diagnosis of oral diseases. 18. Principles of Basic Forensic Odontology (Pre-clinical Forensic Odontology): Introduction, definition, aims & scope. Sex and ethnic (racial) differences in tooth morphology and histological age estimation Determination of sex & blood groups from buccal mucosa / saliva. Dental DNA methods Bite marks, rugae patterns & lip prints. Dental importance of poisons and corrosives. Overview of forensic medicine and toxicology
6 SYLLABUS ORAL MEDICINE AND RADIOLOGY Part-I ORAL MEDICINE AND DIAGNOSTIC AIDS SECTION (A) DIAGNOSTIC METHODS. (1) Definition and importance of Diagnosis and various types of diagnosis (2) Method of clinical examinations. (a) General Physical examination by inspection. (b) Oro-facial region by inspection, palpation and other means (c) To train the students about the importance, role, use of saliva and techniques of diagnosis of saliva as part of oral disease (d) Examination of lesions like swellings, ulcers, erosions, sinus, fistula, growths, pigmented lesions, white and red patches (e) Examination of lymph nodes (f) Forensic examination Procedures for post-mortem dental examination; maintaining dental records and their use in dental practice and post-mortem identification; jurisprudence and ethics. (3) Investigations (a) Biopsy and exfoliative cytology
7 (b) Hematological, Microbiological and other tests and investigations necessary for diagnosis and prognosis SECTION (B) DIAGNOSIS, DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS While learning the following chapters, emphasis shall be given only on diagnostic aspects including differential diagnosis (1) Teeth: Developmental abnormalities, causes of destruction of teeth and their sequelae and discoloration of teeth (2) Diseases of bone and Osteodystrophies: Development disorders: Anomalies, Exostosis and tori, infantile cortical hyperostosis, osteogenisis imperfecta, Marfans syndrome, osteopetrosis. Inflamation Injury, infection and sperad of infection,fascial space infections, osteoradionecrosis. Metabolic disorders Histiocytosis Endocrine Acro-megaly and hyperparathyroidism Miscellaneous Paget s disease, Mono and polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, Cherubism. (3) Temparomandibular joint: Developmental abnormalities of the condyle. Rheumatoid arthritis, Osteoarthritis, Sub-luxation and luxation. 31 (4) Common cysts and Tumors: CYSTS: Cysts of soft tissue: Mucocele and Ranula Cysts of bone: Odontogenic and nonodontogenic. TUMORS: Soft Tissue:
8 Epithelial: Papilloma, Carcinoma, Melanoma Connective tissue: Fibroma, Lipoma, Fibrosarcoma Vascular: Haemangioma, Lymphangioma Nerve Tissue: Neurofibroma, Traumatic Neuroma, Neurofibromatosis Salivary Glands: Pleomorphic adenoma, Adenocarcinoma, Warthin s Tumor, Adenoid cystic carcinoma. Hard Tissue: Non Odontogenic: Osteoma, Osteosarcoma, Osteoclastoma, Chondroma, Chandrosarcoma, Central giant cell rumor, and Central haemangioma Odontogenic: Enameloma, Ameloblastoma, Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic tumor, Adenomatoid Odontogenic tumor, Periapical cemental dysphasia and odontomas (5) Periodontal diseases: Gingival hyperplasia, gingivitis, periodontitis, pyogenic granuloma (6) Granulomatous diseases: Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis, Midline lethal granuloma, Crohn s Disease and Histiocytosis X (7) Miscellaneous Disorders: Burkitt lymphoma, sturge Weber syndrome, CREST syndrome, rendu-osler-weber disease SECTION (C): ORAL MEDICINE AND THERAPEUTICS. The following chapters shall be studied in detail including the eiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, investigations, differential diagnosis, management and prevention (1) Infections of oral and paraoral structures:
9 Bacterial: Streptococcal, tuberculosis, syphillis, vincents, leprosy, actinomycosis, diphtheria and tetanus Fungal: Candida albicans Virus: Herpes simplex, herpes zoster, ramsay hunt syndrome, measles, herpangina, mumps, infectious mononucleosis, AIDS and hepatitis-b (2) Important common mucosal lesions: White lesions: Chemical burns, leukodema, leukoplakia, fordyce spots, stomatitis nicotina palatinus, white sponge nevus, candidiasis, lichenplanus, discoid lupus erythematosis Veiculo-bullous lesions: Herpes simplex, herpes zoster, herpangina, bullous lichen planus, pemphigus, cicatricial pemphigoid erythema multiforme. Ulcers: Acute and chronic ulcers Pigmented lesions: Exogenous and endogenous Red lesions: Erythroplakia, stomatitis venenata and medicamentosa, erosive lesions and denture sore mouth. (3) Cervico-facial lymphadenopathy (4) Facial pain: (i) Organic pain: Pain arising from the diseases of orofacial tissues like teeth, pulp, gingival, periodontal tissue, mucosa, tongue, muscles, blood vessels, lymph tissue, bone, paranasal sinus, salivary glands etc., (ii) Pain arising due to C.N.S. diseases: (a) Pain due to intracranial and extracranial involvement of cranial nerves. (Multiple sclerosis, cerebrovascular diseases, trotter s syndrome etc.) (b) Neuralgic pain due to unknown causes: Trigeminal neuralgia, glossopharyngeal
10 neuralgia, sphenopalatine ganglion neuralgia, periodic migrainous neuralgia and atypical facial pain (iii) Referred pain: Pain arising from distant tissues like heart, spine etc., (5) Altered sensations: Cacogeusia, halitosis (6) Tongue in local and systemic disorders: (Aglossia, ankyloglossia, bifid tongue, fissured tongue, scrotal tongue, macroglossia, microglossia, geographic tongue, median rhomboid glossitis, depapillation of tongue, hairy tongue, atrophic tongue, reactive lymphoid hyperplasia, glossodynia, glossopyrosis, ulcers, white and red patches etc.) (7) Oral manifestations of: 32 (i) Metabolic disordeers: (a) Porphyria (b) Haemochromatosis (c) Histocytosis X diseases (ii) Endocrine disorders: (a) Pituitary: Gigantism, acromegaly, hypopitutarism (b) Adrenal cortex: Addison s disease (Hypofuntion) Cushing s syndrome (Hyperfunction) (c) Parathyroid glands: Hyperparathyroidism. (d) Thyroid gland: (Hypothyroidism) Cretinism, myxedema (e) Pancreas: Diabetes (iii) Nutritional deficiency: Vitamins: riboflavin, nicotinic acid, folic acid Vitamin B12, Vitamin C (Scurvy) (iv) Blood disorders: (a) Red blood cell diseases
11 Defficiency anemias: (Iron deficiency, plummer vinson syndrome, pernicious anemia) Haemolytic anemias: (Thalassemia, sickle cell anemia, erythroblastosis fetalis) Aplastic anemia Polycythemia (b) White Blood cell diseases Neutropenia, cyclic neutropenia, agranulocytosis, infectious mononeucleosis and leukemias (c) Haemorrhagic disorders: Thrombocytopenia, purpura, hemophillia, chrismas disease and von willebrand s disease (8) Disease of salivary glands: (i) Development distrubances: Aplasia, atresia and aberration (ii) Functional disturbances:xerostomia, ptyalism (iii) Inflammatory conditions: Nonspecific sialadenitis, mumps, sarcoidosis heerdfort s syndrome (Uveoparotid fever), Necrotising sialometaplasia (iv) Cysts and tumors: Mucocele, ranula, pleomorphic adenoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma (v) Miscellaneous: Sialolithiasis, sjogren s syndrome, mikuliez s disease and sialosis (9) Dermatological diseases with oral manifestations: (a) Ectodermal dysplasia (b) Hyperkerotosis palmarplantaris with periodont0opathy (c) Scleroderma (d) Lichen planus including ginspan s syndrome (e) Luplus erythematosus (f) Pemphigus (g) Erythema multiforme (h) Psoriasis (10) Immunological diseases with oral manifestations (a) Leukemia (b) Lymphomas (c) Multiple mycloma (d) AIDS clinical manifestations, opportunistic infections, neoplasms (e) Thrombcytopenia (f) Lupus erythematosus (g) Scleroderma (h) dermatomyositis (I) Submucous fibrosis (j) Rhemtoid arthritis (k) Recurrent oral
12 ulcerations including behcet s syndrome and reiter s syndrome (11) Allergy: Local allergic reactions, anaphylaxis, serum sickness (local and systemic allergic manifestations to food drugs and chemicals) (12) Foci of oral infection and their ill effects on general health (13) Management of dental problems in medically comrpomised persons: (i) Physiological changes: Puberty, pregnancy and menopause (ii) The patients suffering with cardiac, respiratory, liver, kidney and bleeding disorders, hypertension, diabetes and AIDS. Post-irradiated patients. (14) Precancerous lesions and conditions (15) Nerve and muscle diseases: (i) Nerves: (a) Neuropraxia (b) Neurotemesis (c) Neuritis (d) Facial nerve paralysis including Bell s palsy, Heerfordt s syndrome, Melkerson Rosenthel syndrome and ramsay hunt syndrome (e) Neuroma (f) Neurofibromatosis (g) Frey syndrome (ii) Muscles: (a) Myositis ossificans (b) Myofascial pain dysfunction syndrome (c) Trismus (16) Forensic odontology: (a) Medicolegal aspects of orofacial injuries (b) Identification of bite marks (c) Determination of age and sex (d) Identification of cadavers by dental appliances, Restorations and tissue remanants 33 (17) Therapeutics: General therapeutic measures drugs commonly used in oral medicine viz., antibiotics, chemotherapeutic agents, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs, astringents, mouth washes, styptics, demelucents, local surface anaesthetic, sialogogues, antisialogogues and drugs used in the treatment of malignancy
13 Part II BEHAVIOURAL SCIENCES AND ETHICS. Part III ORAL RADIOLOGY (1) Scope of the subject and history of origin (2) Physics of radiation: (a) Nature and types of radiations (b) Source of radiations (c) Production of X-rays (d) Properties of X-rays (e) Compton effect (f) Photoelectric effect (g) Radiation measuring units (3) Biological effects of radiation (4) Radiation safety and protection measures (5) Principles of image production (6) Radiographic techniques: (i) Intra-Oral: (a) Periapical radiographs (Bisecting and parallel technics) (b) Bite wing radiographs (c) Occlusal radiographs (ii) Extra-oral: (a) Lateral projections of skull and jaw bones and paranasal sinuses (c) Cephalograms (d) Orthopantomograph (e) Projections of temperomandibular joint and condyle of mandible (f) Projections for Zygomatic arches (iii) Specialised techniques: (a) Sialography (b) Xeroradiography (c) Tomography (7) Factors in production of good radiographs: (a) K.V.P. and ma.of X-ray machine (b) Filters (c) Collimations (d) Intensifying screens (e) Grids (f) X-ray films (g) Exposure time (h) Techniques (i) Dark room (j) Developer and fixer solutions (k) Film processing (8) Radiographic normal anatomical landmarks (9) Faculty radiographs and artefacts in radiographs (10) Interpretation of radiographs in various abnormalities of teeth, bones and other orofacial tissues
14 (11) Principles of radiotherapy of oro-facial malignancies and complications of radiotherapy (12) Cantrast radiography and basic knowledge of radio-active isotopes (13) Radiography in Forensic Odontoloy - Radiographic age estimation and post-mortem radiographic methods PRACTICALS / CLINICALS: 1. Student is trained to arrive at proper diagnosis by following a scientific and systematic proceedure of history taking and examination of the orofacial region. Training is also imparted in management wherever possible. Training also shall be imparted on saliva diagnostic procedures. Training also shall be imparted in various radiographic proceedures and interpretation of radiographs. 2. In view of the above each student shall maintain a record of work done, which shall be evaluated for marks at the time of university examination 3. The following is the minimum of prescribed work for recording (a) Recording of detailed case histories of interesting cases. 10 (b) Intra-oral radiographs (Periapical, bitewing, occlusal) 25 (c) Saliva diagnostic check as routine procedure
4A.4.2 SYLLABUS ( Including Teaching Hours.)
 4A.4.2 SYLLABUS ( Including Teaching Hours.) MUST KNOW 1.Oral medicine and diagnostic AIDS: Section A-Diagnostic Methods 06 HRS (1) Definition and importance of Diagnosis and various types of diagnosis
4A.4.2 SYLLABUS ( Including Teaching Hours.) MUST KNOW 1.Oral medicine and diagnostic AIDS: Section A-Diagnostic Methods 06 HRS (1) Definition and importance of Diagnosis and various types of diagnosis
Syllabus Innovation. 4 th year BDS for Oral Medicine And Radiology TOPICS: 1.Oral medicine and diagnostic AIDS: Section A-Diagnostic Methods
 Syllabus Innovation 4 th year BDS for Oral Medicine And Radiology TOPICS: (Must Know) 1.Oral medicine and diagnostic AIDS: Section A-Diagnostic Methods (1) Definition and importance of Diagnosis and various
Syllabus Innovation 4 th year BDS for Oral Medicine And Radiology TOPICS: (Must Know) 1.Oral medicine and diagnostic AIDS: Section A-Diagnostic Methods (1) Definition and importance of Diagnosis and various
1. Special precautions/ contraindication of anaesthesia and various
 Third Year 1. General Medicine GUIDELINES : Special emphasis should be given throughout on the importance of various diseases as applicable to dentistry. 1. Special precautions/ contraindication of anaesthesia
Third Year 1. General Medicine GUIDELINES : Special emphasis should be given throughout on the importance of various diseases as applicable to dentistry. 1. Special precautions/ contraindication of anaesthesia
ORAL PATHOLOGY & ORAL MICROBIOLOGY III BDS
 ORAL PATHOLOGY & ORAL MICROBIOLOGY III BDS 1. INTRODUCTION:. A bird's eye view of the different pathological processes involving the oral cavity & oral cavity involvement in systemic diseases to be brought
ORAL PATHOLOGY & ORAL MICROBIOLOGY III BDS 1. INTRODUCTION:. A bird's eye view of the different pathological processes involving the oral cavity & oral cavity involvement in systemic diseases to be brought
Contents. 3 Diagnostic Tests and Studies Introduction Examination... 27
 Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Surface Landmarks... 1 1.3 Oral Mucosa... 3 1.4 Tongue... 5 1.5 Floor of Mouth... 6 1.6 Palate... 6 1.7 Dentition... 7 1.8 Temporomandibular Joint...
Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Surface Landmarks... 1 1.3 Oral Mucosa... 3 1.4 Tongue... 5 1.5 Floor of Mouth... 6 1.6 Palate... 6 1.7 Dentition... 7 1.8 Temporomandibular Joint...
Contents. 1 Normal Anatomy Introduction... 17
 Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 Introduction... 1 Surface Landmarks... 1 Oral Mucosa... 1 Tongue... 4 Floor of Mouth... 6 Palate... 7 Dentition... 7 Temporomandibular Joint... 9 Innervation... 10 Jaws and
Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 Introduction... 1 Surface Landmarks... 1 Oral Mucosa... 1 Tongue... 4 Floor of Mouth... 6 Palate... 7 Dentition... 7 Temporomandibular Joint... 9 Innervation... 10 Jaws and
Vascular. Extravasated blood. Melanocytic. Tattoo. Epidermolysis bullosa. Lichen planus. Pemphigoid Pemphigus Lupus. Candidosis. Surface Epithelial
 Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Syllabus for Undergraduate training program ORAL MEDICINE SL NO TOPIC TIME. Definition, Scope & clinical applications, Orientation of the Department
 Syllabus for Undergraduate training program Total no 90 hours (Theory) ORAL MEDICINE SL NO TOPIC TIME Third Year 20 hrs 1 Introduction and scope Definition, Scope & clinical applications, Orientation of
Syllabus for Undergraduate training program Total no 90 hours (Theory) ORAL MEDICINE SL NO TOPIC TIME Third Year 20 hrs 1 Introduction and scope Definition, Scope & clinical applications, Orientation of
The Oral Cavity. Image source:
 The Oral Cavity Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The major structures of the oral cavity are the lips, the teeth, the alveolar ridges (bony areas that
The Oral Cavity Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The major structures of the oral cavity are the lips, the teeth, the alveolar ridges (bony areas that
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT
 MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Index. Dent Clin N Am 49 (2005) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Dent Clin N Am 49 (2005) 273 278 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acanthosis nigricans, familial, 251 Amalgam tattoo, 197 198 Amphotericin B, 62 Ankyloglossia, 11 Anti-inflammatory
Dent Clin N Am 49 (2005) 273 278 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acanthosis nigricans, familial, 251 Amalgam tattoo, 197 198 Amphotericin B, 62 Ankyloglossia, 11 Anti-inflammatory
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinomycosis, 200 201 Adenoid cystic carcinoma, 148 150 Adenomatoid odontogenic tumors, 134, 135 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, 134 Ameloblastoma,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinomycosis, 200 201 Adenoid cystic carcinoma, 148 150 Adenomatoid odontogenic tumors, 134, 135 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, 134 Ameloblastoma,
THE TONGUE. In Clinical Diagnosis
 THE TONGUE In Clinical Diagnosis A Colour Atlas of The Tongue in Clinical Diagnosis D.W. BEAVEN S.E. BROOKS BATES Guide to Physical Examination Lynn s. Bickley רויטל רחימי, תום כספי פנימית ב', תל-השומר
THE TONGUE In Clinical Diagnosis A Colour Atlas of The Tongue in Clinical Diagnosis D.W. BEAVEN S.E. BROOKS BATES Guide to Physical Examination Lynn s. Bickley רויטל רחימי, תום כספי פנימית ב', תל-השומר
Index. oralmaxsurgery.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
TANYA A. WRIGHT, DDS OBJECTIVES
 TANYA A. WRIGHT, DDS OBJECTIVES One will be able to recognize pathological entities One will be able to establish a reasonable differential diagnosis One will be able to identify various types of lesions
TANYA A. WRIGHT, DDS OBJECTIVES One will be able to recognize pathological entities One will be able to establish a reasonable differential diagnosis One will be able to identify various types of lesions
SYLLABUS OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY
 MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY AND SID SYLLABUS OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY (State examination) ACADEMIC YEAR 2015 2016 1. Asepsis
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY AND SID SYLLABUS OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY (State examination) ACADEMIC YEAR 2015 2016 1. Asepsis
SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES. Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS
 SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS Salivary Glands Overview Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary glands - Types 3 Major Salivary Glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual
SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS Salivary Glands Overview Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary glands - Types 3 Major Salivary Glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual
1. Oral Medicine & Radiology
 Fourth Year 1. Oral Medicine & Radiology AIMS : (1) To train the students to diagnose the common disorders of Orofacial region by clinical examination and with the help of such investigations as may be
Fourth Year 1. Oral Medicine & Radiology AIMS : (1) To train the students to diagnose the common disorders of Orofacial region by clinical examination and with the help of such investigations as may be
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis
 RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY ORAL CAVITY. Oral Cavity Subsites 4/10/2013 LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL MUCOUS MEMBRANES PALATE TONGUE ORAL LYMPHOID TISSUES
 LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
CAMOSUN COLLEGE School of Health & Human Services Dental Programs. DHYG 321 Oral Science COURSE OUTLINE
 CAMOSUN COLLEGE School of Health & Human Services Dental Programs 2013 COURSE OUTLINE 1. Instructor Information (a) Instructor Lynne Viczko (b) Office hours Posted on office door (c) Location Dental Building
CAMOSUN COLLEGE School of Health & Human Services Dental Programs 2013 COURSE OUTLINE 1. Instructor Information (a) Instructor Lynne Viczko (b) Office hours Posted on office door (c) Location Dental Building
SYSTEMIC DISEASES IN THE HEAD AND NECK REGION
 SYSTEMIC DISEASES IN THE HEAD AND NECK REGION DEFINITION OF SYSTEMIC DISEASE More organs involved in the process of disease Very often combined with developmental disorders 1000-1500 syndromes written
SYSTEMIC DISEASES IN THE HEAD AND NECK REGION DEFINITION OF SYSTEMIC DISEASE More organs involved in the process of disease Very often combined with developmental disorders 1000-1500 syndromes written
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
That. Name QUIZ. 60 SEPTEMBER 2017 // dentaltown.com
 QUIZ Name That General dentists are first in the line of practitioners that patients see for an oral lesion evaluation; therefore, a sound understanding of oral mucosal diseases and their clinical presentation
QUIZ Name That General dentists are first in the line of practitioners that patients see for an oral lesion evaluation; therefore, a sound understanding of oral mucosal diseases and their clinical presentation
General Pathology Theory Syllabus for II B.D.S.
 General Pathology Theory Syllabus for II B.D.S. Sr. No. Topic (Must Know) (Desirable to know) 1.Introduction to Pathology - Different sections in pathology - The Cell in health - Normal cell structure
General Pathology Theory Syllabus for II B.D.S. Sr. No. Topic (Must Know) (Desirable to know) 1.Introduction to Pathology - Different sections in pathology - The Cell in health - Normal cell structure
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Palatal Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Palatal Lesions Palatal Masses Periapical Abscess Torus Palatinus Mucocele Lymphoid Hyperplasia Adenomatous Hyperplasia Benign Salivary Neoplasms Malignant Salivary
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Palatal Lesions Palatal Masses Periapical Abscess Torus Palatinus Mucocele Lymphoid Hyperplasia Adenomatous Hyperplasia Benign Salivary Neoplasms Malignant Salivary
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions. An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling. John L. Alonge, MS, DDS
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
IV. PREREQUISITES: COMPLETION OF ALL PREREQUISITE DENTAL HYGIENE COURSES WITH A FINAL GRADE OF "C" OR BETTER.
 I. DH 154: ORAL PATHOLOGY II. PREPARED BY: JOY OGAMI AVILA, R.D.H., M.S. III. REVISED FOR: SPRING 2016 IV. PREREQUISITES: COMPLETION OF ALL PREREQUISITE DENTAL HYGIENE COURSES WITH A FINAL GRADE OF "C"
I. DH 154: ORAL PATHOLOGY II. PREPARED BY: JOY OGAMI AVILA, R.D.H., M.S. III. REVISED FOR: SPRING 2016 IV. PREREQUISITES: COMPLETION OF ALL PREREQUISITE DENTAL HYGIENE COURSES WITH A FINAL GRADE OF "C"
Oral Cancer Dr Christine Goodall Consultant Oral Surgeon University of Glasgow Dental School
 Oral Cancer Dr Christine Goodall Consultant Oral Surgeon University of Glasgow Dental School christine.goodall@glasgow.ac.uk Locations Lip, mouth, oropharynx Tongue, floor of mouth, buccal mucosa, palate,
Oral Cancer Dr Christine Goodall Consultant Oral Surgeon University of Glasgow Dental School christine.goodall@glasgow.ac.uk Locations Lip, mouth, oropharynx Tongue, floor of mouth, buccal mucosa, palate,
Lamar Institute of Technology DHYG Course Syllabus Spring
 Lamar Institute of Technology DHYG 1339 Course Syllabus Spring Instructor: Debbie Brown, R.D.H., MS dwbrown@lit.edu TABLE OF CONTENTS SCHEDULE AND ASSIGNMENTS... 3 COURSE DESCRIPTION... 5 COURSE GOALS
Lamar Institute of Technology DHYG 1339 Course Syllabus Spring Instructor: Debbie Brown, R.D.H., MS dwbrown@lit.edu TABLE OF CONTENTS SCHEDULE AND ASSIGNMENTS... 3 COURSE DESCRIPTION... 5 COURSE GOALS
Oral Tumors in Dogs Gingival Enlargement
 Oral Tumors in Dogs Is that lump you re seeing in your dog s mouth normal? Or is it something to be concerned about? The easiest way to know for sure is to have it evaluated by a veterinarian. When you
Oral Tumors in Dogs Is that lump you re seeing in your dog s mouth normal? Or is it something to be concerned about? The easiest way to know for sure is to have it evaluated by a veterinarian. When you
IV. PREREQUISITES: COMPLETION OF ALL PREREQUISITE DENTAL HYGIENE COURSES WITH A FINAL GRADE OF "C" OR BETTER.
 I. DH 154: ORAL PATHOLOGY II. PREPARED BY: JOY OGAMI AVILA, R.D.H., M.S. III. REVISED FOR: SPRING 2014 IV. PREREQUISITES: COMPLETION OF ALL PREREQUISITE DENTAL HYGIENE COURSES WITH A FINAL GRADE OF "C"
I. DH 154: ORAL PATHOLOGY II. PREPARED BY: JOY OGAMI AVILA, R.D.H., M.S. III. REVISED FOR: SPRING 2014 IV. PREREQUISITES: COMPLETION OF ALL PREREQUISITE DENTAL HYGIENE COURSES WITH A FINAL GRADE OF "C"
4Ps LUMPS AND BUMPS B.L.&T. BUMPS, LUMPS, AND TATTOOS. Most Common BUMP in the oral cavity Fibroma INTERDENTAL PAPILLAE LESIONS
 B.L.&T. BUMPS, LUMPS, AND TATTOOS LUMPS AND BUMPS DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS FOR LUMPS AND BUMPS Traumatic Fibroma Papilloma Epulis Fissuratum Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia Lesions of Attached Gingiva
B.L.&T. BUMPS, LUMPS, AND TATTOOS LUMPS AND BUMPS DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS FOR LUMPS AND BUMPS Traumatic Fibroma Papilloma Epulis Fissuratum Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia Lesions of Attached Gingiva
SYLLABUS FOR EXAMINATION OF PRECLINICS IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY
 SYLLABUS FOR EXAMINATION OF PRECLINICS IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY 1. Asepsis and antisepsis in the oral and maxillofacial surgery. Preparation of the hands of the surgeon and the operative field
SYLLABUS FOR EXAMINATION OF PRECLINICS IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY 1. Asepsis and antisepsis in the oral and maxillofacial surgery. Preparation of the hands of the surgeon and the operative field
TRICOLLEGIATE DIPLOMA OF MEMBERSHIP IN ORAL SURGERY (M. Oral Surgery) APPENDIX A LEARNING OUTCOMES & BLUEPRINT
 TRICOLLEGIATE DIPLOMA OF MEMBERSHIP IN ORAL SURGERY (M. Oral Surgery) APPENDIX A LEARNING OUTCOMES & BLUEPRINT A - LEARNING OUTCOMES In brackets below the headings are cross references to corresponding
TRICOLLEGIATE DIPLOMA OF MEMBERSHIP IN ORAL SURGERY (M. Oral Surgery) APPENDIX A LEARNING OUTCOMES & BLUEPRINT A - LEARNING OUTCOMES In brackets below the headings are cross references to corresponding
Oral Pathology Syllabus for English-Speaking Students
 Oral Pathology Syllabus for English-Speaking Students Academic Hours Academic Hours in Years and Semesters I year II year III year IV year V year DISCIPLINE Semester Exam Total Lectures Practicals I II
Oral Pathology Syllabus for English-Speaking Students Academic Hours Academic Hours in Years and Semesters I year II year III year IV year V year DISCIPLINE Semester Exam Total Lectures Practicals I II
Diseases of oral cavity
 Diseases of oral cavity Diseases of Teeth and Supporting Structures Inflammatory/Reactive Lesions Infections Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions Odontogenic Cysts
Diseases of oral cavity Diseases of Teeth and Supporting Structures Inflammatory/Reactive Lesions Infections Oral Manifestations of Systemic Disease Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions Odontogenic Cysts
Diagnostic sieve. Looking Beyond the Vermillion Border. Time bombs for medical GPs! Normal oral mucosa
 Sat 12 June 2010 Millennium WS 28 + 38 2.00-2.55; 3.05-4.00 PM Looking Beyond the Vermillion Border Laurence J. Walsh BDSc, PhD, DDSc, FFOP(RCPA), GCEd, FICD, FPFA, FADI, FIADFE The University of Queensland
Sat 12 June 2010 Millennium WS 28 + 38 2.00-2.55; 3.05-4.00 PM Looking Beyond the Vermillion Border Laurence J. Walsh BDSc, PhD, DDSc, FFOP(RCPA), GCEd, FICD, FPFA, FADI, FIADFE The University of Queensland
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Oral Medicine. Dr. Qianming Ian CHEN
 Oral Medicine Dr. Qianming Ian CHEN ORAL MEDICINE Oral medicine is the specialty of dentistry that is concerned with the oral health care of medically compromised patients and with the diagnosis and nonsurgical
Oral Medicine Dr. Qianming Ian CHEN ORAL MEDICINE Oral medicine is the specialty of dentistry that is concerned with the oral health care of medically compromised patients and with the diagnosis and nonsurgical
SYLLABUS FOR PG STUDENTS
 Basic Paper SYLLABUS FOR PG STUDENTS Applied anatomy of head & neck Development of face, paranasal sinuses & the associated structures & their anomalies, cranial & facial bones, TMJ anatomy & function,
Basic Paper SYLLABUS FOR PG STUDENTS Applied anatomy of head & neck Development of face, paranasal sinuses & the associated structures & their anomalies, cranial & facial bones, TMJ anatomy & function,
TNAGD- ICD 10 Codes- Expanded List A408 Other streptococcal sepsis A409 Streptococcal sepsis, unspecified A498 Other bacterial infections of
 TNAGD- ICD 10 Codes- Expanded List A408 Other streptococcal sepsis A409 Streptococcal sepsis, unspecified A498 Other bacterial infections of unspecified site A5052 Hutchinson's teeth A5131 Condyloma latum
TNAGD- ICD 10 Codes- Expanded List A408 Other streptococcal sepsis A409 Streptococcal sepsis, unspecified A498 Other bacterial infections of unspecified site A5052 Hutchinson's teeth A5131 Condyloma latum
Shawn A. McClure D.M.D., M.D. Miami Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Professor, Director of Research Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery
 Shawn A. McClure D.M.D., M.D. Miami Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Professor, Director of Research Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery NOVA/NSU COLLEGE OF DENTAL MEDICINE 1 Diseases of Head
Shawn A. McClure D.M.D., M.D. Miami Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Professor, Director of Research Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery NOVA/NSU COLLEGE OF DENTAL MEDICINE 1 Diseases of Head
Clinical Oral Medicine and Pathology
 Clinical Oral Medicine and Pathology Jean M. Bruch Nathaniel S. Treister Clinical Oral Medicine and Pathology Jean M. Bruch, DMD, MD Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Boston, MA jean_bruch@meei.harvard.edu
Clinical Oral Medicine and Pathology Jean M. Bruch Nathaniel S. Treister Clinical Oral Medicine and Pathology Jean M. Bruch, DMD, MD Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Boston, MA jean_bruch@meei.harvard.edu
ORAL PATHOLOGY AND MICROBIOLOGY
 ORAL PATHOLOGY AND MICROBIOLOGY Oral Pathology deals with the nature of oral diseases, their causes, processes and effects. I t relates the clinical manifestation of oral diseases to physiologic and anatomic
ORAL PATHOLOGY AND MICROBIOLOGY Oral Pathology deals with the nature of oral diseases, their causes, processes and effects. I t relates the clinical manifestation of oral diseases to physiologic and anatomic
Overview. Call: You will not be assigned to be on call during this rotation. Overall Objectives
 Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Anatomical Pathology and Radiology Rotation Resident PGY5 St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton, McMaster Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) Overview
Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Anatomical Pathology and Radiology Rotation Resident PGY5 St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton, McMaster Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) Overview
Syllabus for Dental Anatomy and Dental Histology (I BDS) Dental Anatomy. know -
 Syllabus for Dental Anatomy and Dental Histology (I BDS) Dental Anatomy Sr.No Topic Must Know 1 Introduction Definitions and Nomenclature in Dental Anatomy Tooth numbering systems Differences between permanent
Syllabus for Dental Anatomy and Dental Histology (I BDS) Dental Anatomy Sr.No Topic Must Know 1 Introduction Definitions and Nomenclature in Dental Anatomy Tooth numbering systems Differences between permanent
Syllabus and Examination pattern for Under Graduate Dental Course Part II NOTIFICATION
 1 Syllabus and Examination pattern for Under Graduate Dental Course Part II NOTIFICATION In exercise of the powers, conferred under section 26 of Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences University, in its
1 Syllabus and Examination pattern for Under Graduate Dental Course Part II NOTIFICATION In exercise of the powers, conferred under section 26 of Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences University, in its
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alveolar osteitis (dry socket), periodontal pain due to, 436 Aphthous stomatitis, recurrent, mucosal pain due to, 439 440 Arthrocentesis/arthroscopy,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alveolar osteitis (dry socket), periodontal pain due to, 436 Aphthous stomatitis, recurrent, mucosal pain due to, 439 440 Arthrocentesis/arthroscopy,
Lesions & Lifestyles
 Lesions & Lifestyles attended a 3 hour Continuing Education Seminar on Oral Pathology presented by Nancy Dewhirst, RDH,BS on (date) at (location):. Course material is directly related patient care. Notes:
Lesions & Lifestyles attended a 3 hour Continuing Education Seminar on Oral Pathology presented by Nancy Dewhirst, RDH,BS on (date) at (location):. Course material is directly related patient care. Notes:
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Gingival Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
الطلاوة = Leukoplakia LEUKOPLAKIA
 LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
Analysis of 340 Cases Visited Rizgary Hospital in Hawler Vol.:8 No.:2 2011
 MDJ Analysis of 340 Cases Visited Rizgary Hospital in Hawler City during 2009-2010 Dr. Shahen Ali Ahmed,* Dr. Ahmed Abdulla Haeder, ** Dr. Hajer Ibrahem Abdulla, *** Abstract During two years period from
MDJ Analysis of 340 Cases Visited Rizgary Hospital in Hawler City during 2009-2010 Dr. Shahen Ali Ahmed,* Dr. Ahmed Abdulla Haeder, ** Dr. Hajer Ibrahem Abdulla, *** Abstract During two years period from
The resident will be assigned to be on call with the Oral and Maxillofacial service. Call will be set according to PARO guidelines.
 Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Resident on the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS) Rotation St. Catharines General Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) During the second year
Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Resident on the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS) Rotation St. Catharines General Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) During the second year
Vitamins Minerals Chapter 12
 DH 250 Water soluble B1 Thiamin B2 Riboflavin B3 Niacin Vitamins Minerals Chapter 12 Role RDA Source Deficiency Toxicity Clinical Use intermediary coenzymes 1.2mg 1.1mg 1.2mg 1.1mg 16mg 14mg dairy B6 Pyridoxine
DH 250 Water soluble B1 Thiamin B2 Riboflavin B3 Niacin Vitamins Minerals Chapter 12 Role RDA Source Deficiency Toxicity Clinical Use intermediary coenzymes 1.2mg 1.1mg 1.2mg 1.1mg 16mg 14mg dairy B6 Pyridoxine
Pathology of the Alimentary System. Lecture 3 Teeth, tonsils, salivary glands & tongue
 Systemic Pathology I - VPM 221 Pathology of the Alimentary System Lecture 3 Teeth, tonsils, salivary glands & tongue Enrique Aburto Fall 2014 II. Diseases of teeth & dental tissues Structure & function
Systemic Pathology I - VPM 221 Pathology of the Alimentary System Lecture 3 Teeth, tonsils, salivary glands & tongue Enrique Aburto Fall 2014 II. Diseases of teeth & dental tissues Structure & function
Oral cavity cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all malignancies and is a significant worldwide health problem.
 Oral cavity cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all malignancies and is a significant worldwide health problem. Majority are SCC ( 5-year survival rate only about 50-60% ) Many SCC arrive from premalignant
Oral cavity cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all malignancies and is a significant worldwide health problem. Majority are SCC ( 5-year survival rate only about 50-60% ) Many SCC arrive from premalignant
BLOCK 12 Viruses of the ENT
 BLOCK 12 Viruses of the ENT Acute infections Introduction Pharyngitis, Common cold, Sinusitis, Otitis media Recurrent infections Herpes zoster oticus Chronic infections HIV and ENT manifestations Neoplasms
BLOCK 12 Viruses of the ENT Acute infections Introduction Pharyngitis, Common cold, Sinusitis, Otitis media Recurrent infections Herpes zoster oticus Chronic infections HIV and ENT manifestations Neoplasms
Neoplasms that present as a swelling in the neck may be either
 Problems in otolaryngology Inflammatory swellings Viral and bacterial infection are frequent causes of swellings in the neck. Enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes is most likely but a dormant branchial
Problems in otolaryngology Inflammatory swellings Viral and bacterial infection are frequent causes of swellings in the neck. Enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes is most likely but a dormant branchial
RISK FACTORS OF BURNING MOUTH SYNDROME: UN UPDATE
 RISK FACTORS OF BURNING MOUTH SYNDROME: UN UPDATE Cristina Popa, Carmen Stelea, Eugenia Popescu Department of Oral and Maxilo-facial Surgery Abstract: Burning mouth syndrome has never been associated with
RISK FACTORS OF BURNING MOUTH SYNDROME: UN UPDATE Cristina Popa, Carmen Stelea, Eugenia Popescu Department of Oral and Maxilo-facial Surgery Abstract: Burning mouth syndrome has never been associated with
CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 ORAL SURGERY TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION
 TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
Metabolic & Endocrine disorders of bone:
 Metabolic & Endocrine disorders of bone: Osteoporosis: Bone apposition < bone resorption Risk factors: Postmenopausal women Hyperthyroidism Hyperparathyroidism Cushing s syndrome bone quantity: thin cortex
Metabolic & Endocrine disorders of bone: Osteoporosis: Bone apposition < bone resorption Risk factors: Postmenopausal women Hyperthyroidism Hyperparathyroidism Cushing s syndrome bone quantity: thin cortex
Preface... Contributors... 1 Embryology... 3
 Contents Preface... Contributors... vii xvii I. Pediatrics 1 Embryology... 3 Pearls... 3 Branchial Arch Derivatives... 3 Branchial Arch Anomalies: Cysts, Sinus, Fistulae... 4 Otologic Development... 4
Contents Preface... Contributors... vii xvii I. Pediatrics 1 Embryology... 3 Pearls... 3 Branchial Arch Derivatives... 3 Branchial Arch Anomalies: Cysts, Sinus, Fistulae... 4 Otologic Development... 4
PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours)
 PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours) First Semester (9 Credit Hours) OSRG 701 Oral Surgery I 1 OSRG 791 Oral Surgery Clinics I 2 OSRG 706 Applied Surgical Anatomy 1 OSRG 707 Pain and Anxiety Control 1
PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours) First Semester (9 Credit Hours) OSRG 701 Oral Surgery I 1 OSRG 791 Oral Surgery Clinics I 2 OSRG 706 Applied Surgical Anatomy 1 OSRG 707 Pain and Anxiety Control 1
Dental Care and Health An Update. Dr. Ranjini Pillai, DDS, MPH, FAGD, FICOI
 Dental Care and Health An Update Dr. Ranjini Pillai, DDS, MPH, FAGD, FICOI WHO s Definition of Health? Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of
Dental Care and Health An Update Dr. Ranjini Pillai, DDS, MPH, FAGD, FICOI WHO s Definition of Health? Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of
A SURVEY OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL BIOPSIES IN CHILDREN. A SINGLE-CENTER RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 20 YEARS IN PELOTAS-BRAZIL
 www.fob.usp.br/jaos or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;6(6):97-402 A SURVEY OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL BIOPSIES IN CHILDREN. A SINGLE-CENTER RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Giana da Silveira LIMA, Silvia Terra
www.fob.usp.br/jaos or www.scielo.br/jaos J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;6(6):97-402 A SURVEY OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL BIOPSIES IN CHILDREN. A SINGLE-CENTER RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Giana da Silveira LIMA, Silvia Terra
INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I. Immunopathology Part I
 INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I Immunopathology Part I Nonspecific & T Cell Mediated Mucosal Inflammatory Lesions Nonspecific and Idiopathic Mucositis Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune T cell mediated Immunoglobulin
INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I Immunopathology Part I Nonspecific & T Cell Mediated Mucosal Inflammatory Lesions Nonspecific and Idiopathic Mucositis Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune T cell mediated Immunoglobulin
Essentials of Oral Pathology
 Contents... 1. Developmental Anomalies of Oral and Paraoral Structures... 1 63 Introduction 1 Developmental anomalies of oral soft tissues 1 Anomalies of lips and palate 1 Lip pits and fistulas 1 Double
Contents... 1. Developmental Anomalies of Oral and Paraoral Structures... 1 63 Introduction 1 Developmental anomalies of oral soft tissues 1 Anomalies of lips and palate 1 Lip pits and fistulas 1 Double
Oral Health & HIV. Professor Sudeshni Naidoo Department of Community Dentistry University of the Western Cape
 Oral Health & HIV Professor Sudeshni Naidoo Department of Community Dentistry University of the Western Cape Importance & relevance of Oral HIV Lesions >70% of HIV+ve patients present with oral manifestations
Oral Health & HIV Professor Sudeshni Naidoo Department of Community Dentistry University of the Western Cape Importance & relevance of Oral HIV Lesions >70% of HIV+ve patients present with oral manifestations
OROPHYRENGEAL CANCERS
 OROPHYRENGEAL CANCERS INTRODUCTION 2 % 4 % of all malignant Tumors in west Asia India 40% Men ^ Age :Over 60 yrs 90% of all oral cancers results from Tobacco and Alcohol Pan (Betel Leaf,Nut, Lime), Reverse
OROPHYRENGEAL CANCERS INTRODUCTION 2 % 4 % of all malignant Tumors in west Asia India 40% Men ^ Age :Over 60 yrs 90% of all oral cancers results from Tobacco and Alcohol Pan (Betel Leaf,Nut, Lime), Reverse
General and Oral Pathology Topic Outlines. Copyright Fehrenbach and rdhedu.com. All rights reserved.
 General and Oral Pathology Topic Outlines Are you ready? Are you Ready? ARE YOU READY? TO LEARN AND EXPERIENCE real ORAL BIOLOGY??? BOOTCAMP STYLE Oral Biology BOOTCAMP through rdhedu.com For Oral Biology
General and Oral Pathology Topic Outlines Are you ready? Are you Ready? ARE YOU READY? TO LEARN AND EXPERIENCE real ORAL BIOLOGY??? BOOTCAMP STYLE Oral Biology BOOTCAMP through rdhedu.com For Oral Biology
Course File 243 DDS Physics of Diagnostic Radiology and Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course File 243 DDS Physics of Diagnostic Radiology and Oral and Maxillofacial
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course File 243 DDS Physics of Diagnostic Radiology and Oral and Maxillofacial
Contents. Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology. Ultrasound Nodule Characteristics
 Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Medical History. Oral Medicine and General Medicine
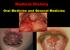 Medical History Oral Medicine and General Medicine Gingivitis herpetica acuta NECROTIZÁLÓ SIALOMETAPLASIA SOOR Medical History The life expectancy has recently increased and increasing By dental prevention
Medical History Oral Medicine and General Medicine Gingivitis herpetica acuta NECROTIZÁLÓ SIALOMETAPLASIA SOOR Medical History The life expectancy has recently increased and increasing By dental prevention
Assessment of Clinical Judgement
 Assessment of Clinical Judgement Examples for Diagnosis, Treatment Planning and Clinical Decision Making Using the information provided, answer questions to on the answer score sheet. Patient: John Doe
Assessment of Clinical Judgement Examples for Diagnosis, Treatment Planning and Clinical Decision Making Using the information provided, answer questions to on the answer score sheet. Patient: John Doe
A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology Anatomical Pathology Discipline
 Oral Lesions & Oral Cancer Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Overview
Oral Lesions & Oral Cancer Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Overview
University of Palestine. Final Exam 2 ed Semester 2014/2015 Total Grade: 60
 Question One: MCQ: 1- Dens in dent occurs most commonly in the : A- Maxillary canines B- Mandibular premolars C- Mandibular second molars D- Maxillary lateral incisors 2- A cyst occurring under the tongue
Question One: MCQ: 1- Dens in dent occurs most commonly in the : A- Maxillary canines B- Mandibular premolars C- Mandibular second molars D- Maxillary lateral incisors 2- A cyst occurring under the tongue
The World of Dermatology
 The World of Dermatology, F.A.A.D. Assistant Professor of Dermatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Director of J. Woodson Dermatology & Associates, LTD Objectives Cite the advances in management
The World of Dermatology, F.A.A.D. Assistant Professor of Dermatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Director of J. Woodson Dermatology & Associates, LTD Objectives Cite the advances in management
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Head and Neck Case Studies
 Head and Neck Case Studies John Chaplin & Nick McIvor www.headneck.co.nz Head and Neck lumps every lump must have a diagnosis Working diagnosis» +/- investigations Review» +/- investigations auckland head
Head and Neck Case Studies John Chaplin & Nick McIvor www.headneck.co.nz Head and Neck lumps every lump must have a diagnosis Working diagnosis» +/- investigations Review» +/- investigations auckland head
Salivary ultrasound. Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK
 Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
Lecture Content and learning outcomes
 DIPLOMA IN PAEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Subject Lecture Content and learning outcomes Craniofacial growth and development The process of pre-natal development The process of post-natal craniofacial growth The
DIPLOMA IN PAEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Subject Lecture Content and learning outcomes Craniofacial growth and development The process of pre-natal development The process of post-natal craniofacial growth The
Teeth and supporting tissues, e.g. dental. Maxillary sinus, salivary gland
 MJDF Facial Pain. Patricia Thomson Always start with SOCRATES S site O onset C character R radiation A associated features T timing E exacerbating/relieving factors S severity Examine the cranial nerves
MJDF Facial Pain. Patricia Thomson Always start with SOCRATES S site O onset C character R radiation A associated features T timing E exacerbating/relieving factors S severity Examine the cranial nerves
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts. SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST
 The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
MUSCULOSKELETAL STUDY GUIDE
 MUSCULOSKELETAL STUDY GUIDE The following pages summarize potential content for the Certifying and Maintenance Examinations in the Musculoskeletal section. The subject matter that may be used for a test
MUSCULOSKELETAL STUDY GUIDE The following pages summarize potential content for the Certifying and Maintenance Examinations in the Musculoskeletal section. The subject matter that may be used for a test
Oral Cancer and Common Oral Lesions seen in HIV Seropositive Patients. Gwen Cohen Brown DDS, FAAOMP Professor New York City College of Technology
 Oral Cancer and Common Oral Lesions seen in HIV Seropositive Patients Gwen Cohen Brown DDS, FAAOMP Professor New York City College of Technology Program Objectives Recognize the oral health needs of the
Oral Cancer and Common Oral Lesions seen in HIV Seropositive Patients Gwen Cohen Brown DDS, FAAOMP Professor New York City College of Technology Program Objectives Recognize the oral health needs of the
Dental Management of the Organ or Stem Cell Transplant Patient
 Dental Management of the Organ or Stem Cell Transplant Patient KEY POINTS Before and after organ or stem cell transplantation, patients require specialized dental management. Optimal dental management
Dental Management of the Organ or Stem Cell Transplant Patient KEY POINTS Before and after organ or stem cell transplantation, patients require specialized dental management. Optimal dental management
Systemic Disorders and the Mouth
 Systemic Disorders and the Mouth http://i686.photobucket.com/albums/vv221/paleoeat/oral-systemic-connection2-2.jpg Clues suggesting systemic disease may be found in the mouth and adjacent structures. A
Systemic Disorders and the Mouth http://i686.photobucket.com/albums/vv221/paleoeat/oral-systemic-connection2-2.jpg Clues suggesting systemic disease may be found in the mouth and adjacent structures. A
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinobacteria, 307 308 Actinomycetes, 307 308 Actinomycosis, in oral cavity, 288 290 Aggregatibacter, 308 309 Amoxicillin, in odontogenic infections,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinobacteria, 307 308 Actinomycetes, 307 308 Actinomycosis, in oral cavity, 288 290 Aggregatibacter, 308 309 Amoxicillin, in odontogenic infections,
Educational Cases EQA November T.J. Palmer Raigmore Hospital Inverness
 Educational Cases EQA November 2013 T.J. Palmer Raigmore Hospital Inverness Case 2 Clinical Details Dob 11 February 1951 PMH: 1964 Extraction of 45 aet 13 yr 1966 Cyst between 44 and 46 enucleated 1973
Educational Cases EQA November 2013 T.J. Palmer Raigmore Hospital Inverness Case 2 Clinical Details Dob 11 February 1951 PMH: 1964 Extraction of 45 aet 13 yr 1966 Cyst between 44 and 46 enucleated 1973
Oral Medicine Update for the dental practitioner Lumps and swellings
 IN BRIEF Lumps have a variety of causes, benign and malignant. Biopsy, imaging or other investigations are often indicated. 8 Oral Medicine Update for the dental practitioner Lumps and swellings C. Scully
IN BRIEF Lumps have a variety of causes, benign and malignant. Biopsy, imaging or other investigations are often indicated. 8 Oral Medicine Update for the dental practitioner Lumps and swellings C. Scully
Table of Contents. Preface xi. Acknowledgments xiii. Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1. 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3
 Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV
 DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
REF: Chap 1 (Pemphigus vulgaris/etiology and
 Chapter 1: Vesiculobullous Diseases Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Intercellular deposits of IgG are consistently found in oral epithelium in which of the following? a. Cicatricial pemphigoid b. Lichen planus
Chapter 1: Vesiculobullous Diseases Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Intercellular deposits of IgG are consistently found in oral epithelium in which of the following? a. Cicatricial pemphigoid b. Lichen planus
ANS: C REF: Chap 1 (Pemphigus vulgaris/etiology and pathogenesis), p 11
 Chapter 1: Vesiculobullous Diseases Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Intercellular deposits of IgG are consistently found in oral epithelium in which of the following? a. Cicatricial pemphigoid b. Lichen planus
Chapter 1: Vesiculobullous Diseases Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Intercellular deposits of IgG are consistently found in oral epithelium in which of the following? a. Cicatricial pemphigoid b. Lichen planus
Types of Oral Surgery Impacted tooth removal Alveoplasty Abscesses Osteomyelitis Fractures Cysts, tumors Dental implant placement Maxillofacial
 By: Dr Arash Khojasteh Oral Surgery The diagnostic and surgical treatment of diseases, injuries, and defects involving both the junctional and the esthetic aspects of the hard and soft tissues of the oral
By: Dr Arash Khojasteh Oral Surgery The diagnostic and surgical treatment of diseases, injuries, and defects involving both the junctional and the esthetic aspects of the hard and soft tissues of the oral
